Studying the Anti-Virulence Activity of Meta-Bromo-Thiolactone against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Phenotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Chemicals, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles (ChNPs) and mBTL Loading
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis of mBTL-Loaded ChNPs
2.4. Determination of mBTL-Loaded ChNP Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%)
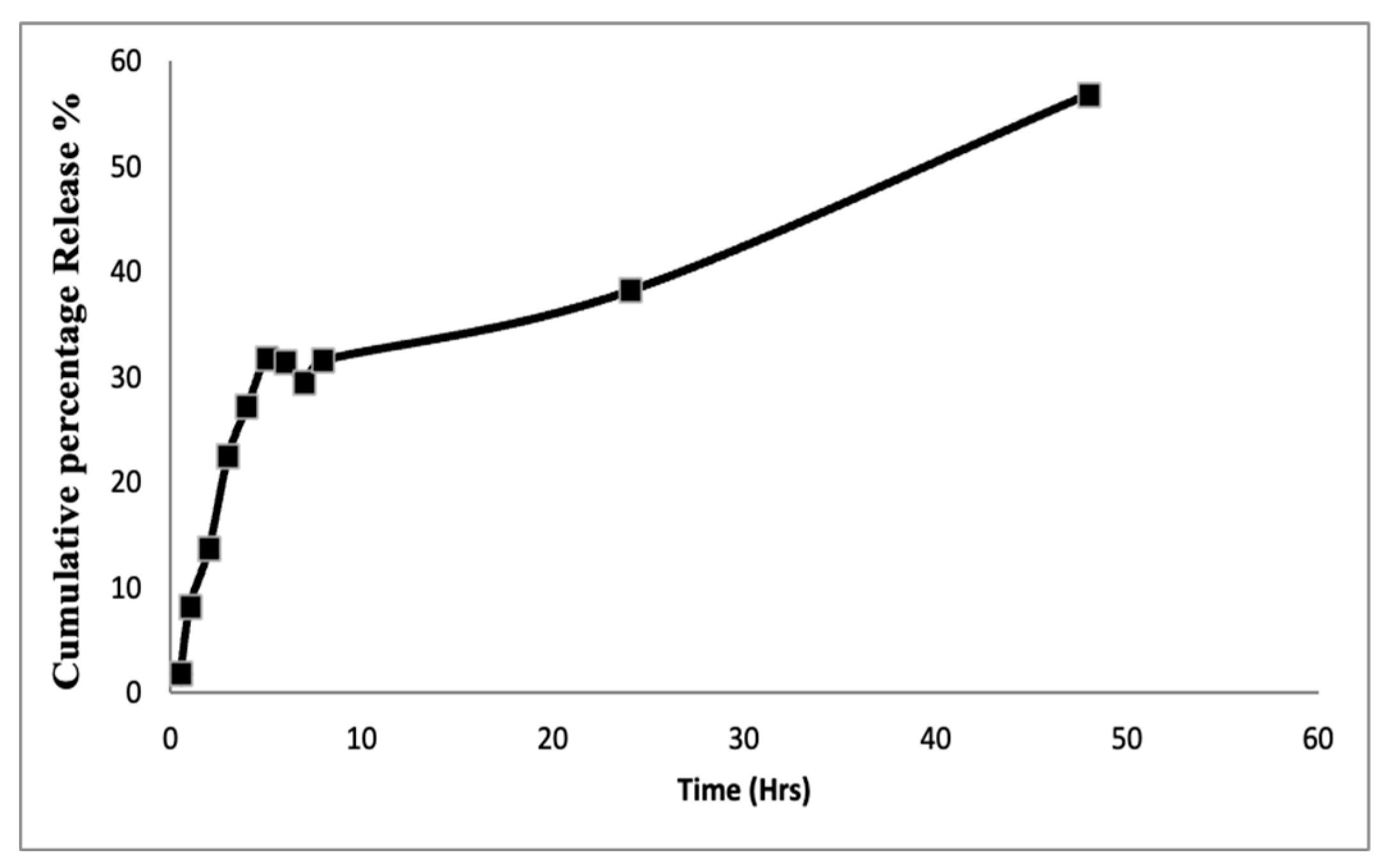
2.5. In Vitro Release of mBTL-ChNPs
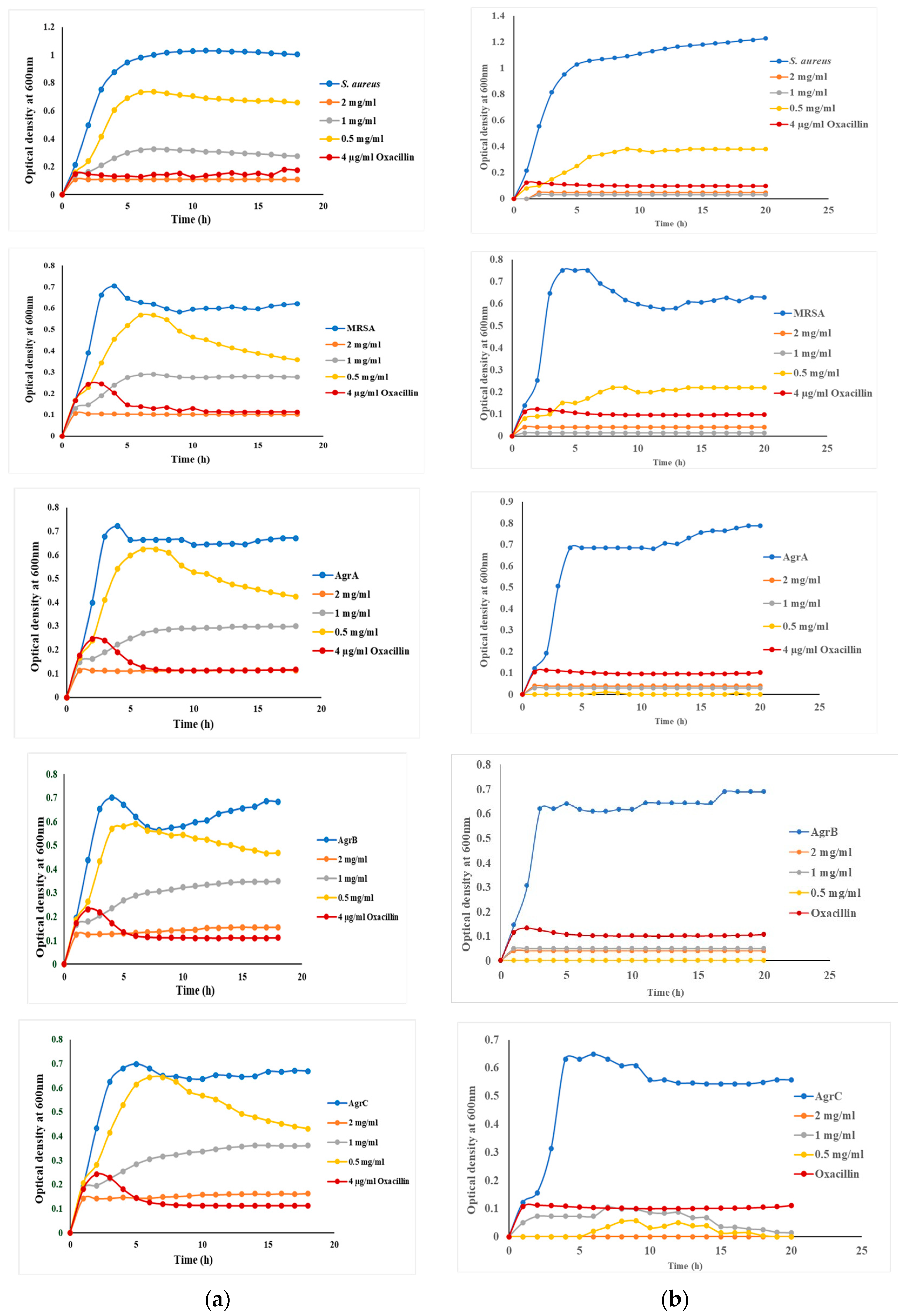
2.6. Growth Curve Construction
2.7. MIC Measurements
2.8. Hemolytic Activity Analysis
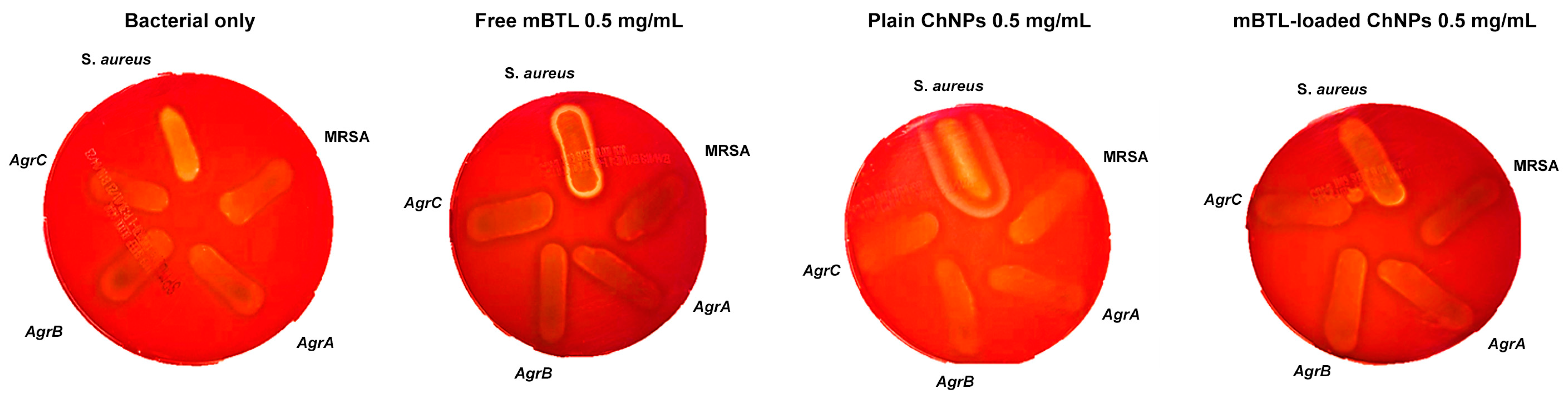
2.9. Biofilm Assay
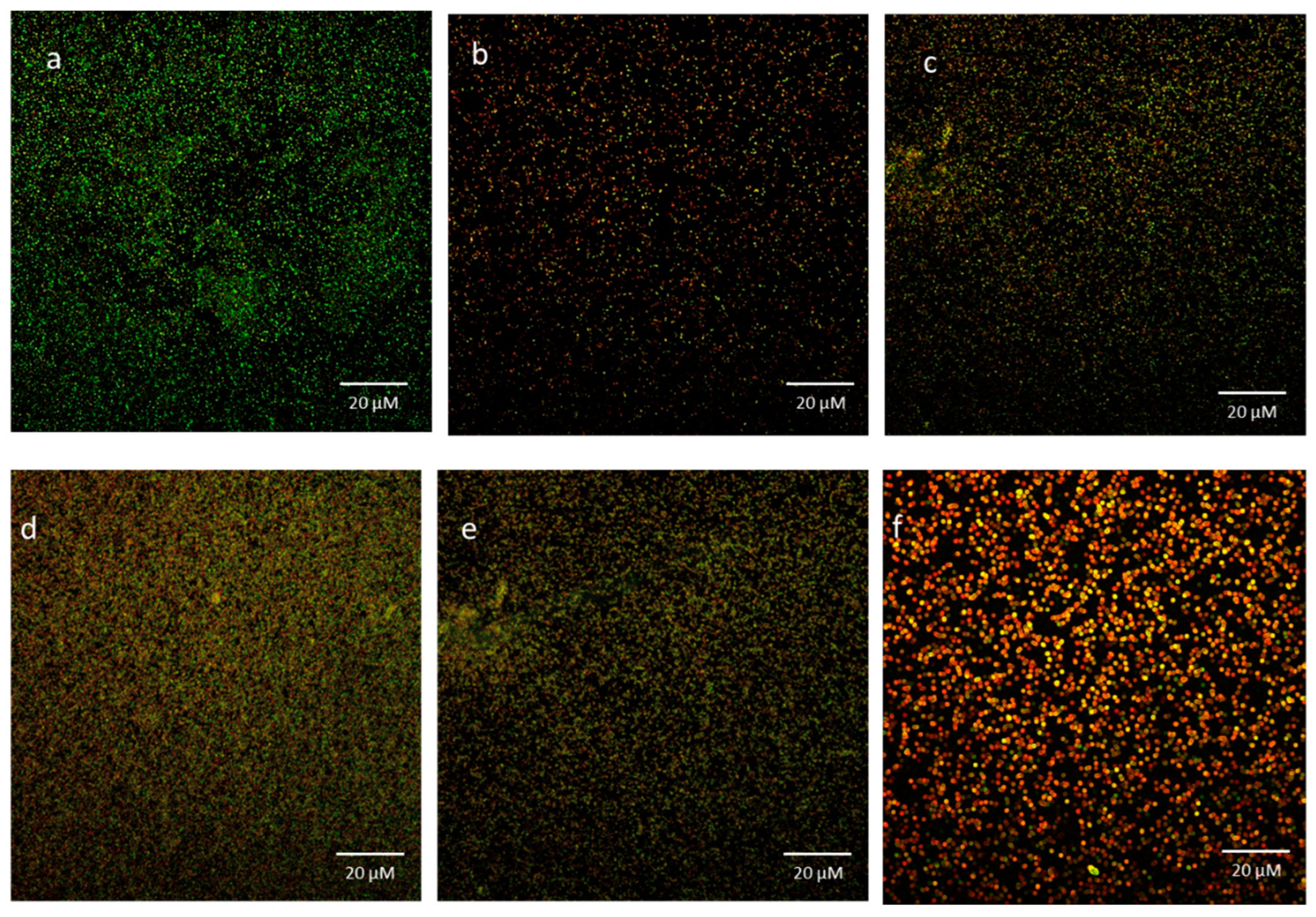
2.10. Confocal Microscopy
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results
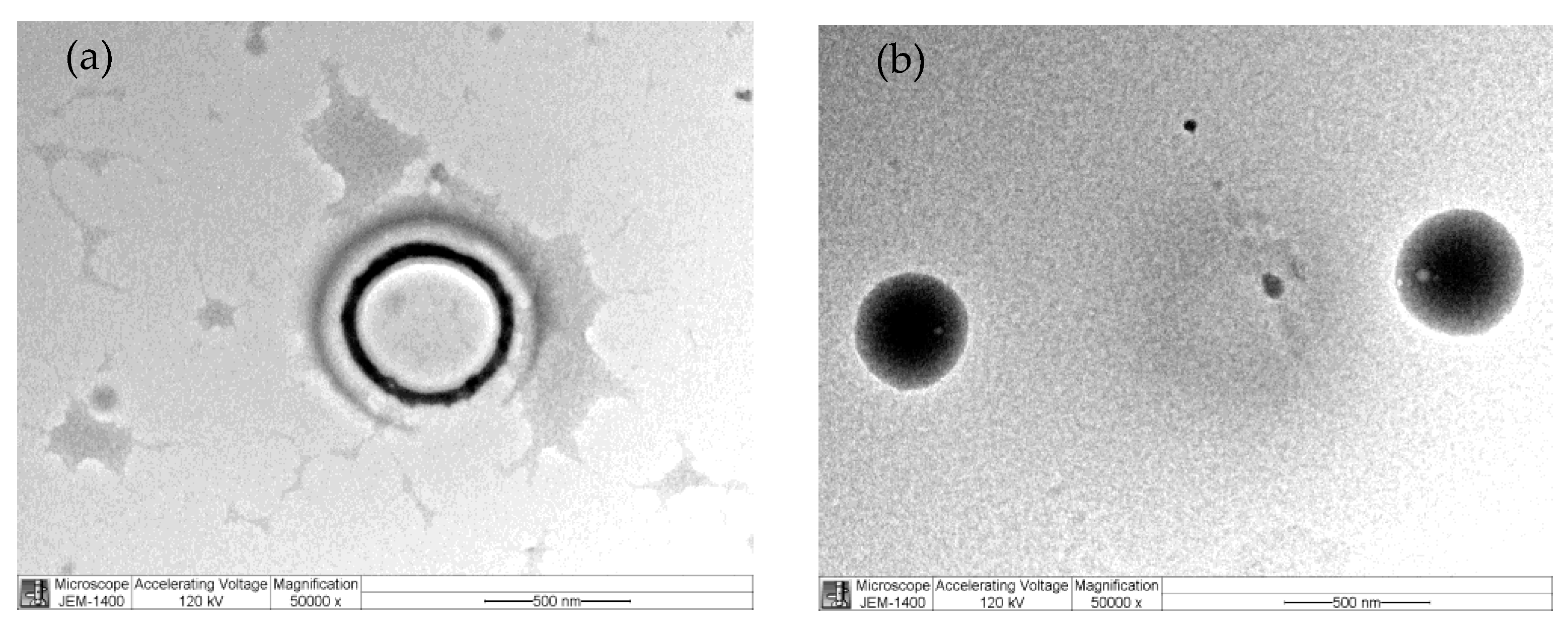
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.2. Encapsulation Efficacy of mBTL-ChNPs
3.3. In Vitro Drug Release
3.4. Growth of S. aureus and Targeted Mutants in the Presence and Absence of mBTL and mBTL-ChNPs
3.5. Biofilm Inhibition by mBTL-ChNPs
3.6. Bacterial Viability in Biofilms Exposed to mBTL-ChNPs
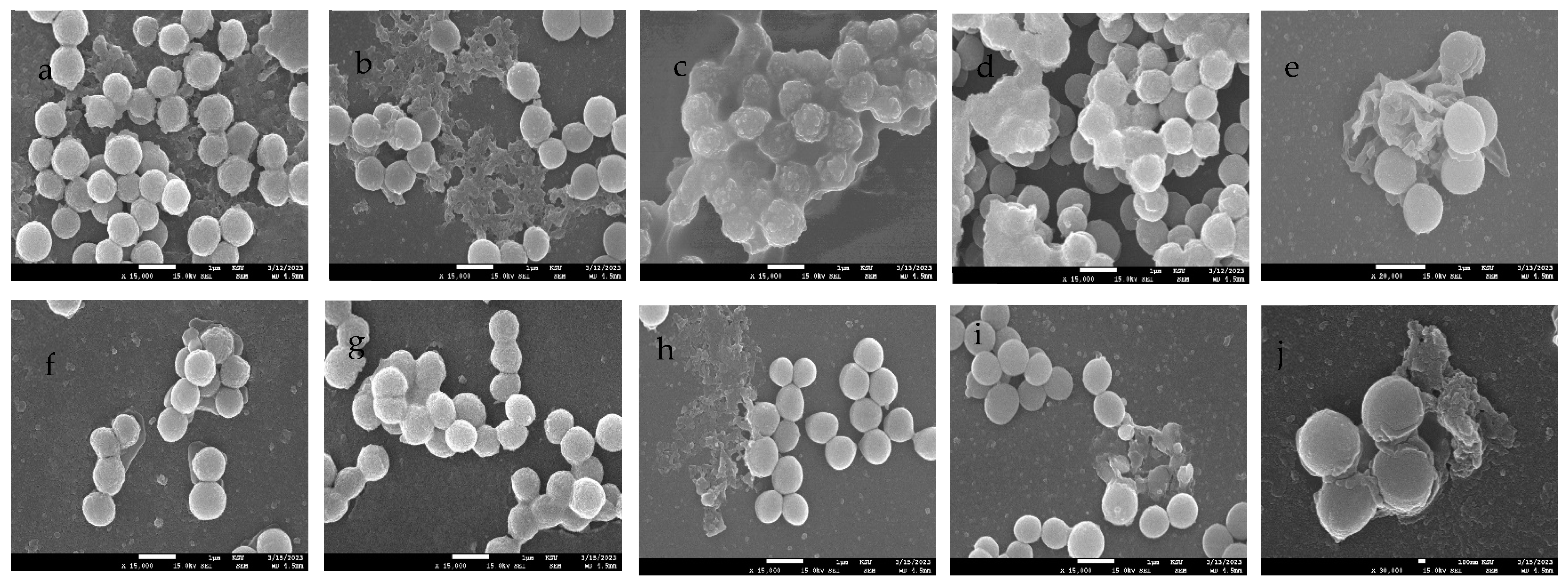
3.7. SEM Imaging of Biofilms Treated with mBTL-ChNPs
3.8. Hemolytic Activity of mBTL-ChNPs on S. aureus Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Bshabshe, A.; Joseph, M.R.P.; Awad El-Gied, A.A.; Fadul, A.N.; Chandramoorthy, H.C.; Hamid, M.E. Clinical relevance and antimicrobial profiling of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (mrsa) on routine antibiotics and ethanol extract of mango kernel. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 415068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.; Månsson, M.; Bojer, M.S.; Gram, L.; Larsen, T.; Novick, R.; Frees, D.; Frøkiær, H.; Ingmer, H. Solonamide B Inhibits quorum sensing and reduces Staphylococcus aureus mediated killing of human neutrophils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, K.S.; Mih, N.; Monk, J.; Kavvas, E.; Yurkovich, J.T.; Sakoulas, G.P.B. The Staphylococcus aureus two-component system AgrAC displays four distinct genomic arrangements that delineate genomic virulence factor signatures. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 9, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Loughlin, C.T.; Miller, L.C.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Graber, C.J. Limitations of antibiotic options for invasive infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Is combination therapy the answer. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsan, A.; Aleanizy, F.S.; Badran, M.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Alfassam, H.; Almalik, A.; Alosaimy, S. Exploring anti-MRSA activity of chitosan-coated liposomal dicloxacillin. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 156, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Luo, Y. Bacterial quorum-sensing systems and their role in intestinal bacteria-host crosstalk. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 611413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.H. The Mechanisms and Applications of Quorum Sensing (QS) and Quorum Quenching (QQ). J. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 18, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.A.; Beveridge, T.J.; Breznak, J.A.; Marzluf, G. Methods for General and Molecular Microbiology; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Burnside, K.; Lembo, A.; de Los Reyes, M.; Iliuk, A.; BinhTran, N.T.; Connelly, J.E.; Lin, W.J.; Schmidt, B.Z.; Richardson, A.R.; Fang, F.C.; et al. Regulation of hemolysin expression and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus by a serine/threonine kinase and phosphatase. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal-Gan, Y.; Stacy, D.M.; Foegen, M.K.; Koenig, D.W.; Blackwell, H.E. Highly potent inhibitors of quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus revealed through a systematic synthetic study of the group-III autoinducing peptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7869–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Tomás, M.; Bou, G. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence: A successful or deleterious association in the bacterial world? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, S.; Sun, B.; Gao, S.; Guo, S.; Zhao, K. Biomedical applications of chitosan and its derivative nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, N.H.; Le Thanh, T.; Sangpueak, R.; Treekoon, J.; Saengchan, C.; Thepbandit, W.; Papathoti, N.K.; Kamkaew, A.; Buensanteai, N. Chitosan nanoparticles-based Ionic gelation method: A promising candidate for plant disease management. Polymers 2022, 14, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, T.; Costerton, J.W. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of in situ bacterial colonization of intravenous and intraarterial catheters. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 19, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikezie, I.O. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) using a novel dilution tube method. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 11, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayb, E.K.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Alsarra, I.A.; Alfaraj, R.; Aleanizy, F.S. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing virulence of biofilm and pyocyanin by mBTL-loaded calcium alginate nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Zhu, X.; Peng, X.; Qin, S. Chitosan antimicrobial and eliciting properties for pest control in agriculture: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamm, V.V.; Ko, J.T.; Mainprize, I.L.; Sanderson, V.P.; Wills, M.K.B. Lyme disease frontiers: Reconciling borrelia biology and clinical conundrums. Pathogens 2019, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Butnariu, M.; Rotariu, L.S.; Sytar, O.; Sestito, S.; Rapposelli, S.; Akram, M.; Iqbal, M.; Krishna, A.; et al. Chitosan nanoparticles as a promising tool in nanomedicine with particular emphasis on oncological treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdiana, Y.; Wathoni, N.; Shamsuddin, S.; Muchtaridi, M. Drug release study of the Chitosan-based nanoparticles. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.F.; Jia, J.F.; Guo, X.K.; Zhao, Y.P.; Chen, D.S.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Reduced Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation in the presence of chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nano Med. 2016, 11, 6499–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleanizy, F.S.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Shazly, G.; Alfaraj, R.; Alsarra, I.; Alshamsan, A.; Gareeb, A.; Hosam, G. Measurement and evaluation of the effects of pH gradients on the antimicrobial and antivirulence activities of chitosan nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suligoy, C.M.; Lattar, S.M.; Noto Llana, M.; González, C.D.; Alvarez, L.P.; Robinson, D.A.; Gómez, M.I.; Buzzola, F.R.; Sordelli, D.O. Mutation of Agr is associated with the adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to the host during chronic osteomyelitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, E.J.; Crowley, R.C.; Truman, A.; Clarke, S.R.; Cottam, J.A.; Jadhav, G.P.; Steele, V.R.; O’Shea, P.; Lindholm, C.; Cockayne, A.; et al. Targeting Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing with nonpeptidic small molecule inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Pati, B.R. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus strains isolated from hospital effluents. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, e87–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, R.P. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1429–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, B.R.; Horswill, A.R. Agr-mediated dispersal of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, J.M.; Bartels, D.J.; Volper, E.M.; Greenberg, E.P. Quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Luong, T.T.; Lee, C.Y. RNAIII of the Staphylococcus aureus agr system activates global regulator MgrA by stabilizing mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14036–14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krismer, B.; Peschel, A. Does Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization involve biofilm formation? Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messias de Souza, G.; Gervasoni, L.F.; Rosa, R.D.S.; de Souza Iacia, M.V.M.; Nai, G.A.; Pereira, V.C.; Winkelströter, L.K. Quercetin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as an alternative for controlling bacterial adhesion to urethral catheter. Int. J. Urol. 2022, 29, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhardha, B.; Pandey, U.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Pala, R.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Elgorban, A.M. Chrysin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles potentiates antibiofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, L.S.; Chen, X.; Sobsey, M.D. Chitosan coagulation to improve microbial and turbidity removal by ceramic water filtration for household drinking water treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekema, D.J.; Richter, S.S.; Heilmann, K.P.; Dohrn, C.L.; Riahi, F.; Tendolkar, S.; McDanel, J.S.; Doern, G.V. Continued emergence of USA 300 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the United States: Results from a nationwide surveillance study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Echazu, M.I.; Olivetti, C.E.; Anesini, C.; Perez, C.J.; Alvarez, G.S.; Desimone, M.F. Development and evaluation of thymol-chitosan hydrogels with antimicrobial-antioxidant activity for oral local delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 81, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Halder, M.; Srivastava, U.; Singh, Y. Antibacterial PEG-chitosan hydrogels for controlled antibiotic/protein delivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5313–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shan, C.L.; Ge, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Xie, G.L.; Sun, G.C. Antibacterial mechanism of chitosan and its applications in protection of plant from bacterial disease. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 10033–10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamov, V.P.; Mysyakina, I.S. Chitosan in biology, microbiology, medicine, and agriculture. Microbiology 2018, 87, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.T.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: Applications and mode of action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Klinkenberg, G.; Emanuel, C.; Onsøyen, E.; Myrvold, R.; Howe, R.A.; Walsh, T.R.; Hill, K.E.; et al. Overcoming drug resistance with alginate oligosaccharides able to potentiate the action of selected antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5134–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Strain Name | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | S. aureus | Wild-type |
| Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus | MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| NE1532 | AgrA | 4 P16 agrA accessory gene regulator protein A SAUSA300_1992 |
| NE95 | AgrB | 1 O21 agrB accessory gene regulator protein B SAUSA300_1989 |
| NE873 | AgrC | 3 B17 agrC accessory gene regulator protein C SAUSA300_1991 |
| Blank ChNPs | mBTL-ChNPs | |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size (nm) | 158.5 ± 1.3 | 283.9 ± 13.55 |
| PDI | 0.327 ± 0.016 | 0.253 ± 0.018 |
| Zeta potential (Mv) | 33.8 ± 0.361 | 19.6 ± 1.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfaraj, R.; Eltayb, E.K.; AlFayez, B.M.; Abohamad, A.; Eltahir, E.; Alenazi, N.A.; Hababah, S.; Alkahtani, H.; Almangour, T.A.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; et al. Studying the Anti-Virulence Activity of Meta-Bromo-Thiolactone against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Phenotypes. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1596-1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040110
Alfaraj R, Eltayb EK, AlFayez BM, Abohamad A, Eltahir E, Alenazi NA, Hababah S, Alkahtani H, Almangour TA, Alqahtani FY, et al. Studying the Anti-Virulence Activity of Meta-Bromo-Thiolactone against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Phenotypes. Microbiology Research. 2023; 14(4):1596-1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfaraj, Rihaf, Esra K. Eltayb, Bashayer M. AlFayez, Amjad Abohamad, Eram Eltahir, Naifa A. Alenazi, Sandra Hababah, Hamad Alkahtani, Thamer A. Almangour, Fulwah Y. Alqahtani, and et al. 2023. "Studying the Anti-Virulence Activity of Meta-Bromo-Thiolactone against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Phenotypes" Microbiology Research 14, no. 4: 1596-1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040110
APA StyleAlfaraj, R., Eltayb, E. K., AlFayez, B. M., Abohamad, A., Eltahir, E., Alenazi, N. A., Hababah, S., Alkahtani, H., Almangour, T. A., Alqahtani, F. Y., & Aleanizy, F. S. (2023). Studying the Anti-Virulence Activity of Meta-Bromo-Thiolactone against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Phenotypes. Microbiology Research, 14(4), 1596-1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040110








