Dietary Mycotoxins Effects on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Microbiomes Can Be Mitigated with Addition of Organically Modified Clinoptilolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Feed Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. RT-PCR
| Name | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Forward (F)/Reverse (R) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Universal Eubacterial gene | 530F (GTCCCAGCMGCNGCGG) | F | [42] |
| 1100R (GGGTTNCGNTCGTTG) | R | ||
| Firmicutes | 928F (TGAAACTYAAAGGAATTGACG) | F | [43] |
| 1040R (ACCATGCACCACCTGTC) | R | ||
| Bacteroidetes | 798cfbF (CRAACAGGATTAGATACCCT) | F | [43] |
| cfb967R (GGTAAGGGTTCCTCGCGTAT) | R | ||
| Actinobacteria | Eub338F (ACGGGCGGTGTGTACA) | F | [44] |
| Act1159R (TCCGAGTTRACCCCGGC) | R | ||
| Proteobacteria | 27F (GAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG) | F | [45] |
| 1529R (CAKAAAGGAGGTGATCC) | R | ||
| Clostridiaceae | Clos-58-f (AAAGGAAGATTAATACCGCATAA) | F | [46] |
| Clos780-r (ATCTTGCGACCGTACTCCCC) | R |
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
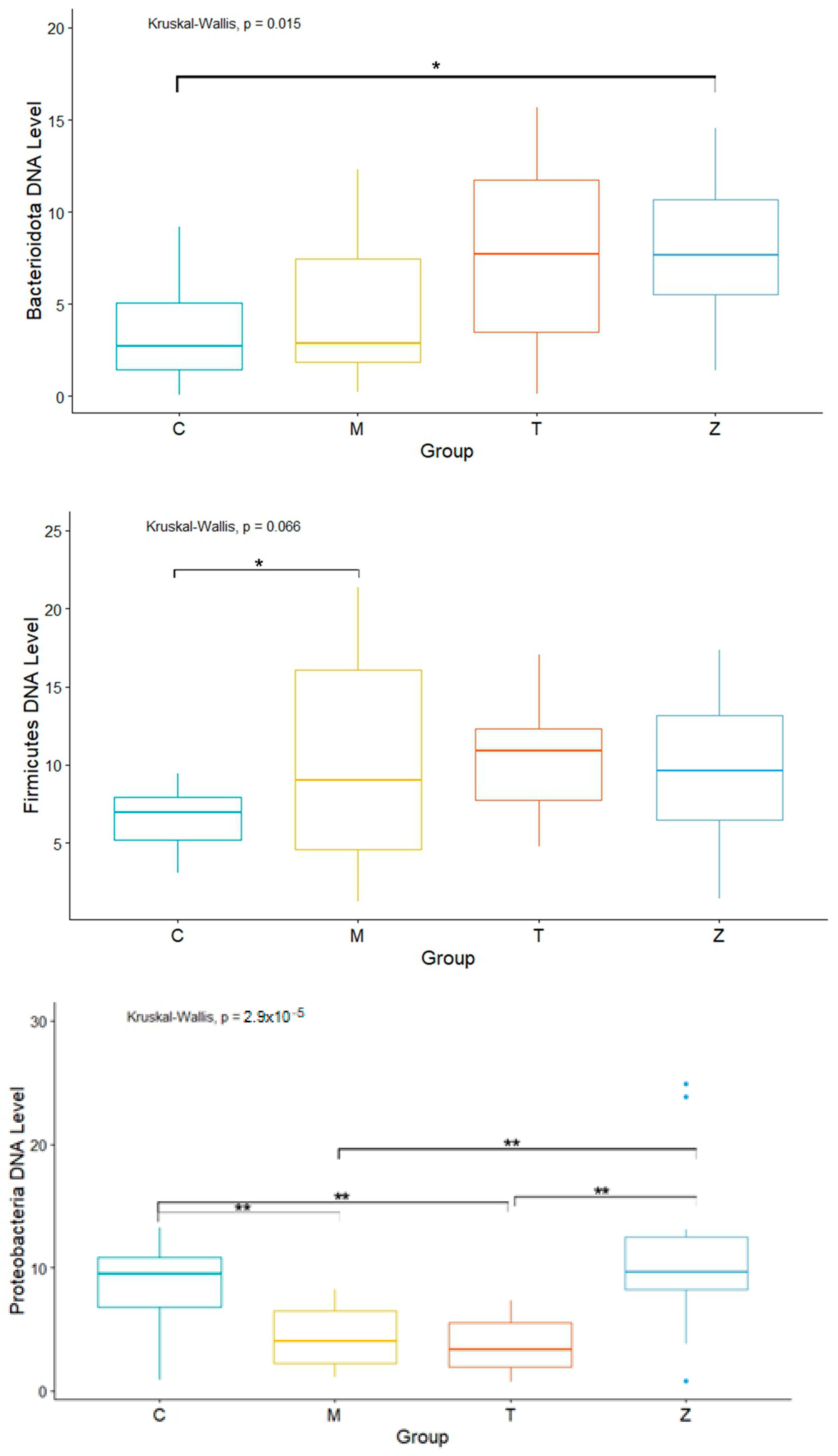
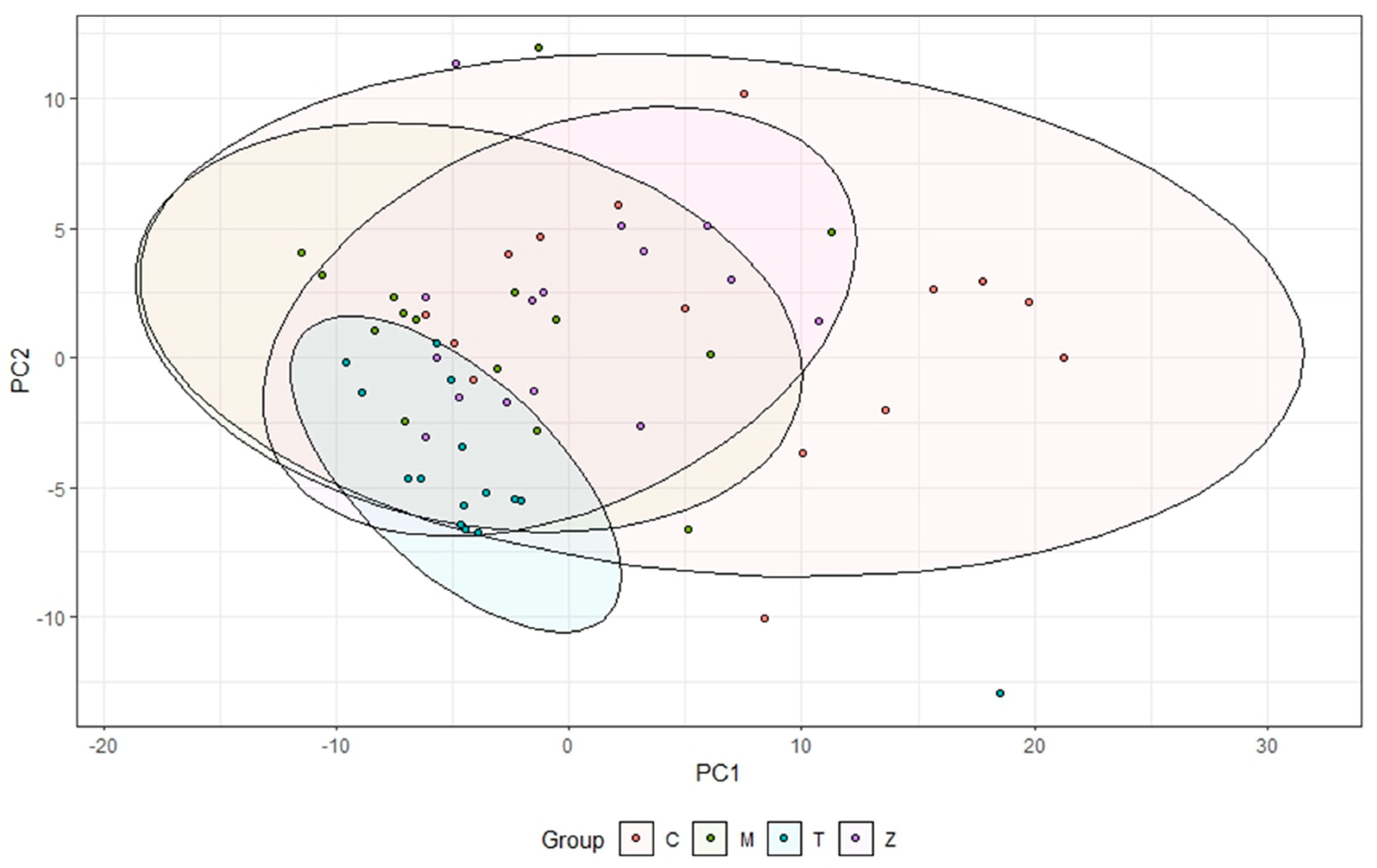
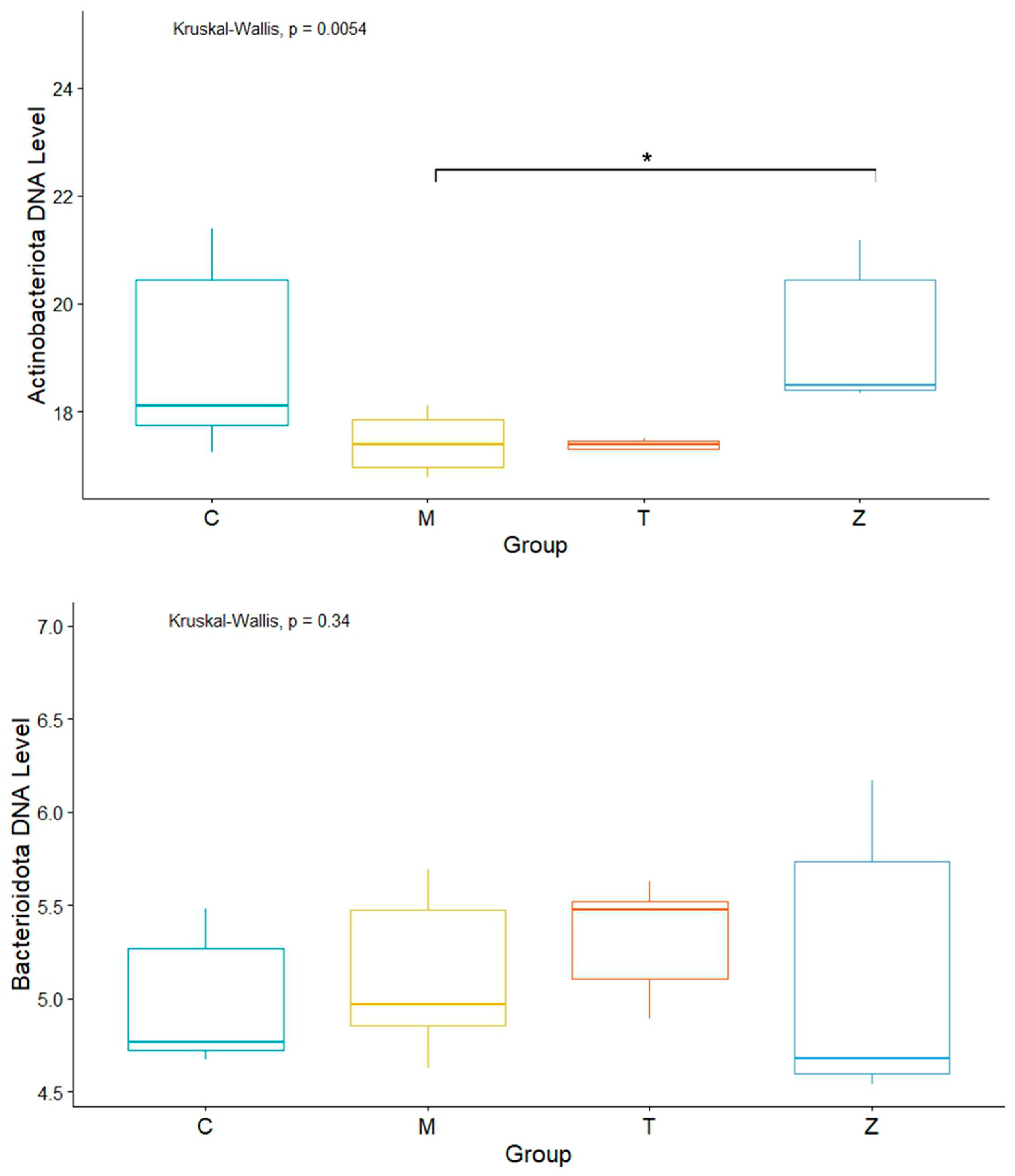
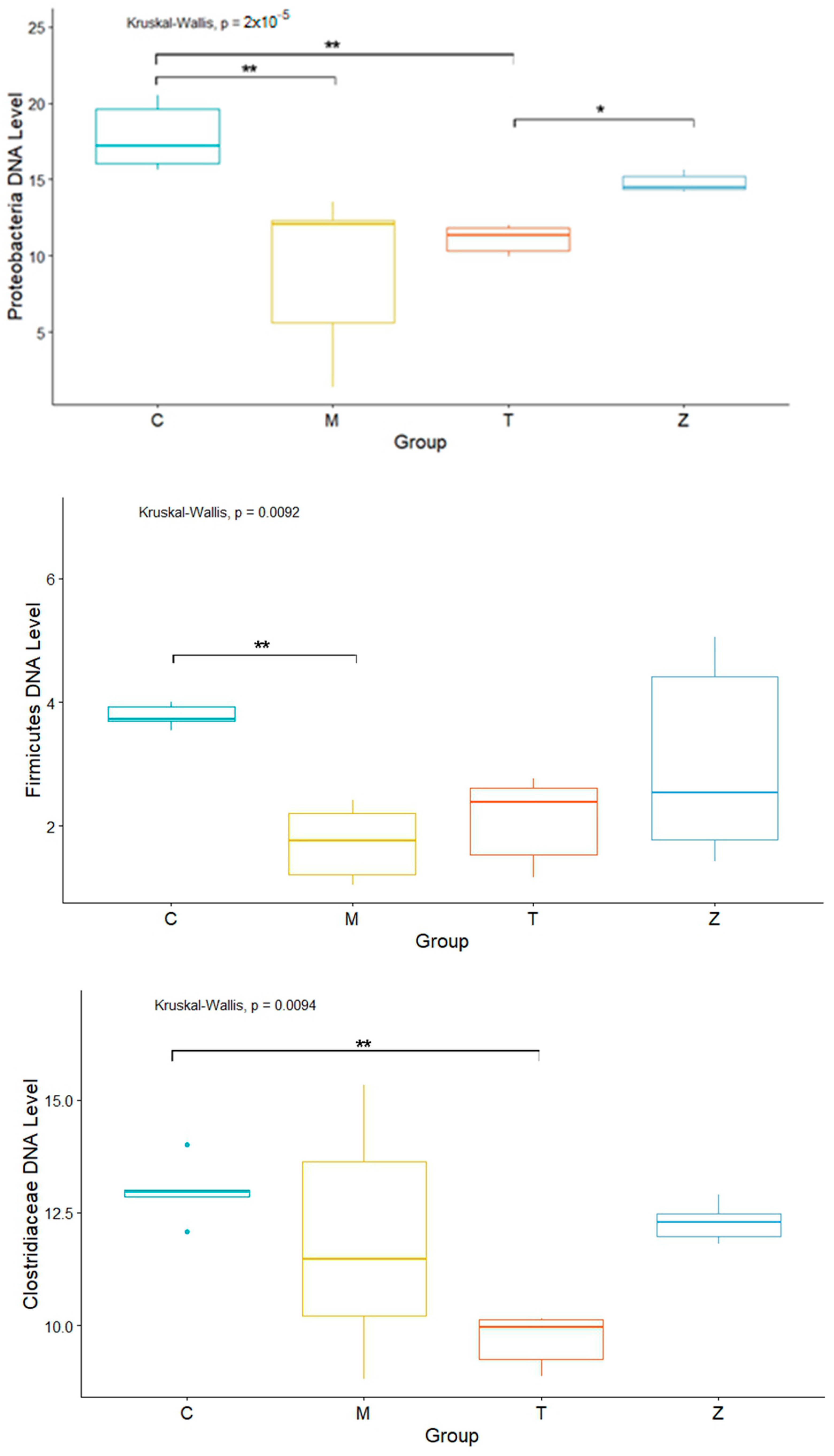
3.1. Gills
3.2. Intestines
3.3. Water
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parata, L.; Sammut, J.; Egan, S. Opportunities for microbiome research to enhance farmed freshwater fish quality and production. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, C.; Nagar, S.; Lal, R.; Negi, R.K. Fish gut microbiome: Current approaches and future perspectives. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A. Environmental and physiological factors shape the gut microbiota of Atlantic salmon parr (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2017, 467, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, E.; Wang, T.; Zou, J.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Secombes, C.J. Characterization of three novel β-defensin antimicrobial peptides in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Rodiles, A. The fish microbiome and its interactions with mucosal tissues. In Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar]
- Mougin, J.; Joyce, A. Fish disease prevention via microbial dysbiosis-associated biomarkers in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Pedà, C.; Cappello, S.; Leonardi, M.; La Ferla, R.; Lo Giudice, A.; Romeo, T. Effects of microplastics on trophic parameters, abundance and metabolic activities of seawater and fish gut bacteria in mesocosm conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30067–30083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Liao, Z.; Ma, X.; Liang, M.; Xu, H.; Mai, K.; Zhang, Y. Response of Intestinal Microbiota of Tiger Puffer (Takifugu rubripes) to the Fish Oil Finishing Strategy. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, C.; Sun, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, G. Effect of dietary soybean meal associated with feeding time on the growth performance and intestinal microbiota composition of northern snakehead. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Kumkhong, S.; Gu, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y. Effects of deoxynivalenol-contaminated diet on the composition and diversity of the intestinal microbial community and intestinal ultrastructure of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejova, I.; Svobodova, Z.; Vakula, J.; Mares, J.; Modra, H. Impact of mycotoxins on aquaculture fish species: A review. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 48, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFSSA. Risk Assessment for Mycotoxins in Human and Animal Food Chains; AFSSA: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Naehrer, K.; Santos, G.A. Occurrence of mycotoxins in commercial aquafeeds in Asia and Europe: A real risk to aquaculture? Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anater, A.; Manyes, L.; Meca, G.; Ferrer, E.; Luciano, F.B.; Pimpão, C.T.; Font, G. Mycotoxins and their consequences in aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2016, 451, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Cao, S.; Wan, S.F.; Chen, Z.; Saleemi, M.K.; Wang, N.; Munawar, J. Mycotoxins–A global one health concern: A review. Agrobiol. Rec. 2020, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijani, E.; Kigadye, E.; Okoth, S. Occurrence of fungi and mycotoxins in fish feeds and their impact on fish health. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 6743065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, M.C.; Neeff, D.V.D.; Jager, A.V.; Corassin, C.H.; Carão, Á.C.D.P.; Albuquerque, R.D.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Mineral adsorbents for prevention of mycotoxins in animal feeds. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derome, N.; Gauthier, J.; Boutin, S.; Llewellyn, M. Bacterial opportunistic pathogens of fish. In The Rasputin Effect: When Commensals and Symbionts Become Parasitic; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 81–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, R.B.; Telli, G.S.; Tachibana, L.; de Carla Dias, D.; Oshiro, E.; Natori, M.M.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics for Nile tilapia: Growth performance and protection against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xia, Y.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.J. Accelerated spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) induced by non-antibiotic conditions: Roles and mechanisms. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, T.; Fang, H.H. Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, M.; Daković, A.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Kragović, M.; Petković, A.; Krajišnik, D.; de Gennaro, B. Adsorption of the mycotoxin zearalenone by clinoptilolite and phillipsite zeolites treated with cetylpyridinium surfactant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 151, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M.; Tassis, P.; Farkaš, H.; Bošnjak-Neumüller, J.; Männer, K. Effects of a modified clinoptilolite zeolite on growth performance, health status and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A in male broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadzadeh Kakhki, R.; Zirjanizadeh, S.; Mohammadpoor, M. A review of clinoptilolite, its photocatalytic, chemical activity, structure and properties: In time of artificial intelligence. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 10555–10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, G.R.; Habib, Y.J.; El Basuini, M.F.; Fayed, W.M.; Shehata, A.I. Synergistic interactions of zeolite, stocking density, and water exchange: A holistic approach to optimizing aquaculture performance of juvenile European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Sci. Afr. 2024, 23, e02043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich-Cristopulos, G.; Schiavo, B.; Romero, F.M.; Hernández-Mendiola, E.; Angulo-Molina, A.; Meza-Figueroa, D. Oral bioaccessibility of metal (oid) s in commercial zeolite used as a dietary supplement: Implications to human health risk. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalena Tomasevic-Canovic, S.M. Patent Co Preduzece Za Proizvodnju Usluge I Pro. EU Patent No. EP1363854B1, 22 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ergün, S.; Yigit, M.; Türker, A. Growth and Feed Consumption of Young Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Exposed To Different Photoperiods. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2003, 55, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; Risha, E.; Hamed, M.; Ibrahim, T.; Palić, D. Dietary mycotoxicosis prevention with modified zeolite (Clinoptilolite) feed additive in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Genc, E.; Palić, D.; Genc, M.A.; Todorović, N.; Sevgili, H.; Guroy, D. Effect of dietary modified zeolite (Clinoptilolite) on growth performance of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) in the recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasai, T.P.; Walsh, K.B.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J.; Van, T.T.; Moore, R.J.; Stanley, D. Zeolite food supplementation reduces abundance of enterobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 195, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, E.; Elazab, M.A.; Soltan, Y.A.; Elkomy, A.E.; El-Zaiat, H.M.; Sallam, S.M.; El-Azrak, K.E.D. Nano and natural zeolite feed supplements for dairy goats: Feed intake, ruminal fermentation, blood metabolites, and milk yield and fatty acids profile. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2023, 295, 115522. [Google Scholar]
- Özogul, F.; Šimat, V.; Gokdogan, S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Özogul, Y. Effect of natural zeolite (Clinoptilolite) on in vitro biogenic amine production by gram positive and gram-negative pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoslavskij, A.; Terentjeva, M.; Eizenberga, I.; Valciņa, O.; Bartkevičs, V.; Bērziņš, A. Major foodborne pathogens in fish and fish products: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, M.; Abd El-Moein, K.; Hamza, E.; Kader, F.A. Occurrence of Clostridium perfringens types A, E, and C in fresh fish and its public health significance. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhao, M.; Ma, L. 2016 The gut microbial commu-nity of antarctic fish detected by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 1, 3241529. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global mycotoxin occurrence in feed: A ten-year survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewińska, P.; Szeligowska, N.; Wojnarowski, K.; Nazar, P.; Greguła-Kania, M.; Junkuszew, A.; Bodkowski, R. Selected bacteria in sheep stool depending on breed and physiology state. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, S.E.; Callaway, T.R.; Wolcott, R.D.; Sun, Y.; McKeehan, T.; Hagevoort, R.G.; Edrington, T.S. Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle using 16S rDNA bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gregoris, T.B.; Aldred, N.; Clare, A.S.; Burgess, J.G. Improvement of phylum-and class-specific primers for real-time PCR quantification of bacterial taxa. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 86, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, C.B.; Oaks, A.; Buyer, J.S. Phylum-and class-specific PCR primers for general microbial community analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6193–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumori, M.; Ajisaka, N.; Tajima, K.; Kajikawa, H.; Kurihara, M. Detection of Proteobacteria from the rumen by PCR using methanotroph-specific primers. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 35, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit-Romach, E.; Sklan, D.; Uni, Z. Microflora ecology of the chicken intestine using 16S ribosomal DNA primers. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Ma, X. Effects of dietary mycotoxins on gut microbiome. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Influence of foods and nutrition on the gut microbiome and implications for intestinal health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareau, M.G.; Sherman, P.M.; Walker, W.A. Probiotics and the gut microbiota in intestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingerslev, H.C.; von Gersdorff Jørgensen, L.; Strube, M.L.; Larsen, N.; Dalsgaard, I.; Boye, M.; Madsen, L. The development of the gut microbiota in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is affected by first feeding and diet type. Aquaculture 2014, 424, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, G.; Ferrara, M.; Medina, A.; Pascale, M.; Magan, N. Toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in a climate change scenario: Ecology, genomics, distribution, prediction and prevention of the risk. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, E.M.; Tarazona, A.; Aznar, R.; Mateo, F. Exploring the impact of lactic acid bacteria on the biocontrol of toxigenic Fusarium spp. and their main mycotoxins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 387, 110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, T.; He, A.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L. Comparative analysis of microbial communities associated with the gill, gut, and habitat of two filter-feeding fish. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastinu, A.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Aria, F.; Memo, M. Zeolite clinoptilolite: Therapeutic virtues of an ancient mineral. Molecules 2019, 24, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozova, P.; Kynicky, J.; Urubek, T.; Nguyen, V.D. Synthesis and modification of clinoptilolite. Molecules 2017, 22, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.J.; Wang, L.C.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, T. Effects of clinoptilolite and modified clinoptilolite on the growth performance, intestinal microflora, and gut parameters of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2023, 92, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, F.; Shen, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Liang, J. Removal of emerging organic pollutants by zeolite mineral (Clinoptilolite) composite photocatalysts in drinking water and watershed water. Catalysts 2024, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Z.; Sourinejad, I.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. Application of zeolites in aquaculture industry: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, N.; Emekci, M.; Athanassiou, C.G. Applications of natural zeolites on agriculture and food production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3487–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Félix, D.; Garibay-Valdez, E.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Fish disease and intestinal microbiota: A close and indivisible relationship. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 820–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kim, N.; Roh, H.J.; Chun, W.K.; Ho, D.T.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.H. Administration of antibiotics can cause dysbiosis in fish gut. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, M.J.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Sialumano, M.; Phiri, S.; Chaklader, M.R.; Fotedar, R.; Tay, A. Zeolite mediated processing of nitrogenous waste in the rearing environment influences gut and sediment microbial community in freshwater crayfish (Cherax cainii) culture. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, J. Ecological effects of antibiotics on aquaculture ecosystems based on microbial community in sediments. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 224, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Caputo, A. Review of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Number | Sample Name | Results(µg/kg) or ppb Relative to Feed with Moisture Content of 12% | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aflatoxin | Ochratoxin A | Zearalenone | Deoxynivalenol | Fumonisin | HAT-2 | T-2 | ||||||
| B1 | B2 | G1 | G2 | B1 | B2 | |||||||
| S22-01-012 | DIET 1 (C) | <0.4 | <0.4 | <0.4 | <0.4 | <1.6 | <16 | <64 | <40 | <40 | <9.6 | <9.6 |
| S22-01-013 | DIET 2 (Z) | <0.4 | <0.4 | <0.4 | <0.4 | <1.6 | <16 | <64 | <40 | <40 | <9.6 | <9.6 |
| S22-01-014 | DIET 3 (T) | 31.67 | Feb 45 | <0.4 | <0.4 | <1.6 | 53.48 | 145 | 405 | 124 | <9.6 | <9.6 |
| S22-01-015 | DIET 4 (M) | 35.85 | Feb 41 | <0.4 | <0.4 | <1.6 | 51.39 | 148 | 421 | 137 | <9.6 | <9.6 |
| Water Parameters | C | T | M | Z | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | |
| DO (mg/L) | 8.14 | 0.01 | 7.74 | 0.01 | 7.85 | 0.50 | 7.86 | 0.11 |
| Temperature (°C) | 27.16 | 0.50 | 27.16 | 0.50 | 27.16 | 0.51 | 27.17 | 0.50 |
| NO2 (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| NO3 (mg/L) | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| KH (°dH) | 14.36 | 2.31 | 14.20 | 1.99 | 14.30 | 1.43 | 13.88 | 1.96 |
| Component | Volume Per 10 μL Reaction |
|---|---|
| SsoAdvanced™ Universal SYBR® Green Supermix | 5 μL |
| Forward and reverse primers | 1 μL (0.8 μM) |
| DNA template | 2 μL (0.04–0.015 × 10−4) |
| Nuclease–free water | 2 μL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussein, W.; Cholewińska, P.; Wojnarowski, K.; Szeligowska, N.; Hu, F.; Greguła-Kania, M.; Rojtinnakorn, J.; Palić, D. Dietary Mycotoxins Effects on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Microbiomes Can Be Mitigated with Addition of Organically Modified Clinoptilolites. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 2232-2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040149
Hussein W, Cholewińska P, Wojnarowski K, Szeligowska N, Hu F, Greguła-Kania M, Rojtinnakorn J, Palić D. Dietary Mycotoxins Effects on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Microbiomes Can Be Mitigated with Addition of Organically Modified Clinoptilolites. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(4):2232-2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040149
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussein, Wanvisa, Paulina Cholewińska, Konrad Wojnarowski, Natalia Szeligowska, Fangyuan Hu, Monika Greguła-Kania, Jiraporn Rojtinnakorn, and Dušan Palić. 2024. "Dietary Mycotoxins Effects on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Microbiomes Can Be Mitigated with Addition of Organically Modified Clinoptilolites" Microbiology Research 15, no. 4: 2232-2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040149
APA StyleHussein, W., Cholewińska, P., Wojnarowski, K., Szeligowska, N., Hu, F., Greguła-Kania, M., Rojtinnakorn, J., & Palić, D. (2024). Dietary Mycotoxins Effects on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Microbiomes Can Be Mitigated with Addition of Organically Modified Clinoptilolites. Microbiology Research, 15(4), 2232-2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040149








