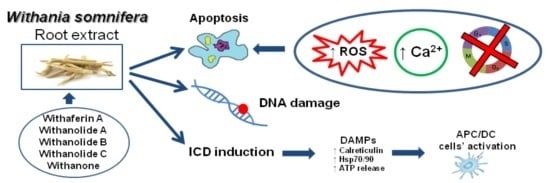
Withania somnifera Induces Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Effects on Human T Leukemia Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. WE Contains Withaferin A (WFA), Whitanolide A (WDA), Withanolide B in Trace Amount
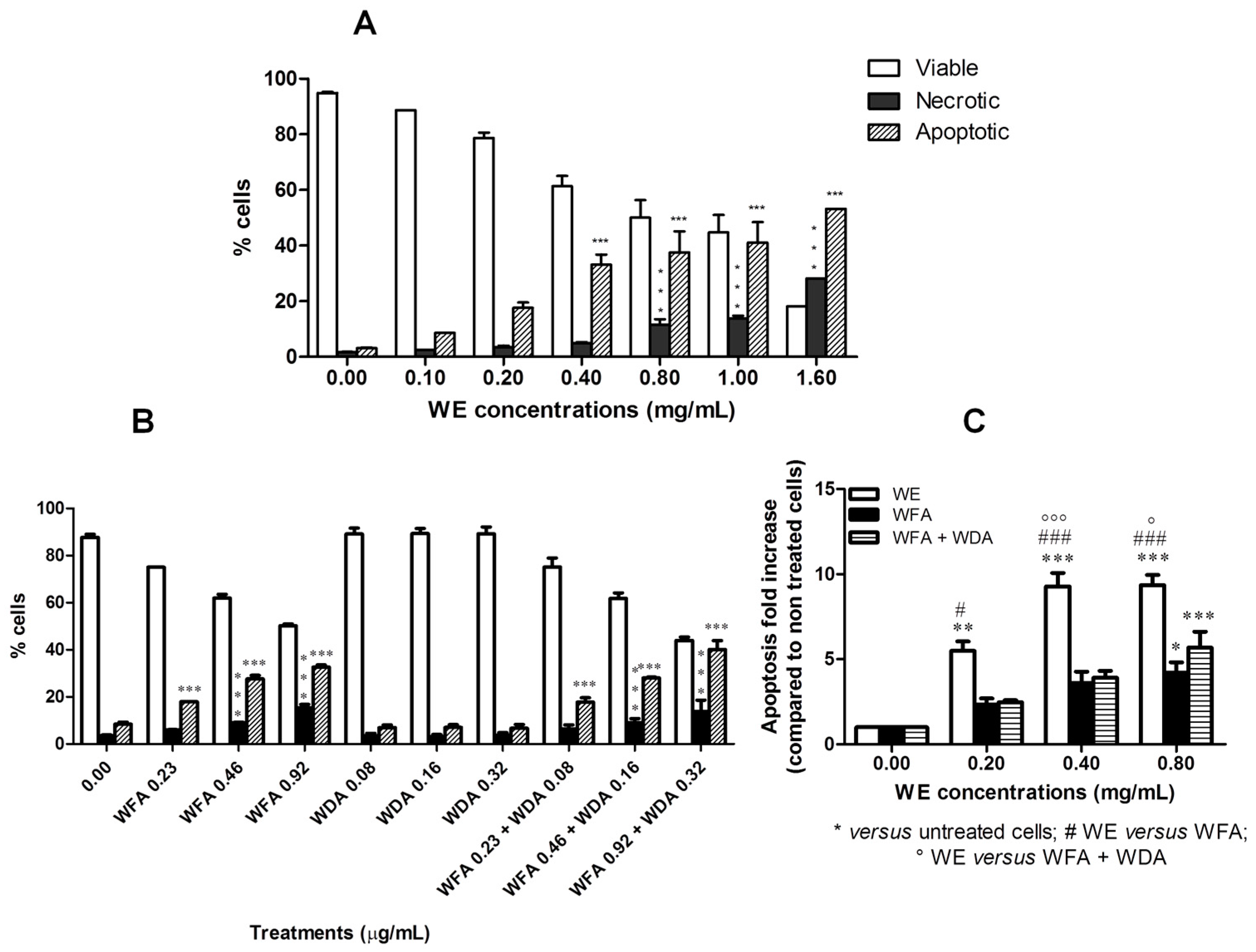
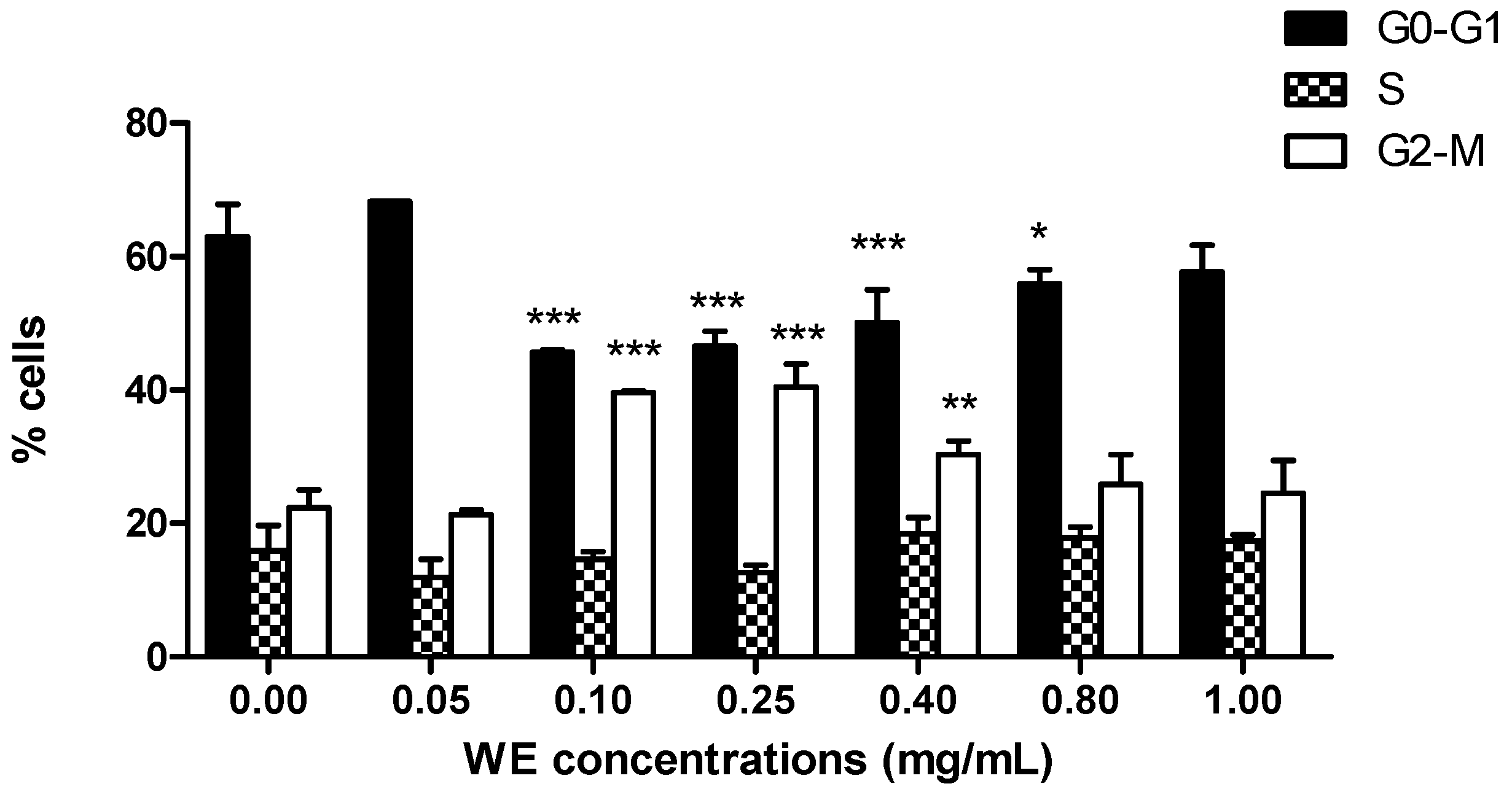
2.2. WE Induces Apoptosis and Alters Cell-Cycle Residence
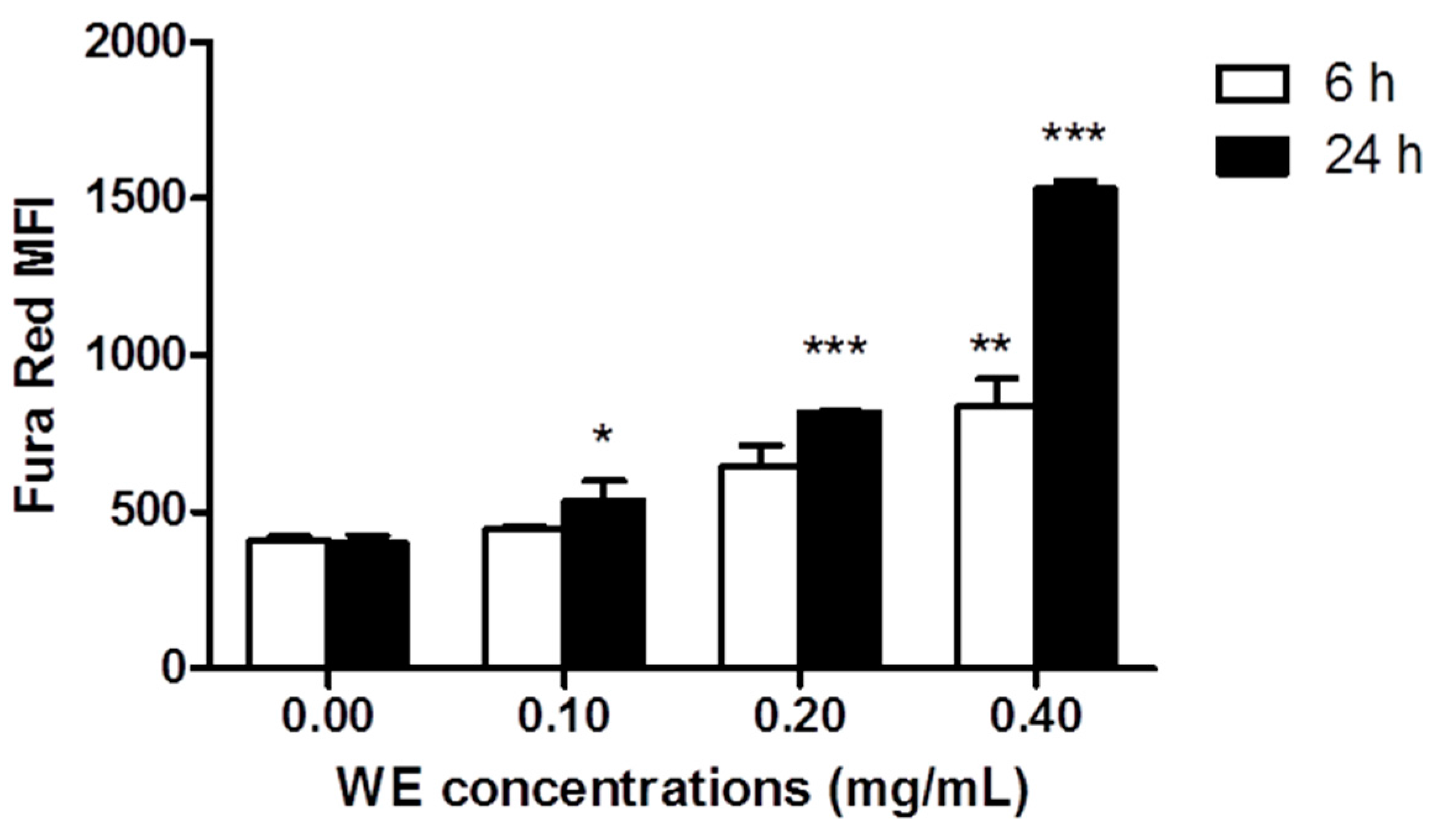
2.3. WE Increases Intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i)
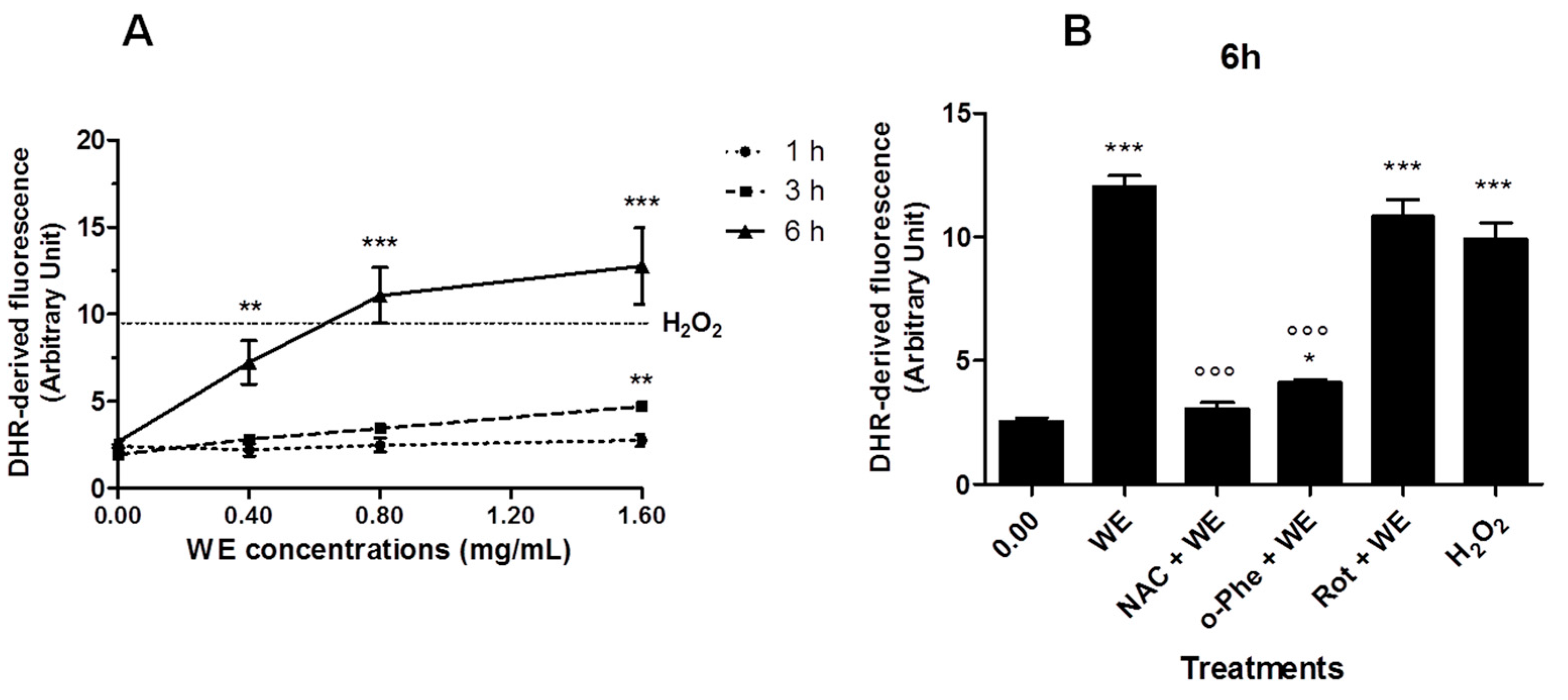
2.4. WE Induces Oxidative Stress
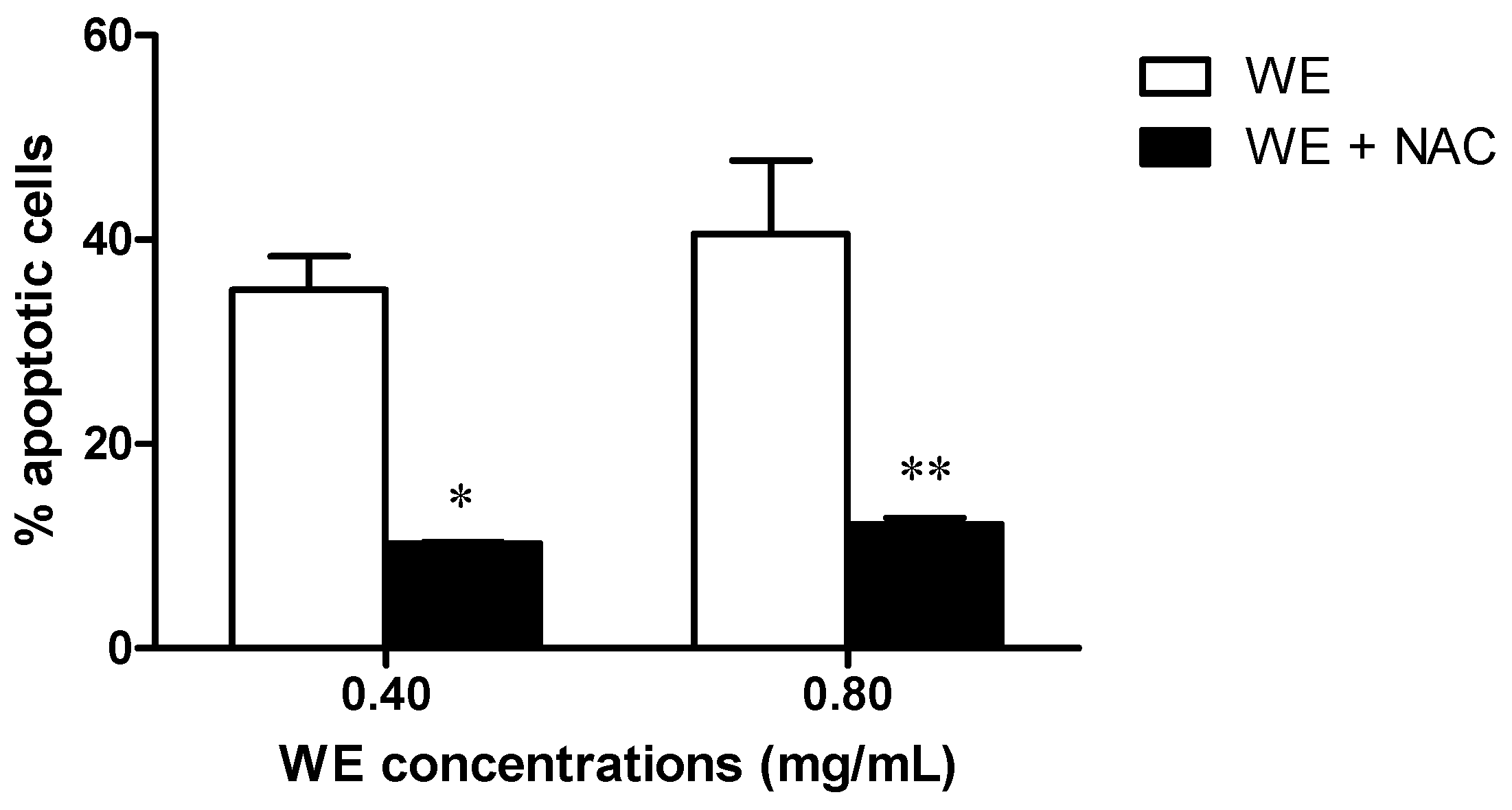
2.5. Co-Treatment of Cells with WE and NAC Significantly Decreases WE-Induced Apoptosis
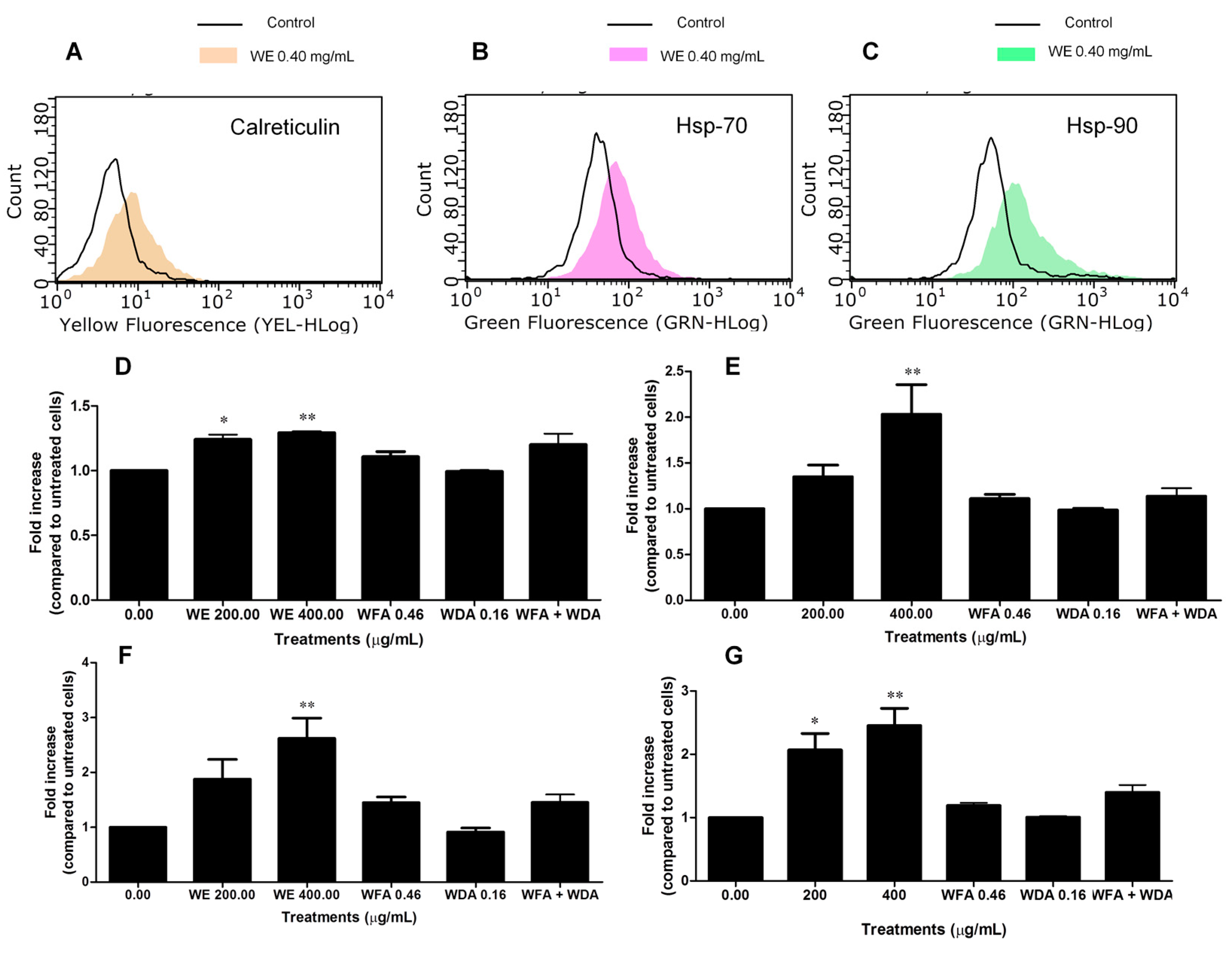
2.6. WE Induces ICD
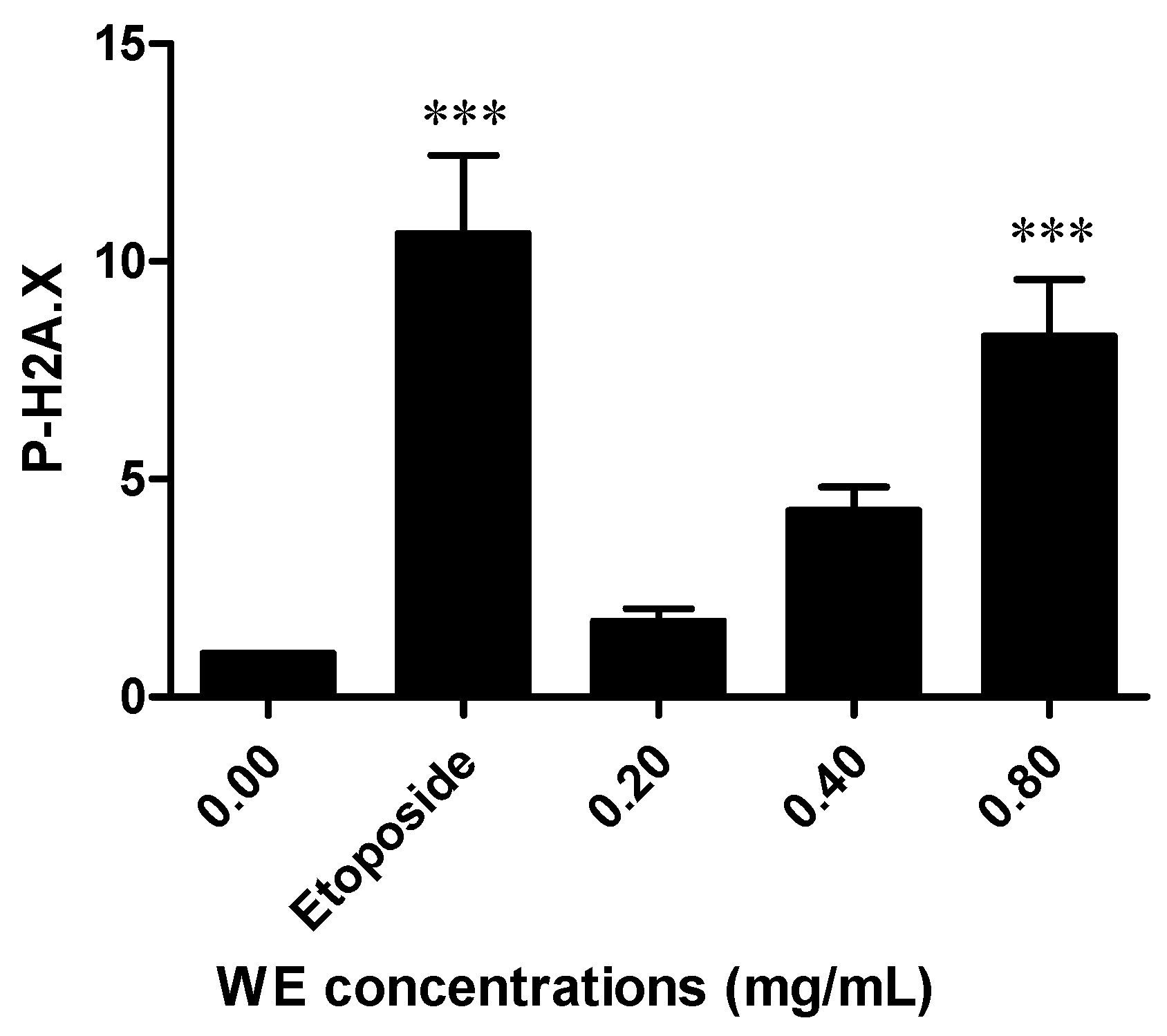
2.7. WE Induces DNA Damage
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. WE Preparation
4.2. HPLC Analysis
4.3. Validation
4.4. Cell Cultures
4.5. Cell Treatment
4.6. Analysis of Cell Viability and Induction of Apoptosis
4.7. Cell-Cycle Analysis
4.8. Measurement of [Ca2+]i
4.9. Detection of ROS Production
4.10. Analysis of Calreticulin Translocation, Hsp-70 and Hsp-90 Expression, and ATP Release
4.11. DNA Damage Analysis
4.12. Flow Cytometry
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014. Available online: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/ (accessed on 22 December 2015).
- Fimognari, C.; Ferruzzi, L.; Turrini, E.; Carulli, G.; Lenzi, M.; Hrelia, P.; Cantelli-Forti, G. Metabolic and toxicological considerations of botanicals in anticancer therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, E.; Gomez, H. Chemotherapy resistance in metastatic breast cancer: The evolving role of ixabepilone. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12 (Suppl. 2), 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Chen, R.; Zeh, H.J., III; Kang, R.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. Strange attractors: DAMPs and autophagy link tumor cell death and immunity. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Dou, J.; Temple, R.; Agarwal, R.; Wu, K.M.; Walker, S. New therapies from old medicines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nance, C.L. Clinical efficacy trials with natural products and herbal medicines. In Phytotherapies: Efficacy, Safety and Regulation; Ramzan, I., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Zent, C.S.; Leis, J.F.; LaPlant, B.; Bowen, D.A.; Roos, M.; Laumann, K.; Ghosh, A.K.; Lesnick, C.; et al. Phase 2 trial of daily, oral Polyphenon E in patients with asymptomatic, Rai stage 0 to II chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2013, 119, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.K.; Dhir, A. Withania somnifera: An Indian ginseng. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masevhe, N.A.; McGaw, L.J.; Eloff, J.N. The traditional use of plants to manage candidiasis and related infections in Venda, South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Pandey, M.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Natural products as a gold mine for arthritis treatment. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosalova, G.; Fleskova, D.; Jurecek, L.; Sadlonova, V.; Ray, B. Herbal polysaccharides and cough reflex. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 187, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Shukla, S.D.; Sharma, K.; Bhatnagar, M. Neuroprotective effects of Withania somnifera Dunn. in hippocampal sub-regions of female albino rat. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Jogee, P.S.; Agarkar, G.; Santos, C.A. Anticancer activities of Withania somnifera: Current research, formulations, and future perspectives. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasiya, N.D.; Uniyal, G.C.; Lal, P.; Misra, L.; Sangwan, N.S.; Tuli, R.; Sangwan, R.S. Analysis of withanolides in root and leaf of Withania somnifera by HPLC with photodiode array and evaporative light scattering detection. Phytochem. Anal. 2008, 19, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyas, A.R.; Singh, S.V. Molecular targets and mechanisms of cancer prevention and treatment by withaferin a, a naturally occurring steroidal lactone. AAPS. J. 2014, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudharymy, M.I.; Yousuf, S.; Atta-Ur-Rahman. Withanolides: Chemistry and antitumor activity. In Natural Products; Ramawat, K.G., Merillon, J.M., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 3465–3495. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, H.; Takada, Y.; Shishodia, S.; Jayaprakasam, B.; Nair, M.G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Withanolides potentiate apoptosis, inhibit invasion, and abolish osteoclastogenesis through suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation and NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, Z.A.; Westfall, M.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. Cell-cycle dysregulation and anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Harper, J.W. Anticancer drug targets: Cell cycle and checkpoint control. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Lee, T.J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, T.K. Induction of apoptosis by withaferin A in human leukemia U937 cells through down-regulation of Akt phosphorylation. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil, V.; Ramadevi, S.; Venkatakrishnan, V.; Giridharan, P.; Lakshmi, B.S.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Balakrishnan, A. Withanolide induces apoptosis in HL-60 leukemia cells via mitochondria mediated cytochrome c release and caspase activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 167, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruman, I.; Guo, Q.; Mattson, M.P. Calcium and reactive oxygen species mediate staurosporine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in PC12 cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 51, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, P.; Orrenius, S. The role of calcium in apoptosis. Cell Calcium 1998, 23, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioli, S.; Ardizzoni, A.; Franceschi, C.; Cossarizza, A. JC-1, but not DiOC6(3) or rhodamine 123, is a reliable fluorescent probe to assess ∆Ψ changes in intact cells: Implications for studies on mitochondrial functionality during apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 1997, 411, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, V.P.; Parmar, P.P.; Kumar, S.; Subramanian, R.B. Anticancer properties of highly purified l-asparaginase from Withania somnifera L. against acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, E.R.; Moura, M.B.; Kelley, E.E.; Van, H.B.; Shiva, S.; Singh, S.V. Withaferin A-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Tian, R.; Shi, C.; Xu, M.; Peng, F.; et al. Synergistic antitumor activity of withaferin A combined with oxaliplatin triggers reactive oxygen species-mediated inactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, F.; Kumar, A.; Bhushan, S.; Khan, S.; Bhatia, A.; Suri, K.A.; Qazi, G.N.; Singh, J. Reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial dysfunction in the apoptotic cell death of human myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells by a dietary compound withaferin A with concomitant protection by N-acetyl cysteine. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 2115–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayola, E.; Gallerne, C.; Esposti, D.D.; Martel, C.; Pervaiz, S.; Larue, L.; Debuire, B.; Lemoine, A.; Brenner, C.; Lemaire, C. Withaferin A induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species and down-regulation of Bcl-2. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Okuzaki, D.; Fukushima, K.; Mukai, S.; Ohno, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Yabuta, N.; Nojima, H. Withaferin A Induces Cell Death Selectively in Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer Cells but Not in Normal Fibroblast Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachootham, D.; Alexandre, J.; Huang, P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakar, S.S.; Jala, V.R.; Fong, M.Y. Synergistic cytotoxic action of cisplatin and withaferin A on ovarian cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.M.; Kim, S.J. Production of reactive oxygen species by withaferin A causes loss of type collagen expression and COX-2 expression through the PI3K/Akt, p38, and JNK pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2822–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.M.; Kim, S.J. Withaferin A-caused production of intracellular reactive oxygen species modulates apoptosis via PI3K/Akt and JNKinase in rabbit articular chondrocytes. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestili, P.; Diamantini, G.; Bedini, A.; Cerioni, L.; Tommasini, I.; Tarzia, G.; Cantoni, O. Plant-derived phenolic compounds prevent the DNA single-strand breakage and cytotoxicity induced by tert-butylhydroperoxide via an iron-chelating mechanism. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeter, M.E.; Baginsky, M.L.; Hatefi, Y. Ectopic inhibition of the complexes of the electron transport system by rotenone, piericidin A, demerol and antimycin A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1969, 172, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; Garg, A.D.; Kaczmarek, A.; Krysko, O.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.V.; Ellerby, H.M.; Bredesen, D.E. Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.D.; Nowis, D.; Golab, J.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V.; Agostinis, P. Immunogenic cell death, DAMPs and anticancer therapeutics: An emerging amalgamation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1805, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.K.; Gachuki, B.W.; Alhakeem, S.S.; Oben, K.N.; Rangnekar, V.M.; Gupta, R.C.; Bondada, S. Anti-cancer activity of withaferin A in B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hamza, A.; Zhang, T.; Gu, M.; Zou, P.; Newman, B.; Li, Y.; Gunatilaka, A.A.; Zhan, C.G.; Sun, D. Withaferin A targets heat shock protein 90 in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, A.; Shandilya, A.; Agrawal, V.; Pratik, P.; Bhasme, D.; Bisaria, V.S.; Sundar, D. Hsp90/Cdc37 chaperone/co-chaperone complex, a novel junction anticancer target elucidated by the mode of action of herbal drug Withaferin A. BMC Bioinf. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, F.; Singh, J.; Khajuria, A.; Suri, K.A.; Satti, N.K.; Singh, S.; Kaul, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Bhatia, A.; Qazi, G.N. A standardized root extract of Withania somnifera and its major constituent withanolide-A elicit humoral and cell-mediated immune responses by up regulation of Th1-dominant polarization in BALB/c mice. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjamurthy, K.; Manoharan, S.; Balakrishnan, S.; Suresh, K.; Nirmal, M.R.; Senthil, N.; Alias, L.M. Protective effect of Withaferin-A on micronucleus frequency and detoxication agents during experimental oral carcinogenesis. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjamurthy, K.; Manoharan, S.; Menon, V.P.; Nirmal, M.R.; Senthil, N. Protective role of withaferin-A on 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced genotoxicity in bone marrow of Syrian golden hamsters. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2008, 22, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, K.; Szczurko, O.; Perri, D.; Mills, E.J.; Bernhardt, B.; Zhou, Q.; Seely, D. Naturopathic care for anxiety: A randomized controlled trial ISRCTN78958974. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.K.; Mahdi, A.A.; Shukla, K.K.; Islam, N.; Rajender, S.; Madhukar, D.; Shankhwar, S.N.; Ahmad, S. Withania somnifera improves semen quality by regulating reproductive hormone levels and oxidative stress in seminal plasma of infertile males. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, A.; Lavin, P.; Patwardhan, B.; Chitre, D. A 32-week randomized, placebo-controlled clinical evaluation of RA-11, an Ayurvedic drug, on osteoarthritis of the knees. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2004, 10, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, E.R.; Ferry, H.; Greaves, D.R.; Keshav, S. Ratiometric analysis of fura red by flow cytometry: A technique for monitoring intracellular calcium flux in primary cell subsets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verriere, V.; Higgins, G.; Al-Alawi, M.; Costello, R.W.; McNally, P.; Chiron, R.; Harvey, B.J.; Urbach, V. Lipoxin A4 stimulates calcium-activated chloride currents and increases airway surface liquid height in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royall, J.A.; Ischiropoulos, H. Evaluation of 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin and dihydrorhodamine 123 as fluorescent probes for intracellular H2O2 in cultured endothelial cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 302, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Amount (μg/mL) | LOD | LOQ | Amount (mg/g of Dried Extract) | Recovery % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WFA | 113.65 ± 2.84 | 6.54 ± 0.11 | 19.81 ± 0.63 | 5.68 ± 0.14 | 96.85 ± 1.98 |
| WDA | 39.42 ± 1.44 | 1.64 ± 0.07 | 4.96 ± 0.26 | 1.97 ± 0.07 | 110.57 ± 2.11 |
| withanolide B | tr | 2.03 ± 0.34 | 6.36 ± 0.65 | - | - |
| withanone | - | 1.99 ± 0.29 | 15.95 ± 1.18 | - | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turrini, E.; Calcabrini, C.; Sestili, P.; Catanzaro, E.; De Gianni, E.; Diaz, A.R.; Hrelia, P.; Tacchini, M.; Guerrini, A.; Canonico, B.; et al. Withania somnifera Induces Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Effects on Human T Leukemia Cells. Toxins 2016, 8, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050147
Turrini E, Calcabrini C, Sestili P, Catanzaro E, De Gianni E, Diaz AR, Hrelia P, Tacchini M, Guerrini A, Canonico B, et al. Withania somnifera Induces Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Effects on Human T Leukemia Cells. Toxins. 2016; 8(5):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050147
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurrini, Eleonora, Cinzia Calcabrini, Piero Sestili, Elena Catanzaro, Elena De Gianni, Anna Rita Diaz, Patrizia Hrelia, Massimo Tacchini, Alessandra Guerrini, Barbara Canonico, and et al. 2016. "Withania somnifera Induces Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Effects on Human T Leukemia Cells" Toxins 8, no. 5: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050147
APA StyleTurrini, E., Calcabrini, C., Sestili, P., Catanzaro, E., De Gianni, E., Diaz, A. R., Hrelia, P., Tacchini, M., Guerrini, A., Canonico, B., Papa, S., Valdrè, G., & Fimognari, C. (2016). Withania somnifera Induces Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Effects on Human T Leukemia Cells. Toxins, 8(5), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050147