Investigations into the Toxicology of Spirolides, a Group of Marine Phycotoxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algal Material
2.2. Culturing of A. ostenfeldii Clonal Isolates
2.3. Isolation of Spirolides from Cultured A. ostenfeldii
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Determination of Acute Toxicities
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Spirolides on Cells in Culture

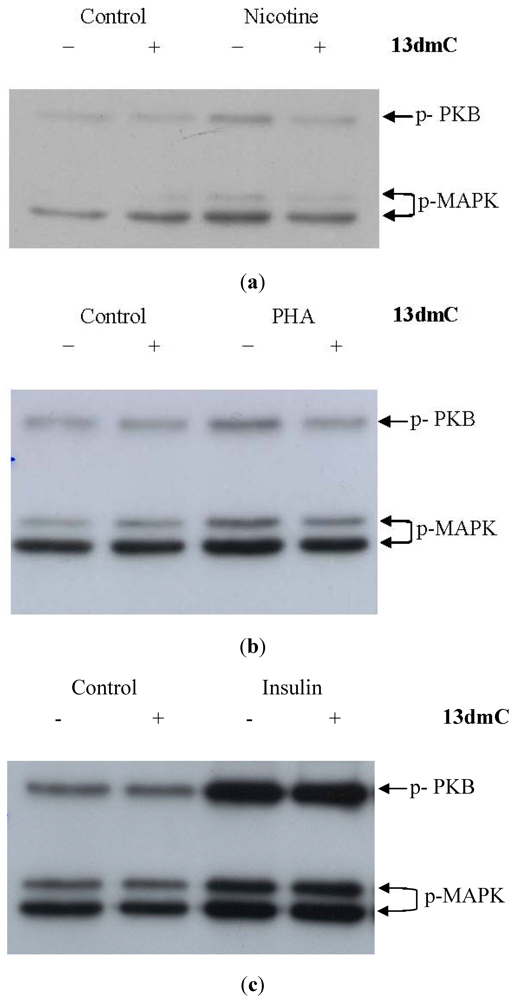
Effect of 13dmC on Cell Signaling from the Nicotinic AChR
3.2. Acute Toxicities
| Compound | State of alimentation | LD50 (µg/kg body weight) a | LD50 (µmol/kg body weight) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spirolide A | Fed | 37 (35–44) | 0.054 (0.051–0.064) |
| Spirolide B | Fed | 99 (ND) | 0.14 (ND) |
| Spirolide C | Fed | 8.0 (4.6–16) | 0.011 (0.0065–0.023) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fed | 6.9 (5.0–8.0) | 0.010 (0.0072–0.012) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fasted | 6.9 (5.0–8.0) | 0.010 (0.0072–0.012) |
| 20-Methyl spirolide G | Fed | 8.0 (3.9–14) | 0.011 (0.0055–0.020) |
| Compound | State of alimentation | LD50 (µg/kg body weight) a | LD50 (µmol/kg body weight) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spirolide A | Fed | 550 (436–690) | 0.80 (0.63–1.0) |
| Spirolide C | Fed | 180 (ND) | 0.25 (ND) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fed | 160 (123–198) | 0.23 (0.18–0.29) |
| 20-Methyl spirolide G | Fed | 160 (ND) | 0.23 (ND) |
| Spirolide A | Fasted | 240 (188–298) | 0.34 (0.27–0.43) |
| Spirolide B | Fasted | 440 (320–500) | 0.63 (0.46–0.72) |
| Spirolide C | Fasted | 53 (50–63) | 0.075 (0.071–0.089) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fasted | 130 (87–166) | 0.18 (0.13–0.24) |
| 20-Methyl spirolide G | Fasted | 88 (27–120) | 0.13 (0.038–0.17) |
| Compound | State of alimentation | Vehicle | LD50 (µg/kg body weight) a | LD50 (µmol/kg body weight) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spirolide A | Fed | Cream cheese | 1300 (1250–1580) | 1.9 (1.8–2.3) |
| Spirolide C | Fed | Cream cheese | 780 (ND) | 1.1 (ND) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fed | Cream cheese | 1000 (861–1290) | 1.5 (1.2–1.9) |
| 20-Methyl spirolide G | Fed | Cream cheese | 630 (476–882) | 0.89 (0.68–1.3) |
| Spirolide A | Fasted | Cream cheese | 1200 (1047–3690) | 1.7 (1.5–5.4) |
| Spirolide C | Fasted | Cream cheese | 500 (353–657) | 0.71 (0.50–0.93) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fasted | Dry mousefood | 630 (547–829) | 0.90 (0.79–1.2) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fasted | Moist mousefood | 590 (500–625) | 0.85 (0.72–0.90) |
| 13-Desmethyl spirolide C | Fasted | Cream cheese | 500 (381–707) | 0.72 (0.55–1.0) |
| 20-Methyl spirolide G | Fasted | Cream cheese | 500 (381–707) | 0.71 (0.54–1.0) |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Oshima, Y.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Watson-Wright, W.M.; Wright, J.L.C. Spirolides B and D, two novel macrocycles isolated from the digestive glands of shellfish. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 2159–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Uemura, D.; Chou, T.; Haino, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Fukuzawa, S.; Zheng, S.; Chen, H. Pinnatoxin A: A toxic amphoteric macrocycle from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, N.; Umemura, N.; Suenaga, K.; Chou, T.; Nagatsu, S.; Haino, T.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Pinnatoxins B and C, the most toxic components in the pinnatoxins series from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.-K.; Lee, G.-H.; Huang, R.; Chou, H.-N. Spiro-prorocentrimine, a novel macrocyclic lactone from a benthic Prorocentrum sp. of Taiwan. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 42, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, T.; Satake, M.; MacKenzie, L.; Kasper, H.F.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnodimine, a new marine toxin of unprecedented structure isolated from New Zealand oysters and the dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 7093–7096. [Google Scholar]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. Spirolide composition in micro-extracted pooled cells isolated from natural plankton assemblages and from cultures of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologica 2000, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Moestrup, O. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: Paralytic shellfish toxin concentration, composition, and toxicity to a tintinnid ciliate. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of biologically inactive spirolides E and F: Identification of the spirolide pharmacophore. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7671–7674. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, D.; Arsenault, E.; Cembella, A.; Quilliam, M. Investigations into the Toxicology and Pharmacology of Spirolides, a Novel Group of Shellfish Toxins. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Harmful Microalgae, Hobart, Australia, 6–11 February 2001; Hallegraeff, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J., Lewis, R.J., Eds.; pp. 383–386.
- Bourne, Y.; Radic, Z.; Araoz, R.; Talley, T.T.; Benoit, E.; Servent, D.; Taylor, P.; Molgo, J.; Marchot, P. Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar]
- Wandscheer, C.B.; Vilarino, N.; Espina, B.; Louzao, M.C.; Botana, L.M. Human muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are a target of the marine toxin 13-desmethyl C spirolide. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, L.; Triemer, R.E. Preliminary Studies of Cell Wall Formation in Temporary Cysts of Gonyaulax tamarensis. In Toxic Dinoflagellates; Anderson, D.M., White, A.W., Baden, D.G., Eds.; Elsevier-North Holland: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Burton, I.W.; Cembella, A.D.; Curtis, J.M.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of spirolides A, C and 13-desmethyl C, New marine toxins isolated from toxic plankton and contaminated shellfish. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.; MacKinnon, S.L.; LeBlanc, P.; Walter, W.A.; Hovgaard, P.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Detection and identification of spirolides in Norwegian shellfish and plankton. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, J.S.; LeBlanc, P.; Lewis, N.I.; Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; MacKinnon, S.L. Characterization of a dispiroketal spirolide subclass from Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD guideline for testing of chemicals 425. Acute oral toxicity-up and down procedure. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, 2001. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/oppfead1/harmonization/docs/E425guideline.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2011).
- EPA. User documentation for the AOT425StatPgm program prepared for the US Environmental Protection Agency by Westat, May 2001; updated by USEPA September 2002. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/19/57/1839830.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2011).
- Munday, R.; Towers, N.R.; Mackenzie, L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.T.; Miles, C.O. Acute toxicity of gymnodimine to mice. Toxicon 2004, 44, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, T.; Sørby, R.; Yasumoto, T.; Ramstad, H.; Landsverk, T. Comparison of oral and intraperitoneal toxicity of yessotoxin towards mice. Toxicon 2002, 40, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Assessment of potential activation of gonyautoxin V in the stomach of mice and rats. Toxicon 1984, 22, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R. Toxicological requirements for risk assessment of shellfish contaminants: A review. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashiell, O.L.; Kennedy, G.L. The effects of fasting on the acute oral toxicity of nine chemicals in the rat. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1984, 4, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, A.; Nishikawa, J. The effect of fasting on oral acute toxicity of drugs in rats and mice. Lab. Anim. 1981, 15, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, R.M.; McElligott, T.E.; Racz, W.J. Acetaminophen toxicity in fed and fasted mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1982, 60, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strubelt, O.; Dost-Kempf, E.; Siegers, C.-P.; Younes, M.; Völpel, M.; Preuss, U.; Dreckmann, J.G. The influence of fasting on the susceptibility of mice to hepatotoxic injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1981, 60, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavanet, P.; Joly, V.; Rigaud, D.; Bolard, J.; Carbon, C.; Yeni, P. Influence of diet on experimental toxicity of amphotericin B deoxycholate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, V.F.; Miller, M.G.; Jollow, D.J. Mechanisms of fasting-induced potentiation of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in the rat. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantle, P.G. Risk assessment and the importance of ochratoxins. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2002, 50, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R. Toxicology of Cyclic Imines: Gymnodimine, Spirolides, Pinnatoxins, Pteriatoxins, Prorocentrolide, Spiro-Procentrimine and Symbioimines. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins, Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection, 2nd; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 581–594. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Bermudez, R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data of spirolides after oral and intraperitoneal administration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R.; Aune, T.; Rossini, G.P. Toxicology of the Yessotoxins. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins, Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection, 2nd; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 329–339. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; LeBlanc, P.; Lewis, N.; Gallant, P.; Sperker, S.A.; Ewart, H.S.; MacKinnon, S.L. Investigations into the Toxicology of Spirolides, a Group of Marine Phycotoxins. Toxins 2012, 4, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4010001
Munday R, Quilliam MA, LeBlanc P, Lewis N, Gallant P, Sperker SA, Ewart HS, MacKinnon SL. Investigations into the Toxicology of Spirolides, a Group of Marine Phycotoxins. Toxins. 2012; 4(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunday, Rex, Michael A. Quilliam, Patricia LeBlanc, Nancy Lewis, Pamela Gallant, Sandra A. Sperker, H. Stephen Ewart, and Shawna L. MacKinnon. 2012. "Investigations into the Toxicology of Spirolides, a Group of Marine Phycotoxins" Toxins 4, no. 1: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4010001
APA StyleMunday, R., Quilliam, M. A., LeBlanc, P., Lewis, N., Gallant, P., Sperker, S. A., Ewart, H. S., & MacKinnon, S. L. (2012). Investigations into the Toxicology of Spirolides, a Group of Marine Phycotoxins. Toxins, 4(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4010001