Effects of Common Anti-Inflammatories on Adenovirus Entry and Their Physicochemical Properties: An In-Depth Study Using Cellular and Animal Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Purification and Propagation of the Ad-BGal Vector
2.2. Reagents
2.3. In Vitro Assay
2.4. In Vivo Assay
2.5. Processing and Histological Analysis
2.6. Structure–Activity Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of the In Vitro Assay
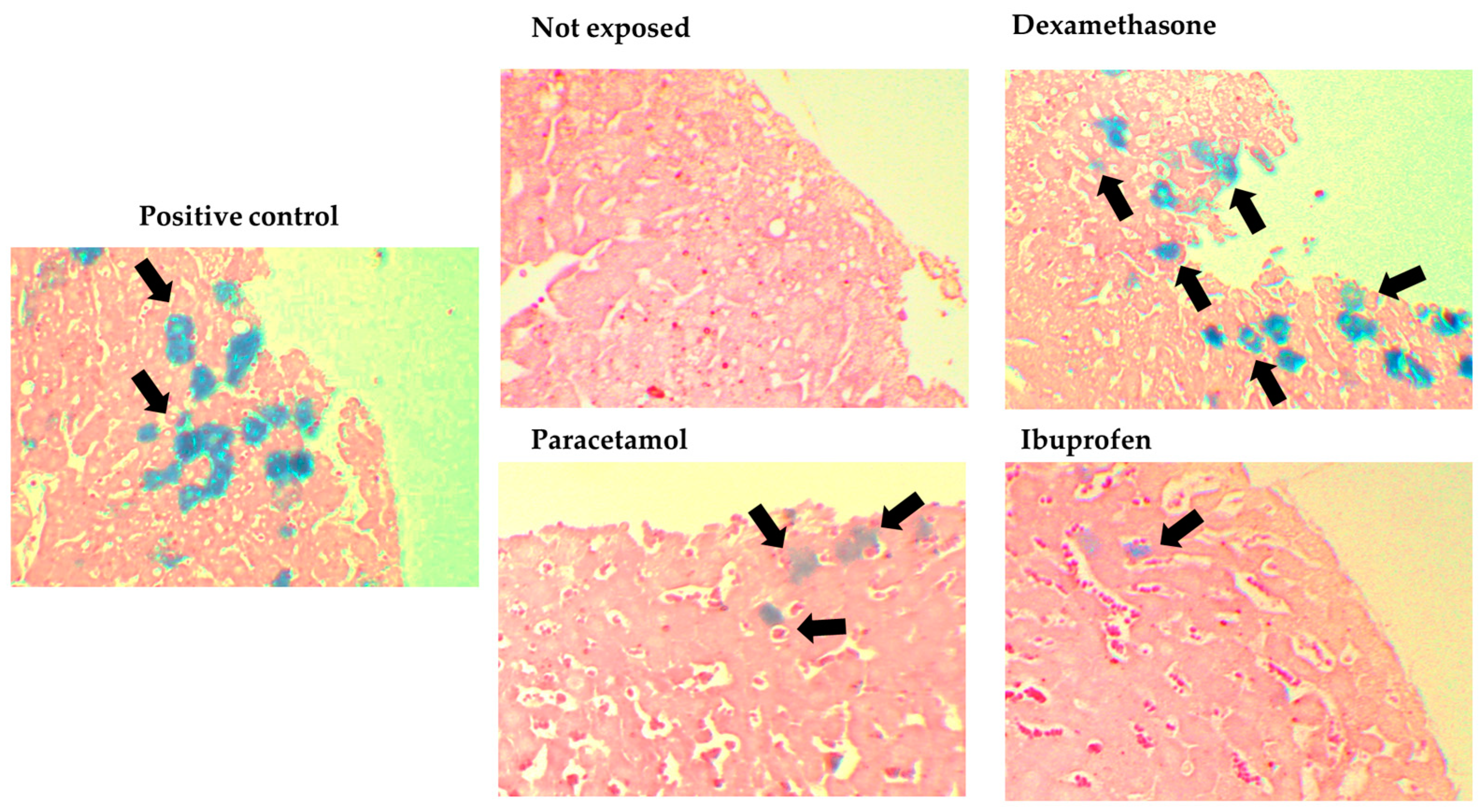
3.2. Results of the In Vivo Assay (Intravenous)
3.3. Results of the In Vivo Assay (Oral Administration)
3.4. Structure Relationships Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forni, G.; Mantovani, A. COVID-19 Vaccines: Where We Stand and Challenges Ahead. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, S.L.; Amaya, A.K.; Alexander, I.E.; Edelstein, M.; Abedi, M.R. Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Worldwide to 2017: An Update. J Gene Med. 2018, 20, e3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pormohammad, A.; Zarei, M.; Ghorbani, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Razizadeh, M.H.; Turner, D.L.; Turner, R.J. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Vaccines 2021, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.H.; Hashmi, Z.; Goel, A.; Ahmad, R.; Gupta, K.; Khan, N.; Alam, I.; Ahmed, F.; Ansari, M.A. COVID-19 Pandemic and Vaccines Update on Challenges and Resolutions. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 690621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoushtari, M.; Roohvand, F.; Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Arashkia, A.; Bakhshi, H.; Azadmanesh, K. Adenovirus Vector-Based Vaccines as Forefront Approaches in Fighting the Battle against Flaviviruses. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2079323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, F.; Tachibana, M.; Mizuguchi, H. Adenovirus Vector-Based Vaccine for Infectious Diseases. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 42, 100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.-H.; Burckhardt, C.J.; Yakimovich, A.; Greber, U.F. Imaging, Tracking and Computational Analyses of Virus Entry and Egress with the Cytoskeleton. Viruses 2018, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einfeld, D.A.; Roelvink, P.W. Advances towards Targetable Adenovirus Vectors for Gene Therapy. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2002, 4, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, A.M.; Smith, A.N.; Spangler, E.A.; Whitley, E.M.; Schleis, S.E.; Bird, R.C.; Curiel, D.T.; Thacker, E.E.; Smith, B.F. Resistance of Canine Lymphoma Cells to Adenoviral Infection Due to Reduced Cell Surface RGD Binding Integrins. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.A.G.; Idamakanti, N.; Marshall-Neff, J.; Rollence, M.L.; Wright, P.; Kaloss, M.; King, L.; Mech, C.; Dinges, L.; Iverson, W.O.; et al. Receptor Interactions Involved in Adenoviral-Mediated Gene Delivery After Systemic Administration in Non-Human Primates. Hum. Gene Ther. 2003, 14, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greber, U.F.; Flatt, J.W. Adenovirus Entry: From Infection to Immunity. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Sayedahmed, E.E.; Mittal, S.K. Significance of Preexisting Vector Immunity and Activation of Innate Responses for Adenoviral Vector-Based Therapy. Viruses 2022, 14, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, N.; Schneider, A.-K.; Reus, P.; Talmon, S.; Ciesek, S.; Bojkova, D.; Cinatl, J.; Lodhi, I.; Charlesworth, B.; Sinclair, S.; et al. Ibuprofen, Flurbiprofen, Etoricoxib or Paracetamol Do Not Influence ACE2 Expression and Activity In Vitro or in Mice and Do Not Exacerbate In-Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, S.; Oyegbami, O.; Saito, S.; Osman, M.; Sligl, W.; Elahi, S. Differential Effects of Age, Sex and Dexamethasone Therapy on ACE2/TMPRSS2 Expression and Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1021928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Karakiulakis, G.; Roth, M. Are Patients with Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus at Increased Risk for COVID-19 Infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saheb Sharif-Askari, N.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, F.; Mdkhana, B.; Al Heialy, S.; Ratemi, E.; Alghamdi, M.; Abusnana, S.; Kashour, T.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R. Effect of Common Medications on the Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Receptors in Liver Tissue. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 4037–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabbab, I.L.N.; Manalo, R.V.M. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System: Current Knowledge and Potential Effects on Early SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Virus Res. 2021, 291, 198190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Hernandez, M.A.; Guzman-Esquivel, J.; Ramos-Rojas, M.A.; Santillan-Luna, V.V.; Sanchez-Ramirez, C.A.; Hernandez-Fuentes, G.A.; Diaz-Martinez, J.; Melnikov, V.; Rojas-Larios, F.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; et al. Differences in the Evolution of Clinical, Biochemical, and Hematological Indicators in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 According to Their Vaccination Scheme: A Cohort Study in One of the World’s Highest Hospital Mortality Populations. Vaccines 2024, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, A.; Johnson, S.; Chen, N.-W. Timing of Corticosteroids Impacts Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Esquivel, J.; Galvan-Salazar, H.; Guzman-Solorzano, H.; Cuevas-Velazquez, A.; Guzman-Solorzano, J.; Mokay-Ramirez, K.; Paz-Michel, B.; Murillo-Zamora, E.; Delgado-Enciso, J.; Melnikov, V.; et al. Efficacy of the Use of Mefenamic Acid Combined with Standard Medical Care vs. Standard Medical Care Alone for the Treatment of COVID-19: A Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleni, M.T. Early Use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in COVID-19 Might Reverse Pathogenesis, Prevent Complications and Improve Clinical Outcomes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Enciso, I.; Cervantes-García, D.; Martínez-Dávila, I.A.; Ortiz-López, R.; Alemany-Bonastre, R.; Silva-Platas, C.I.; Lugo-Trampe, Á.; Barrera-Saldaña, H.A.; Galván-Salazar, H.R.; Coronel-Tene, C.G.; et al. A Potent Replicative Delta-24 Adenoviral Vector Driven by the Promoter of Human Papillomavirus 16 That Is Highly Selective for Associated Neoplasms. J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Rana, D.; Patel, V. Comparison of Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Pyretic Efficacy of Diclofenac, Paracetamol and Their Combination in Experimental Animals. Int. J. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estados Unidos Mexicanos; Consejo de Salubridad General Edición 2018 Del Cuadro Básico y Catálogo de Medicamentos. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5544613&fecha=23/11/2018#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Jasso, L.; Lifshitz, A.; Arrieta, O.; Burgos, R.; Campillo Serrano, C.; Celis, M.Á.; De la Llata, M.; Domínguez, J.; Halabe, J.; Islas-Andrade, S.; et al. Importancia Del Cuadro Básico de Medicamentos En La Prescripción Médica. Gac. Med. Mex. 2020, 156, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blizzard, C.; McLaurin, E.B.; Driscoll, A.; Silva, F.Q.; Vantipalli, S.; Metzinger, J.L.; Goldstein, M.H. Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Dexamethasone Following Administration of a Dexamethasone Intracanalicular Insert in Healthy Adults. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, G.G.; Davies, M.J.; Day, R.O.; Mohamudally, A.; Scott, K.F. The Modern Pharmacology of Paracetamol: Therapeutic Actions, Mechanism of Action, Metabolism, Toxicity and Recent Pharmacological Findings. Inflammopharmacology 2013, 21, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermelstein, F.; Hamilton, D.A.; Wright, C.; Lacouture, P.G.; Ramaiya, A.; Carr, D.B. Single-Dose and Multiple-Dose Pharmacokinetics and Dose Proportionality of Intravenous and Intramuscular HPβCD-Diclofenac (Dyloject) Compared with Other Diclofenac Formulations. Pharmacother. J. Human. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2013, 33, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Ibuprofen. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 34, 101–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesza, A.; Zielniok, K.; Hawryluk, J.; Paczek, L.; Burdzinska, A. Ibuprofen in Therapeutic Concentrations Affects the Secretion of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells, but not Their Proliferative and Migratory Capacity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resman-Thrgoff, B.H. Ketorolac: A Parenteral Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drug. DICP 1990, 24, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festing, M.F.W. The “Completely Randomised” and the “Randomised Block” Are the Only Experimental Designs Suitable for Widespread Use in Pre-Clinical Research. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aluja, A.S. Laboratory Animals and Official Mexican Norms (NOM-062-ZOO-1999). Gac. Med. Mex. 2002, 138, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-309-15400-0. [Google Scholar]
- Owoeye, O.; Malomo, A.O.; Elumelu, T.N.; Salami, A.A.; Osuagwu, F.C.; Akinlolu, A.A.; Adenipekun, A.; Shokunbi, M.T. Radiation Nephritis: Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Dexamethasone in Adult Wistar Rats (Rattus Norvegicus). Int. J. Morphol. 2008, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lahoti, A.; Kalra, B.; Tekur, U. Evaluation of the Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Fixed Dose Combination: Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Experimental Animals. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2014, 25, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, B.; Shalini; Chaturvedi, S.; Tayal, V.; Gupta, U. Evaluation of Gastric Tolerability, Antinociceptive and Antiinflammatory Activity of Combination NSAIDs in Rats. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2009, 20, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.X.X.; Irwin, M.G.; Cheung, K.M.C.; Chan, D. An Effective Dose of Valdecoxib in Experimental Mouse Models of Pain. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 29, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estados Unidos Mexicanos; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales Norma Oficial Mexicana. Protección Ambiental-Salud Ambiental-Residuos Peligrosos Biológico-Infecciosos-Clasificación y Especificaciones de Manejo; Secretaría de Gobernación: Mexico city, Mexico, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, T. Assessment of Efficiency and Safety of Adenovirus Mediated Gene Transfer into Normal and Damaged Murine Livers. Gut 2000, 47, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.; Idamakanti, N.; Kylefjord, H.; Rollence, M.; King, L.; Kaloss, M.; Kaleko, M.; Stevenson, S.C. In Vivo Hepatic Adenoviral Gene Delivery Occurs Independently of the Coxsackievirus–Adenovirus Receptor. Mol. Ther. 2002, 5, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.H.; Geller, D.A.; Kibbe, M.R.; Watkins, S.C.; Fung, J.J.; Starzl, T.E.; Murase, N. Adenovirus-Mediated Gene Transfer to Liver Grafts: An Improved Method to Maximize Infectivity. Transplantation 1998, 66, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leary, S.R.A.; Underwood, W.; Raymond, A.; Samuel, C.; Greenacre, C.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; Grandin, T.; McCrackin, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Miller, D.; et al. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.-S.; Troiano, N.; Kacena, M. β-Galactosidase Detection as an Indicator of Endogenous PTHrP in Cartilage. Biotech. Histochem. 2008, 83, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PerkinElmer Informatics. ChemDraw 3D; Version 20.0; PerkinElmer Informatics: Waltham, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhatia, K.S. Physicochemical Significance of ChemDraw and Dragon Computed Parameters: Correlation Studies in the Sets with Aliphatic and Aromatic Substituents. J. Math. Chem. 2024, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, J.C. Prediction of Physicochemical Properties. In Computational Toxicology. Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 929, pp. 93–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Abed, S.N.; Al-Attraqchi, O.; Kuche, K.; Tekade, R.K. Computer-Aided Prediction of Pharmacokinetic (ADMET) Properties. In Dosage Form Design Parameters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 731–755. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, S.; Doerksen, R. Topological Polar Surface Area: A Useful Descriptor in 2D-QSAR. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergazin, T.D.; Tielker, N.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, J.; Gunner, M.R.; Francisco, K.; Ballatore, C.; Kast, S.M.; Mobley, D.L. Evaluation of Log P, PKa, and Log D Predictions from the SAMPL7 Blind Challenge. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2021, 35, 771–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoke, O.; Oluwole, J.; Parashurama, N. Bioengineering Considerations in Liver Regenerative Medicine. J. Biol. Eng. 2017, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.R.; Sarles, W.B. Some Considerations of the Biological Importance of Intestinal Microorganisms. Bacteriol. Rev. 1949, 13, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoud, T.C.; Boiselle, P.M.; Trotman-Dickenson, B. Diseases of Altered Immunologic Activity. In Thoracic Radiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 216–241. [Google Scholar]
- Flatt, J.W.; Butcher, S.J. Adenovirus Flow in Host Cell Networks. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, C.R. New Insights to Adenovirus-Directed Innate Immunity in Respiratory Epithelial Cells. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanerva, A.; Lavilla-Alonso, S.; Raki, M.; Kangasniemi, L.; Bauerschmitz, G.J.; Takayama, K.; Ristimäki, A.; Desmond, R.A.; Hemminki, A. Systemic Therapy for Cervical Cancer with Potentially Regulatable Oncolytic Adenoviruses. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, A.; Runnebaum, I.B. CAR Is a Cell–Cell Adhesion Protein in Human Cancer Cells and Is Expressionally Modulated by Dexamethasone, TNFα, and TGFβ. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminki, A.; Kanerva, A.; Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Alvarez, R.D.; Siegal, G.P.; Curiel, D.T. Modulation of Coxsackie-Adenovirus Receptor Expression for Increased Adenoviral Transgene Expression. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jornot, L.; Morris, M.A.; Petersen, H.; Moix, I.; Rochat, T. N-acetylcysteine Augments Adenovirus-mediated Gene Expression in Human Endothelial Cells by Enhancing Transgene Transcription and Virus Entry. J. Gene Med. 2002, 4, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Li, X.; Bangari, D.S.; Mittal, S.K. Adenovirus Receptors and Their Implications in Gene Delivery. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seregin, S.S.; Appledorn, D.M.; McBride, A.J.; Schuldt, N.J.; Aldhamen, Y.A.; Voss, T.; Wei, J.; Bujold, M.; Nance, W.; Godbehere, S.; et al. Transient Pretreatment With Glucocorticoid Ablates Innate Toxicity of Systemically Delivered Adenoviral Vectors Without Reducing Efficacy. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Smith, J.S.; Tian, J.; Byrnes, A.P. Induction of Shock After Intravenous Injection of Adenovirus Vectors: A Critical Role for Platelet-Activating Factor. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Feng, Q.; Li, K.; Gao, H.; Qian, S.; Xu, L.; Xie, Z. A Fatal Case of Viral Sepsis and Encephalitis in a Child Caused by Human Adenovirus Type 7 Infection. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straussberg, R.; Harel, L.; Levy, Y.; Amir, J. A Syndrome of Transient Encephalopathy Associated With Adenovirus Infection. Pediatrics 2001, 107, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, I.; Tsuboi, I.; Tanaka, H.; Nakao, M.; Shichijo, S.; Itoh, K. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Differentially Regulate Cytokine Production in Human Lymphocytes: Up-Regulation of TNF, IFN-γ and IL-2, in Contrast to down-Regulation of IL-6 Production. Cytokine 1995, 7, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasheva, S.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Cytokine Responses to Adenovirus and Adenovirus Vectors. Viruses 2022, 14, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupalo, E.M.; Buryachkovskaya, L.I.; Chumachenko, P.V.; Mironova, N.A.; Narusov, O.Y.; Tereschenko, S.N.; Golitsyn, S.P.; Othman, M. Implication of Inflammation on Coxsackie Virus and Adenovirus Receptor Expression on Cardiomyocytes and the Role of Platelets in Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2022, 60, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, X. Protective Role of Coxsackie-Adenovirus Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7207268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprinou, M.; Sachinidis, A.; Stamoula, E.; Vavilis, T.; Papazisis, G. COVID-19 Vaccines Adverse Events: Potential Molecular Mechanisms. Immunol. Res. 2023, 71, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremkow, J.; Luck, M.; Huster, D.; Müller, P.; Scheidt, H.A. Membrane Interaction of Ibuprofen with Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Membranes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Leite, C.; Jamal, S.K.; Almeida, J.P.; Coutinho, A.; Prieto, M.; Cuccovia, I.M.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Neutral Diclofenac Causes Remarkable Changes in Phosphatidylcholine Bilayers: Relevance for Gastric Toxicity Mechanisms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 97, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudeja, P.K.; Dahiya, R.; Brown, M.D.; Brasitus, T.A. Dexamethasone Influences the Lipid Fluidity, Lipid Composition and Glycosphingolipid Glycosyltransferase Activities of Rat Proximal-Small-Intestinal Golgi Membranes. Biochem. J. 1988, 253, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Varghese, R.; Debroy, R.; Ramaiah, S.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Anbarasu, A. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Ketorolac and Etodolac Can Augment the Treatment against Pneumococcal Meningitis by Targeting Penicillin-Binding Proteins. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 170, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
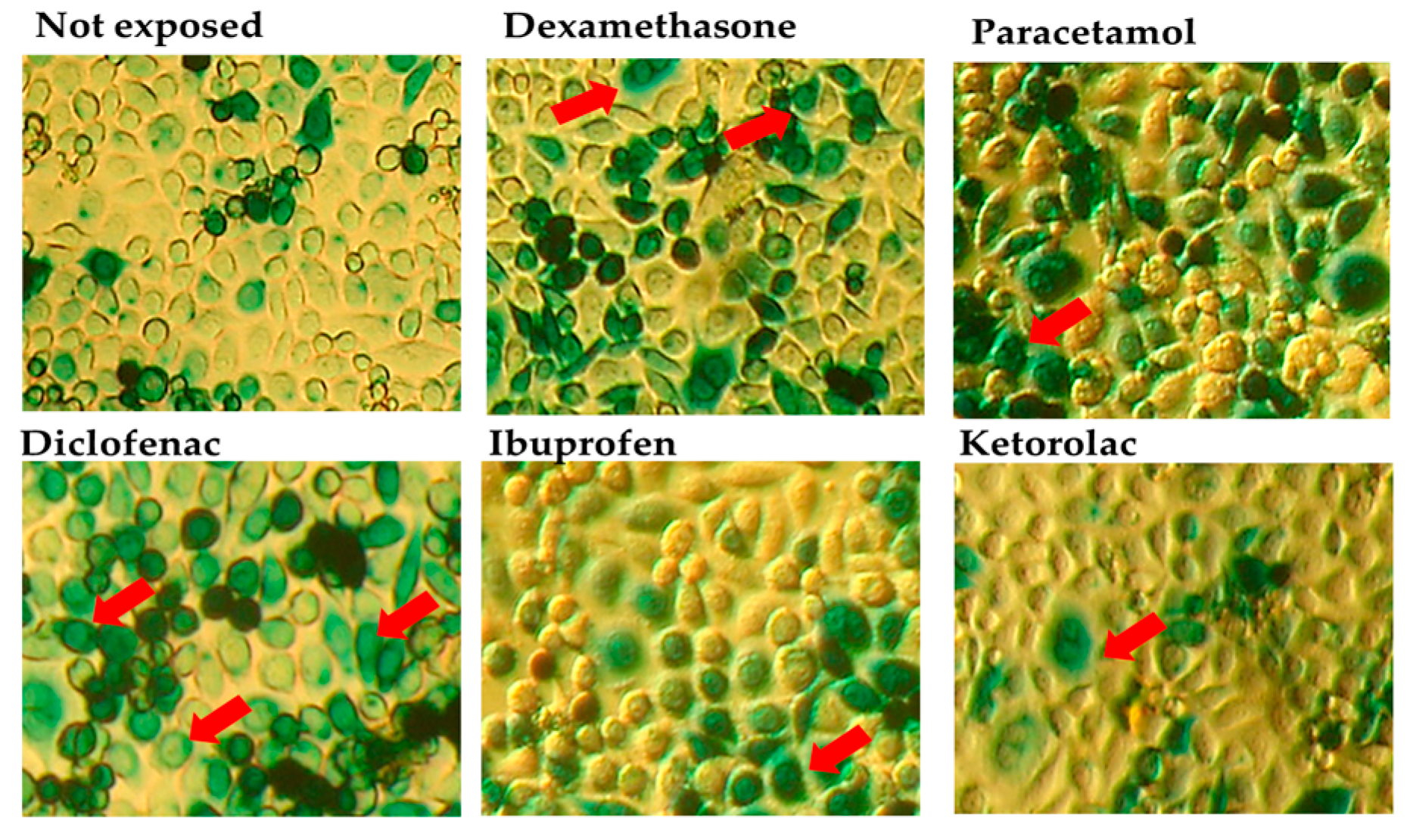
| Group | Not Exposed (n = 15) % | Dexamethasone (n = 15) % | Paracetamol (n= 15) % | Diclofenac (n= 15) % | Ibuprofen (n= 15) % | Ketorolac (n= 15) % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQM | 30.79 | 45.21 | 40.19 | 54.77 | 40.00 | 33.19 |
| Q1–Q3 | 30.50–31.20 | 45.05–45.50 | 39.60–40.80 | 54.05–55.15 | 39.40–40.50 | 33.00–33.45 |
| p vs. not exposed | NA | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.098 |
| Group | Not Exposed n = 17 (%) | Dexamethasone n = 14 (%) | Paracetamol n = 17 (%) | Diclofenac n = 17 (%) | Ibuprofen n = 16 (%) | Ketorolac n = 17 (%) | p ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 0 | 10 * (71.42) | 5 *(29.41) | 0 | 4 * (25) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Heart | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 * (6.25) | 0 | 0.395 |
| Intestine | 0 | 1 * (7.14) | 1 * (5.88) | 1 * (5.88) | 3 * (18.75) | 2 * (11.76) | 0.486 |
| Kidney | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Lung | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Brain | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Peritoneum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Group | Not Exposed (n = 17) (µm2) | Dexamethasone (n = 14) (µm2) | Paracetamol (n = 17) (µm2) | Ibuprofen (n = 16) (µm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQM (µm2/10,000 µm2) | 0.0000 | 10.2082 | 0.1499 | 0.0071 |
| Q1–Q3 (µm2) | 0.0000 | 0.0000–37.1358 | 0.0000–5.2957 | 0.0000–0.1484 |
| Min–Max (µm2) | 0.0000–0.0000 | 0.0000–1065.3062 | 0.0000–47.0628 | 0.0000–0.7234 |
| p vs. not exposed | NA | <0.001 * | 0.018 * | 0.031 * |
| Group | Not Exposed n = 10 (%) | Dexamethasone n = 10 (%) | Paracetamol n = 10 (%) | Diclofenac n = 10 (%) | Ibuprofen n = 10 (%) | Ketorolac n = 10 (%) | p ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tongue | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Pharynx | 0 | 7 * (70%) | 0 | 0 | 1 * (10.0) | 0 | 0.001 |
| Esophagus | 0 | 4 * (40.0) | 0 | 0 | 1 * (10.0) | 1 * (10.0) | 0.201 |
| Chemical Properties | Dexamethasone | Paracetamol | Diclofenac | Ibuprofen | Ketorolac |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW (g/mol) | 392.20 | 151.06 | 295.02 | 206.13 | 255.27 |
| LogP | 0.72 | 0.55 | 4.12 | 3.75 | 1.64 |
| MR [cm3/mol] | 103.95 | 40.25 | 73.53 | 61.2 | 68.78 |
| tPSA | 94.83 | 49.33 | 49.33 | 37.3 | 57.61 |
| CMR | 10.3188 | 4.1737 | 7.6677 | 6.124 | 6.9954 |
| LogS | −2.682 | −1.058 | −4.712 | −3.119 | −3.048 |
| ClogP | 1.7852 | 0.494 | 4.57624 | 3.679 | 1.622 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galvan-Salazar, H.R.; Delgado-Machuca, M.; Hernandez-Fuentes, G.A.; Aurelien-Cabezas, N.S.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Mendoza-Hernandez, M.A.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; Zaizar-Fregoso, S.A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, I.P.; et al. Effects of Common Anti-Inflammatories on Adenovirus Entry and Their Physicochemical Properties: An In-Depth Study Using Cellular and Animal Models. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1590-1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030105
Galvan-Salazar HR, Delgado-Machuca M, Hernandez-Fuentes GA, Aurelien-Cabezas NS, Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Garza-Veloz I, Mendoza-Hernandez MA, Martinez-Fierro ML, Zaizar-Fregoso SA, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, et al. Effects of Common Anti-Inflammatories on Adenovirus Entry and Their Physicochemical Properties: An In-Depth Study Using Cellular and Animal Models. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(3):1590-1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030105
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalvan-Salazar, Hector R., Marina Delgado-Machuca, Gustavo A. Hernandez-Fuentes, Nomely S. Aurelien-Cabezas, Alejandrina Rodriguez-Hernandez, Idalia Garza-Veloz, Martha A. Mendoza-Hernandez, Margarita L. Martinez-Fierro, Sergio A. Zaizar-Fregoso, Iram P. Rodriguez-Sanchez, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Common Anti-Inflammatories on Adenovirus Entry and Their Physicochemical Properties: An In-Depth Study Using Cellular and Animal Models" Microbiology Research 15, no. 3: 1590-1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030105
APA StyleGalvan-Salazar, H. R., Delgado-Machuca, M., Hernandez-Fuentes, G. A., Aurelien-Cabezas, N. S., Rodriguez-Hernandez, A., Garza-Veloz, I., Mendoza-Hernandez, M. A., Martinez-Fierro, M. L., Zaizar-Fregoso, S. A., Rodriguez-Sanchez, I. P., Rojas-Larios, F., Del-Toro-Equihua, M., Ceja-Espiritu, G., & Delgado-Enciso, I. (2024). Effects of Common Anti-Inflammatories on Adenovirus Entry and Their Physicochemical Properties: An In-Depth Study Using Cellular and Animal Models. Microbiology Research, 15(3), 1590-1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030105