Design of Novel POB/h-BN Co-Filled PTFE Composites with Enhanced Thermal–Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
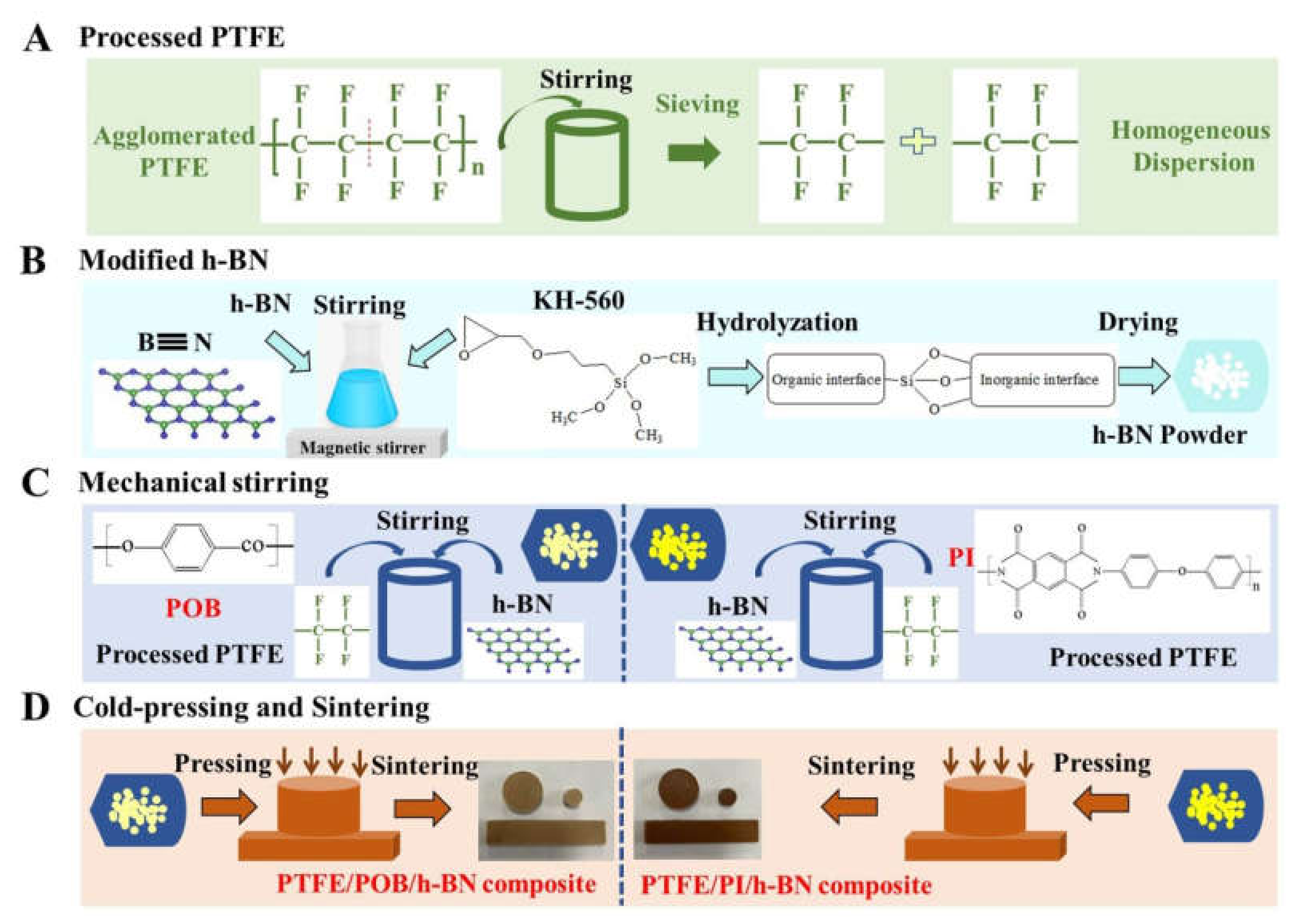
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
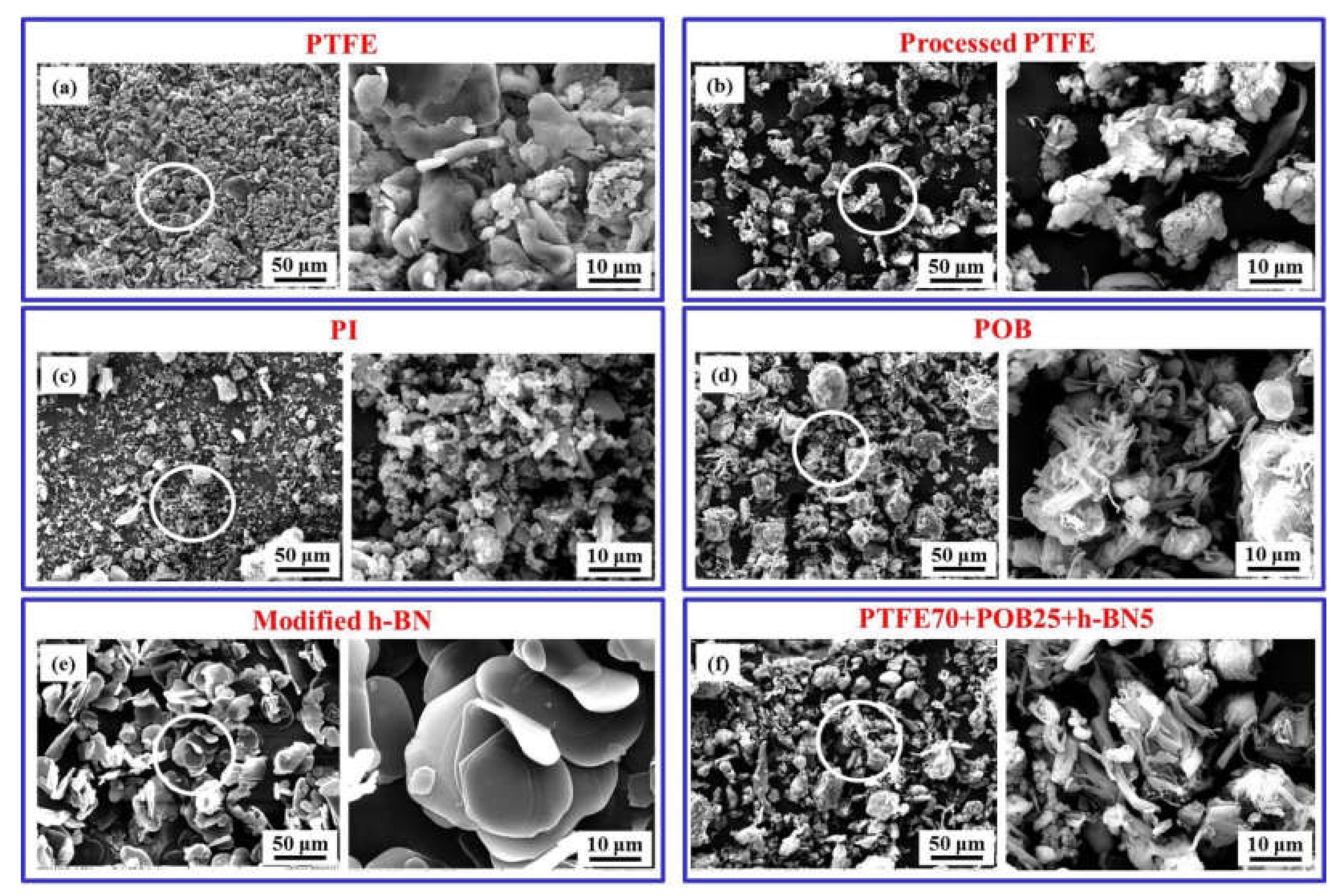
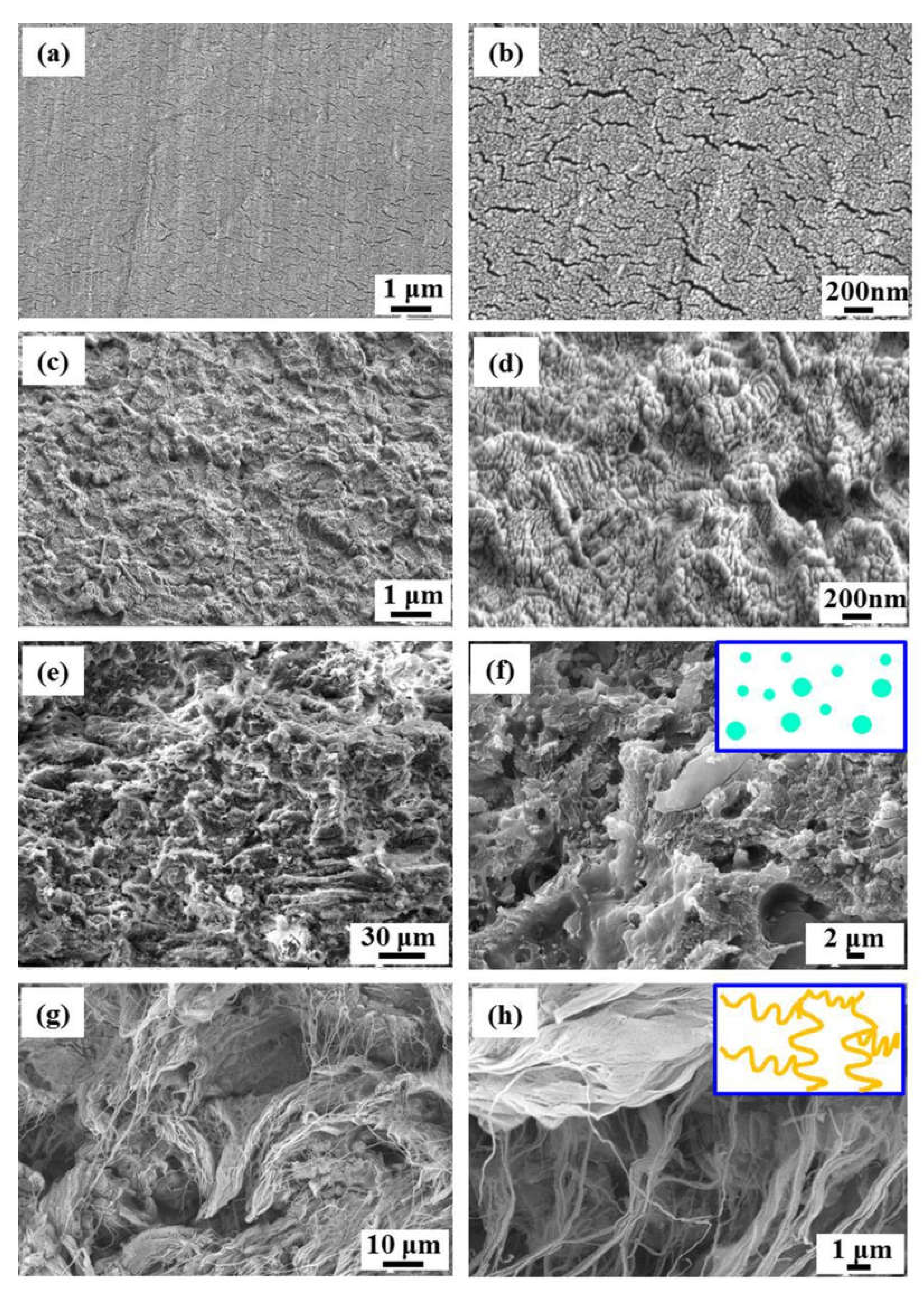
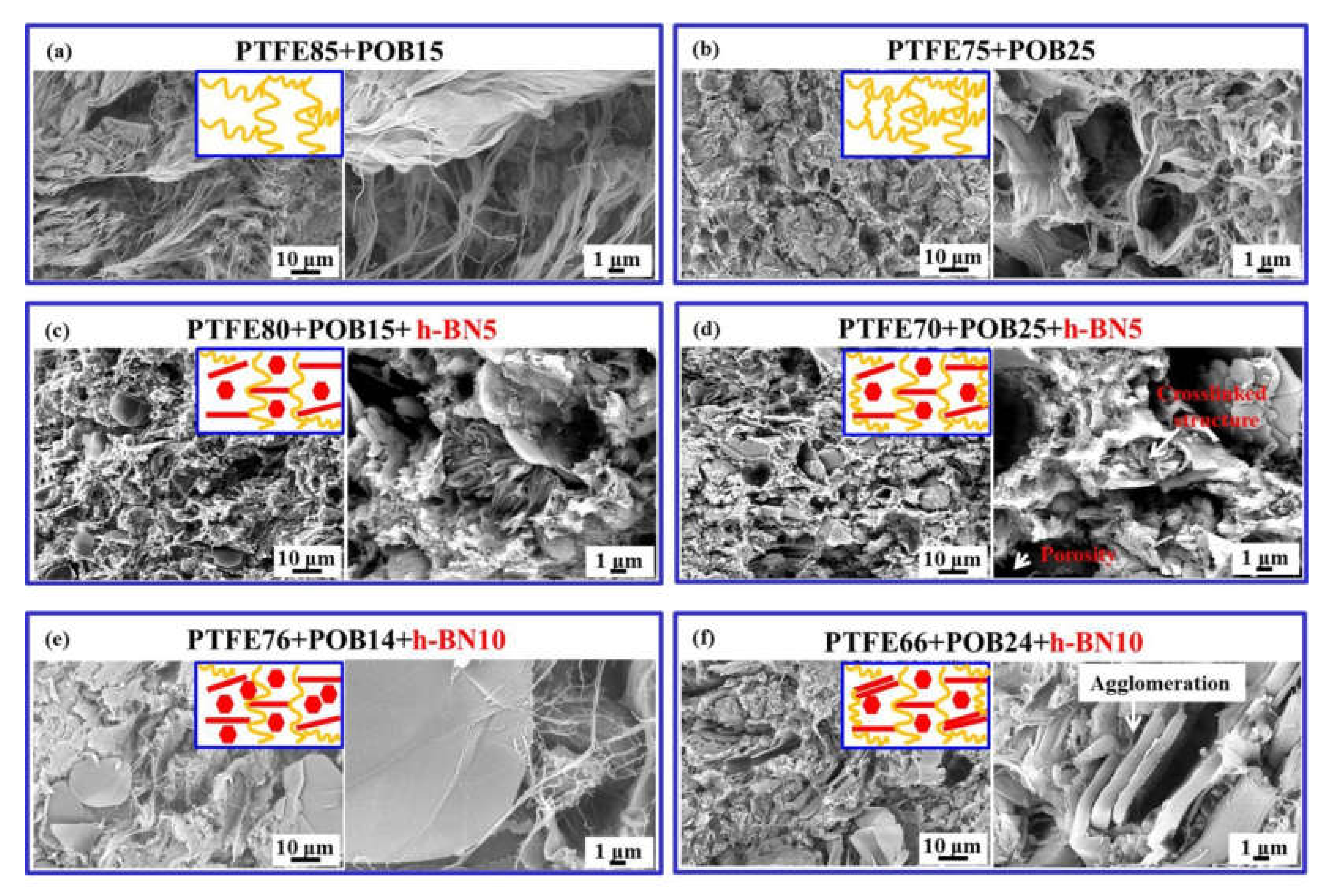
3.1. Microstructure of Powders
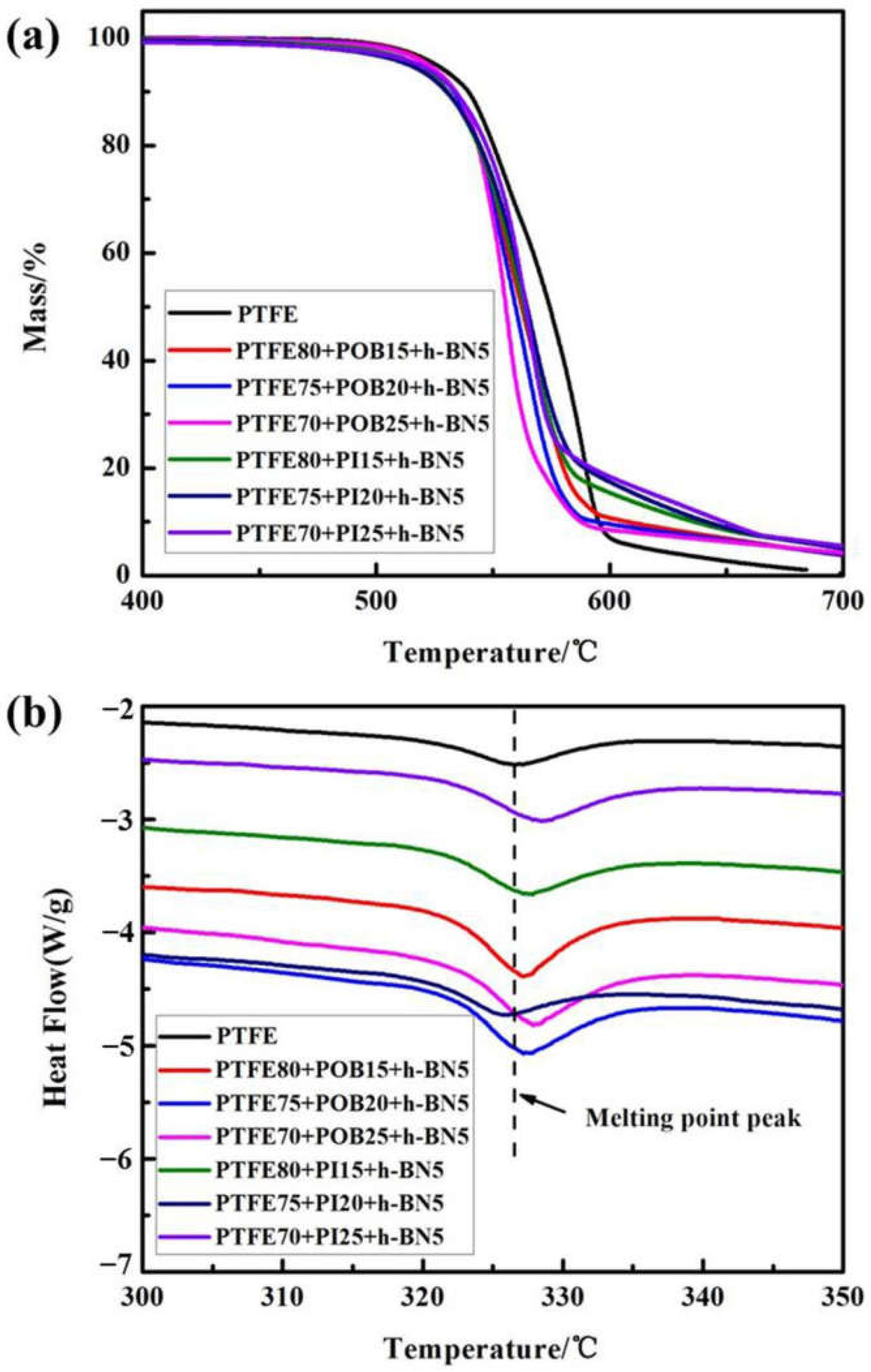
3.2. Thermal Stability and Melting Point
3.3. Vicat Softening Temperature
3.4. Thermal Diffusivity and Thermal Conductivity
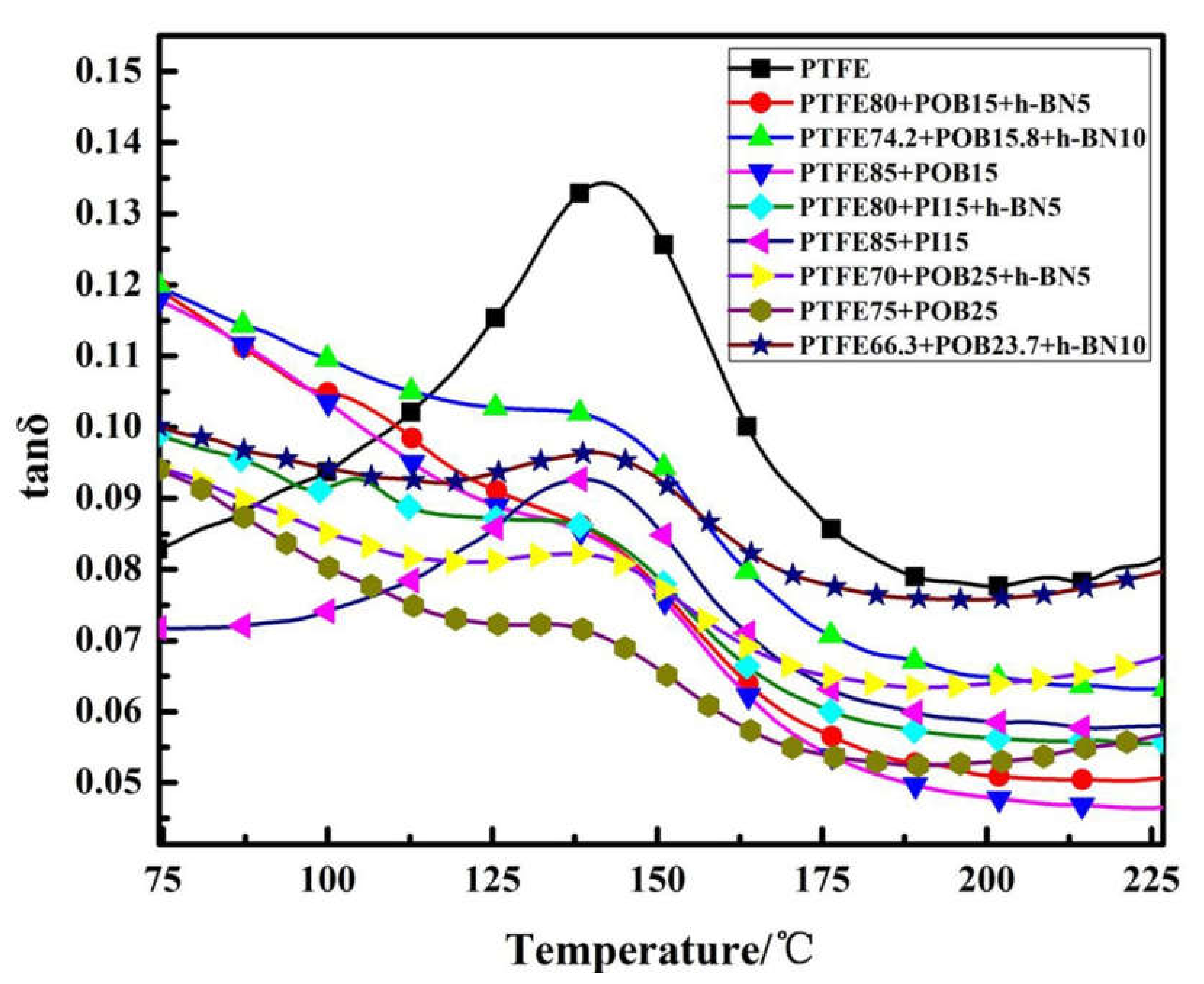
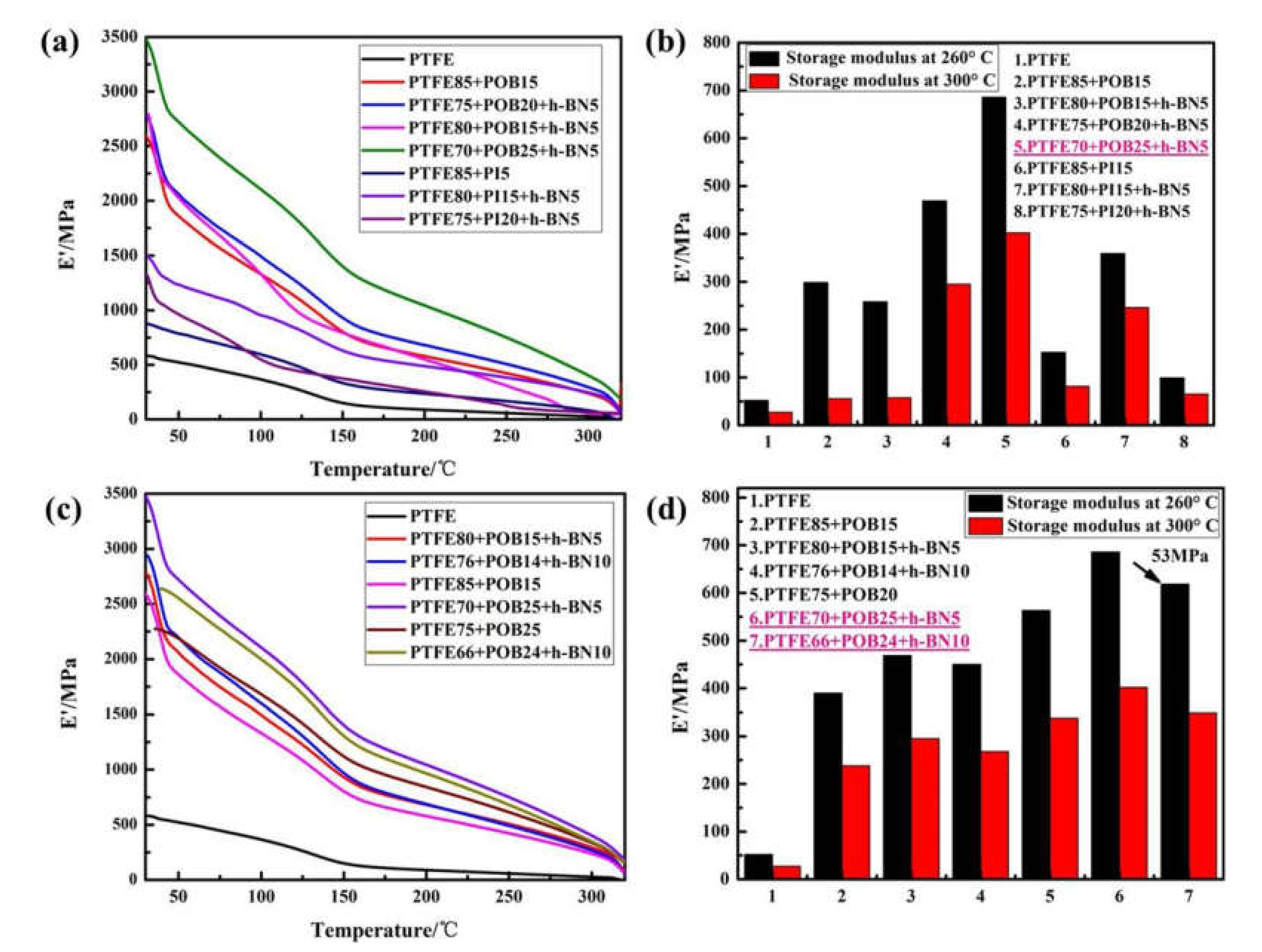
3.5. Dynamic Thermomechanical Analysis
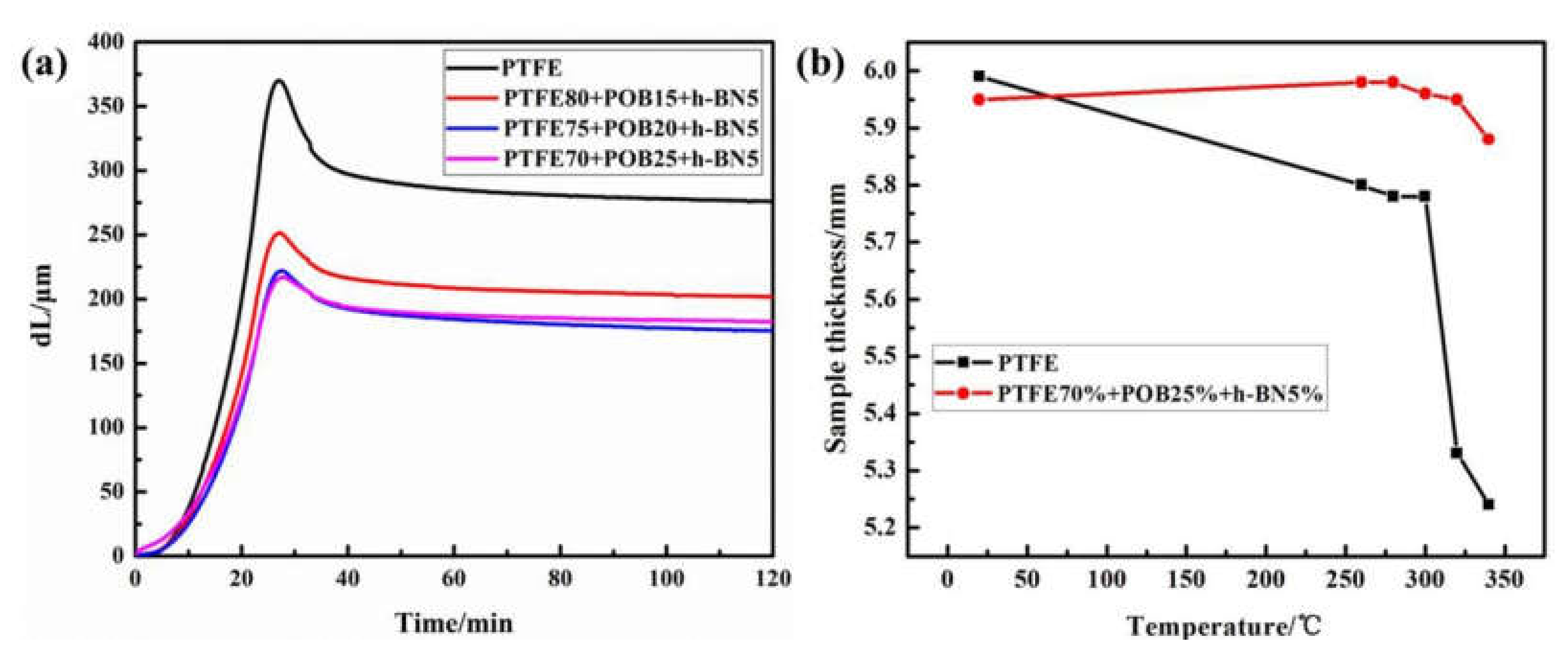
3.6. High-Temperature Creep Behavior
4. Discussion
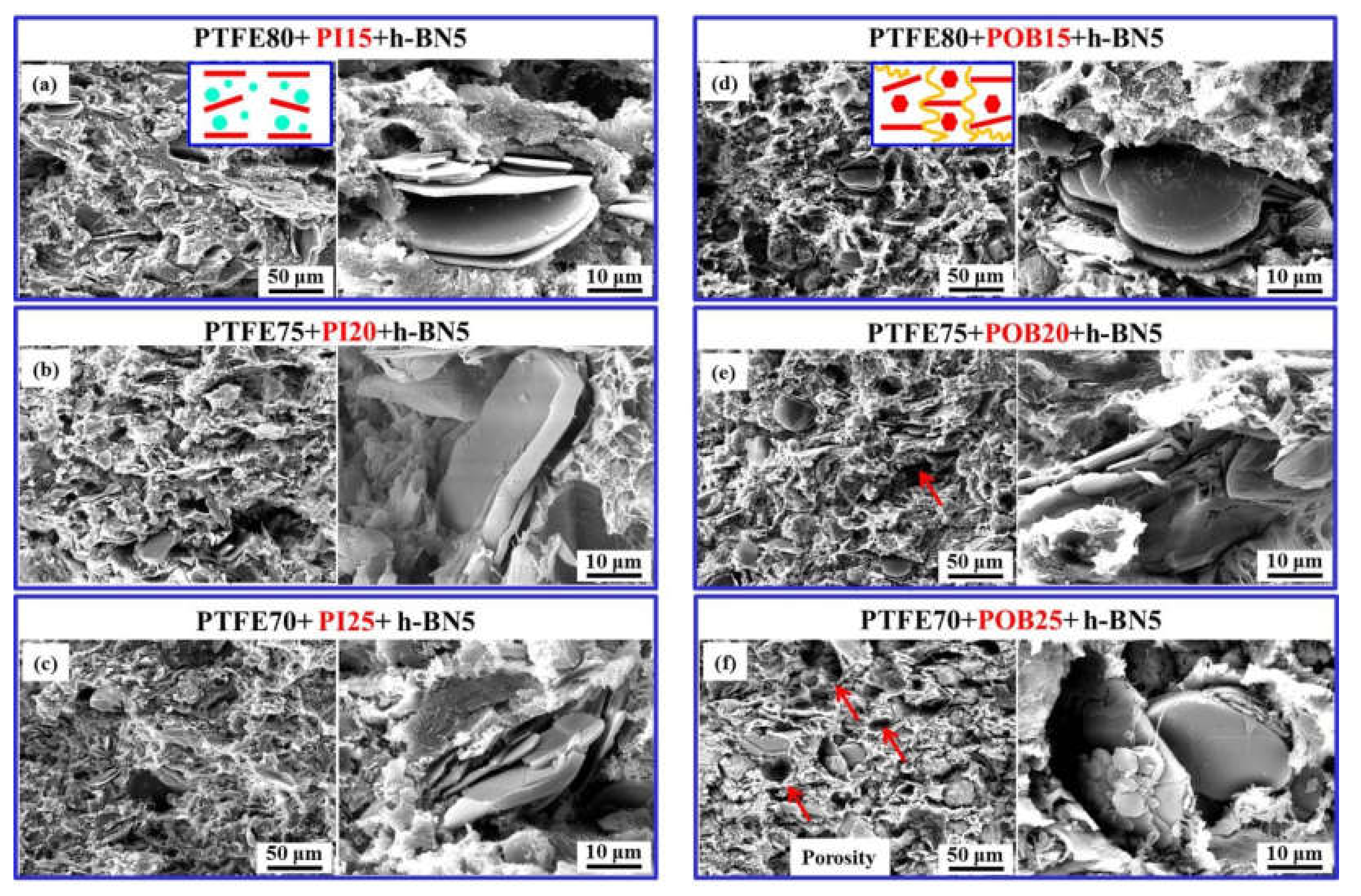
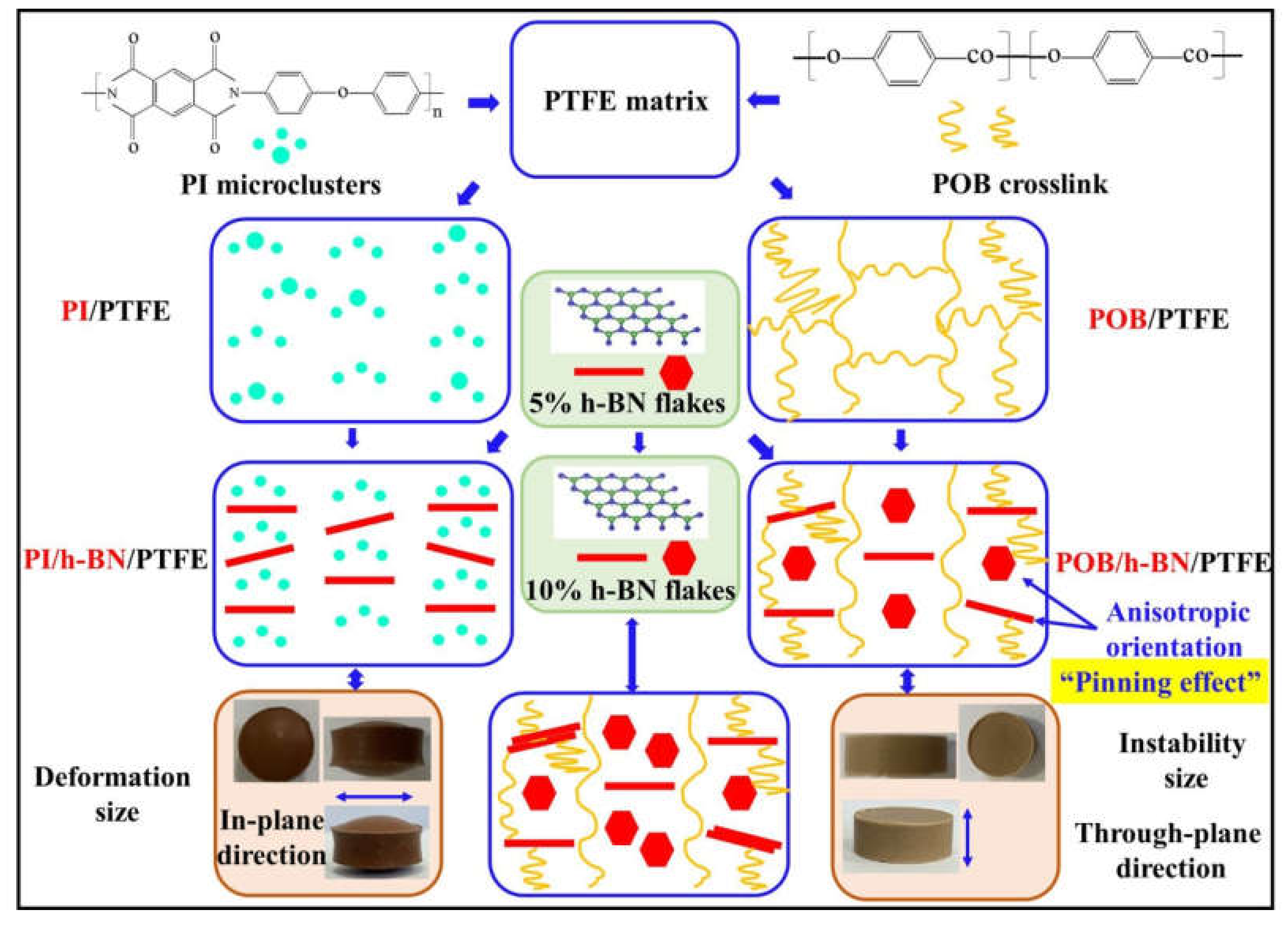
4.1. Effect of Morphology and Molecular Structure on the Thermal–Mechanical Properties
4.2. Effect of Crystallization Orientation on Thermal–Mechanical Properties
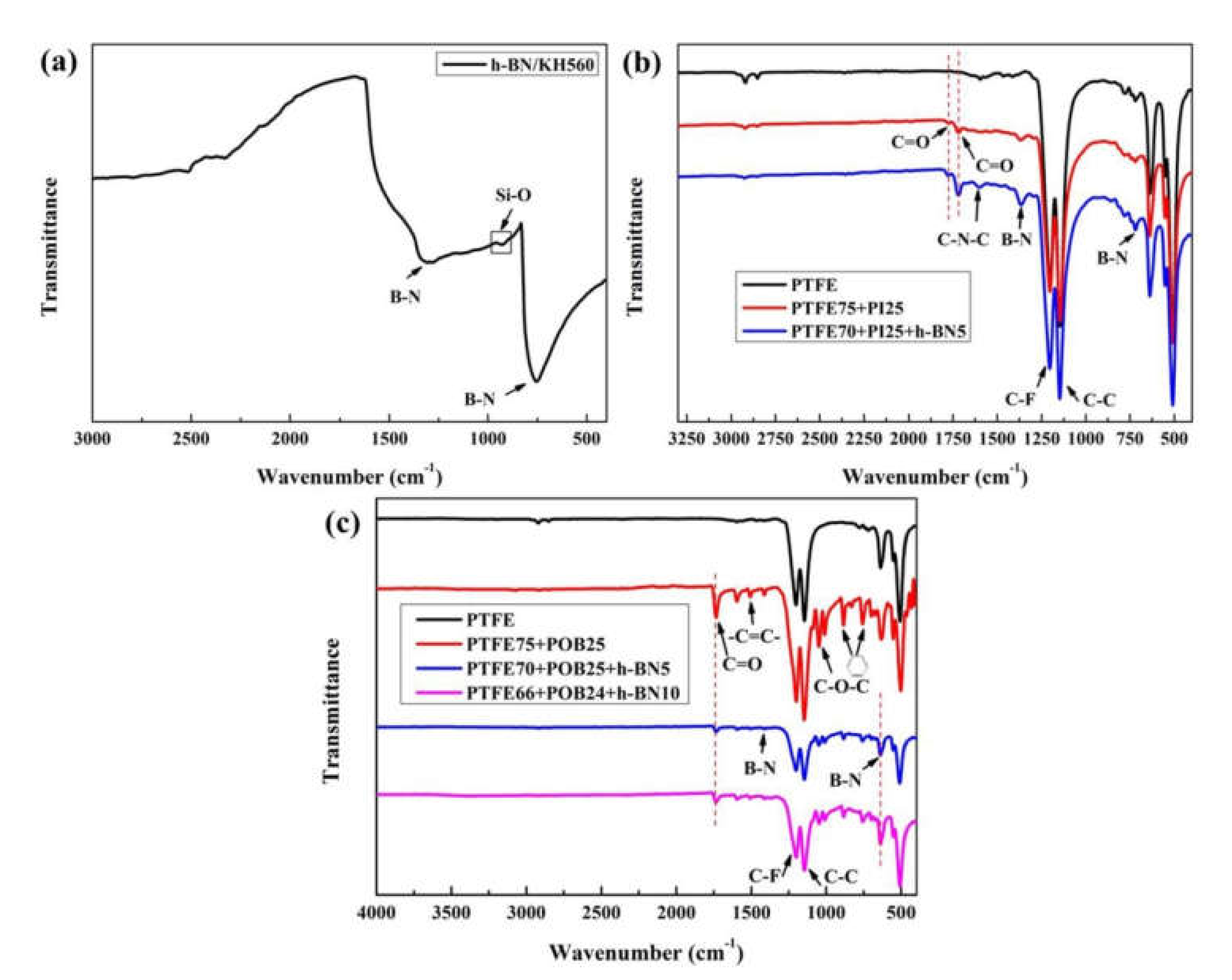
4.3. Thermal Stability of PTFE-Based Composites with Multi-Component Fillers
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- POB/h-BN co-filled PTFE composites exhibited good thermal–mechanical properties compared with PI/h-BN/PTFE material at high temperatures. The optimal ratio of POB and h-BN fillers was 25 wt.% and 5 wt.%, respectively.
- (2)
- The Vicat softening temperature of POB/h-BN co-filled PTFE composites with the optimal ratio increased by 38 °C. The storage modulus value at 260 °C displayed 685.76 MPa and reached 187.82 MPa at 320 °C.
- (3)
- The cross-linked reticulation structure with regular pores and the higher crystallization degree were beneficial to the enhancement of thermal property. The pinning effect of uniform distribution and anisotropic orientation of h-BN flakes were further promoted the thermal–mechanical properties of composites.
- (4)
- The practical temperature of the 25 wt.% POB/5 wt.% h-BN/PTFE composite increased by 60 °C compared with pure PTFE, which greatly expanded its operational range in the application of sealing elements at high temperatures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.L.; Martinez-vega, J.; Malec, D. Morphological evolution of polytetrafluoroethylene in extreme temperature conditions for aerospace applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudem, B.; Kim, D.H.; Mule, A.R.; Yu, J.S. Enhanced performance of microarchitectured PTFE-based triboelectric nanogenerator via simple thermal imprinting lithography for self-powered electronics. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 2018, 10, 24181–24192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.Q.; Chang, Q.X.; Huang, X.J.; Bo, J. Improved mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced PTFE composites by growing graphene oxide on carbon fiber surface. Compos. Interfaces 2018, 25, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Vijayan, K. Friction and wear of PTFE—A review. Wear 1992, 158, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.B.; Wu, C.L.; Rong, M.Z.; Czigany, T.; Ruan, W.H.; Zhang, M.Q. Improvement of creep resistance of polytetrafluoroethylene films by nano-inclusions. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckford, S.; Cai, J.Y.; Fleming, R.A.; Zou, M. The effects of graphite filler on the tribological properties of polydopamine/PTFE coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 64, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Ren, H.S.; Dang, M.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.Y.; Yao, X.G.; Lin, H.X. The dimensional effect of MgTiO3 ceramic filler on the microwave dielectric properties of PTFE/MgTiO3 composite with ultra-low dielectric loss. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 6680–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Zhu, X.T.; Ren, G.; Men, X.H.; Guo, F.; Li, P.L.; Zhang, Z.Z. Influence of air-plasma treatment and hexagonal boron nitride as filler on the high temperature tribological behaviors of hybrid PTFE/Nomex fabric/phenolic composite. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Kou, K.C.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wu, G.L.; Feng, A.L. Fabrication and characterization of micro-nano AlN co-filled PTFE composites with enhanced thermal conductivity: A morphology-promoted synergistic effect. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 11909–11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kou, K.C.; Zhang, S.C.; Ji, T.Z. Improving thermal properties of ultrafine-glass-fiber reinforced PTFE hybrid composite via surface modification by (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.H.; Gong, J.; Qi, Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, H.G.; Ren, J.F.; Chen, S.S. Tribological Behavior of Nano-ZrO2 Reinforced PTFE-PPS Composites. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2019, 34, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckford, S.; Cai, J.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Zou, M. Use of Au nanoparticle-filled PTFE films to produce low-friction and low-wear surface coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 56, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, H.; Ye, X.Z.; Tian, K.H.; Huang, W.Q.; He, J.; Guo, Y.L.; Tian, X.Y. Anisotropic thermally conductive flexible polymer composites filled with hexagonal born nitride (h-BN) platelets and ammine carbon nanotubes (CNT-NH2): Effects of the filler distribution and orientation. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z.; Kaldonski, T.; Pai, R.; Bayraktar, E.; Oloyede, A. A comparative study on the tribological behaviour of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) as lubricating micro-particles-An additive in porous sliding bearings for a car clutch. Wear 2009, 267, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Ma, F.C.; Liang, W.J.; Sun, M.T. Electrical properties and applications of graphene, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), and graphene/h-BN heterostructures. Mater. Today Phys. 2017, 2, 6–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoo, M.S.; Wani, M.F. Tribological properties of h-BN nanoparticles as lubricant additive on cylinder liner and piston ring. Lubr. Sci. 2017, 29, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.C.; Sato, K.; Hotta, Y.J.; Shibuya, H.; Sugie, M.; Saruyama, T. Effect of the addition of Al2O3 and h-BN fillers on the thermal conductivity of a cellulose nanofiber/nanodiamond composite film. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5281–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, M.; Yamagata, T.; Miyata, K.; Ando, S. Anisotropic thermal diffusivity of hexagonal boron nitride-Filled polyimide films: Effects of filler particle size, aggregation, orientation, and polymer chain rigidity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4374–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Raman, S.; Mohanan, P.; Sebastian, M.T. Effect of coupling agent on the thermal and dielectric properties of PTFE/Sm2Si2O7 composites. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W. Effect of coupling agents on the thermal conductivity of aluminum particle/epoxy resin composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3883–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.L.; Li, H.Q.; Liu, M.Y.; Xu, L.S.; Xu, J.M.; Wang, S.; Ni, H.Z.; Wang, Z. Effect of “bridge” on the performance of organic-inorganic crosslinked hybrid proton exchange membranes via KH550. J. Power Sources 2017, 340, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Zhou, J.X.; An, L.L.; Ji, C.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Liu, W.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, H.T.; Wen, G.W.; Zhao, K.; et al. The effects of the hexagonal boron nitride nanoflake properties on the thermal conductivity of hexagonal boron nitride nanoflake/silicone rubber composites. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 127, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Kou, K.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Wu, G.L. Enhanced through-plane thermal conductivity of PTFE composites with hybrid fillers of hexagonal boron nitride platelets and aluminum nitride particles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Kou, K.C.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.L.; Ji, T.Z. Improved thermal conductivity and dielectric properties of hBN/PTFE composites via surface treatment by silane coupling agent. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 111, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudresh, B.; Kumar, B.R. Influence of experimental parameters on friction and wear mechanisms of PA66/PTFE blend reinforced with glass fiber. T. Indian I. Met. 2018, 71, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Mu, L.W.; Shi, Y.J. Tribological properties of polyimide-graphene composite coatings at elevated temperatures. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 142, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, D.A.; Yurdakul, Ö.; Şahin, O.; Öztürk, Z. The new metal complex templated polyoxoborate(s) (POB(s)) structures. Synthesis, structural characterization, and hydrogen storage capacities. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1134, 806–813. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Qi, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q. Distinct tribological mechanisms of various oxide nanoparticles added in PEEK composite reinforced with carbon fibers. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 97, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Qi, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q. Significant friction and wear reduction by assembling two individual PEEK composites with specific functionalities. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Friction and wear properties of PTFE composites filler with PA6. Polym. Compos. 2010, 31, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Pan, L. Tribological behavior of poly (phenyl p-hydroxybenzoate)/polytetrafluoroethylene composites filled with hexagonal boron nitride under dry sliding condition. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.W.; Wang, H.G.; Ren, J.F.; Gao, G.; Zhao, G.R.; Chen, S.S.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.Q. Multi-environment adaptability of self-lubricating core/shell PTFE@PR composite: Tribological characteristics and transfer mechanism. Tribol. Int. 2021, 154, 106718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.X.; Huang, Q.L.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S.W.; Xiao, C.F.; Hu, Q. Pore structure design of NFES PTFE membrane for membrane emulsification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y. Experimental investigation on frictional behavior and sealing performance of different composites for seal application. Wear 2015, 342, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.D.; Gong, J. Tribological and mechanical behavior of different fillers filled PTFE composites. Lubr. Eng. 2014, 39, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.B.; Mao, Y. Mechanical and tribological properties of PTFE composites filled with POB. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2011, 194–196, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhao, G.; Wang, F. Properties of POB reinforced PTFE-based friction material for ultrasonic motors. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.L.; Qi, X.W.; Ma, J.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.L. Effects of polyimide/silica and polyimide/pores fillers on the morphology, thermal, mechanical, and tribological properties of polytetrafluoroethylene composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 3438–3452. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.J.; Mu, L.W.; Feng, X.; Lu, X.H. The tribological behavior of nanometer and micrometer TiO2 particle-filled polytetrafluoroethylene/polyimide. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.J.; Wang, K.J. Synergistic modification of the tribological properties of polytetrafluoroethylene with polyimide and boron nitride. Friction 2020, 40544, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Kou, K.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Ji, T.Z.; Wu, G.L. Investigation of the dielectric and thermal conductive properties of core-shell structured HGM@hBN/PTFE composites. Mat. Sci. Eng. B Adv. 2018, 238–239, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Li, J.L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.X. Dynamic thermal mechanical analysis and its application in the research on fluorinated polymer materials. Chem. Prod. Technol. 2016, 60, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Xu, J.J.; Wang, X.B.; Li, W.; Tian, K.; Zhang, X.G.; Hou, Y.L. Insight into the property enhancement mechanism of chemically prepared multi-main-phase (Nd,Ce)2Fe14B. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 46549–46556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseiny, S.M.; Jafari, S.H.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Hemmati, F.; Kalaee, M.R. A correlation between morphology and mechanical performance of injected-molded PE/EVA/clay nanocomposites: Insight into phase miscibility and interfacial phenomena. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharajak, J.; Palathai, T.; Sombatsompop, N. Morphological and physical properties and friction/wear behavior of h-BN filled PEEK composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 273, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zha, J.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wen, Y.; Dang, Z. Enhanced thermal conductivity and mechanical property through boron nitride hot string in polyvinylidene fluoride fibers by electrospinning. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.G.; Li, Z.J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Fejjari, K.; Kang, W.M.; Liao, Y. Electrospun PTFE/PI bi-component membranes with robust 3D superhydrophobicity and high water permeability for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, Y.H.; Zhao, W.Z.; Yu, S.H.; Ji, Z.P. Preparation and performance of lubrication composite coating based on poly(4-oxybenzoyl) (I). Surf. Eng. 2013, 27, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.F.; Supancic, P.H. Thermal conductivity of platelet-filled polymer composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Duan, B.; Li, L.; Xie, B.; Huang, M.; Luo, X. Thermal conductivity of polymerbased composites with magnetic aligned hexagonal boron nitride platelets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13000–13006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Zhang, J.; Kou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. Investigation of the through-plane thermal conductivity of polymer composites with in-plane oriented hexagonal boron nitride. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 120, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | PTFE | POB | PI | h-BN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 100 | — | — | — |
| S2 | 85 | 15 | — | — |
| S3 | 80 | 20 | — | — |
| S4 | 75 | 25 | — | — |
| S5 | 80 | 15 | — | 5 |
| S6 | 75 | 20 | — | 5 |
| S7 | 70 | 25 | — | 5 |
| S8 | 76 | 14 | — | 10 |
| S9 | 71 | 19 | — | 10 |
| S10 | 66 | 24 | — | 10 |
| P1 | 75 | — | 25 | — |
| P2 | 80 | — | 15 | 5 |
| P3 | 75 | — | 20 | 5 |
| P4 | 70 | — | 25 | 5 |
| Samples | Component | Vicat Softening Temperature/°C |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | PTFE | 92 |
| P1 | PTFE75 + PI25 | 95 |
| S4 | PTFE75 + POB25 | 120 |
| S5 | PTFE80 + POB15 + h-BN5 | 79 |
| S6 | PTFE75 + POB20 + h-BN5 | 113 |
| S7 | PTFE70 + POB25 + h-BN5 | 130 |
| S8 | PTFE76 + POB14 + h-BN10 | 97 |
| S10 | PTFE66 + POB24 + h-BN10 | 121 |
| Samples | Density (g·cm−3) | Temperature (°C) | Specific Heat Capacity (J·g−1·K−1) | Thermal Diffusivity (mm2·s−1) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | 2.1686 | 25 | 1.293 | 0.116 ± 0.012 | 0.326 ± 0.034 |
| 260 | 1.802 | 0.11 ± 0.003 | 0.429 ± 0.013 | ||
| PTFE75 + POB25 | 1.9190 | 25 | 0.694 | 0.153 ± 0.007 | 0.23 ± 0.011 |
| 260 | 1.001 | 0.108 ± 0.001 | 0.234 ± 0.003 | ||
| PTFE80 + POB15 + h-BN5 | 2.0223 | 25 | 0.865 | 0.123 ± 0.006 | 0.214 ± 0.01 |
| 260 | 1.068 | 0.082 ± 0.002 | 0.177 ± 0.004 | ||
| PTFE75 + POB20 + h-BN5 | 2.2116 | 25 | 0.769 | 0.135 ± 0.011 | 0.229 ± 0.018 |
| 260 | 1.214 | 0.103 ± 0.004 | 0.276 ± 0.01 | ||
| PTFE70 + POB25 + h-BN5 | 1.6052 | 25 | 1.133 | 0.141 ± 0.023 | 0.256 ± 0.041 |
| 260 | 1.745 | 0.091 ± 0.004 | 0.256 ± 0.01 | ||
| PTFE76 + POB14 + h-BN10 | 2.0207 | 25 | 0.86 | 0.139 ± 0.1 | 0.241 ± 0 |
| 260 | 1.486 | 0.101 ± 0.006 | 0.303 ± 0.018 | ||
| PTFE66 + POB24 + h-BN10 | 2.1712 | 25 | 0.849 | 0.189 ± 0.008 | 0.349 ± 0.015 |
| 260 | 1.309 | 0.12 ± 0.002 | 0.34 ± 0.006 | ||
| PTFE80 + PI15 + h-BN5 | 1.8193 | 25 | 0.58 | 0.07 ± 0.007 | 0.073 ± 0.008 |
| 260 | 1.875 | 0.076 ± 0.003 | 0.258 ± 0.009 | ||
| PTFE75 + PI20 + h-BN5 | 1.6998 | 25 | 1.021 | 0.095 ± 0.023 | 0.165 ± 0.039 |
| 260 | 2.058 | 0.086 ± 0.004 | 0.3 ± 0.012 | ||
| PTFE70 + PI25 + h-BN5 | 1.0895 | 25 | 1.003 | 0.109 ± 0.033 | 0.119 ± 0.036 |
| 260 | 0.711 | 0.12 ± 0.003 | 0.224 ± 0.006 |
| Samples | Value of Deformation |
| PTFE | 4.35% |
| PTFE80 + POB15 + h-BN5 | 3.60% |
| PTFE75 + POB20 + h-BN5 | 2.90% |
| PTFE70 + POB25 + h-BN5 | 3.15% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; He, T.; Jia, H.; Chang, Z.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Ma, Y. Design of Novel POB/h-BN Co-Filled PTFE Composites with Enhanced Thermal–Mechanical Properties. Crystals 2021, 11, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070778
Wang Y, Liu Q, Bai Y, Liu H, He T, Jia H, Chang Z, Liu X, Su H, Ma Y. Design of Novel POB/h-BN Co-Filled PTFE Composites with Enhanced Thermal–Mechanical Properties. Crystals. 2021; 11(7):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070778
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Qi Liu, Yu Bai, Haibo Liu, Tao He, Hua Jia, Zhandong Chang, Xin Liu, Haixia Su, and Yushan Ma. 2021. "Design of Novel POB/h-BN Co-Filled PTFE Composites with Enhanced Thermal–Mechanical Properties" Crystals 11, no. 7: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070778
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, Q., Bai, Y., Liu, H., He, T., Jia, H., Chang, Z., Liu, X., Su, H., & Ma, Y. (2021). Design of Novel POB/h-BN Co-Filled PTFE Composites with Enhanced Thermal–Mechanical Properties. Crystals, 11(7), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070778






