Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This study highlights the importance of shaping for functional materials (i.e., catalysts and adsorbents) in industrial-scale applications, because these materials in powder form impose a pressure drop in catalytic reactors and process units. In addition, efficient shaping including appropriate geometry of the final body as well as textural properties like porosity can directly impact the process parameters such as reactor size. However, shaping in most cases needs utilization of a binder (e.g., inorganic oxides like silica or alumina or mineral clays like kaolin) which can adversely impact the physicochemical properties of the functional material. To address these disadvantages, our developed hard-templating technique preserves the original physicochemical properties of zeolite because no extra additives like binders are used during the synthesis. This could be further explained as follows: Obtaining zeolite Y spheres with large particle size (ca. 0.5–1 mm) without application of any binder;
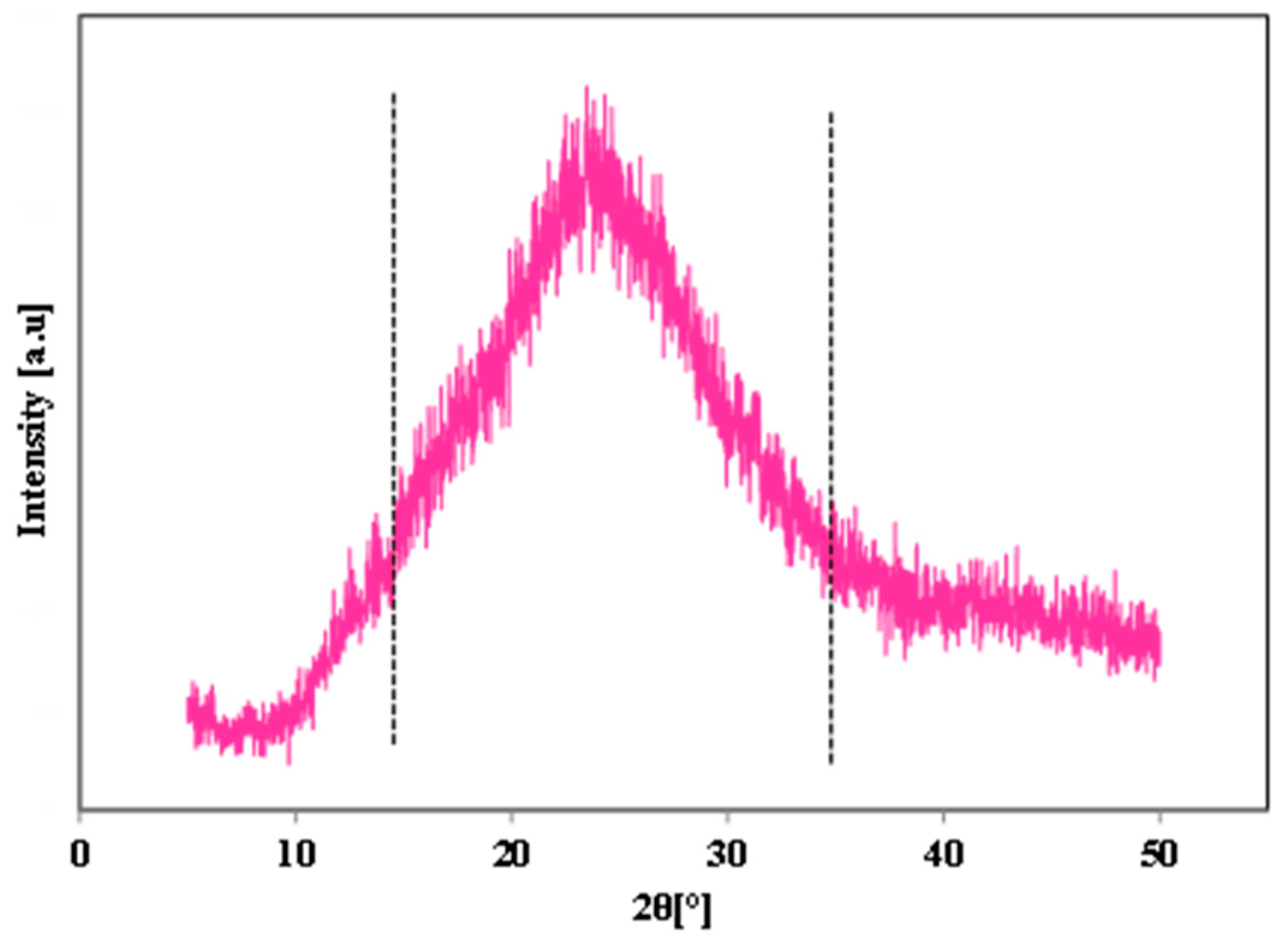
- These particles have pure zeolite Y and partially amorphous SiO2. But the crystallinity was significantly improved by prolongation of aging time at ambient temperature as discussed in the preceding sections;
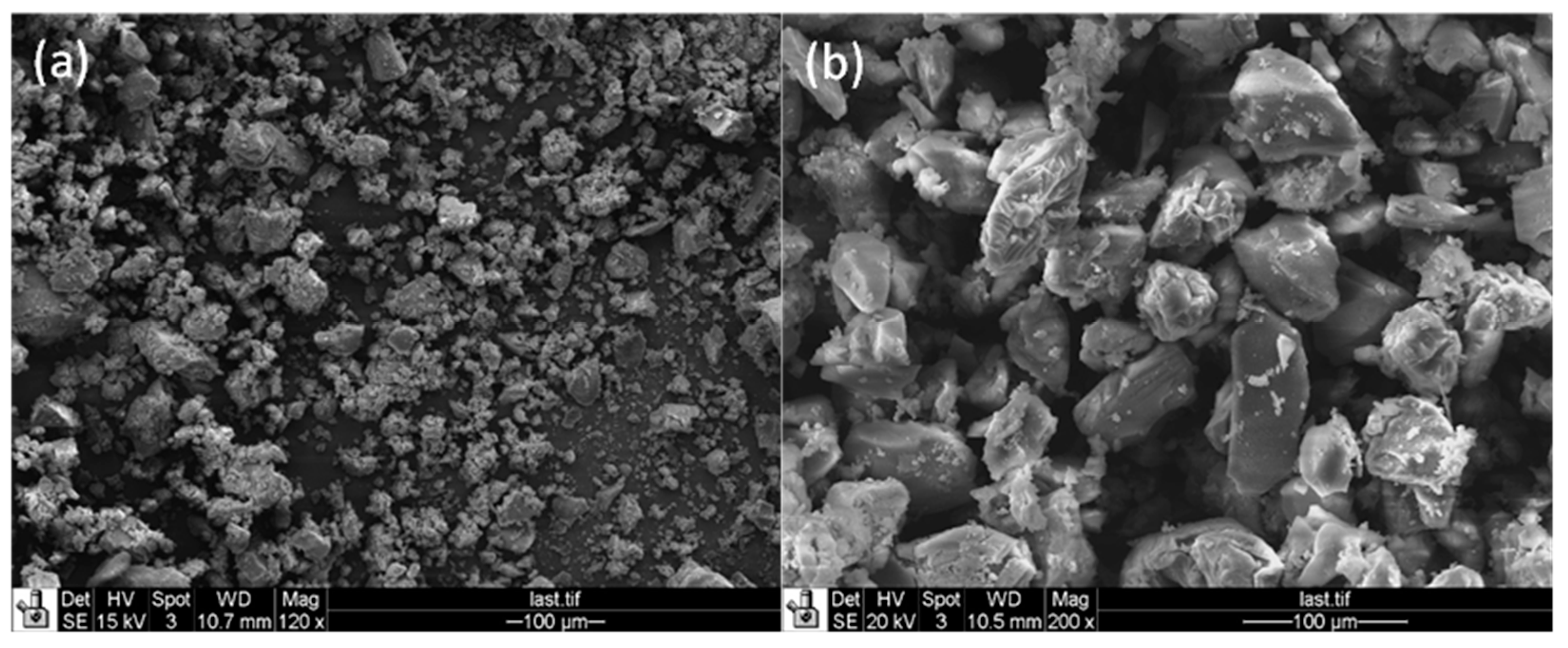
- These particles have hierarchical structures with higher levels of porosity (i.e., secondary meso- and macropores) plus inherent micropores which can alleviate the diffusion limitations originating from zeolite micropores.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Zeolite Y
2.2.1. Synthesis in the Absence Organic SDA (Method 1)
2.2.2. Synthesis in the Presence of Organic SDA (Method 2)
2.3. Characterization of Zeolite Y
3. Results and Discussion
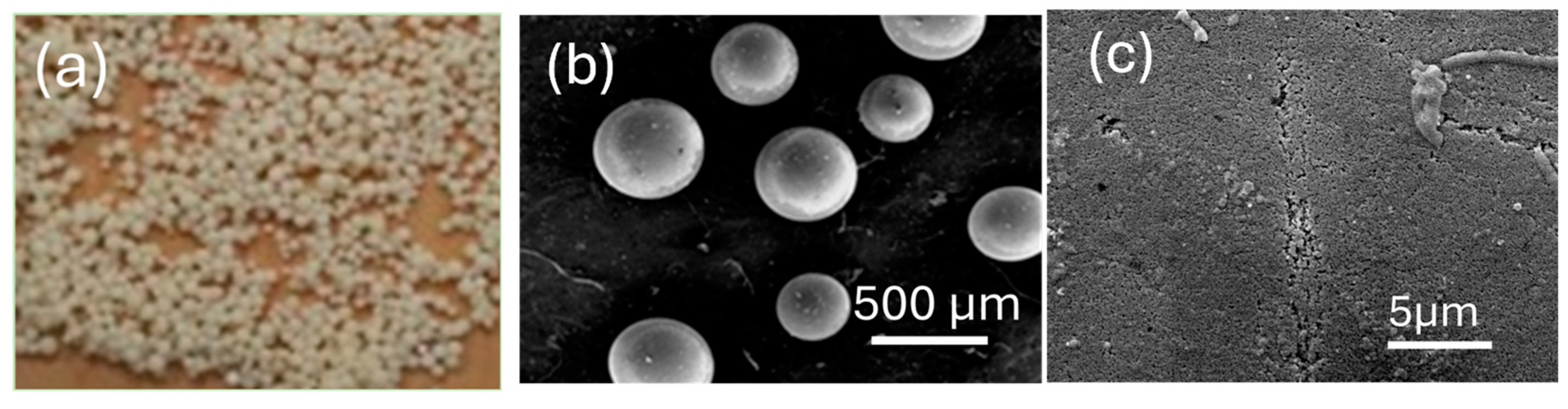
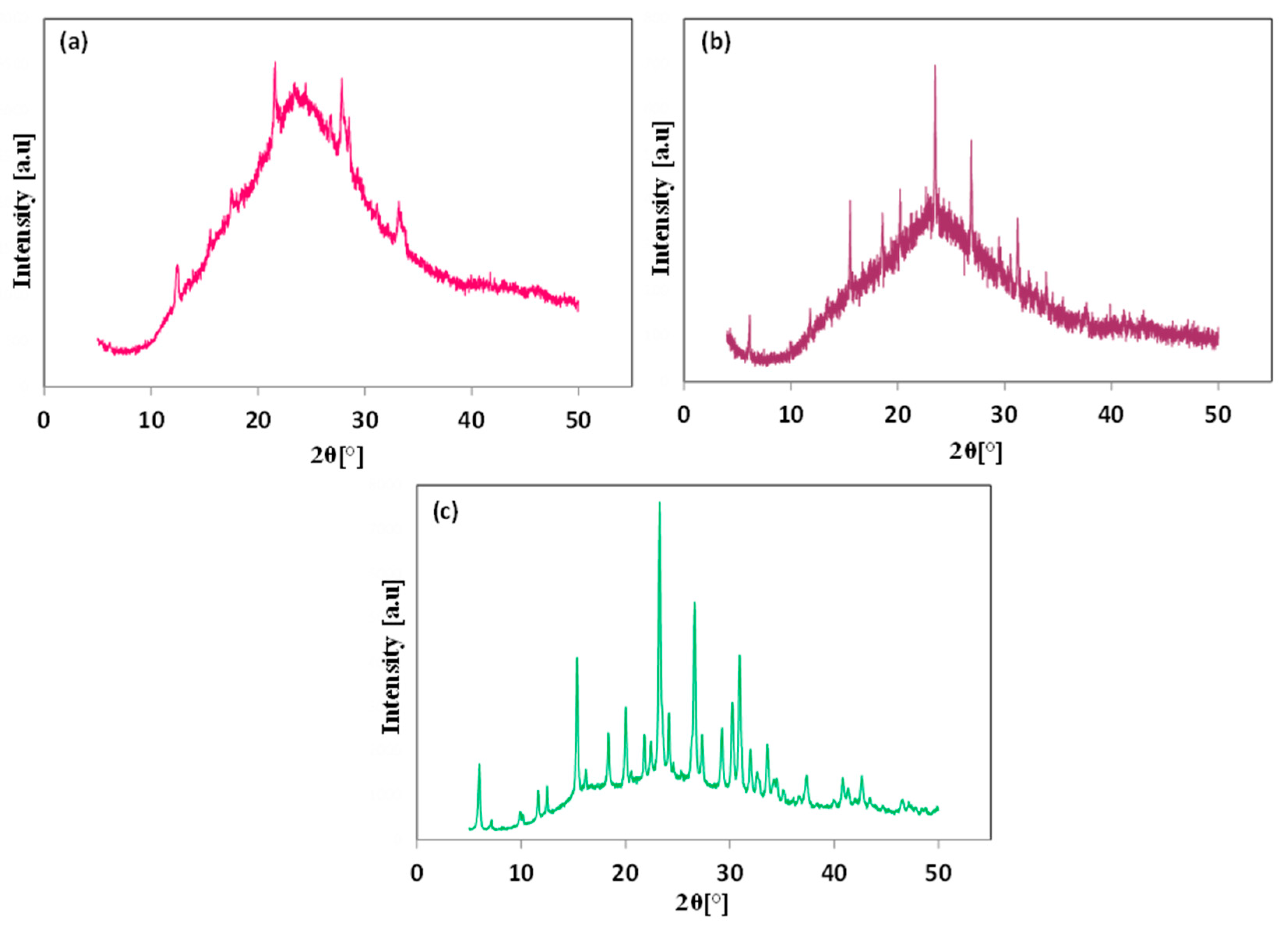
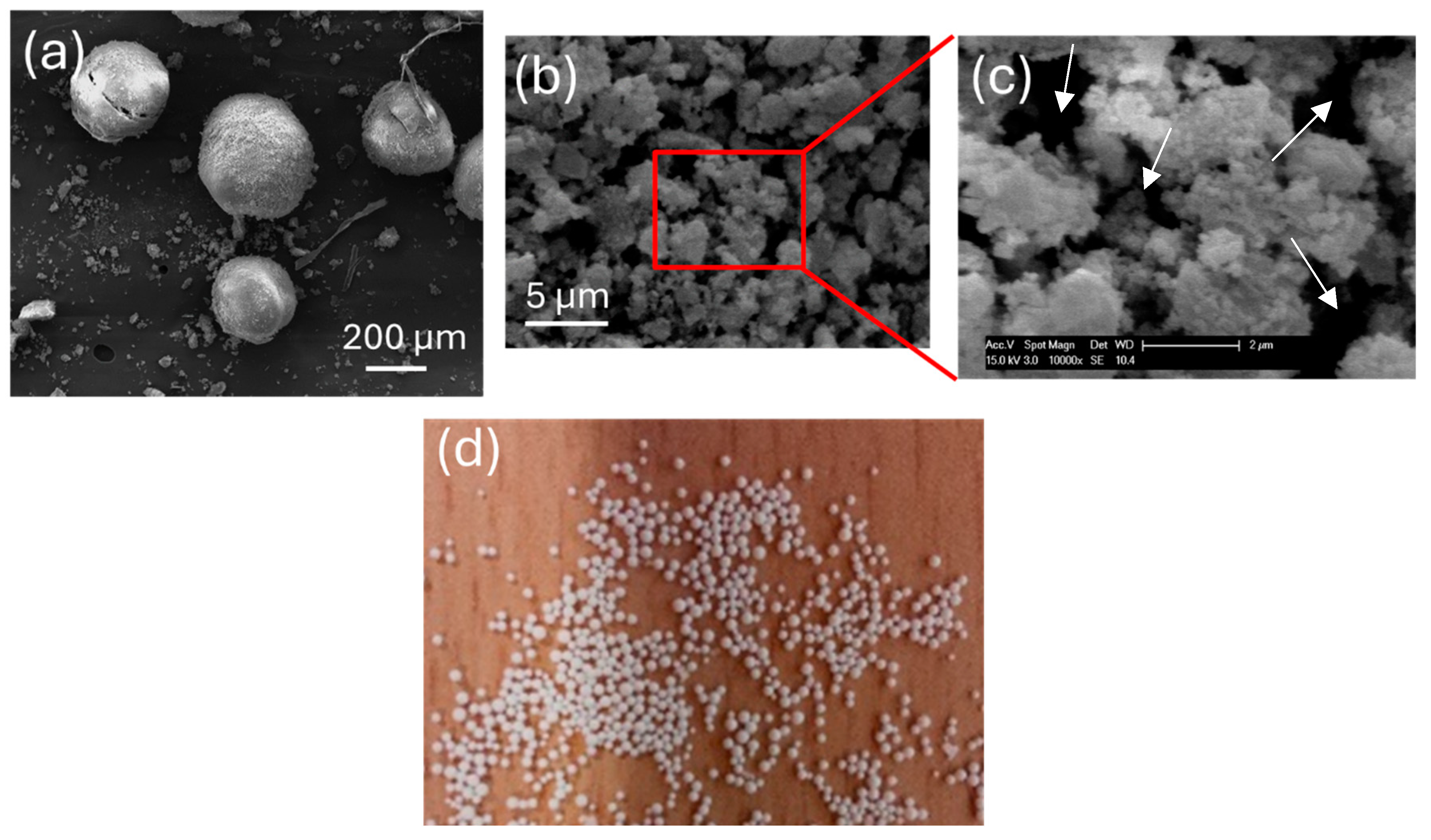
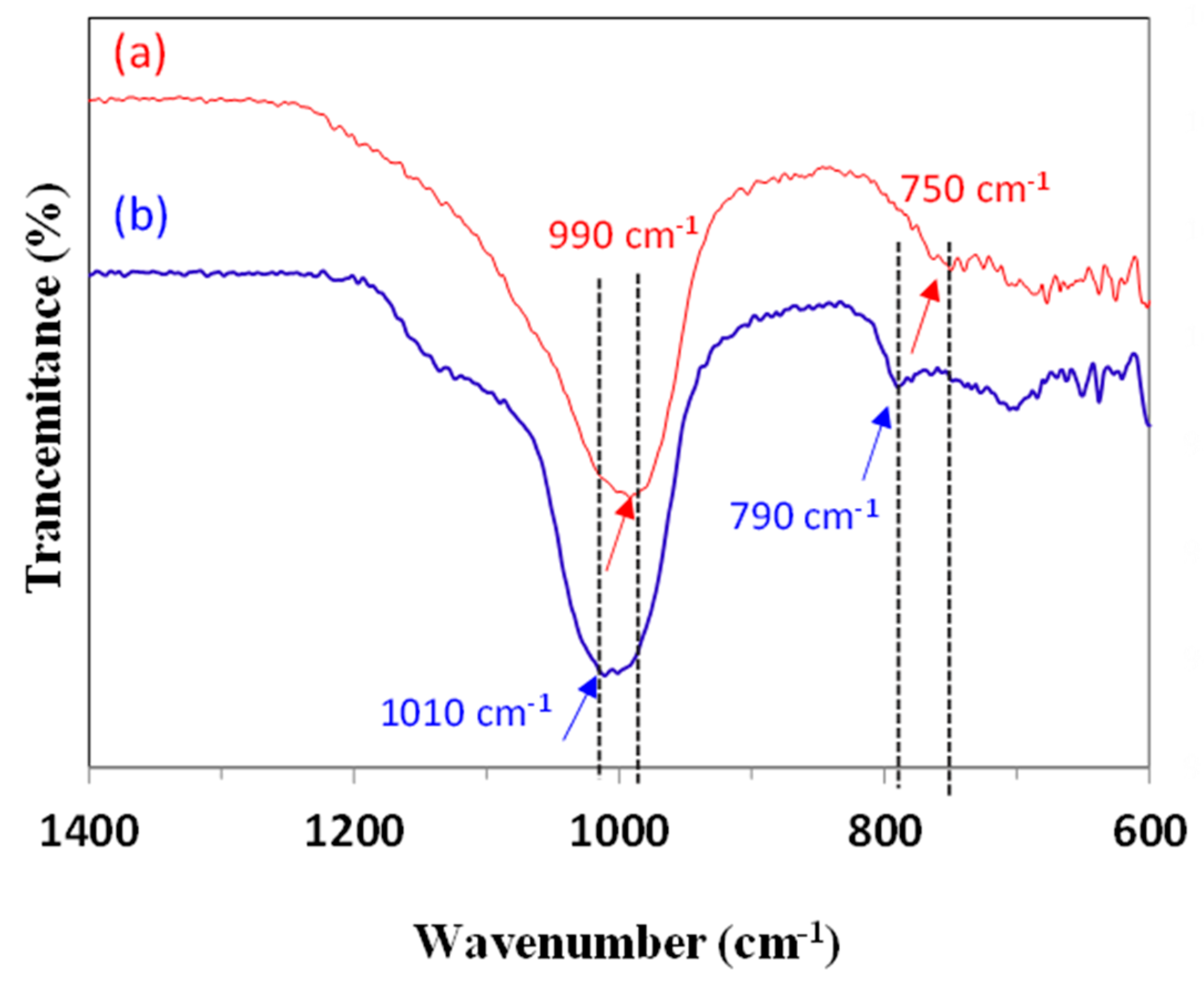
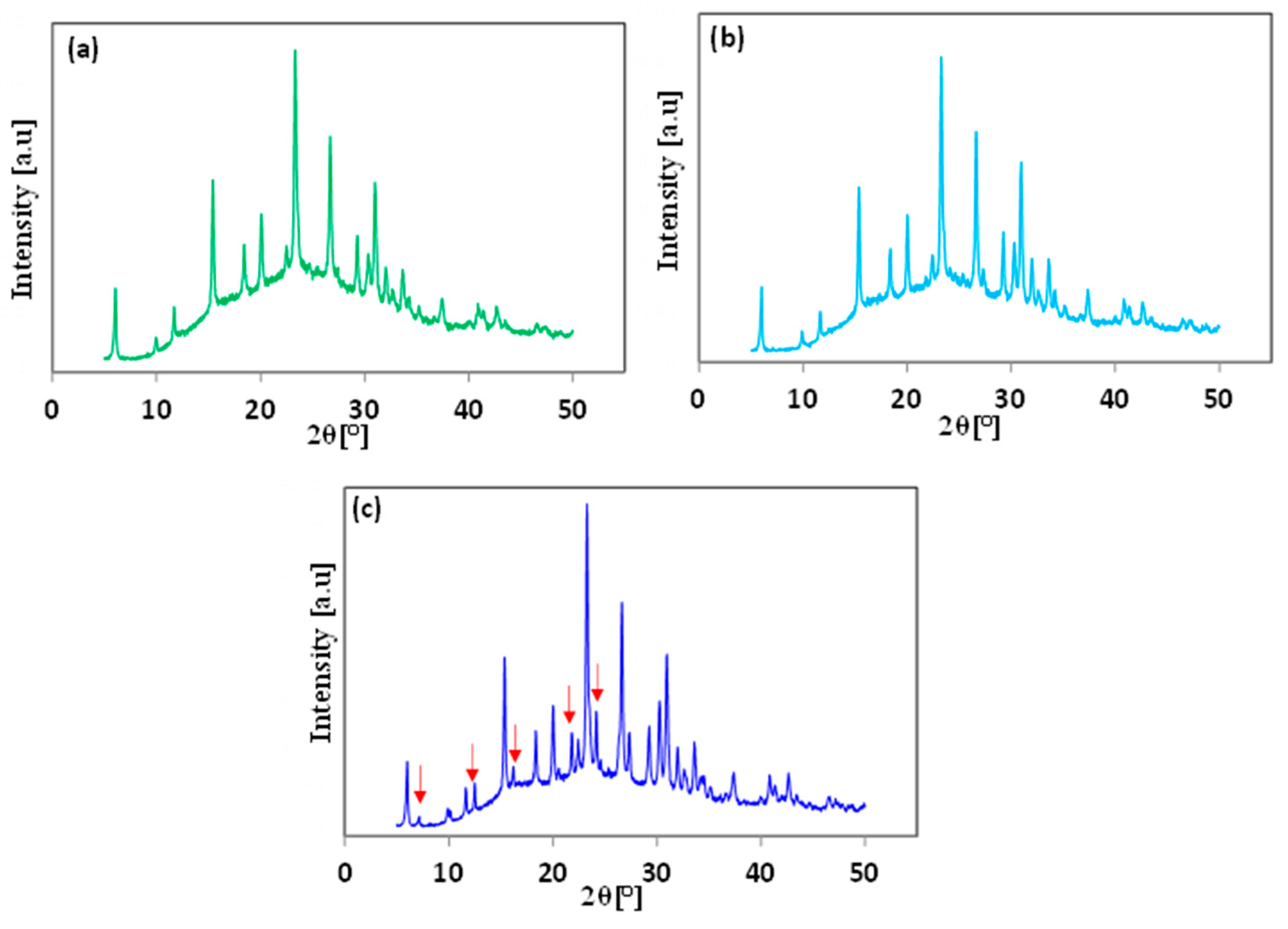
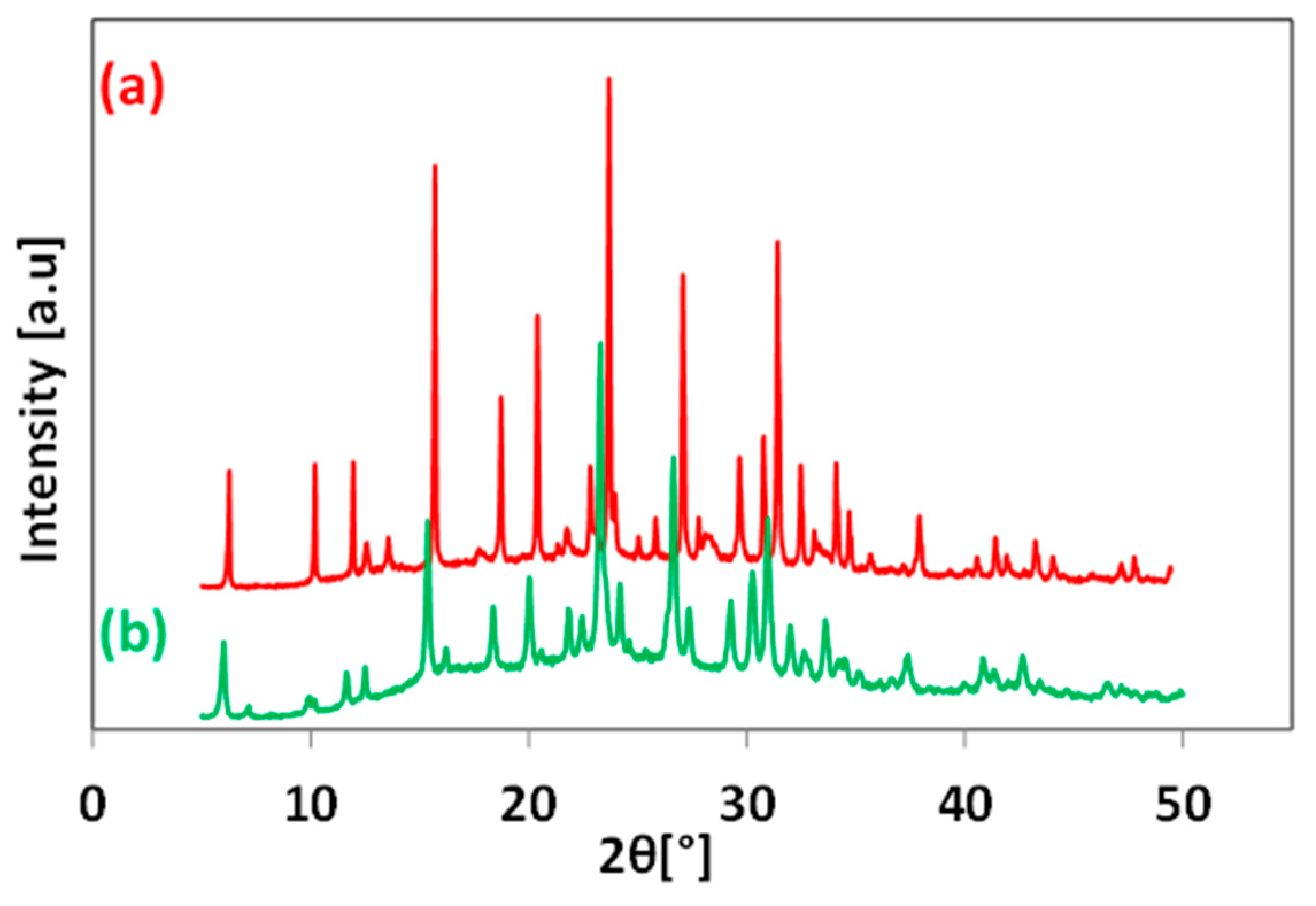
3.1. Effect of the Application of Organic SDA
3.2. Effect of Aging Time
3.3. Effect of Hydrothermal Temperature Program
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhodes, C.J. Properties, and applications of zeolites. Sci. Prog. 2010, 93, 223–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesic, A.; Meseldzija, S.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Onjia, A. Novel biocomposite films based on high methoxyl pectin reinforced with zeolite Y for food packaging applications. Foods 2022, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigermann, P.; Kärger, J.; Valiullin, R. Diffusion in microporous materials with embedded mesoporosities. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 178, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Gao, X.H.; Yan, Z.F.; Mintova, S. Diffusion and catalyst efficiency in hierarchical zeolite catalysts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1726–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ostraat, M.L. Innovations in hierarchical zeolite synthesis. Catal. Today 2016, 264, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hua, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Tian, Q.; Han, Y. Recent progress in the direct synthesis of hierarchical zeolites: Synthetic strategies and characterization methods. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 2195–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghfirah, A.; Ilmi, M.M.; Fajar, A.T.N.; Kadja, G.T.M. A review on the green synthesis of hierarchically porous zeolite. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Abduljawad, M.M.; Alassmy, Y.A.; Cardon, L.; Van Steenberge, P.H.; Sebakhy, K.O. A Comparative review of binder-containing extrusion and alternative shaping techniques for structuring of zeolites into different geometrical bodies. Catalysts 2023, 13, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.B.; Sun, M.N.; Xie, F.; Ren, D.D. Dry-gel synthesis of hierarchical TS-1 zeolite by using P123 and polyurethane foam as template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 183, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhchoune, M.; Duan, X.; Villalobos, L.F.; Avalos, C.E.; Agrawal, K.V. Hydrogen-sieving zeolitic films by coating zeolite nanosheets on porous polymeric support. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 672, 121454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosheva, L.; Valtchev, V.; Sterte, J. Silicalite-1 containing microspheres prepared using shape-directing macro-templates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 35–36, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosheva, L.; Sterte, J. ZSM-5 spheres prepared by resin templating. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2002, 142, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosheva, L.; Mihailova, B.; Valtchev, V.; Sterte, J. Zeolite beta spheres. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 48, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Koelewijn, R.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; van der Wel, P.C.; Sebakhy, K.O.; Pescarmona, P.P. Binder-free zeolite beta beads with hierarchical porosity: Synthesis and application as heterogeneous catalysts for anisole acylation. ChemCatChem 2022, 14, e202200518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassmy, Y.A.; Asgar Pour, Z.; Pescarmona, P.P. Efficient and easily reusable metal-free heterogeneous catalyst beads for the conversion of CO2 into cyclic carbonates in the presence of water as hydrogen-bond donor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7993–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breck, D.W. Crystalline Zeolite Y. U.S. Patent 3,130,007, 21 April 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Sebakhy, K.O. A review on the effects of organic structure-directing agents on the hydrothermal synthesis and physicochemical properties of zeolites. Chemistry 2022, 4, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, B.A.; Wang, H.; Norbeck, J.M.; Yan, Y. Controlling size and yield of zeolite Y nanocrystals using tetramethylammonium bromide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 59, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, I.; Widiastuti, N. Activation of zeolite-Y templated carbon with KOH to enhance the CO2 adsorption capacity. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2019, 15, 240–253. [Google Scholar]
- Król, M.; Koleżyński, A.; Mozgawa, W. Vibrational spectra of zeolite Y as a function of ion exchange. Molecules 2021, 26, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaabed, R.; Elknidri, H.; Elkhalfaouy, R.; Abdellah; Addaou; Laajab, A.; Lahsini, A. Zeolite Y synthesis without organic template: The effect of synthesis parameters. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, W.; Hongzhu, M. Factors affecting the synthesis of microsized NaY zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 25, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginting, S.B.; Yulia, Y.; Wardono, H.; Hanif, M.; Iryani, D.A. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite lynde type A (LTA): Effect of aging time. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1376, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihian, H.; Godazandeha, N. Synthesis of nano crystalline zeolite Y from bentonite. J. Porous Mater. 2009, 16, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebakhy, K.O.; Vitale, G.; Pereira-Almao, P. Dispersed Ni-doped aegirine nanocatalysts for the selective hydrogenation of olefinic molecules. ACS Appl. Nano Mater 2018, 1, 6269–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebakhy, K.O.; Vitale, G.; Pereira-Almao, P. Production of highly dispersed Ni within nickel silicate materials with the MFI structure for the selective hydrogenation of olefins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 8597–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Alassmy, Y.; Sebakhy, K.O. A survey on zeolite synthesis and the crystallization process: Mechanism of nucleation and growth steps. Crystals 2023, 13, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Abduljawad, M.M.; Alassmy, Y.; Alnafisah, M.S.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Van Steenberge, P.H.M.; Sebakhy, K.O. Synergistic catalytic effects of alloys of noble metal nanoparticles supported on two different supports: Crystalline zeolite Sn-Beta and carbon nanotubes for glycerol conversion to methyl lactate. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, D.G.; Asgar Pour, Z.; Langerak, J.; Bakker, B.; Pescarmona, P. P Binderless Faujasite beads with hierarchical porosity for selective CO2 adsorption for biogas upgrading. Molecules 2023, 28, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asgar Pour, Z.; Abu Zeitoun, E.; Alassmy, Y.A.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Van Steenberge, P.H.M.; Sebakhy, K.O. Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates. Crystals 2024, 14, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14121051
Asgar Pour Z, Abu Zeitoun E, Alassmy YA, El Hariri El Nokab M, Van Steenberge PHM, Sebakhy KO. Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates. Crystals. 2024; 14(12):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14121051
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsgar Pour, Zahra, Edrees Abu Zeitoun, Yasser A. Alassmy, Mustapha El Hariri El Nokab, Paul H. M. Van Steenberge, and Khaled O. Sebakhy. 2024. "Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates" Crystals 14, no. 12: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14121051
APA StyleAsgar Pour, Z., Abu Zeitoun, E., Alassmy, Y. A., El Hariri El Nokab, M., Van Steenberge, P. H. M., & Sebakhy, K. O. (2024). Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates. Crystals, 14(12), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14121051







