Gangliosides Block Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA)-Mediated Hemolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Isolation of Human RBCs
2.3. Preparation of LtxA and LtxA-FITC
2.4. Ganglioside Blocking Assays
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
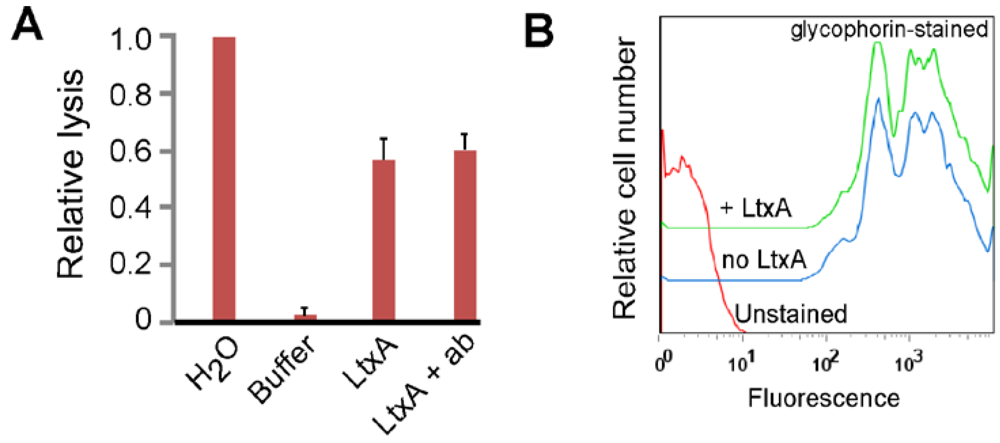
3.1. LtxA Does Not Use Glycophorin as a Receptor
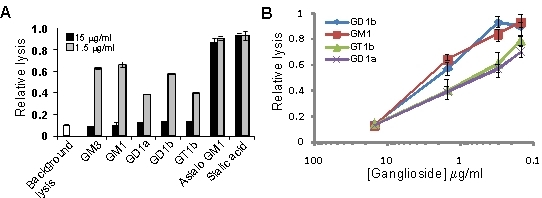
3.2. Gangliosides Block LtxA-Mediated Hemolysis
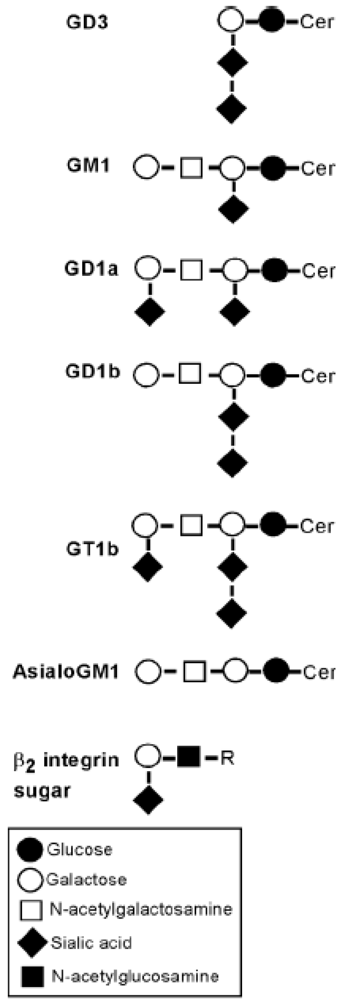

| Compound | Blocking |
|---|---|
| α-lactose | - |
| D (-) fructose | - |
| D (+) galactose | - |
| D-glucose | - |
| D-maltose | - |
| D-arabinose | - |
| D-ribose | - |
| Sucrose | - |
| D (+) mannose | - |
| D (+) xylose | - |
| N-acetylmuramic acid | - |
| Ganglioside GM1 | + |
| Ganglioside GD1b | + |
3.3. LtxA Binds to Gangliosides on Glioma Cells

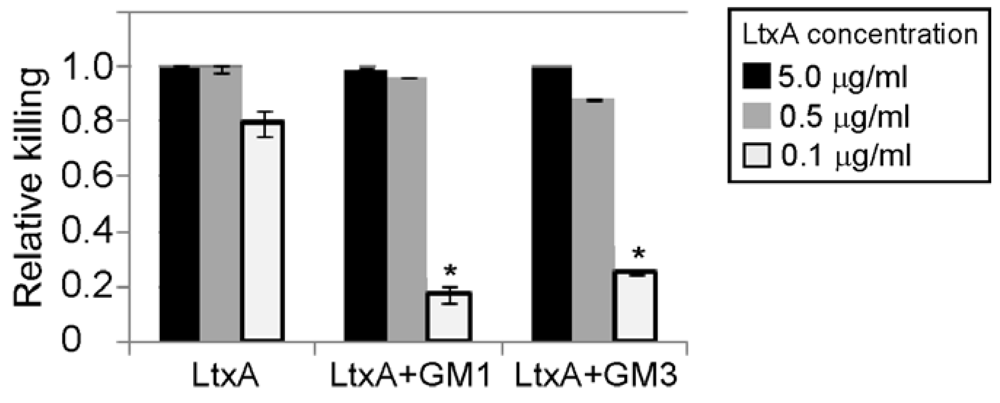
3.4. Gangliosides Inefficiently Block LtxA-Mediated Killing of WBCs
4. Discussion
Acknowledgements
References
- Fine, D.H.; Kaplan, J.B.; Kachlany, S.C.; Schreiner, H.C. How we got attached to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: A model for infectious diseases. Periodontol 2000 2006, 42, 114–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slots, J.; Ting, M. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in human periodontal disease: Occurrence and treatment. Periodontol 2000 1999, 20, 82–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zambon, J.J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1985, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamell, C.W.; Griffen, A.L.; McClellan, D.L.; Leys, E.J. Acquisition and colonization stability of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leys, E.J.; Griffen, A.L.; Strong, S.J.; Fuerst, P.A. Detection and strain identification of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by nested PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loe, H.; Brown, L.J. Early onset periodontitis in the United States of America. J. Periodontol. 1991, 62, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Berbari, E.F.; Cockerill, F.R., 3rd.; Steckelberg, J.M. Infective endocarditis due to unusual or fastidious microorganisms. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 1997, 72, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Badley, A.D.; Cockerill, F.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Wilson, W.R. Infective endocarditis caused by HACEK microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Paturel, L.; Casalta, J.P.; Habib, G.; Nezri, M.; Raoult, D. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans endocarditis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachlany, S.C. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin: From Threat to Therapy. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachlany, S.C.; Fine, D.H.; Figurski, D.H. Secretion of RTX leukotoxin by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6094–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, R.A. RTX toxin structure and function: A story of numerous anomalies and few analogies in toxin biology. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 257, 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Balashova, N.V.; Shah, C.; Patel, J.K.; Megalla, S.; Kachlany, S.C. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans LtxC is required for leukotoxin activity and initial interaction between toxin and host cells. Gene 2009, 443, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, E.T.; Kieba, I.R.; Sato, A.; Green, C.L.; Rosenbloom, J.; Korostoff, J.; Wang, J.F.; Shenker, B.J.; Ortlepp, S.; Robinson, M.K.; Billings, P.C. RTX toxins recognize a beta2 integrin on the surface of human target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30463–30469. [Google Scholar]
- Asada, M.; Furukawa, K.; Kantor, C.; Gahmberg, C.G.; Kobata, A. Structural study of the sugar chains of human leukocyte cell adhesion molecules CD11/CD18. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, N.; Harvey, J.; Cabanas, C.; Landis, R.C. Control of leukocyte integrin activation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, S55–S59. [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi, T. Intracellular signalling controlling integrin activation in lymphocytes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 546–559. [Google Scholar]
- Korostoff, J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Miller, M.; Kieba, I.; Lally, E.T. Perturbation of mitochondrial structure and function plays a central role in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin-induced apoptosis. Microb. Pathog. 2000, 29, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachlany, S.C.; Schwartz, A.B.; Balashova, N.V.; Hioe, C.E.; Tuen, M.; Le, A.; Kaur, M.; Mei, Y.; Rao, J. Anti-leukemia activity of a bacterial toxin with natural specificity for LFA-1 on white blood cells. Leukemia Res. 2010, 34, 777–785. [Google Scholar]
- Balashova, N.V.; Crosby, J.A.; Al Ghofaily, L.; Kachlany, S.C. Leukotoxin confers beta-hemolytic activity to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balashova, N.V.; Diaz, R.; Balashov, S.V.; Crosby, J.A.; Kachlany, S.C. Regulation of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin secretion by iron. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8658–8661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.L.; Whitworth, L.C.; Clinkenbeard, K.D.; Clinkenbeard, P.A. Hemolytic activity of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 3209–3212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cortajarena, A.L.; Goni, F.M.; Ostolaza, H. Glycophorin as a receptor for Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin in erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12513–12519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.; Ghofaily, L.A.; Patel, J.; Balashova, N.V.; Freitas, A.C.; Labib, I.; Kachlany, S.C. Characterization of leukotoxin from a clinical strain of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Microb. Pathog. 2006, 40, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachlany, S.C.; Fine, D.H.; Figurski, D.H. Purification of secreted leukotoxin (LtxA) from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidels, L.; Proia, R.L.; Hart, D.A. Membrane receptors for bacterial toxins. Microbiol. Rev. 1983, 47, 596–620. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, P.H. Role of membrane gangliosides in the binding and action of bacterial toxins. J. Membr. Biol. 1982, 69, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, J.; Osborne, J.C., Jr.; Fishman, P.H.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Vaughan, M.; Brady, R.O. Effect of gangliosides and substrate analogues on the hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.L.; Moss, J.; Alving, C.R.; Fishman, P.H.; Brady, R.O. Choleragen (cholera toxin): A bacterial lectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, P.H.; Schnaar, R.L. Gangliosides in cell recognition and membrane protein regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 549–557. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, S.W.; Cuatrecasas, P. Mobility of cholera toxin receptors on rat lymphocyte membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 3844–3848. [Google Scholar]
- Nedelkoska, L.; Benjamins, J.A. Binding of cholera toxin B subunit: A surface marker for murine microglia but not oligodendrocytes or astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 53, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Jolivet-Reynaud, C.; Hauttecoeur, B.; Alouf, J.E. Interaction of Clostridium perfringens delta toxin with erythrocyte and liposome membranes and relation with the specific binding to the ganglioside GM2. Toxicon 1989, 27, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morova, J.; Osicka, R.; Masin, J.; Sebo, P. RTX cytotoxins recognize beta2 integrin receptors through N-linked oligosaccharides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5355–5360. [Google Scholar]
- Kiguchi, K.; Henning-Chubb, C.B.; Huberman, E. Glycosphingolipid patterns of peripheral blood lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes are cell specific. J. Biochem. 1990, 107, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yohe, H.C.; Wallace, P.K.; Berenson, C.S.; Ye, S.; Reinhold, B.B.; Reinhold, V.N. The major gangliosides of human peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages: Absence of ganglio series structures. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Coote, J.G. Structural and functional relationships among the RTX toxin determinants of gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 8, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Goni, F.M.; Ostolaza, H. E. coli alpha-hemolysin: A membrane-active protein toxin. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1998, 31, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lally, E.T.; Hill, R.B.; Kieba, I.R.; Korostoff, J. The interaction between RTX toxins and target cells. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Atapattu, D.N.; Albrecht, R.M.; McClenahan, D.J.; Czuprynski, C.J. Dynamin-2-dependent targeting of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin to mitochondrial cyclophilin D in bovine lymphoblastoid cells. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5357–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atapattu, D.N.; Czuprynski, C.J. Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin induces apoptosis of bovine lymphoblastoid cells (BL-3) via a caspase-9-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5504–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, K.P.; Pacheco, C.M.; Otis, L.L.; Baranwal, S.; Kieba, I.R.; Harrison, G.; Hersh, E.V.; Boesze-Battaglia, K.; Lally, E.T. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin requires lipid microdomains for target cell cytotoxicity. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelk, P.; Johansson, A.; Claesson, R.; Hanstrom, L.; Kalfas, S. Caspase 1 involvement in human monocyte lysis induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4448–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, G.; Cornett, P.A.; Tierney, L.M., Jr. Hemolytic anemia. Am. Fam. Physician 2004, 69, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Seewann, H.L. The hemolytic syndrome in subacute bacterial endocarditis. Acta Med. Austriaca 1979, 6, 192–194. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Forman, M.S.; Nishikubo, J.B.; Han, R.K.; Le, A.; Balashova, N.V.; Kachlany, S.C. Gangliosides Block Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA)-Mediated Hemolysis. Toxins 2010, 2, 2824-2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2122824
Forman MS, Nishikubo JB, Han RK, Le A, Balashova NV, Kachlany SC. Gangliosides Block Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA)-Mediated Hemolysis. Toxins. 2010; 2(12):2824-2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2122824
Chicago/Turabian StyleForman, Michael S., Jason B. Nishikubo, Rebecca K. Han, Amy Le, Nataliya V. Balashova, and Scott C. Kachlany. 2010. "Gangliosides Block Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA)-Mediated Hemolysis" Toxins 2, no. 12: 2824-2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2122824
APA StyleForman, M. S., Nishikubo, J. B., Han, R. K., Le, A., Balashova, N. V., & Kachlany, S. C. (2010). Gangliosides Block Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA)-Mediated Hemolysis. Toxins, 2(12), 2824-2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2122824