Botulinum Toxin for Neuropathic Pain: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
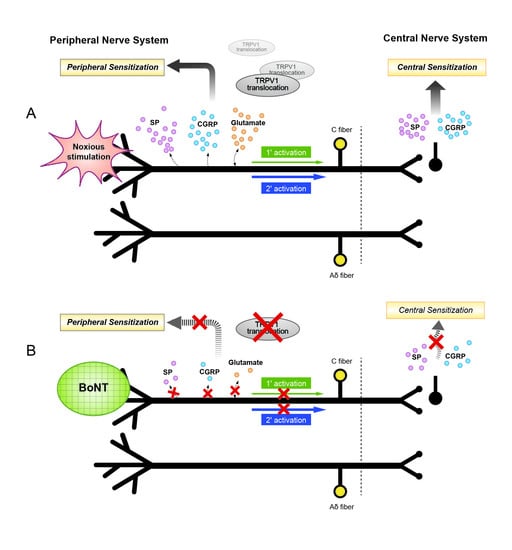
2. Mechanisms of the Antinociceptive Effects of Botulinum Toxin
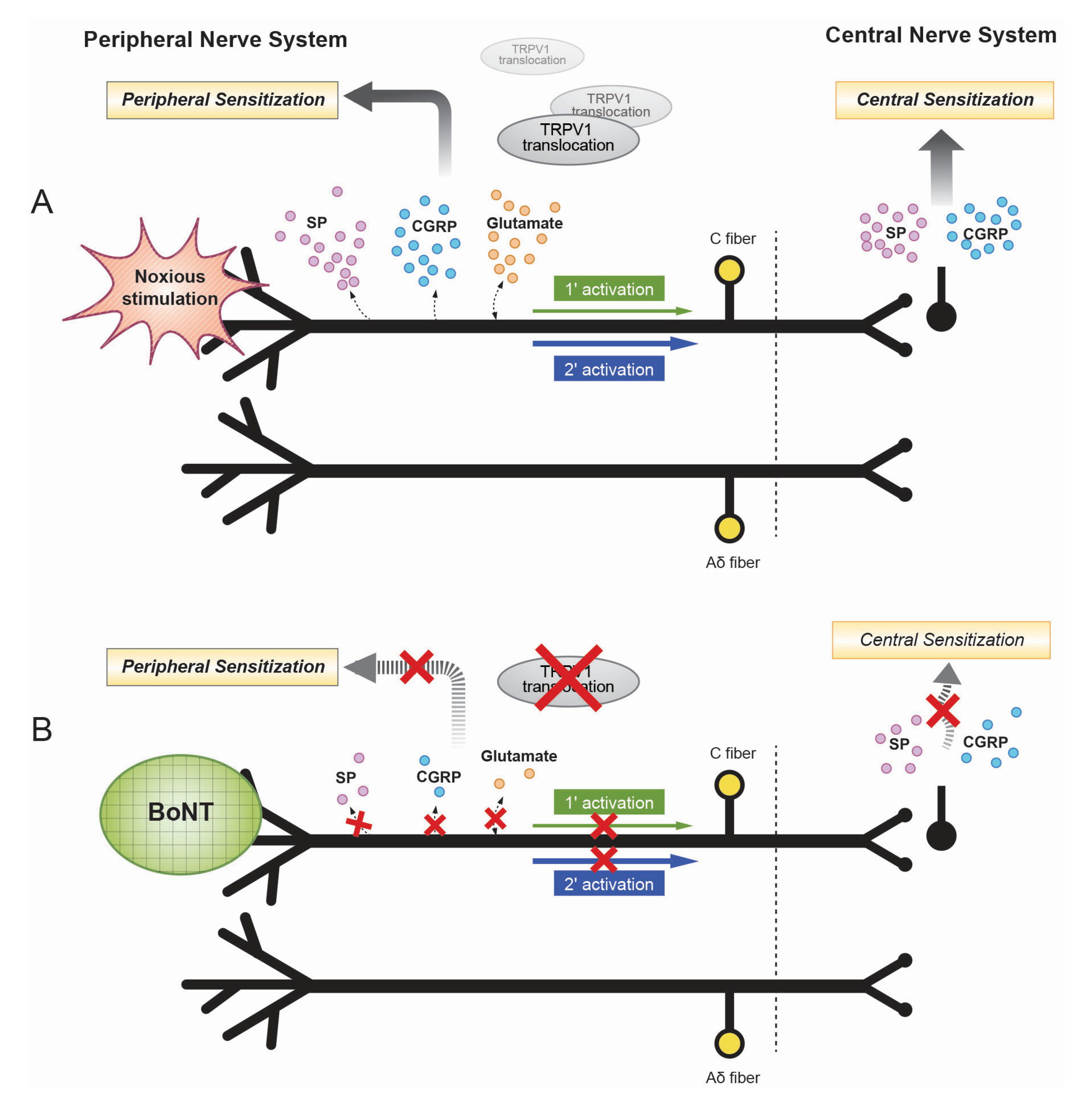
3. Axonal Transport of Botulinum Toxin
4. Botulinum Toxin and Inflammation
5. Clinical Evidence of Botulinum Toxin for Neuropathic Pain
| References | AAN Class | Study Type (Design) | Number of Patients | Diagnosis | Injection Route/Site/Serotype/Dose | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiao et al. [18] (2010) | I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 60 | Post-herpetic neuralgia | Subcutaneously/over the area of allodynia/BoNT/A/5 IU per site | VAS reduction and sleep quality improvement; superior to control group |
| Apalla et al. [67] (2013) | I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 30 | Post-herpetic neuralgia | Subcutaneously/over the affected area in a chessboard manner/BoNT/A/5 IU per point (Total 100 IU) | VAS at least 50% reduction in 13 patients in the intervention group and significant reduction in sleep scored |
| Ranoux et al. [16] (2008) | I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 29 (4 post-herpetic) | Post-herpetic neuralgia or post-traumatic/post-surgery neuropathy | Intradermally/into painful area/BoNT/A/20–190 IU | Decreased VAS, burning sensation, allodynic brush sensitivity, a reduced number of pain paroxysms, and improvements in quality of life |
| Liu et al. [68] (2006) | IV | Case report | 1 | Post-herpetic neuralgia | Subcutaneously/over the all painful area in a fan pattern/BoNT/A/100 IU | VAS reduction from 10 to 1 (lasting for 52 days) |
| Sotiriou et al. [69] (2009) | IV | Case series | 3 | Post-herpetic neuralgia | Subcutaneously/20 injection in a chessboard pattern/BoNT/A/100 IU | VAS decreased within three days (lasting for 64 days) |
| Wu et al. [70] (2012) | I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel design | 42 (22 BoNT, 20 placebo) | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Intradermally or submucosally/into trigger zones/BoNT/A/75 IU | Reduction in VAS (>50%) in 68% (BoNT group) vs. 15% (placebo group) |
| Bohluli et al. [71] (2011) | IV | Prospective, open, case series | 15 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Not specified injection mode/into trigger zones/BoNT/A/50–100 IU | 100% improvement in global assessment scale, frequency of pain attacks, and VAS scores |
| Zúñiga et al. [72] (2008) | IV | Prospective, open, case series | 12 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Subcutaneously/into trigger zones/BoNT/A/20–50 IU | Reduction in VAS (from 8.8 to 4) and number of paroxysmal attacks in 10 patients (lasting for two months) |
| Türk et al. [73] (2005) | IV | Prospective, open, case series | 8 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Two points (depth 1.5–2 cm) around zygomatic arch/BoNT/A/50 IU per point (total 100 units) | Reduction in VAS and the frequency of attacks (100%) |
| Piovesan et al. [74] (2005) | IV | Prospective, open pilot study | 13 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Subdermally/painful area in a grid pattern/BoNT/A/3 IU per point (total 6–9 IU) | Reduction in VAS for 60 days (100%: Pain-free (4), more than 50% reduction (9)) |
| Borodic et al. [75] (2002) | IV | Prospective, open pilot study | 11 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Subdermally or Intradermally/subcutaneous trigger zones (depth 1–3 mm, 10 mm apart)/BoNT/A/total 30–50 IU | Reduction in pain (>50%) in eight patients and frequency (lasting for 2–4 months) |
| Ngeow and Nair [76] (2001) | IV | Case report | 1 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Subcutaneously/two trigger zones over painful area/BoNT/A/100 IU total | Complete pain relief in nasal area and partial at mental region |
| Yoon et al. [77] (2010) | IV | Case report | 1 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Subcutaneously/one point in the middle chin/BoNT/A/10 IU | Decreased painful area and pain intensity |
| Allam et al. [78] (2005) | IV | Case report | 1 | Trigeminal Neuralgia | Subcutaneous/eight points along the area of V1 and V2/BoNT/A/2 IU per point (total 16 IU) | Reduction in pain (lasting for 90 days) |
| Layeeque et al. [79] (2004) | IV | Prospective, non-randomized, placebo-controlled | 48 (22 BoNT, 26 control) | Post-surgical neuralgia | Pectoralis major, serratus anterior, and rectus abdominis muscles/BoNT/A/100 IU | Significantly reduced post-surgical pain and facilitated reconstruction with tissue expander |
| Yuan et al. [17] (2009) | II | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial | 20 | Diabetic neuropathy | Intradermally/into the dorsum of the foot in a grid distribution patterns/BoNT/A/4 IU per site (50 units into each foot) | Significant VAS reduction at one, eight, and 12 weeks after injection (lasting for 12 weeks) and improvement in sleep quality in BoNT group |
| Ghasemi et al. [80] (2014) | I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 40 | Diabetic neuropathy | Intradermally/in a grid distribution pattern of 12 sites across the dorsum of the affected foot/BoNT/A/100 IU | Reduced NPS scores and DN4 scores and 30% patients pain-free in intervention groups |
| Kapural et al. [81] (2007) | IV | Retrospective, open, case series | 6 | Occipital Neuralgia | Perineural/occipital nerve block/BoNT/A/50 IU | Reduction of VAS and Pain Disability Index Scores in five of six patients at four weeks |
| Taylor et al. [82] (2008) | IV | Prospective, open, case series | 6 | Occipital Neuralgia | Perineural/around the occipital nerve/BoNT/A/100 IU | Significant improvement in sharp/shooting pain scores |
| Breuer et al. [83] (2006) | I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 20 | Carpal tunnel syndrome | Intramuscularly/into three hypothenar muscles/BoNT/B/2500 IU | No difference compared with the placebo group |
| Tsai et al. [84] (2006) | IV | Prospective, open, pilot study | 5 | Carpal tunnel syndrome | Intracarpally/on each side of the carpal tunnel/BoNT/A/60 IU | Insignificant trend toward pain improvement at three months without change in conduction time by NCS in three patients |
| Safarpour et al. [85] (2010) | III | 1. Randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled study; 2. uncontrolled, unblended, open-label study | 14 (8 BoNT/A, 6 control) | CRPS | Intradermally and subcutaneously/into the allodynic area/BoNT/A/5 IU per point (total 40–200 units) | No response to the BoNT in VAS; study terminated prematurely because of injection intolerance |
| Carroll et al. [86] (2009) | III | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial | 18 (9 crossover study) | CRPS | Lumbar sympathetic block/BoNT/A/Bupivacaine 0.5% + 75 IU of BoNT/A | Longer duration of pain reduction (median 71 days) in BoNT/A group than the control group (median 10 days) |
| Kharkar et al. [87] (2011) | IV | Retrospective, uncontrolled, nblended study | 37 | CRPS | Intramuscularly/neck or upper limb girdle muscles/BoNT/A/10–20 IU per muscle (total 100 IU) | The 97% patients reported reduction of pain by 43% |
| Argoff et al. [54] (1999) | IV | Prospective, open, case series | 11 | CRPS | Subcutaneously/into shoulder girdle muscles/BoNT/A/25–50 IU (total 300 IU) | Reduction in VAS, allodynia, and hyperalgesia and improved skin color |
| Safarpour and Jabbari [88] (2010) | IV | Case series | 2 | CRPS | Intramuscularly/trigger points in the proximal muscles/BoNT/A/20 IU per site | Reduction in proximal and distal pain of myofascial pain syndrome and CPRS |
| Wu et al. [89] (2012) | III | Prospective, randomized, double-blind pilot study | 14 | Residual limb pain or phantom limb pain | Intramuscular and cutaneous/subcutaneously/into focal tender points BoNT/A, 50 IU per site (total 250–300 IU) | Reduced residual limb pain, compared with the lidocaine/depomedrol group; not effective for phantom limb pain |
| Jin et al. [90] (2009) | IV | Case series | 3 | Residual limb pain or phantom limb pain | Electromyography (EMG)-guided injection/into the painful stumps points with strong fasciculation/BoNT/A/500 IU | Significant pain reduction, improved prosthesis tolerance, and reduced pain medication (100%) |
| Kern et al. [91] (2004) | IV | Case report | 1 | Residual limb pain or phantom limb pain | Into trigger points of the stump/BoNT/A/4 × 25 IU | Almost completely pain-free and reduced pain medication |
| Uyesugi et al. [92] (2010) | IV | Case report | 1 | Painful keloid | Subcutaneously/throughout the scar in a fan-like distribution BoNT/A, total 100 IU | Reduction in VAS (from 8 to 6) at five weeks and time periods of pain-free increased |
| Jabbari et al. [93] (2003) | IV | Case Report | 2 | Spinal cord injury | Subcutaneously/into the area of burning pain and allodynia (16 to 20 sites)/BoNT/A, 5 IU per site | Significant improvement in VAS (burning pain and allodynia lasting at least three months) |
| Han et al. [94] (2014) | IV | Case Report | 1 | Spinal cord injury | Subcutaneously/into 10 most painful sites of each sole/BoNT/A/20 IU per site | Reduction in VAS from 96 mm to 68 mm and decreased intensity of the paroxysmal bursts VAS 23 mm after eight weeks |
5.1. Post-Herpetic Neuralgia
5.2. Trigeminal Neuralgia
5.3. Post-Traumatic Neuralgia or Post-Surgical Neuralgia
5.4. Diabetic Neuropathy
5.5. Occipital Neuralgia
5.6. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
5.7. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
5.8. Residual Limb Pain or Phantom Limb Pain
5.9. Miscellaneous
6. Administration Routes and Dosage
7. Potential Adverse Effects
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kao, I.; Drachman, D.B.; Price, D.L. Botulinum toxin: Mechanism of presynaptic blockade. Science 1976, 193, 1256–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blersch, W.; Schulte-Mattler, W.J.; Przywara, S.; May, A.; Bigalke, H.; Wohlfarth, K. Botulinum toxin A and the cutaneous nociception in humans: A prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 205, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenganatt, M.A.; Fahn, S. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of movement disorders. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2012, 12, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellizzari, R.; Rossetto, O.; Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins: Mechanism of action and therapeutic uses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, L.L. The origin, structure, and pharmacological activity of botulinum toxin. Pharmacol. Rev. 1981, 33, 155–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mense, S. Neurobiological basis for the use of botulinum toxin in pain therapy. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, I1–I7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verderio, C.; Grumelli, C.; Raiteri, L.; Coco, S.; Paluzzi, S.; Caccin, P.; Rossetto, O.; Bonanno, G.; Montecucco, C.; Matteoli, M. Traffic of botulinum toxins A and E in excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Traffic 2007, 8, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R. Review of a Proposed Mechanism for the Antinociceptive Action of Botulinum Toxin Type A. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeynes, L.C.; Gauci, C.A. Evidence for the use of botulinum toxin in the chronic pain setting: A review of the literature. Pain Pract. 2008, 8, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R. Future aspects of botulinum neurotoxins. J. Neural. Trans. 2008, 115, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Khanijou, S.; Rubino, J.; Aoki, K.R. Subcutaneous administration of botulinum toxin A reduces formalin-induced pain. Pain 2004, 107, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodick, D.W.; Turkel, C.C.; de Gryse, R.E.; Aurora, S.K.; Silberstein, S.D.; Lipton, R.B.; Diener, H.C.; Brin, M.F. OnobotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phases of the PREEMPT clinical program. Headache 2010, 50, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, M.G.; Stanek, J.J. Botulinum neurotoxin A: A review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2012, 65, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, R.; Zhang, X.; Levy, D.; Aoki, K.R.; Brin, M.F. Selective inhibition of meningeal nociceptors by botulinum neurotoxin type A: Therapeutic implications for migraine and other pains. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, T.S.; Baron, R.; Haanpaa, M.; Kalso, E.; Loeser, J.D.; Rice, A.S.; Treede, R.D. A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 2011, 152, 2204–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranoux, D.; Attal, N.; Morain, F.; Bouhassira, D. Botulinum toxin type A induces direct analgesic effects in chronic neuropathic pain. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.Y.; Sheu, J.J.; Yu, J.M.; Chen, W.T.; Tseng, I.J.; Change, H.H.; Hu, C.J. Botulinum toxin for diabetic neuropathic pain: A randomized double-blind crossover trial. Neurology 2009, 72, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Mackey, S.; Hui, H.; Xong, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D. Subcutaneous injection of botulinum toxin A is beneficial in postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.H.; Shin, T.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.K.; Suh, H.W.; Lee, S.C.; Seo, K. Intrathecal administration of botulinum neurotoxin type A attenuates formalin-induced antinociceptive responses in mice. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 112, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.J.; Purkiss, J.R.; Foster, K.A. Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2000, 38, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, P.L.; Cady, R. Regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide secretion from trigeminal nerve cells by botulinum toxin type A: Implications for migraine therapy. Headache 2004, 44, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argoff, C.E. The use of botulinum toxins for chronic pain and headaches. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2003, 5, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morenilla-Palao, C.; Planells-Cases, R.; Garcia-Sanz, N.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. Regulated exocytosis contributes to protein kinase C potentiation of vanilloid receptor activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25665–25672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Duffney, L.J.; Yan, Z. SNARE proteins are essential in the potentiation of NMDA receptors by group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 3935–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, H.T.; Foran, P.; Dolly, J.O.; Verhage, M.; Wiegant, V.M.; Nicholls, D.G. Tetanus toxin and botulinum toxins type A and B inhibit glutamate, F-aminobutyric acid, aspartate, and met-enkephalin release from synaptosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 21338–21343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S.; Lucchetti, F.; Marchi, F.; Cobianchi, S.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C.; Pavone, F. Botulinum neurotoxins and formalin-induced pain: Central vs. peripheral effects in mice. Brain Res. 2006, 1082, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, K.; Lolignier, S.; Wood, J.N.; McMahon, S.B.; Bennett, D.L. Botulinum toxin-A treatment reduces human mechanical pain sensitivity and mechanotransduction. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, L.J.; Rugiero, F.; Cesare, P.; Gale, J.E.; Abrahamsen, B.; Bowden, S.; Heinzmann, S.; Robinson, M.; Brust, A.; Colless, B.; et al. High-threshold mechanosensitive ion channels blocked by a novel conopeptide mediate pressure-evoked pain. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Castro, A.; Drew, L.J.; Wood, J.N.; Cesare, P. Modulation of sensory neuron mechanotransduction by PKC- and nerve growth factor-dependent pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, J.K.; Eisen, A.; Stoessl, A.J.; Calne, S.; Calne, D.B. Double-blind study of botulinum toxin in spasmodic torticollis. Lancet 1986, 2, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stell, R.; Thompson, P.D.; Marsden, C.D. Botulinum toxin in spasmodic torticollis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R. Evidence for antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin type A in pain management. Headache 2003, 43, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, B.; Schwartz, M. Temporal relationship of muscle weakness and pain reduction in subjects treated with botulinum toxin A. J. Pain 2003, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relja, M.; Klepac, N. Different doses of botulinum toxin A and pain responsiveness in cervical dystonia. Neurology 2002, 58, A474. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Cheng, J.; Dai, J.; Zhang, D. Botulinum Toxin Decreases Hyperalgesia and Inhibits P2X3 Receptor Over-Expression in Sensory Neurons Induced by Ventral Root Transection in Rats. Pain Med. 2011, 12, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, Z.; Chang-Chien, G.; Marshall, B.; Huang, M.; Harden, R.N. Phantom limb pain: A systematic neuroanatomical-based review of pharmacologic treatment. Pain Med. 2014, 15, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qerama, E.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Jensen, T.S. The role of botulinum toxin in management of pain: An evidence-based review. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 23, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matak, I.; Lackovic, Z. Botulinum toxin A, brain and pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 119–120, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Meng, J.; Lawrence, G.W.; Zurawski, T.H.; Sasse, A.; Bodeker, M.O.; Gilmore, M.A.; Fernández-Salas, E.; Francis, J.; Steward, L.E.; et al. Novel chimeras of botulinum neurotoxins A and E unveil contributions from the binding, translocation, and protease domains to their functional characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16993–17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zurawski, T.H.; Meng, J.; Lawrence, G.W.; Aoki, K.R.; Wheeler, L.; Dolly, J.O. Novel chimeras of botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins yield insights into their distinct sites of neuroparalysis. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 5035–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zurawski, T.H.; Bodeker, M.O.; Meng, J.; Boddul, S.; Aoki, K.R.; Dolly, J.O. Longer-acting and highly potent chimaeric inhibitors of excessive exocytosis created with domains from botulinum neurotoxin A and B. Biochem. J. 2012, 444, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restani, L.; Antonucci, F.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossi, C.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Evidence for anterograde transport and transcytosis of botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A). J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15650–15659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfrancesci, L.; Rosetto, O.; Calleo, M. Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Rojecky, L.; Lackovic, Z. Central origin of the antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A. Parmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Rojecky, L.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M.; Lackovic, Z. Botulinum toxin type A reduces pain supersensitivity in experimental diabetic neuropathy: Bilateral effects after unilateral injection. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 633, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre-Guilmard, C.; Auguet, M.; Chabrier, P.E. Different antinociceptive effects of botulinum toxin type A in inflammatory and peripheral polyneuropathic rat models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 617, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, H.; Erdmann, G.; Wellhoner, H.H. 125I-labelled botulinum A neuro-toxin: Pharmacokinetics in cats after intramuscular injection. Naunyn Schmie Arch. Pharmacol. 1976, 292, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang-Liu, D.D.; Aoki, K.R.; Dolly, J.O.; de Paiva, A.; Houchen, T.L.; Chasseaud, L.F.; Webber, C. Intramuscular injection of 125I-botulinum neurotoxin-com-plex vs. 125I-botulinum-free neurotoxin: Time course of tissue distribution. Toxicon 2003, 42, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, B.; Matak, I.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Lackovic, Z. Central action of peripherally applied botulinum toxin type A on pain and dural protein extravasation in rat model of trigeminal neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matak, I.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Filipovic, B.; Lackovic, Z. Behavioral and immunohistochemical evidence for central antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin A. Neuroscience 2011, 186, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Vacca, V.; Ricordy, R.; Uggenti, C.; Tata, A.M.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F. The analgesic effect on neuropathic pain of retrogradely transported botulinumneurotoxin A involves Schwann cells and astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.J.; Terashima, T.; Steinauer, J.J.; Eddinger, K.A.; Yaksh, T.L.; Xu, Q. Botulinum toxin B in the sensory afferent: Transmitter release, spinal activation, and pain behavior. Pain 2014, 155, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Shan, X.F.; Cong, X.; Yang, N.Y.; Wu, L.L.; Yu, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.G. Pre- and Post-synaptic Effects of Botulinum Toxin A on Submandibular Glands. J. Dent. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argoff, C.E. Botulinum toxin type A treatment of myofascial pain in patients with CRPS Type 1 (reflex sympathetic dystrophy): A pilot study. In Proceedings of the World Pain Congress (IASP) Meeting, Vienna, Austria, 22–27 August 1999.
- Chuang, Y.C.; Yoshimura, N.; Huang, C.C.; Wu, M.; Chiang, P.H.; Chancellor, M.B. Intraprostatic botulinum toxin a injection inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 expression and suppresses prostatic pain on capsaicin induced prostatitis model in rat. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namazi, H. Intravesical botulinum toxin A injections plus hydrodistension can reduce nerve growth factor production and control bladder pain in interstitial cystitis: A molecular mechanism. Urology 2008, 72, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Rojecky, L.; Dominis, M.; Lackovic, Z. Lack of anti-inflammatory effects of botulinum toxin A in experimental models of inflammation. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 22, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugnoli, V.; Capone, J.G.; Eleopra, R.; Quatrale, R.; Sensi, M.; Gastaldo, E.; Tola, M.R.; Geppetti, P. Botulinum toxin type A reduces capsaicin-evoked pain and neurogenic vasodilatation in human skin. Pain 2007, 130, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, G.E.; Tan, H.; Green, M. Do botulinum toxins have a role in the management of neuropathic pain? A focused review. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieglgänsberger, W.; Berthele, A.; Tölle, T.R. Understanding neuropathic pain. CNS Spectr. 2005, 10, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bach-Rojecky, L.; Relja, M.; Lackovic, Z. Botulinum toxin type A in experimental neuropathic pain. J. Neural. Trans. 2005, 112, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drinovac, V.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Matak, I.; Lackovic, Z. Involvement of μ-opioid receptors in antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A. Neuropharmacology 2013, 70, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, C.; Moon, D.E. The effects of botulinum toxin A on mechanical and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Can. J. Anaesth. 2006, 53, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S.; Cobianchi, S.; Pavone, F. Anti-allodynic efficacy of botulinum neurotoxin A in a model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Luvisetto, S.; Cobianchi, S.; Makuch, W.; Obara, I.; Mezzaroma, E.; Caruso, M.; Straface, E.; Przewlocka, B.; Pavone, F. Botulinum neurotoxin type A counteracts neuropathic pain and facilitates functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury in animal models. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, J.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Korostynski, M.; Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S.; Pavone, F.; Przewlocka, B. The effect of botulinum neurotoxin A on sciatic nerve injury-induced neuroimmunological changes in rat dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord. Neuroscience 2011, 175, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalla, Z.; Sotiriou, E.; Lallas, A.; Lazaridou, E.; Ioannides, D. Botulinum toxin A in postherpetic neuralgia: A parallel, randomized, double-blind, single-dose, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. J. Pain 2013, 29, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Tsai, S.K.; Kao, M.C.; Hu, J.S. Botulinum toxin A relieved neuropathic pain in a case of post-herpetic neuralgia. Pain Med. 2006, 7, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriu, E.; Apalla, Z.; Panagiotidou, D.; Ioannidis, D. Severe post-herpetic neuralgia successfully treated with botulinum toxin A: Three case reports. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2009, 89, 214–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.J.; Lian, Y.J.; Zheng, Y.K.; Zhang, H.F.; Chen, Y.; Xie, N.C.; Wang, L.J. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgias: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cephalgia 2012, 32, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohluli, B.; Motamedi, M.H.; Bagheri, S.C.; Bayat, M.; Lassemi, E.; Navi, F.; Moharamnejad, N. Use of botulinum toxin A for drug-refractory trigeminal neuralgia: Preliminary report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 111, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuniga, C.; Diaz, S.; Piedimonte, F.; Micheli, F. Beneficial effects of botulinum toxin type A in trigeminal neuralgia. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2008, 66, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, U.; Ilhan, S.; Alp, R.; Sur, H. Botulinum toxin and intractable trigeminal neuralgia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2005, 28, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piovesan, E.J.; Teive, H.G.; Kowacs, P.A.; Della Coletta, M.V.; Werneck, L.C.; Silberstein, S.D. An open study of botulinum-A toxin treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurology 2005, 65, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodic, G.E.; Acquadro, M.A. The use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of chronic facial pain. J. Pain 2002, 1, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngeow, W.C.; Nair, R. Injection of botulinum toxin type A (BOTOX) into trigger zone of trigeminal neuralgia as a means to control pain. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 109, e47–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Merril, R.L.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.T. Use of botulinum toxin type A injection for neuropathic pain after trigeminal nerve injury. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, N.; Brasil-Neto, J.P.; Brown, G.; Tomaz, C. Injections of botulinum toxin type A produce alleviation of intractable trigeminal neuralgia. Clin. J. Pain. 2005, 21, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layeeque, R.; Hochberg, J.; Siegel, E.; Kunkel, K.; Kepple, J.; Henry-Tillman, R.S.; Dunlap, M.; Seibert, J.; Klimberg, V.S. Botulinum toxin infiltration for pain control after mastectomy and expander reconstruction. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Ansari, M.; Basiri, K.; Shaigannejad, V. The effects of intradermal botulinum toxin type A injections on pain symptoms of patients with diabetic neuropathy. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kapural, L.; Stillman, M.; Kapural, M.; Mclntyre, P.; Guirgius, M.; Mekhail, N. Botulinum toxin occipital nerve block for the treatment of severe occipital neuralgia: A case series. Pain Pract. 2007, 7, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; Silva, S.; Cottrell, C. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of occipital neuralgia: A pilot study. Headache 2008, 48, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, B.; Sperber, K.; Wallenstein, S.; Kiprovski, K.; Calapa, A.; Snow, B.; Pappagallo, M. Clinically significant placebo analgesic response in a pilot trial of botulinum B in patients with hand pain and carpel tunnel syndrome. Pain Med. 2006, 7, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.P.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, K.P.; Wnag, K.C. Efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in the relief of carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin. Drug Investig. 2006, 26, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarpour, D.; Salardini, A.; Richardson, D.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum toxin A for treatment of allodynia of complex regional pain syndrome: A pilot study. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, I.; Clark, J.D.; Mackey, S. Sympathetic block with botulinum toxin to treat complex regional pain syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharkar, S.; Ambady, P.; Venkatesh, Y.; Schwartzman, R.J. Intramuscular botulinum toxin in complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review. Pain Phys. 2011, 14, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Safarpour, D.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum toxin a (Botox) for treatment of proximal myofascial pain in complex regional pain syndrome: Two cases. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Sultana, R.; Taylor, K.B.; Szabo, A. A prospective randomized double-blinded pilot study to examine the effect of botulinum toxin type A injection vs. Lidocaine/Depomedrol injection on residual and phantom limb pain. Clin. J. Pain 2012, 28, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Kollewe, K.; Krampfl, K.; Dengler, R.; Mohammadi, B. Treatment of phantom limb pain with botulinum toxin type A. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kern, U.; Martin, C.; Scheicher, S.; Muler, H. Long-term treatment of phantom and stump pain with Botulinum toxin type A over 12 months. A first clinical observation. Nervenarzt 2004, 75, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyesugi, B.; Lippincott, B.; Dave, S. Treatment of a painful keloid with botulinum toxin type A. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 89, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, B.; Maher, N.; Difazio, M.P. Botulinum toxin A improved burning pain and allodynia in two patients with spinal cord pathology. Pain Med. 2003, 4, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.A.; Song, D.H.; Chung, M.E. Effect of subcutaneous injection of botulinum toxin A on spinal cord injury-associated neuropathic pain. Spinal Cord 2014, 52, S5–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.T.; Yuan, R.Y.; Chiang, S.C.; Sheu, J.J.; Yu, J.M.; Tseng, I.J.; Yang, S.K.; Chang, H.H.; Hu, C.J. OnabotulinumtoxinA improves tactile and mechanical pain perception in painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Clin. J. Pain 2013, 29, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, G.; Asensio-Samper, J.M.; Palmisani, S.; Villanueva-Perez, V.L.; Andres, J.D. Subcuaneous botulinum toxin for chronic post-thoracotomy pain. Pain Pract. 2012, 13, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Yeh, F.; Tepp, W.H.; Dean, C.; Johnson, E.A.; Janz, R.; Chapman, E.R. SV2 is the protein receptor for botulinum neurotoxin A. Science 2006, 312, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, A.; Kiene, K.; Carruthers, J. Botulinum A exotoxin use in clinical dermatology. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996, 34, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarasso, S.L. Complications of botulinum A exotoxin for hyperfunctional lines. Dermatol. Surg. 1998, 24, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarasso, A.; Deva, A.K. Botulinum toxin. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 109, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, D.J.; Rubin, M.; Greene, P.E.; Kang, U.J.; Moskowitz, C.B.; Brin, M.F.; Lovelace, R.E.; Fahn, S. Distant effects of locally injected botulinum toxin: A double-blind study of single fiber EMG changes. Muscle Nerve 1991, 14, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Velasco, D.N.; Tepper, D. Botulinum Toxin-A for Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: A Meta-Analysis. Pain Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurora, S.K.; Dodick, D.W.; Diener, H.C.; de Gryse, R.E.; Turkel, C.C.; Lipton, R.B.; Silberstein, S.D. OnabotulinumtoxinA for chronic migraine: Efficacy, safety, and tolerability in patients who received all five treatment cycles in the PREEMPT clinical program. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.C.; Dodick, D.W.; Aurora, S.K.; Turkel, C.C.; de Gryse, R.E.; Lipton, R.B.; Silberstein, S.D.; Brin, M.F.; PREEMPT 2 Chronic Migraine Study Group. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 2 trial. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, H.-M.; Chung, M.E. Botulinum Toxin for Neuropathic Pain: A Review of the Literature. Toxins 2015, 7, 3127-3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7083127
Oh H-M, Chung ME. Botulinum Toxin for Neuropathic Pain: A Review of the Literature. Toxins. 2015; 7(8):3127-3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7083127
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Hyun-Mi, and Myung Eun Chung. 2015. "Botulinum Toxin for Neuropathic Pain: A Review of the Literature" Toxins 7, no. 8: 3127-3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7083127
APA StyleOh, H.-M., & Chung, M. E. (2015). Botulinum Toxin for Neuropathic Pain: A Review of the Literature. Toxins, 7(8), 3127-3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7083127