ESI-MS/MS Identification of a Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide from Amazon Bothrops atrox Snake Venom Using a Hybrid Qq-oaTOF Mass Spectrometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Venom
2.2. Peptide Isolation
2.3. MS Parameters and Data Acquisition
2.4. MS/MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
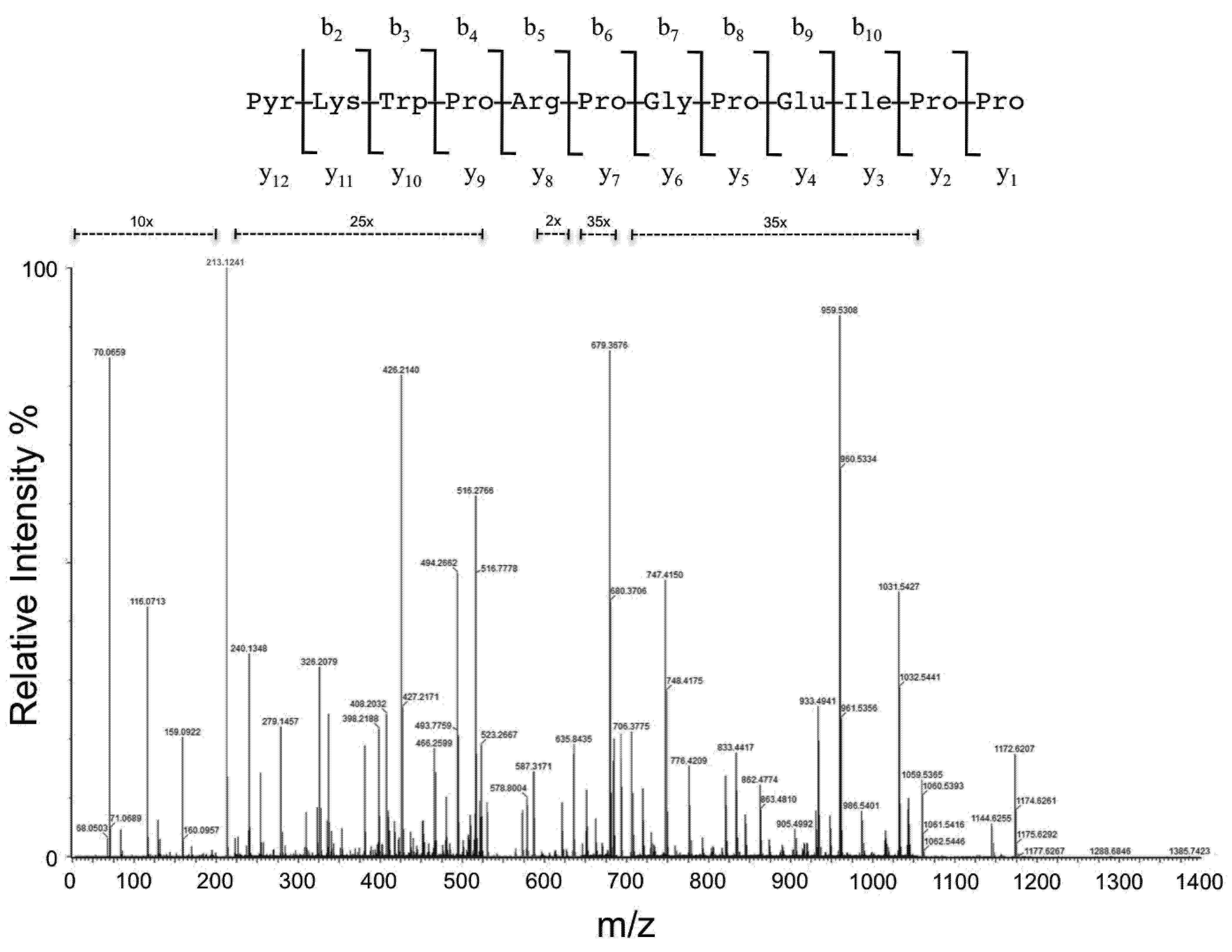
| Aminoacid Residue | Fragment | Theoretical (m/z) | Measured (m/z) | Intensity (counts) | Accuracy (ppm) | Fragment | Theoretical (m/z) | Measured (m/z) | Intensity (counts) | Accuracy (ppm) | Fragment | Theoretical (m/z) | Measured (m/z) | Intensity (counts) | Accuracy (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | b1 | 112.0399 | - | - | - | a1 | 84.0688 | - | - | - | y12 | 1384.7377 | 1384.7548 | 1.6 × 102 | 11.7 |
| K | b2 * | 223.1083 | 223.1082 | 2.7 × 103 | 0.2 | a2 * | 195.1134 | 195.1134 | 4.0 × 103 | −0.2 | y11 | 1273.7057 | 1273.6853 | 1.6 × 102 | 16.0 |
| b2 | 240.1348 | 240.1348 | 5.2 × 104 | 0.1 | a2 | 212.1399 | 212.1405 | 6.1 × 103 | −2.9 | y11 * | 1256.6792 | - | - | - | |
| W | b3 | 426.2141 | 426.2140 | 1.2 × 105 | 0.3 | a3 | 398.2192 | 398.2188 | 3.3 × 104 | 1.0 | y10 | 1145.6107 | 1145.6276 | 2.0 × 105 | 14.8 |
| P | b4 | 523.2669 | 523.2667 | 2.9 × 104 | 0.4 | a4 | 495.2720 | 495.2684 | 3.1 × 104 | 7.2 | y9 | 959.5314 | 959.5308 | 9.9 × 104 | 0.6 |
| R | b5 * | 662.3415 | 622.3417 | 7.0 × 103 | −0.4 | a5 * | 634.3466 | 634.3317 | 3.7 × 104 | 23.4 | y8 | 862.4786 | 862.4774 | 1.3 × 104 | 1.4 |
| b5 | 679.3680 | 679.3676 | 9.3 × 104 | 0.6 | a5 | 651.3731 | 651.3705 | 1.2 × 104 | 4.0 | y8 * | 845.4520 | 845.4680 | 6.0 × 103 | −18.9 | |
| P | b6 | 776.4208 | 776.4209 | 1.7 × 104 | −0.2 | a6 | 748.4259 | 748.4175 | 3.0 × 104 | 11.2 | y7 | 706.3775 | 706.3775 | 2.3 × 104 | 0.0 |
| G | b7 | 833.4422 | 833.4417 | 1.9 × 104 | −0.6 | a7 | 805.4473 | 805.4473 | 1.8 × 103 | 0.0 | y6 | 609.3248 | 609.3238 | 3.6 × 102 | 1.6 |
| P | b8 | 930.4950 | 930.4941 | 8.4 × 103 | 1.0 | a8 | 902.5001 | 902.5016 | 1.2 × 103 | −1.7 | y5 | 552.3033 | 552.3032 | 4.8 × 103 | 0.2 |
| E | b9 # | 1041.5273 | 1041.5265 | 2.0 × 103 | 0.8 | a9 # | 1013.5321 | 1013.5197 | 4.4 × 102 | 12.2 | y4 | 455.2505 | 455.2492 | 3.7 × 102 | 2.8 |
| b9 | 1059.5376 | 1059.5365 | 5.0 × 105 | 1.0 | a9 | 1031.5427 | 1031.5427 | 4.9 × 104 | 0.0 | y4 # | 437.2399 | 437.2360 | 6.3 × 103 | 9.0 | |
| I/L | b10 | 1172.6206 | 1172.6207 | 6.6 × 105 | −0.1 | a10 | 1144.6257 | 1144.6255 | 2.1 × 105 | 0.2 | y3 | 326.2081 | 326.2079 | 4.9 × 104 | 0.7 |
| P | b11 | 1269.6734 | - | - | - | a11 | 1241.6785 | - | - | - | y2 | 213.1241 | 213.1241 | 3.8 × 106 | −0.1 |
| P | b12 | 1366.7261 | - | - | - | a12 | 1338.7312 | - | - | - | y1 | 116.0712 | 116.0713 | 1.6 × 105 | −1.2 |
| Fragments | b-Type ions | a-Type ions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical (m/z) | Measured (m/z) | Intensity (counts) | Accuracy (ppm) | Theoretical (m/z) | Measured (m/z) | Intensity (counts) | Accuracy (ppm) | |
| KWPRPGP | 819.4629 | - | - | - | 791.46799 | - | - | - |
| KWPRPGP * | 802.4364 | 802.4401 | 2.3 × 102 | −4.6 | 774.44149 | - | - | - |
| KWPRPG | 722.4102 | - | - | - | 694.41529 | - | - | - |
| KWPRPG * | 705.3836 | 705.3939 | 8.2 × 102 | −14.6 | 677.38869 | 677.3793 | 1.0 × 103 | 13.9 |
| KWPRP | 665.3887 | - | - | - | 637.39379 | - | - | - |
| KWPRP * | 648.3622 | - | - | - | 620.36729 | - | - | - |
| KWPR | 568.3359 | - | - | - | 540.34099 | 540.3436 | 1.7 × 102 | −4.8 |
| KWPR * | 551.3094 | - | - | - | 523.31449 | - | - | - |
| KWP | 412.2349 | 412.2426 | 4.9 × 102 | −18.7 | 384.23999 | - | - | - |
| KWP * | 395.2083 | - | - | - | 367.21339 | - | - | - |
| KW | 315.1821 | 315.1797 | 2.2 × 102 | 7.6 | 287.18719 | - | - | - |
| KW * | 298.1556 | 298.1567 | 6.3 × 102 | −3.7 | 270.16069 | 270.1608 | 1.9 × 103 | −0.4 |
| WPRPGPEIP | 1030.5474 | 1030.5469 | 1.0 × 103 | 0.5 | 1002.5525 | 1002.5590 | 1.3 × 102 | −6.5 |
| WPRPGPEIP * | 1013.5209 | 1013.5197 | 4.4 × 102 | 1.1 | 985.5259 | - | - | - |
| WPRPGPEI | 933.4946 | 933.4941 | 2.8 × 104 | 0.5 | 905.4997 | 905.4992 | 5.0 × 103 | 0.5 |
| WPRPGPEI * | 916.4681 | 916.4681 | 2.5 × 103 | 0.0 | 888.4731 | 888.4796 | 9.8 × 102 | −7.3 |
| WPRPGPE | 820.4106 | 820.4102 | 1.5 × 104 | 0.5 | 792.4157 | 792.4160 | 3.4 × 103 | −0.4 |
| WPRPGPE * | 803.3841 | 803.3862 | 1.5 × 103 | −2.7 | 775.3891 | 775.3857 | 6.3 × 102 | 4.4 |
| WPRPGP | 691.3680 | 691.3715 | 7.7 × 102 | −5.1 | 663.3731 | - | - | - |
| WPRPGP * | 674.3415 | - | - | - | 646.3465 | 646.3524 | 3.0 × 102 | −9.1 |
| WPRPG | 594.3152 | 594.3206 | 2.4 × 103 | −9.1 | 566.3203 | - | - | - |
| WPRPG * | 577.2887 | 577.2831 | 1.9 × 102 | 9.6 | 549.2937 | - | - | - |
| WPRP | 537.2938 | - | - | - | 509.2989 | - | - | - |
| WPRP * | 520.2673 | - | - | - | 492.2723 | 492.2757 | 1.6 × 102 | −6.8 |
| WPR | 440.2410 | 440.2399 | 4.6 × 103 | 2.5 | 412.2461 | - | - | - |
| WPR * | 423.2145 | 423.2138 | 2.2 × 103 | 1.5 | 395.2195 | 395.2174 | 8.6 × 102 | 5.4 |
| WP | 284.1399 | - | - | - | 256.1450 | 256.1468 | 5.5 × 102 | −7.1 |
| PRPGPEIP | 844.4681 | 844.4672 | 7.8 × 103 | 1.1 | 816.4732 | - | - | - |
| PRPGPEIP * | 827.4416 | 827.4381 | 1.6 × 102 | 4.2 | 799.4466 | - | - | - |
| PRPGPEI/RPGPEIP | 747.4153 | 747.4150 | 5.1 × 104 | 0.4 | 719.4204 | 719.4196 | 1.3 × 104 | 1.1 |
| PRPGPEI */RPGPEIP * | 730.3888 | 730.3976 | 4.4 × 103 | −12.1 | 702.3938 | 702.4028 | 1.4 × 103 | −12.7 |
| PRPGPE | 634.3313 | 634.3317 | 3.7 × 104 | −0.6 | 606.3364 | 606.3362 | 1.1 × 104 | 0.3 |
| PRPGPE * | 617.3048 | 617.3059 | 3.4 × 103 | −1.9 | 589.3098 | 589.3193 | 2.2 × 103 | −16.0 |
| PRPGP | 505.2887 | 505.2886 | 1.6 × 103 | 0.2 | 477.2938 | 477.295 | 3.9 × 102 | −2.5 |
| PRPGP * | 488.2622 | 488.2668 | 1.4 × 102 | −9.5 | 460.2672 | - | - | - |
| PRPG/RPGP | 408.2359 | 408.2354 | 2.2 × 103 | 1.2 | 380.2410 | 380.2346 | 5.6 × 102 | 16.8 |
| PRPG */RPGP * | 391.2094 | - | - | - | 363.2144 | - | - | - |
| PRP | 351.2145 | 351.2112 | 2.1 × 103 | 9.4 | 323.2196 | - | - | - |
| PRP * | 334.1880 | 334.1869 | 6.7 × 102 | 3.2 | 306.1930 | - | - | - |
| PR/RP | 254.1617 | 254.1616 | 2.2 × 104 | 0.4 | 226.1668 | - | - | - |
| PR/RP * | 237.1352 | 237.136 | 2.8 × 103 | −3.6 | 209.1402 | 209.1388 | 4.1 × 102 | 6.9 |
| RPGPEI | 650.3626 | 650.3616 | 4.7 × 103 | 1.5 | 622.3677 | - | - | - |
| RPGPEI * | 633.3361 | - | - | - | 605.3411 | 605.3397 | 1.2 × 103 | 2.4 |
| RPGPE | 537.2785 | 537.2814 | 2.9 × 103 | −5.4 | 509.2836 | 509.2862 | 2.2 × 103 | −5.1 |
| RPGPE * | 520.2520 | 520.2515 | 9.3 × 102 | 0.9 | 492.2570 | 492.2552 | 6.2 × 102 | 3.7 |
| RPG | 311.1832 | - | - | - | 283.1883 | - | - | - |
| RPG * | 294.1567 | 294.1559 | 2.4 × 102 | 2.6 | 266.1617 | - | - | - |
| IP | 211.1446 | 211.1445 | 3.1 × 103 | 0.5 | 183.14969 | 183.1503 | 1.2 × 103 | −3.3 |
| BPP name | Sequence | Bothrops specie | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPP-BAX12 | ZKWPRPGPEIPP | Bothrops atrox | this work |
| - | ZKWPRPGPEIPP | B. moojeni | [6] |
| - | ZNWPRPGPEIPP | B. moojeni | [6] |
| BPP3_BOTNU, BPP13_BOTMO, BPP13_BOTLC, BPP13_BOTER, BPP13_BOTAL, BNP_BOTIN, BNP2_BOTJA, BNP1_BOTJA, Q8QG90_BOTIN, BNP_BOTJR # | ZGGWPRPGPEIPP | B. neuwiedi, B. moojeni, B. leucurus, B. erythromelas, B. alternatus, B. insularis, B. jararaca, B. jararaca, B. insularis, B. jararacussu | [1,9,10,11,12,13] |
| BPP-13a | ZGGWPRPGPEIPP | B. cotiara, B. fonsecai | [14] |
| BPP-13b | ZGGLPRPGPEIPP | B. cotiara, B. fonsecai | [14] |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Wermelinger, L.S.; Dutra, D.L.; Oliveira-Carvalho, A.L.; Soares, M.R.; Bloch, C., Jr.; Zingali, R.B. Fast analysis of low molecular mass compounds present in snake venom: Identification of ten new pyroglutamate-containing peptides. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.H.; Neshich, G.; Camargo, A.C.M. Using bradykinin-potentiating peptide structures to develop new antihypertensive drugs. Genet. Mol. Res. 2004, 3, 554–563. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.H. A Bradykinin-potentiating factor (BPF) present in the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 1965, 24, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.G.; Vane, J.R. The Discovery of Captopril. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 788–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, P.; Quinton, L.; Nicholson, G.M. Venomics: Unravelling the complexity of animal venoms with mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menin, L.; Perchuc, A.; Favreau, P.; Perret, F.; Michalet, S.; Schöni, R.; Wilmer, M.; Stöcklin, R. High throughput screening of bradykinin-potentiating peptides in Bothrops moojeni snake venom using precursor ion mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1288–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianzer, D.; Konno, K.; Marques-Porto, R.; Portaro, F.C.V.; Stöcklin, R.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Pimenta, D.C. Identification of five new bradykinin potentiating peptides (BPPs) from Bothrops jararaca crude venom by using electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry after a two-step liquid chromatography. Peptides 2004, 25, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, J.; Zinn, N.; Boehm, M.E.; Lehmann, W.D. De novo sequencing of peptides by MS/MS. Proteomics 2010, 10, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.F.; Galle, A.; Raida, M.; Schrader, M.; Lebrun, I.; Habermehl, G. Isolation: Analysis and properties of three bradykinin-potentiating peptides (BPP-II, BPP-III, and BPP-V) from Bothrops neuwiedi venom. J. Protein Chem. 1998, 17, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.H.M.F.; Catharino, R.R.; Ifa, D.R.; Eberlin, M.N.; Hyslop, S. Peptide fingerprinting of snake venoms by direct infusion nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: Potential use in venom identification and taxonomy. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, A.C.O.; Vieira, C.A.; Giglio, J.R. Primary structure and biological activity of bradykinin potentiating peptides from Bothrops insularis snake venom. J. Protein Chem. 1990, 9, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.A.F.; Murbach, A.F.; Ianzer, D.; Portaro, F.C.V.; Prezoto, B.C.; Fernandes, B.L.; Silveira, P.F.; Silva, C.A.; Pires, R.S.; Britto, L.R.G.; et al. The C-type natriuretic peptide precursor of snake brain contains highly specific inhibitors of the angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, A.K.; Zelanis, A.; Kitano, E.S.; Ianzer, D.; Melo, R.L.; Rioli, V.; Sant’anna, S.S.; Schenberg, A.C.; Camargo, A.C.; Serrano, S.M. Peptidomics of three bothrops snake venoms: Insights into the molecular diversification of proteomes and peptidomes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2012, 11, 1245–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioli, V.; Prezoto, B.C.; Konno, K.; Melo, R.L.; Klitzke, C.F.; Ferro, E.S.; Ferreira-Lopes, M.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Portaro, F.C.V. A novel bradykinin potentiating peptide isolated from Bothrops jararacussu venom using catallytically inactive oligopeptidase EP24.15. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2442–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Pérez, A.; Borges, A.; Vargas, A.M.; Lomonted, B.; Angulo, Y.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Mourão, R.H.V.; et al. Snake population venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops atrox: Paedomorphism along its transamazonian dispersal and implications of geographic venom variability on snakebite management. J. Proteomics 2011, 74, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guércio, R.A.P.; Shevchenko, A.; Shevchenko, A.; López-Lozano, J.L.; Paba, J.; Sousa, M.V.; Ricart, C.A.O. Ontogenetic variations in the venom proteome of the Amazonian snake Bothrops atrox. Proteome Sci. 2006, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiva, M.; Arraes, F.B.M.; Souza, J.V.; Radis-Baptista, G.; Silva, A.R.B.P.; Walter, M.E.M.T.; Brigido, M.M.; Yamane, T.; Lopez-Lozano, J.L.; Astolfi-Filho, S. Transcriptome analysis of the Amazonian viper Bothrops atrox venom gland using expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Toxicon 2009, 53, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Coutinho-Neto, A.; Caldeira, C.A.S.; Souza, G.H.M.F.; Zaqueo, K.D.; Kayano, A.M.; Silva, R.S.; Zuliani, J.P.; Soares, A.M.; Stábeli, R.G.; Calderon, L.A. ESI-MS/MS Identification of a Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide from Amazon Bothrops atrox Snake Venom Using a Hybrid Qq-oaTOF Mass Spectrometer. Toxins 2013, 5, 327-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5020327
Coutinho-Neto A, Caldeira CAS, Souza GHMF, Zaqueo KD, Kayano AM, Silva RS, Zuliani JP, Soares AM, Stábeli RG, Calderon LA. ESI-MS/MS Identification of a Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide from Amazon Bothrops atrox Snake Venom Using a Hybrid Qq-oaTOF Mass Spectrometer. Toxins. 2013; 5(2):327-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoutinho-Neto, Antonio, Cleópatra A. S. Caldeira, Gustavo H. M. F. Souza, Kayena D. Zaqueo, Anderson M. Kayano, Rodrigo S. Silva, Juliana P. Zuliani, Andreimar M. Soares, Rodrigo G. Stábeli, and Leonardo A. Calderon. 2013. "ESI-MS/MS Identification of a Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide from Amazon Bothrops atrox Snake Venom Using a Hybrid Qq-oaTOF Mass Spectrometer" Toxins 5, no. 2: 327-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5020327
APA StyleCoutinho-Neto, A., Caldeira, C. A. S., Souza, G. H. M. F., Zaqueo, K. D., Kayano, A. M., Silva, R. S., Zuliani, J. P., Soares, A. M., Stábeli, R. G., & Calderon, L. A. (2013). ESI-MS/MS Identification of a Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptide from Amazon Bothrops atrox Snake Venom Using a Hybrid Qq-oaTOF Mass Spectrometer. Toxins, 5(2), 327-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5020327






