Benefits of Cartilage Conduction Hearing Aids for Speech Perception in Unilateral Aural Atresia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
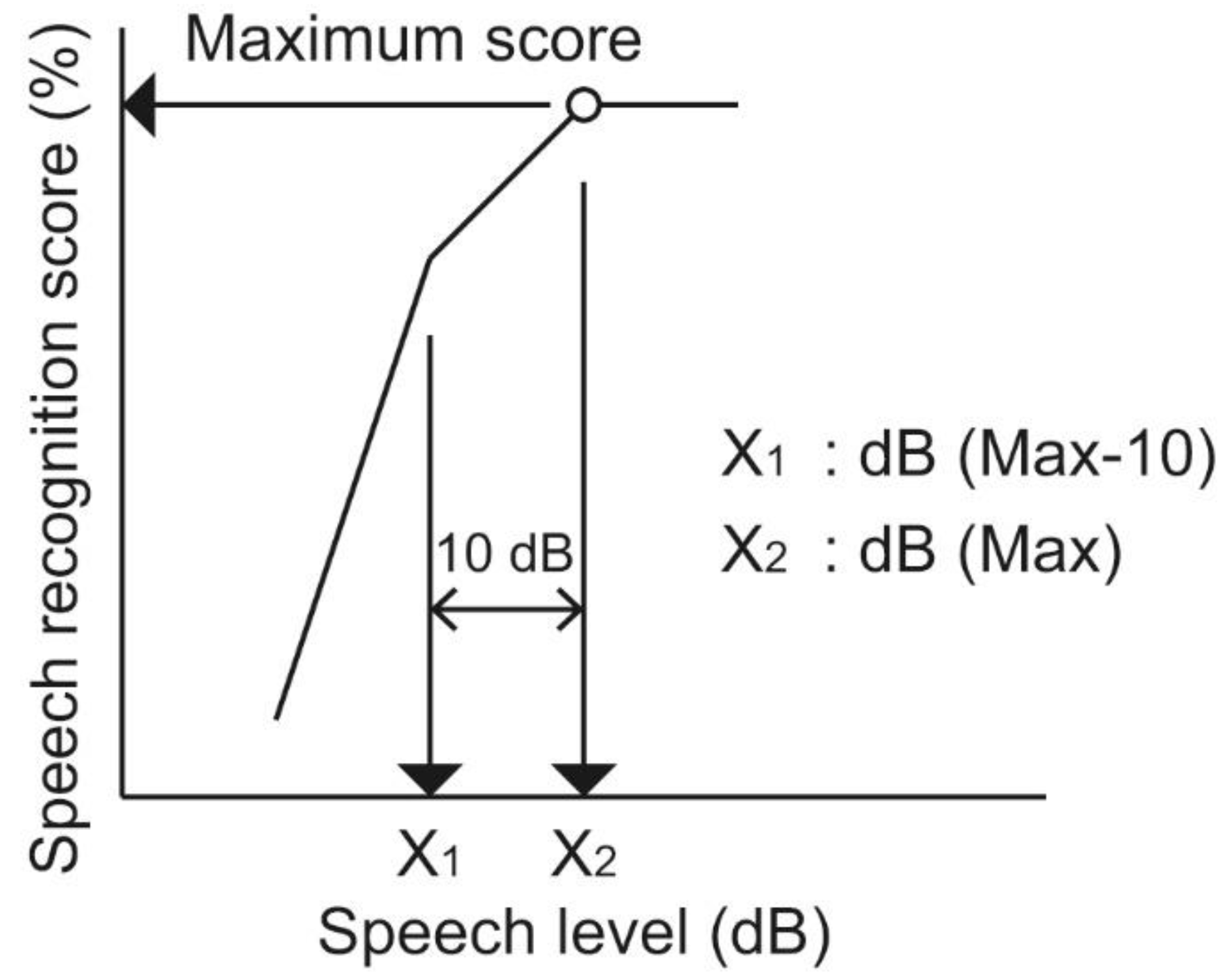
2.1. Measurement of Speech Recognition at Low Speech Levels
2.2. Measurement of Speech Recognition in Noise
2.3. Statistical Analysis
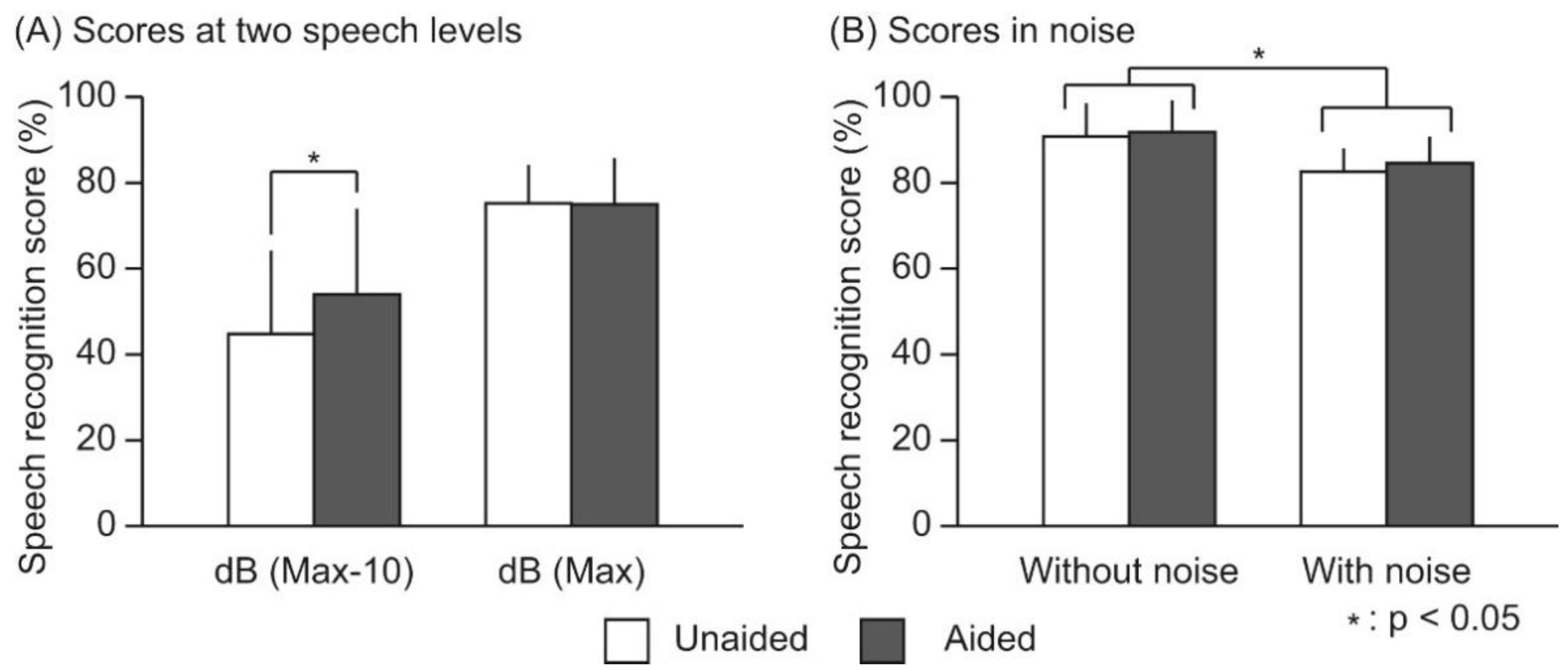
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huttunen, K.; Erixon, E.; Löfkvist, U.; Mäki-Torkko, E. The impact of permanent early-onset unilateral hearing impairment in children—A systematic review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 120, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagatto, M.; DesGeorges, J.; King, A.; Kitterick, P.; Laurnagaray, D.; Lewis, D.; Roush, P.; Sladen, D.P.; Tharpe, A.M. Consensus practice parameter: Audiological assessment and management of unilateral hearing loss in children. Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, K.; Kral, A. Animal and human studies on developmental monaural hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2019, 380, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, G. Early prelingual auditory development of infants and toddlers with unilateral hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, H. Hearing Aids; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, J.F.; Tsang, W.S.; Yu, J.Y.; Ho, O.Y.; Ku, P.K.; Tong, M.C. Contemporary hearing rehabilitation options in patients with aural atresia. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 761579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, R.; Hidaka, H.; Murata, T.; Miyazaki, H.; Katori, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Vibrant Soundbridge implantation via a retrofacial approach in a patient with congenital aural atresia. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, B.; Reinfeldt, S.; Persson, A.C.; Jansson, K.F.; Rigato, C.; Hultcrantz, M.; Eeg-Olofsson, M. The bone conduction implant—A review and 1-year follow-up. Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Goh, E.K.; Choi, S.W.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, I.W.; Kong, S.K. Audiologic, surgical and subjective outcomes of active transcutaneous bone conduction implant system (Bonebridge). Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curca, I.A.; Parsa, V.; Macpherson, E.A.; Scollie, S.; Vansevenant, K.; Zimmerman, K.; Lewis-Teeter, J.; Allen, P.; Parnes, L.; Agrawal, S. Audiological outcome measures with the BONEBRIDGE transcutaneous bone conduction hearing implant: Impact of noise, reverberation and signal processing features. Int. J. Audiol. 2020, 59, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokura, R.; Hosoi, H.; Nishimura, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Levitt, H. Cartilage conduction hearing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Miyamae, R.; Shimokura, R.; Matsui, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Levitt, H. Is cartilage conduction classified into air or bone conduction? Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Miyamae, R.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T.; Levitt, H. Cartilage conduction is characterized by vibrations of the cartilaginous portion of the ear canal. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Miyamae, R.; Shimokura, R.; Matsui, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T.; Levitt, H. Cartilage conduction efficiently generates airborne sound in the ear canal. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015, 42, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, H.; Nishimura, T.; Shimokura, R.; Kitahara, T. Cartilage conduction as the third pathway for sound transmission. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Akasaka, S.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T. Effect of fixation place on airborne sound in cartilage conduction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoi, H.; Yanai, S.; Nishimura, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Iwakura, T.; Yoshino, K. Development of cartilage conduction hearing aid. Arch. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2010, 42, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Miyamae, R.; Shimokura, R.; Matsui, T.; Iwakura, T. Benefit of a new hearing device utilizing cartilage conduction. Auris Nasus Larynx 2013, 40, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokura, R.; Hosoi, H.; Iwakura, T.; Nishimura, T.; Matsui, T. Development of monaural and binaural behind-the-ear cartilage conduction hearing aids. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T. Cartilage Conduction Hearing Aids for Severe Conduction Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Shimokura, R.; Morimoto, C.; Kitahara, T. Cartilage Conduction Hearing and Its Clinical Application. Audiol. Res. 2021, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokura, R.; Hosoi, H.; Nishimura, T.; Iwakura, T.; Yamanaka, T. Simulating cartilage conduction sound to estimate the sound pressure level in the external auditory canal. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 20, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, C.; Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Fukuda, F.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T. Sound transmission by cartilage conduction in ear with fibrotic aural atresia. J. Rehabil Res. Dev. 2014, 51, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamae, R.; Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T. Perception of speech in cartilage conduction. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Miyamae, R.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T. Frequency characteristics and speech recognition in cartilage conduction. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Shimada, A.; Nakano, S.; Kondo, E.; Takeyama, T.; Fukuda, J.; Udaka, J.; Okamoto, H.; Takeda, N. Effects of FM system fitted into the normal hearing ear or cartilage conduction hearing aid fitted into the affected ear on speech-in-noise recognition in Japanese children with unilateral congenital aural atresia. J. Med. Investig. 2020, 67, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, T.; Oishi, N.; Ogawa, K. Who are good adult candidates for cartilage conduction hearing aids? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, T.; Oishi, N.; Ogawa, K. Efficacy of cartilage conduction hearing aids in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 142, 110628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Sugiuchi, T.; Matsumoto, N.; Nishiyama, T.; Takano, K.; Sugimoto, S.; Yazama, H.; Sato, T.; Komori, M. Cartilage conduction hearing aid fitting in clinical practice. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Shimokura, R.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitahara, T. Sound localisation ability using cartilage conduction hearing aids in bilateral aural atresia. Int. J. Audiol. 2020, 59, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, P.M.; Nábĕlek, A.K.; Robertson, V.S. Sound localization acuity in children with unilateral hearing loss who wear a hearing aid in the impaired ear. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2010, 21, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.E.; Hamadain, E.; Galster, J.A.; Johnson, M.F.; Spankovich, C.; Windmill, I. Outcomes of Hearing Aid Use by Individuals with Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss (USNHL). J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Audiological Society. Methods of speech audiometry. Audiol. Japan. 2003, 46, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Okayasu, T.; Saito, O.; Shimokura, R.; Yamashita, A.; Yamanaka, T.; Hosoi, H.; Kitahara, T. An examination of the effects of broadband air-conduction masker on the speech intelligibility of speech-modulated bone-conduction ultrasound. Hear. Res. 2014, 317, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, K.; Hosoi, H.; Okamoto, M.; Manabe, T.; Kanda, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Sugiuchi, T.; Suzuki, K.; Tauchi, H.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Guidelines for the evaluation of hearing aid fitting (2010). Auris Nasus Larynx 2016, 43, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Haggard, M.; Bell, I. Magnitude of diotic summation in speech-in-noise tasks: Performance region and appropriate baseline. Br. J. Audiol. 1990, 24, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, E.; Sutojo, S.; van de Par, S. Better-ear rating based on glimpsing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilly, O.; Sokolov, M.; Finkel, R.B.; Zavdy, O.; Shemesh, R.; Attias, J. Hearing in noise with unilateral versus bilateral bone conduction hearing aids in adults with pseudo-conductive hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisser, A.; Buchholz, J.M. Conversational speech levels and signal-to-noise ratios in realistic acoustic conditions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L.; Geiling, L.; Hauth, C.; Hocke, T.; Plontke, S.; Rahne, T. Improved binaural speech reception thresholds through small symmetrical separation of speech and noise. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, M.K.; Snik, A.F.; Mylanus, E.A.; Cremers, C.W. Does the bone-anchored hearing aid have a complementary effect on audiological and subjective outcomes in patients with unilateral conductive hearing loss? Audiol. Neurootol. 2005, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunst, S.J.; Leijendeckers, J.M.; Mylanus, E.A.; Hol, M.K.; Snik, A.F.; Cremers, C.W. Bone-anchored hearing aid system application for unilateral congenital conductive hearing impairment: Audiometric results. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akasaka, S.; Nishimura, T.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, O.; Shimokura, R.; Morimoto, C.; Kitahara, T. Benefits of Cartilage Conduction Hearing Aids for Speech Perception in Unilateral Aural Atresia. Audiol. Res. 2021, 11, 284-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11020026
Akasaka S, Nishimura T, Hosoi H, Saito O, Shimokura R, Morimoto C, Kitahara T. Benefits of Cartilage Conduction Hearing Aids for Speech Perception in Unilateral Aural Atresia. Audiology Research. 2021; 11(2):284-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkasaka, Sakie, Tadashi Nishimura, Hiroshi Hosoi, Osamu Saito, Ryota Shimokura, Chihiro Morimoto, and Tadashi Kitahara. 2021. "Benefits of Cartilage Conduction Hearing Aids for Speech Perception in Unilateral Aural Atresia" Audiology Research 11, no. 2: 284-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11020026
APA StyleAkasaka, S., Nishimura, T., Hosoi, H., Saito, O., Shimokura, R., Morimoto, C., & Kitahara, T. (2021). Benefits of Cartilage Conduction Hearing Aids for Speech Perception in Unilateral Aural Atresia. Audiology Research, 11(2), 284-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11020026







