Muscle Strength, Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis Are Improved with Ursolic Acid Treatment in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Grip Strength Test
2.5. Sample Collections
2.6. Measurement of Serum Lipids
2.7. Observation and Analysis of Histopathology
2.8. Measurement of Serum Hormones
2.9. Real-Time PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
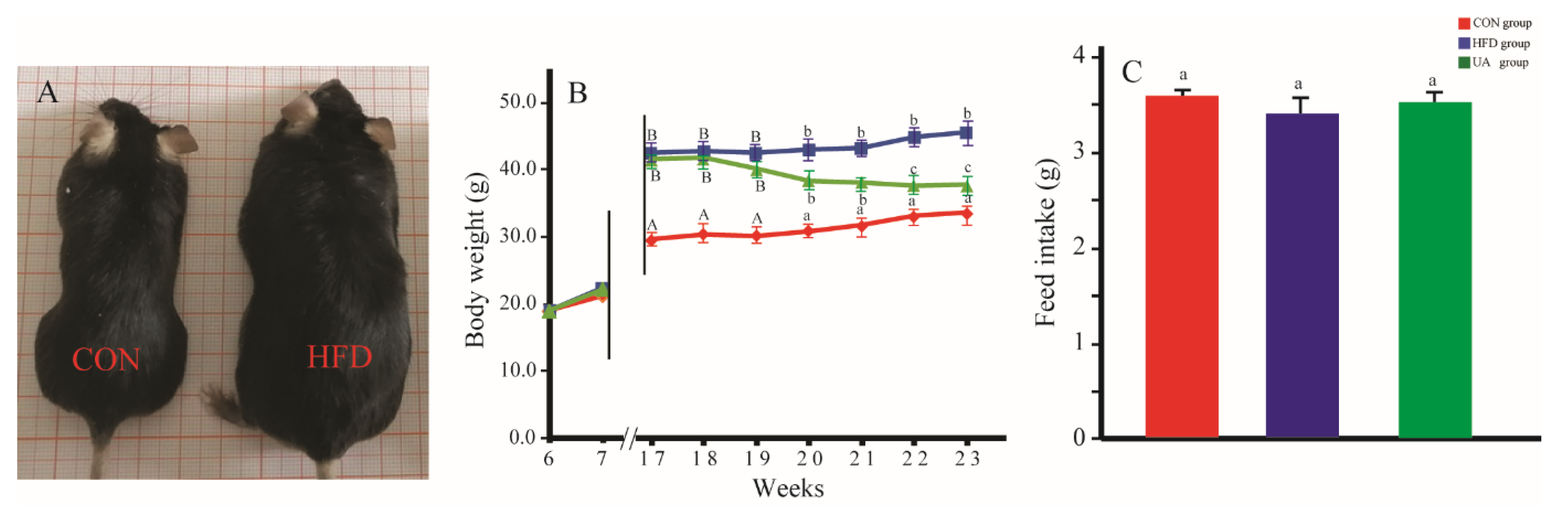
3.1. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Body Weight and Feed Intake
3.2. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Abdominal Fat and Liver Weight
3.3. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Grip Strength and Muscle Weight
3.4. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Serum Lipids
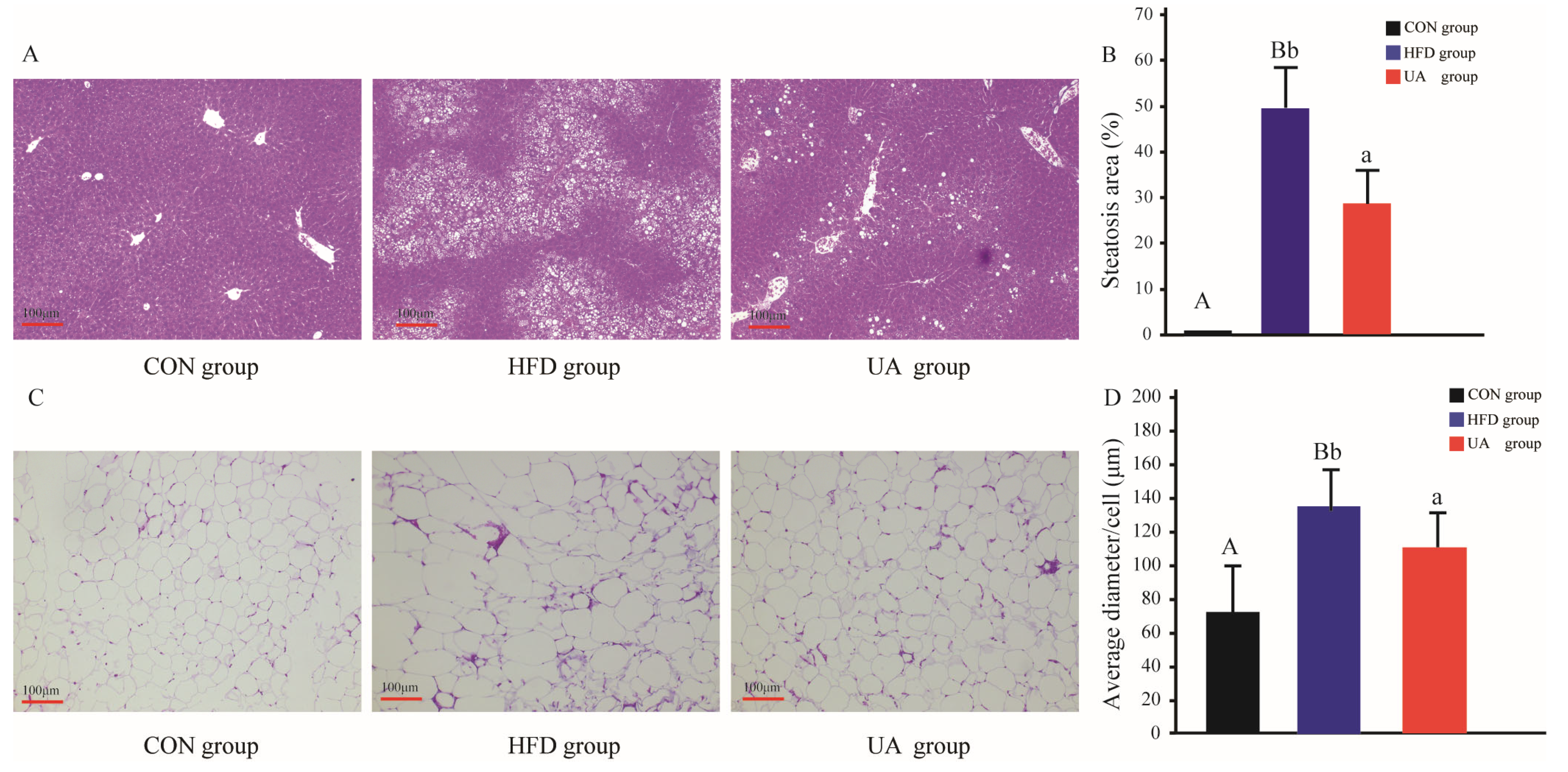
3.5. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Histological Changes in Liver and Abdominal Adipose Tissues
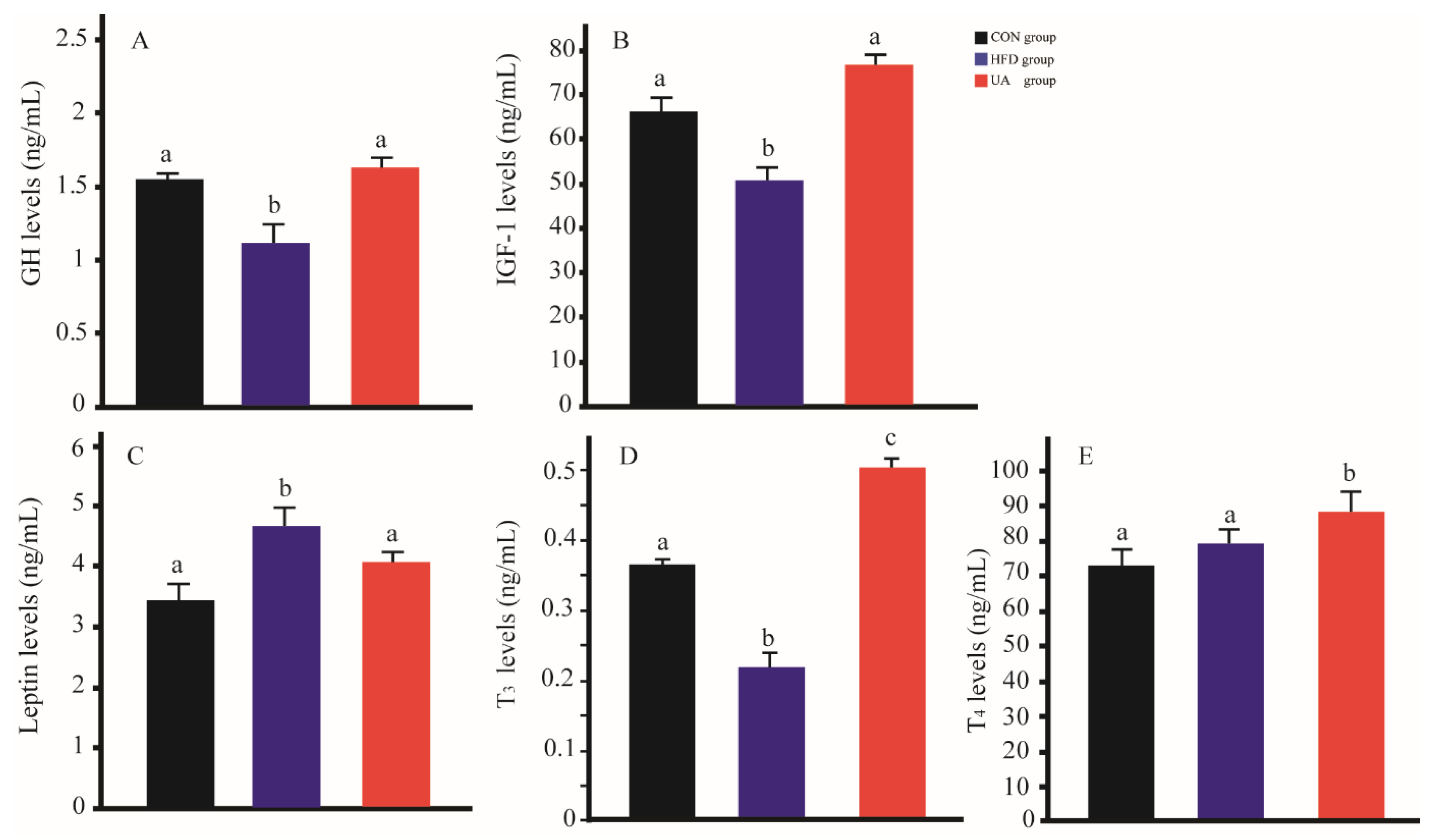
3.6. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on Serum Hormones
3.7. The Effect of Ursolic Acid on the Expression of Inflammation-Associated Genes in Abdominal Adipose Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| SO | Sarcopenic obesity |
| NAFLD | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| UA | Ursolic acid |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| TH | Thyroxine |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
References
- The World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight; WHO Media Center: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mopuri, R.; Ganjayi, M.; Banavathy, K.S.; Parim, B.N.; Meriga, B. Evaluation of anti-obesity activities of ethanolic extract of Terminalia paniculata bark on high fat diet-induced obese rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naomi, R.; Teoh, S.H.; Embong, H.; Balan, S.S.; Othman, F.; Bahari, H.; Yazid, M.D. The role of oxidative stress and inflammation in obesity and its impact on cognitive impairments-a narrative review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; Fernando, K.H.N.; Oh, J.Y.; Li, X.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ryu, B. Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of ishige okamurae. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The epidemiology of obesity: A big picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.S.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, H.D.; Kang, M.H.; Ji, Y.J.; Kim, G.S.; Jang, G.Y. Anti-obesity activity in 3T3-L1 cells of Cornus officinalis fruits harvested at different times. Processes 2022, 10, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.O. Genetics of obesity: What genetic association studies have taught us about the biology of obesity and its complications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Writing group for the european working group on sarcopenia in older people 2 (EWGSOP2), and the extended group for EWGSOP2. sarcopenia: Revised european consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Panjawatanan, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Jaruvongvanich, V.; Ungprasert, P. Sarcopenia and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A metaanalysis. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Vachliotis, I.D.; Mantzoros, C.S. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2023, 147, 155676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffl, M.; Chrudimsky, J.; Tufano, J.J. Using relative handgrip strength to identify children at risk of sarcopenic obesity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Busetto, L.; Cederholm, T.; Dicker, D.; Toplak, H.; Van Gossum, A.; Yumuk, V.; Vettor, R. Sarcopenic obesity: Time to meet the challenge. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh Pahlavani, H. Exercise therapy for people with sarcopenic obesity: Myokines and adipokines as effective actors. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 811751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaki, C.; Liatis, S.; Dalamaga, M.; Kokkinos, A. Sarcopenic obesity: Epidemiologic evidence, pathophysiology, and therapeutic perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Hong, S.; Kim, E.Y. Reference values of skeletal muscle mass for korean children and adolescents using data from the korean national health and nutrition examination survey 2009–2011. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodoshi, T.; Orkin, S.; Arce Clachar, A.C.; Bramlage, K.; Sun, Q.; Fei, L.; Beck, A.F.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Trout, A.T.; Mouzaki, M. Muscle mass is linked to liver disease severity in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Pediatr. 2020, 223, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, R.; Correa-Burrows, P.; Reyes, M.; Blanco, E.; Albala, C.; Gahagan, S. High cardiometabolic risk in healthy Chilean adolescents: Associations with anthropometric, biological and lifestyle factors. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, D.C.D.; Tan, T.M. Skeletal muscle loss and sarcopenia in obesity pharmacotherapy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, S.; Dyar, K.A.; Ciciliot, S.; Blaauw, B.; Sandri, M. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4294–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes. Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Park, H.Y. Association between muscular strength, abdominal obesity, and incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Korean population. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Choi, K.M. Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: Sarcopenic obesity. Metabolism 2023, 144, 155577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.M.; Nariya, D.M. Handgrip strength as a predictor of muscular strength and endurance: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2021, 15, YC01–YC04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, H.S.; Choi, W.S. Low muscle strength as risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in different metabolic conditions. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2024, 45, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.; Shardell, M.; Alley, D.; Cawthon, P.; Fragala, M.; Harris, T.; Kenny, A.M.; Pe-ters, K.W.; Luigi, F.; Guralnik, J.M. Criteria for clinically relevant weakness and low lean mass and their longitudinal association with incident mobility impairment and mortality: The foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) sarcopenia project. J. Gerontol. 2014, 69, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik Mohamed Sayed, U.F.; Moshawih, S.; Goh, H.P.; Kifli, N.; Gupta, G.; Singh, S.K.; Chellappan, D.K.; Dua, K.; Hermansyah, A.; Ser, H.L.; et al. Natural products as novel anti-obesity agents: Insights into mechanisms of action and potential for therapeutic management. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1182937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.; Ferreira, T.; Nascimento-Gonçalves, E.; Castro-Ribeiro, C.; Lemos, S.; Rosa, E.; Antunes, L.M.; Oliveira, P.A. Obesity rodent models applied to research with food products and natural compounds. Obesities 2022, 2, 171–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.; Ng, S.W.; Tan, J.Z.X.; Gupta, G.; Chellappan, D.K. Natural products in the management of obesity: Fundamental mechanisms and pharmacotherapy. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 143, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Yadav, V.; Jha, S.; Dighe, S.; Jain, S. Unveiling the potential of ursolic acid modified hyaluronate nanoparticles for combination drug therapy in triple negative breast cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 338, 122196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, A.; Sachithanandam, V.; Lalitha, P.; Adhikari, P.; Prakash, S.; Ramasubburayan, R.; Dhillon, D.; Muthukumaran, J.; Vinithkumar, N.V.; Sridhar, R.; et al. Decoding the multi-functional potential of ursolic acid: Antioxidant, antiproliferative, molecular dynamics, and biodegradability evaluations of a mangrove-derived terpenoid. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2025, 39, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miatmoko, A.; Jauhari, A.A.; Faradisa, A.A.; Cahyani, D.M.; Hariawan, B.S.; Susanto, J.; Pa-rumasivam, T.; Hendradi, E.; Sari, R. Oral curative therapeutic study of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced mouse liver damage of chitosan-coated ursolic acid nio-somes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, S.; Khan, K.; Hafeez, A.; Irfan, M.; Armaghan, M.; Rahman, A.U.; Gürer, E.S.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Butnariu, M.; Bagiu, I.C. Ursolic acid: A natural modulator of signaling networks in different cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Qin, P.; Cheng, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, R.; Gao, W. Ursolic acid: Biological functions and application in animal husbandry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1251248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Mao, J.; Zhou, S. Using network pharmacology and molecular docking verification to explore the mechanism of ursolic acid in the treatment of osteoporosis. Medicine 2022, 101, e32222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, S.D.; Elmore, C.J.; Bongers, K.S.; Ebert, S.M.; Fox, D.K.; Dyle, M.C.; Bullard, S.A.; Adams, C.M. Ursolic acid increases skeletal muscle and brown fat and decreases diet-induced obesity, glucose intolerance and fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Hu, X.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Yan, X.; Peng, D.; Ping, J.; Yan, Y. Ursolic acid induces white adipose tissue beiging in high-fat-diet obese male mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6490–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Z.; Zuo, G.W.; Yao, L.; Yuan, C.L.; Li, H.F.; Lai, Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.Q.; Yamahara, J.; et al. Ursolic acid ameliorates adipose tissue insulin resistance in aged rats via activating the Akt-glucose transporter 4 signaling pathway and inhibiting inflammation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liao, X.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Meng, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Therapeutic role of ursolic Acid on ameliorating hepatic steatosis and improving metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, A.R.; Rosa, J.M.; Cunha, M.P.; Rodrigues, A.L. Anxiolytic-like effects of ursolic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 758, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannampuzha, S.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Protective role of ursolic acid against cispla-tin-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis in the liver of Swiss albino mice. Med. Oncol. 2025, 42, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, M.; Tsujikawa, H.; Effendi, K.; Ojima, H.; Harada, K.; Zen, Y.; Kondo, F.; Nakano, M.; Kage, M.; Sumida, Y.; et al. Pathological findings of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pathol. Int. 2017, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, M.E.; Dent, R.R.M.; McPherson, R. High-quality weight loss in obesity: Importance of skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2025, 74, dbi250003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.; Kim, H.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Reza, M.M.; Martin, K.A.; Kundu, P.; Cox, L.M.; Selkrig, J.; Posma, J.M.; Zhang, H.; et al. The gut microbiota influences skeletal muscle mass and function in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 1, eaan5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, Í.M.P.; Argilés, J.M.; Rueda, R.; Ramírez, M.; Pedrosa, J.M.L. Skeletal muscle atrophy and dysfunction in obesity and type-2 diabetes mellitus: Myocellular mechanisms involved. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.W.; Khang, A.R.; Lee, H.W.; Son, S.M.; Kang, Y.H. Relative handgrip strength as a marker of metabolic syndrome: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) VI (2014-2015). Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2018, 11, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, C.; Wu, D.; Feng, Q. Handgrip strength and low muscle strength rate in chinese adults-China, 2020. China CDC Wkly. 2024, 6, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, J.M.; Nakaishi, A.P.M.; Cangussu-Oliveira, L.M.; Freire Júnior, R.C.; Spilla, S.B.; Abreu, D.C.C. Relationship between grip strength and global muscle strength in community-dwelling older people. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 82, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W. Muscle strength: Clinical and prognostic value of hand-grip dynamometry. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, H.; Kato, K.; Sawada, S.S.; Gando, Y.; Kawakami, R.; Miyachi, M.; Nagatomi, R.; Tashiro, M.; Matsubayashi, Y.; Kodama, S.; et al. Physical fitness and dyslipidemia among japanese: A cohort study from the niigata wellness study. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Gavrilova, O.; Pack, S.; Jou, W.; Mullen, S.; Sumner, A.E.; Cushman, S.W.; Periwal, V. Hypertrophy and/or hyperplasia: Dynamics of adipose tissue growth. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Dossus, L.; Barquera, S.; Blottière, H.M.; Franks, P.W.; Gunter, M.; Hwalla, N.; Hursting, S.D.; Leitzmann, M.; Margetts, B.; et al. Energy balance and obesity: What are the main drivers? Cancer Causes Control 2017, 28, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bays, H.E.; Toth, P.P.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Abate, N.; Aronne, L.J.; Brown, W.V.; Gonzalez-Campoy, J.M.; Jones, S.R.; Kumar, R.; La Forge, R.; et al. Obesity, adiposity, and dyslipidemia: A consensus statement from the national lipid association. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013, 7, 304–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaumerova, B.; Rosolova, H. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijet, M.; Pijet, B.; Litwiniuk, A.; Pajak, B.; Gajkowska, B.; Orzechowski, A. Leptin impairs myogenesis in C2C12 cells through JAK/STAT and MEK signaling pathways. Cytokine 2013, 61, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skubic, C.; Drakulić, Ž.; Rozman, D. Personalized therapy when tackling nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A focus on sex, genes, and drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, T.E.; Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. Adipokines and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Multiple interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, T.; Ara, I.; Guadalupe-Grau, A.; Larsen, S.; Stallknecht, B.; Olmedillas, H.; Santana, A.; Helge, J.W.; Calbet, J.A.; Guerra, B. Leptin receptor 170 kDa (OB-R170) protein expression is reduced in obese human skeletal muscle: A potential mechanism of leptin resistance. Exp. Physiol. 2010, 95, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, K.; Ochi, M.; Tabara, Y.; Nagai, T.; Igase, M.; Miki, T. Leptin in sarcopenic visceral obesity: Possible link between adipocytes and myocytes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, S.; Salgado Nunez Del Prado, S.; Celi, F.S. Thyroid hormone action and energy expenditure. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.S.; Zhao, Y.F.; Song, Y.F.; Xu, C.; Yang, J.M.; Xuan, S.M.; Yan, H.L.; Yu, C.X.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Dietary high-fat lard intake induces thyroid dysfunction and abnormal morphology in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, E.; Wanke, R.; Schenck, E.; Hermanns, W.; Brem, G. Effects of growth hormone overproduction on grip strength of transgenic mice. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1995, 133, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpani, A.; Welch, L.; Plummer, D.; Churilla, J.; Benson, M.; Hossain, J.; Permuy, J.; Carakushansky, M.; Mauras, N. Impact of growth hormone on skeletal muscle strength, power, endurance, and agility in prepubertal boys with short stature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 2, dgaf203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ge, X. Meat science and muscle biology symposium—Mechanism of growth hormone stimulation of skeletal muscle growth in cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudman, D.; Feller, A.G.; Nagraj, H.S.; Gergans, G.A.; Lalitha, P.Y.; Goldberg, A.F.; Schlenker, R.A.; Cohn, L.; Rudman, I.W.; Mattson, D.E. Effects of human growth hormone in men over 60 years old. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathes, S.; Fahrner, A.; Luca, E.; Krützfeldt, J. Growth hormone/IGF-I-dependent signaling restores decreased expression of the myokine SPARC in aged skeletal muscle. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Morikawa, M.; Nixon, T. A dual effector theory of growth-hormone action. Differentiation 1985, 29, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappola, A.R.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Wand, G.S.; Volpato, S.; Fried, L.P. Association of IGF-I levels with muscle strength and mobility in older women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilade, S.; Christensen, M.B.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. An overview of obesity mechanisms in humans: Endocrine regulation of food intake, eating behaviour and common determinants of body weight. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romacho, T.; Glosse, P.; Richter, I.; Elsen, M.; Schoemaker, M.H.; van Tol, E.A.; Eckel, J. Nutritional ingredients modulate adipokine secretion and inflammation in human primary adipocytes. Nutrients 2015, 7, 865–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Panigrahi, D.P.; Patil, S.; Bhutia, S.K. Autophagy in health and disease: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.K. Skeletal muscle as an endocrine organ: The role of myokines in muscle-fat cross-talk. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, S275–S276. [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.A.; Ranganathan, S.; Li, C.; Wood, L.; Ranganathan, G. Adipose tissue tumor ne-crosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E745–E751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, M.; Ji, H.; Su, W.; Song, W.; Zhang, D.; Su, W.; Liu, S. Hypolipidemic and anti-obesity effect of anserine on mice orally administered with high-fat diet via regulating SREBP-1, NLRP3, and UCP-1. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2024, 68, e2300471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebkar, A. Potential efficacy of ginger as a natural supplement for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Rodrigues, K.C.D.C.; Anaruma, C.P.; Sant’Ana, M.R.; de Campos, T.D.P.; Gaspar, R.S.; Canciglieri, R.D.S.; de Melo, D.G.; Mekary, R.A.; da Silva, A.S.R.; et al. Short-term strength training reduces gluconeogenesis and NAFLD in obese mice. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 241, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Perakakis, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Fatty liver in lipodystrophy: A review with a focus on therapeutic perspectives of adiponectin and/or leptin replacement. Metabolism 2019, 96, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Huo, X.; Sun, P.; Ma, X.; Peng, J.; Liu, K. Effects of calycosin against high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Forward Primer (5′−3′) | Reverse Primer (5′−3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | TGCCACCTTTTGACAGTGATG | TTCTTGTGACCCTGAGCGAC |
| TNF-α | TCTTTCGGAGAAGGTTGCCC | AGAAGTCCTGCCACTTCACG |
| β-actin | AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC | CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT |
| Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | HFD | UA | |
| Grip strength (g force (gf)) | 118.34 ± 13.24 a | 99.68 ± 14.71 b | 112.86 ± 11.52 a |
| Triceps (mg) | 234.77 ± 25.14 a | 198.64 ± 17.75 b | 242.54 ± 15.68 a |
| Quadriceps (mg) | 415.31 ± 39.03 a | 369.61 ± 38.73 b | 364.00 ± 27.38 b |
| Gastrocnemius (mg) | 288.61 ± 21.89 a | 271.64 ± 17.43 b | 290.29 ± 21.82 a |
| Soleus (mg) | 14.26 ± 1.06 | 16.58 ± 0.95 | 15.14 ± 1.32 |
| Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | HFD | UA | |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.64 ± 0.04 a | 1.18 ± 0.07 b | 0.86 ± 0.05 a |
| TC (mmol/L) | 2.53 ± 0.28 a | 4.69 ± 0.23 b | 3.07 ± 0.31 a |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.34 ± 0.14 a | 3.64 ± 0.17 b | 3.24 ± 0.25 b |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 0.21 ± 0.03 a | 0.42 ± 0.05 b | 0.26 ± 0.08 a |
| FFA (mmol/L) | 0.37 ± 0.04 a | 0.78 ± 0.11 b | 0.44 ± 0.06 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.; Cao, L. Muscle Strength, Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis Are Improved with Ursolic Acid Treatment in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193158
Kang D, Cao L. Muscle Strength, Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis Are Improved with Ursolic Acid Treatment in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193158
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Dongyang, and Li Cao. 2025. "Muscle Strength, Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis Are Improved with Ursolic Acid Treatment in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193158
APA StyleKang, D., & Cao, L. (2025). Muscle Strength, Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis Are Improved with Ursolic Acid Treatment in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients, 17(19), 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193158






