Efficient Photo-Response of Azobenzene-based Compounds for Holographic Recording
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
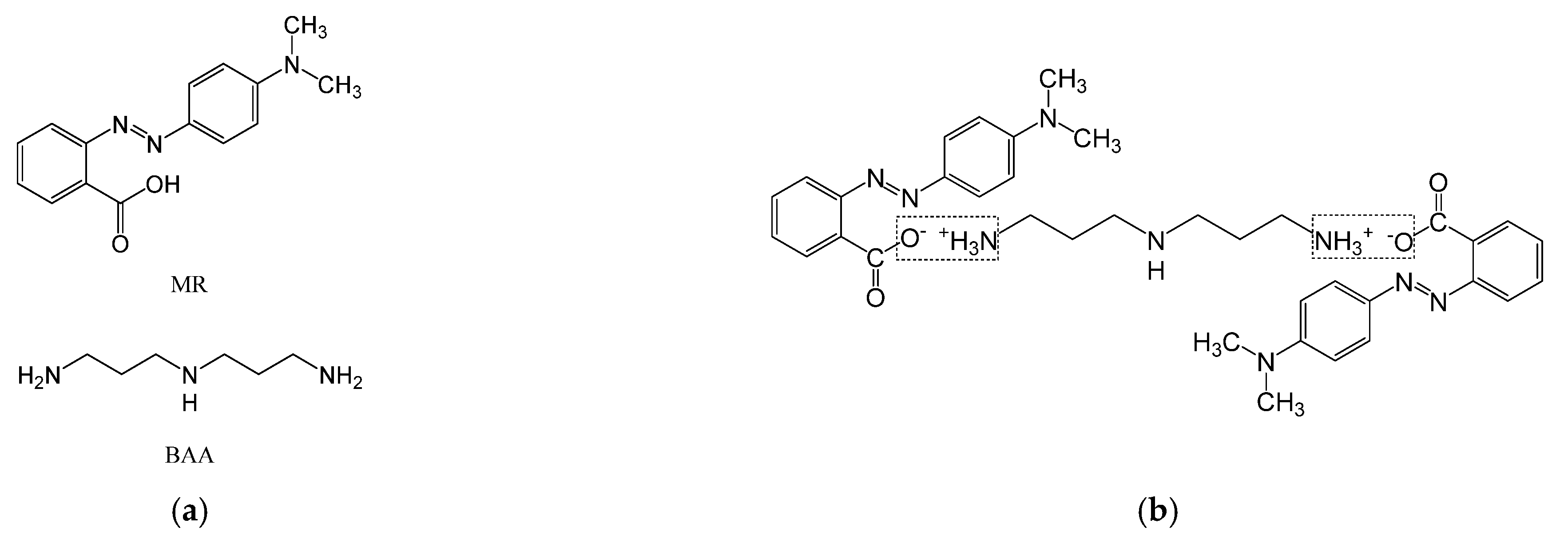
2.1. Materials and synthesis
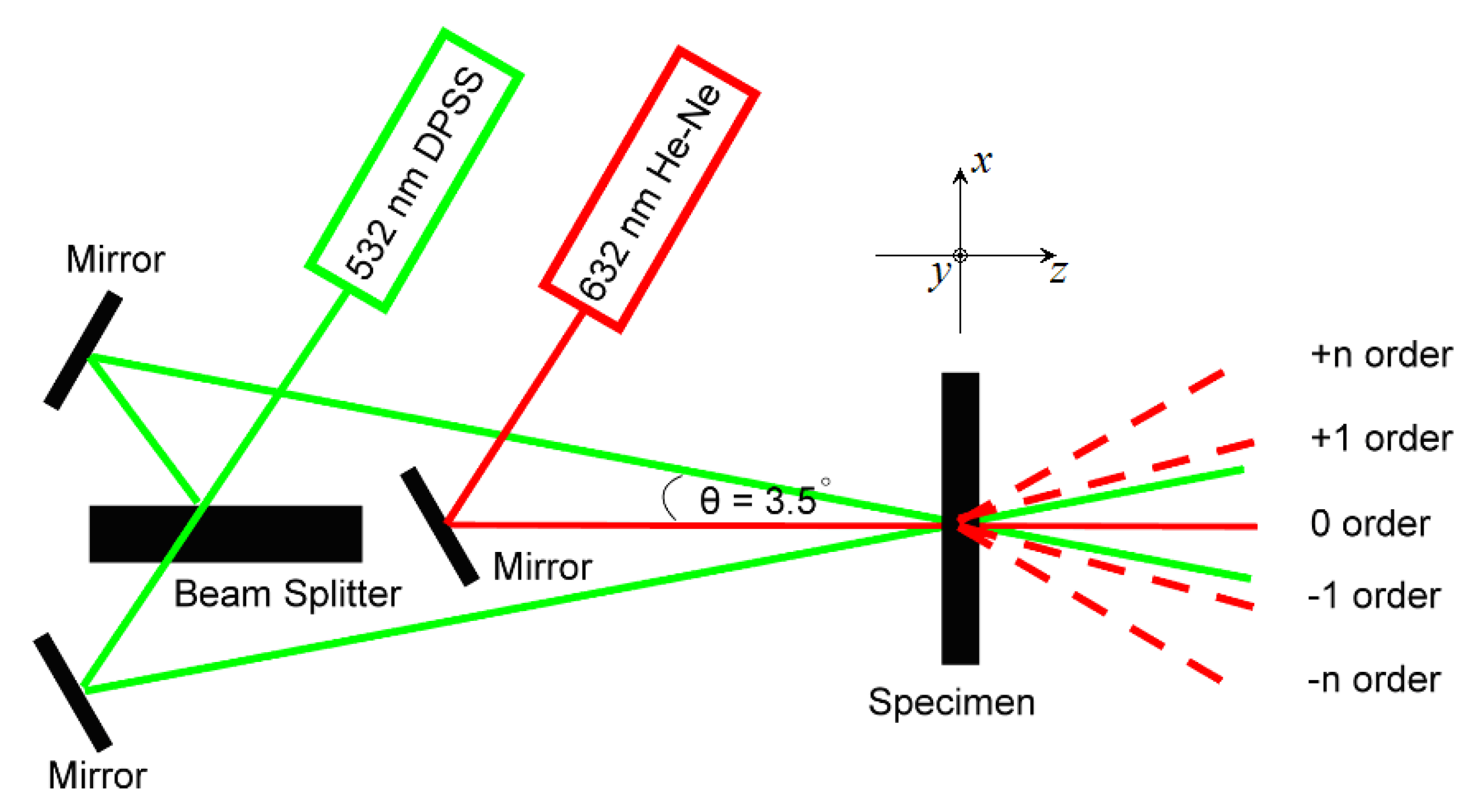
2.2. Optical Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
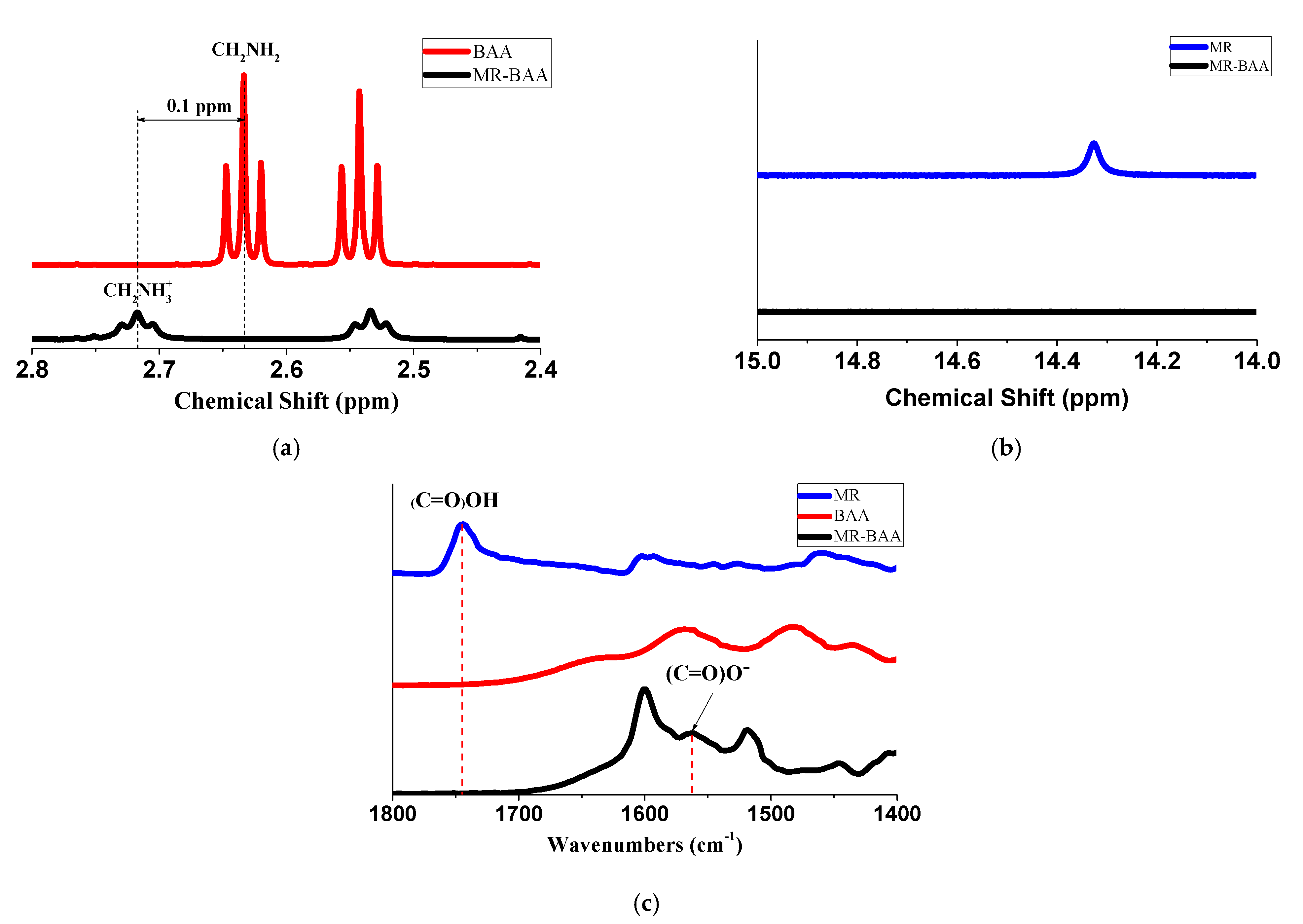
3.1. Ionic bonding formation
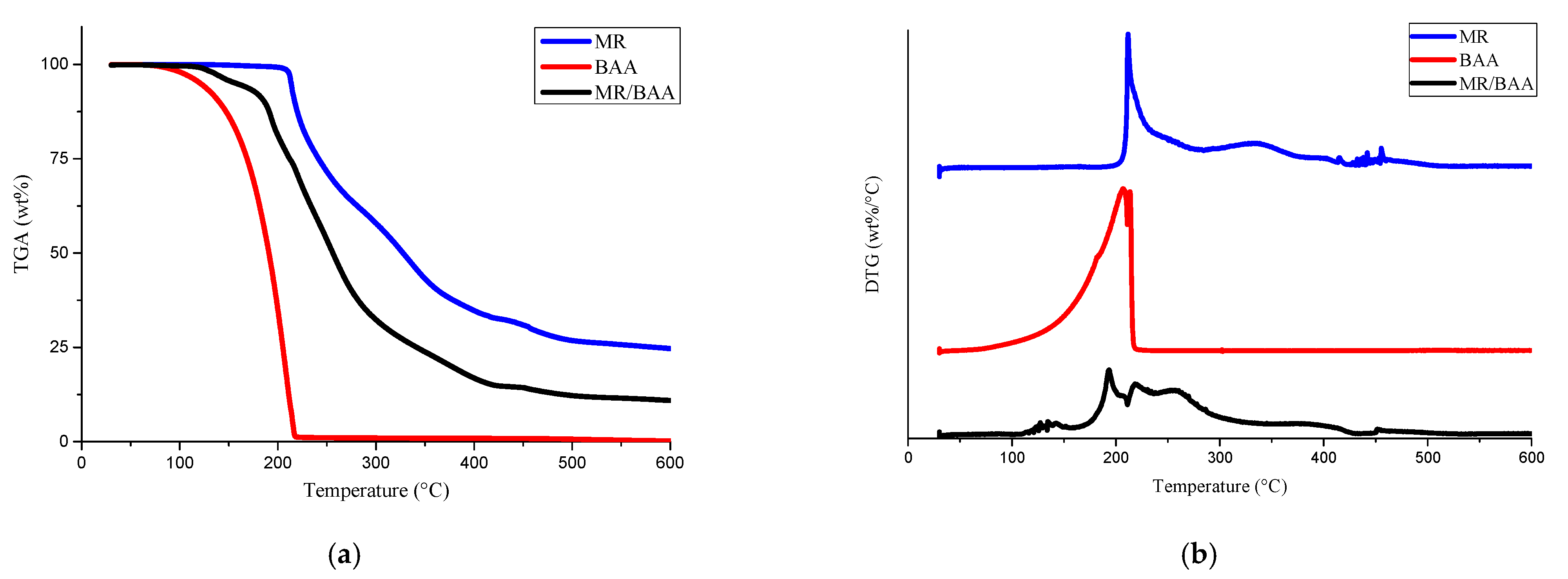
3.2. Bonding Stability
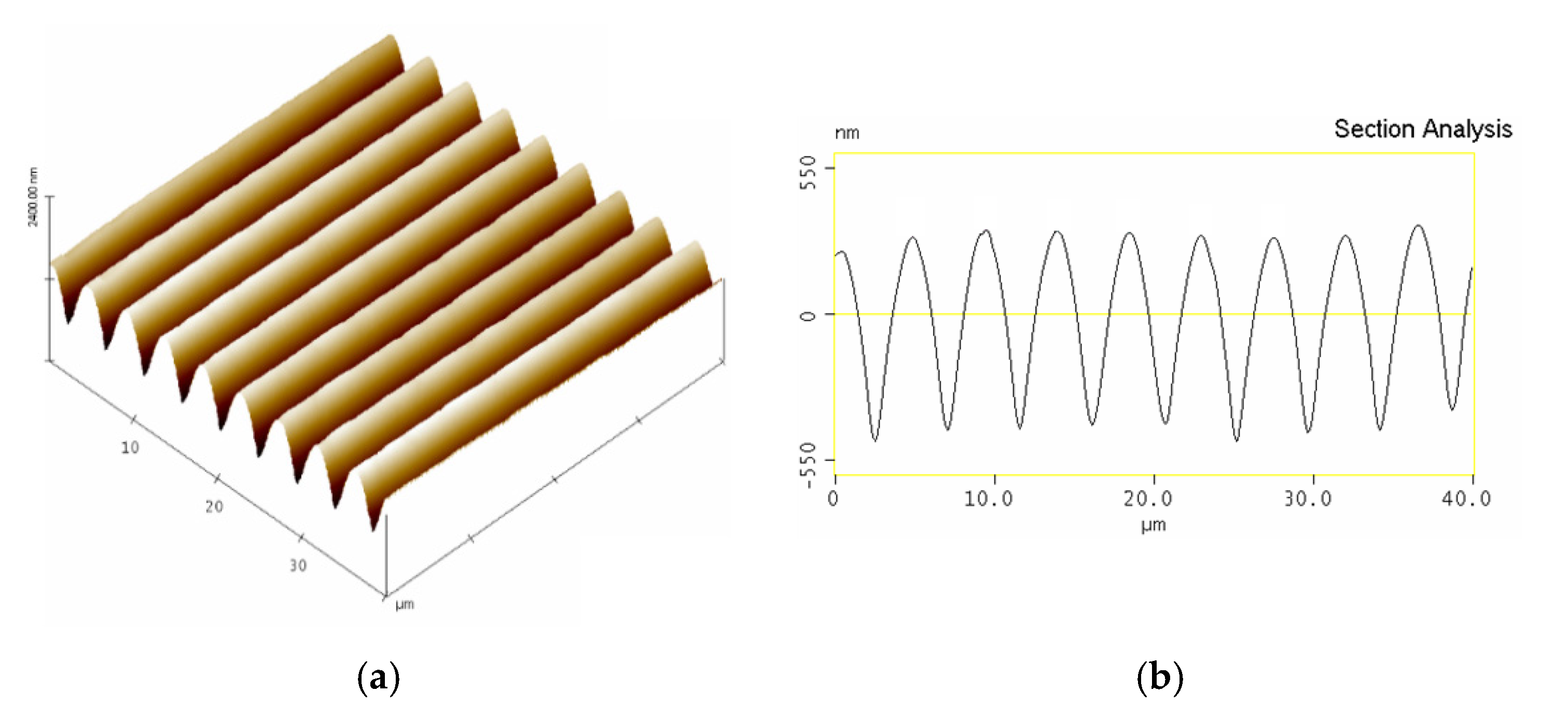
3.3. Surface Relief Grating Morphology and Diffraction Efficiency
3.4. Comments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daisuke, S.; Kenji, H.; Daisuke, B.; Takashi, F. Chemical Etching Using KOH Aqueous Solution for Corona-Charge Micropatterning of Soda-Lime Glass. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 036701. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.L.; Li, L.; Kumar, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Tripathy, S.K. Unusual Polarization Dependent Optical Erasure of Surface Relief Gratings on Azobenzene Polymer Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2502–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Várhegyi, P.; Kerekes, Á.; Sajti, S.; Ujhelyi, F.; Koppa, P.; Szarvas, G.; Lőrincz, E. Saturation Effect in Azobenzene Polymers Used for Polarization Holography. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 76, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Su, Y. Holographic Display and Storage Based on Photo-Responsive Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2016, 4, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, K.G.; Barrett, C.J. All-Optical Patterning of Azo Polymer Films. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2001, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhno, O.; Goldenberg, L.; Wegener, M.; Stumpe, J. Deep Surface Relief Grating in Azobenzene-Containing Materials Using a Low-Intensity 532 Nm Laser. Opt. Mater. X 2019, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natansohn, A.; Rochon, P. Photoinduced Motions in Azo-Containing Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4139–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Kim, H.B.; Ikeda, T.; Ichimura, K. Photoisomerization of an Azobenzene in Sol-Gel Glass Films. Chem. Mater. 1992, 4, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapaavuori, J.; Bazuin, C.G.; Priimagi, A. Supramolecular Design Principles for Efficient Photoresponsive polymer–azobenzene Complexes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 2168–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kijima, M.; Se, K.; Fujimoto, T. Photochemical Isomerization of p,p′-bis(chloromethyl)azobenzene Incorporated in poly(tertiary aminostyrene)s by Cross Linkage. Polymer 1992, 33, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Vapaavuori, J.; Wang, X.X.; Sabat, R.G.; Pellerin, C.; Bazuin, C.G. Influence of Supramolecular Interaction Type on Photoresponsive Azopolymer Complexes: A Surface Relief Grating Formation Study. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4923–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Takahashi, T.; Kadota, T.; Shirota, Y. Formation of a Surface Relief Grating Using a Novel Azobenzene-Based Photochromic Amorphous Molecular Material. J. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikovska, O.; Goldenberg, L.; Kulikovsky, L.; Stumpe, J. Smart Ionic Sol−Gel-Based Azobenzene Materials for Optical Generation of Microstructures. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3528–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikovska, O.; Goldenberg, L.M.; Stumpe, J. Supramolecular Azobenzene-Based Materials for Optical Generation of Microstructures. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3343–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikovsky, L.; Kulikovska, O.; Goldenberg, L.; Stumpe, J. Phenomenology of Photoinduced Processes in the Ionic Sol−Gel-Based Azobenzene Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, R.; Pariser, R. The Chlorophyll-Sensitized Photoöxidation of Phenylhydrazine by Methyl Red. II. Reactivity of the Several Forms of Methyl Red1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, A.S.; Anand, S.C. A Textbook of Physical Chemistry; Wiley Eastern: New Delhi, India, 1985; p. 584. [Google Scholar]
- Ramette, R.W.; Kelly, P.W.; Dratz, E.A. Acid-Base Equilibria of Methyl Red. J Phys Chem-Us 1962, 66, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.W.; De Paula, J. Elements of Physical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 2009; p. 185. [Google Scholar]
- Tobey, S.W. The Acid Dissociation Constant of Methyl Red. A Spectrophotometric Measurement. J. Chem. Educ. 1958, 35, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.-M.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Xu, C.-W. Determination of Acid Dissociation Constant of Methyl Red by Multi-Peaks Gaussian Fitting Method Based on UV-Visible Absorption Spectrum. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2012, 28, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Ainsa, S.; Alcalá, R.; Barberá, J.; Marcos, M.; Sánchez, C.; Serrano, J.L. Ionic Photoresponsive Azo-Codendrimer With Room Temperature Mesomorphism and High Photoinduced Optical Anisotropy. Macromol. 2010, 43, 2660–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Jain, S.; Tiwary, A.K. Investigations on microbially triggered system for colon delivery of budesonide. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, S.-M.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Chiang, C.-L.; Teng, C.-C. Morphology and Properties of Aminosilane Grafted MWCNT/Polyimide Nanocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2008, 2008, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, M.M.; Adel, E.-D. Structural, thermal, spectroscopic, and spectral dispersion studies of nanocrystalline methyl red thin films. Japanese. Int. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 042401. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, F.; EvansD, G. Synthesis and Thermo-Optical Stability of O-Methyl Red-Intercalated Ni–Fe Layered Double Hydroxide Material. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelchev, L.; Mateev, G.; Strijkova, V.; Salgueiriño, V.; Schmool, D.S.; Berberova-Buhova, N.; Stoykova, E.; Nazarova, D. Tunable Polarization and Surface Relief Holographic Gratings in Azopolymer Nanocomposites with Incorporated Goethite (α-FeOOH) Nanorods. Photonics 2021, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Tanino, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ando, H.; Shirota, Y. Relationship between molecular structure and photoinduced surface relief grating formation using azobenzene-based photochromic amorphous molecular materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, L.M.; Kulikovsky, L.; Kulikovska, O.; Tomczyk, J.; Stumpe, J. Thin Layers of Low Molecular Azobenzene Materials With Effective Light-Induced Mass Transport. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2214–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarins, E.; Balodis, K.; Ruduss, A.; Kokars, V.; Ozols, A.; Augustovs, P.; Saharovs, D. Molecular glasses of azobenzene for holographic data storage applications. Opt. Mater. 2018, 79, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priimagi, A.; Lindfors, K.; Kaivola, M.; Rochon, P. Efficient Surface-Relief Gratings in Hydrogen-Bonded Polymer−Azobenzene Complexes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapaavuori, J.; Priimagi, A.; Kaivola, M. Photoinduced Surface-Relief Gratings in Films of Supramolecular polymer–bisazobenzene Complexes. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5260–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, J.E.; Vapaavuori, J.; Ras, R.H.A.; Priimagi, A. Light-Driven Surface Patterning of Supramolecular Polymers With Extremely Low Concentration of Photoactive Molecules. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolewska, A.; Bartkiewicz, S.; Priimagi, A. High-Modulation-Depth Surface Relief Gratings Using s–s Polarization Configuration in Supramolecular Polymer–Azobenzene Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 23279–23284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Barrett, C.J.; Bazuin, C.G. Spacer-Free Ionic Dye−Polyelectrolyte Complexes: Influence of Molecular Structure on Liquid Crystal Order and Photoinduced Motion. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3216–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Azo-Based Material | Bonding | MW (g/mol) | L (nm) | ΔL (nm) | I (mW/cm2) | T (min) | Th (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAZO [27] | Covalent | - | 450 | 170 | 950 | 50 | 50 |
| DBAB [28] | 501 | 10,000–50,000 | 200–230 | - | 4 | 3–4 | |
| BBMAB [28] | 572 | 10,000–50,000 | 90–100 | - | 2 | 1–2 | |
| BFIAB [12] | 581 | 5000–10,000 | 450–490 | 80 | 10 | - | |
| AAB-BTC [29] | 747 | 240 | 380 | 300 | 20 | 20 | |
| ZGD-1 [30] | 925 | 300 | 300 | 3100 | 3.1 | - | |
| AAB-Epoxy [6] | 1052 | 1700 | 750 | 160 | 110 | 110 | |
| PADA-PVPh [31] | H-bonding | 1226–5226 | 400 | 440 | 200 | - | - |
| DY7-P4VP [32] | 5716 | 620 | 625 | 300 | 18 | - | |
| OH-DMA-P4VP [33] | 1241 | >2500 | 400 | 200 | 10 | - | |
| OH-DMA-P4VP [34] | 3441 | ~2000 | 590 | 280 | - | - | |
| MR-PEI [14] | Ionic | - | ~2000 | 1800 | 250 | - | 55 |
| MR-AP [13] | 490 | 500–2000 | 550 | 500 | - | - | |
| MO-PDM [35] | 20,0327 | 650 | 305 | - | - | - | |
| MO-P4VP [35] | 20,0327 | 305 | 360 | - | - | - | |
| MR-BAA | 670 | 762 | 758 | 200 | 5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, T.-C.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lee, F.-Y.; Su, W.-H. Efficient Photo-Response of Azobenzene-based Compounds for Holographic Recording. Crystals 2022, 12, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12030397
Hsu T-C, Wang L-Y, Lee F-Y, Su W-H. Efficient Photo-Response of Azobenzene-based Compounds for Holographic Recording. Crystals. 2022; 12(3):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12030397
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Tzu-Chien, Lu-Yu Wang, Fang-Yong Lee, and Wei-Hung Su. 2022. "Efficient Photo-Response of Azobenzene-based Compounds for Holographic Recording" Crystals 12, no. 3: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12030397
APA StyleHsu, T.-C., Wang, L.-Y., Lee, F.-Y., & Su, W.-H. (2022). Efficient Photo-Response of Azobenzene-based Compounds for Holographic Recording. Crystals, 12(3), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12030397






