Abstract
Biodegradable alloys in Mg have the advantages of traditional metallic materials and those of biodegradable polymers with superior strength, lower density and ideal rigidity for fixing bone fractures. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of the five concentrations of Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys used were assessed using clinical and laboratory examinations that followed over time: tissue reaction, histological and imaging (RX, CT and SEM) evolution at 1, 2, 4 and 8 weeks after implant. The main purpose of this study was to investigate in vivo the long-term effect of Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys in rats. The results confirmed that Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys are biocompatible and biodegradable and are recommended to be used as possible materials for new orthopedics devices.
1. Introduction
Most commonly used fracture fixing elements are stainless metals, titanium (Ti) alloys, as well as a class of alloys based on cobalt (Co), chromium (Cr) or molybdenum (Mo). All of the above have superior mechanical strength, are bioinerted and remain in the body, usually, requiring further surgery to remove them, a procedure that can create additional surgical risks for the patient [1,2]. Fasteners made of biodegradable materials can be a suitable solution, magnesium-based alloys (Mg) being increasingly studied due to their qualities. Mg is the fourth essential mineral in the body with more than half of its total content in bone tissue [3,4]. In the physiological environment of the body, Mg is degraded by corrosion reactions that have as by-products Mg2+, OH and H2 ions. It has been shown that the presence of Mg2+ ions increases cell adhesion and osteoblastic activity, resulting in better bone regeneration and faster healing [5,6]. Mg corrosion is accelerated in chlorine-containing solutions [7], which leads to a continuous corrosion of materials with Mg. The rare metal alloys with Mg have been made to slow down the corrosion of the material in the physiological environment [8]. It should be noted that these elements do not exist naturally in the body and that their long-term effects are still unknown [9]. Alloys of two or more elements composed of Mg with different concentrations of strontium (Sr), calcium (Ca), aluminum (Al), manganese (Mn), zirconium (Zr), silicon (Si), etc., have been used as orthopedic implants [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Tissular (soft tissue) reaction around the implanted material and biodegradation aspects for five concentrations of Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys were assessed using “in vivo” experiments and imaging diagnosis (RX, CT, SEM; histopathology, EDX (EDS) for evaluation at 1, 2, 4 and 8 weeks after implantation.
2. Materials and Methods
The alloys were obtained of Mg-0.5%Ca with variable amounts of zirconium (x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3 wt%). Mg-0.5Ca-xZr experimental samples were casted using an induction facility under protective argon atmosphere, in a similar procedure to that developed by Istrate et al. [18]. Raw materials of Mg-15Ca and Mg-25Zr master alloys were introduced in graphite crucibles and melted at a temperature of 700 °C ± 10 °C for approximately 30 min. Cylinder bar ingots resulted and were cut in small dimension samples in order to be implanted in rats. The alloys were marked with Zr1 for the alloy Mg-0.5wt%Ca-0.5wt%Zr; with Zr2 for Mg-0.5wt%Ca-1.0wt%Zr; Zr3 for Mg-0.5wt%Ca-1.5wt%-Zr; Zr4 for Mg-0.5wt%Ca-2.0wt%Zr and with Zr5 for Mg-0.5wt%Ca-3.0wt%Zr. The used implants had rounded corners and were of parallelepiped shape, with dimensions as follows: 10–13 mm length, 4–6 mm width and 1–2 mm height. Animal experiments were performed according with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the European legislation on animal use.
2.1. Experimental Animals and Model
The selection of animal model was established following the published literature on testing Mg alloys which evaluate their biocompatibility and biodegradation in vivo behavior closer to this study [5,6,7,13,14,15,17,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
In this experimental project, in order to use as few animals as possible, on the same animal has been being used two implants, in the two different regions to save any cost and animal life. Twenty Sprague Dawley rats between approximately 30 and 32 weeks of age, with a body weight of 350 ± 15 g were randomly divided into five groups, corresponding to the five concentrations studied. The pre-experiment acclimatization of the rats was assured by hosting them in constant temperature (22 ± 0.7 °C) and humidity (60 ± 10%) conditions, and the circadian cycle (light/darkness) was established to 12 hours each.
The animals were kept for 5 days in the laboratory conditions and were daily monitored and clinical examined for possible disease conditions or abnormal behavior. The animals were purchased from the Cantacuzino National Institute of Research and Development for Microbiology and Immunology (Bucharest, Romania). On lumbar and femoral regions, two pieces of each alloy were implanted in each rat. Images of the surgical sites were taken and are shown in Figure 1.
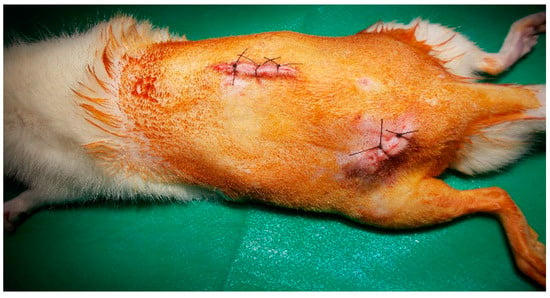
Figure 1.
Rat, Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys implanted in the lumbar and femoral regional.
2.2. Surgical Procedure
The authors chose two anatomical regions because one of the aims for this study was to use the implant in the human vertebral column and long bones pathology. In the state of art literature, the studies regarding Mg alloys were successfully conducted in the femoral region [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Rats were operated under general anesthesia, intramuscular injection with xylazine and maintained with a mixture of isoflurane 1–2% and oxygen via mask inhalation. First, the pre-operatory consideration of the rats was performed and then the animals were placed on the operating table lying in sternoabdominal recumbency. The biodegradable alloy pieces were implanted using a combination of sharp and blunt dissection. The implanted materials were placed in the paravertebral muscles of lumbar area and closed to the femur diaphysis. Before the femoral implantation, the periosteum and a thin cortical bone were removed. After insertion, the muscular, subcutaneous layer and skin were closed. The animals were allowed to move freely in their cages after the operation and were monitored daily for visual assessment of their mobility. No side effects were observed.
Radiological examinations were performed with sedation, in the sternoabdominal recumbency and, if necessary, the use of auxiliary supports. Computed radiography was used to obtain digital diagnostic images interpreted directly on a computer monitor using Examion XCR Smart (Fellbach, Germany).
Immediately after the euthanasia, the tissue samples with femoral implants (thigh region with femoral bone) were removed, fixed in 10% buffer formalin for 24 h, demineralized with 5% trichloroacetic acid solution for 4 days, molded and then embedded in paraffin.
The tissue samples containing the implants from the dorsal region were removed (soft tissue), fixed in 10% buffer formalin for 24 h, molded and then embedded in paraffin.
All the samples were sectioned at five microns and then stained by trichrome Masson method. For examination of the samples, photonic microscope Olympus® BX51 (Tokyo, Japan) and the Olympus Cell B imaging soft (Tokyo, Japan) were used.
All animals in the groups subjected to surgical experimentation were euthanized according to a well-established protocol, so that, from beginning to end, we could assess the degree of biocompatibility but also the resorption of the implanted material.
To obtain surface and chemical information about the nano and Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys’ microstructures in tissues, the used samples were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde solution in phosphate buffer, dehydrated in successive baths of alcohol (alcohol 30%, 50%, 70%, 90%, absolute alcohol and acetone), dried freely in air and finally covered with silver. Microstructural, morphology and EDS analysis were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM FEI Quanta 200 3D, dual beam, equipped with energy dispersive X-Ray spectroscopy analysis unit—Xflash Bruker, Harvard, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Clinical Results
Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloy implant tissue reactions were observed using general semiological clinical examination methods. All animals that underwent surgery were assessed for signs of local or systemic reactions every day. Hydrogen gas release occurred immediately after implantation in all studied alloys in both anatomical regions (Figure 2).
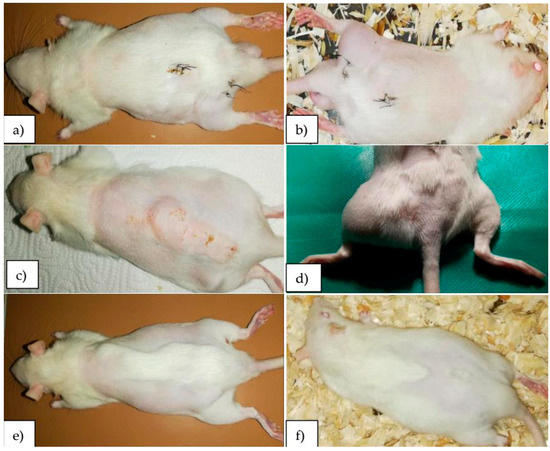
Figure 2.
Clinical aspects, representative images of rats at (a,b) one week, (c,d) two weeks, (e) four weeks and (f) eight weeks post-surgery.
Hydrogen gas was confirmed not only around the implants but also in the adjacent soft tissues (connective tissue, muscle tissue). Clinical examinations found an increase in volume of the region, distension of the skin and crackling on palpation (Table 1). The intensity of the local reaction was noted for: severe (+++), medium (++), mild (+) and its lack with (−). Corresponding to the five concentrations studied, the rat groups were marked as follows: Zr1 for 0.5 wt% zirconium, Zr2 for 1.0 wt% zirconium, Zr3 for 1.5 wt% zirconium, Zr4 for 2.0 wt% zirconium and with Zr5 for 3.0 wt% zirconium.

Table 1.
Tissue reactions, Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloy implants clinical exam results.
In the following 24 h after the surgical intervention, a local variable intensity reaction both in the lumbar and femoral region was noticed. The degradation of the Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloy implants in all five rat clusters caused an immediate hydrogen gas releasing. A bigger quantity of hydrogen gas was observed in the Zr2, Zr3 and Zr4 rat groups. None of the reactions significantly affected the physiological functionality of the surrounding tissue.
Clinical examinations found an average local reaction for Zr2 and Zr4 rat groups, compared to Zr1, Zr3 and Zr5 rat groups in which mild local reactions were present. Hydrogen formation and absorption rates for Zr1, Zr3 and Zr5 rat groups were faster, while for Zr2 and Zr4 rat groups, a higher gas bubble formation with a slower absorption rate was evaluated. No adverse effects due to the formation of subcutaneous gas were observed for all rat clusters. These results are consistent with those of Witte et al. [5], who showed that the in vivo degradation of magnesium-based alloys with rare earth element combinations do not have adverse effects due to the formation of subcutaneous gas.
3.2. Imagistic Results
Imaging investigations by X-ray were performed in order to highlight the morphological changes associated with clinically expressed symptoms. Radiological examinations (Figure 3) showed an increase in volume of the region with increased radiopacity due to the accumulation of gas in the soft tissues, the presence of hydrogen gas released of variable intensity and alloys implanted in the lumbar and femoral region (a,c,e,g) dorso-ventral and (b,d,f,h) latero-lateral recumbency. For all alloys, in the first week, large gas deposits were highlighted, both around the alloy and in the adjacent tissues.
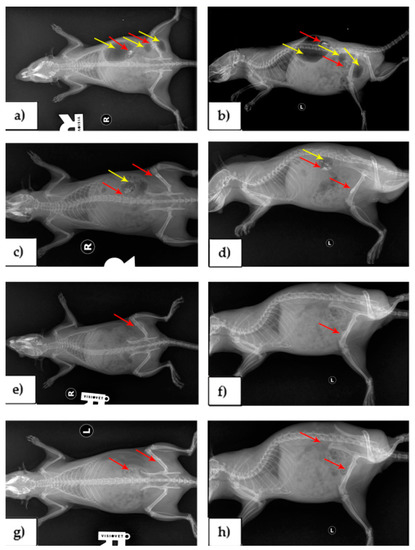
Figure 3.
Rats, representative X-ray imaging appearance, gas deposits (yellow arrows) and alloy (red arrows). At one week post-surgery, (a) dorso-ventral recumbency, (b) latero-lateral recumbency. At two weeks post-surgery, (c) dorso-ventral recumbency, (d) latero-lateral recumbency. At one month post-surgery, (e) dorso-ventral recumbency, (f) latero-lateral recumbency. At two months post-surgery, (g) dorso-ventral recumbency, (h) latero-lateral recumbency.
CT imaging investigations (Figure 4) performed at 1, 2, 4 and 8 weeks post-surgery revealed the presence of alloys surrounded by gas deposits, as well as in the adjacent soft tissues for both regions. In the following weeks, gas deposits in both anatomical regions were declining. Two months after the operation, although no changes in the volume of the regions were visible, small gas deposits were seen. The results revealed that the tissue swelling decreased at all implants at 2 and 4 weeks after implantation and became significantly lower after 8 weeks, as reported previously in Mg-Ca alloys for bone implant applications [19].
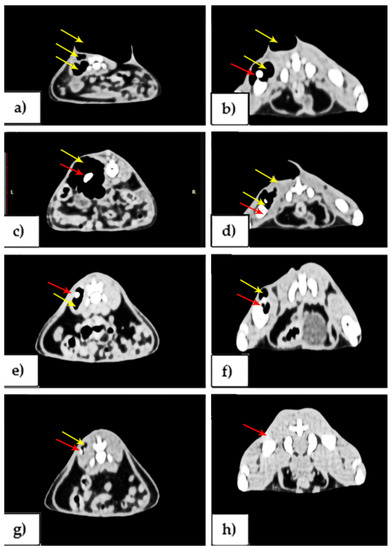
Figure 4.
Rats, CT imaging appearance, gas deposits (yellow arrows) and alloy (red arrows). At one week post-surgery, (a) lumbar region, (b) femoral and lumbar regions. At two weeks post-surgery, (c) lumbar region, (d) femoral and lumbar regions. At one month post-surgery, (e) lumbar region, (f) femoral region. At two months post-surgery, (g) lumbar region, (h) femoral region.
3.3. Histological Results
The histological feature for exams performed at one, two, four and eight weeks after surgery intervention (Figure 5) was a medium intensity inflammatory reaction, highlighted by the presence of macrophages and neutrophils around the implanted material, as well as peripheral reaction evidenced by the hyperplasia of fibroblasts and collagen fibers. Small empty spaces around the implanted material were observed due to gas accumulations caused by the resorption of material. Some studies of the histological approach [17,19,20,21] revealed that the inflammatory cells and mild fibrosis at 1, 2 and 4 weeks expected post-surgery reaction for an inert biomaterial, and can be a sign of implant integration.
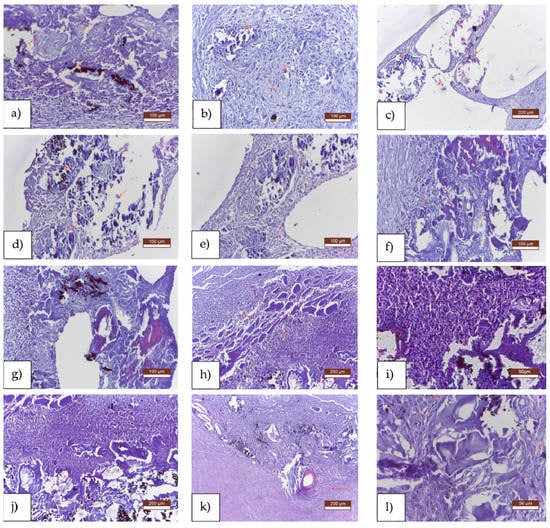
Figure 5.
Standard histological results of MTC (trichrome Masson method) stained sections of rat tissues after Mg-0,5Ca-xZr alloy was implanted. Aspect after one week: (a) medium inflammatory reaction, (b) unformed connective tissue with isolation of material fragments, (c) large vacuolar-looking spaces and small fragments of incompletely resorbed material. Aspect after two weeks: (d) numerous vacuolar spaces surround alloy, (e) inflammatory reaction areas, represented by macrophages, lymphocytes and histiocytes, (f) large vacuolar-looking spaces with the presence of macrophages and neutrophils around the implanted material. Aspect after four weeks: (g) large vacuolar-looking spaces with the presence of macrophages and neutrophils around the implanted material, (h) inflammatory reaction, represented by polymorpho nuclear cells, (i) necrotic detritus around the implanted material. Aspect after eight weeks: (j) eosinocytes in large numbers, massive leukocyte influx around partially resorbed material, (k) areas of partially resorbed implanted material, delimited by a peripheral fibrous reaction, vacuoles delimited by the unformed connective tissue near the material, (l) peripheral fibrous reaction, large vacuoles near the alloy.
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Results
Figure 6 shows SEM images for biodegradable Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys in tissue samples after one week of surgical implant. The obtained images identify areas covered by tissular reaction cells, the presence of Zirconium grains with a polyhedral structure between the structures of muscle tissue.
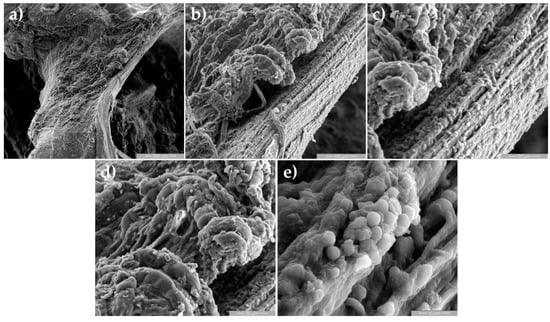
Figure 6.
SEM images for biodegradable Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys close to femoral bone at one week after the surgical procedure implant, at magnification 100× (a), 500× (b), 1000× (c,d) and 5000× (e), show the healing process of inflammatory cells due implantation procedure of Mg-0,5Ca-xZr alloy.
Microscopic morphological images for one week after surgery of the peri-implant tissue samples from the femoral bone area, at magnification 100× (Figure 6a), 500× (Figure 6b), 1000× (Figure 6c,d) and 5000× (Figure 6e), show the increased inflammatory cell activities. At this level, there is a layer of cell populations specific to the inflammatory reaction.
At a higher magnification (Figure 7), the morphology of the cells on the Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloy surface after eight weeks of surgery revealed the presence of bone neo-formation tissue. This finding is in accordance with results obtained by Mushahary et al. [21].
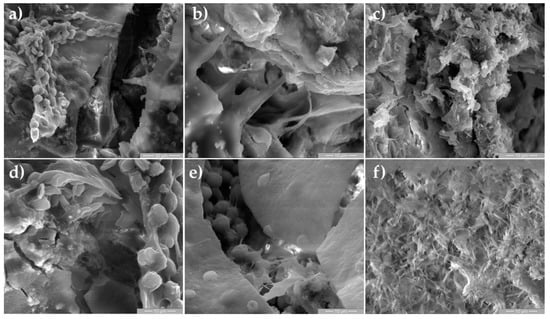
Figure 7.
SEM images of osteoblast cells for eight weeks of surgery at different magnifications, 200× (a), 4000× (b) and 5000× (c–f).
The SEM micrographs after two weeks (Figure 8), four weeks (Figure 9) and eight weeks (Figure 10) from surgery highlight the presence of morphological modification induced by biodegradable alloy. The red rectangles indicate the regions that were magnify and analyzed by the EDS analysis for the composition. The chemical composition is shown in mass percentages (wt%) and atomic percentages (at%). According to the EDS spectrum shown in Figure 8d, Figure 9d and Figure 10d, the main elements detected on the surface are shown. Thus, the complete biodegradation of the alloys did not occur after eight weeks, and quantities of zirconium particles were detected by EDS analysis. According to the EDS spectrum shown in Figure 8d, Figure 9c and Figure 10c, the main elements detected on the surface are presented in Table 2. In the EDS surface chemical composition analysis, fewer organic chemicals such as C and O were present, but more Zr and Mg content was observed.
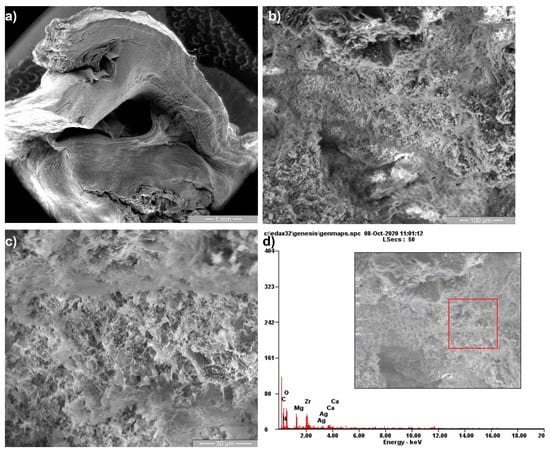

Figure 8.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and their corresponding energy-dispersive X-ray (EDS) analysis of tissue samples at two weeks of surgery at 50× (a), 500× (b), 2000× (c) magnification and EDS spectrum (d).
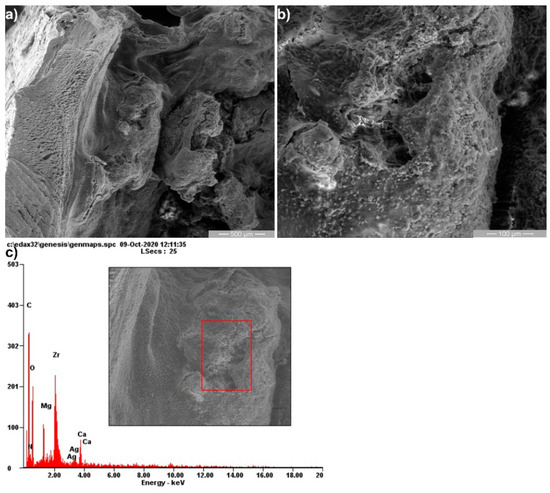
Figure 9.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and their corresponding energy-dispersive X-ray (EDS) analysis of tissue samples at four weeks of surgery at 100× (a), 500× (b) magnification and EDS spectrum (c).
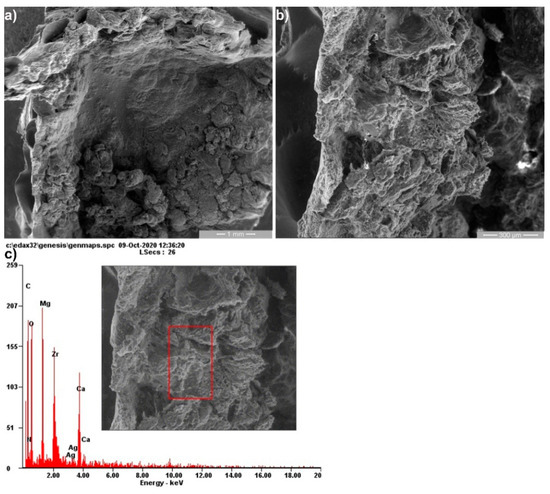
Figure 10.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and their corresponding energy-dispersive X-ray (EDS) analysis of tissue samples at eight weeks of surgery at 50× (a), 200× (b) magnification and EDS spectrum (c).

Table 2.
EDS chemical composition after different period of time of implantation.
The data represent the average values of at least three different areas of tissue and implant.
EDS results at two weeks revealed that the surface morphology and composition (rectangular area in Figure 8) were rich in Zr with a small amount of Mg and Ca. At 4 and 8 weeks after implantation (Figure 9 and Figure 10), a decreased amount of Zr was shown, which indicates the slow alloys degradation. These results were comparable to those of Makkar et al. [20]. The large amount of C observed at 4 and 8 weeks was a result of the presence of organic compounds (e.g., proteins in blood, muscle) which interact with the alloy in the biodegradation progressive process. Additionally, the higher amount of O at 4 and 8 weeks shows that the Mg alloys biodegradation was more accelerated than till 2 weeks. Our results are in accordance with other studies, where it was mentioned that the presence of Zr in different ratios at the tissue level after a long post-implant period was the result of bioaccumulation. Furthermore, it is well known that Zr is not metabolized like Mg or Ca in the body fluids [19,20,21,22].
4. Conclusions
In the present study, five differently prepared biodegradable Mg alloys, Mg-0.5Ca-0.5Zr, Mg-0.5Ca-1Zr, Mg-0.5Ca-1.5Zr, Mg-0.5Ca-2Zr and Mg-0.5Ca-3Zr, were investigated using “in vivo” experiments and laboratory examinations that followed over time: tissue reaction, histological and imaging (RX, CT and SEM) evolution at 1, 2, 4 and 8 weeks after implant. The results can be concluded as follows:
Clinical exams found inflammatory response, observed by the presence of inflammatory cells (neutrophils, macrophages, histiocytes, rare lymphocytes) present in the following 24 h after surgical intervention in all groups, both in the lumbar and femoral regions. The degradation of the Mg-0.5Ca-xZralloy implants in experimental groups revealed an immediate hydrogen gas release. None of the reactions significantly affected the physiological functionality of the surrounding tissue.
Imaging investigations by X-ray and CT performed at 1, 2, 4 and 8 weeks post-surgery revealed the presence of alloys surrounded by gas deposits, as well as in the adjacent soft tissues for both regions. In the following weeks, gas deposits in both anatomical regions were declining. Two months after the operation, although no changes in the volume of the regions were visible, small gas deposits were seen.
The histological feature for exams performed at one, two, four and eight weeks after surgery intervention was a medium intensity inflammatory reaction, highlighted by the presence of macrophages and neutrophils around the implanted material, as well as peripheral reaction evidenced by the hyperplasia of fibroblasts and collagen fibers. Small empty spaces around the implanted material were observed due to gas accumulations caused by the resorption of material.
The SEM micrographs after one, two, four and eight weeks from surgery highlight the presence of zirconium microparticles according to the EDS spectrum analysis.
The current results confirmed that Mg-0.5Ca-xZr alloys are biocompatible and biodegradable, properties that recommend these alloys as possible materials for new orthopedics devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.-V.S., S.A.P. and C.M.; methodology, E.-V.S., S.A.P. and I.M.; validation, E.-V.S., C.M. and B.I.; investigation, E.-V.S., I.M., M.E.H. and B.I.; resources, C.M. and B.I.; data curation, E.-V.S. and S.A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, E.-V.S. and I.M.; writing—review and editing, E.-V.S., C.M. and M.E.H.; supervision, E.-V.S., C.M. and I.M.; funding acquisition, C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant of the Romanian Ministry of Research and Innovation, CCCDI-UEFSCDI, project number PN-III-P1-1.2-PCCDI-207-0239/60PCCDI 2018, within PNCDI III.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of “Veterinary Medicine Faculty” of “Ion Ionescu de la Brad” University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Iasi (protocol code No. 16/24.04.2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ayers, R.A.; Burger, E.L.; Kleck, C.J.; Patel, V. Metallurgy of Spinal Instrumentation. In Advances in Metallic Biomaterials; Niinomi, M., Narushima, T., Nakai, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Bostman, O.; Pihlajamaki, H. Routine implant removal after fracture surgery: A potentially reducible consumer of hospital resources in trauma units. J. Trauma 1996, 41, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, E.K.; Ehrensberg, M.T. Bio-Corrosion of Magnesium Alloys for Orthopaedic Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, S.; Rammelt, S.; Scharnwebwr, D.; Simon, J.C. Immune responses to implanta—A review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6692–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, F.; Kaese, V.; Haferkamp, H.; Switzer, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wirth, C.J.; Windhagen, H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, F.; Ulrich, H.; Palm, C.; Willbold, E. Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds: Part II: Peri-implant bone remodeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 81, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, C.; Lindtner, R.A.; Hausbrandt, P.; Tschegg, E.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S.E.; Zanoni, G.; Beck, S.; Weinberg, A.M. Bone-implant interface strength and osseointegration: Biodegradable magnesium alloy versus standard titanium control. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrens, A.; Song, G.-L.; Liu, M.; Shi, Z.; Cao, F.; Dargusch, M.S. Review of recent developments in the field of magnesium corrosion. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 400–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, N.T. Magnesium biomaterials: Past, present and future. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.N.; Xie, X.H.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.F.; Qin, L. In vitro and in vivo studies on a Mg-Sr binary alloy system developed as a new kind of biodegradable metal. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2360–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghion, E.; Levy, G.; Ovadia, S. In vivo behavior of biodegrardable Mg-Nd-Y-Zr-Ca alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 2, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.J.; Jang, Y.S.; Park, S.; Yun, Y.H.; Bae, T.S.; Lee, M.H. Corrosion behaviour and cytotoxicity of Mg-35Zn-3Ca alloy for surface modified biodegradable implant material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2012, 100, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huehnerschulte, T.A.; Reifenrath, J.; von Rechenberg, B.; Dziuba, D.; Seitz, J.M.; Bormann, D.; Windhagen, H.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. In vivo assessment of the host reactions to the biodegradation of the two novel magnesium alloys ZEK100 and AX30 in an animal model. Biomed. Eng. Online 2012, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Xu, L.; Yu, G.; Pan, F.; Yang, K. In vivo evaluation of biodegradable magnesium alloy bone implant in the first 6 months implantation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 90, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guan, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, C.; Zhu, S.; Chen, K. In vivo degradation behavior of Ca-deficient hydroxyapetite coated Mg-Zn-Ca alloy for bone implant application. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2011, 8, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Seitz, J.M.; Waizy, H.; Angrisani, N.; Reifenrath, J. Long-term in vivo degradation behaviour and biocompatibility of the magnesium alloy ZEK100 for use as a biodegradable bone implant. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8548–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, I.S.; Jacobs, B.Y.; Allen, K.D.; Kim, S.E.; Pozzi, A.; Allen, J.B.; Manuel, M.V. Peri-implant tissue response and biodegradation performance of a Mg–1.0Ca–0.5Sr alloy in rat tibia. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 62, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, B.; Munteanu, C.; Lupescu, S.; Chelariu, R.; Vlad, M.D.; Vizureanu, P. Electrochemical Analysis and In Vitro Assay of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, J.; Bartsch, I.; Willbold, E.; Schuchardt, S.; Holz, O.; Hort, N.; Höche, D.; Heineman, W.R.; Witte, F. Fast Escape of Hydrogen from Gas Cavities Around Corroding Magnesium Implants. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8714–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, P.; Sarkar, S.K.; Padalhin, A.P.; Moon, B.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.T. In vitro and in vivo assessment of biomedical Mg-Ca alloys for bone implant applications. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2018, 16, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushahary, D.; Sravanthi, R.; Li, Y.; Kumar, M.J.; Harishankar, N.; Hodgson, P.D.; Wen, C.; Pande, G. Zirconium, calcium, and strontium contents in magnesium based biodegradable alloys modulate the efficiency of implant-induced osseointegration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2887–2902. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, D.T.; Hong, D.; Oksuz, S.; Schweizer, R.; Roy, A.; Lee, B.; Shridhar, P.; Gorantla, V.; Kumta, P.N. Corrosion and bone healing of Mg-Y-Zn-Zr-Ca alloy implants: Comparative in vivo study in a non-immobilized rat femoral fracture model. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 1178–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ren, Z.; Xu, Y.D.; Pang, S.; Zhao, X.B.; Zhao, Y. Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys Developed as Bone Repair Materials: A Review. Hindawi Scanning 2018, 2018, 9216314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, N.; Nakao, Y.; Ishikawa, R.; Tsuchida, D.; Iijima, M. Degradation and Biocompatibility of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Implants In Vitro and In Vivo: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study in Rats. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.S.; Chan, L.C.; Lai, C.P.; Ip, W.Y.; Lu, Y.F. Magnesium-Alloy for Orthopedic Application: Long Term Evaluation on Bone Compatibility and Degradation Under In Vivo Environment. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Odashima, K.; Sano, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Mukai, T.; Ikeo, N.; Takahashi, T.; Kumamoto, H. In vitro and in vivo analysis of the biodegradable behavior of a magnesium alloy for biomedical applications. Dent. Mater J. 2018, 38, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).