Antimicrobial Resistance in Swine and Cattle Farms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
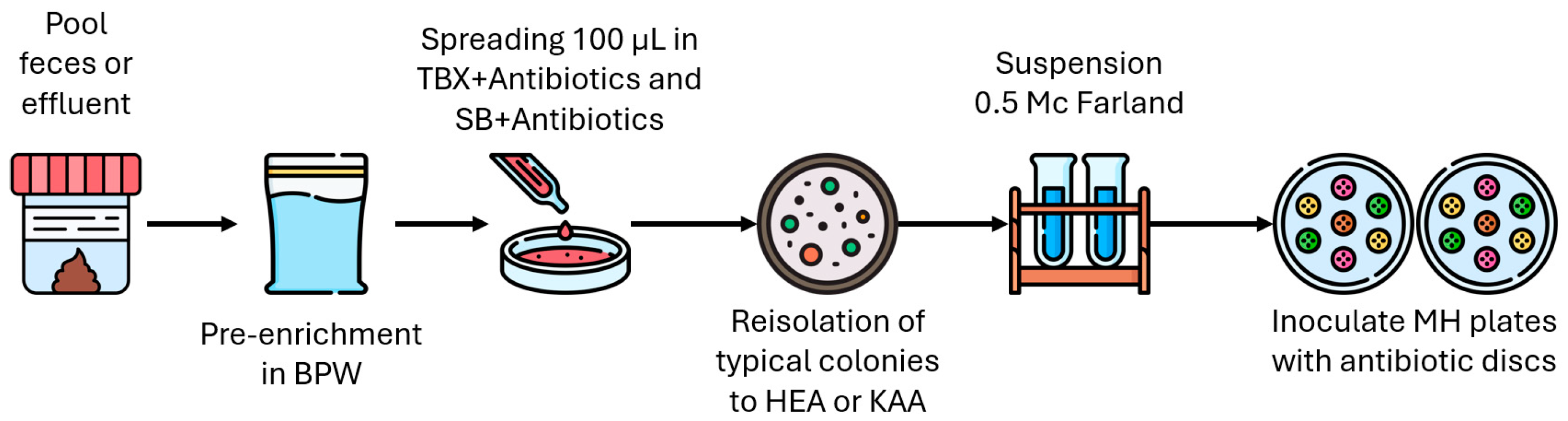
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Data and Statistical Analysis
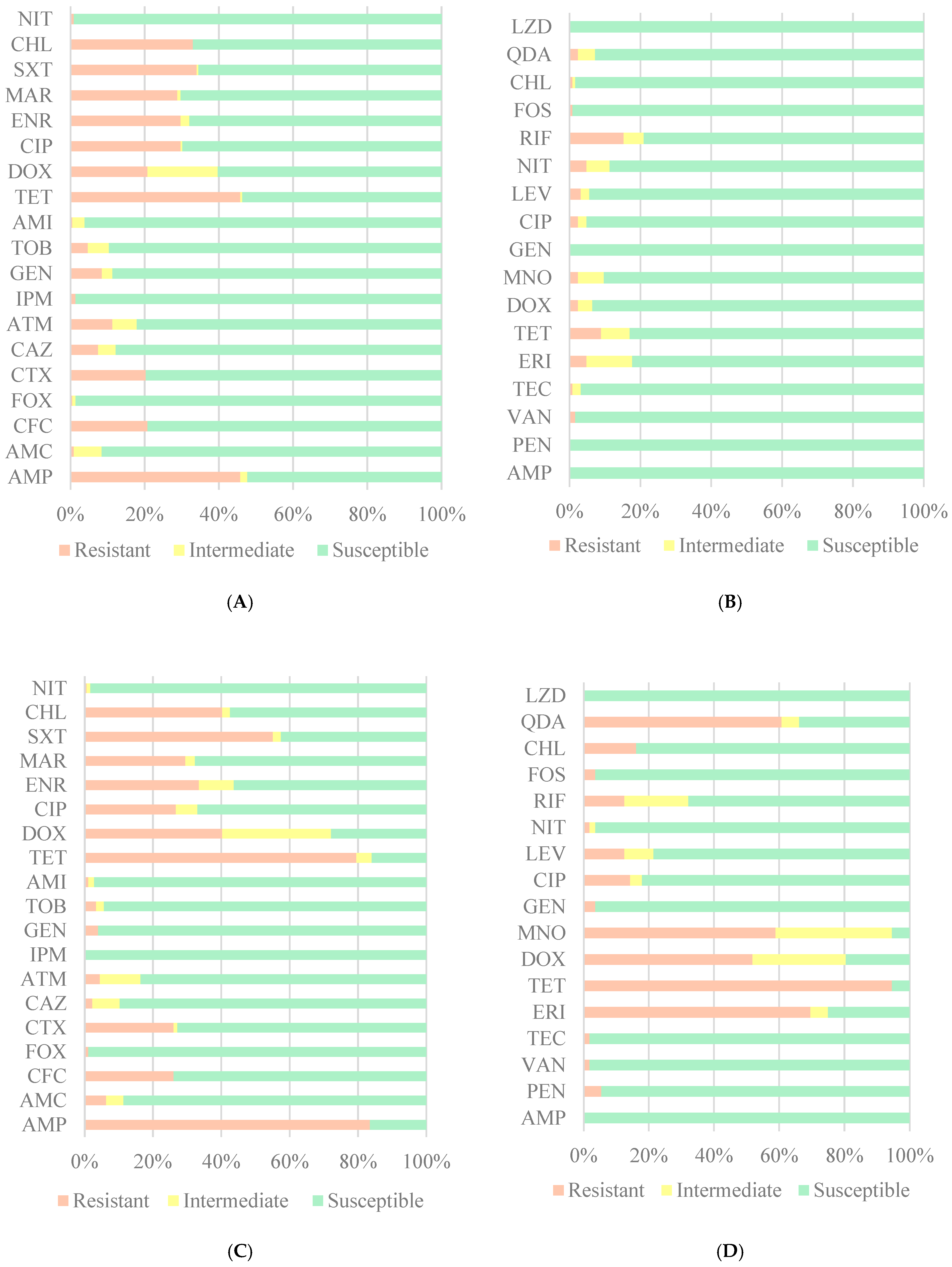
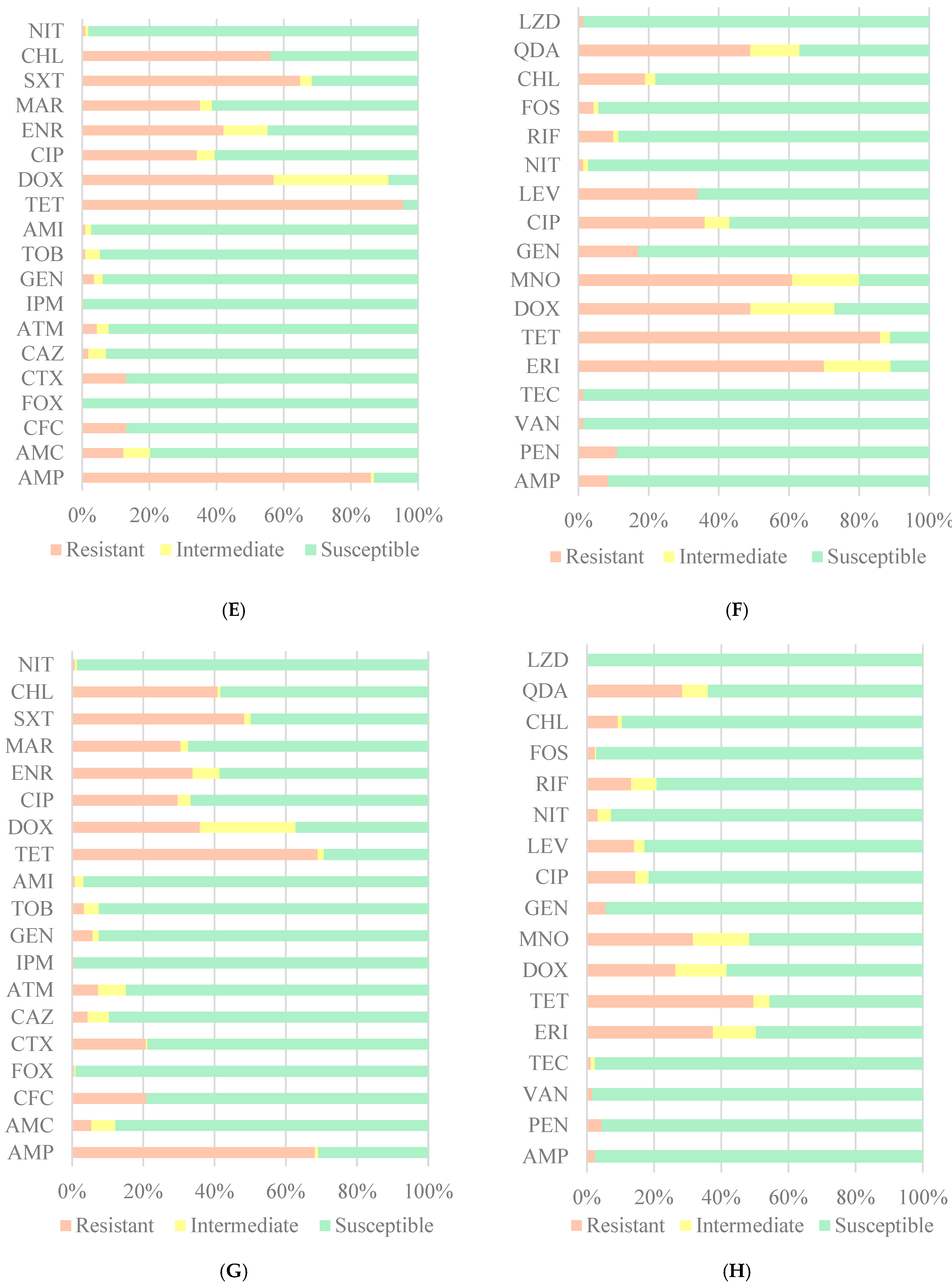
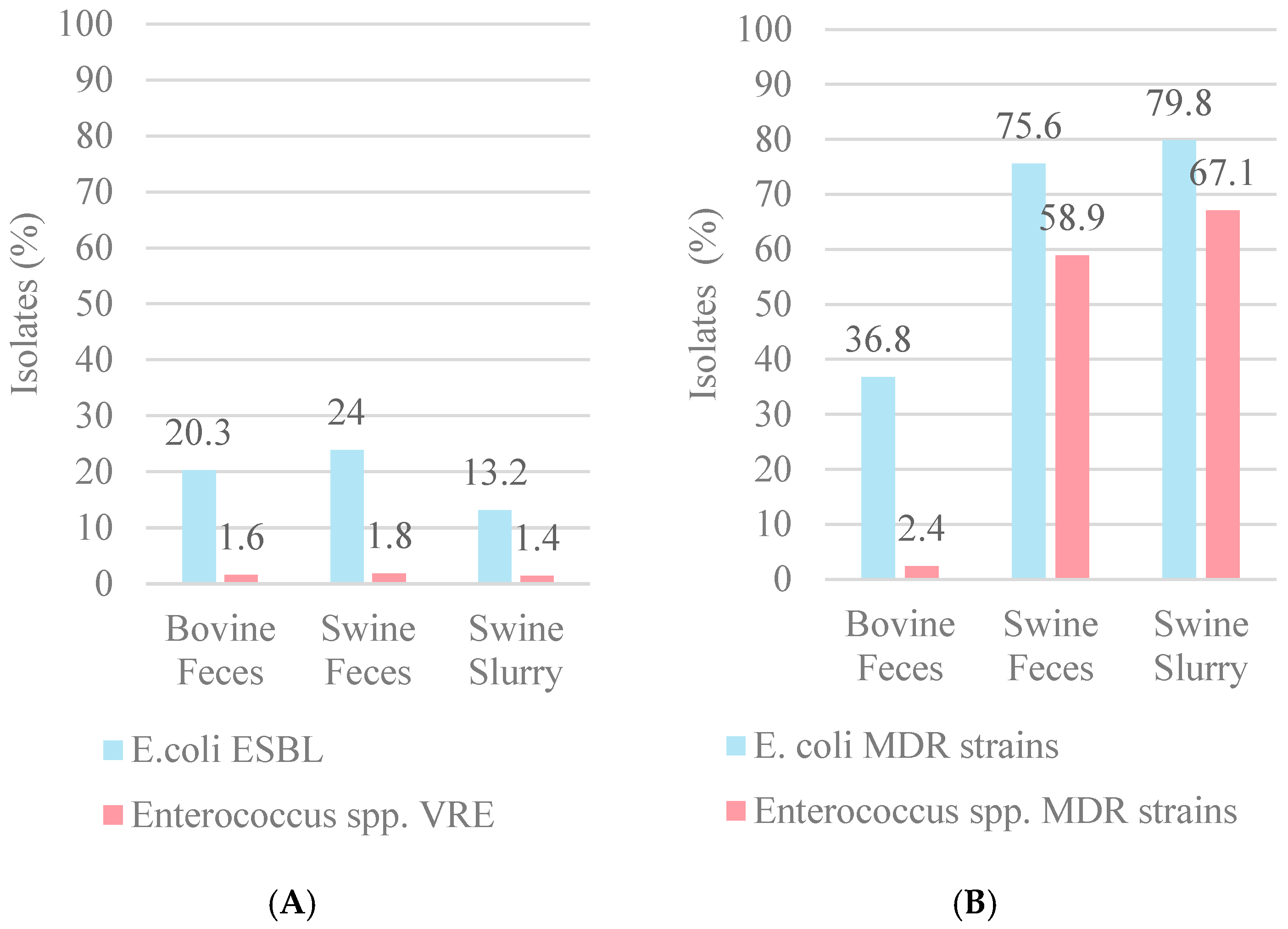
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Henriques, I.; Freitas, H.; Costa, J.; Silva, V.; Poeta, P.; Pereira, J. One Health: Um Planeta, Uma Saúde, Uma Ética; Avenida D. Carlos I, n° 134-5° andar 1200-651; CNECV: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Comissão Europeia. Ban on Antibiotics as Growth Promoters in Animal Feed Enters into Effect; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2005; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_05_1687 (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Stockton, B.; Davies, M. Antibiotic Use Plummets on US Farms After Ban on Using Drugs to Make Livestock Grow Faster. TBIJ. Available online: https://www.thebureauinvestigates.com/stories/2018-12-19/antibiotic-use-falls-on-us-farms-after-ban-on-using-drugs-to-make-livestock-grow-faster (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Gaskins, H.R.; Collier, C.T.; Anderson, D.B. Antibiotics as growth promotants: Mode of action. Anim. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, T. Veterinary Drug Residues in Food-animal Products: Its Risk Factors and Potential Effects on Public Health. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Igrejas, G.; Pereira, J.; Maltez, L.; Poeta, P. Resistências aos Antibióticos no Contexto “One Health”: Um Mundo, uma Luta, uma só Saúde; Avenida D. Carlos I, n° 134-5° andar 1200-651; CNECV: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- INSA. Vigilância Epidemiológica das Resistências aos Antimicrobianos Categoria. Available online: https://www.dgs.pt/upload/membro.id/ficheiros/i018609.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Burmeister, A.R. Horizontal Gene Transfer. Evol. Med. Public Health 2015, 2015, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, M.K. Comparison of Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated From Swine, Poultry, and Farm Workers in the Respective Livestock Farming Units in Greece. Cureus 2023, 15, e51073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boireau, C.; Cazeau, G.; Jarrige, N.; Calavas, D.; Madec, J.-Y.; Leblond, A.; Haenni, M.; Gay, É. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from mastitis in dairy cattle in France, 2006–2016. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9451–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. 2023. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8442 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Brito, T.; Portugal, C.; Sancho, L.; Carvalho, C.; Grima, B.; Alves, J.D. Sensibilidade das Enterobacteriáceas Produtoras de Beta-Lactamases de Espectro Alargado à Fosfomicina. Trimestral 2015, 22, 131–135. Available online: http://www.spmi.pt/revista/vol22/vol22_n3_2015_131_135.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Levitus, M.; Rewane, A.; Perera, T.B. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513233/ (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mencía-Ares, O.; Argüello, H.; Puente, H.; Gómez-García, M.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Carvajal, A.; Rubio, P. Antimicrobial resistance in commensal Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. is influenced by production system, antimicrobial use, and biosecurity measures on Spanish pig farms. Porc. Health Manag. 2021, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, T.H. Tetracycline Antibiotics and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.N.; Flonta, M.; Gurler, N.; Cepparulo, M.; Mendes, R.E.; Castanheira, M. Resistance surveillance program report for selected European nations (2011). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I. Caracterização da Utilização de Antimicrobianos em Produção Animal-Alimentos Medicamentosos em Suinicultura.pdf. Dissertação de Mestrado, Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária da Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal. 2014. Available online: https://www.repository.utl.pt/bitstream/10400.5/7093/1/Caracteriza%C3%A7%C3%A3o%20da%20Utiliza%C3%A7%C3%A3o%20de%20Antimicrobianos%20em%20Produ%C3%A7%C3%A3o%20Animal-Alimentos%20Medicamentosos%20em%20Suinicultura.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Barton, M.D. Impact of antibiotic use in the swine industry. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 19, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis, J. Estratégias Nutricionais na Prevençao de Doenças Digestivas dos Suínos. Dissertação de Mestrado; Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária da Universidade de Lisboa: Lisbon, Portugal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Jiang, T.; Yan, H.; Guo, C.; Liu, J.; Su, H.; Alugongo, G.M.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; et al. Ecological Restoration of Antibiotic-Disturbed Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Foregut and Hindgut of Cows. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, X.C.; Gilbert, A.-A.; Saucier, L.; Vincent, A.T. Antibiotic Resistance: From Pig to Meat. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2022—Trends from 2010 to 2022—Thirteenth ESVAC Report; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothrock, M.J.; Min, B.R.; Castleberry, L.; Waldrip, H.; Parker, D.; Brauer, D.; Pitta, D.; Indugu, N. Antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial residues, and bacterial community diversity in pasture-raised poultry, swine, and beef cattle manures. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, C.S.-S.; Sanders, P.; Gaugain, M.; Viel, A.; Paboeuf, F.; Taillandier, J.-F.; Houée, P.; Valentin, C.; Perrin-Guyomard, A. Selection of antibiotic resistance in pigs after exposure to feed cross-contaminated with oxytetracycline. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 287, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, L.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Dai, M. The Influencing Factors of Bacterial Resistance Related to Livestock Farm: Sources and Mechanisms. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2, 650347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Sassoubre, L.M. Enterococci as Indicators of Environmental Fecal Contamination. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Gilmore, M.S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK190421/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK579461/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Mencía-Ares, O.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Cobo-Díaz, J.F.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Gómez-García, M.; Puente, H.; Cotter, P.D.; Crispie, F.; Carvajal, A.; Rubio, P.; et al. Antimicrobial use and production system shape the fecal, environmental, and slurry resistomes of pig farms. Microbiome 2020, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barathe, P.; Kaur, K.; Reddy, S.; Shriram, V.; Kumar, V. Antibiotic pollution and associated antimicrobial resistance in the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2024, 5, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B.A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Johnson, T.A.; Su, J.-Q.; Qiao, M.; Guo, G.-X.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Hashsham, S.A.; Tiedje, J.M. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3435–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, S.R.; Li, X.; Snow, D.D.; Gilley, J.E.; Woodbury, B.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L. Fate of antimicrobials and antimicrobial resistance genes in simulated swine manure storage. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Munk, P.; Njage, P.; Van Bunnik, B.; McNally, L.; Lukjancenko, O.; Röder, T.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Kjeldgaard, J.; et al. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Phan, D.; Ashworth, D.; Schmidt, M.P.; Murinda, S.E.; Obayiuwana, A.; Murry, M.A.; Schwartz, G.; Lundquist, T.; et al. Potential reservoirs of antimicrobial resistance in livestock waste and treated wastewater that can be disseminated to agricultural land. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chessa, L.; Jechalke, S.; Ding, G.-C.; Pusino, A.; Mangia, N.P.; Smalla, K. The presence of tetracycline in cow manure changes the impact of repeated manure application on soil bacterial communities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Kong, L.; Gao, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X. A Review of Current Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics in Food Animals. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 822689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtiya, M.; Matthews, K.R.; Dhewa, T.; Puniya, A.K. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Food Chain: Trends, Mechanisms, Pathways, and Possible Regulation Strategies. Foods 2022, 11, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Mrozik, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Antibiotics in the Soil Environment—Degradation and Their Impact on Microbial Activity and Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Q.; Wei, B.; Xu, C.Y.; Qiao, M.; Zhu, Y.G. Functional metagenomic characterization of antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soils from China. Environ. Int. 2014, 65, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, W. Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Mao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, Y.; Cai, B. The Source and Distribution of Tetracycline Antibiotics in China: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, C.; Zeng, Q.; Ding, D.; Gu, J.; Mo, J. Field study on loss of tetracycline antibiotics from manure-applied soil and their risk assessment in regional water environment of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Shen, Q.; Liu, F.; Ma, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M. Antibiotic resistance gene abundances associated with antibiotics and heavy metals in animal manures and agricultural soils adjacent to feedlots in Shanghai; China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Rotini, A.; Thaller, M.C. Low Doses of Tetracycline Trigger the E. coli Growth: A Case of Hormetic Response. Dose-Response 2013, 11, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Sengeløv, G.; Tjørnelund, J. Toxicity of Tetracyclines and Tetracycline Degradation Products to Environmentally Relevant Bacteria, Including Selected Tetracycline-Resistant Bacteria. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Maximum Levels of Cross-Contamination for 24 Antimicrobial Active Substances in Non-Target Feed. Part 12: Tetracyclines: Tetracycline, Chlortetracycline, Oxytetracycline, and Doxycycline; EFSA Journal; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6864 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Xie, X.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, D.; Guo, J.; Bao, Y. Toxic effect of tetracycline exposure on growth, antioxidative and genetic indices of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelkova, B.; Beklova, M.; Kovacova, V.; Hlavkova, D.; Pikula, J. Ecotoxicity of selected antibiotics for organisms of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2016, 37 (Suppl. 1), 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, fate, and risk assessment of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10712:1995; Water Quality—Pseudomonas Putida Growth Inhibition Test (Pseudomonas Cell Multiplication Inhibition Test). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/18800.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- OECD. Test No. 209: Activated Sludge, Respiration Inhibition Test (Carbon and Ammonium Oxidation); OECD: Paris, France, 2010; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/test-no-209-activated-sludge-respiration-inhibition-test_9789264070080-en.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Strotmann, U.; Durand, M.-J.; Thouand, G.; Eberlein, C.; Heipieper, H.J.; Gartiser, S.; Pagga, U. Microbiological toxicity tests using standardized ISO/OECD methods—Current state and outlook. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensão, F. Aproveitamento do Leite de Rejeição na Alimentação de Vitelos: Implicação nas Resistências aos Antimicrobianos. Dissertação de Mestrado, Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas Abel Salazar da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal. 2022. Available online: https://repositorio-aberto.up.pt/bitstream/10216/141011/2/555309.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Bacanlı, M.G. The two faces of antibiotics: An overview of the effects of antibiotic residues in foodstuffs. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ma, L.; Yu, Q.; Yang, J.; Su, W.; Hilal, M.G.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, H. The source, fate and prospect of antibiotic resistance genes in soil: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 976657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.B.; Arnipalli, S.R.; Ziouzenkova, O. Antibiotics in Food Chain: The Consequences for Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Bin Emran, T.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP—UN Environment Programme. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Threat. Available online: http://www.unep.org/topics/chemicals-and-pollution-action/pollution-and-health/antimicrobial-resistance-global-threat (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.P.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.I.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilurdoz, M.S.; Sadhwani, J.J.; Reboso, J.V. Antibiotic removal processes from water & wastewater for the protection of the aquatic environment—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, K.; Xu, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Jones, D.L.; Zou, J. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soils: A systematic analysis. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Hong, Y.; Mo, C.; Huang, P.; Liao, X.; Yang, Y. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes during livestock wastewater treatment processes: Review and prospects. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1054316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunai, A.; Spohn, R.; Farkas, Z.; Lázár, V.; Györkei, Á.; Apjok, G.; Boross, G.; Szappanos, B.; Grézal, G.; Faragó, A.; et al. Rapid decline of bacterial drug-resistance in an antibiotic-free environment through phenotypic reversion. eLife 2019, 8, e47088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Elena, A.X.; Kunath, M.A.; Berendonk, T.U.; Klümper, U. Reduced selection for antibiotic resistance in community context is maintained despite pressure by additional antibiotics. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuku, C.; Gazdag, Z.; Melegh, S. Occurrence of antibiotics and bacterial resistance genes in wastewater: Resistance mechanisms and antimicrobial resistance control approaches. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; El Fels, L.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly-Chatain, M.H. The factors affecting effectiveness of treatment in phages therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Escherichia coli | Enterococcus spp. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations | Antibiotics | Concentrations (μg) | Abbreviations | Antibiotics | Concentrations (μg) |
| AMI | Amikacin | 30 | AMP | Ampicillin | 30 |
| AMC | Amoxicillin-clavulanate | 30 | CHL | Chloramphenicol | 30 |
| AMP | Ampicillin | 10 | CIP | Ciprofloxacin | 5 |
| ATM | Aztreonam | 30 | GEN | Gentamicin | 120 |
| CHL | Chloramphenicol | 30 | DOX | Doxycycline | 30 |
| CAZ | Ceftazidime | 30 | ERI | Erythromycin | 15 |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin | 5 | NIT | Nitrofurantoin | 300 |
| GEN | Gentamicin | 30 | FOS | Fosfomycin | 200 |
| CTX | Cefotaxime | 30 | LEV | Levofloxacin | 5 |
| DOX | Doxycycline | 30 | LZD | Linezolid | 30 |
| ENR | Enrofloxacin | 5 | MNO | Minocycline | 30 |
| NIT | Nitrofurantoin | 300 | PEN | Penicillin G | 30 |
| FOX | Cefoxitin | 30 | QDA | Quinupristin-dalfopristin | 15 |
| IPM | Imipenem | 10 | RIF | Rifampicin | 30 |
| CFC | Cefazolin | 30 | TET | Tetracycline | 30 |
| MAR | Marbofloxacin | 5 | TEC | Teicoplanin | 30 |
| SXT | Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 25 | VAN | Vancomycin | 30 |
| TET | Tetracycline | 30 | |||
| TOB | Tobramycin | 10 | |||
| Samples (n) | Isolates (n) | TET Resistance (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | Enterococcus spp. | E. coli | Enterococcus spp. | ||
| CF | 24 | 212 | 124 | 97 (45.8%) | 11 (8.9%) |
| SF | 14 | 176 | 56 | 140 (79.5%) | 53 (94.6%) |
| SS | 11 | 114 | 70 | 109 (95.6%) | 60 (85.7%) |
| Total | 49 | 502 | 250 | 346 (68.9%) | 124 (49.6%) |
| E. coli | Enterococcus spp. | |
|---|---|---|
| Cow Feces/Swine Feces | 6 | 1 |
| Cow Feces/Swine Slurry | 2 | 1 |
| Swine Feces/Swine Slurry | 14 | 5 |
| Cow Feces/Swine Feces/Swine Slurry | 6 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, B.F.; Silva, S.A.M.; Rodrigues, I.C.; Lopes-Jorge, J.M.; Niza-Ribeiro, J.; Prata, J.C.; Costa, P.M.d. Antimicrobial Resistance in Swine and Cattle Farms. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16040083
Pinto BF, Silva SAM, Rodrigues IC, Lopes-Jorge JM, Niza-Ribeiro J, Prata JC, Costa PMd. Antimicrobial Resistance in Swine and Cattle Farms. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16040083
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Bruna F., Sara A. M. Silva, Inês C. Rodrigues, J. M. Lopes-Jorge, J. Niza-Ribeiro, Joana C. Prata, and Paulo Martins da Costa. 2025. "Antimicrobial Resistance in Swine and Cattle Farms" Microbiology Research 16, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16040083
APA StylePinto, B. F., Silva, S. A. M., Rodrigues, I. C., Lopes-Jorge, J. M., Niza-Ribeiro, J., Prata, J. C., & Costa, P. M. d. (2025). Antimicrobial Resistance in Swine and Cattle Farms. Microbiology Research, 16(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16040083








