Stimuli-Sensitive Aggregation-Induced Emission of Organogelators Containing Mesogenic Au(I) Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
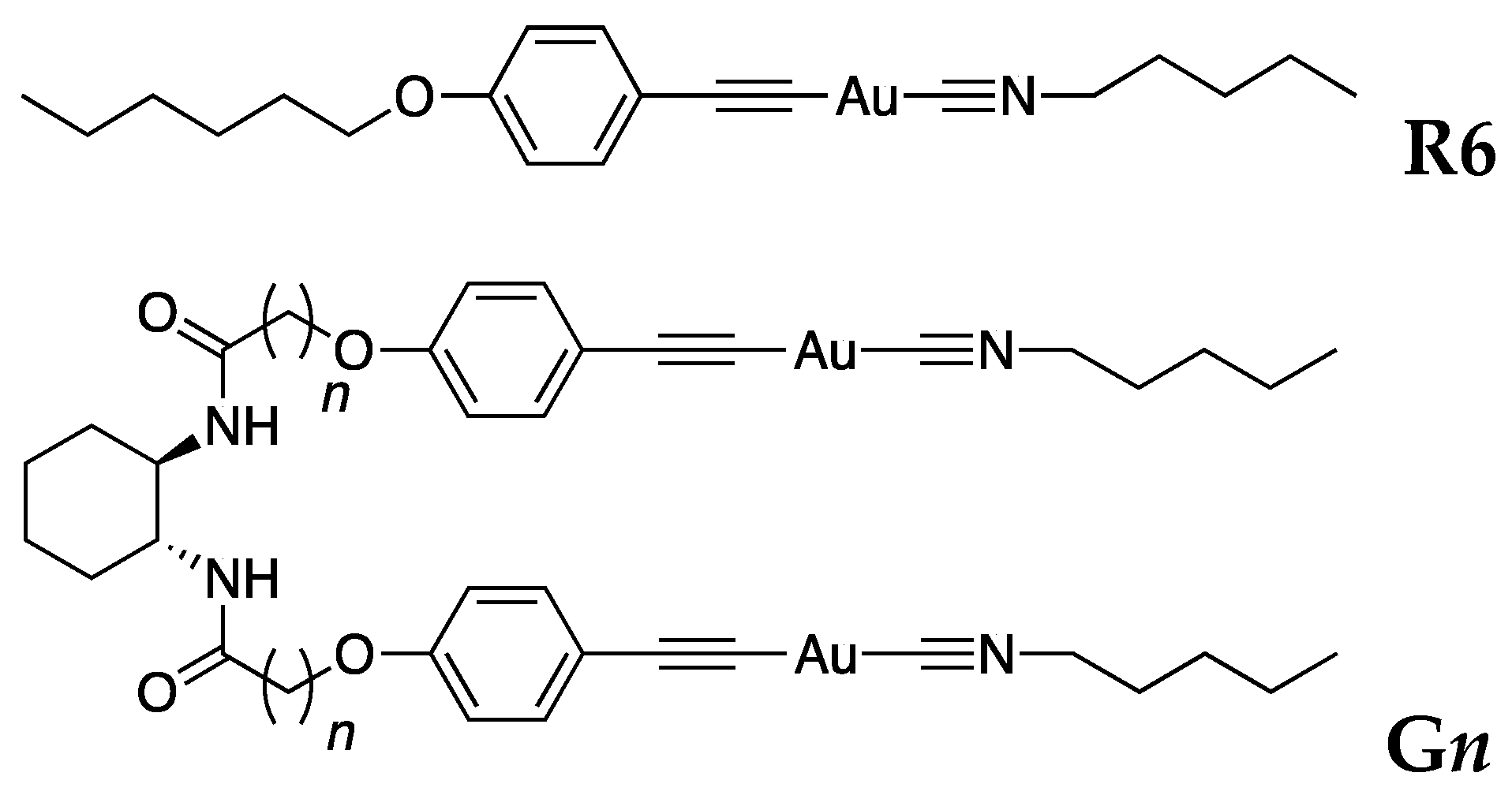
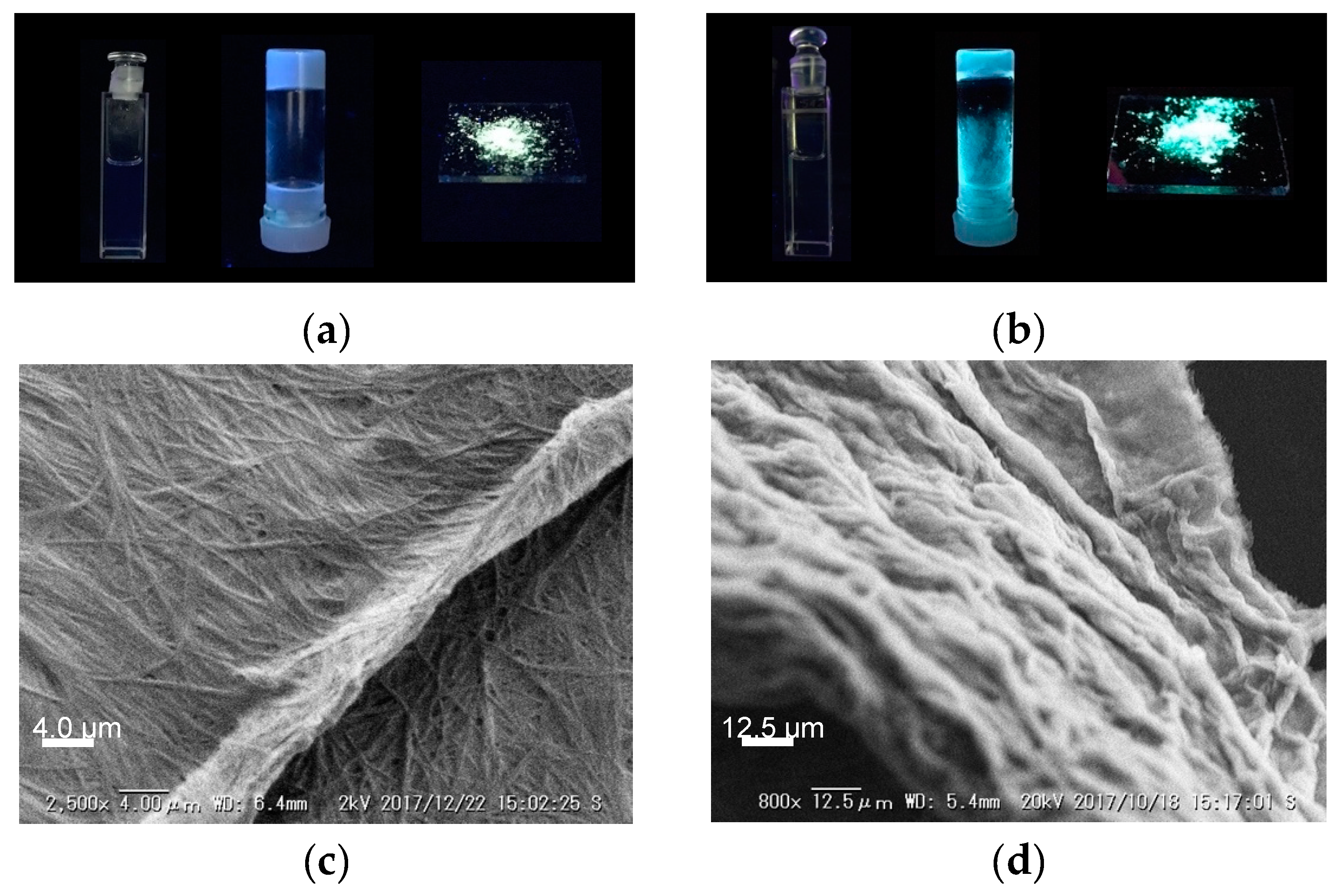
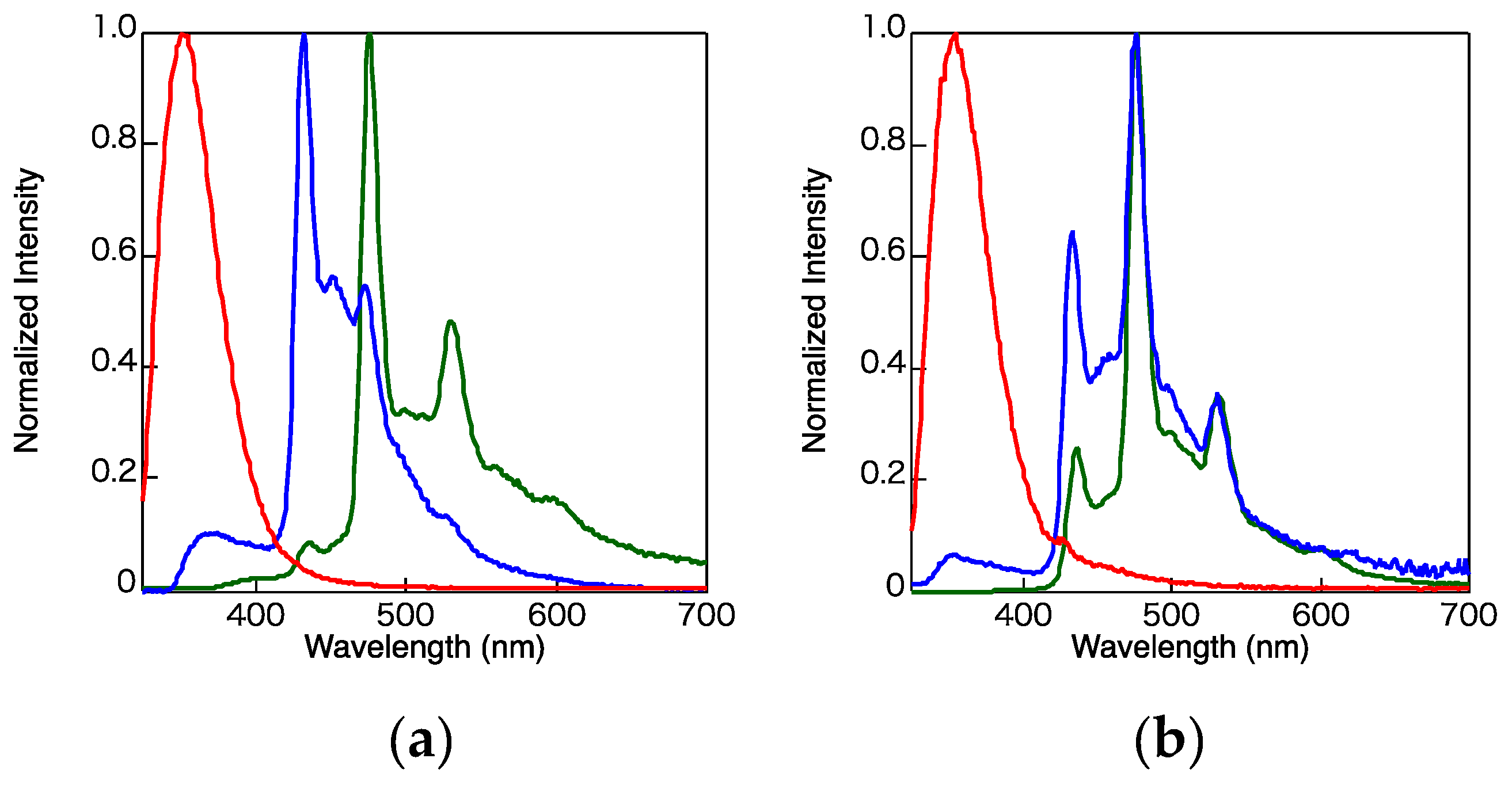
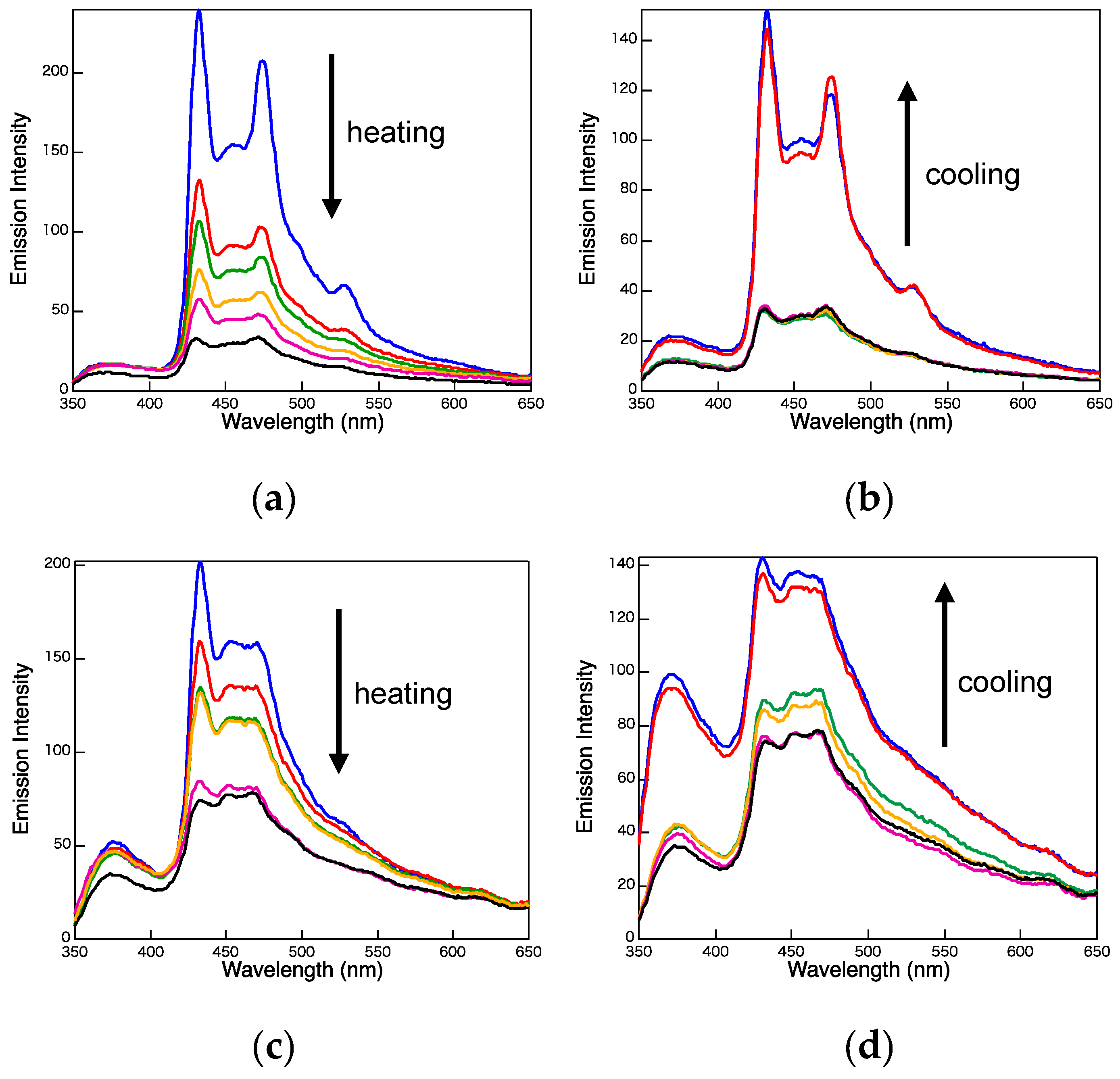
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Materials
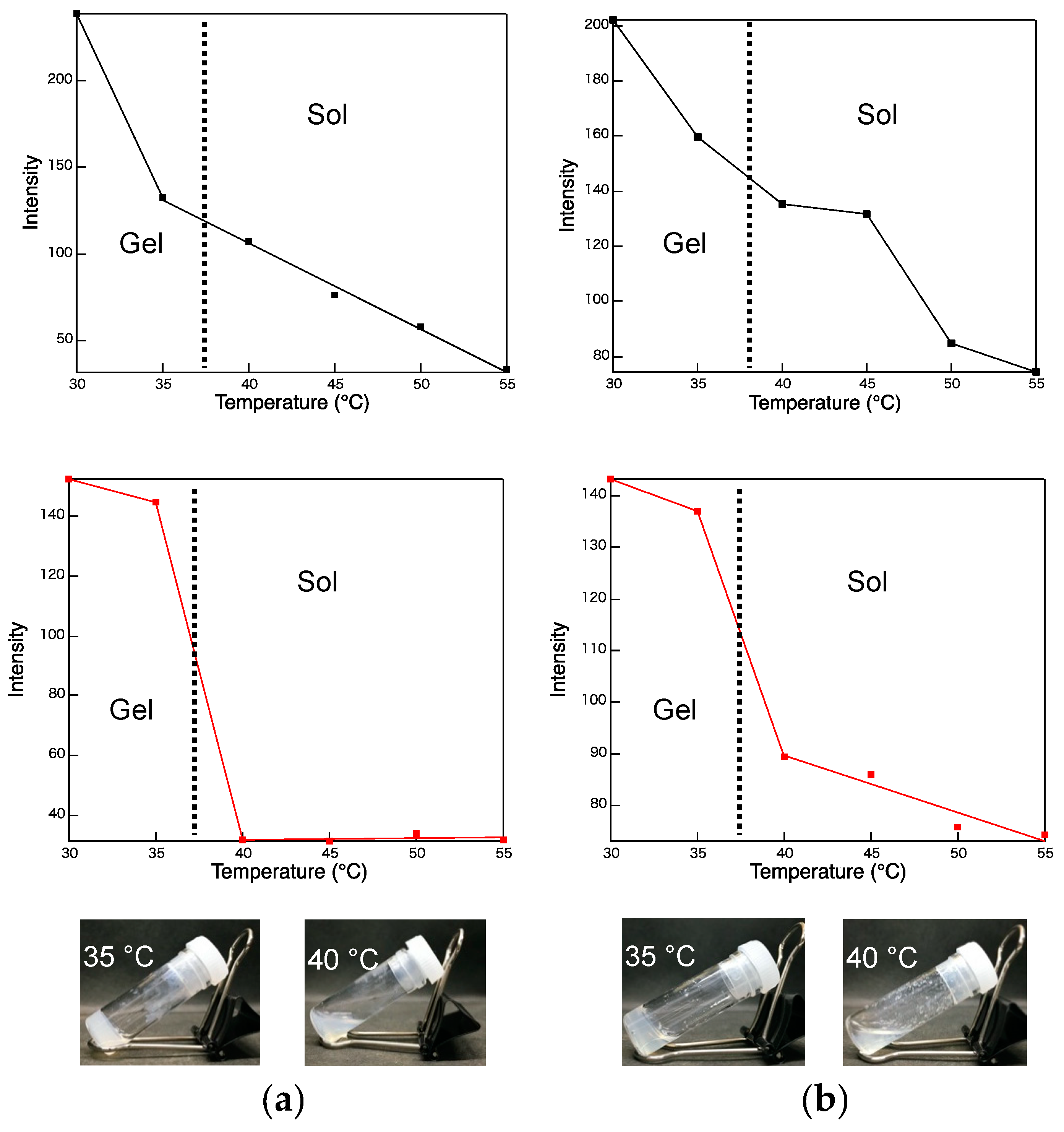
3.2. Gelation Ability
3.3. Photophysical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shinar, J.; Savvateev, V. Introduction to organic light-emitting devices. In Organic Light-Emitting Devices: A Survey; Shinar, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Park, Y.; Jung, J.; Han, W.-S. Blue-shifted aggregation-induced emission of siloles by simple structure modification and their application as nitro explosive chemosensors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2017, 16, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhoa, Q.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Luminescent chemodosimeters for bioimaging. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 192–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, H.; Qui, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Svahn, N.; Lima, J.C.; Rodríguez, L. Aggregation induced emission of gold(I) complexes in water or water mixtures. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 11125–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Wang, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, X. Luminescent oraganometallic nanomaterials with aggregation-induced emission. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 48, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, H.; Lei, J.; He, B.; He, X.; Sung, H.H.Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Zheng, L.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Multifunctional AuI-based AIEgens: Manipulating molecular structures and boosting specific cancer cell imaging and theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 7163–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Yin, J.; Yu, G.-A.; Liu, S.H. A novel fluorene-based aggregation-induced emission (AIE)-active gold(I) complex with crystallization-induced emission enhancement (CIEE) and reversible mechanochromism characteristics. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, V.W.-W.; Au, V.K.-M.; Leung, S.Y.-L. Light-emitting self-assembled materials based on d8 and d10 transition metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7589–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Kawakami, N.; Onishi, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Tamai, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Tsutsumi, O. Photoluminescent properties of liquid crystalline gold(I) isocyanide complexes with a rod-like molecular structure. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 5359–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Rokusha, Y.; Kawano, R.; Fujisawa, K.; Tsutsumi, O. Mesogenic gold complexes showing aggregation-induced enhancement of phosphorescence in both crystalline and liquid-crystalline phases. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 196, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Srinivas, K.; Sathayanarayana, A.; Prabusankar, G.; Hisano, K.; Tsustsumi, O. Thermochemically stable liquid-crystalline gold(I) complexes showing enhanced room temperature phosphorescence. Crystals 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, O.; Tamaru, M.; Nakasato, H.; Shimai, S.; Panthai, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Fujisawa, K.; Hisano, K. Highly efficient aggregation-induced room-temperature phosphorescence with extremely large Stokes shift emitted from trinuclear gold(I) complex crystals. Molecules 2019, 24, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, O. Gold–gold interactions. In Modern Supramolecular Gold Chemistry: Gold-Metal Interactions and Applications; Laguna, A., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 65–129. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidbaur, H. The aurophilicity phenomenon: A decade of experimental findings, theoretical concepts and emerging applications. Gold Bull. 2000, 33, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidbaur, H.; Schier, A. Aurophilic interactions as a subject of current research: An up-date. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 370–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.; Tubaro, C.; Biffis, A.; Basato, M.; Graiff, C.; Poater, A.; Cavallo, L.; Armaroli, N.; Accorsi, G. Blue-emitting dinuclear N-heterocyclic dicarbene gold(I) complex featuring a nearly unit quantum yield. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 1178–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lòpez-de-Luzuriaga, J.M. Luminescence of supramolecular gold-containing materials. In Modern Supramolecular Gold Chemistry: Gold-Metal Interactions and Applications; Laguna, A., Ed.; Willey-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 347–401. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimura, A.; Yamashita, T.; Aida, T. Phosphorescent organogels via “mettalophilic” interactions for reversible RGB-color switching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White-Morris, R.L.; Olmstead, M.M.; Attar, S.; Balch, A.L. Intermolecular interactions in polymorphs of trinuclear gold(I) complexes: Insight into the solvoluminescence of AuI3(MeN=COMe)3. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 5021–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, A.L.; Olmstead, M.M.; Vickery, J.C. Gold(I) compounds without significant aurophilic intermolecular interactions: Synthesis, structure, and electronic properties of Ph3PAuC(O)NHMe and Au3(PhCH2N=COMe)3: Comparative monomeric and trimeric analogues of the solvoluminescent trimer, Au3(MeN=COMe)3. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 3494–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Vickery, J.C.; Olmstead, M.M.; Fung, E.Y.; Balch, A.L. Solvent-stimulated luminescence from the supramolecular aggregation of a trinuclear gold(I) complex that displays extensive intermolecular AuċAu interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Saito, T.; Oshima, N.; Kitamura, N.; Ishizaka, S.; Hinatsu, Y.; Wakeshima, M.; Kato, M.; Tsuge, K.; Sawamura, M.; et al. Reversible mechanochromic luminescence of [(C6F5Au]2(µ-1,4-diisocyanobenzene)]. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10044–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Muromoto, M.; Kurenuma, S.; Ishizaka, S.; Kitamura, N.; Sato, H.; Seki, T. Mechanical stimulation and solid seeding trigger single-crystal-to-single-crystal molecular domino transformations. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Sakurada, K.; Muromoto, M.; Ito, H. Photoinduced single-crystal-to-single-crystal phase transition and photosalient effect of a gold(I) isocyanide complex with shortening of intermolecular aurophilic bonds. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Takamatsu, Y.; Ito, H. A screening approach for the discovery of mechanochromic gold(I) isocyanide complexes with crystal-to-crystal phase transitions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6252–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyanarayana, A.; Nakamura, S.; Hisano, K.; Tsutsumi, O.; Srinivas, K.; Prabusankar, G. Controlling the solid-state luminescence of gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes through changes in the structure of molecular aggregates. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Yamada, S.; Yanagi, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kiyohara, A.; Tsutsumi, O. Tuning the photoluminescence of condensed-phase cyclic trinuclear Au(I) complexes through control of their aggregated structures by external stimuli. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, O.; Rokusha, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Fujisawa, K.; Yamada, S.; Tsutsumi, O. Effect of molecular structure and aggregated structure on photoluminescence properties of liquid-crystalline gold(I) complexes with various aromatic rings. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 617, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D. Liquid crystalline AIE luminogens: Properties and applications. In Aggregation-Induced Emission: Materials and Applications; Fujiki, M., Liu, B., Tang, B.Z., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series 1227; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Cai, Z.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Gan, S.; He, Q.; Chen, W.; Dong, Y.; et al. A stabilized lamellar liquid crystalline phase with aggregation-induced emission features based on pyrrolopyrrole derivatives. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, D.; Luo, Z.-W.; Xu, J.-R.; Li, M.-L.; Yang, L.-H.; Yu, Z.-Q.; Chen, E.-Q.; Xie, H.-L. High efficiency luminescent liquid crystalline polymers based on aggregation-induced emission and “jacketing” effect: Design, synthesis, photophysical property, and phase structure. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 9607–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A. Mechanochromic fluorescent polymers with aggregation-induced emission features. Sensors 2019, 19, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Pu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Cai, Y.; Gu, X.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Fluorescence turn-on visualization of microscopic processes for self-healing gels by AIEgens and anticounterfeiting application. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5683–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, J.; Pye, S.; Reza, A.H.M.M.; Xie, N.; Qin, J.; Raston, C.L.; Tang, B.Z.; Tang, Y. Tuning aggregation-induced emission nanoparticle properties under thin film formation. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Mitsuhashi, F.; Anukul, P.; Taneki, K.; Younis, O.; Tsutsumi, O. Photoluminescence behavior of liquid-crystalline gold(I) complexes with a siloxane group controlled by molecular aggregate structures in condensed phases. Polym. J. 2018, 50, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Okuda, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Nagamatsu, A.; Rokusha, Y.; Sadaike, Y.; Tsutsumi, O. Reversible thermal-mode control of luminescence from liquid-crystalline gold(I) complexes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3549–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhange, G.; Zhang, D. A new gelator based on tetraphenylethylene and diphenylalanine: Gel formation and reversible fluorescence tuning. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 4284–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Song, S.-S.; Fan, Y.-Q.; Guan, X.-W.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, T.-B.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.-M. A novel supramolecular AIE gel acts as a multi-analyte sensor array. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 18059–18065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschmann, D.; Riebe, S.; Neumann, T.; Killa, D.; Ostwaldt, J.-E.; Wölper, C.; Schmuck, C.; Voskuhl, J. A stimuli responsive two component supramolecular hydrogelator with aggregation-induced emission properties. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 7117–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D.; García-Frutos, E.M. Aggregation-induced emission of organogels based on self-assembled 5-(4-nonylphenyl)-7-azaindoles. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8697–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D. Fluorescence enhancement upon gelation and thermally-driven fluorescence switches based on tetraphenylsilole-based organic gelators. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 475, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, H.; Jiang, S. Multi-stimuli responsive supramolecular gels based on a D-π—A structural cyanostilbene derivative with aggregation induced emission properties. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Shang, H.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, S. Supramolecular organogels and nanowires based on a V-shaped cyanostilbene amide derivative with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4472–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Externbrink, M.; Riebe, S.; Schmuck, C.; Voskuhl, J. A dual pH-responsive supramolecular gelator with aggregation-induced emission properties. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 6166–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Li, M. Fluorescence-enhanced organogels and mesomorphic superstructure based on hydrazine derivatives. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10183–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.S.; Praveen, V.K.; Ajayaghosh, A. Function π-gelators and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1973–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Xue, P.; Peng, J.; Zhai, L.; Sun, M.; Sun, J.; Lu, R. Red-emitting dyes base on phenothiazine-modified 2-hydroxychalcone analogues: Mechanofluorochromism and gelation-induced emission enhancement. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Chen, D.; Iqbal, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Multistimuli-responsive benzothiadiazole-cored phenylene vinylene derivative with nanoassembly properties. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6323–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; An, B.K.; Park, S.Y. A thermoreversible and proton-induced gel-sol phase transition with remarkable fluorescence variation. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6750–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Miao, W.; Ma, X. Aggregation-induced emission organogel formed by both sonication and thermal processing base on tetraphenylethylene and cholesterol derivative. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 165, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Lan, H.; Xiao, S.; Li, Y.; Tan, R.; Yi, T. A fluorescent non-conventional oranogelator with gelation-assisted piezochromic and fluoride-sensing properties. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 137, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.; Ge, X.; Li, Y.; Zhen, X.; Yi, T. Visual recognition of aliphatic and aromatic amines using a fluorescent gel: Application of sonication-triggered organogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 24, 13569–13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, K.; Meng, L.; Mo, S.; Zhang, M.; Mao, Y.; Cao, X.; Huang, C.; Yi, T. Colour change and luminescence enhancement in a cholesterol-based terpyridyl platinum metallogel via sonication. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, J. A thermos-responsive supramolecular gel and its luminescence enhancement induced by rare earth Y3+. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 8027–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.B.; Ma, X.Q.; Fan, Y.Q.; Jiang, X.M.; Dong, H.Q.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yao, H.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission supramolecular organic framework (AIE SOF) gels constructed from tri-pillar[5]arene-based foldamer for ultrasensitive detection and separation of multi-analytes. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 6753–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanabusa, K.; Yamada, M.; Kimura, M.; Shirai, H. Prominent gelation and chiral aggregation of alkylamides derived from trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 1949–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.C.; Rodríguez, L. Supramolecular gold metallogelators: The key role of metallophilic interactions. Inorganics 2015, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A.Y.-Y.; Yam, V.W.-W. Recent advances in metallogels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1540–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.Z.; Shen, X.Y.; Zhao, H.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, L.; Lu, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Crystallization-induced phosphorescence of pure organic luminogens at room temperature. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6090–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Chen, G.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, W.Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Achieving persistent room temperature phosphorescence and remarkable mechanochromism from pure organic luminogens. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6195–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, R.; Younis, O.; Ando, A.; Rokusha, Y.; Yamada, S.; Tsutsumi, O. Photoluminescence from Au(I) complexes exhibiting color sensitivity to the structure of the molecular aggregates. Chem. Lett. 2016, 45, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Solvent (v/v) | G5 | G10 |
|---|---|---|
| Hexane | IS | IS |
| Hexane/CH2Cl2 (1/2) | G | S |
| Hexane/CH2Cl2 (2/3) | – | G |
| CH2Cl2 | S | S |
| THF | P | G |
| EtOAc/CH2Cl2 (1/2) | G | S |
| EtOAc/CH2Cl2 (2/3) | – | G |
| EtOAc | IS | IS |
| Hexane/CHCl3 (1/2) | G | S |
| Hexane/CHCl3 (2/3) | PG | G |
| CHCl3 | S | S |
| EtOH | IS | IS |
| CH3CN | IS | IS |
| DMF | S | S |
| Complex | Lifetime, τ (µs) | Quantum Yield, Φ (%) |
|---|---|---|
| G5 | 0.23 (74%) 19 (26%) | 1.9 |
| G10 | 1.1 (72%) 38 (28%) | 16 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panthai, S.; Fukuhara, R.; Hisano, K.; Tsutsumi, O. Stimuli-Sensitive Aggregation-Induced Emission of Organogelators Containing Mesogenic Au(I) Complexes. Crystals 2020, 10, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050388
Panthai S, Fukuhara R, Hisano K, Tsutsumi O. Stimuli-Sensitive Aggregation-Induced Emission of Organogelators Containing Mesogenic Au(I) Complexes. Crystals. 2020; 10(5):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050388
Chicago/Turabian StylePanthai, Supattra, Ryota Fukuhara, Kyohei Hisano, and Osamu Tsutsumi. 2020. "Stimuli-Sensitive Aggregation-Induced Emission of Organogelators Containing Mesogenic Au(I) Complexes" Crystals 10, no. 5: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050388
APA StylePanthai, S., Fukuhara, R., Hisano, K., & Tsutsumi, O. (2020). Stimuli-Sensitive Aggregation-Induced Emission of Organogelators Containing Mesogenic Au(I) Complexes. Crystals, 10(5), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050388






