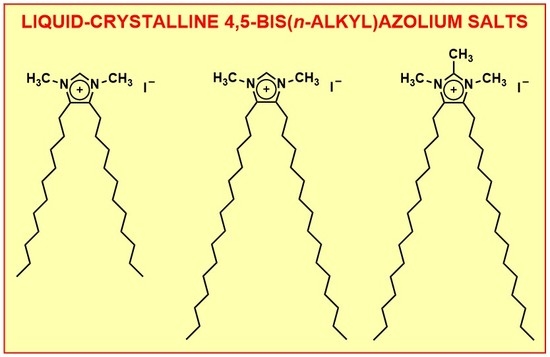
Substituted Azolium Disposition: Examining the Effects of Alkyl Placement on Thermal Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowlas, C.J.; Bruce, D.W.; Seddon, K.R. Liquid-Crystalline Ionic Liquids. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.M.; Holbrey, J.D.; Kennedy, A.R.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquid Crystals: Hexafluorophosphate Salts. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Seddon, K.R. The Phase Behaviour of 1-Alkyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborates; Ionic Liquids and Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1999, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, K.; Lava, K.; Nockemann, P.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Driesen, K.; Görller-Walrand, C.; Binnemans, K.; Cardinaels, T. Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquid Crystals. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 656–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, K.; Lava, K.; Bielawski, C.W.; Binnemans, K. Ionic Liquid Crystals: Versatile Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4643–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansueto, M.; Laschat, S. Ionic Liquid Crystals. In Handbook of Liquid Crystals. Volume 6: Nanostructured and Amphiphilic Liquid Crystals, 2nd ed.; Goodby, J.W., Collings, P.J., Kato, T., Tschierske, C., Gleeson, H., Raynes, P., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 231–280. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, A.A.; Kouwer, P.H.J. Key Developments in Ionic Liquid Crystals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Yoshio, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Soberats, B.; Ohno, H.; Funahashi, M. Transport of Ions and Electrons in Nanostructured Liquid Crystals. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Uchida, J.; Ichikawa, T.; Sakamoto, T. Functional Liquid Crystals towards the Next Generation of Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4355–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Kawano, R.; Kubo, W.; Kitamura, T.; Wada, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yanagida, S. Ionic Liquid Crystal as a Hole Transport Layer of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Commun. 2005, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Kawano, R.; Kubo, W.; Masaki, N.; Kitamura, T.; Wada, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yanagida, S. Dye-Sensitized TiO2 Solar Cells Using Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Crystal Systems As Effective Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4763–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, D.; Soberats, B.; Yatagai, R.; Uchida, S.; Yoshio, M.; Kloo, L.; Segawa, H.; Kato, T. Liquid-Crystalline Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: Design of Two-Dimensional Molecular Assemblies for Efficient Ion Transport and Thermal Stability. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6493–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.W.; Gao, Y.A.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Shimizu, K.; Slattery, J.M. Liquid-Crystalline Ionic Liquids As Ordered Reaction Media for the Diels-Alder Reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16113–16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazaki, S.; Funahashi, M.; Kato, T. An Electrochromic Nanostructured Liquid Crystal Consisting of π-Conjugated and Ionic Moieties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13206–13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazaki, S.; Funahashi, M.; Kagimoto, J.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Nanostructured Liquid Crystals Combining Ionic and Electronic Functions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7702–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneduci, A.; Cospito, S.; La Deda, M.; Veltri, L.; Chidichimo, G. Electrofluorochromism in π-Conjugated Ionic Liquid Crystals. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Structure and Nanostructure in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6357–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, Y.; Saielli, G. Effect of the Chain Length on the Structure of Ionic Liquids: From Spatial Heterogeneity to Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, F.; Kofu, M.; Yamamuro, O. Thermal and Structural Studies of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with and Without Liquid-Crystalline Phases: The Origin of Nanostructure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 5028–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russina, O.; Lo Celso, F.; Plechkova, N.; Jafta, C.J.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Triolo, A. Mesoscopic Organization in Ionic Liquids. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russina, O.; Lo Celso, F.; Plechkova, N.V.; Triolo, A. Emerging Evidences of Mesoscopic-Scale Complexity in Neat Ionic Liquids and Their Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.W.; Cabry, C.P.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Costen, M.L.; D’Andrea, L.; Grillo, I.; Marshall, B.C.; McKendrick, K.G.; Minton, T.K.; Purcell, S.M.; et al. Nanosegregation and Structuring in the Bulk and at the Surface of Ionic-Liquid Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6002–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontoni, D.; Haddad, J.; Di Michiel, M.; Deutsch, M. Self-Segregated Nanostructure in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6947–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosby, T.; Vicars, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sangoro, J. Dynamic-Mechanical and Dielectric Evidence of Long-Lived Mesoscale Organization in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3544–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, F.; Kofu, M.; Nagao, M.; Ohishi, K.; Takata, S.; Suzuki, J.; Yamada, T.; Shibata, K.; Ueki, T.; Kitazawa, Y.; et al. Neutron Scattering Studies on Short- and Long-Range Layer Structures and Related Dynamics in Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 054502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabry, C.P.; D’Andrea, L.; Shimizu, K.; Grillo, I.; Li, P.; Rogers, S.; Bruce, D.W.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Slattery, J.M. Exploring the Bulk-Phase Structure of Ionic Liquid Mixtures Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Faraday Discuss. 2018, 206, 265–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.D.; Wang, Y.T.; Saielli, G. Metastable State During Melting and Solid-Solid Phase Transition of [CnMim][NO3] (n = 4-12) Ionic Liquids by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douce, L.; Suisse, J.-M.; Guillon, D.; Taubert, A. Imidazolium-Based Liquid Crystals: A Modular Platform for Versatile New Materials with Finely Tuneable Properties and Behaviour. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bara, J.E.; Shannon, M.S. Beyond 1,3-Difunctionalized Imidazolium Cations. Nanomater. Energy 2012, 1, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalfani, V.F.; Alshaikh, A.A.; Bara, J.E. Analysis of the Frequency and Diversity of 1,3-Dialkylimidazolium Ionic Liquids Appearing in the Literature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15971–15981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Awad, W.H.; Gilman, J.W.; Maupin, P.H.; De Long, H.C.; Trulove, P.C. Flammability, Thermal Stability, and Phase Change Characteristics of Several Trialkylimidazolium Salts. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Yoshio, M.; Kato, T.; Ohno, H. Effect of Methyl Groups Onto Imidazolium Cation Ring on Liquid Crystallinity and Ionic Conductivity of Amphiphilic Ionic Liquids. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1630–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Yoshio, M.; Kato, T.; Yoshizawa-Fujita, M.; Ohno, H. Self-Organization of Protonated 2-Heptadecylimidazole as an Effective Ion Conductive Matrix. Electrochemistry 2005, 73, 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Kouwer, P.H.J.; Swager, T.M. Synthesis and Mesomorphic Properties of Rigid-Core Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14042–14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshio, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Shimura, H.; Kagata, T.; Hamasaki, A.; Mukai, T.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Columnar Liquid-Crystalline Imidazolium Salts. Effects of Anions and Cations on Mesomorphic Properties and Ionic Conductivity. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Motoyanagi, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Kim, J.; Kato, K.; Takata, M.; Saeki, A.; Seki, S.; Tagawa, S.; et al. “Bicontinuous Cubic” Liquid Crystalline Materials from Discotic Molecules: A Special Effect of Paraffinic Side Chains with Ionic Liquid Pendants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17722–17723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.H.; He, J.H.; Liu, J.H.; Qian, L.A.; Yu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Q.L.; He, C.X. Liquid Crystalline Phases of 1,2-Dimethyl-3-Hexadecylimidazolium Bromide and Binary Mixtures With Water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, K.; Wellens, S.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Cardinaels, T.; Binnemans, K. T-Shaped Ionic Liquid Crystals Based on the Imidazolium Motif: Exploring Substitution of the C-2 Imidazolium Carbon Atom. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4291–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.A.; de Haan, L.T.; Kouwer, P.H.J. Towards Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, S.T.; Heinrich, B.; Sykora, R.A.; Zhang, X.; McManus, G.J.; Douce, L.; Mirjafari, A. Methimazolium-Based Ionic Liquid Crystals: Emergence of Mesomorphic Properties via a Sulfur Motif. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5456–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindman, M.S.; Stanton, A.D.; Christopher Irvin, A.; Wallace, D.A.; Moon, J.D.; Reclusado, K.R.; Liu, H.; Belmore, K.A.; Liang, Q.; Shannon, M.S.; et al. Synthesis of 1,2-Dialkyl-, 1,4(5)-Dialkyl-, and 1,2,4(5)-Trialkylimidazoles via a One-Pot Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 11880–11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Roveda, J.D.; Mittenthal, M.S.; Shannon, M.S.; Bara, J.E. Experimental Densities and Calculated Fractional Free Volumes of Ionic Liquids With Tri- and Tetra-Substituted Imidazolium Cations. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumino, K.; Wulf, A.; Ludwig, R. Strong, Localized, and Directional Hydrogen Bonds Fluidize Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8731–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumino, K.; Wulf, A.; Ludwig, R. The Potential Role of Hydrogen Bonding in Aprotic and Protic Ionic Liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 8790–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.; Peppel, T.; Fumino, K.; Köckerling, M.; Ludwig, R. The Importance of Hydrogen Bonds for the Structure of Ionic Liquids: Single-Crystal X-ray Diffraction and Transmission and Attenuated Total Reflection Spectroscopy in the Terahertz Region. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 10221–10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulf, A.; Fumino, K.; Ludwig, R. Spectroscopic Evidence for an Enhanced Anion-Cation Interaction from Hydrogen Bonding in Pure Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppel, T.; Roth, C.; Fumino, K.; Paschek, D.; Köckerling, M.; Ludwig, R. The Influence of Hydrogen-Bond Defects on the Properties of Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6661–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumino, K.; Peppel, T.; Geppert-Rybczynska, M.; Zaitsau, D.H.; Lehmann, J.K.; Verevkin, S.P.; Köckerling, M.; Ludwig, R. The Influence of Hydrogen Bonding on the Physical Properties of Ionic Liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 14064–14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugar, K.M.; Kostalik, H.A.; Coates, G.W. Imidazolium Cations with Exceptional Alkaline Stability: A Systematic Study of Structure-Stability Relationships. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8730–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Richter, C.; Rühling, A.; Drücker, P.; Siegmund, D.; Metzler-Nolte, N.; Glorius, F.; Galla, H.-J. A Remarkably Simple Class of Imidazolium-Based Lipids and Their Biological Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15123–15126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühling, A.; Wang, D.; Ernst, J.B.; Wulff, S.; Honeker, R.; Richter, C.; Ferry, A.; Galla, H.-J.; Glorius, F. Influence of the Headgroup of Azolium-Based Lipids on Their Biophysical Properties and Cytotoxicity. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5920–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drücker, P.; Rühling, A.; Grill, D.; Wang, D.; Draeger, A.; Gerke, V.; Glorius, F.; Galla, H.-J. Imidazolium Salts Mimicking the Structure of Natural Lipids Exploit Remarkable Properties Forming Lamellar Phases and Giant Vesicles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakers, L.; Glorius, F. Flexible Design of Ionic Liquids for Membrane Interactions. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondla, R.; Lee, C.K.; Lu, J.T.; Lin, I.J.B. Symmetrical 1,3-Dialkylimidazolium Based Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2013, 60, 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Heinemann, F.W.; Yang, M.; Melcher, B.U.; Fekete, M.; Mudring, A.-V.; Wasserscheid, P.; Meyer, K. A New Class of Double Alkyl-Substituted, Liquid Crystalline Imidazolium Ionic Liquids—A Unique Combination of Structural Features, Viscosity Effects, and Thermal Properties. Chem. Commun. 2009, 7405–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Vogel, C.S.; Heinemann, F.W.; Wasserscheid, P.; Meyer, K. Solid-State Structures of Double-Long-Chain Imidazolium Ionic Liquids: Influence of Anion Shape on Cation Geometry and Crystal Packing. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 1974–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sternberg, M.; Kohler, F.T.U.; Melcher, B.U.; Wasserscheid, P.; Meyer, K. Long-Alkyl-Chain-Derivatized Imidazolium Salts and Ionic Liquid Crystals with Tailor-Made Properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12476–12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Mallick, B.; Mudring, A.-V. A Systematic Study on the Mesomorphic Behavior of Asymmetrical 1-Alkyl-3-Dodecylimidazolium Bromides. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Peng, H.H.; Lin, I.J.B. Liquid Crystals of N,N′-Dialkylimidazolium Salts Comprising Palladium(II) and Copper(II) Ions. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.L.; LeCompte, K.; Hargens, L.; McEwen, A.B. Thermal Properties of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 357, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Goossens, K.; Shin, T.J.; Bielawski, C.W. Dicyanamide Salts That Adopt Smectic, Columnar, or Bicontinuous Cubic Liquid-Crystalline Mesophases. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6399–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, M.; Giménez, R.; Serrano, J.L.; Donnio, B.; Heinrich, B.; Guillon, D. Dendromesogens: Liquid Crystal Organizations of Poly(Amidoamine) Dendrimers Versus Starburst Structures. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchet, J.; Douce, L.; Heinrich, B.; Welter, R.; Louati, A. A Convenient Method for Preparing Rigid-Core Ionic Liquid Crystals. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2009, 5, No. 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbs, W.; Douce, L.; Heinrich, B. 1-(4-Alkyloxybenzyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium Organic Backbone: A Versatile Smectogenic Moiety. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2009, 5. No. 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, H.D.B.; Roobottom, H.K.; Passmore, J.; Glasser, L. Relationships among Ionic Lattice Energies, Molecular (Formula Unit) Volumes, and Thermochemical Radii. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 3609–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzyuba, S.V.; Bartsch, R.A. New Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids with C2-Symmetrical Imidazolium Cations. Chem. Commun. 2001, 16, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, K.; Nockemann, P.; Driesen, K.; Goderis, B.; Görller-Walrand, C.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Pouzet, E.; Binnemans, K.; Cardinaels, T. Imidazolium Ionic Liquid Crystals With Pendant Mesogenic Groups. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C. Liquid Crystal Engineering—New Complex Mesophase Structures and Their Relations to Polymer Morphologies, Nanoscale Patterning and Crystal Engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1930–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Yoshio, M.; Hamasaki, A.; Taguchi, S.; Liu, F.; Zeng, X.; Ungar, G.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Induction of Thermotropic Bicontinuous Cubic Phases in Liquid-Crystalline Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2634–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungar, G.; Liu, F.; Zeng, X. Cubic and Other 3D Thermotropic Liquid Crystal Phases and Quasicrystals. In Handbook of Liquid Crystals. Volume 5: Non-Conventional Liquid Crystals, 2nd ed.; Goodby, J.W., Collings, P.J., Kato, T., Tschierske, C., Gleeson, H., Raynes, P., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 363–436. [Google Scholar]
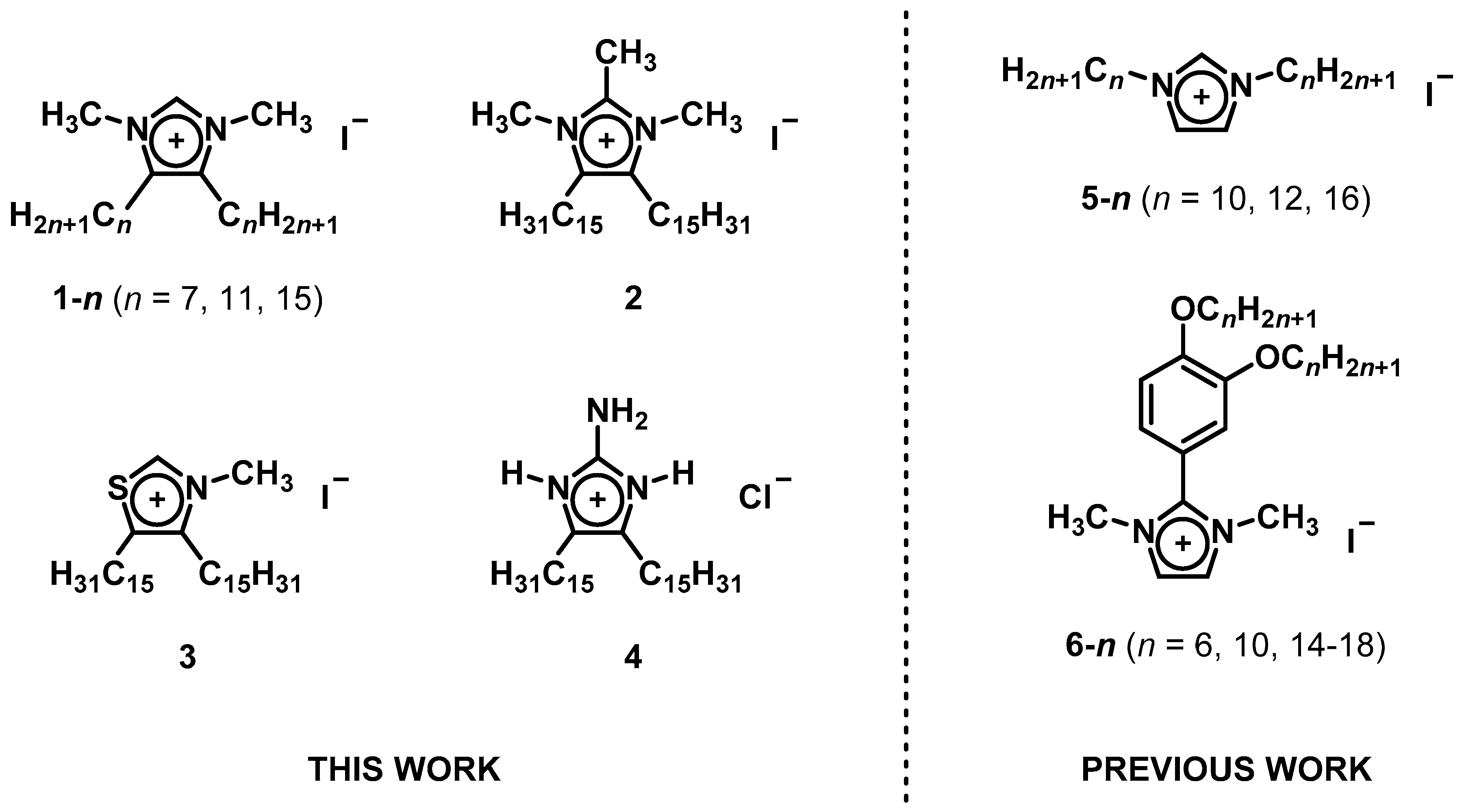
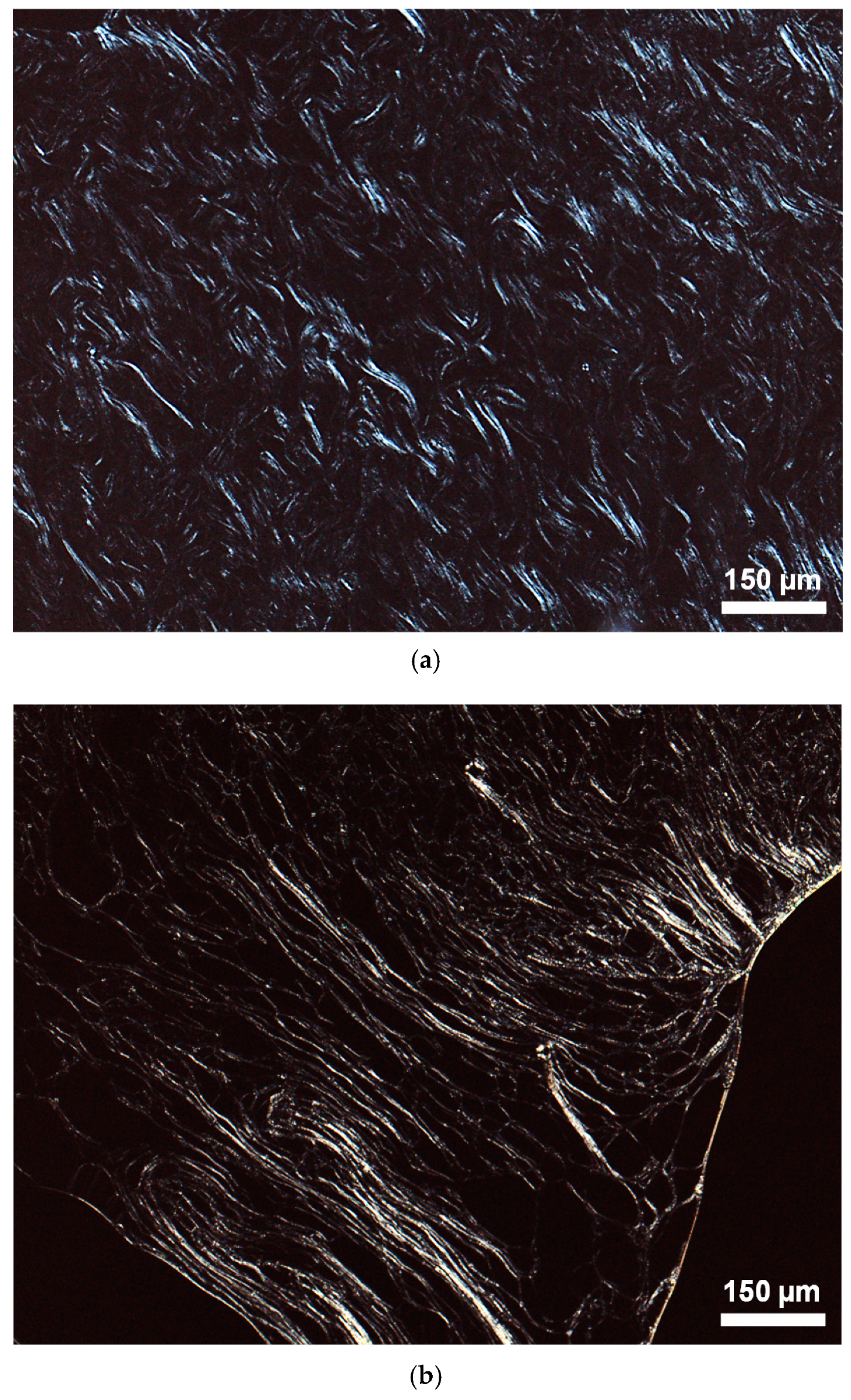
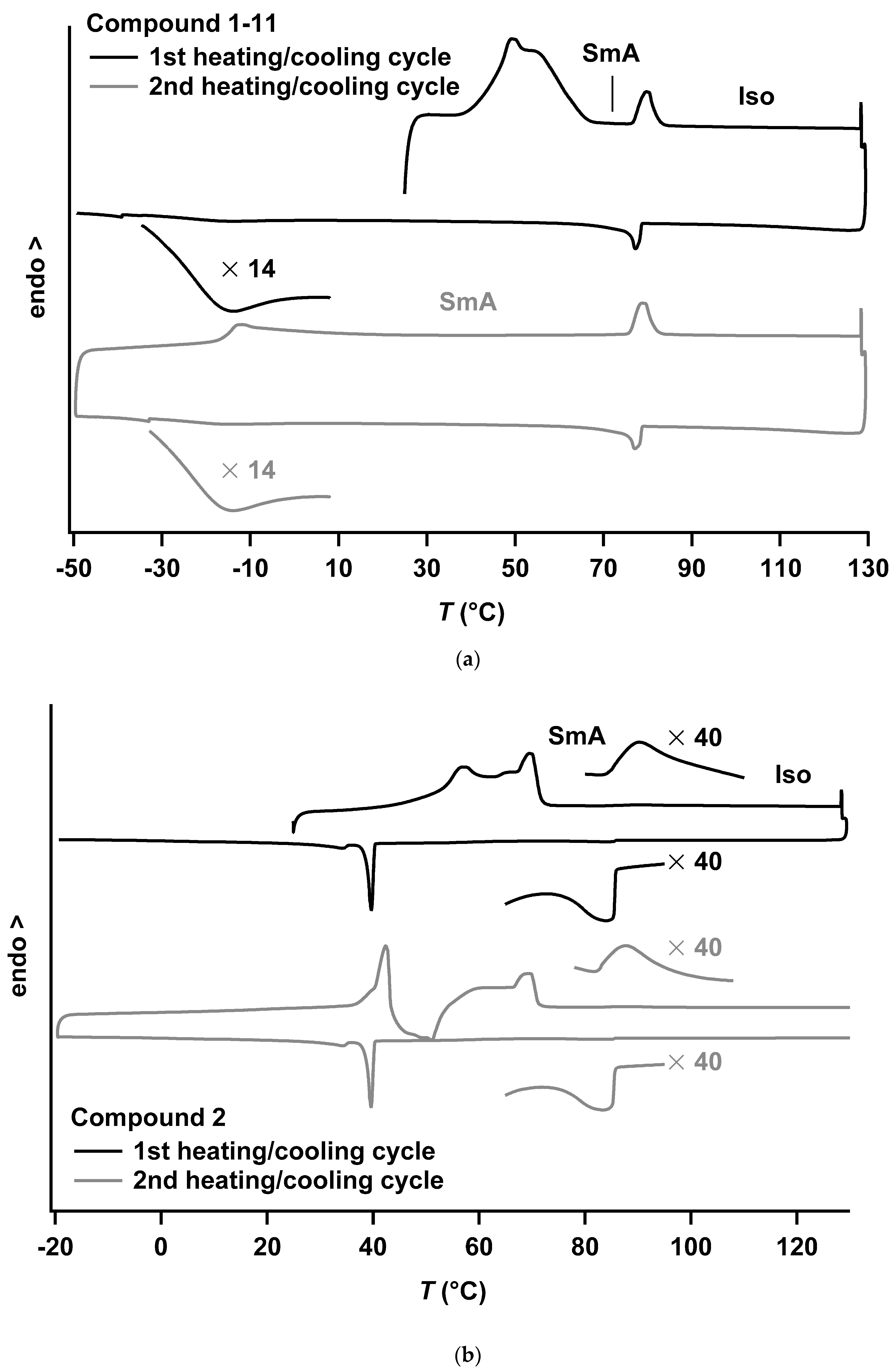
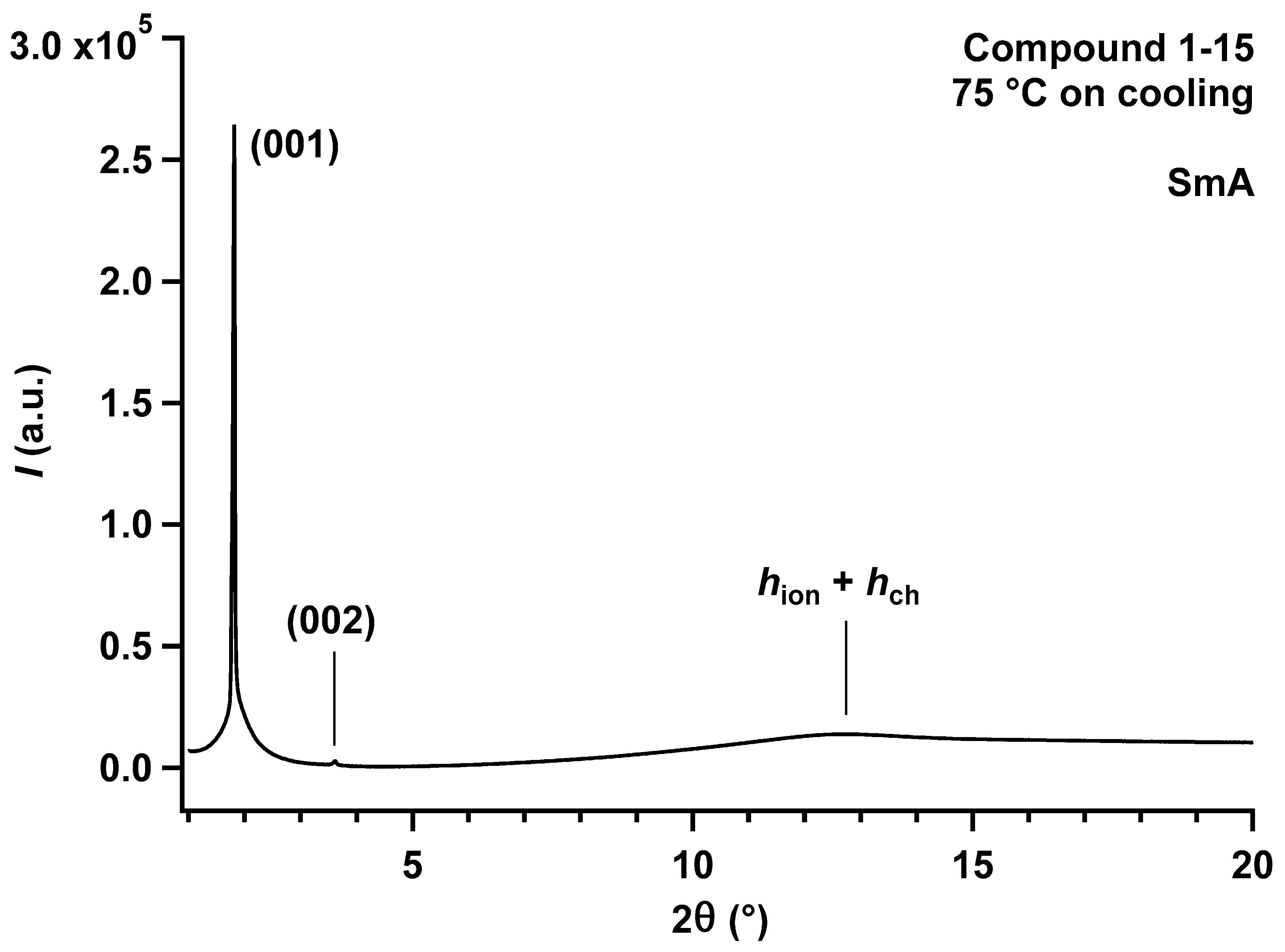
| Compound | Transition 1 | T (°C) 2 | ΔH (kJ·mol−1) 3 | T1% (°C) 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-7 | Cr → Iso 5 | 26 | 0.7 | n.d. | |
| 1-11 | HR1: | Cr → SmA 6 | 50, 55 6 | 21.6 6 | n.d. |
| SmA → Iso | 77 | 2.3 | |||
| HR2: | g → SmA | ~−14 | – | ||
| SmA → Iso | 76 | 2.2 | |||
| 1-15 | Cr → SmA | 76 | 38.3 | ~181 | |
| SmA → Iso | 88 7 | 0.7 | |||
| 2 | Cr → SmA 8 | 70 8 | – 8 | ~194 | |
| SmA → Iso | 88 7 | 0.5 | |||
| 3 | Cr → Iso 9 | 73 7 | 16.4 | ~135 | |
| 4 | Cr → Iso 9 | 68 7 | 38.1 | ~206 | |
| Cpd. | Type of LC Mesophase | T (°C) | dobs. (Å) 1 | I2 | hkl3 | dcalcd. (Å) 1 | Structural Parameters of the LC Mesophases 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-15 | SmA | 75 | 31.63 | VS (sh) | 001 | 31.68 | d = 31.68 Å |
| (upon | 15.86 | W (sh) | 002 | 15.84 | Vmol ≈ 1072 Å3 | ||
| cooling) | 4.5–4.6 | br | h1 | AM ≈ 67.7 Å2 | |||
| σch ≈ 22.1 Å2 | |||||||
| 2 | SmA | 78 | 32.91 | VS (sh) | 001 | 32.88 | d = 32.88 Å |
| 16.42 | W (sh) | 002 | 16.44 | Vmol ≈ 1098 Å3 | |||
| 4.4–4.5 | br | h1 | AM ≈ 66.8 Å2 | ||||
| σch ≈ 22.2 Å2 |
| Compound 1 | Phase Transition Temperatures (°C) 2 |
|---|---|
| 1-7 | Cr · 26 · Iso |
| 1-11 | HR1: Cr · ~55 3 · SmA · 77 · Iso |
| HR2: g · ~−14 · SmA · 76 · Iso | |
| 1-15 | Cr · 76 · SmA · 88 · Iso |
| 2 | Cr · 70 · SmA · 88 · Iso |
| [C10C10im][I] (5-10) [54] | Cr · < 0 · SmA · 55 · Iso |
| [C12C12im][I] (5-12) [56] | Cr · 40 · SmA · 89 · Iso |
| [C16C16im][I] (5-16) [54] | Cr · 67 · SmA · 147 · Iso |
| [C10C10im][BF4] [57] | Cr · 18 · SmA · 25 · Iso |
| [C12C12im][BF4] [57] | Cr · 50 · SmA · 69 · Iso |
| [C14C14im][BF4] [57] | Cr · 63 · SmA · 106 · Iso |
| [C16C16im][BF4] [57] | Cr · 70 · SmA · 125 · Iso |
| [C10C10im][PF6] [54,66] | Cr · 16 · Iso |
| [C12C12im][PF6] [54,57] | Cr · 45 · Iso |
| [C14C14im][PF6] [54] | Cr · 59 · SmA · 81 · Iso |
| [C16C16im][PF6] [54] | Cr · 68 · SmA · 105 · Iso |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goossens, K.; Rakers, L.; Shin, T.J.; Honeker, R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Glorius, F. Substituted Azolium Disposition: Examining the Effects of Alkyl Placement on Thermal Properties. Crystals 2019, 9, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010034
Goossens K, Rakers L, Shin TJ, Honeker R, Bielawski CW, Glorius F. Substituted Azolium Disposition: Examining the Effects of Alkyl Placement on Thermal Properties. Crystals. 2019; 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoossens, Karel, Lena Rakers, Tae Joo Shin, Roman Honeker, Christopher W. Bielawski, and Frank Glorius. 2019. "Substituted Azolium Disposition: Examining the Effects of Alkyl Placement on Thermal Properties" Crystals 9, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010034
APA StyleGoossens, K., Rakers, L., Shin, T. J., Honeker, R., Bielawski, C. W., & Glorius, F. (2019). Substituted Azolium Disposition: Examining the Effects of Alkyl Placement on Thermal Properties. Crystals, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010034