Biomedical Sensing with Free-Standing Complementary Supercell Terahertz Metasurfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
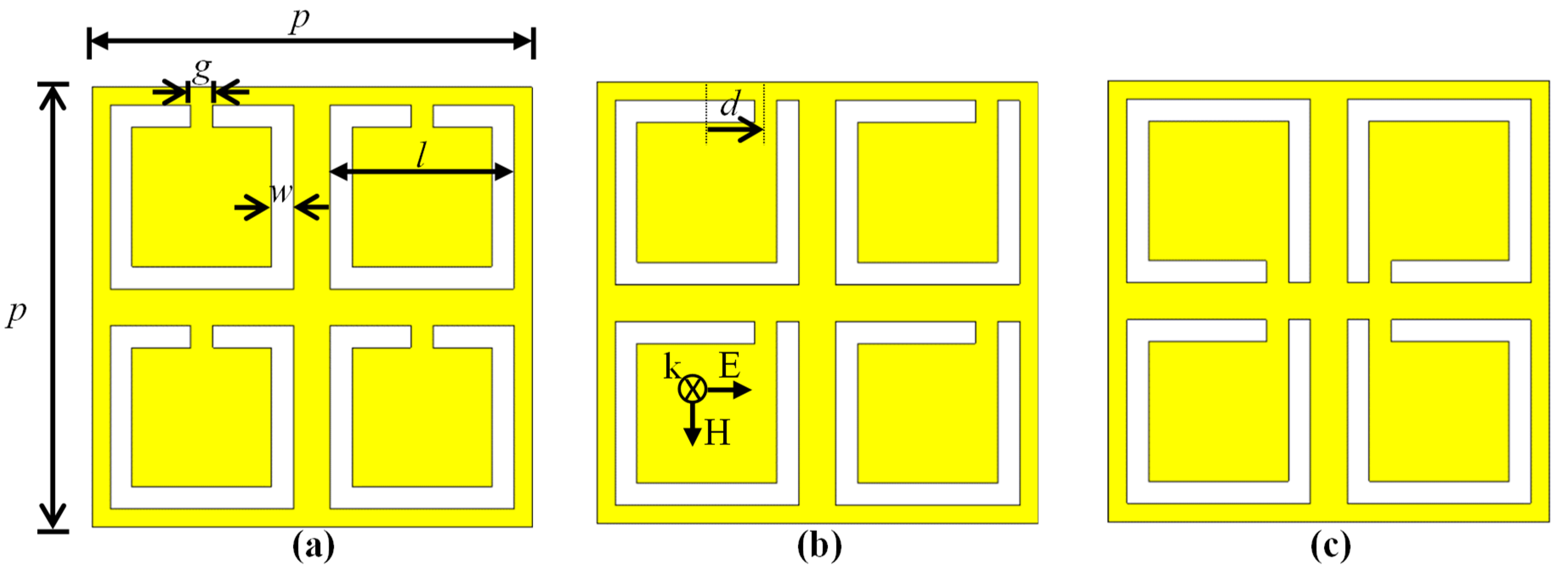
2. Sensor Design and Simulation Methods
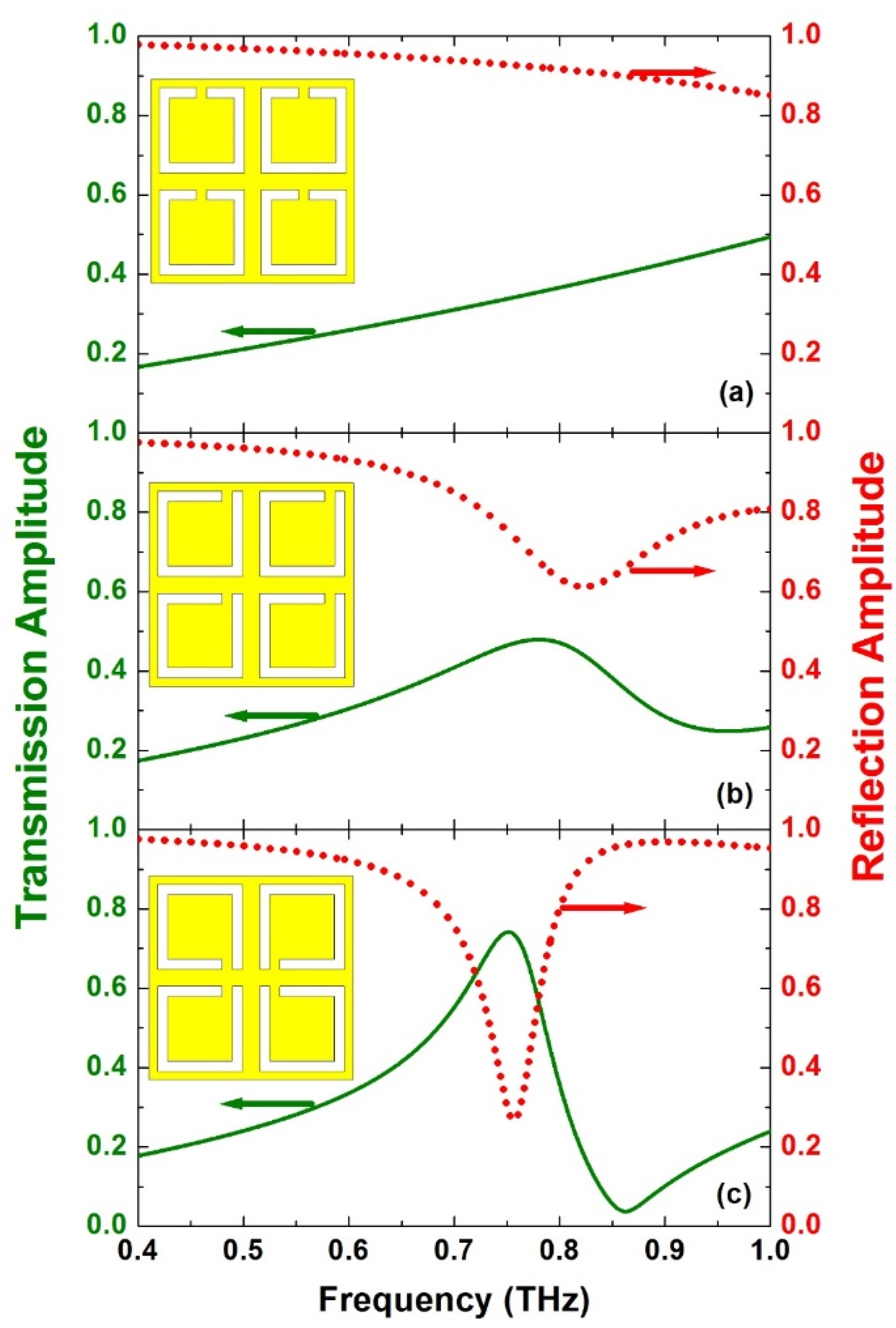
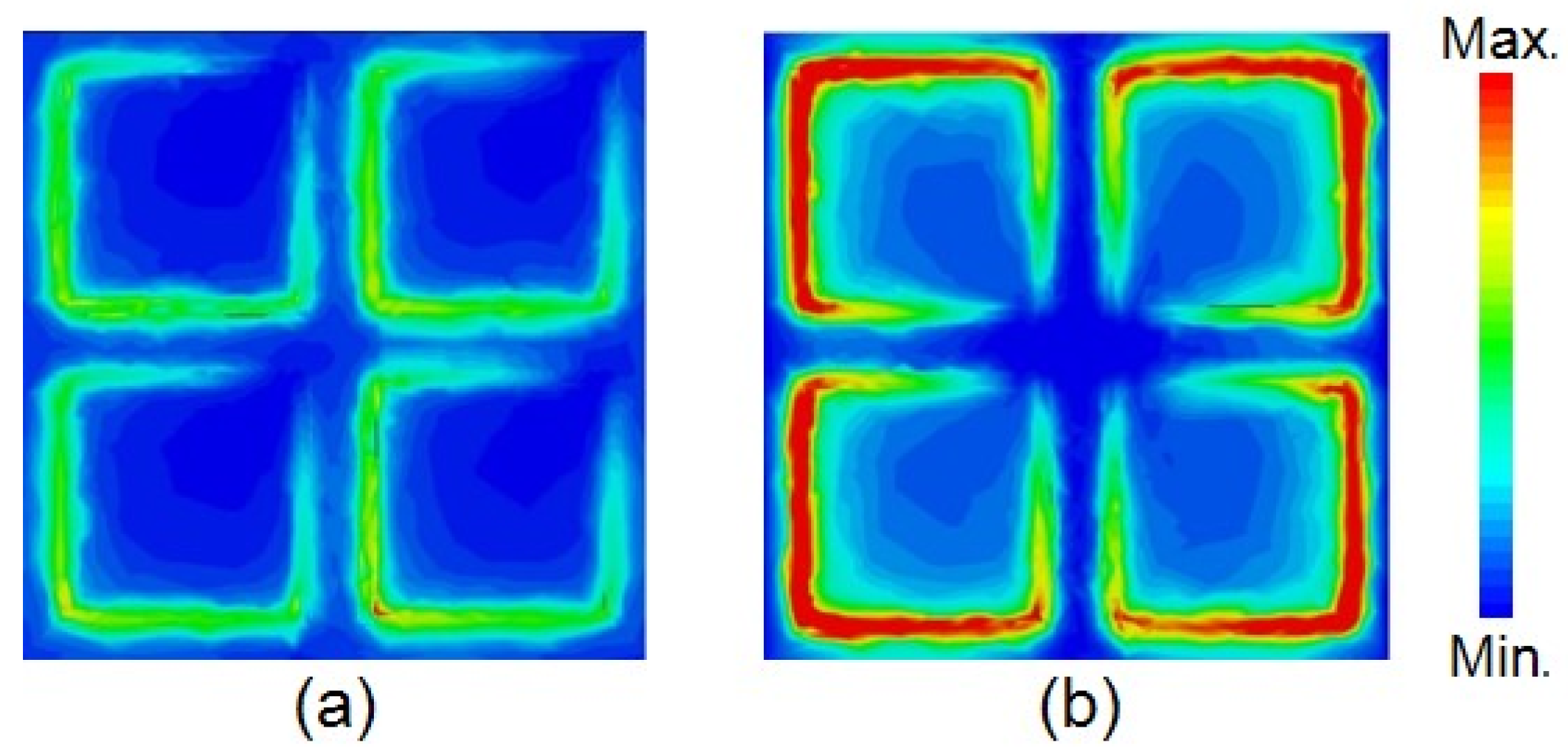
3. Mirrored vs. Nonmirrored Supercells Results and Discussion
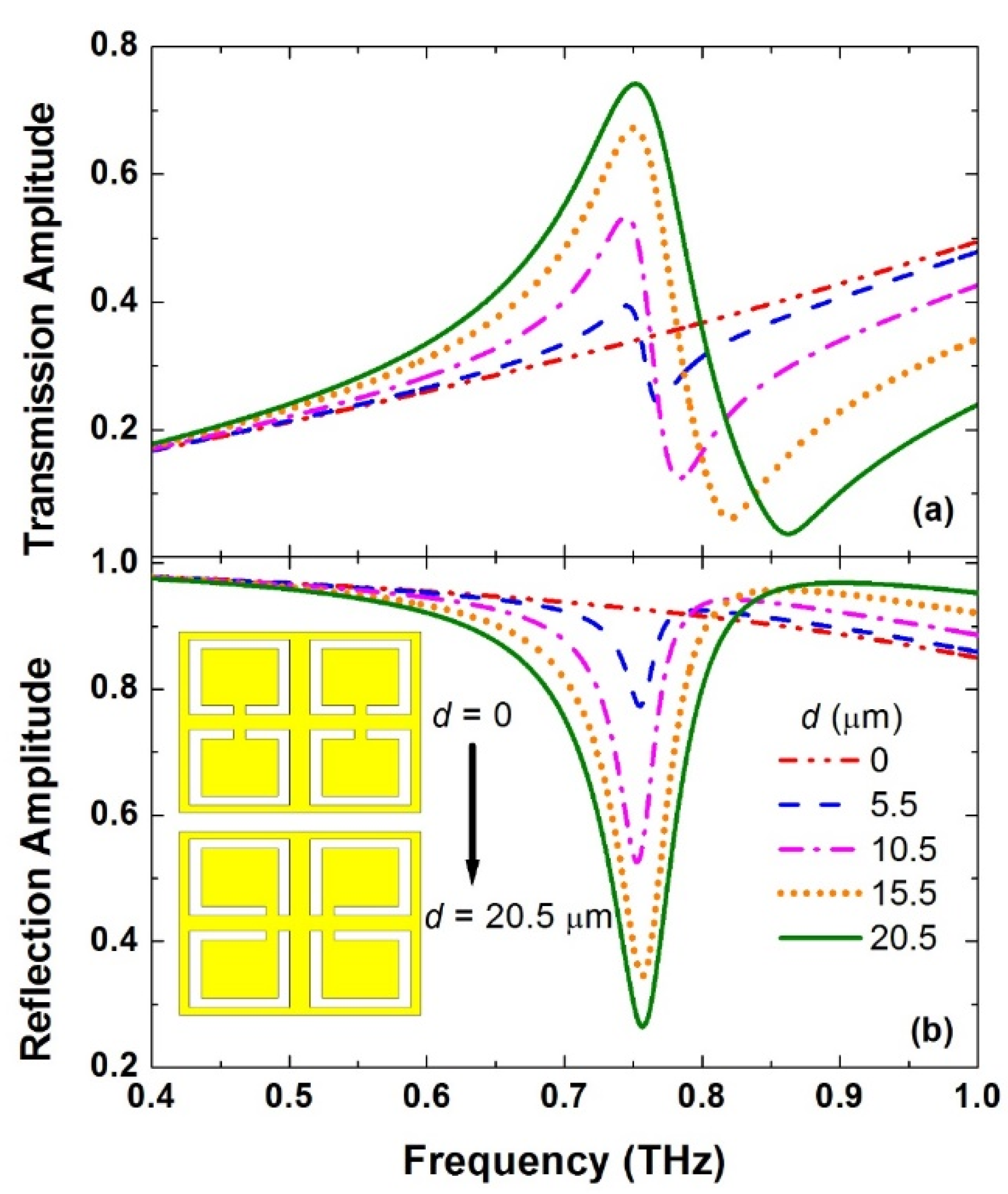
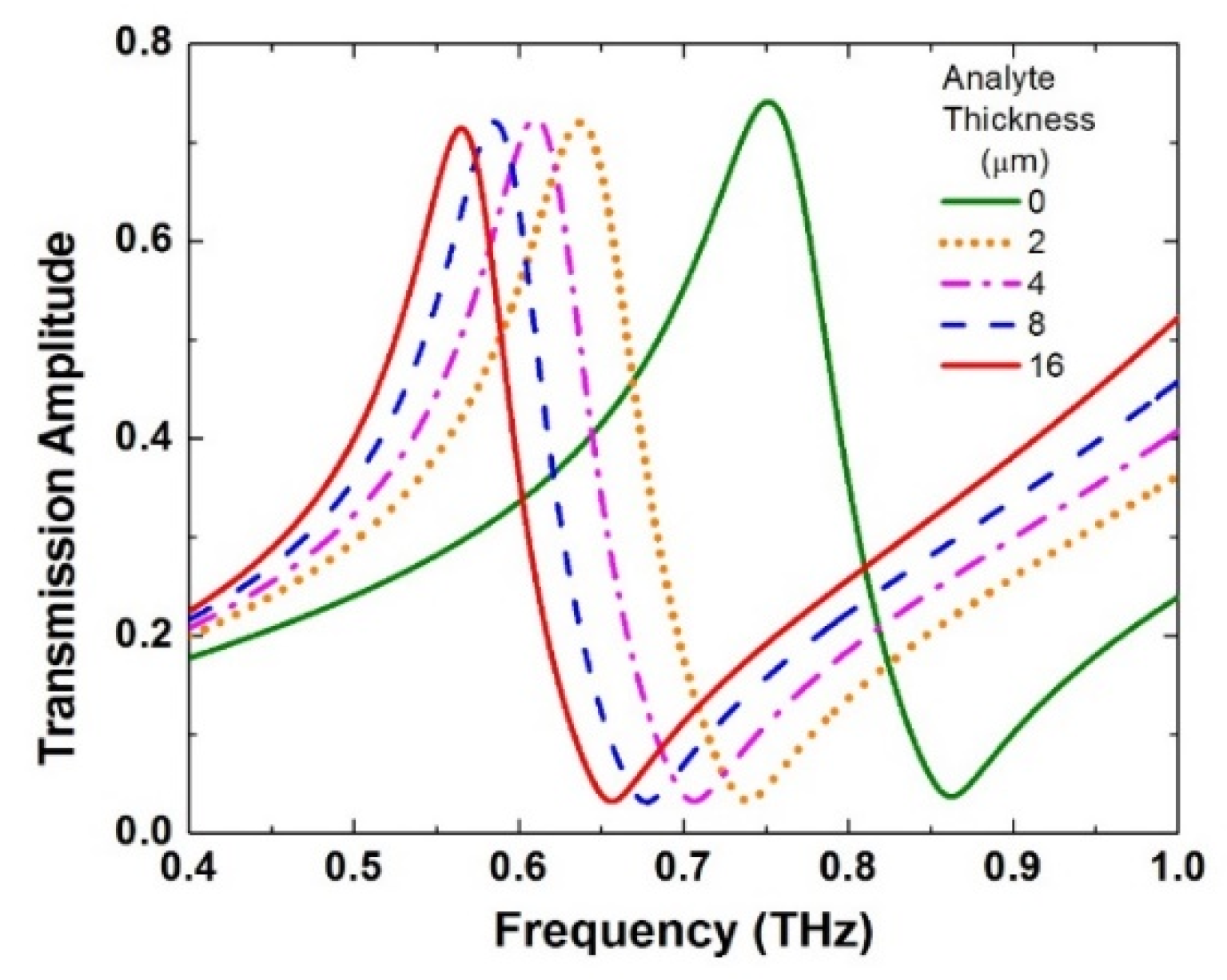
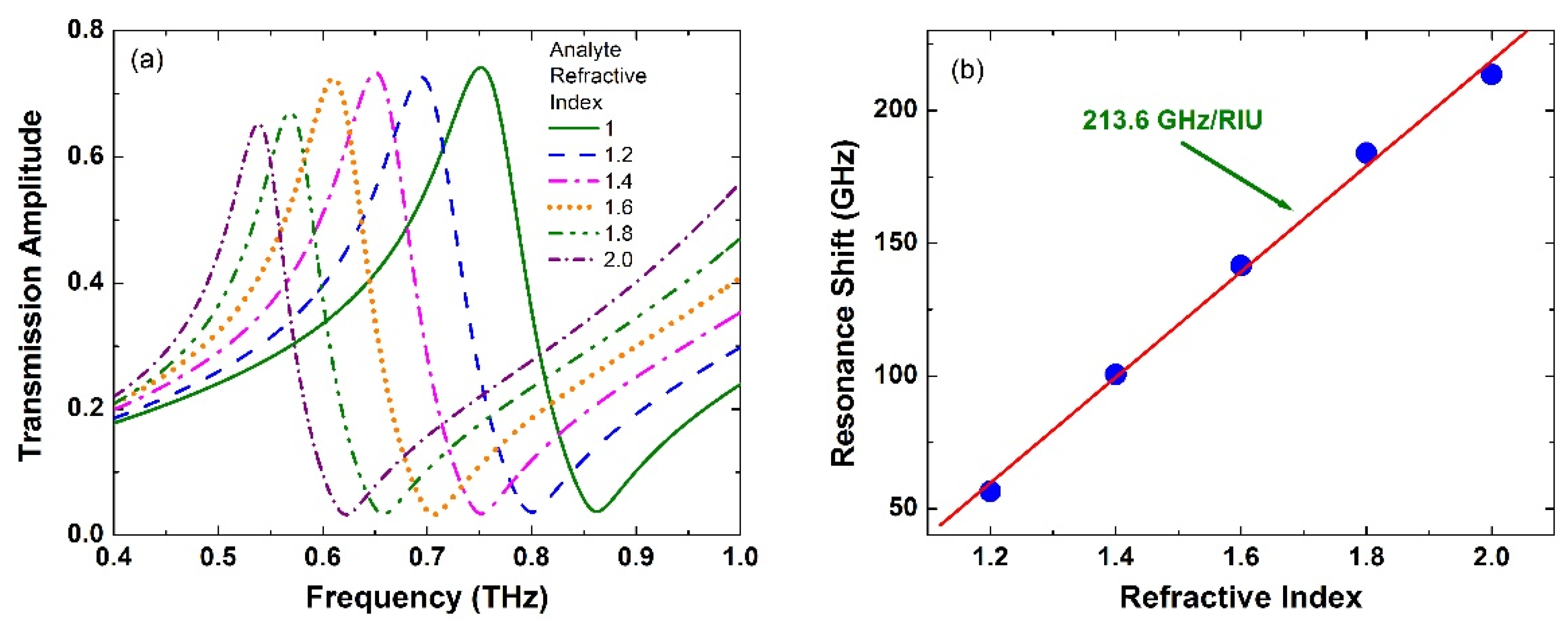
4. Mirrored Supercell Sensor Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Averitt, R.D. Metamaterials: A stamp of quality. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 396–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Khanikaev, A.B.; Adato, R.; Arju, N.; Yanik, A.A.; Altug, H.; Shvets, G. Fano-resonant asymmetric metamaterials for ultrasensitive spectroscopy and identification of molecular monolayers. Nat. Mater. 2011, 11, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendry, J. Optics: All smoke and metamaterials. Nature 2009, 460, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Kang, S.B.; Shin, J.; Kwak, M.H.; Kang, K.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, N.; Min, B. A terahertz metamaterial with unnaturally high refractive index. Nature 2011, 470, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukoulis, C.M.; Linden, S.; Wegener, M. Negative refractive index at optical wavelengths. Science 2007, 315, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendry, J.B. A chiral route to negative refraction. Science 2004, 306, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-T.; Taylor, A.J.; Yu, N. A review of metasurfaces: Physics and applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 76401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, J.F.O.; Singh, R.; Brener, I.; Smirnova, E.; Han, J.; Taylor, A.J.; Zhang, W. Thin-film sensing with planar terahertz metamaterials: Sensitivity and limitations. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Padilla, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Averitt, R.D. Recent progress in electromagnetic metamaterial devices for Terahertz applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2011, 17, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I.; Withayachumnankul, W. Recent Progress in Terahertz Metasurfaces. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2017, 38, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.F.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Al-Naib, I. A Review on Thin-film Sensing with Terahertz Waves. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 33, 245–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I.; Singh, R.; Shalaby, M.; Ozaki, T.; Morandotti, R. Enhanced Q-factor in Optimally Coupled Macrocell THz Metamaterials: Effect of Spatial Arrangement. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2013, 19, 8400807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucherseifer, M.; Nagel, M.; Haring Bolivar, P.; Kurz, H.; Bosserhoff, A.; Buettner, R. Label-free probing of the binding state of DNA by time-domain terahertz sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 4049–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I. Biomedical sensing with conductively coupled terahertz metamaterial resonators. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 4700405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I. Thin-Film Sensing via Fano Resonance Excitation in Symmetric Terahertz Metamaterials. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2018, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Tan, S.; Yahiaoui, R.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W.; Singh, R. Experimental demonstration of ultrasensitive sensing with terahertz metamaterial absorbers: A comparison with the metasurfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 31107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Cao, W.; Al-Naib, I.; Cong, L.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Zhang, W. Ultrasensitive terahertz sensing with high-Q Fano resonances in metasurfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Srivastava, Y.K.; Manjappa, M.; Singh, R. Sensing with Toroidal Metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 121108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Chieffo, L.R.; Brenckle, M.A.; Siebert, S.M.; Liu, M.; Strikwerda, A.C.; Fan, K.; Kaplan, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Averitt, R.D.; et al. Metamaterials on paper as a sensing platform. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Al-Naib, I.A.I.; Born, N.; Koch, M. Terahertz metasurfaces with high Q-factors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 51109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Q.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, S.M.; Cao, J.X.; Zhu, Z.H.; Dong, Z.G.; Zhu, S.N.; Zhang, X. Suppression of radiation loss by hybridization effect in two coupled split-ring resonators. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 115113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, V.A.; Rose, M.; Prosvirnin, S.L.; Papasimakis, N.; Zheludev, N.I. Sharp trapped-mode resonances in planar metamaterials with a broken structural symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 147401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Al-Naib, I.A.I.; Koch, M.; Zhang, W. Sharp Fano resonances in THz metamaterials. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 6312–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luk’Yanchuk, B.; Zheludev, N.I.; Maier, S.A.; Halas, N.J.; Nordlander, P.; Giessen, H.; Chong, C.T. The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Naib, I.A.I.; Jansen, C.; Koch, M. Thin-film sensing with planar asymmetric metamaterial resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 083507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Al-Naib, I.A.I.; Koch, M.; Zhang, W. Asymmetric planar terahertz metamaterials. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 13044–13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Al-Naib, I.; Cao, W.; Rockstuhl, C.; Koch, M.; Zhang, W. The Fano Resonance in Symmetry Broken Terahertz Metamaterials. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, K.; Pitchappa, P.; Manjappa, M.; Ho, C.P.; Singh, R.; Lee, C. Microfluidic metamaterial sensor—Selective trapping and remote sensing of microparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 023102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, K.; Pitchappa, P.; Jin, L.; Chen, C.; Singh, R.; Lee, C. Nanofluidic terahertz metasensor for sensing in aqueous environment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 071105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, K.V.; Sreejith, S.; Alapan, Y.; Sitti, M.; Lim, C.T.; Singh, R. Microfluidics Integrated Lithography-Free Nanophotonic Biosensor for the Detection of Small Molecules. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I.; Singh, R.; Rockstuhl, C.; Lederer, F.; Delprat, S.; Rocheleau, D.; Chaker, M.; Ozaki, T.; Morandotti, R. Excitation of a high-Q subradiant resonance mode in mirrored single-gap asymmetric split ring resonator terahertz metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 071108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I.; Hebestreit, E.; Rockstuhl, C.; Lederer, F.; Christodoulides, D.; Ozaki, T.; Morandotti, R. Conductive coupling of split ring resonators: A path to THz metamaterials with ultrasharp resonances. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 183903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Naib, I.; Yang, Y.; Dignam, M.M.; Zhang, W.; Singh, R. Ultra-high Q even eigenmode resonance in terahertz metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I. Novel terahertz metasurfaces based on complementary coupled split ring resonators. Opt. Mater. 2020, 99, 109596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I.A.I.; Jansen, C.; Koch, M. Applying the Babinet principle to asymmetric resonators. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 1228–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, N.; Gente, R.; Al-Naib, I.; Koch, M. Laser beam machined free-standing terahertz metamaterials. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, F.; Al-Naib, I.; Koch, M. Free-Standing Complementary Asymmetric Metasurface for Terahertz Sensing Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CST Studio Suite 3D EM Simulation and Analysis Software. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/simulia/products/electromagnetic-simulation/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Vieweg, N.; Rettich, F.; Deninger, A.; Roehle, H.; Dietz, R.; Göbel, T.; Schell, M. Terahertz-time domain spectrometer with 90 dB peak dynamic range. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, R.; Strikwerda, A.C.; Jepsen, P.U. Terahertz plasmonic structure with enhanced sensing capabilities. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Naib, I. Biomedical Sensing with Free-Standing Complementary Supercell Terahertz Metasurfaces. Crystals 2020, 10, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050372
Al-Naib I. Biomedical Sensing with Free-Standing Complementary Supercell Terahertz Metasurfaces. Crystals. 2020; 10(5):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050372
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Naib, Ibraheem. 2020. "Biomedical Sensing with Free-Standing Complementary Supercell Terahertz Metasurfaces" Crystals 10, no. 5: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050372
APA StyleAl-Naib, I. (2020). Biomedical Sensing with Free-Standing Complementary Supercell Terahertz Metasurfaces. Crystals, 10(5), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050372




