Ochratoxin A: In Utero Exposure in Mice Induces Adducts in Testicular DNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals and Treatment
2.2.1. Acute Gavage Feeding Studies
2.2.2. Subchronic Feeding Studies
2.2.3. Transplacental Studies
2.3. OTA and OTA Metabolites Determination in Tissues
2.3.1. Analysis of OTA Content in Tissues of Adult Mice
2.3.2. Analysis of OTA Metabolites in Tissues of Adult Mice
2.4. DNA Adduct Detection and Identification of C-C8dG OTA Adduct
3. Results
3.1. Acute and Subchronic Effect of OTA on Adult Male Mice
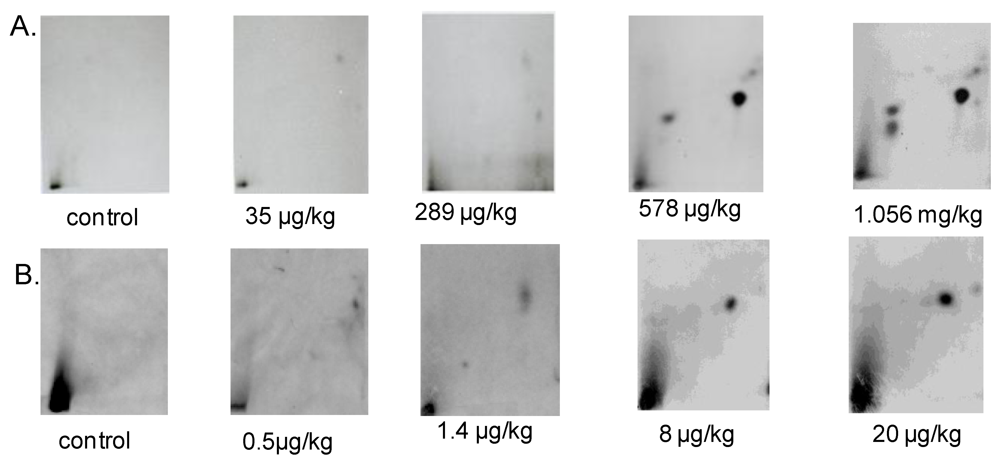
3.1.1. DNA Adduct Detection


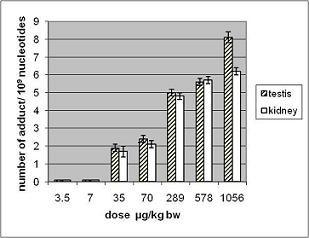
3.1.2. Amount of OTA in Kidney and Testis of Adult Mice
| OTA administered by gavage µg/kg b.w. | OTA content in testis* ng/g | OTA content in kidney* ng/g |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | nd** | nd |
| 3.5 | nd | 3.5 ± 1.4* |
| 7 | nd | 8.2 ± 0.7 |
| 35 | nd | 110 ± 2.5 |
| 70 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 123 ± 2 |
| 289 | 3 ± 0.1 | 110 ± 27 |
| 578 | 9.6 ± 1.5 | 210 ± 30 |
| 1056 | 50 ± 15 | 330 ± 60 |
3.1.3. Identification of OTA Metabolites in Tissues

3.2. Effect of Transplacental OTA Contamination on Male Mice Pup
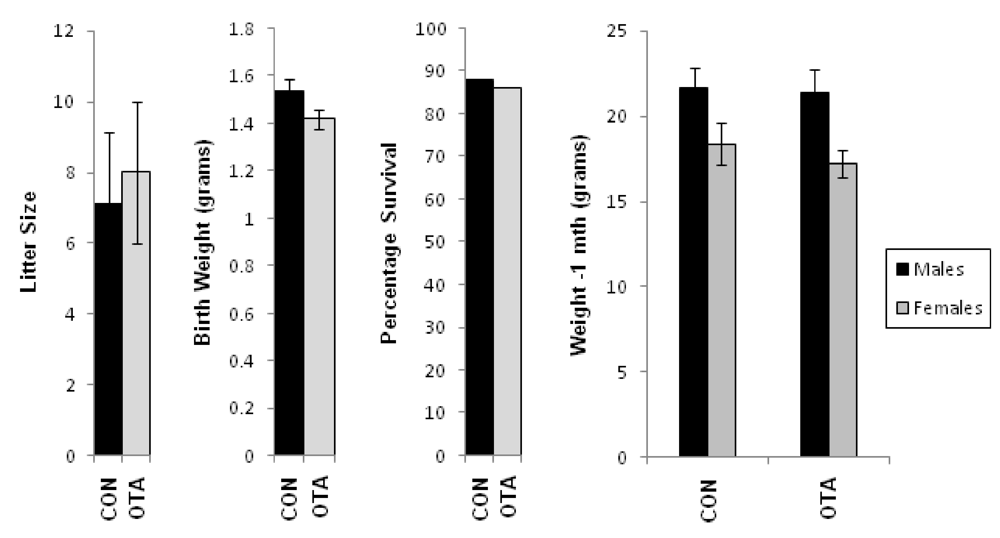
3.2.1. Transplacental Toxicity
3.2.2. DNA Adduct Analysis in Kidney and Testis of Male Mice Pup
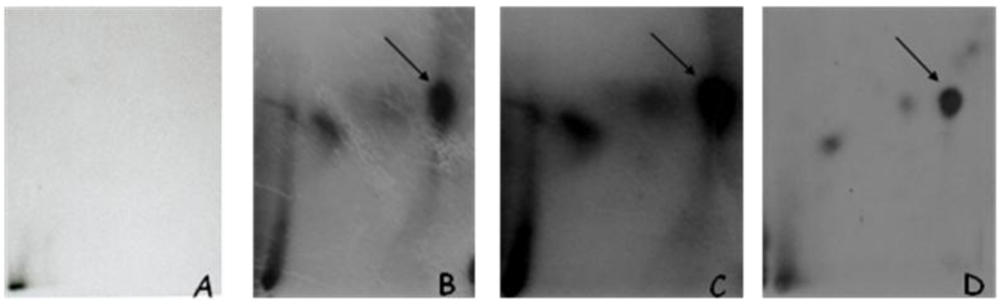

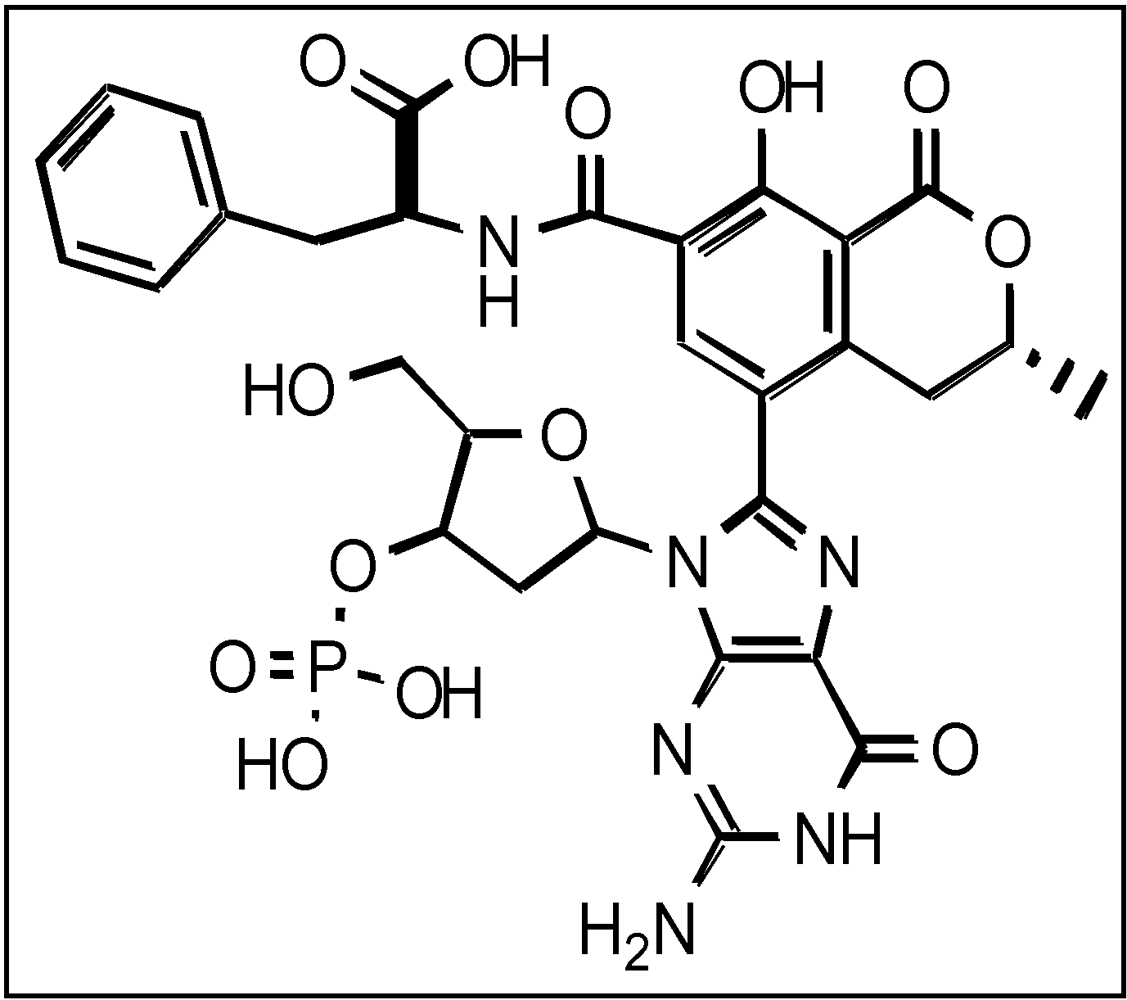
| Animal Numbering | C-C8dG OTA in Testis | C-C8dG OTA in Kidney | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mother 1 | 1 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 4.8 ± 0.2 |
| 2 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | |
| 3 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | |
| Mother 2 | 4 | 7.3 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 0.2 |
| 5 | 8.3 ± 0.5 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | |
| 6 | 7.7 ± 0.3 | 6.9 ± 0.5 | |
| 7 | 7 ± 0.6 | 6.6 ± 0.3 | |
| 8 | 7.8 ± 0.4 | 6.8 ± 0.5 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- O’Brien, E.; Dietrich, D.R. Ochratoxin A: The continuing enigma. Critical Reviews. Toxicology 2005, 35, 33–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 61–99. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, L.; Boohla, K. Ochratoxins—Food Contaminants: Impact on Health. Toxins 2010, 2, 771–779. [Google Scholar]
- Krogh, P. Epidemiology of mycotoxic porcine nephropathy. Nord. Vet. Med. 1976, 28, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Stoev, S.D. The role of ochratoxin A as a possible cause of Balkan endemic nephropathy and its risk evaluation. Vet. Human Toxicol. 1998, 40, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Chernozemsky, I.N.; Stoyanov, I.S.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.K.; Nicolov, I.G.; Draganov, I.V.; Stoichev, I.I.; Tanchev, Y.; Naidenov, D.; Kalcheva, N.D. Geographic correlation between the occurrence of endemic nephropathy and urinary tract tumours in Vratza district, Bulgaria. Int. J. Cancer 1977, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Chernozemsky, I.N.; Castegnaro, M. Balkan endemic nephropathy and the associated urinary tract tumours: Review on etiological causes, potential role of mycotoxins. Food Add. Contam. 2002, 19, 282–302. [Google Scholar]
- Castegnaro, M.; Chernozemsky, I.; Bartsch, H. Endemic nephropathy and urinary tract tumours in the Balkans. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 3608–3609. [Google Scholar]
- Huyghe, E.; Plante, P.; Thonneau, P.F. Testicular cancer variations in time and space in Europe. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, G.G. Hypothesis: Does ochratoxin A cause testicular cancer? Cancer Causes Control 2002, 13, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ueta, E.; Kodama, M.; Sumino, Y.; Kurome, M.; Ohta, K.; Katagiri, R.Y.; Naruse, I. Gender-dependent differences in the incidence of ochratoxin A-induced neural tube defects in the Pdn/Pdn mouse. Congenit. Anom. (Kyoto) 2010, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raymond, C.S.; Murphy, M.W.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Bardwell, V.J.; Zarkower, D. Dmrt1, a gene related to worm and fly sexual regulators, is required for mammalian testis differentiation. Genes Develop. 2000, 14, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar]
- Mantle, P.G.; Nolan, C.C. Pathological Outcomes in Kidney and Brain in Male Fischer Rats Given Dietary Ochratoxin A, Commencing at One Year of Age. Toxins 2010, 2, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Mantle, P.G.; Kulinskaya, E.; Nestler, S. Renal tumourigenesis in male rats in response to chronic dietary ochratoxin A. Food Addit. Contam. A 2005, 22, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Grosse, Y.; Kane, A.; Gharbi, A.; Baudrimont, I.; Obrecht, S.; Creppy, E.E.; Dirheimer, G. Is the oxidative pathway implicated in the genotoxicity of ochratoxin A? In Human Ochratoxicosis and Related Pathologies; Libbey, J., Ed.; Colloque INSERM: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gharbi, A.; Trillon, O.; Betbeder, A.M.; Counord, J.; Gauret, M.F.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Dirheimer, G.; Creppy, E.E. Some effects of ochratoxin A, a mycotoxin contaminating feeds and food, on rat testis. Toxicology 1993, 83, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Stoichev, I.I.; Chernozemsky, I.N.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Formation of DNA adducts in tissues of mouse progeny through transplacental contamination and/or lactation after administration of a single dose of ochratoxin A to the pregnant mother. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1998, 32, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Hadjiolov, D.; Spirov, K. Investigation on the genotoxicity of Ochratoxin A by measurement of DNA-adducts in different organs of Syrian hamsters. Rev. Med. Vet. 1998, 149, 658. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, M. Histogenesis and organogenesis of the gonad in human embryos. J. Anat. 1991, 177, 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- Smith’s General Urology, 16th; Tanagho, E.A.; McAninich, J.W. (Eds.) McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2004.
- Manderville, R.A.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Bioactivation and DNA adduction as a rationale for Ochratoxin A carcinogenesis. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 357–367. [Google Scholar]
- Faucet, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Dai, J.; Castegnaro, M.; Manderville, R.A. Evidence for covalent DNA adduction by Ochratoxin A following chronic exposure to rat and subacute exposure to pig. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Gillman, I.G.; Clark, T.N.; Manderville, R.A. Oxidation of ochratoxin A by an FE-Porphyrin system Model for enzymatic activation and DNA cleavage. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1999, 12, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Molinié, A.; Faucet, V.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-leszkowicz, A. Analysis of some breakfast cereals collected on the French market for their content in ochratoxin A, citrinin and fumonisin B1. Development of a new method for simultaneous extraction of ochratoxin A and citrinin. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Toslovanu, M.; Tran, T.L.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Occurrence of aflatoxin B1, citrinin and ochratoxin a in rice in five provinces of central region in Vietnam. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Garren, L.; Grosso, F.; Nikolov, I.; Vrabcheva, T.; Dragacci, S.; Chernozemsky, I. Analysis of ochratoxin A in serum and urine of inhabitants from an area with Balkan Endemic Nephropathy: A one month follow up study. Facta Universitatis series: Med. Biol. 2003, 10, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Faucet-Marquis, V.; Pont, F.; Størmer, F.; Rizk, T.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Evidence of a new dechlorinated OTA derivative formed in opossum kidney cell cultures after pre-treatment by modulators of glutathione pathways. Correlation with DNA adducts formation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 531–542. [Google Scholar]
- Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.; Tozlovanu, M.; Juzio, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R. Structure-activity relationships for the fluorescence of ochratoxin A: Insight for detection of ochratoxin A metabolites. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 617, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Castegnaro, M. Further arguments in favour of direct covalent binding of Ochratoxin A (OTA) after metabolic biotransformation. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mantle, P.; Faucet-Marquis, V.; Manderville, R.; Sciqualli, B.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Structures of covalent adducts between DNA and ochratoxin A: A new factor in debate about genotoxicity and human risk assessment. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Pinelli, E.; Bartsch, H.; Mohr, U.; Castegnaro, M. Sex and Strain differences in ochratoxin A metabolism and DNA adduction in two strains of rats. Mol. Carcino. 1998, 23, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pinelli, E.; El Adlouni, C.; Pipy, B.; Quartulli, F.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Respective implication of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase in ochratoxin A genotoxicity on human epithelial lung cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol 1999, 7, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- El Adlouni, C.; Pinelli, E.; Azémar, B.; Zaoui, D.; Beaune, P.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Role of CYP 2C and microsomal glutathione-S-transferase in modulating susceptibility to ochratoxin A genotoxicity. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petkova-Bocharova, T.; El Adlouni, C.; Faucet, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Mantle, P. Analysis for DNA adducts, ochratoxin A content and enzymes expression in kidneys of pigs exposed to mild experimental chronic ochratoxicosis. Facta universitatis, series: Med. Biol. 2003, 10, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Bartsch, H.; Azémar, B.; Mohr, U.; Estève, J.; Castegnaro, M. MESNA protects rats against nephrotoxicity but not carcinogenicity induced by ochratoxin A, implicating two separate pathways. Facta universitatis, series: Med. Biol. 2002, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.; Chakraborty, D. Emblica officinalis aqueous extract ameliorates ochratoxin-induced lipid peroxidation in the testis of mice. Acta Poliniae Pharm. Drug Res. 2008, 65, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kamataki, T.; Maeda, K.; Yamazoe, Y.; Nagai, T.; Kato, R. Sex difference of cytochrome P-450 in the rat: Purification, characterization, and quantitation of constitutive forms of cytochrome-P450 from liver microsomes of male and female rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1983, 225, 758–777. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J.A.; Mode, A.; Norstedt, G.; Skett, P. Sex steroid induced changes in hepatic enzymes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1983, 45, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Atanasova, S.Y.; Von Ahsen, N.; Toncheva, D.; Dimitrov, T.G.; Oellerich, M.; Armstrong, V.W. Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 among patients with Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN). Clin. Biochem 2005, 38, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Grosse, Y.; Castegnaro, M.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Nicolov, I.G.; Chernozemsky, I.N.; Bartsch, H.; Betbeder, A.M.; Creppy, E.E.; Dirheimer, G. Ochratoxin A related DNA adducts in urinary tract tumours of Bulgarian subjects. IARC Sci. Publ. 1993, 124, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Tozlovanu, M.; Manderville, R.; Peraica, M.; Castegnaro, M.; Stefanovic, V. New molecular and field evidences for the implication of mycotoxins but not aristolochic acid in Human Nephropathy and Urinary tract tumor. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Ochratoxin A and aristolochic acid in the Nephropathies and Associated Urothelial Tract Tumours development. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2009, 60, 465–483. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, P.; Tsolova, S.; Georgieva, R.; Bozhilova, D.; Simeonov, V.; Bonev, A.; Karmaus, W. Clinical markers in adult offspring of families with and without Balkan Endemic Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 723–729. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, H. Clues to the aetiology of testicular germ cell tumours from descriptive epidemiology. Eur. Eurol. 1993, 23, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpert-De Meyts, E. Developmental model for the pathogenesis of testicular carcinoma in situ: Genetic and environmental aspects. Human Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, K.; Asklund, C.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Andersson, A.-M. Testicular dysgenesis syndrome: Possible role of endocrine disrupters. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 21, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Fenske, M.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Effects of fungal metabolites on testosterone secretion in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 1990, 64, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Sinha, S.P. Modulation of ochratoxin-produced genotoxicity in mice by vitamin C. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 533–537. [Google Scholar]
- Solti, L.; Pécsi, T.; Barna-Vetro, I.; Szasz, F.; Szabo, F. Analysis of serum and seminal plasma after feeding ochratoxin A with breeding boars. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 1999, 56, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Biro, K.; Barna-Vetro, I.; Pesci, T.; Szabo, E.; Winkler, G.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; Solti, L. Evaluation of spermatological parameters in ochratoxin A-challenged boars. Theriogenology 2003, 60, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangikar, P.T.; Dwivedi, P.; Sinha, N. Effect in rats of simultaneous prenatal exposure to Ochratoxin A and Aflatoxin B1/I. Maternal toxicity and fetal malformations. Birth Defects Res. B 2004, 71, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.D.; Dwivedi, P.; Sharma, A.K. Critical period and minimum single oral dose of ochratoxin A for inducing developmental toxicity in pregnant Wistar rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 697–687. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, N.; Karpova, T.; Hornbaker, K.I.; Rice, D.A.; Heckert, L.L. Distinct transcriptional mechanisms direct expression of the rat Dmrt1 Promoter in Sertoli cells and germ cells of transgenic mice. Biol. Reproduct. 2009, 81, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jennings-Gee, J.E.; Tozlovanu, M.; Manderville, R.; Miller, M.S.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Schwartz, G.G. Ochratoxin A: In Utero Exposure in Mice Induces Adducts in Testicular DNA. Toxins 2010, 2, 1428-1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061428
Jennings-Gee JE, Tozlovanu M, Manderville R, Miller MS, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Schwartz GG. Ochratoxin A: In Utero Exposure in Mice Induces Adducts in Testicular DNA. Toxins. 2010; 2(6):1428-1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061428
Chicago/Turabian StyleJennings-Gee, Jamie E., Mariana Tozlovanu, Richard Manderville, Mark Steven Miller, Annie Pfohl-Leszkowicz, and Gary G. Schwartz. 2010. "Ochratoxin A: In Utero Exposure in Mice Induces Adducts in Testicular DNA" Toxins 2, no. 6: 1428-1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061428
APA StyleJennings-Gee, J. E., Tozlovanu, M., Manderville, R., Miller, M. S., Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A., & Schwartz, G. G. (2010). Ochratoxin A: In Utero Exposure in Mice Induces Adducts in Testicular DNA. Toxins, 2(6), 1428-1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061428