Difference in F-Actin Depolymerization Induced by Toxin B from the Clostridium difficile Strain VPI 10463 and Toxin B from the Variant Clostridium difficile Serotype F Strain 1470
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
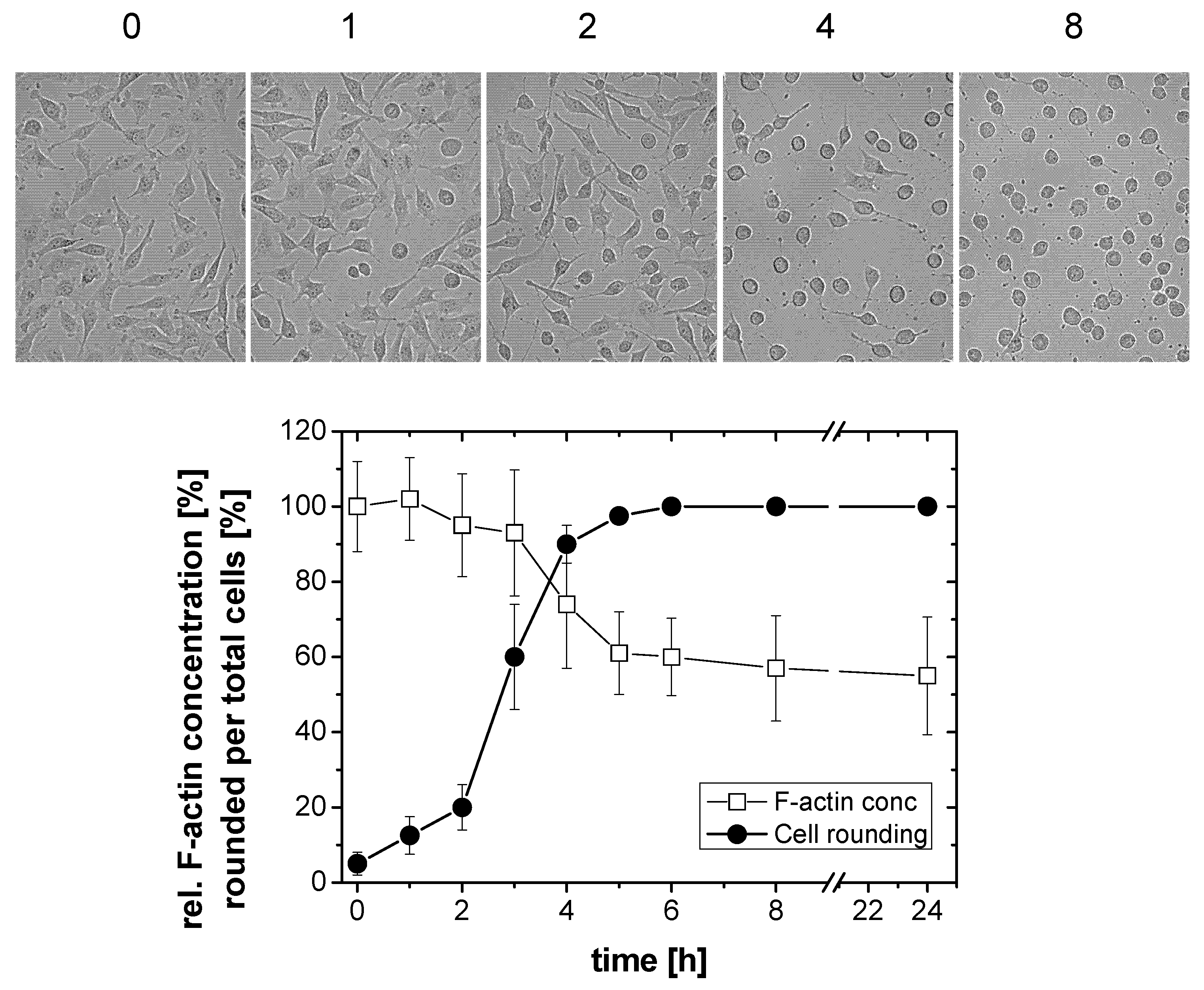
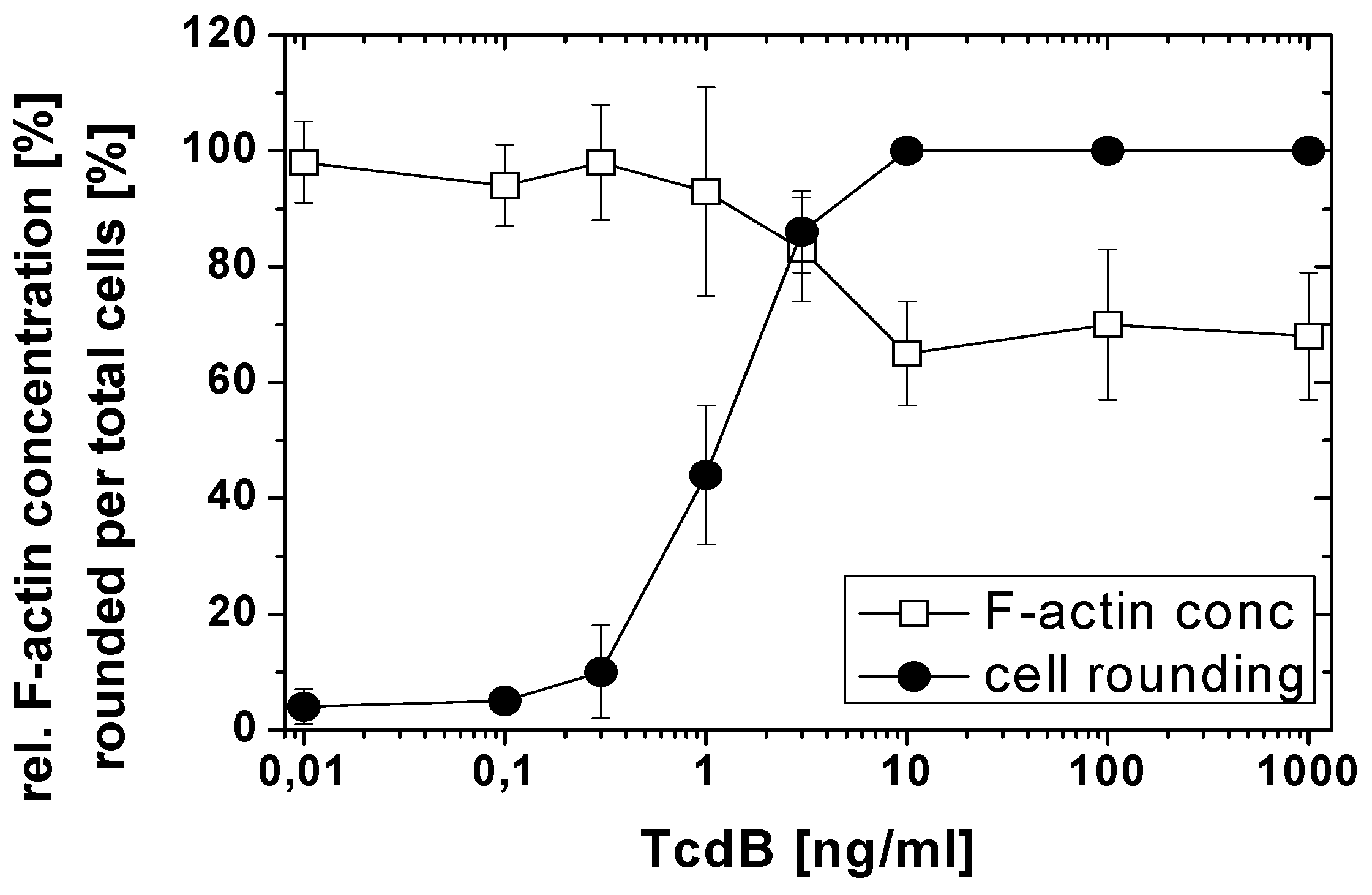
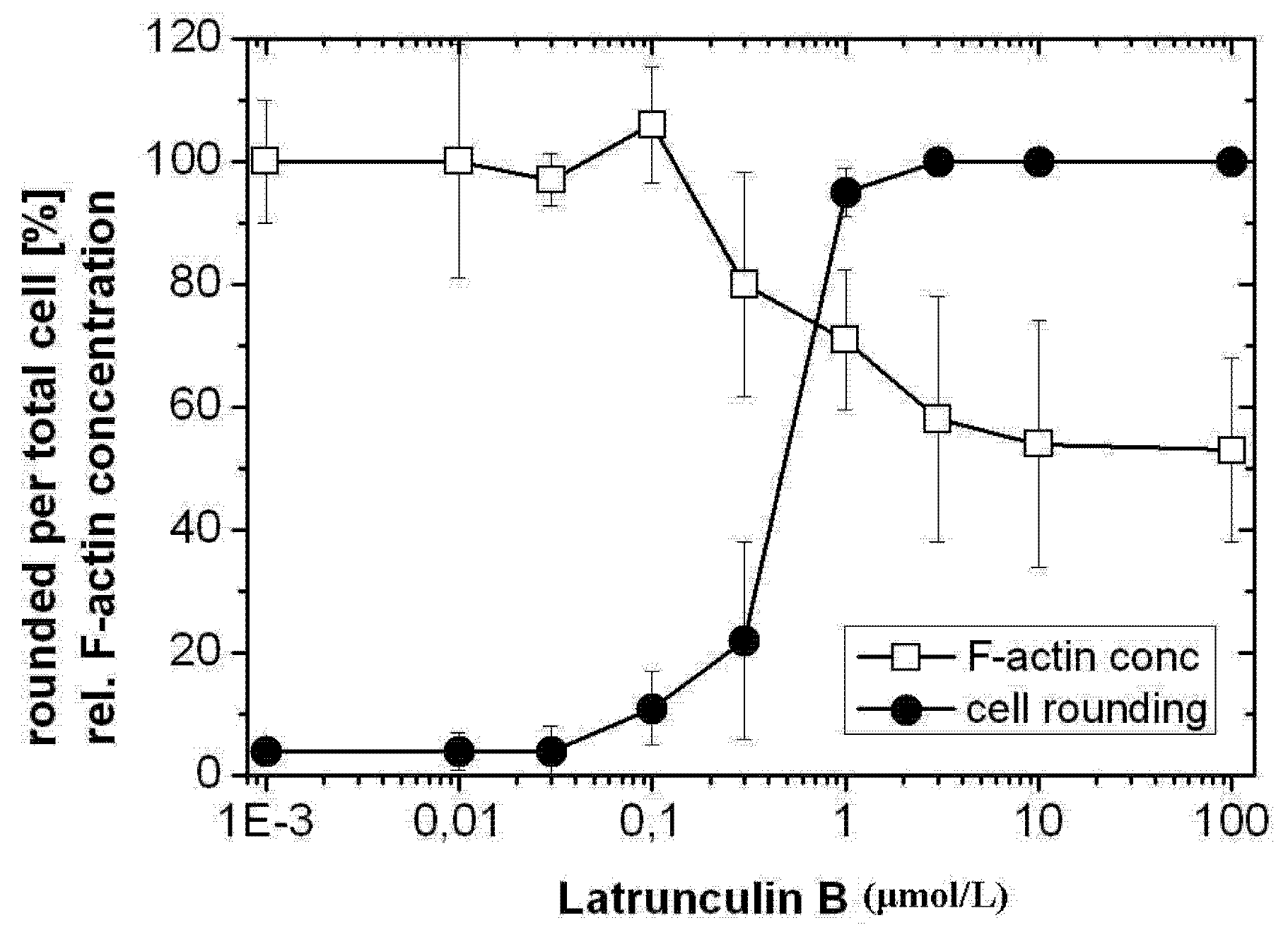
2.1. TcdB-Induced F-Actin Depolymerization
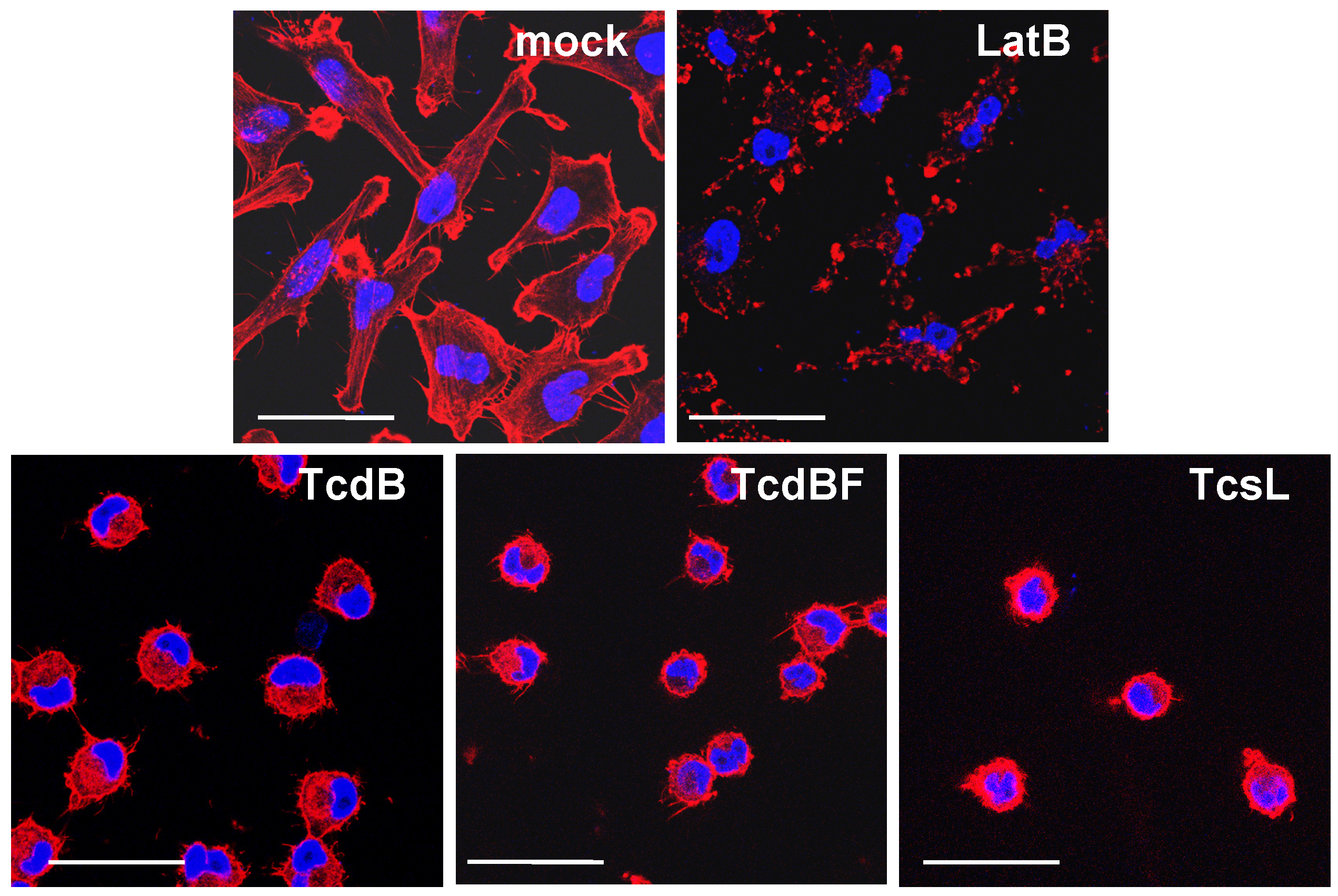


2.2. No F-Actin Depolymerization in Cells Treated with the Variant C. difficile Toxin B and C. sordellii Lethal Toxin

2.3. F-Actin Depolymerization Results in Paxillin Dephosphorylation
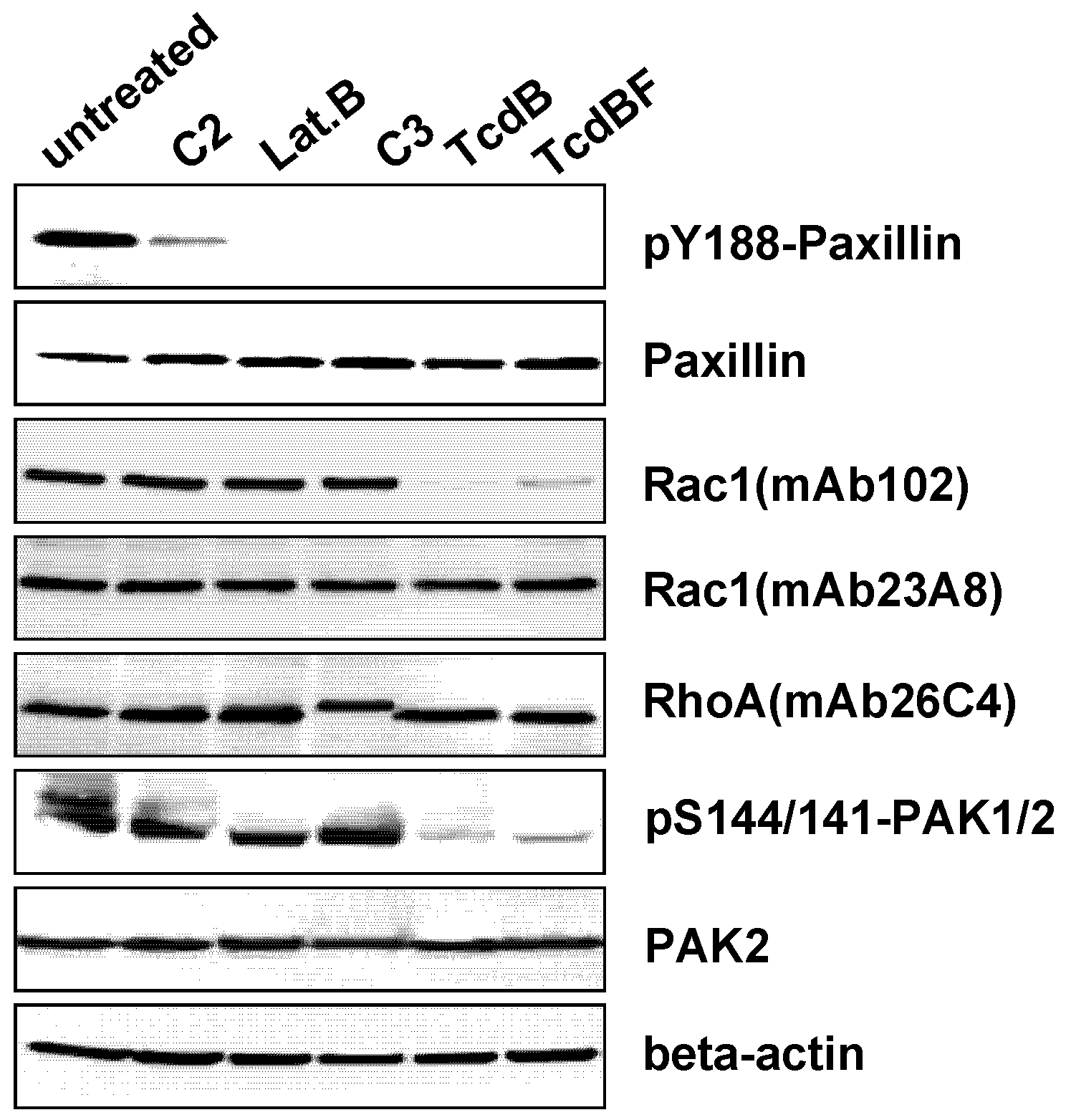
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Toxin Purification
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Measurement of Filamentous Actin by Rhodamine-Phalloidin Fluorescence Assay
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Immunocytochemistry and Immunofluorescence
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
Supplementary Files
References
- Voth, D.E.; Ballard, J. Clostridium difficile Toxins: Mechanism of action and role in disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genth, H.; Dreger, S.C.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Just, I. Clostridium difficile toxins: More than mere inhibitors of Rho proteins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jank, T.; Aktories, K. Structure and mode of action of clostridial glucosylating toxins: The ABCD model. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olling, A.; Goy, S.; Hoffmann, F.; Tatge, H.; Just, I.; Gerhard, R. The repetitive oligopeptide sequences modulate cytopathic potency but are not crucial for cellular uptake of Clostridium difficile toxin A. PLoS One 2011, 6, e17623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.; Dreger, S.; Gerhard, R.; Barth, H.; Just, I.; Genth, H. Difference in the Cytotoxic Effects of Toxin B from Clostridium difficile Strain VPI 10463 and Toxin B from Variant Clostridium difficile Strain 1470. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genth, H.; Aktories, K.; Just, I. Monoglucosylation of RhoA at Threonine-37 blocks cytosol-membrane cycling. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29050–29056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehr, P.; Joseph, G.; Genth, H.; Just, I.; Pick, E.; Aktories, K. Glucosylation and ADP-ribosylation of Rho proteins—Effects on nucleotide binding, GTPase activity, and effector-coupling. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 5296–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Gruszczynska, M.; Rohde, M.; Hartig, R.; Genth, H.; Schmidt, G.; Keo, T.; Konig, W.; Miller, W.G.; Konkel, M.E.; Backert, S. Role of the small Rho GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42 in host cell invasion of Campylobacter jejuni. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, S.; Descot, A.; Julien, S.; Genth, H.; Posern, G. Epithelial cell-cell contacts regulate SRF-mediated transcription via Rac-actin-MAL signalling. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsch, K.; de Jong, S.J.; Albrecht, J.C.; Steger, J.; Genth, H.; Posern, G.; Biesinger, B. Actin-dependent activation of serum response factor in T cells by the viral oncoprotein tip. Cell Commun. Signal. 2012, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplazes, J.; Fuchs, M.; Rauser, S.; Genth, H.; Lengyel, E.; Busch, R.; Luber, B. Rac1 and Rho contribute to the migratory and invasive phenotype associated with somatic E-cadherin mutation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3632–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases: Biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadriraju, K.; Yang, M.; alom Ruiz, S.; Pirone, D.; Tan, J.; Chen, C.S. Activation of ROCK by RhoA is regulated by cell adhesion, shape, and cytoskeletal tension. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3616–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrier, A.L.; Yamada, K.M. Cell-matrix adhesion. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.M.; Lim, L.; Manser, E. PAK is regulated by PI3K, PIX, CDC42, and PP2Calpha and mediates focal adhesion turnover in the hyperosmotic stress-induced p38 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24949–24961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.J.; Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.F. Adhesion assembly, disassembly and turnover in migrating cells—Over and over and over again. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E97–E100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.C.; Turner, C.E. Paxillin: Adapting to change. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1315–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorte, L.; Rodrigues, S.; Sangwan, V.; Turner, C.E.; Park, M. Crk associates with a multimolecular Paxillin/GIT2/β-PIX complex and promotes Rac-dependent relocalization of Paxillin to focal contacts. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2818–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayal, A.; Webb, D.J.; Brown, C.M.; Schaefer, E.M.; Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Horwitz, A.R. Paxillin phosphorylation at Ser273 localizes a GIT1-PIX-PAK complex and regulates adhesion and protrusion dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Kolbe, T.; Wang, T.; Schmidt, G.; Genth, H. Increased Cell-Matrix Adhesion upon Constitutive Activation of Rho Proteins by Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors from E. Coli and Y. Pseudotuberculosis. J. Signal. Transduct. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geny, B.; Grassart, A.; Manich, M.; Chicanne, G.; Payrastre, B.; Sauvonnet, N.; Popoff, M.R. Rac1 inactivation by lethal toxin from Clostridium sordellii modifies focal adhesions upstream of actin depolymerization. Cell Microbiol. 2010, 12, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Laughon, B.E.; Lin, S. Biochemical studies on the effect of Clostridium difficile toxin B on actin in vivo and in vitro. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machesky, L.M.; Hall, A. Role of actin polymerization and adhesion to extracellular matrix in Rac- and Rho-induced cytoskeletal reorganization. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 138, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, M.; Marvaud, J.C.; Pereira, Y.; Hale, M.L.; Stiles, B.G.; Boquet, P.; Lamaze, C.; Popoff, M.R. Differential requirement for the translocation of clostridial binary toxins: Iota toxin requires a membrane potential gradient. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttorp, N.; Polley, M.; Seybold, J.; Schnittler, H.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F.; Aktories, K. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of G-actin by C. botulinum C2 toxin increases endothelial permeability in vitro. J. Clin. Invest. 1991, 87, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Olarte, E.; Löw, P.; Freer, E.; Norlin, T.; Weidmann, M.; von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Thelestam, M. A novel cytotoxin from Clostridium difficile serogroup F is a functional hybrid between two other large clostridial cytotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11046–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genth, H.; Just, I. Functional implications of lethal toxin-catalysed glucosylation of (H/K/N)Ras and Rac1 in Clostridium sordellii-associated disease. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreger, S.C.; Schulz, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Gerhard, R.; Hofmann, F.; Just, I.; Genth, H. Killing of rat basophilic leukemia cells by lethal toxin from Clostridium sordellii: Critical role of phosphatidylinositide 3'-OH kinase/Akt signaling. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, S.C.; Klose, I.; Reichenbach, M.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Genth, H. Distinct kinetics of (H/K/N)Ras glucosylation and Rac1 glucosylation catalysed by Clostridium sordellii lethal toxin. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3133–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Blöcker, D.; Aktories, K. The uptake machinery of clostridial actin ADP-ribosylating toxins—A cell delivery system for fusion proteins and polypeptide drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 366, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genth, H.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Hartmann, B.; Hofmann, F.; Just, I.; Gerhard, R. Cellular stability of Rho-GTPases glucosylated by Clostridium difficile toxin B. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 3565–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalmann, J.; Janik, K.; May, M.; Sommer, K.; Ebeling, J.; Hofmann, F.; Genth, H.; Klos, A. Actin re-organization induced by Chlamydia trachomatis serovar D—Evidence for a critical role of the effector protein CT166 targeting Rac. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabi-Cabezon, I.; Huelsenbeck, J.; May, M.; Ladwein, M.; Rottner, K.; Just, I.; Genth, H. Prevention of the cytopathic effect induced by Clostridium difficile Toxin B by active Rac1. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3751–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottner, K.; Stradal, T.E. Actin dynamics and turnover in cell motility. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, M. Heterogeneity of large clostridial toxins: Importance of Clostridium difficile toxinotypes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
May, M.; Wang, T.; Müller, M.; Genth, H. Difference in F-Actin Depolymerization Induced by Toxin B from the Clostridium difficile Strain VPI 10463 and Toxin B from the Variant Clostridium difficile Serotype F Strain 1470. Toxins 2013, 5, 106-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010106
May M, Wang T, Müller M, Genth H. Difference in F-Actin Depolymerization Induced by Toxin B from the Clostridium difficile Strain VPI 10463 and Toxin B from the Variant Clostridium difficile Serotype F Strain 1470. Toxins. 2013; 5(1):106-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010106
Chicago/Turabian StyleMay, Martin, Tianbang Wang, Micro Müller, and Harald Genth. 2013. "Difference in F-Actin Depolymerization Induced by Toxin B from the Clostridium difficile Strain VPI 10463 and Toxin B from the Variant Clostridium difficile Serotype F Strain 1470" Toxins 5, no. 1: 106-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010106
APA StyleMay, M., Wang, T., Müller, M., & Genth, H. (2013). Difference in F-Actin Depolymerization Induced by Toxin B from the Clostridium difficile Strain VPI 10463 and Toxin B from the Variant Clostridium difficile Serotype F Strain 1470. Toxins, 5(1), 106-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010106



