The Effect of Process Parameters on the Properties and Microstructure of A380 Aluminum Alloy Casting with Different Wall Thicknesses
Abstract
1. Introduction
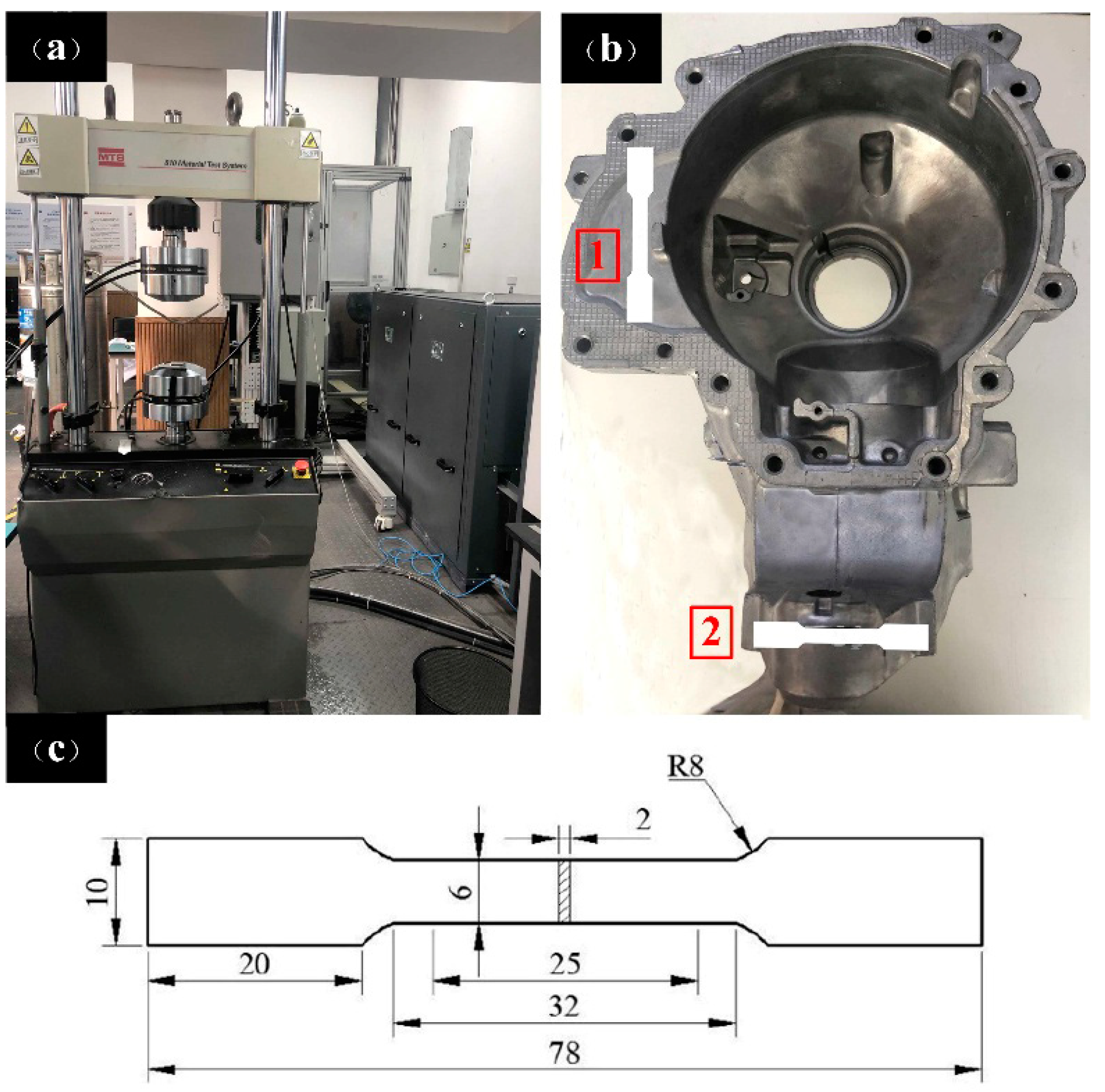
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Material and Tensile Tests
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
3. Experimental Results
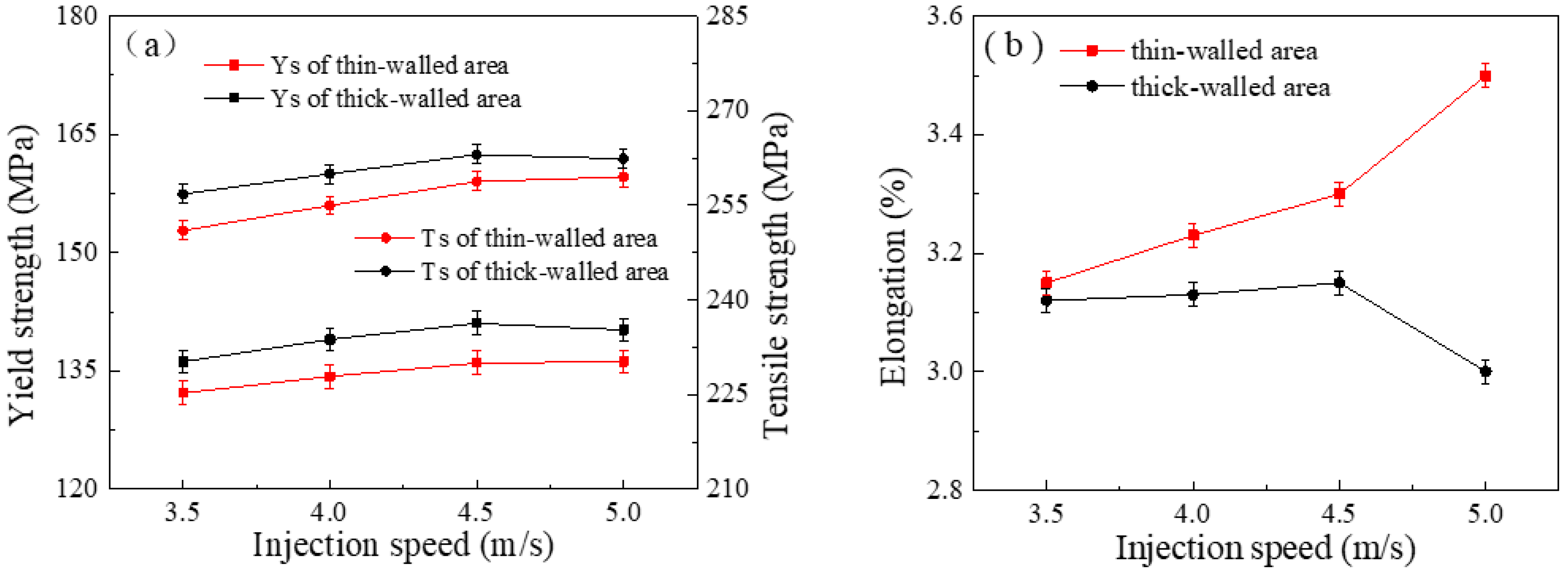
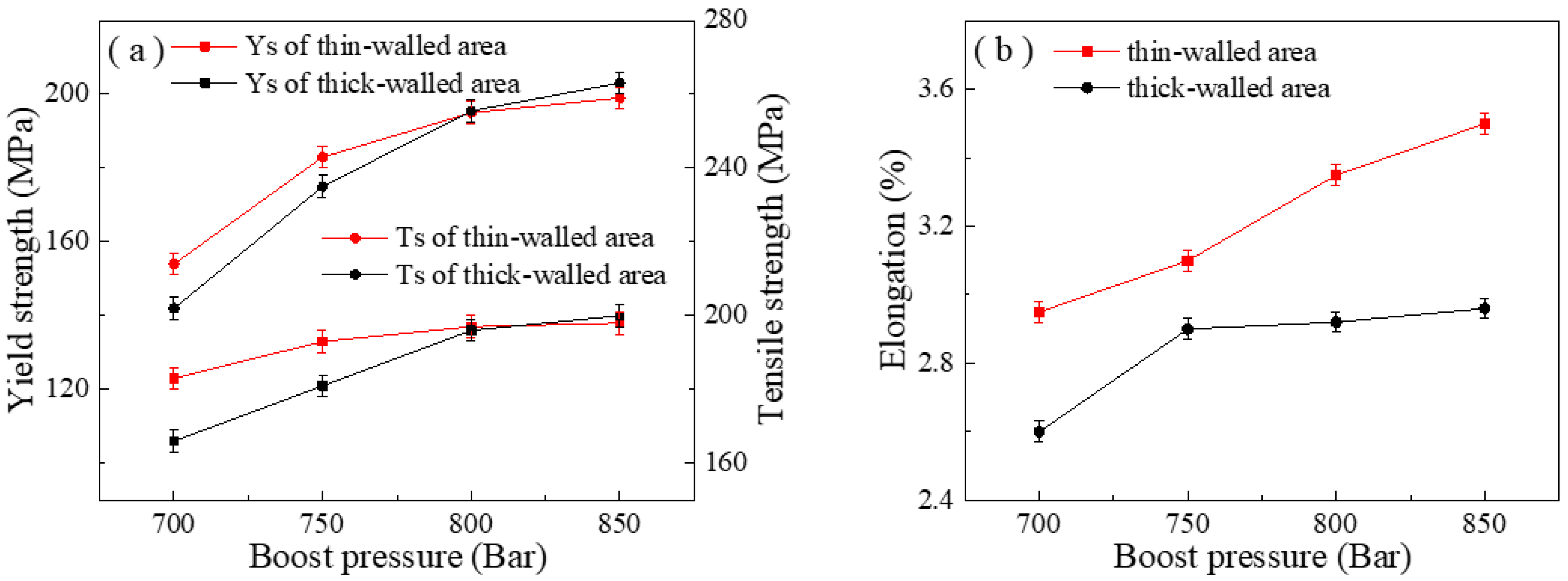
3.1. Mechanical Properties of Castings with Different Wall Thickness Areas
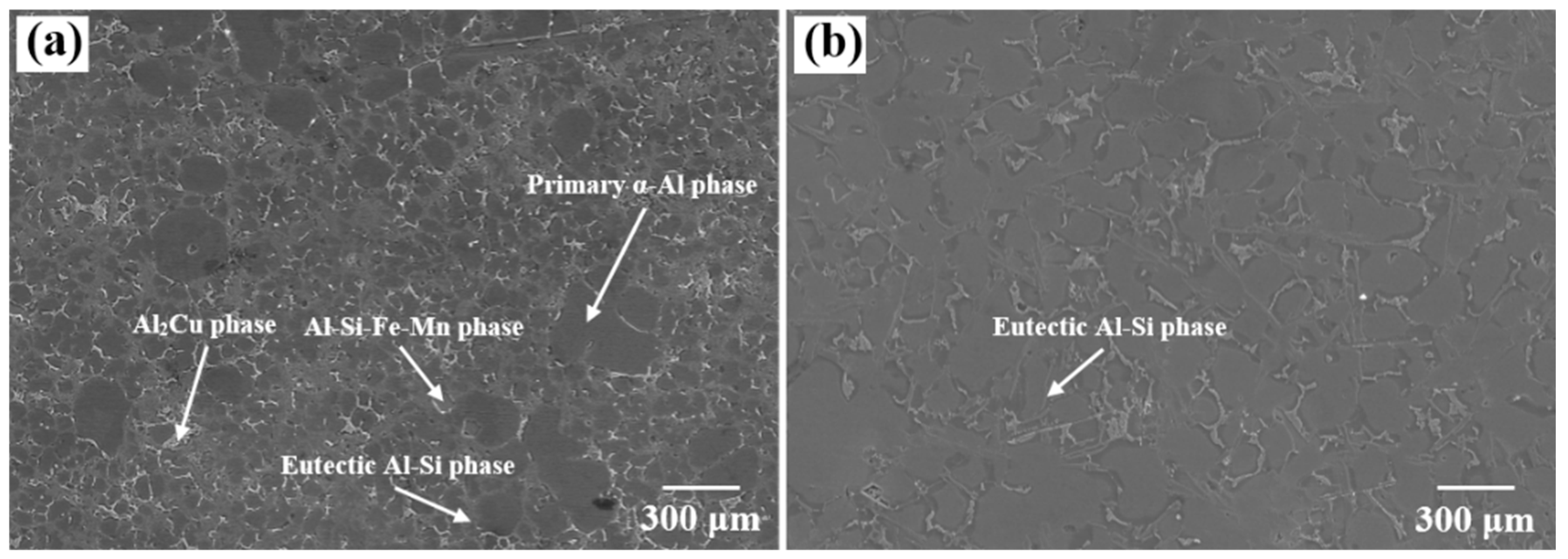
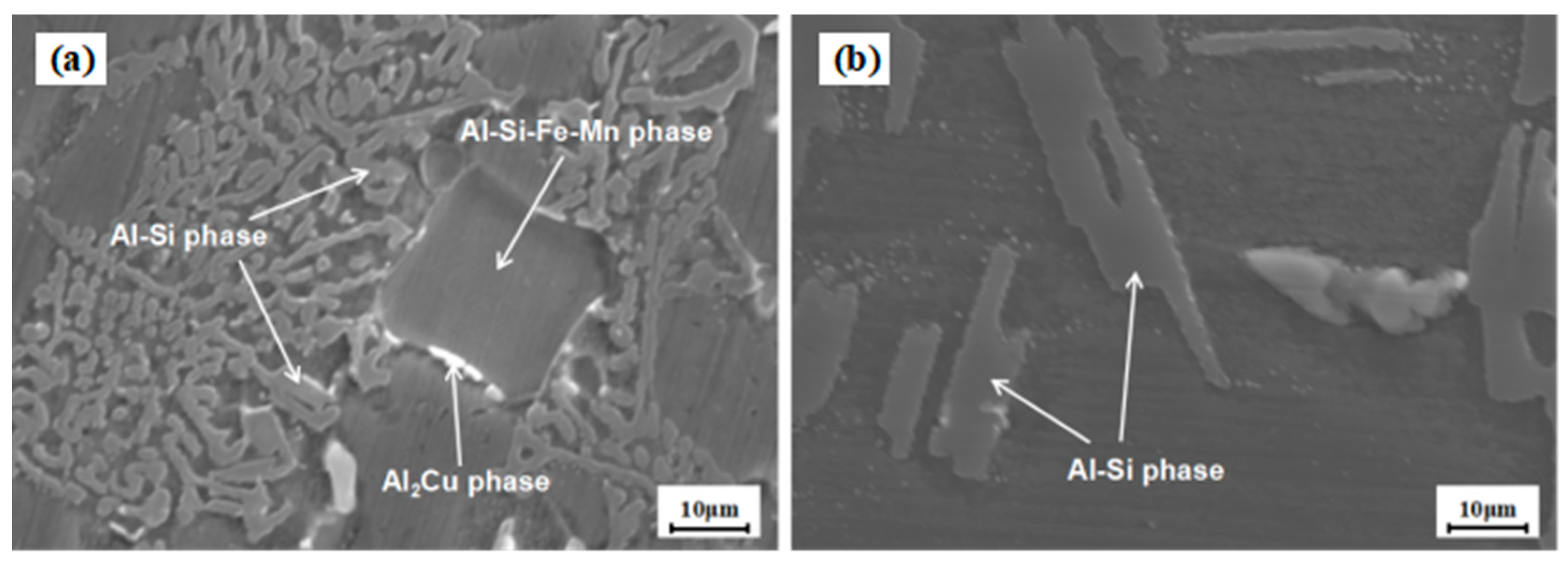
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
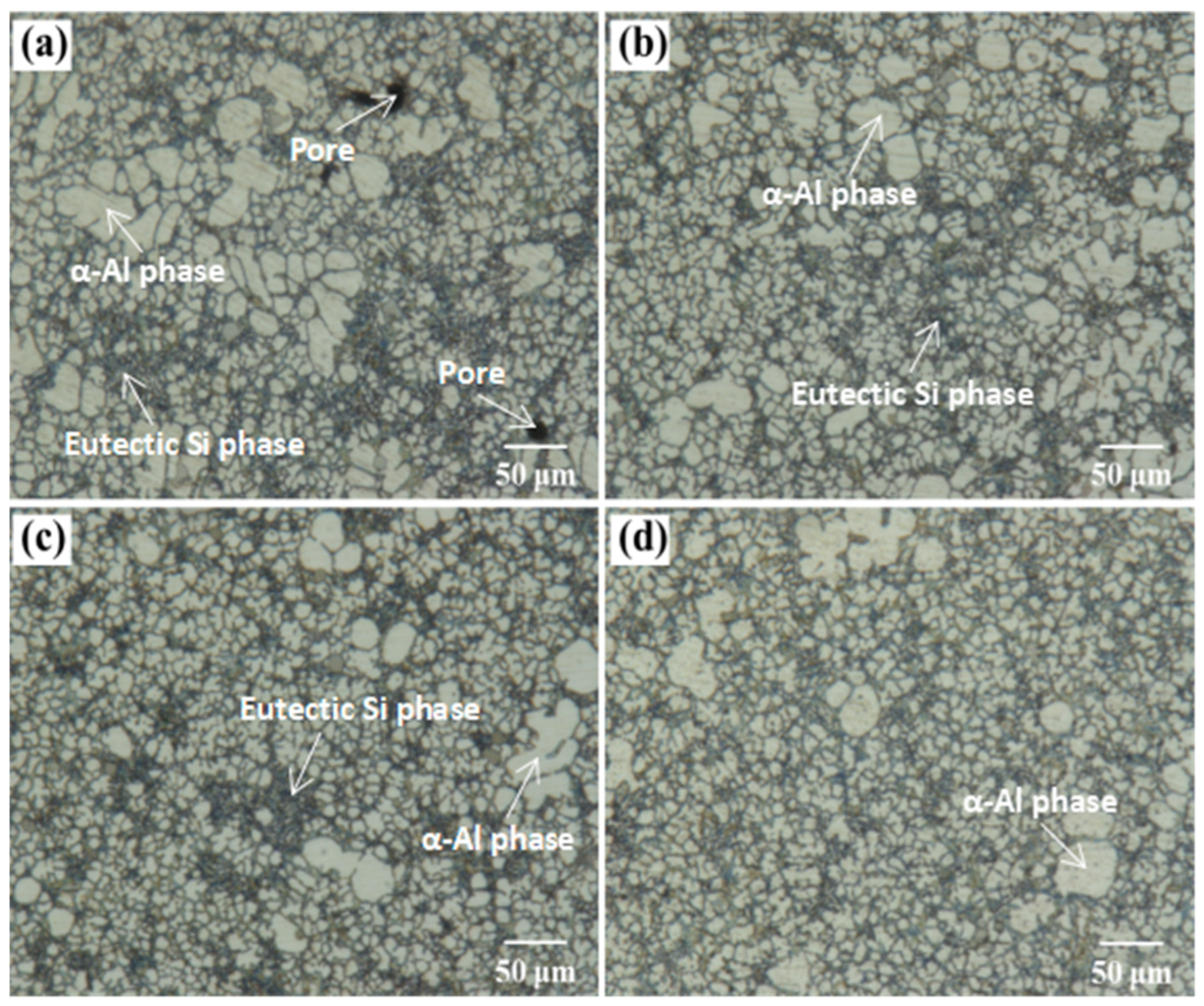
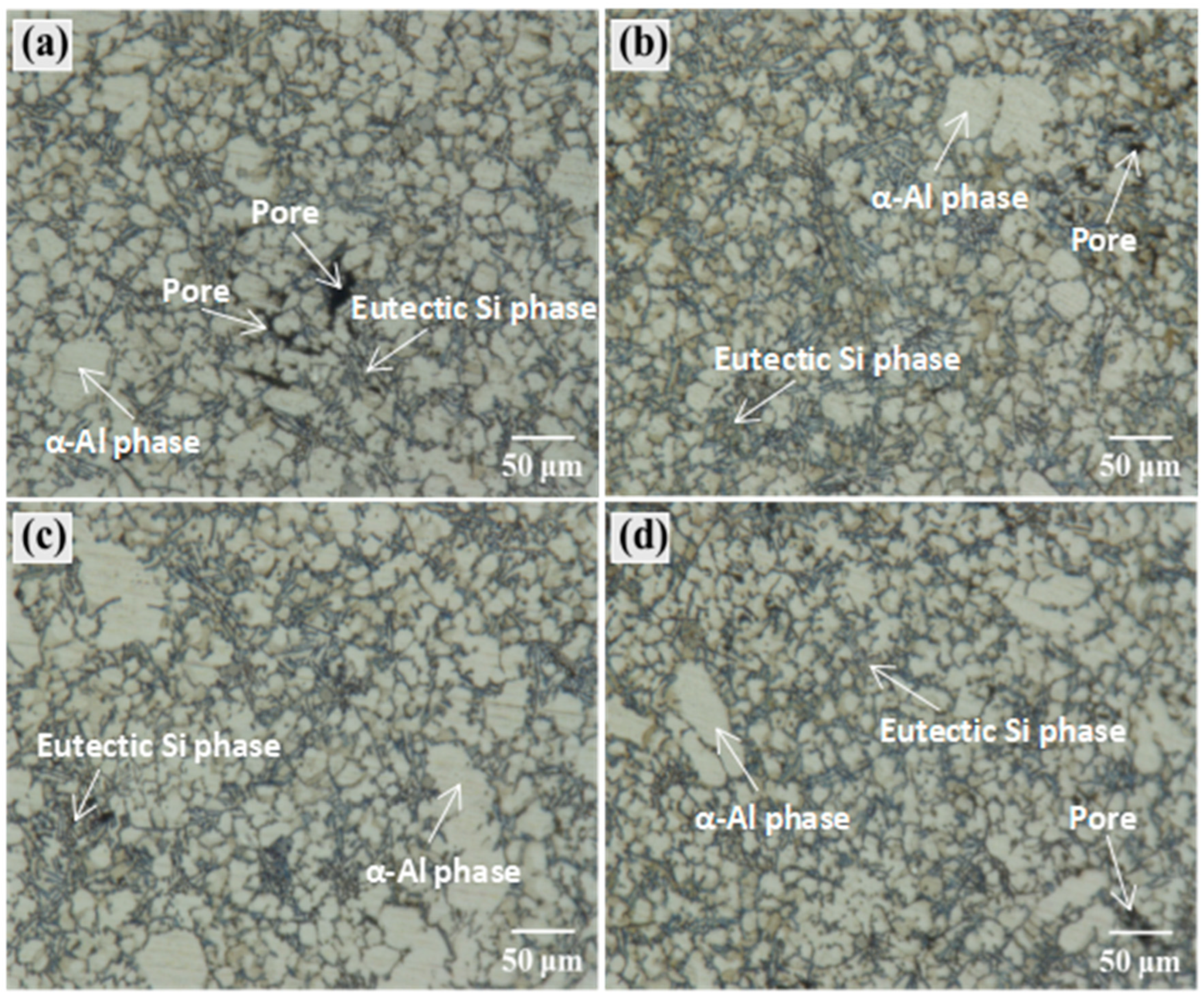
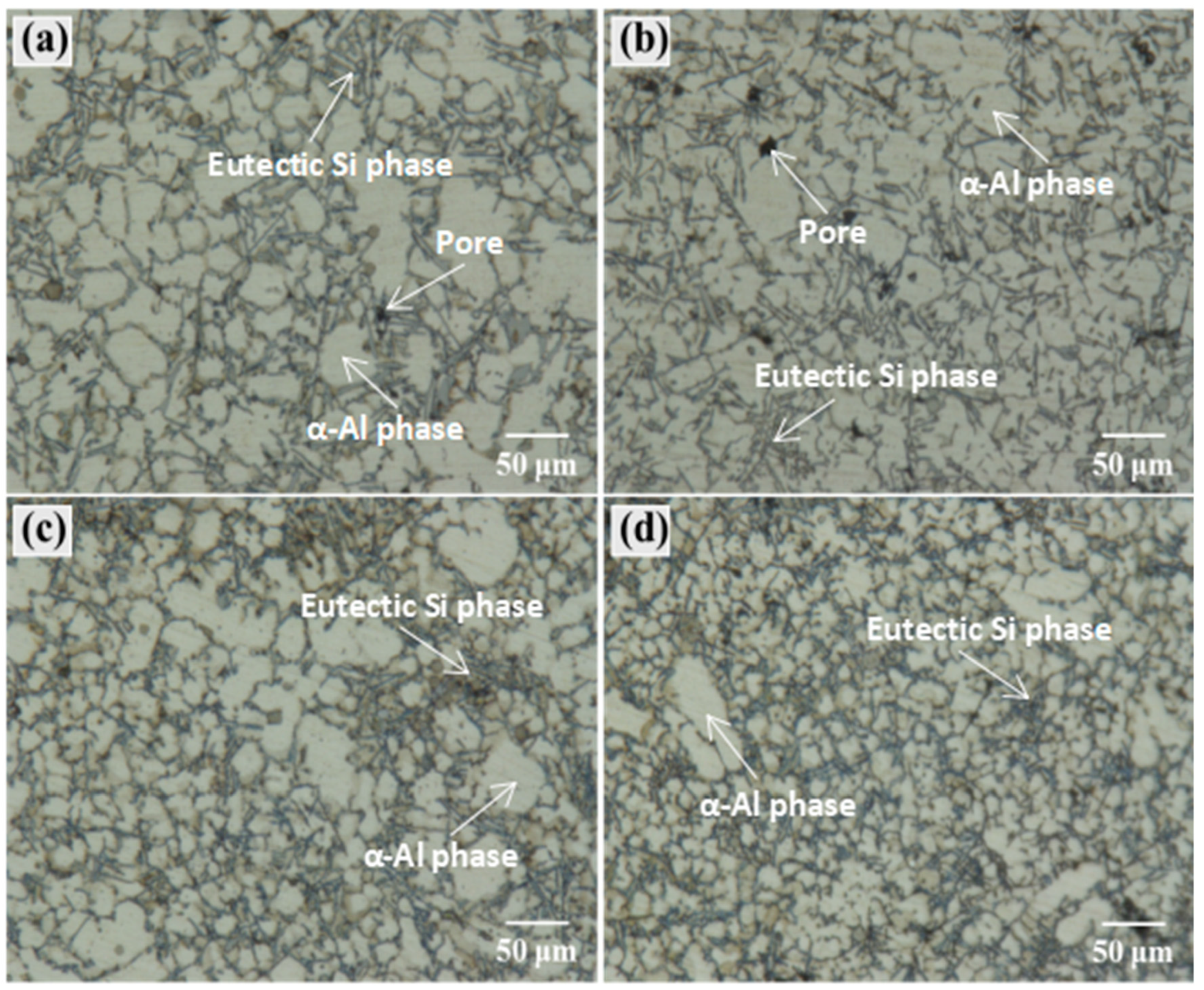
3.2.1. Microstructure Analysis at Different Wall Thicknesses
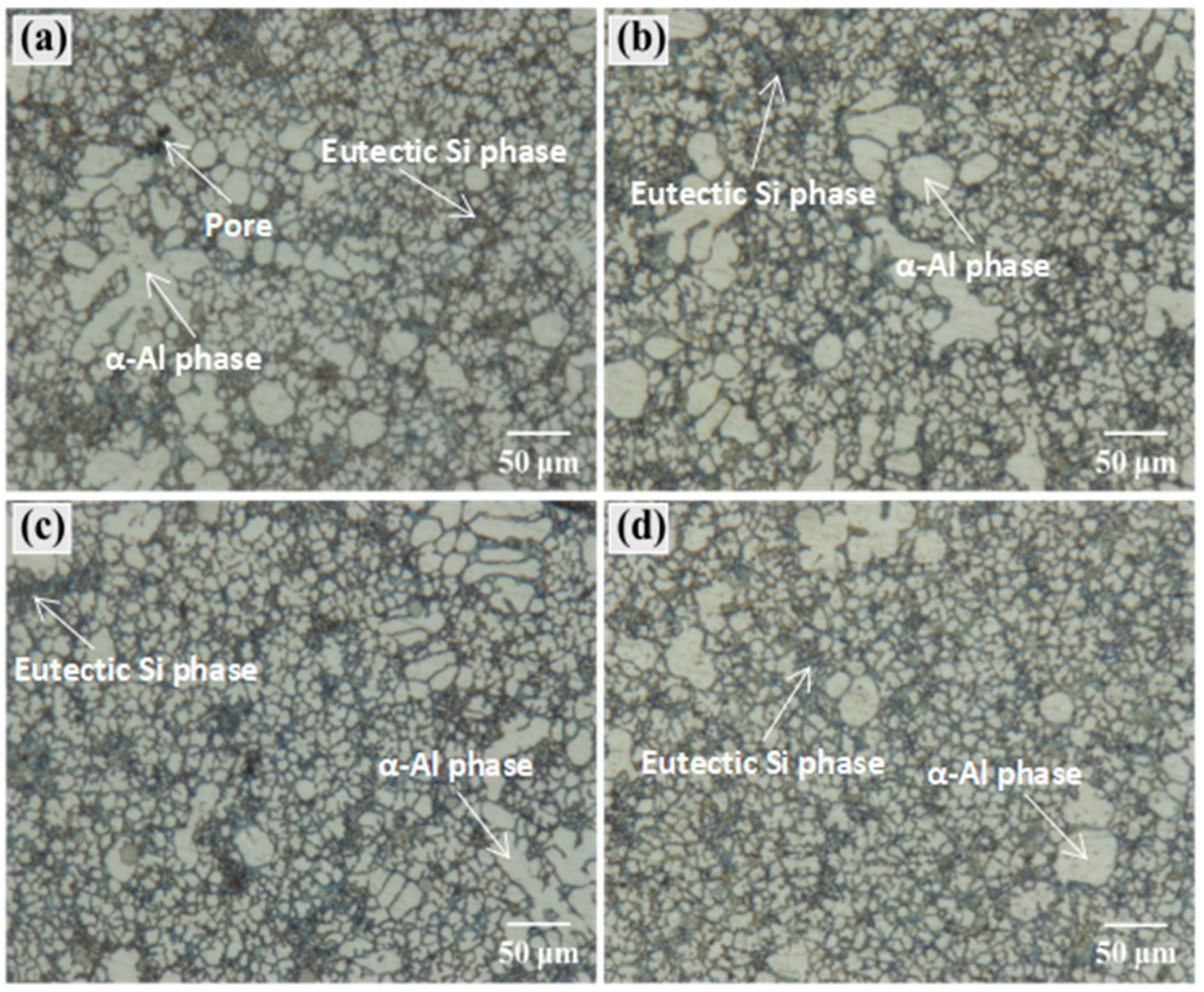
3.2.2. Effect of Injection Speed on the Microstructure at Different Wall Thicknesses of the Casting
3.2.3. Effect of Boost Pressure on the Microstructure at Different Wall Thicknesses of the Casting
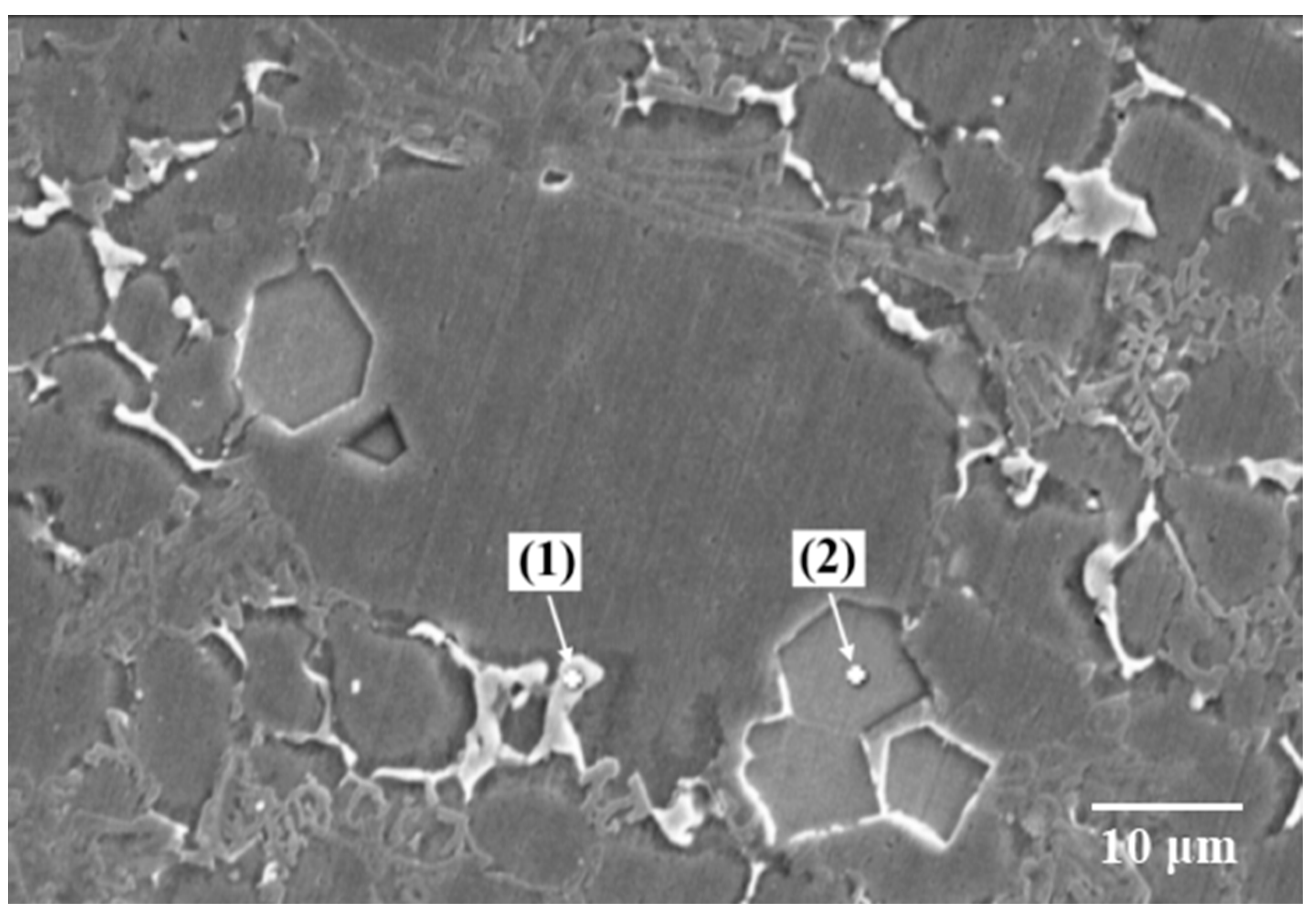
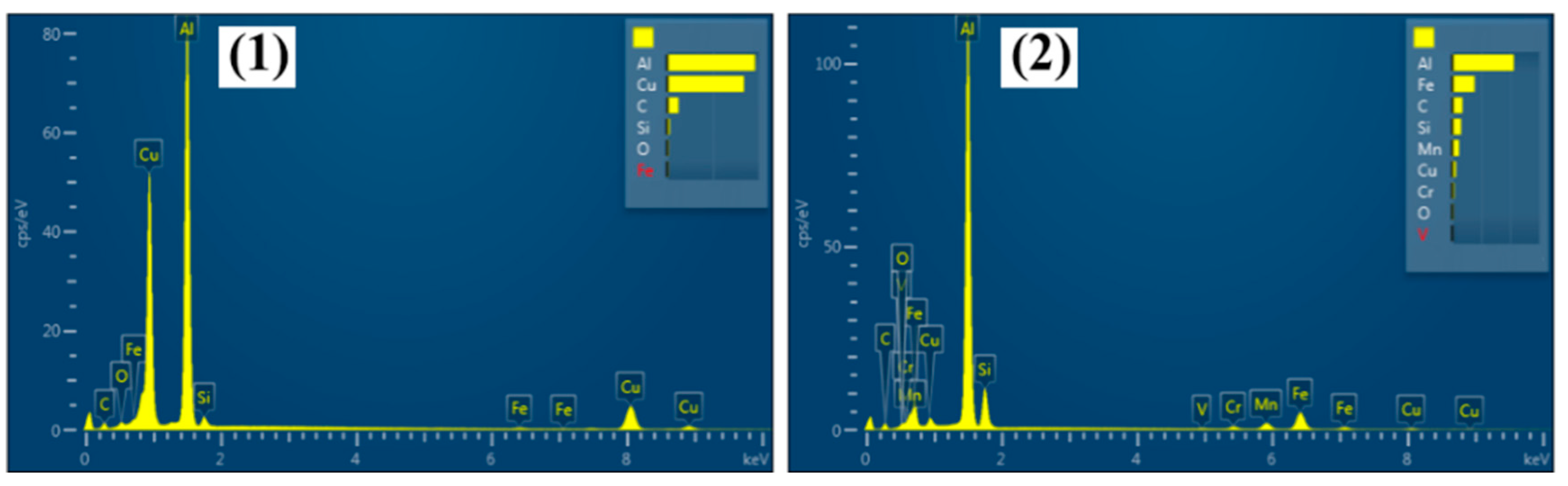
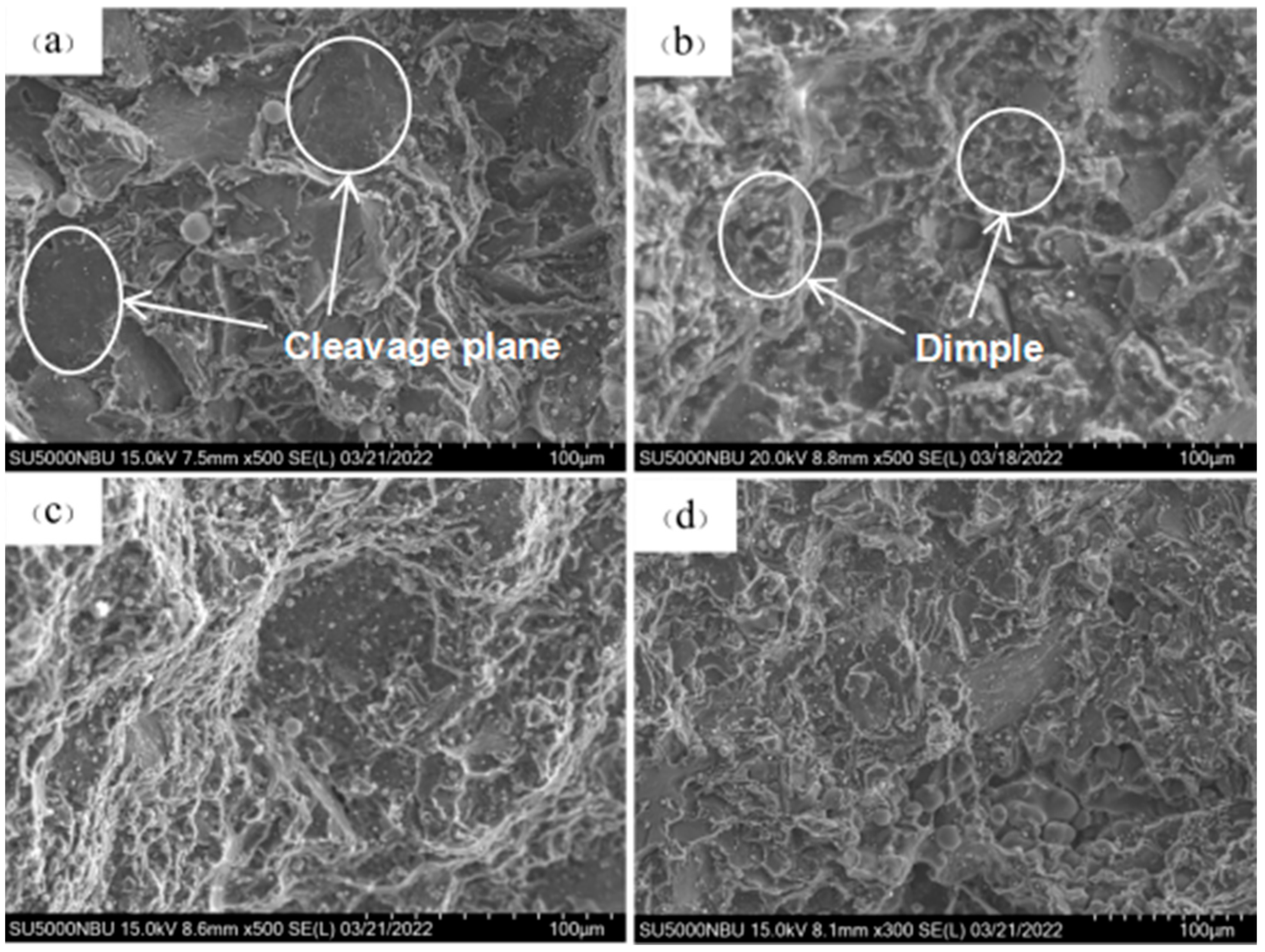
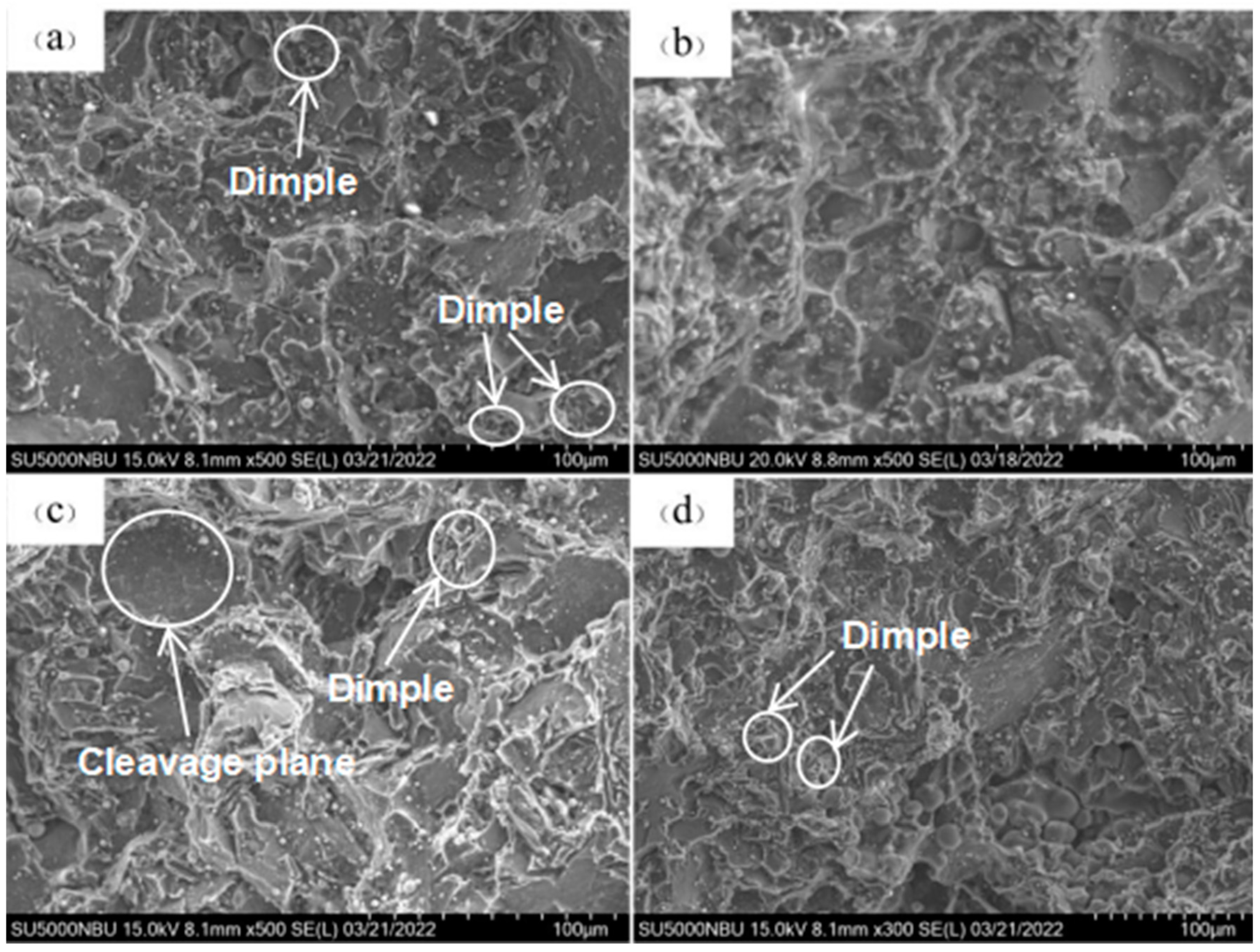
3.2.4. Fracture Morphology Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Injection Speed on the Mechanical Properties at Different Wall Thicknesses of the Casting
4.2. Effect of Boost Pressure on the Mechanical Properties at Different Wall Thicknesses of the Casting
4.3. Effect of Process Parameters on the Microstructure at Different Wall Thicknesses of the Casting
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The effects of injection speed and boost pressure on the mechanical properties of castings with different wall thicknesses are significant. Among them, the effect of injection speed on the mechanical properties of the thin-walled area of the casting is more significant. The strength and elongation of the thin-walled area of the casting gradually increase as the injection speed increases. The boost pressure has a greater effect on the mechanical properties of the thick-walled area of the member. The strength and elongation of the thick-walled area of the member increase significantly with the increase in boost pressure.
- (2)
- Increasing the boost pressure can significantly improve the microstructure of the casting, while the boost pressure has a significant effect on the microstructure of the thick-walled area of the casting. The primary α-Al phase and secondary α-Al phase in the thick-walled area of the casting are gradually refined as the boost pressure increases. In addition, the eutectic Si phase and Al-Si-Fe-Mn phase in the alloy are more uniformly distributed. Therefore, the selection of suitable boost pressure and injection speed has an important influence on the overall forming quality of the casting. In this work, by comprehensively considering the microstructure and overall mechanical properties changes in both thick-walled and thin-walled areas, it is found that the overall properties of the casting are the best when the injection speed is 4.5 m/s and the pressure boosting pressure is 850 bar.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torshizian, M.R.; Aliakbari, K.; Ghonchegi, M. Failure analysis of ductile iron differential housing spline in 4WD passenger car. Int. J. Metalcast. 2021, 15, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Finite element analysis for die casting parameters in high-pressure die casting process. China Foundry 2019, 16, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargusch, M.S.; Dour, G.; Schauer, N.; Dinnis, C.M.; Savage, G. The influence of pressure during solidification of high pressure die cast aluminium telecommunications components. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 180, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verran, G.O.; Mendes, R.P.K.; Rossi, M.A. Influence of injection parameters on defects formation in die casting Al12Si1, 3Cu alloy: Experimental results and numeric simulation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 179, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Choi, K.S.; Li, D. Predicting the influence of pore characteristics on ductility of thin-walled high pressure die casting magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 572, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasegaram, D.R.; Givord, M.; O’Donnell, R.G.; Finnin, B.R. Improvements engineered in UTS and elongation of aluminum alloy high pressure die castings through the alteration of runner geometry and plunger velocity. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timelli, G.; Fabrizi, A. The effects of microstructure heterogeneities and casting defects on the mechanical properties of high-pressure die-cast AlSi9Cu3 (Fe) alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5486–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otarawanna, S.; Gourlay, C.M.; Laukli, H.I.; Dahle, A.K. Microstructure formation in AlSi4MgMn and AlMg5Si2Mn high-pressure die castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Wang, A.; Su, M. Numerical Simulation of Temperature and Fluid Fields in Solidification Process of Ferritic Stainless Steel under Vibration Conditions. Crystals 2019, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, E. 2D cellular automaton–finite element simulation of grain structure and macrosegregation during solidification of Al-4wt% Cu Alloy. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2016, 29, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Lu, Y.; Cinkilic, E.; Miao, J.; Klarner, A.; Yan, X.; Luo, A. Predicting grain structure in high pressure die casting of aluminum alloys: A coupled cellular automaton and process model. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 161, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiong, S. Effect of as-cast microstructure heterogeneity on aging behavior of a high-pressure die-cast A380 alloy. Mater. Charact. 2018, 135, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Limodin, N.; Tandjaoui, A.; Quaegebeur, P.; Osmond, P.; Balloy, D. Influence of Sr, Fe and Mn content and casting process on the microstructures and mechanical properties of AlSi7Cu3 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 689, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, B.; Fan, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y. Microstructures and mechanical properties of heat-treated Al-5.0Cu-0.5Fe squeeze cast alloys with different Mn/Fe ratio. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 588, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, B.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y. Microstructures and mechanical properties of squeeze cast Al-5.0Cu-0.6Mn alloys with different Fe content. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, M.; Tian, B.; Li, X.; Xiong, S. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of defect bands in vacuum-assisted high-pressure die casting AE44 alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 1852–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xiong, S. The correlation between as-cast and aged microstructures of high-vacuum die-cast Mg-9Al-1Zn magnesium alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zheng, M.; Qiao, X.; Wu, K.; Peng, Q.; Yang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of WE43 magnesium alloy fabricated by direct-chill casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 684, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Patel, G.R.; Gokhale, A.M. Inverse surface macro-segregation in high-pressure die-cast AM60 magnesium alloy and its effects on fatigue behavior. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vončina, M.; Medved, J.; Bončina, T. Effect of Ce on morphology of α(Al)-Al2Cu eutectic in Al-Si-Cu alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Suetsugu, S.; Tsunekawa, Y. Refinement of eutectic Si phase in Al−5Si alloys with Yb additions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Prabhu, K.N. Modification of eutectic silicon in Al-Si alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 3009–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, M.M.; Guthy, H.V. The aluminum-silicon eutectic reaction: Mechanisms and crystallography. J. Light Met. 2001, 1, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Caceres, C.H.; Griffiths, J.R. Damage by eutectic particle cracking in aluminum casting alloys A356/357. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 2901–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarbarmas, M.; Emamy, M.; Alipour, M. Microstructure, hardness and tensile properties of A380 aluminum alloy with and without Li additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 582, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, D.; Mao, F.; Jian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y. Effect of cooling rate on eutectic Si in Al-7.0Si-0.3Mg alloys modified by La additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschini, L.; Morri, A.; Morri, A.; Pivetti, G. Predictive equations of the tensile properties based on alloy hardness and microstructure for an A356 gravity die cast cylinder head. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Jia, G.; Hao, Z. Non-equilibrium microstructure of hyper-eutectic Al-Si alloy solidified under superhigh pressure. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 4149–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Yong, Z.; Zheng, S. New model of Gibbs free energy difference for bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, M.; Gao, M.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W. Solidification of FeSi2 alloy under high pressure. Acta Phys. Sin. 2004, 53, 2378. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El-khair, M.T. Microstructure characterization and tensile properties of squeeze-cast AlSiMg alloys. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, X. Morphologies and growth mechanisms of α-Al (FeMn) Si in Al-Si-Fe-Mn alloy. Mater. Lett. 2013, 110, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, S.; Lü, S.; Ping, A.; Wu, H. Effects of high-pressure rheo-squeeze casting on the Fe-rich phases and mechanical properties of Al-17Si-(1,1.5)Fe alloys. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2018, 25, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiekea, K.N.; Aku, S.Y.; Yawas, D.S. Effects of pressure on the mechanical properties and microstructure of die cast aluminum A380 alloy. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2014, 2, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, J.; Liu, X. Evolution of Fe-rich phases in Mg melt and a novel method for separating Al and Fe from Al-Si-Fe alloys. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Element | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Cr | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 7.5~9.5 | 0.79 | 3.0~4.0 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 1.44 | 0.03 | 0.03 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, W.; Lin, B.; Shao, Y.; Lin, L.; Fu, B.; Yu, Z. The Effect of Process Parameters on the Properties and Microstructure of A380 Aluminum Alloy Casting with Different Wall Thicknesses. Crystals 2023, 13, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040587
Li H, Zhang H, Peng W, Lin B, Shao Y, Lin L, Fu B, Yu Z. The Effect of Process Parameters on the Properties and Microstructure of A380 Aluminum Alloy Casting with Different Wall Thicknesses. Crystals. 2023; 13(4):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040587
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, He, Han Zhang, Wenfei Peng, Bo Lin, Yiyu Shao, Longfei Lin, Bangjie Fu, and Ziming Yu. 2023. "The Effect of Process Parameters on the Properties and Microstructure of A380 Aluminum Alloy Casting with Different Wall Thicknesses" Crystals 13, no. 4: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040587
APA StyleLi, H., Zhang, H., Peng, W., Lin, B., Shao, Y., Lin, L., Fu, B., & Yu, Z. (2023). The Effect of Process Parameters on the Properties and Microstructure of A380 Aluminum Alloy Casting with Different Wall Thicknesses. Crystals, 13(4), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13040587






