Tungsten Bronze-Type Ceramics for Temperature-Stable Energy Storage Properties: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
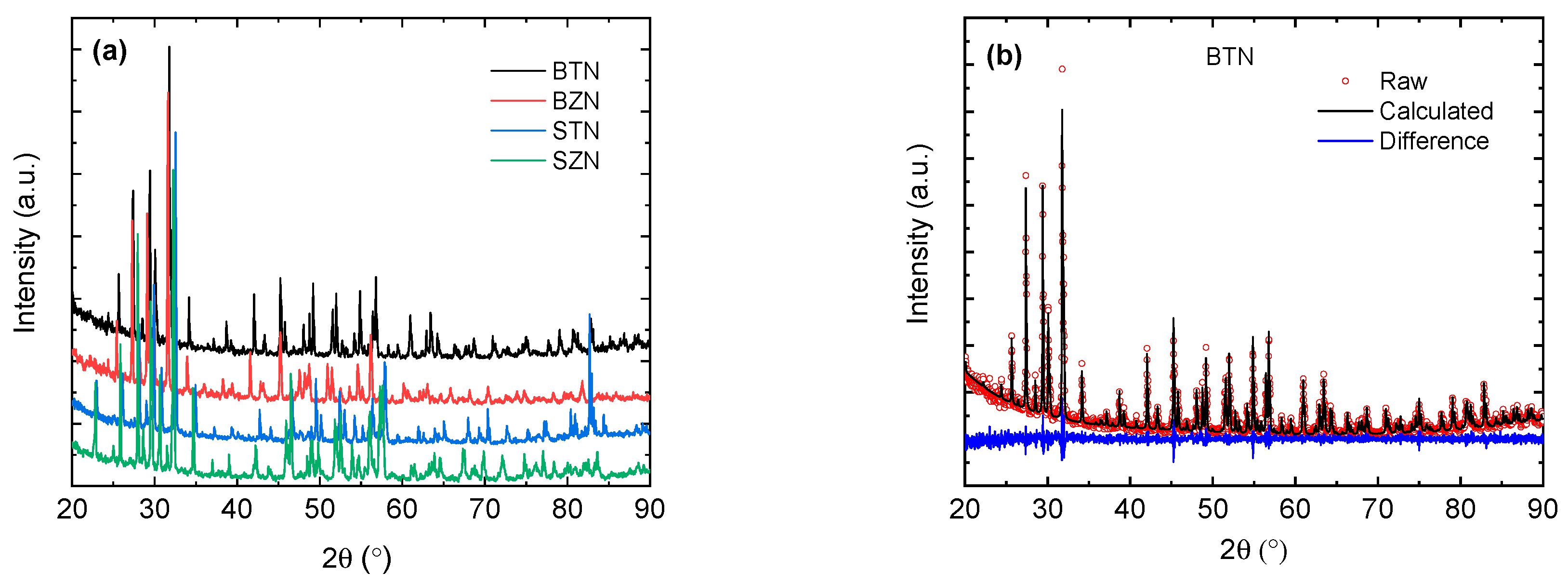
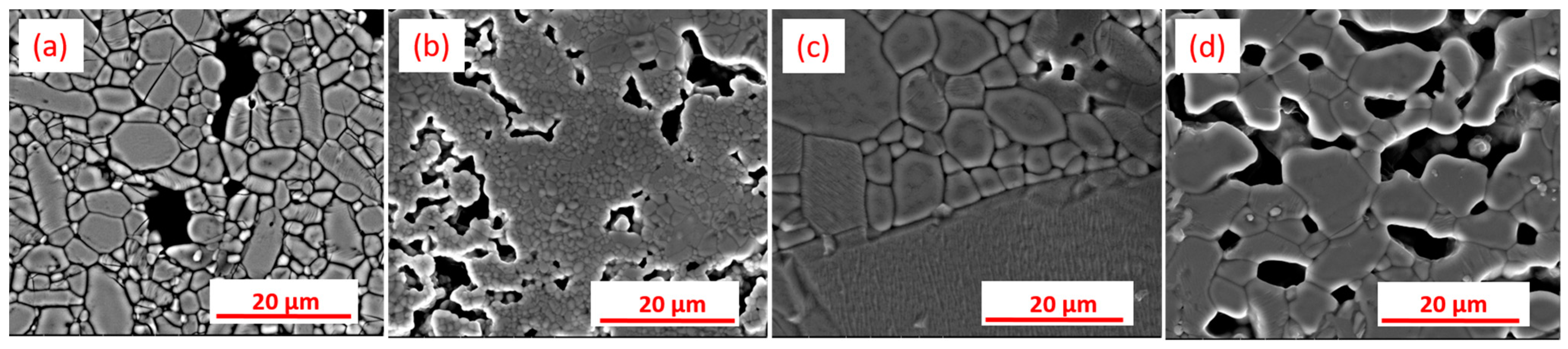
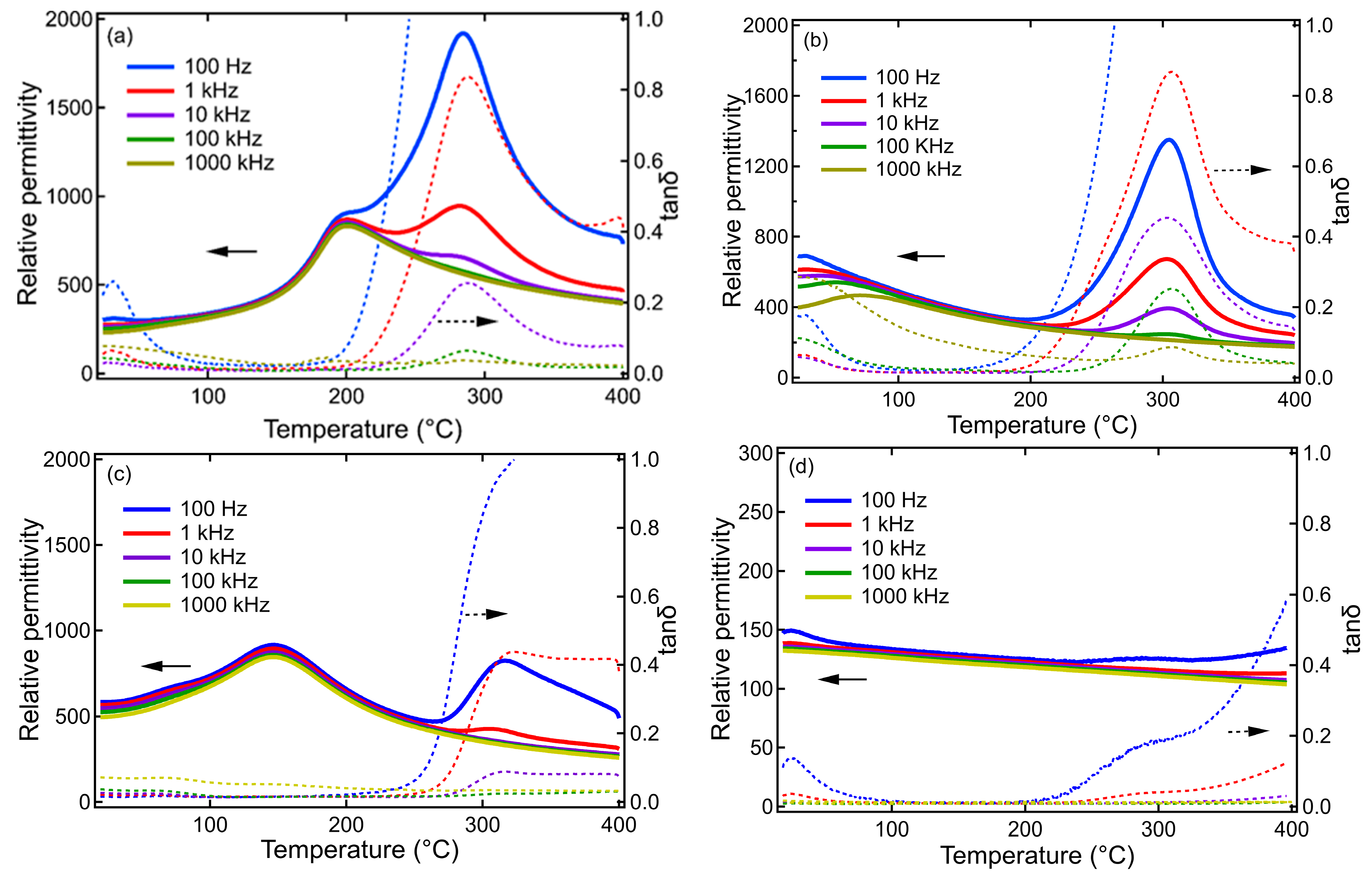
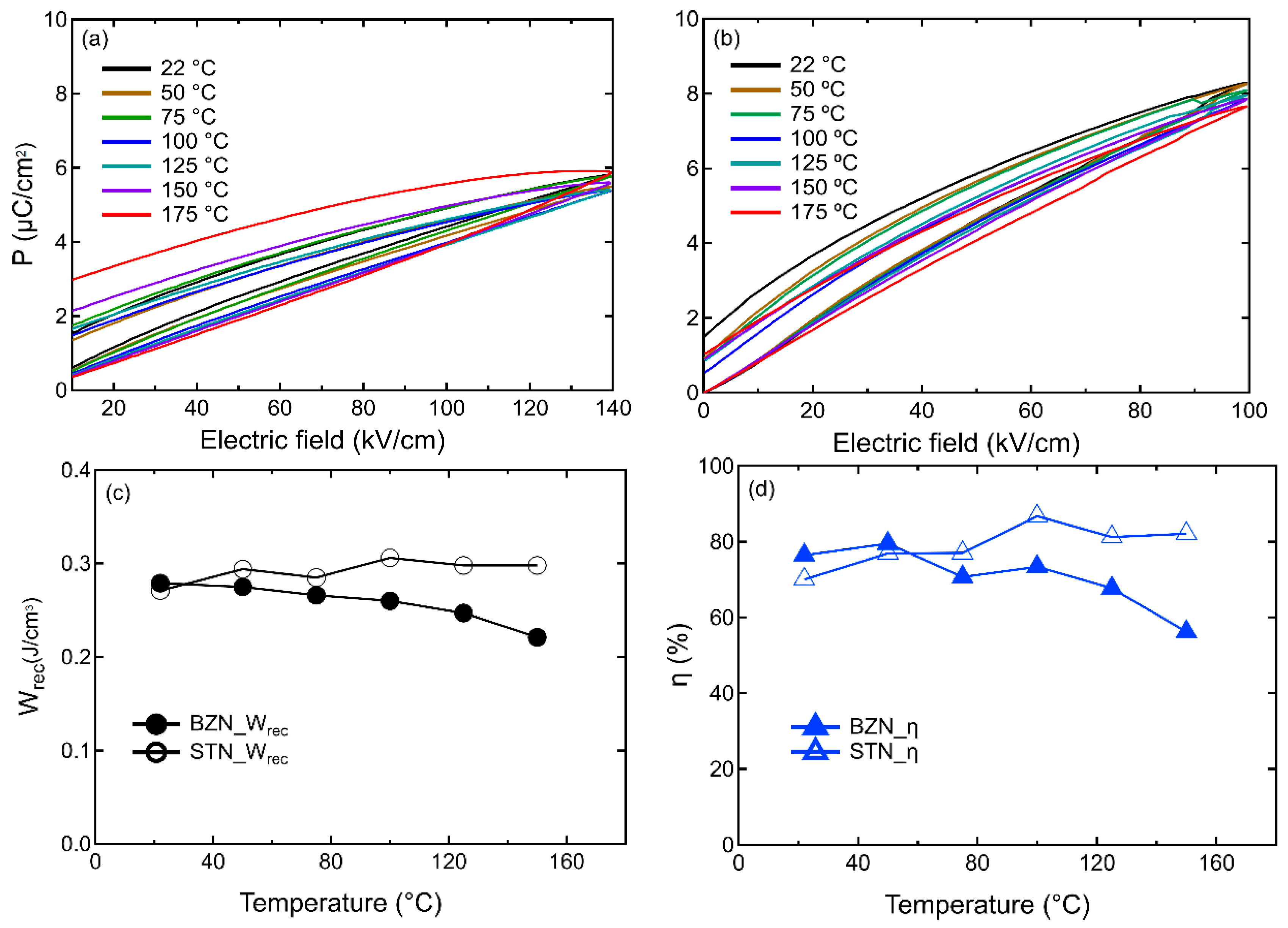
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Ye, W.; Bu, X.; Zheng, P.; Li, L.; Wen, F.; Bai, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Remarkable capacitive performance in novel tungsten bronze ceramics. Dalton Trans. 2020, 50, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, C.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, W.; Yuan, C.; Chen, G.; Rao, G. Tailoring antiferroelectricity with high energy-storage properties in Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–BaTiO3 ceramics by modulating Bi/Na ratio. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 10810–10815. [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara, H.; Randall, C.A.; Trolier-McKinstry, S. High-energy density capacitors utilizing 0.7BaTiO3–0.3BiScO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Du, H.; Qu, S.; Hou, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, Z. Significantly enhanced recoverable energy storage density in potassium–sodium niobate-based lead free ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13778–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, P.; Abrahams, S.; Bernstein, J.L. Ferroelectric tungsten bronze-type crystal structures. I. Barium Strontium niobate Ba0.27Sr0.75Nb2O5. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 5048–5057. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, E.; Zhang, S. Crystal structure relaxor behaviors and energy storage performance of (Sr0.7Ba0.3)5LaNb7Ti3O30 tungsten bronze ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2019, 46, 6108–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Wang, P.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, S.-H. Site Occupancy and Dielectric Characteristics of Strontium Barium Niobate Ceramics: Sr/Ba Ratio Dependence. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, 7042–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, S.; Vasishth, A.; Devi, S.; Anand, G. A review on tungsten bronze ferroelectric ceramics as electrically tunable devices. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2018, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Ravez, J. Solid-state chemistry and non-linear properties of tetragonal tungsten bronzes materials. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-X.; Krogstad, M.J.; Zheng, H.; Osborn, R.; Rosenkranz, S.; Phelan, D. Active and passive defects in tetragonal tungsten bronze relaxor ferroelectrics. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2022, 34, 405401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, T.A.; Lu, T.; Blanchard, P.; Hester, J.R.; Gu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Schmid, S. Synthesis, structure and dielectric properties of the Sr3Ti1−xZrxNb4O15, (0 ≤ x≤ 1), series of tungsten bronze type compounds. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 4994–5001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.-H.; Qi, B. Effect of CASP glass doping on sintering and dielectric properties of SBN ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 473, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Yuan, G.; Chen, J.; Gu, Z.B.; Yang, B.; Yin, J.; Cao, W. Structural evolving sequence and porous Ba6Zr2Nb8O30 ferroelectric ceramics with ultrahigh breakdown field and zero strain. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Z. Exploring determinants of lattice structure and high energy storage properties of Fe-doped SBN ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 11109–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, N.C. The crystal structure of the tetragonal bronze, Ba6Ti2Nb8O30. Acta Crystallogr. 1965, 18, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ekren, D.; Azough, F.; Day, S.J.; Chen, K.; Mahajan, A.; Kepaptsoglou, D.M.; Ramasse, Q.M.; Reece, M.J.; Freer, R. The structure and thermoelectric properties of tungsten bronze Ba6Ti2Nb8O30. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 125115. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, G.; Cava, R.; Peck, W.; Krajewski, J. Dielectric properties of barium titanium niobates. J. Mater. Res. 1997, 12, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, Y.; Iwasaki, H. Ferroelectric and optical properties of Ba6Ti2Nb8O30 single crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1973, 34, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarotti, V.; Capsoni, D.; Bini, M.; Azzoni, C.B.; Mozzati, M.C.; Galinetto, P.; Chiodelli, G. Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Pure and Doped Ba6Ti2Nb8O30 Tungsten Bronze. Cheminform 2006, 37, 17798–17805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Schmid, S.; Chen, X.; Peng, B.; Li, C.; Hu, C.; Liu, L.; Hinterstein, M. Structure and relaxor ferroelectric behavior of the novel tungsten bronze type ceramic Sr5BiTi3Nb7O30. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 131, 164102. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, E.O.; Gandini, A.; Ok, K.M.; Zhang, L.; Halasyamani, P.S. Syntheses, structures, second-harmonic generating, and ferroelectric properties of tungsten bronzes: A6M2M ‘8O30 (A= Sr2+, Ba2+, or Pb2+; M= Ti4+, Zr4+, or Hf4+; M ‘= Nb5+ or Ta5+). Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3616–3622. [Google Scholar]
- Neurgaonkar, R.; Nelson, J.; Oliver, J. Ferroelectric properties of the tungsten bronze M2+6M4+2Nb8O30 solid solution systems. Mater. Res. Bull. 1992, 27, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D. Tungsten Bronze Structured Compounds for Thermoelectric Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Manchester, Manchester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.S.; Subrahmanyam, A.S.V.; Viswarupachary, P. Microstructural and anomalous resistivity behavior of modified ferroelectric Ba6Ti2Nb8O30. Ferroelectrics 1998, 215, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Wu, Y.J. Diffused ferroelectrics of Ba6Ti2Nb8O3 and Br6Ti2Nb8O3 with filled tungsten-bronze structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 084110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.J.; Akimune, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Hirosaki, N.; Sekiya, T. Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of tetragonal tungsten bronze Sr2−xCaxNaNb5O15 (x= 0.05–0.35) ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 835–837. [Google Scholar]
- Bendahhou, A.; Marchet, P.; El-Houssaine, A.; El Barkany, S.; Abou-Salama, M. Relationship between structural and dielectric properties of Zn-substituted Ba5CaTi2−xZnxNb8O30 tetragonal tungsten bronze. CrystEngComm 2021, 23, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, B.; Das, P.R.; Padhee, R.; Choudhary, R. Phase transition and conduction mechanism of rare earth based tungsten-bronze compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 540, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.R.; Biswal, L.; Behera, B.; Choudhary, R.N.P. Structural and electrical properties of Na2Pb2Eu2W2Ti4X4O30 (X= Nb, Ta) ferroelectric ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Bu, X.; Zheng, P.; Li, L.; Wen, F.; Bai, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhai, J.; et al. Simultaneously Realizing Superior Energy Storage Properties and Outstanding Charge–Discharge Performances in Tungsten Bronze-Based Ceramic for Capacitor Applications. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 6559–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Shen, S.; Hao, R.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, D.; Liang, P.; Chao, X.; Wei, L.; Yang, Z. Relaxor nature and superior energy storage performance of Sr2Ag0.2Na0.8Nb5O15-based tungsten bronze ceramics through B-site substitution. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 433, 133812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Lou, X.; Gao, Y.; Shi, P.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Cui, J.; Wei, L.; Sun, S. Interfaces, Enhancing Comprehensive Energy Storage Properties in Tungsten Bronze Sr0.53Ba0.47Nb2O6-Based Lead-free Ceramics by B-Site Doping and Relaxor Tuning. ACS Appl. Mater. 2022, 14, 34855–34866. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Hao, R.; Yan, Z.; Hou, S.; Peng, Z.; Wu, D.; Liang, P.; Chao, X.; Wei, L.; Yang, Z. Enhanced energy storage properties and superior thermal stability in SNN-based tungsten bronze ceramics through substitution strategy. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 2781–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. Ferroelectric Relaxor Quantum Crystals. J. Cryst. 2018, 8, 180. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Khansur, N.H. Tungsten Bronze-Type Ceramics for Temperature-Stable Energy Storage Properties: A Feasibility Study. Crystals 2023, 13, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13071073
Shi X, Khansur NH. Tungsten Bronze-Type Ceramics for Temperature-Stable Energy Storage Properties: A Feasibility Study. Crystals. 2023; 13(7):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13071073
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xi, and Neamul H. Khansur. 2023. "Tungsten Bronze-Type Ceramics for Temperature-Stable Energy Storage Properties: A Feasibility Study" Crystals 13, no. 7: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13071073
APA StyleShi, X., & Khansur, N. H. (2023). Tungsten Bronze-Type Ceramics for Temperature-Stable Energy Storage Properties: A Feasibility Study. Crystals, 13(7), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13071073








