Posterior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence with Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Reduction for the Affected Canal at the Video-Head Impulse Test: Considerations to Pathomechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Description
2.1. Case 1
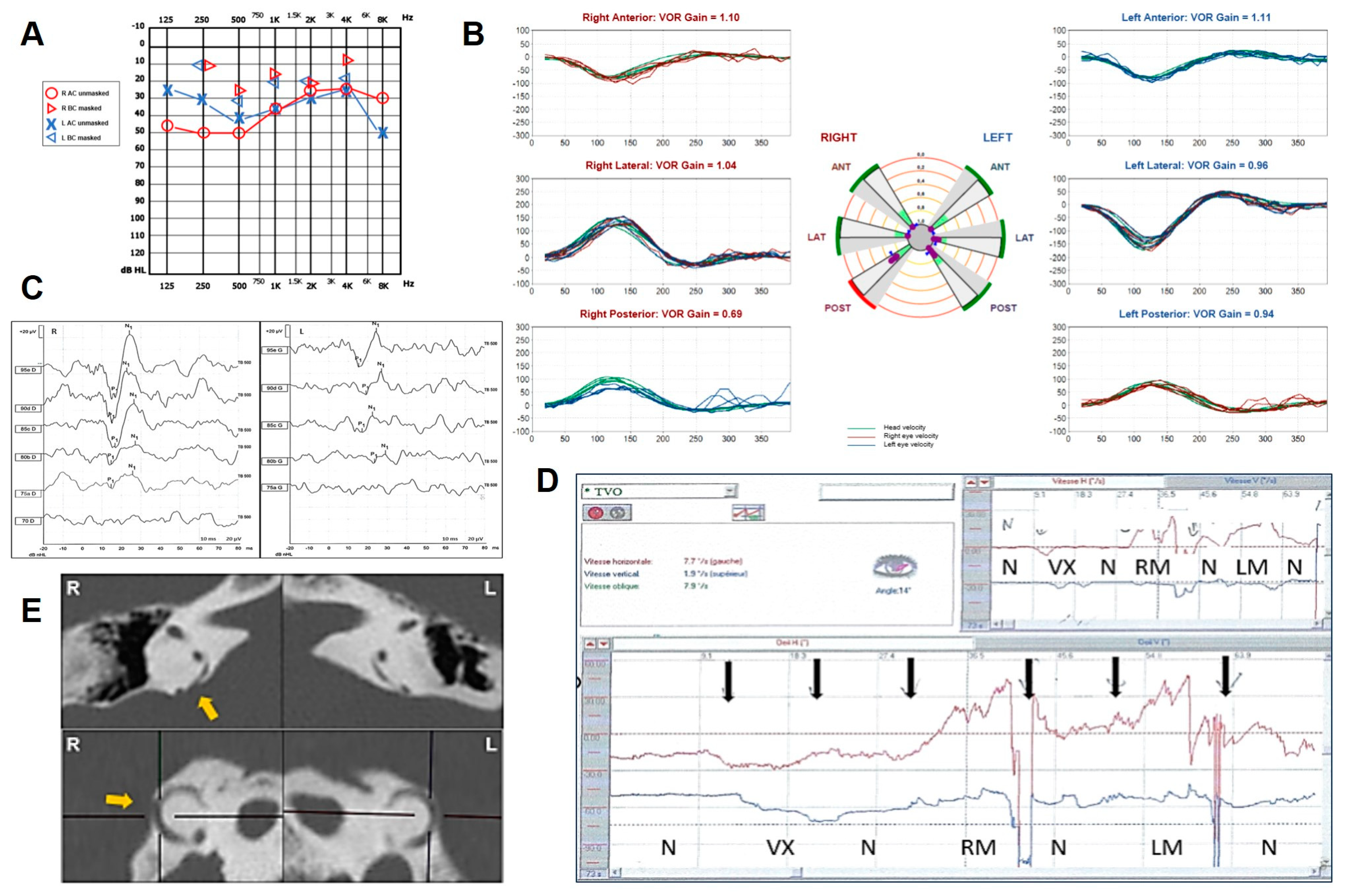
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
2.4. Case 4
2.5. Case 5
2.6. Case 6
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Minor, L.B.; Solomon, D.; Zinreich, J.S.; Zee, D.S. Sound- and/or pressure-induced vertigo due to bone dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1998, 124, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Gopen, Q.; Poe, D.S. Clinical and Diagnostic Characterization of Canal Dehiscence Syndrome: A Great Otologic Mimicker. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, S.N.; Rosowski, J.J. Conductive hearing loss caused by third-window lesions of the inner ear. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, W.W.; Carey, J.P.; Minor, L.B. Canal dehiscence. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.-L. Third Window Lesions. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 57–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, M.M.; Rabbitt, R.D. Biomechanics of Third Window Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Smith, C.M.; Burgess, A.M.; Dlugaiczyk, J. A Review of Neural Data and Modelling to Explain How a Semicircular Canal Dehiscence (SCD) Causes Enhanced VEMPs, Skull Vibration Induced Nystagmus (SVIN), and the Tullio Phenomenon. Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, G.; Curthoys, I.S.; Castellucci, A.; Dumas, L.; Perrin, P.; Schmerber, S. A bone-conducted Tullio phenomenon—A bridge to understand skull vibration induced nystagmus in superior canal dehiscence. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1183040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldè, M.; Cantarella, G. Commentary on “Assessment of the Eustachian tube: A review”. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackym, P.A.; Balaban, C.D.; Zhang, P.; Siker, D.A.; Hundal, J.S. Third Window Syndrome: Surgical Management of Cochlea-Facial Nerve Dehiscence. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynard, P.; Idriss, S.; Ltaief-Boudrigua, A.; Bertholon, P.; Pirvan, A.; Truy, E.; Thai-Van, H.; Ionescu, E.C. Proposal for a Unitary Anatomo-Clinical and Radiological Classification of Third Mobile Window Abnormalities. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 792545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianoli, G.; Soileau, J.; Shore, B. Description of a New Labyrinthine Dehiscence: Horizontal Semicircular Canal Dehiscence at the Tympanic Segment of the Facial Nerve. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 879149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, E.C.; Reynard, P.; Damien, M.; Ltaief-Boudrigua, A.; Hermann, R.; Gianoli, G.J.; Thai-Van, H. Why should multiple dehiscences of the otic capsule be considered before surgically treating patients with superior semicircular canal dehiscence? A radiological monocentric review and a case series. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1209567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Hong, J.; Morris, R.; Iqbal, J.; Lennox-Bowley, A.; Saniasiaya, J. X-Linked Gusher Disease DFNX2 in Children, a Rare Inner Ear Dysplasia with Mixed Hearing and Vestibular Loss. Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Paladin, A.; Phillips, G.; Raske, M.; Vega, L.; Peterson, D.; Sie, K.C. Semicircular canal dehiscence in the pediatric population. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiklejohn, D.A.; Corrales, C.E.; Boldt, B.M.; Sharon, J.D.; Yeom, K.W.; Carey, J.P.; Blevins, N.H. Pediatric Semicircular Canal Dehiscence: Radiographic and Histologic Prevalence, with Clinical Correlation. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxby, A.J.; Gowdy, C.; Fandiño, M.; Chadha, N.K.; Kozak, F.K.; Sargent, M.A.; Lea, J. Radiological prevalence of superior and posterior semicircular canal dehiscence in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.A.; Liu, Y.F.; Nguyen, S.A.; McRackan, T.R.; Meyer, T.A.; Rizk, H.G. Posterior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence: Case Series and Systematic Review. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, J.E.; Crowson, M.G.; DeAngelo, E.J.; Belden, C.J.; Saunders, J.E. Posterior semicircular canal dehiscence: CT prevalence and clinical symptoms. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiya, S.; Cureoglu, S.; Kariya, S.; Morita, N.; Nomiya, R.; Schachern, P.A.; Nishizaki, K.; Paparella, M.M. Posterior semicircular canal dehiscence: A histopathologic human temporal bone study. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimmer, H.; Hamann, K.F.; Zeiter, S.; Naumann, A.; Rummeny, E.J. Semicircular canal dehiscence in HR multislice computed tomography: Distribution, frequency, and clinical relevance. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2012, 269, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmali, M.; Polat, A.V.; Kucuk, H.; Atmaca, S.; Aksoy, A. Semicircular canal dehiscence: Frequency and distribution on temporal bone CT and its relationship with the clinical outcomes. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e606–e609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bulck, P.; Leupe, P.-J.; Forton, G.E. Children with posterior semicircular canal dehiscence: A case series. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 123, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanspauwen, R.; Salembier, L.; Van den Hauwe, L.; Parizel, P.; Wuyts, F.L.; Van de Heyning, P.H. Posteri-or semicircular canal dehiscence: Value of VEMP and multidetector CT. B-ENT 2006, 2, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gopen, Q.; Zhou, G.; Poe, D.; Kenna, M.; Jones, D. Posterior semicircular canal dehiscence: First reported case series. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, Z.W.; McEvoy, T.P.; Mikulec, A.A. Quantification of hearing loss in patients with posterior semicircular canal dehiscence. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2015, 135, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, A.; Mammen, M.D.; Lepcha, A.; Alex, A. Posterior semicircular canal dehiscence: A diagnostic and surgical conundrum. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e229573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasic, M.; Trang, A.; Chung, L.K.; Ung, N.; Thill, K.; Zarinkhou, G.; Gopen, Q.S.; Yang, I. Clinical Characteristics of Posterior and Lateral Semicircular Canal Dehiscence. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2015, 76, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci, A.; Botti, C.; Bettini, M.; Fernandez, I.J.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Crocetta, F.M.; Fornaciari, M.; Lusetti, F.; Renna, L.; et al. Case Report: Could Hennebert’s Sign Be Evoked Despite Global Vestibular Impairment on Video Head Impulse Test? Considerations upon Pathomechanisms Underlying Pressure-Induced Nystagmus due to Labyrinthine Fistula. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 634782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassim, M.K.; Patel, K.G.; Buchman, C.A. Lateral Semicircular Canal Dehiscence. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-C.; Sha, Y.; Dai, C.-F. Another etiology for vertigo due to idiopathic lateral semicircular canal bony defect. Auris Nasus Larynx 2011, 38, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janky, K.L.; Patterson, J.N.; Shepard, N.T.; Thomas, M.L.A.; Honaker, J.A. Effects of Device on Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) Gain. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dooren, T.S.; Starkov, D.; Lucieer, F.M.P.; Vermorken, B.; Janssen, A.M.L.; Guinand, N.; Pérez-Fornos, A.; Van Rompaey, V.; Kingma, H.; van de Berg, R. Comparison of three video head impulse test systems for the diagnosis of bilateral vestibulopathy. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.L.; Kong, J.; Flanagan, S.; Pogson, J.; Croxson, G.; Pohl, D.; Welgampola, M.S. Prevalence of vestibular dysfunction in patients with vestibular schwannoma using video head-impulses and vestibular-evoked potentials. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.L.; McGarvie, L.A.; Reid, N.; Young, A.S.; Halmagyi, G.M.; Welgampola, M.S. Vestibular neuritis affects both superior and inferior vestibular nerves. Neurology 2016, 87, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnutzer, A.A.; Bockisch, C.J.; Buffone, E.; Weber, K.P. Association of posterior semicircular canal hypofunction on video-head-impulse testing with other vestibulo-cochlear deficits. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Brandolini, C.; Del Vecchio, V.; Giordano, D.; Ghidini, A.; Ferri, G.G.; Pirodda, A. Isolated horizontal canal hypofunction differentiating a canalith jam from an acute peripheral vestibular loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-U.; Kim, H.-J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Koo, J.-W.; Yang, X.; Kim, J.-S. Evolution in the Findings of Head-Impulse Tests during the Attacks of Menière’s Disease. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e744–e750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Botti, C.; Delmonte, S.; Quaglieri, S.; Rebecchi, E.; Armato, E.; Ralli, M.; Manfrin, M.L.; et al. Feasibility of using the video-head impulse test to detect the involved canal in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo presenting with positional downbeat nystagmus. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 578588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Piras, G.; Del Vecchio, V.; Ferri, G.G.; Ghidini, A.; Brandolini, C. Which inner ear disorders lie behind a selective posterior semicircular canal hypofunction on video head impulse test? Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Botti, C.; Delmonte, S.; Bettini, M.; Lusetti, F.; Brizzi, P.; Ruberto, R.; Gamberini, L.; Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; et al. Vestibular assessment in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Role in the prediction of hearing outcome and in the early detection of vascular and hydropic pathomechanisms. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1127008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamer, L.; Bassant, S.; Alhazmi, R.; Alzahrani, M. Rare otologic presentation of cat eye syndrome. Ann. Saudi Med. 2019, 39, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Ratnayake, S.; Crunkhorn, R.; Iqbal, J.; Strachan, L.; Avula, S. Audiovestibular Quantification in Rare Third Window Disorders in Children. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Piras, G.; Del Vecchio, V.; Crocetta, F.M.; Maiolo, V.; Ferri, G.G.; Ghidini, A.; Brandolini, C. The effect of superior canal dehiscence size and location on audiometric measurements, vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials and video-head impulse testing. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Chiarovano, E.; Cheng, K.; Manzari, L.; McGarvie, L.A.; MacDougall, H.G. Video-head impulse test in superior canal dehiscence. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2021, 141, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikka, T.; Slim, M.A.M.; Gaggini, M.; Kontorinis, G. Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) Findings in Patients with Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence: A Case–Control Study. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2021, 17, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; Botti, C.; Del Vecchio, V.; Brandolini, C.; Ferri, G.G.; Ghidini, A.; Armato, E. Possible pathomechanisms accounting for both sound/pressure-induced eye movements and video head impulse test data in superior canal dehiscence. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2021, 141, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renteria, A.E.; Elblidi, A.; Altamami, N.; Alhabib, S.; Saliba, I. Video Head Impulse Test Demonstrates a Residual Function after Plugging of Dehiscent Superior Semicircular Canal. Otol. Neurotol. 2023, 44, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Alfarghal, M.; Brandolini, C.; Piras, G.; Armato, E.; Ruberto, R.R.; Brizzi, P.; Presutti, L.; et al. Impaired Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex on Video Head Impulse Test in Superior Canal Dehiscence: “Spontaneous Plugging” or Endolymphatic Flow Dissipation? Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 802–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.P.; Migliaccio, A.A.; Minor, L.B. Semicircular canal function before and after surgery for superior canal dehiscence. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantokoudis, G.; Tehrani, A.S.S.; Wong, A.L.; Agrawal, Y.; Wenzel, A.; Carey, J.P. Adaptation and Compensation of Vestibular Responses Following Superior Canal Dehiscence Surgery. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, O.A.; Elmoazen, D.M.; Abd-Elbaky, F.A. Towards a new staging of Ménière’s disease: A vestibular approach. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2019, 39, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaci, B.; Nooristani, M.; Mijovic, T.; Maheu, M. Usefulness of Video Head Impulse Test Results in the Identification of Meniere’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 581527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büki, B.; Hanschek, M.; Jünger, H. Vestibular neuritis: Involvement and long-term recovery of individual semicircular canals. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navari, E.; Cerchiai, N.; Casani, A.P. Assessment of Vestibulo-ocular Reflex Gain and Catch-up Saccades during Vestibular Rehabilitation. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e1111–e1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Yanagi, H.; Morita, S.; Hoshino, K.; Fukuda, A.; Nakamaru, Y.; Homma, A. Evaluation of Vertical Semicircular Canal Function in Patients with Vestibular Schwannoma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulueta-Santos, C.; Lujan, B.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Perez-Fernandez, N. The vestibulo-ocular reflex assessment in patients with Ménière’s disease: Examining all semicircular canals. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2014, 134, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-U.; Kim, H.-J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-S. Ictal downbeat nystagmus in Ménière disease: A cross-sectional study. Neurology 2020, 95, e2409–e2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A.; Malara, P.; Martellucci, S.; Delmonte, S.; Ghidini, A. Fluctuating Posterior Canal Function in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Depending on How and Where Otoconia Are Disposed. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e193–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wolf, M.J.F.; Dawe, N.; Jervis, S.; Kumar, R.; Dalton, C.L.; Lindley, K.; Irving, R. Transmastoid Occlusion Surgery for Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Syndrome Improves Patient-Reported Quality-of-Life Measures and corrects cVEMP Thresholds and Amplitudes. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.K.; van de Berg, R.; van Rompaey, V.; Bisdorff, A.; Hullar, T.E.; Welgampola, M.S.; Carey, J.P. Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome: Diagnostic criteria consensus document of the committee for the classification of vestibular disorders of the Bárány Society. J. Vestib. Res. 2021, 31, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Manzari, L. A Simple Specific Functional Test for SCD: VEMPs to High Frequency (4000 Hz) Stimuli—Their Origin and Explanation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 612075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, S.T.; Aw, G.E.; Todd, M.J.; Bradshaw, A.P.; Halmagyi, G.M. Three-dimensional vibration-induced vestibulo-ocular reflex identifies vertical semicircular canal dehiscence. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2011, 12, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.L.; Andresen, N.S.; Chari, D.A.; Pogson, J.M.; Lauer, A.M.; Rabbitt, R.D.; Carey, J.P.; Santos, F.; Ward, B.K. Otolith Membrane Herniation, not Semicircular Canal Duct Dilation, Is Associated with Decreased Caloric Responses in Ménière’s Disease. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2023, 24, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, M.; Yoshida, T.; Morimoto, K.; Teranishi, M.; Nakashima, T.; Naganawa, S. Endolymphatic hydrops in superior canal dehiscence and large vestibular aqueduct syndromes. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanis, M.; De Jong, R.; Miao, T.; Hwang, L.; Lum, M.; Kaur, T.; Willis, S.; Arsenault, J.J.; Duong, C.; Yang, I.; et al. Concurrent superior semicircular canal dehiscence and endolymphatic hydrops: A novel case series. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 78, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Hautefort, C.; Guichard, J.P.; Horion, J.; Herman, P.; Kania, R.; Houdart, E.; Verillaud, B.; Vitaux, H.; Attyé, A.; et al. MRI contribution for the detection of endolymphat-ic hydrops in patients with superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, I.; Maniakas, A.; Benamira, L.Z.; Nehme, J.; Benoit, M.; Montreuil-Jacques, V. Superior canal dehiscence syndrome: Clinical manifestations and radiologic correlations. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2014, 271, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.W.; Janky, K.; Minor, L.B.; Carey, J.P. Superior canal dehiscence size: Multivariate assessment of clinical impact. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Rajagopal, R.; Lloyd, G. Systematic Review of Round Window Operations for the Treatment of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2019, 15, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
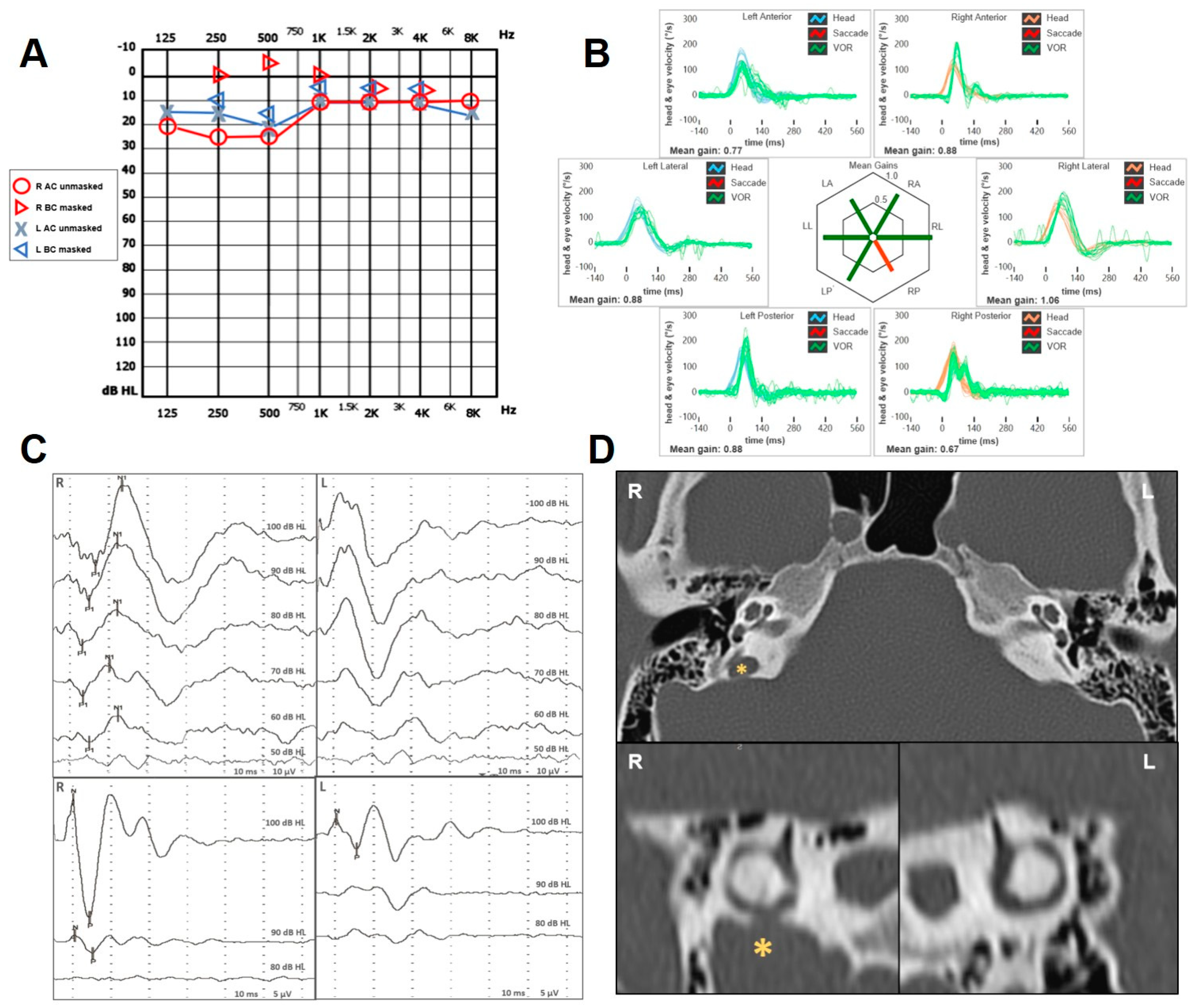

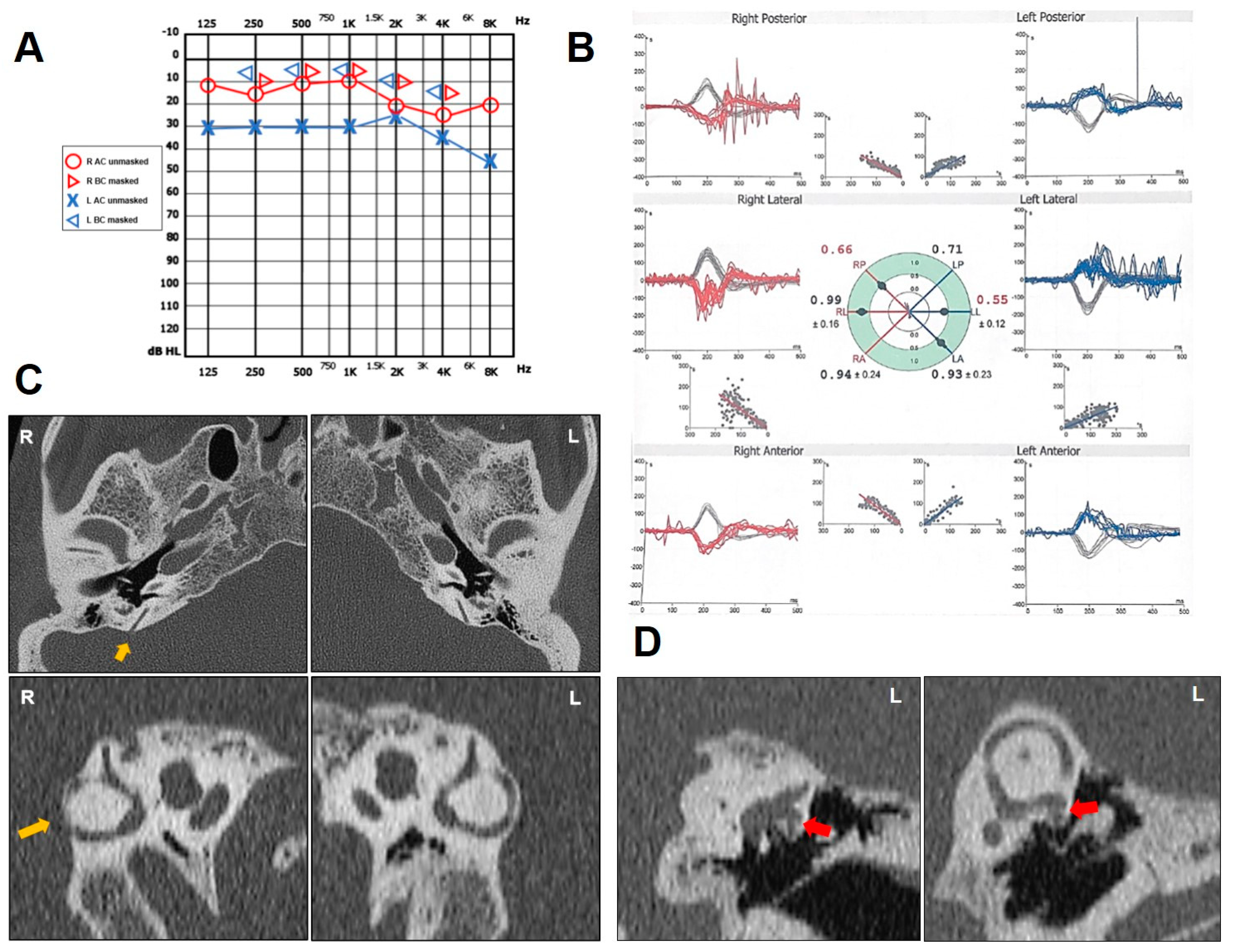
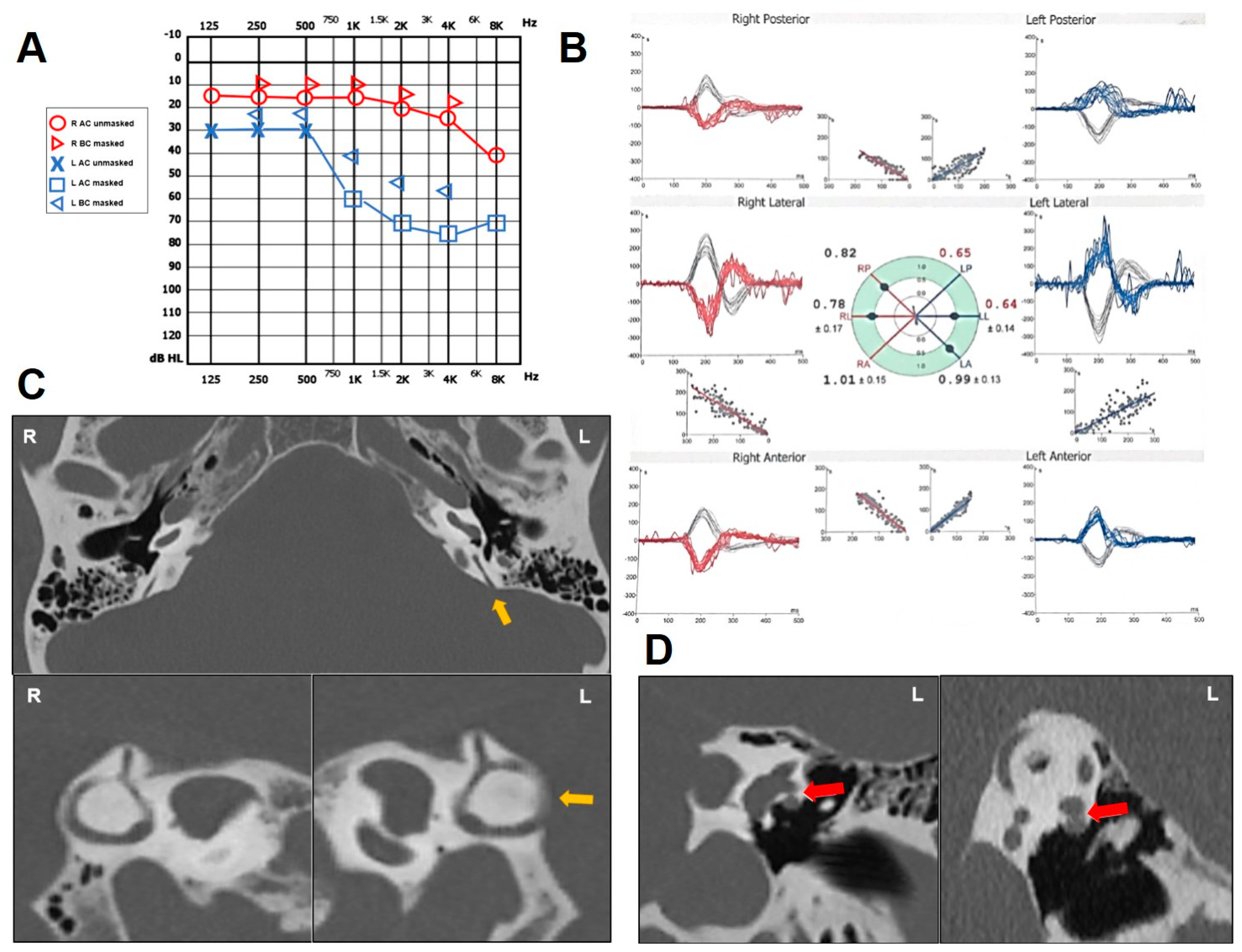
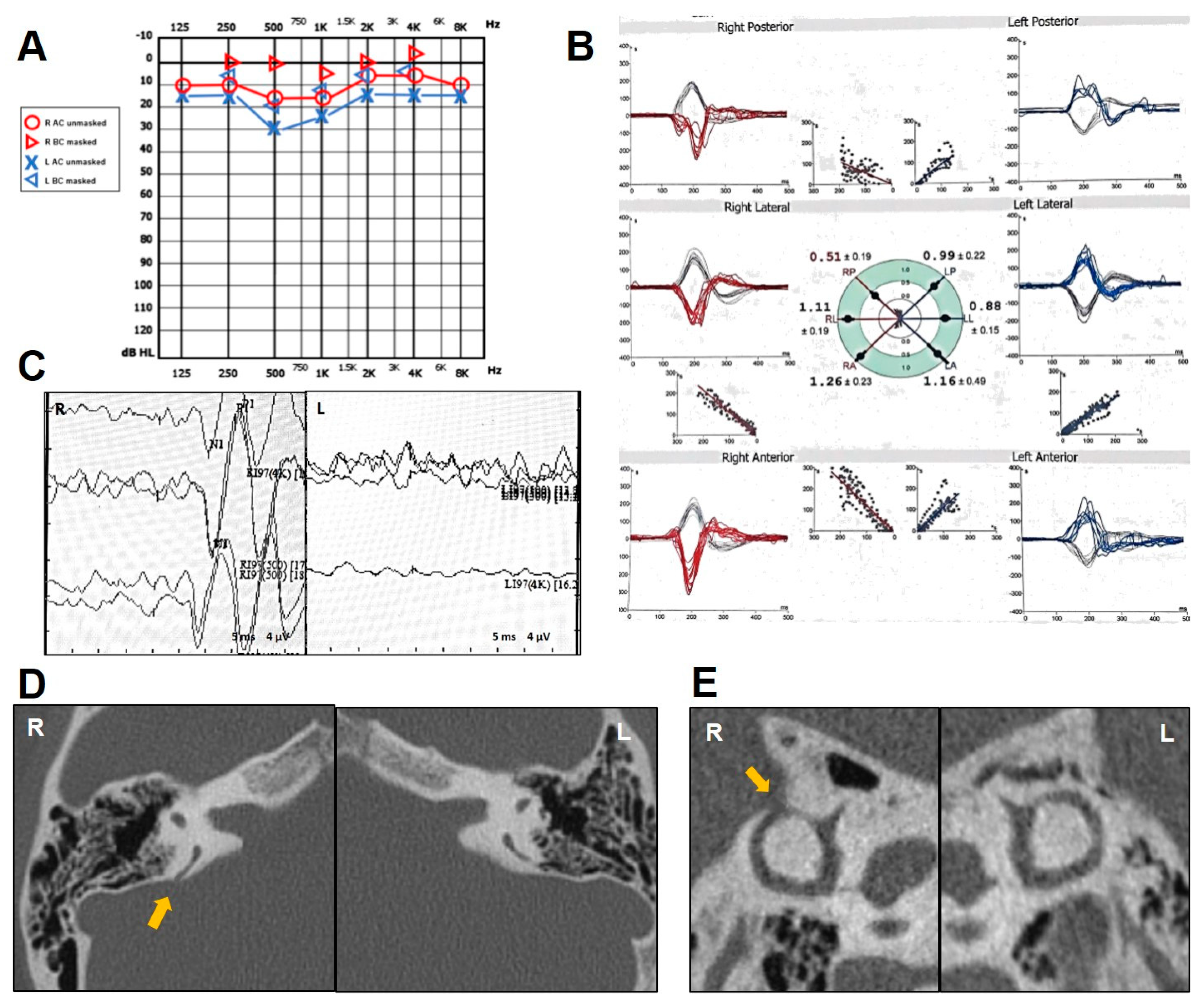
| n | Age (y), Sex | PSCD Side | Other Findings | Auditory Symptoms and Signs | Vestibular Symptoms and Signs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HL | Pulsatile Tinnitus | Hyperacusis | Autophony | Aural Fullness | Audiometry | Dizziness | Acute Vertigo | H/T | VEMPs | Caloric Test | VOR Reduction on vHIT | ||||
| 1 | 18, F | R | − | − | + | + | + | + | pseudo-CHL | − | − | − | enhanced | − | R PSC |
| 2 | 44, F | L | − | + | + | − | − | + | up-sloping mixed HL | + | L PSC BPPV | − | enhanced | normal | L PSC |
| 3 | 59, M | R | L HSCD with FN | − | + | − | + | − | normal | + | − | − | enhanced | − | R PSC, L HSC |
| 4 | 68, M | L | L HSCD with FN | + | + | − | + | − | down-sloping mixed HL | − | + | − | enhanced | − | L PSC, L HSC |
| 5 | 13, F | R | - | - | + | - | - | - | CHL | - | + | + | enhanced | - | R PSC |
| 6 | 65, F | R | - | + | - | - | - | + | mixed HL | + | - | + | enhanced | - | R PSC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellucci, A.; Dumas, G.; Abuzaid, S.M.; Armato, E.; Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; Alfarghal, M.; Ruberto, R.R.; Brizzi, P.; Ghidini, A.; et al. Posterior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence with Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Reduction for the Affected Canal at the Video-Head Impulse Test: Considerations to Pathomechanisms. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 317-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14020028
Castellucci A, Dumas G, Abuzaid SM, Armato E, Martellucci S, Malara P, Alfarghal M, Ruberto RR, Brizzi P, Ghidini A, et al. Posterior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence with Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Reduction for the Affected Canal at the Video-Head Impulse Test: Considerations to Pathomechanisms. Audiology Research. 2024; 14(2):317-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellucci, Andrea, Georges Dumas, Sawsan M. Abuzaid, Enrico Armato, Salvatore Martellucci, Pasquale Malara, Mohamad Alfarghal, Rosanna Rita Ruberto, Pasquale Brizzi, Angelo Ghidini, and et al. 2024. "Posterior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence with Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Reduction for the Affected Canal at the Video-Head Impulse Test: Considerations to Pathomechanisms" Audiology Research 14, no. 2: 317-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14020028
APA StyleCastellucci, A., Dumas, G., Abuzaid, S. M., Armato, E., Martellucci, S., Malara, P., Alfarghal, M., Ruberto, R. R., Brizzi, P., Ghidini, A., Comacchio, F., & Schmerber, S. (2024). Posterior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence with Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Reduction for the Affected Canal at the Video-Head Impulse Test: Considerations to Pathomechanisms. Audiology Research, 14(2), 317-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14020028












