Bacterial and Physicochemical Dynamics During the Vermicomposting of Bovine Manure: A Comparative Analysis of the Eisenia fetida Gut and Compost Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Laboratory Work
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Physicochemical Analysis
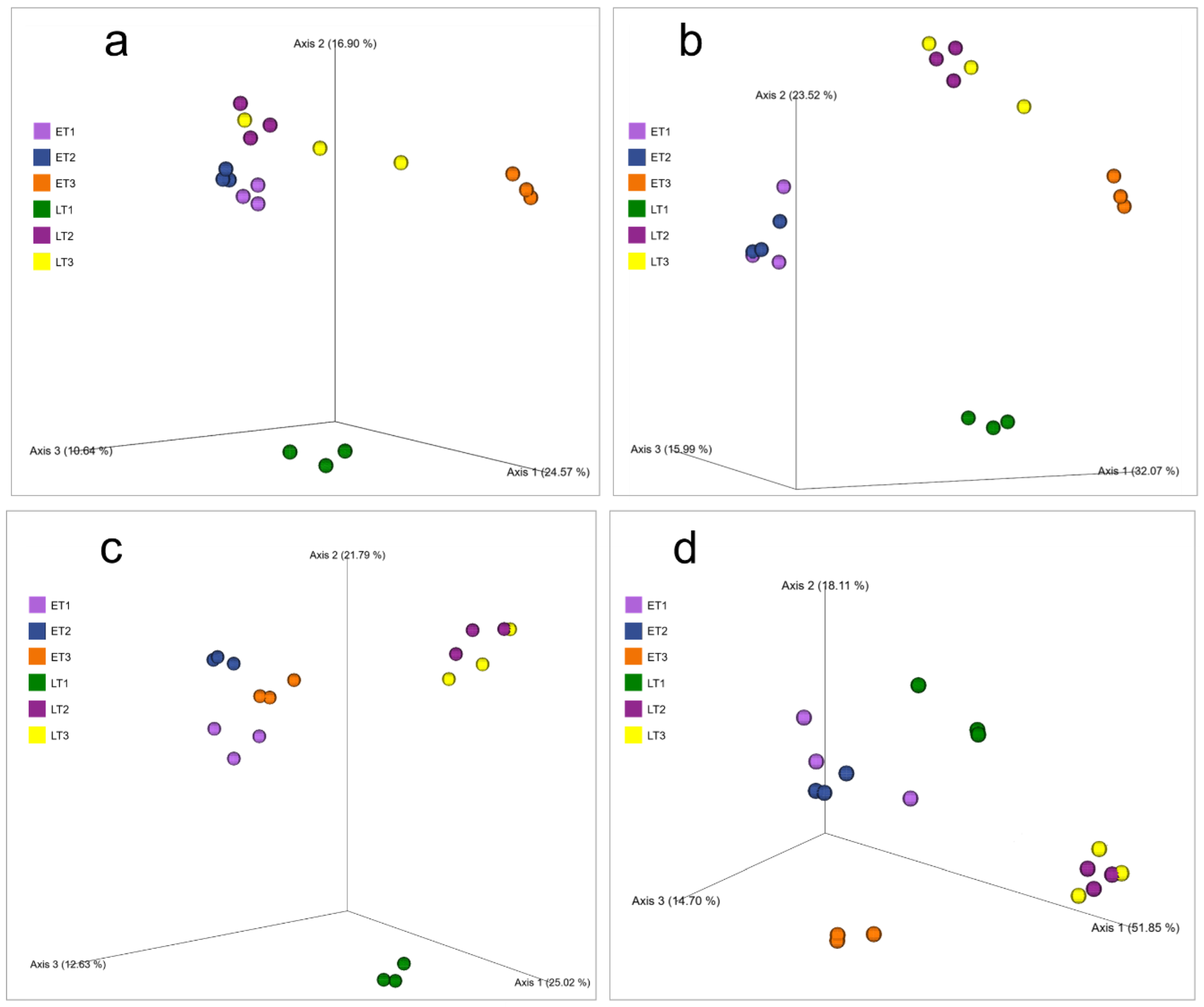
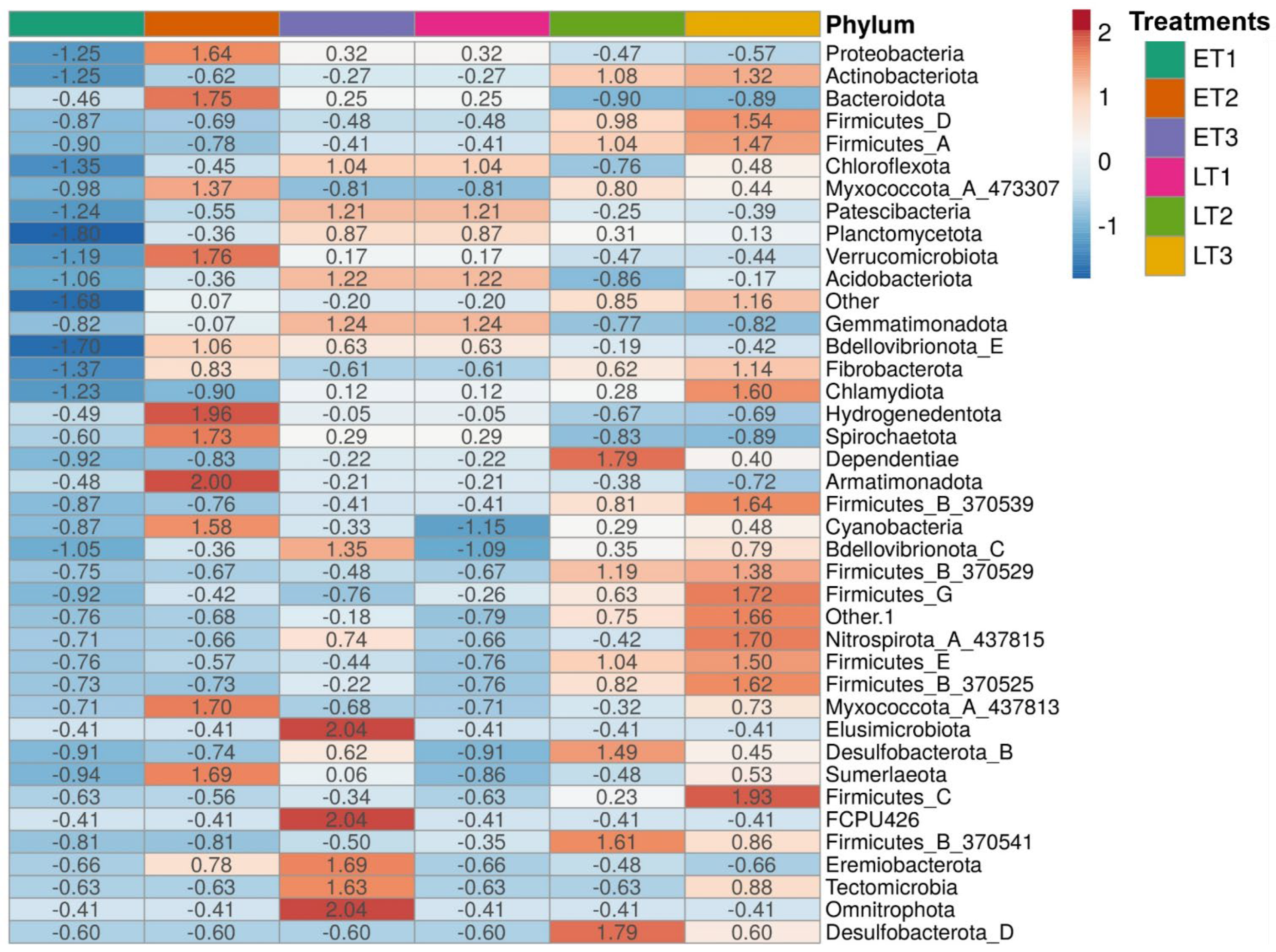
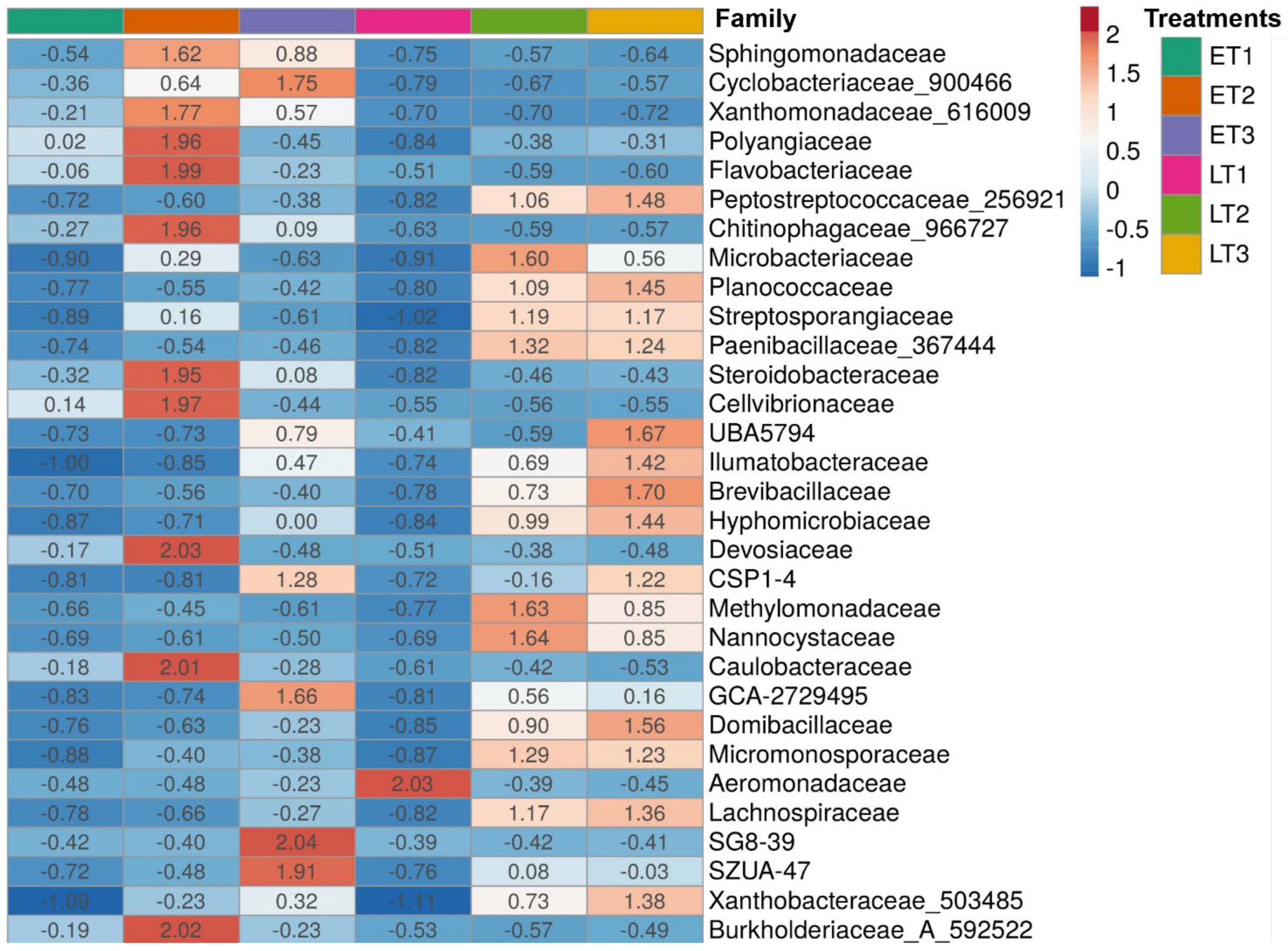
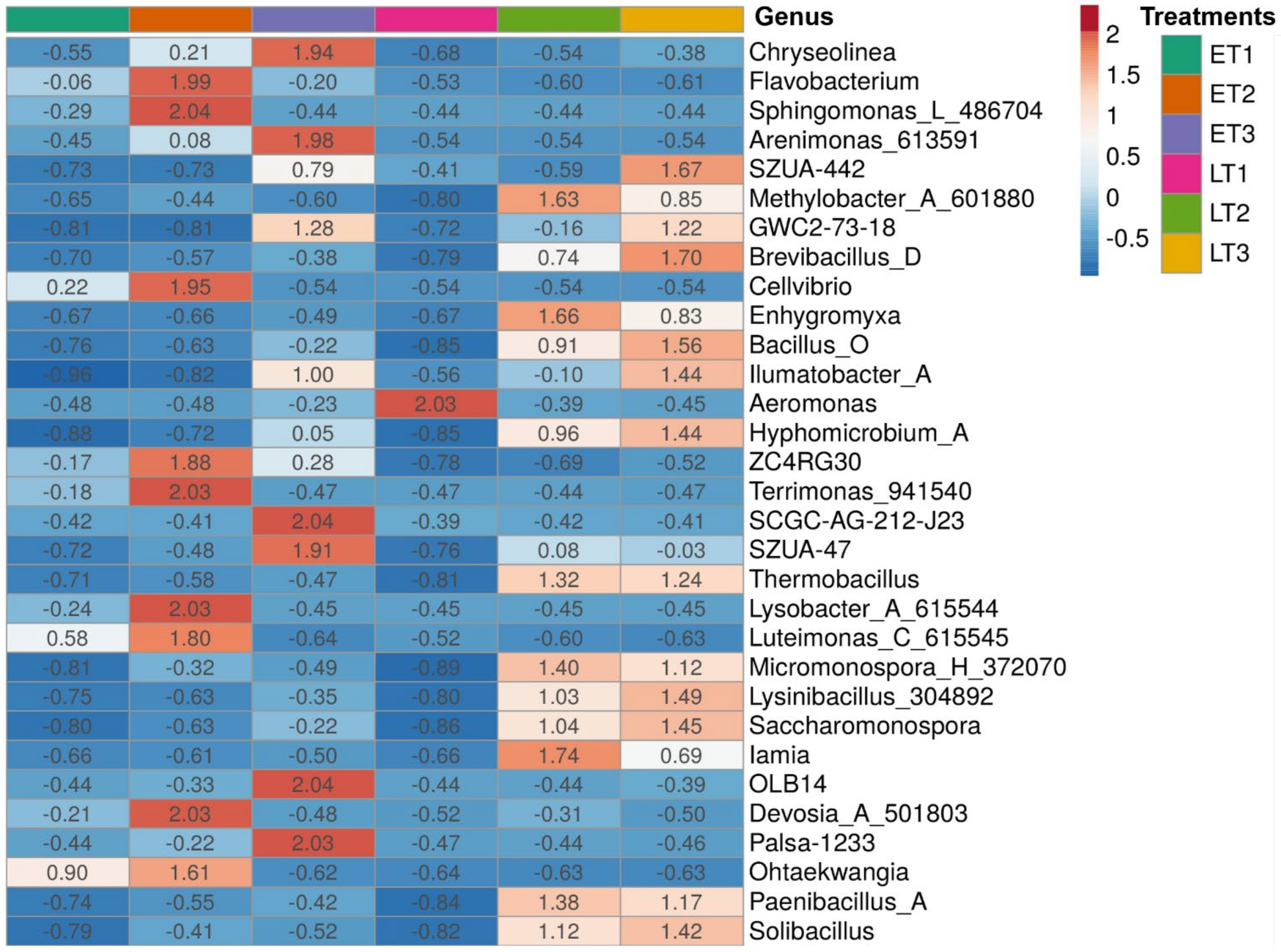
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| rRNA | ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| QIIME2 | Quantitative Insights into Microbial Ecology |
| ASVs | amplicon sequence variants |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| PCoA | principal coordinate analysis |
| PERMANOVA | permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| SIMPER | similarity percentage analysis |
| pH | potential of hydrogen |
| EC | electrical conductivity |
| M | moisture |
| OM | organic matter |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| C/N | carbon/nitrogen ratio |
| P | phosphorus |
| K | potassium |
| Mg | magnesium |
| Ca | calcium |
References
- Suthar, S.; Singh, S. Vermicomposting of domestic waste by using two epigeic earthworms (Perionyx excavatus and Perionyx sansibaricus). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lian, B.; Wu, C.; Guo, P. A comparative study of gut microbiota profiles of earthworms fed in three different substrates. Symbiosis 2017, 74, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.; Aira, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M. Vermicomposting: Earthworms enhance the work of microbes. In Microbes at Work; Insam, H., Franke-Whittle, I., Goberna, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Domínguez, J. Selective reduction of the pathogenic load of cow manure in an industrial-scale continuous-feeding vermireactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Epigeic earthworms exert a bottleneck effect on microbial communities through gut associated processes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musyoka, S.; Liti, D.; Ogello, E.; Meulenbroek, P.; Waidbacher, H. Using earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to bio-convert agro-industrial wastes for aquaculture nutrition. BioResources 2020, 15, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Suthar, S. Vermicomposting of invasive weed Ageratum conyzoides: Assessment of nutrient mineralization, enzymatic activities, and microbial properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirikum, K.; Kakati, L.N.; Thyug, L.; Mozhui, L. Vermicomposting: An eco-friendly approach for waste management and nutrient enhancement. Trop. Ecol. 2022, 63, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Olcina, J.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Characterization of the bacterial communities of casts from Eisenia andrei fed with different substrates. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Microbial and nutrient stabilization of two animal manures after the transit through the gut of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, Z.; Magwaza, L.S.; Sithole, N.J.; Mditshwa, A.; Odindo, A.O. Physico-chemical analysis of vermicompost mixtures. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, Q.; Shafiqi, S. Vermicompost: Significance and benefits for agriculture. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 3, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, G.S.J.; Hermes, P.H.; Miriam, S.V.; López, A.M. Benefits of vermicompost in agriculture and factors affecting its nutrient content. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 4898–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majlessi, M.; Eslami, A.; Najafi Saleh, H.; Mirshafieean, S.; Babaii, S. Vermicomposting of food waste: Assessing the stability and maturity. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Singh, J.; Vig, A.P. Instrumental characterization of organic wastes for evaluation of vermicompost maturity. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Bell, T.H.; Martin, V.J.J.; Gélinas, Y. Dynamics of physicochemical variables and cultivable bacteria in vermicompost during steady food waste addition and upon feed interruption. Compost Sci. Util. 2015, 24, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K. Quality of vermicompost and microbial community diversity affected by the contrasting temperature during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathma, J.; Sakthivel, N. Microbial diversity of vermicompost bacteria that exhibit useful agricultural traits and waste management potential. SpringerPlus 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooch, Y.; Jalilvand, H. Earthworms as ecosystem engineers and the most important detritivors in forest soils. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Crandall, K.A.; Domínguez, J. Composition, structure and diversity of soil bacterial communities before, during and after transit through the gut of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Deng, X.; Xie, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z. Pharmacological effects of bioactive agents in earthworm extract: A comprehensive review. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2024, 7, 653–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.; Maresca, M.; Canaan, S.; Cavalier, J.-F.; Mabrouk, K.; Boidin-Wichlacz, C.; Olleik, H.; Zeppilli, D.; Brodin, P.; Massol, F.; et al. Worms’ antimicrobial peptides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, S.; Pelosi, C.; Barraud, A.; Péry, A.R.R.; Cheviron, N.; Grondin, V.; Mougin, C.; Crouzet, O. Earthworms mitigate pesticide effects on soil microbial activities. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Squartini, A.; Masi, A.; Sarkar, A.; Singh, R.P. Metabarcoding analysis of the bacterial succession during vermicomposting of municipal solid waste employing the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, A.R.; Aira, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Bacterial succession and functional diversity during vermicomposting of the white grape marc Vitis vinifera v. Albariño. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundee, K.; Akeprathumchai, S.; Tripetchkul, S.; Salaipeth, L. Unveiling the microbial dynamics in vermicomposting with coir pith as earthworm substrate. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.S.; Lone, A.R.; Tiwari, N.; Jain, S.K.; Yadav, S. Metagenomic exploration of bacterial community structure of earthworms’ gut. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 1156–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, J.; Pegu, R.; Mondal, H.; Roy, R.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Earthworm stocking density regulates microbial community structure and fatty acid profiles during vermicomposting of lignocellulosic waste: Unraveling the microbe-metal and mineralization-humification interactions. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Lu, F.; Yang, L.; Li, T. Cultivation of earthworms and analysis of associated bacterial communities during earthworms’ growth using two types of agricultural wastes. Bioresour. Bioprocess 2024, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Fu, X. Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia foetida. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 150, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Roel, A.; Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Vermicomposting enhances microbial detoxification of sewage sludge, enabling potential application of the treated product in agroecosystems. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková, P.; Hanč, A.; Dvořák, J.; Roubalová, R.; Drešlová, M.; Částková, T.; Šustr, V.; Škanta, F.; Pacheco, N.I.N.; Bilej, M. Contribution of Eisenia andrei earthworms in pathogen reduction during vermicomposting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 26267–26278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuria, D.; Schmidt, O.; Finan, D.; Egan, D.; Doohan, F.M. Gut wall bacteria of earthworms: A natural selection process. ISME J. 2010, 4, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.A.; Moraes, L.C.; Mogollón, M.C.T.; Borja, C.J.F.; Duarte, M.; Buttrós, V.H.T.; Luz, J.M.Q.; Pasqual, M.; Dória, J. Cultivating biodiversity to harvest sustainability: Vermicomposting and inoculation of microorganisms for soil preservation and resilience. Agronomy 2023, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-L.; Jin, W.-Z.; Tao, X.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) strengthen the metabolic function of food waste biodegradation by gut microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; Cui, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; He, P.; Lü, F. Compost quality, earthworm activities and microbial communities in biochar-augmented vermicomposting of dewatered activated sludge: The role of biochar particle size. Biochar 2024, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastesh, F.; Alikhani, H.A.; Etesami, H. Vermicompost enriched with phosphate–solubilizing bacteria provides plant with enough phosphorus in a sequential cropping under calcareous soil conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Ooya, T.; Miyatsuchi, D.; Fuchigami, H.; Terakado, K.; Nakayama, S.-Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nagata, Y.; Ando, A. Molecular characterization and antifungal activity of a family 46 chitosanase from Amycolatopsis sp. CsO-2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 293, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, W.; Li, P.; Yao, D.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Z.; Cao, H.; et al. Variations in bacterial taxonomic profiles and potential functions in response to the gut transit of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) feeding on cow manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Paria, D.S.; Chatterjee, S. Comparative study on bacterial population dynamics of foregut, midgut, and hindgut content of Perionyx excavatus (Perrier) isolated from eco-friendly, non-hazardous vermicompost. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 6126–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Qiu, J. Dynamics of bacterial community in the foregut and hindgut of earthworms with the nutrition supplied by kitchen waste during vermicomposting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Aira, M.; Kolbe, A.R.; de Andrade, N.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Rapid bacterial community changes during vermicomposting of grape marc derived from red winemaking. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant–microbiome interactions: From community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Singh, J.; Bakshi, M. Biofortification of vermicompost with beneficial microorganisms and its field performance in horticultural crops. J. Adv. Zool. 2023, 44, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Wang, L.; Aspe, N.M.; Han, A.C.; Chen, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, D. Seasonal dynamics of gut microbiome: A study of multi-kingdom microbiota of earthworm gut in an urban park. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 195, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.-W.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Lassen, S.B.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Su, J.-Q. Earthworm gut: An overlooked niche for anaerobic ammonium oxidation in agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; De Castro, F.; Aprile, A.; Benedetti, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. Vermicompost: Enhancing Plant Growth and Combating Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Ni, J.; Zou, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Shi, K.; Ruan, H. Earthworms regulate soil microbial and plant residues through decomposition. Geoderma 2024, 450, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, P.; Sachan, K.; Singh, B.V.; Saikanth, D.R.K.; Kumar, R.K.M.H.; Gautam, R.; Singh, O. Earthworm castings in ecosystem health through their elemental composition. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation: Preparing 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Amplicons for the Illumina MiSeq System. 2019. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Illumina. Nextera XT DNA Library Prep Kit Reference Guide. 2019. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-support/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/samplepreps_nextera/nexteradna/nextera-dna-library-prep-reference-guide-15027987-01.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Jiang, Y.; Balaban, M.; Cantrell, K.; Zhu, Q.; Gonzalez, A.; Morton, J.T.; Nicolaou, G.; Parks, D.H.; Karst, S.M.; et al. Greengenes2 unifies microbial data in a single reference tree. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 42, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. GigaScience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomich, M.; Mage, I.; Rud, I.; Berget, I. Analysing microbiome intervention design studies: Comparison of alternative multivariate statistical methods. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. Clustvis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaly, M.; Senthilkumar, A.K.; Arumugam, S.; Kaliyaperumal, C.; Karupannan, N. Vermicomposting of distillery sludge waste with tea leaf residues. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-021-RECNAT-2000. Que Establece las Especificaciones de Fertilidad, Salinidad y Clasificación de Suelos. Estudios, Muestreo y Análisis. 2002. Available online: https://www.ordenjuridico.gob.mx/Documentos/Federal/wo69255.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Qian, X.; Gu, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.-J.; Su, J.-Q.; Stedfeld, R. Diversity, abundance, and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in various types of animal manure following industrial composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, J.; Aira, M.; Crandall, K.A.; Pérez-Losada, M. Earthworms drastically change fungal and bacterial communities during vermicomposting of sewage sludge. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Xing, M.; Yang, J. Exploring the effects of earthworms on bacterial profiles during vermicomposting process of sewage sludge and cattle dung with highthroughput sequencing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12528–12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, D.P.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, K.; Singh, R.V.; Singh, S.; Prasanna, R.; Saxena, A.K.; Nain, L. Taxonomic and functional annotation of gut bacterial communities of Eisenia foetida and Perionyx excavatus. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 175, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S, K.K.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Quaik, S.; Ismail, S.A. Microbial Ecology Associated with Earthworm and Its Gut. In Prospects of Organic Waste Management and the Significance of Earthworms. Applied Environmental Science and Engineering for a Sustainable Future; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Zou, X.; Cheng, T.; Li, J. Aerobic co-composting of mature compost with cattle manure: Organic matter conversion and microbial community characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 382, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Aira, M.; Santana, N.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Temporal dynamics of bacterial communities in a pilot-scale vermireactor fed with distilled grape marc. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Ren, N. Succession of bacterial community function in cow manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Bacterial succession during vermicomposting of silver wattle (Acacia dealbata Link). Microorganisms 2021, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Kang, Y. The bacterial community structures in response to the gut passage of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) feeding on cow dung and domestic sludge: Illumina high-throughput sequencing-based data analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Schrader, S.; Tebbe, C.C. Legacy effects of earthworms on soil microbial abundance, diversity, and community dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 190, 109294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Yang, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, S.; Syed, A.; Verma, M.; Ravindran, B. Bacterial community dynamics and co-occurrence network patterns during different stages of biochar-driven composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Rong, X.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Hu, W.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Xiao, R.; Deng, X.; Xie, G.; et al. Community succession of microbial populations related to C-N-P-S biological transformations regulates product maturity during cow-manure-driven composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.L.; de Souza, A.J.; Mendes, L.W.; Gontijo, J.B.; Rodrigues, M.M.; Coscione, A.R.; Oliveira, F.C.; Regitano, J.B. Physicochemical and bacterial changes during composting of vegetable and animal-derived agro-industrial wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Harrasi, A. Sphingomonas: From diversity and genomics to functional role in environmental remediation and plant growth. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, A.B.; Hunger, S.; Drake, H.L. Differential engagement of fermentative taxa in gut contents of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01851-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Bybee, S.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Feeding on microbiomes: Effects of detritivory on the taxonomic and phylogenetic bacterial composition of animal manures. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupani, P.F.; Embrandiri, A.; Garg, V.K.; Abbaspour, M.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L. Vermicomposting of green organic wastes using Eisenia fetida under field conditions: A case study of a green campus. Waste Biomass Valor. 2023, 14, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuković, A.; Velki, M.; Ečimović, S.; Vuković, R.; Štolfa Čamagajevac, I.; Lončarić, Z. Vermicomposting—Facts, benefits and knowledge gaps. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Wu, T.Y.; Lim, P.N.; Shak, K.P. The use of vermicompost in organic farming: Overview, effects on soil and economics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehrei, F.; Ameen, F. Vermicomposting: A management tool to mitigate solid waste. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3284–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel-Alegre, S.; Khan, A.H.A.; Rad, C.; Velasco-Arroyo, B.; Rumbo, C.; Rivilla, R.; Durán, D.; Redondo-Nieto, M.; Borràs, E.; Molognoni, D.; et al. Bioaugmentation and vermicompost facilitated the hydrocarbon bioremediation: Scaling up from lab to field for petroleum-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, P.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, J. Vermicomposting with microbial amendment: Implications for bioremediation of industrial and agricultural waste. Biotechnologia 2022, 103, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores-Silva, P.R.; Cotta, J.A.O.; Landgraf, M.D.; Rezende, M.O.O. The application of the vermicomposting process in the bioremediation of diesel contaminated soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2019, 54, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, F.; Marini, E.; De Bernardi, A.; Vischetti, C.; Brunetti, G.; Casucci, C. A bioremediation and soil fertility study: Effects of vermiremediation on soil contaminated by chlorpyrifos. Environments 2025, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Mata, O.; Aguilera Flores, M.M.; Ureño García, B.G.; Ávila Vázquez, V.; Cabañas García, E.; Franco Villegas, E.A. Bioremediation of automotive residual oil-contaminated soils by biostimulation with enzymes, surfactant, and vermicompost. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, S.; Masin, C.E.; Zalazar, C.S.; Lescano, M.R. Bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil using local organic materials and earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, S.S.; Edoukou, F.E.; Kouassi, K.I.; Barsan, N.; Nedeff, V.; Bi Zoro, I.A. Vermicompost utilization: A way to food security in rural area. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, B.; Chimdessa, D.; Sori, G. Preparation and characterization of vermicompost nutrients made from different sources of organic materials. Sci. J. Anal. Chem. 2025, 13, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelon, S.M.; Orilla, A.A.; Mahilum, J.A.; Adtoon, J.J. Automated vermiculture monitoring and compost segregating system using microcontrollers. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Bioinformatics Research and Applications (ICBRA ’19), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 19–21 December 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enebe, M.C.; Erasmus, M. Vermicomposting technology—A perspective on vermicompost production technologies, limitations and prospects. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kurovsky, A.V.; Babenko, A.S. The role of microbial enzymes in vermicomposting of organic wastes. Sci. Innov. 2024, 3, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, H. Vermicomposting of livestock manure as affected by carbon-rich additives (straw, biochar and nanocarbon): A comprehensive evaluation of earthworm performance, microbial activities, metabolic functions and vermicompost quality. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharat, K.R.; Mote, M.G.; Deokar, D.K.; Patil, V.S. Comparative study of chemical parameters of vermicompost prepared from different types of livestock manures. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2025, 10, 176–180. Available online: https://www.veterinarypaper.com/pdf/2025/vol10issue1/PartC/10-1-34-472.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Raza, S.T.; Zhu, B.; Tang, J.L.; Ali, Z.; Anjum, R.; Bah, H.; Iqbal, H.; Ren, X.; Ahmad, R. Nutrients recovery during vermicomposting of cow dung, pig manure, and biochar for agricultural sustainability with gases emissions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.F.; Santana, N.A.; Andrade, N.; Romagna, I.S.; Tirloni, B.; Silveira, A.O.; Domínguez, J.; Jacques, R.J.S. Vermicomposting of cow manure: Effect of time on earthworm biomass and chemical, physical, and biological properties of vermicompost. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
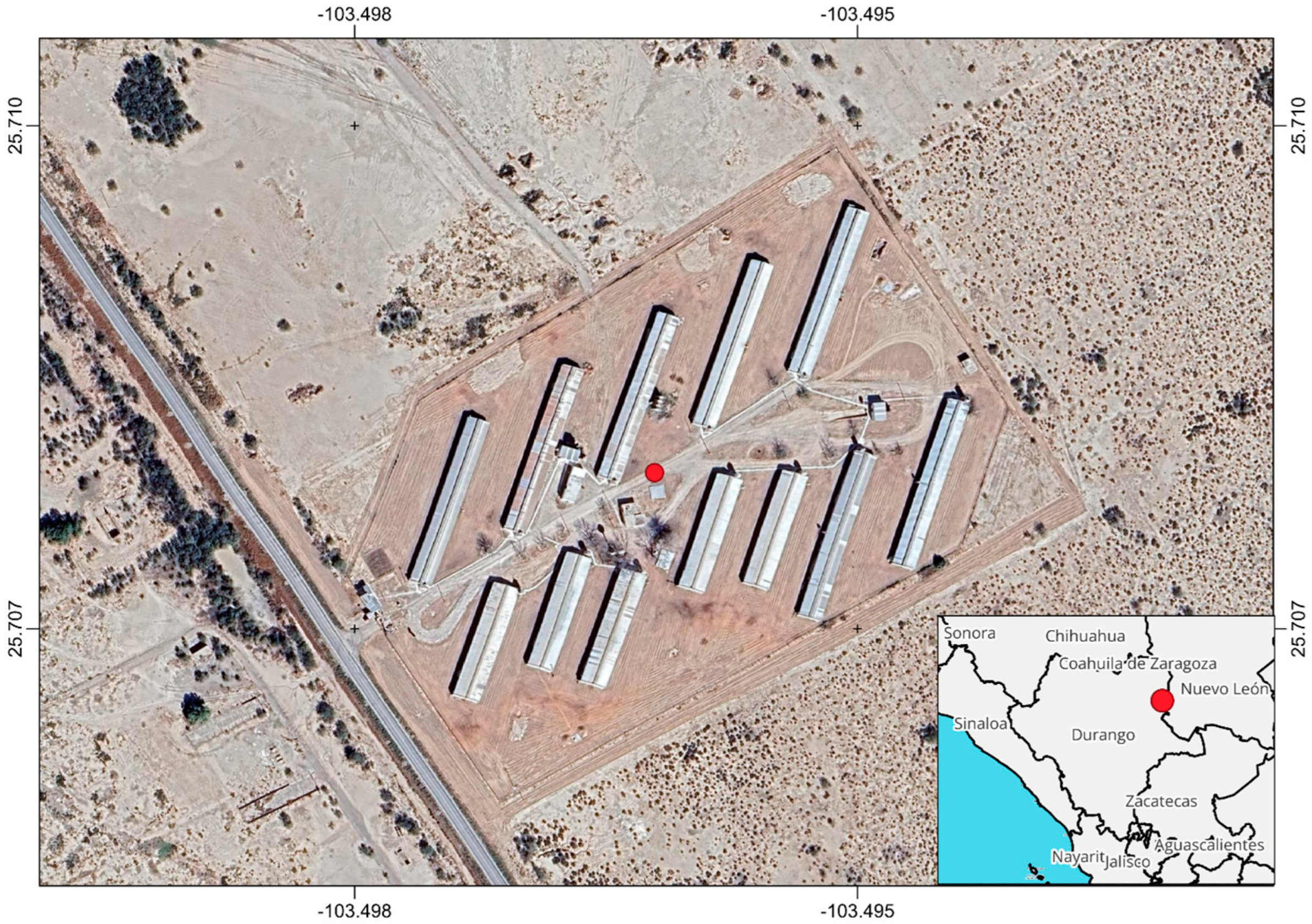

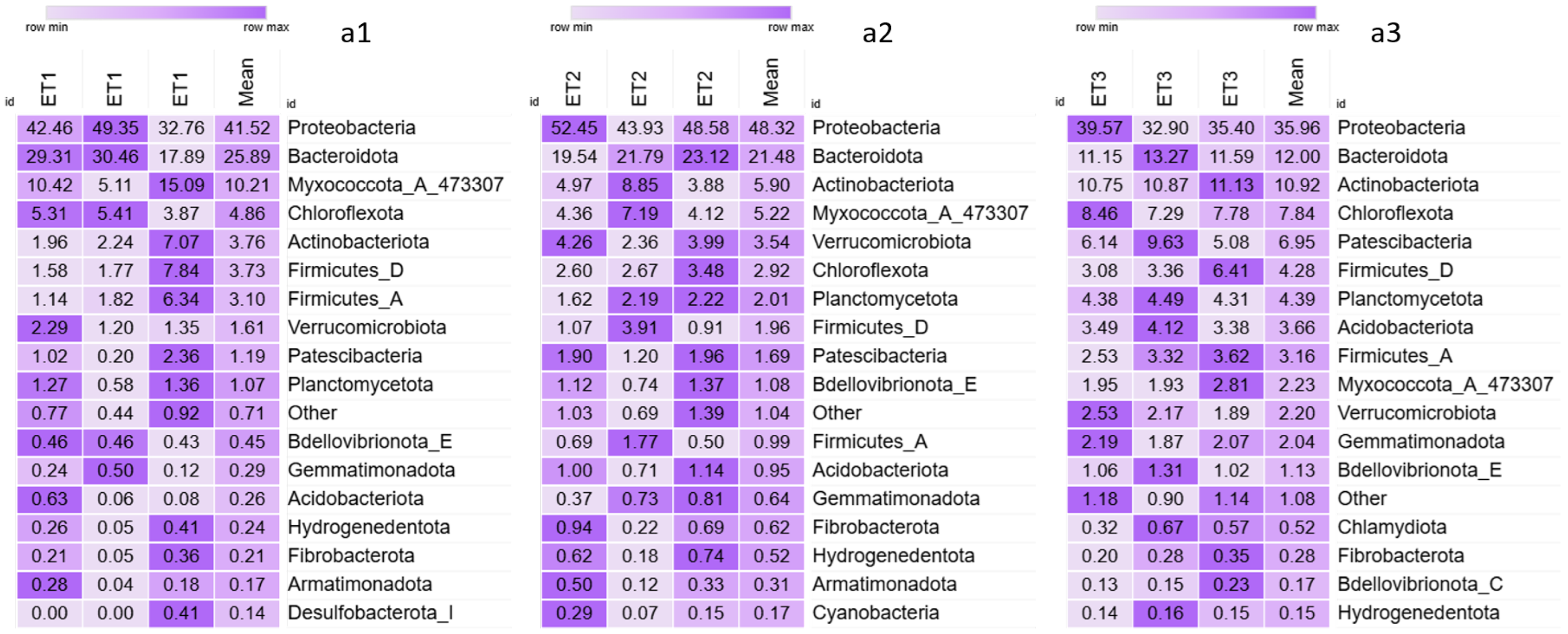
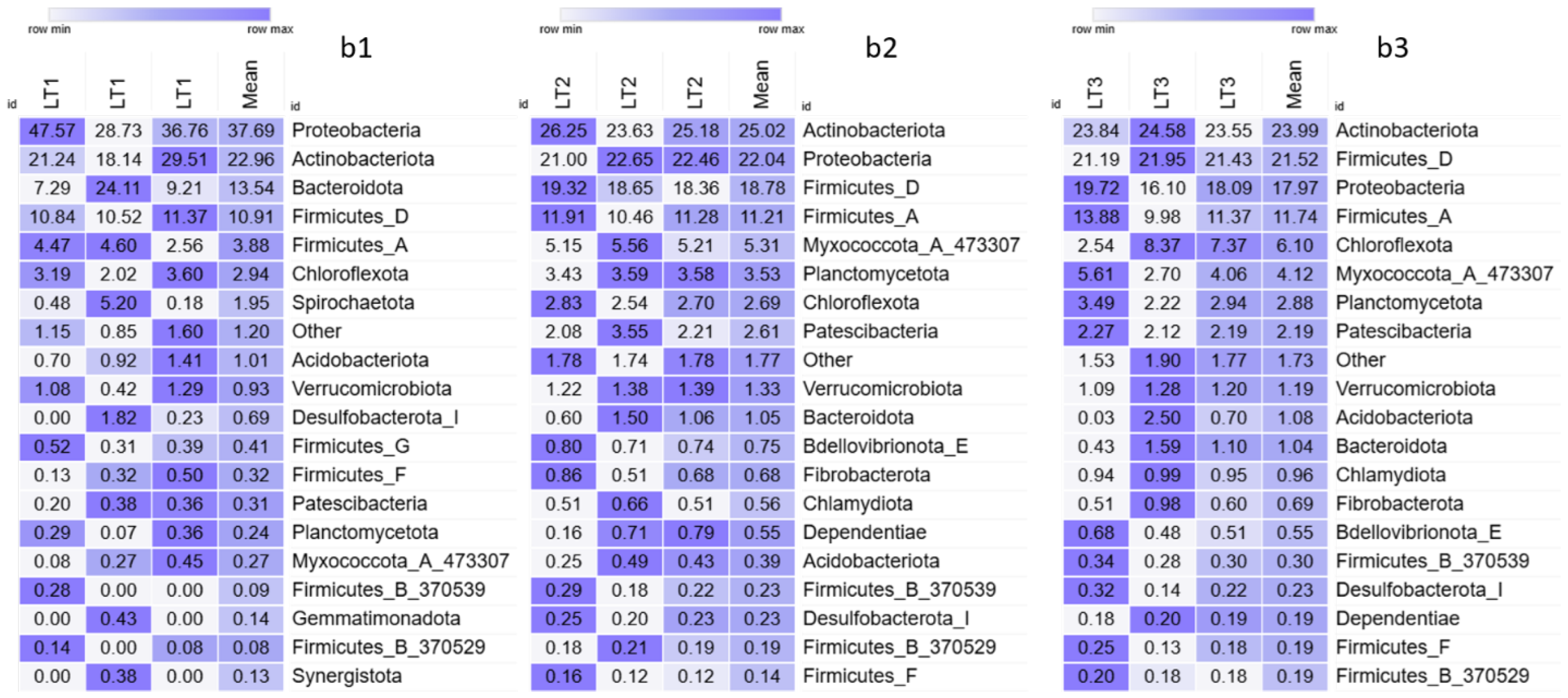

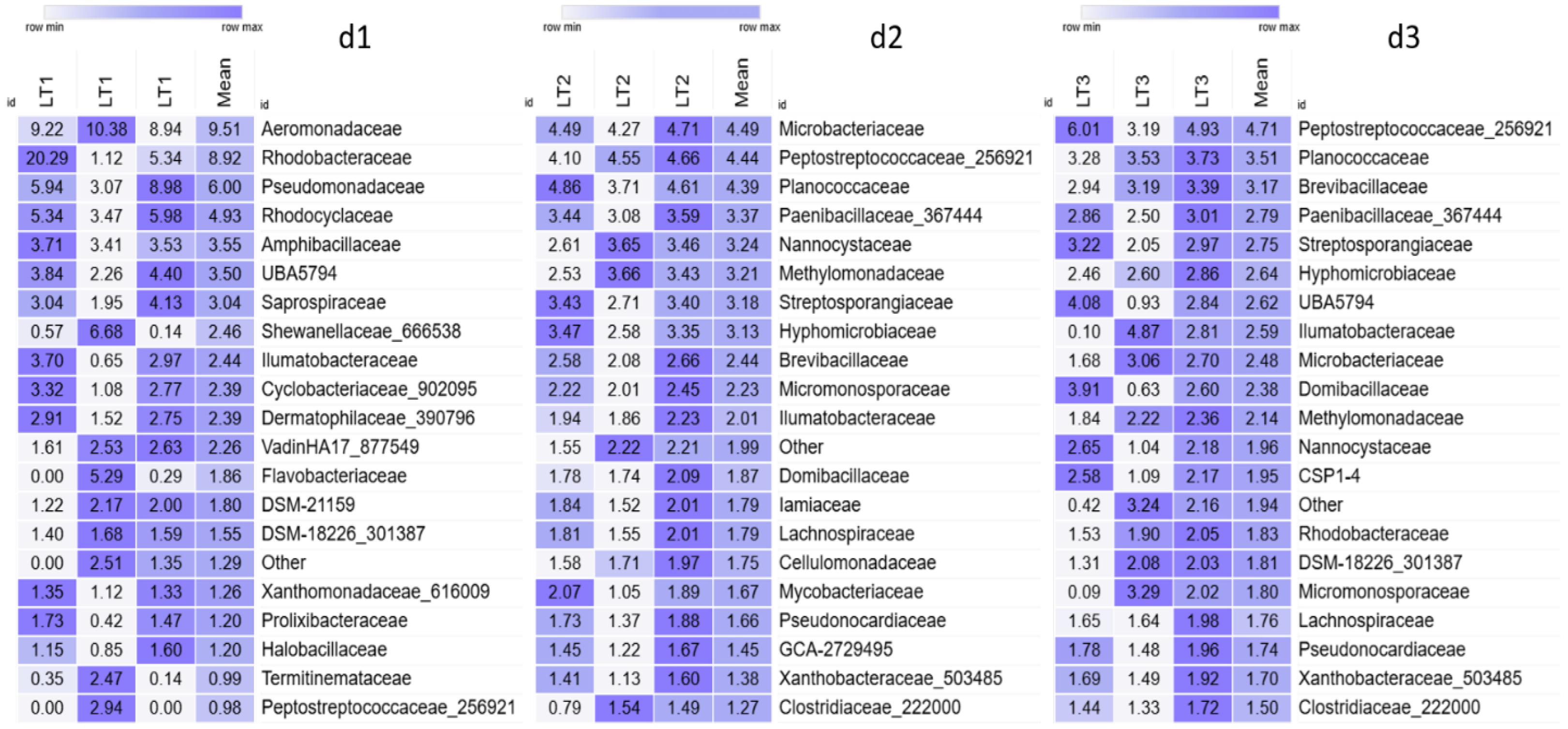
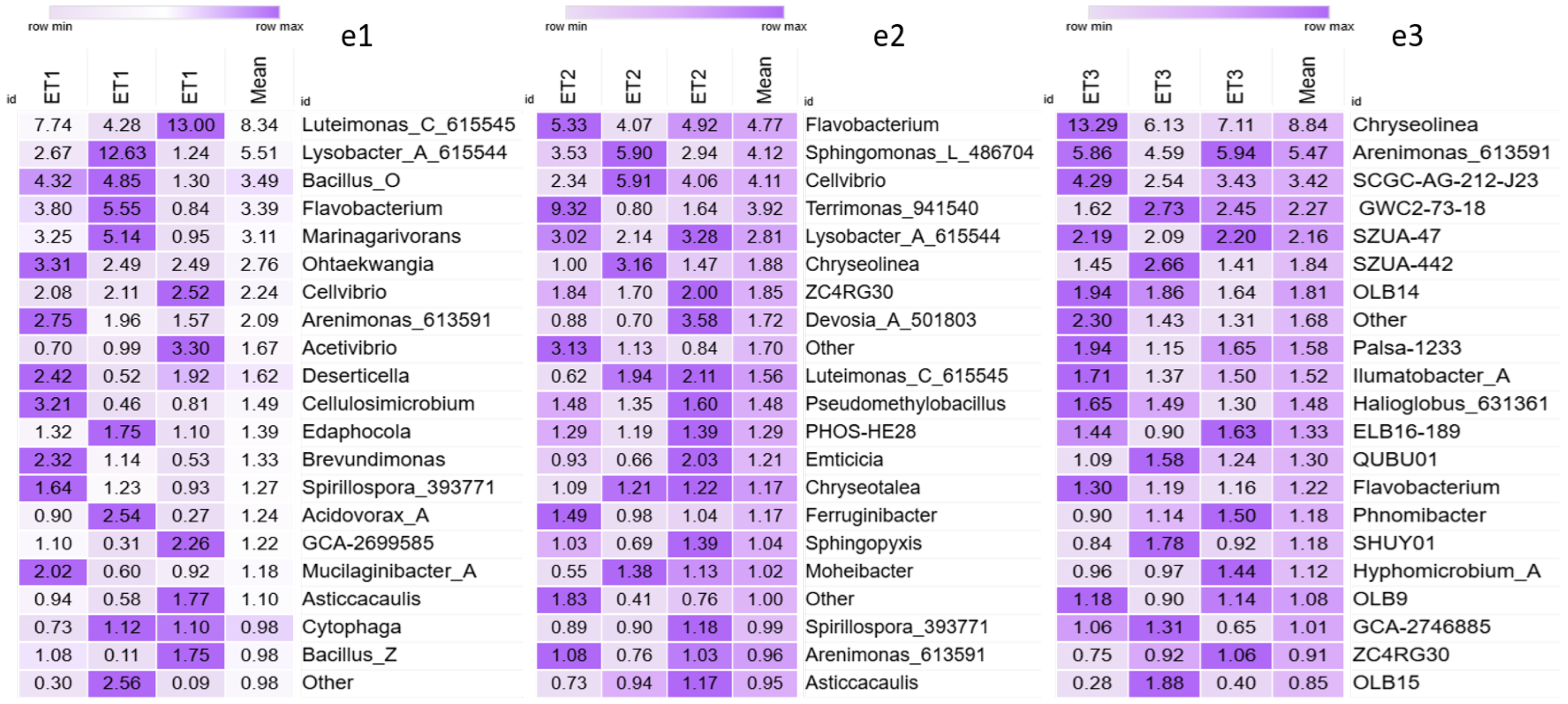
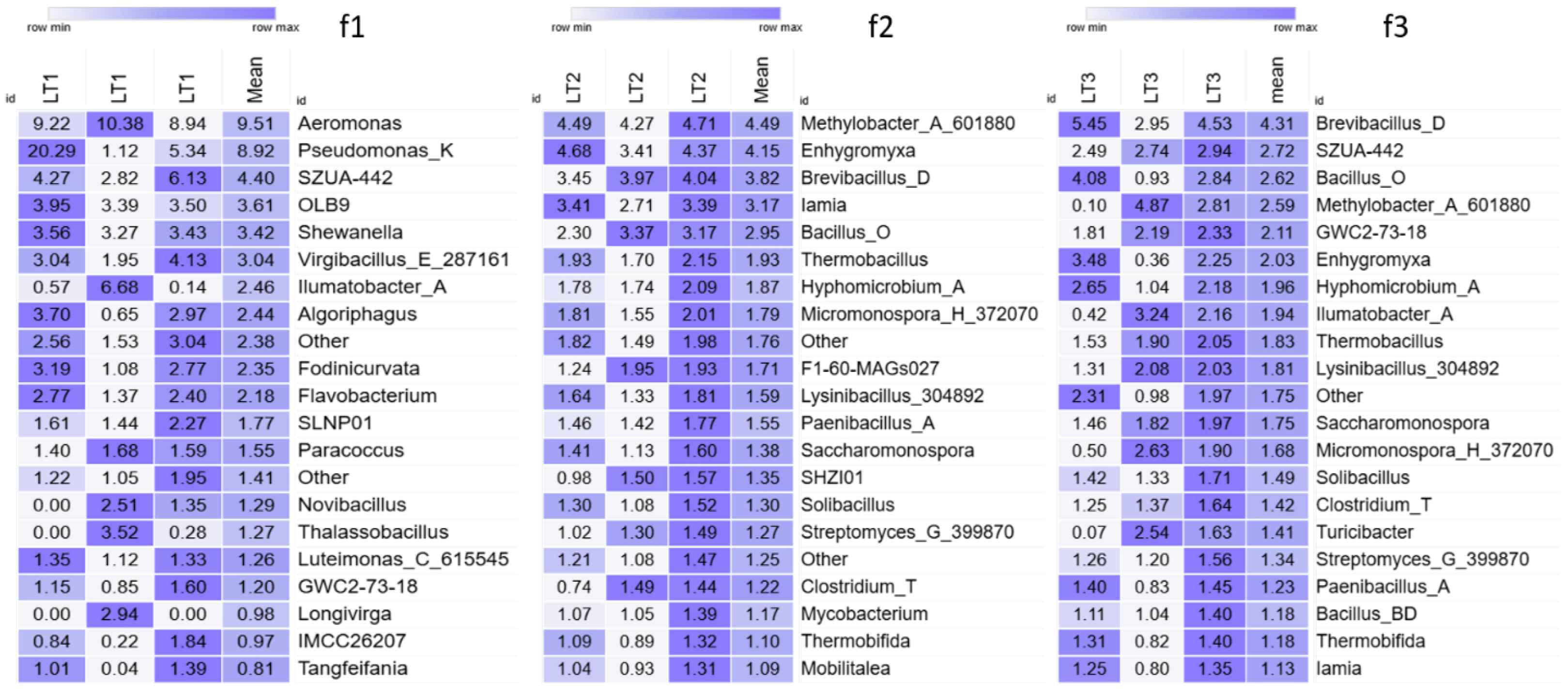
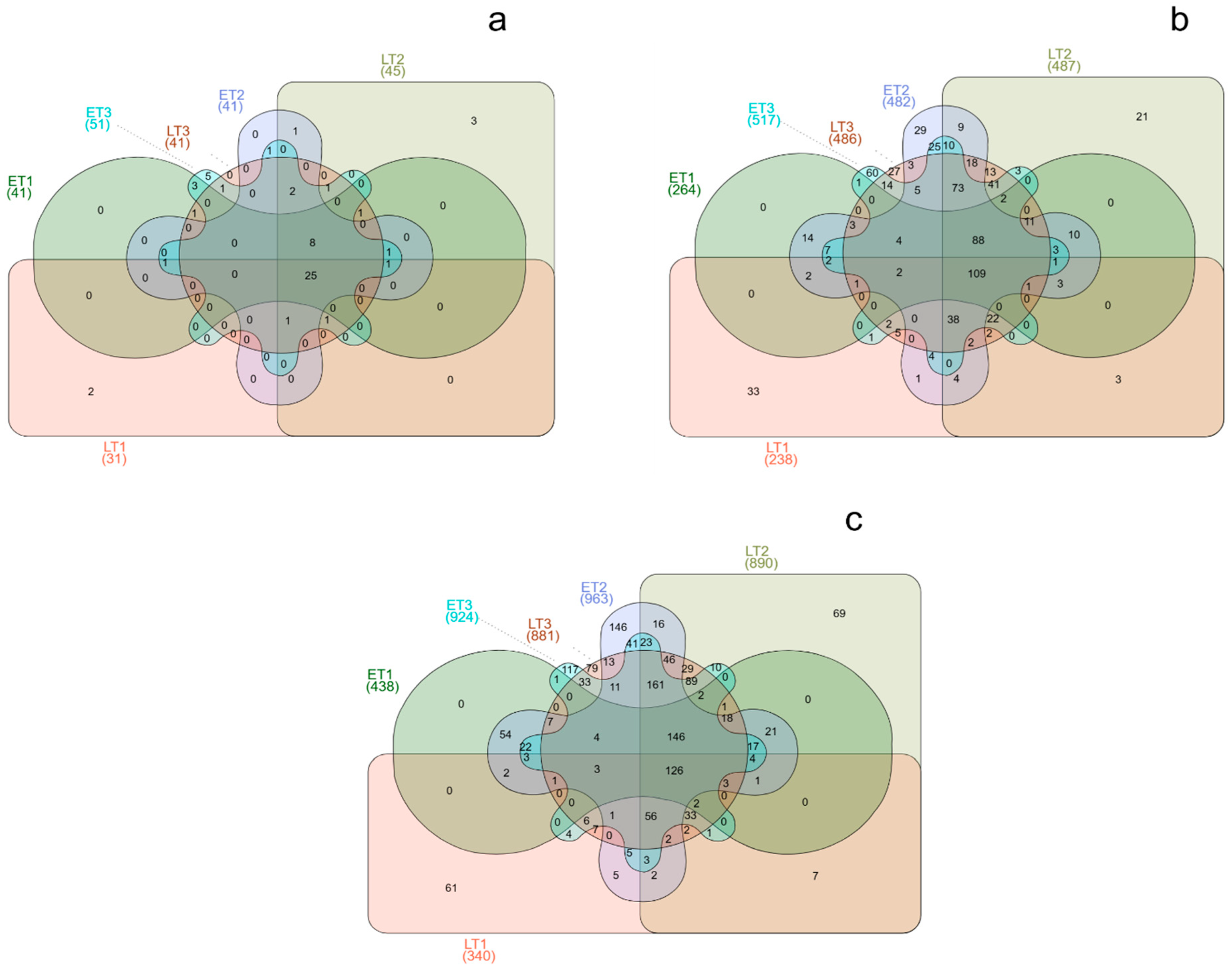

| Treatment | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET1 | 31 | 59 | 162 | 264 | 438 | 523 |
| ET2 | 41 | 94 | 269 | 482 | 963 | 1224 |
| ET3 | 51 | 111 | 294 | 517 | 924 | 843 |
| LT1 | 31 | 55 | 150 | 238 | 340 | 378 |
| LT2 | 45 | 95 | 268 | 487 | 891 | 1089 |
| LT3 | 41 | 95 | 264 | 486 | 881 | 1073 |
| Stage | pH | EC (dS/m) | M (%) | OM (%) | TOC (%) | TN (%) | C/N Ratio | P (%) | K (%) | Mg (%) | Ca (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET1 | 8.07 ± 0.04 | 1.97 ± 0.03 | 63.33 ± 1.52 | 79.47 ± 1.62 | 46.10 ± 0.94 | 1.70 ± 0.05 | 27.13 ± 0.40 | 1.14 ± 0.08 | 0.740 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.85 ± 0.03 |
| ET2 | 7.66 ± 0.04 | 1.37 ± 0.01 | 80.13 ± 0.04 | 64.47 ± 2.21 | 37.40 ± 1.25 | 1.890 ± 0.04 | 19.82 ± 0.81 | 1.26 ± 0.01 | 1.22 ± 0.006 | 0.450 ± 0.02 | 1.35 ± 0.03 |
| ET3 | 7.28 ± 0.05 | 1.38 ± 0.03 | 80.12 ± 0.03 | 47.80 ± 1.45 | 27.73 ± 0.84 | 2.23 ± 0.06 | 12.40 ± 0.02 | 1.41 ± 0.01 | 1.50 ± 0.05 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 2.81 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velásquez-Chávez, T.E.; Sáenz-Mata, J.; Quezada-Rivera, J.J.; Palacio-Rodríguez, R.; Muro-Pérez, G.; Servín-Prieto, A.J.; Hernández-López, M.; Preciado-Rangel, P.; Salazar-Ramírez, M.T.; Ontiveros-Chacón, J.C.; et al. Bacterial and Physicochemical Dynamics During the Vermicomposting of Bovine Manure: A Comparative Analysis of the Eisenia fetida Gut and Compost Matrix. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080177
Velásquez-Chávez TE, Sáenz-Mata J, Quezada-Rivera JJ, Palacio-Rodríguez R, Muro-Pérez G, Servín-Prieto AJ, Hernández-López M, Preciado-Rangel P, Salazar-Ramírez MT, Ontiveros-Chacón JC, et al. Bacterial and Physicochemical Dynamics During the Vermicomposting of Bovine Manure: A Comparative Analysis of the Eisenia fetida Gut and Compost Matrix. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(8):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080177
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelásquez-Chávez, Tania Elizabeth, Jorge Sáenz-Mata, Jesús Josafath Quezada-Rivera, Rubén Palacio-Rodríguez, Gisela Muro-Pérez, Alan Joel Servín-Prieto, Mónica Hernández-López, Pablo Preciado-Rangel, María Teresa Salazar-Ramírez, Juan Carlos Ontiveros-Chacón, and et al. 2025. "Bacterial and Physicochemical Dynamics During the Vermicomposting of Bovine Manure: A Comparative Analysis of the Eisenia fetida Gut and Compost Matrix" Microbiology Research 16, no. 8: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080177
APA StyleVelásquez-Chávez, T. E., Sáenz-Mata, J., Quezada-Rivera, J. J., Palacio-Rodríguez, R., Muro-Pérez, G., Servín-Prieto, A. J., Hernández-López, M., Preciado-Rangel, P., Salazar-Ramírez, M. T., Ontiveros-Chacón, J. C., & Peña, C. G.-D. l. (2025). Bacterial and Physicochemical Dynamics During the Vermicomposting of Bovine Manure: A Comparative Analysis of the Eisenia fetida Gut and Compost Matrix. Microbiology Research, 16(8), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080177








