Leptospirosis Incidence Post-Flooding Following Storm Daniel: The First Case Series in Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Series Presentation
Statistical and Laboratory Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organisation. Human Leptospirosis: Guidance for Diagnosis, Surveillance and Control. 2003. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/human-leptospirosis-guidance-for-diagnosis-surveillance-and-control (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- WHO. Fact Sheet. Leptospirosis. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/205437/B4221.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- De Brito, T.; Silva, A.M.G.D.; Abreu, P.A.E. Pathology and pathogenesis of human leptospirosis: A commented review. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2018, 60, e23, Erratum in: Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2018, 60, e23err. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, A.R.; Nally, J.E.; Ricaldi, J.N.; Matthias, M.A.; Diaz, M.M.; Lovett, M.A.; Levett, P.N.; Gilman, R.H.; Willig, M.R.; Gotuzzo, E.; et al. Leptospirosis: A zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003, 3, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, D.D.; Hanson, C.; Ir, P.; Mölsted Alvesson, H.; von Schreeb, J. The effect of seasonal floods on health: Analysis of six years of national health data and flood maps. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; FitzGerald, G.J.; Clark, M.; Hou, X.Y. Health impacts of floods. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2010, 25, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, M.L.; Adibhatla, S.; Dudek, O.; Ramsel-Miller, J. Categorization and analysis of disaster health publications: An inventory. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2017, 32, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier, D.D.; Ribacke Brolin, K.; Von Schreeb, J. No calm after the storm: A systematic review of human health following flood and storm disasters. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2017, 32, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, C.; Reid, S.A.; Aye, S.N.; Htet, N.H.; Ambu, S. Risk factors for human leptospirosis following flooding: A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanasco, N.B.; Schmeling, M.F.; Lottersberger, J.; Costa, F.; Ko, A.I.; Tarabla, H.D. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of human leptospirosis in Argentina (1999–2005). Acta Trop. 2008, 107, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathne, K.B.; Senevirathna, E.M. Identify the risk for leptospirosis disease during flooding periods (Special reference to Medirigiriya Divisional Secretariat Division in Polonnaruwa district). Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.B.; Dore, M.M. Leptospirosis: A clinical review of evidence-based diagnosis, treatment and prevention. World J. Clin. Infect Dis. 2016, 6, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, G. Spirochaetal Jaundice. BMJ. 1927, 1, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Prasad, M.L.; Kumar, M.; Munda, S.S.; Vidyapati. An insight in to various manifestations of leptospirosis: A unique case series from a state in eastern India. Cureus 2024, 16, e56802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EODY. Greek National Agency of Public Health, Epidemiological Data on Leptospirosis in Greece (2004–2022). Available online: https://eody.gov.gr/disease/leptospeirosi/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Gkentzi, D.; Lagadinou, M.; Bountouris, P.; Dimitrakopoulos, O.; Triantos, C.; Marangos, M.; Paliogianni, F.; Assimakopoulos, S.F. Epidemiology, clinical and laboratory findings of leptospirosis in Southwestern Greece. Infect. Dis. 2020, 52, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO); International Leptospirosis Society ILS. Human Leptospirosis: Guidance for Diagnosis, Surveillance, and Control. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42667 (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Suwanpakdee, S.; Kaewkungwal, J.; White, L.; Asensio, N.; Ratanakorn, P.; Singhasivanon, P.; Panngum, W. Spatio-temporal patterns of leptospirosis in Thailand: Is flooding a risk. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Hagan, J.E.; Costa, F.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Goris, M.G.; Stein, C.; Ko, A.I.; Abela-Ridder, B. Global burden of leptospirosis: Estimated in terms of disability adjusted life years. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrier, G.; Hie, P.; Gourinat, A.C.; Huguon, E.; Polfrit, Y.; Goarant, C.; D’Ortenzio, E.; Missotte, I. Association between age and severity to leptospirosis in children. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, A.B.; Mohd Fuzi, N.M.H.; Wan Mohammad, W.M.Z.; Amran, F.; Ismail, N.; Arshad, M.M.; Kamarudin, S. Leptospirosis and workplace environmental risk factors among cattle farmers in northeastern Malaysia. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 9, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.A.; Lockaby, G. Leptospirosis and the environment: A review and future directions. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Mutalip, M.H.; Mahmud, M.A.F.; Lodz, N.A.; Yoep, N.; Muhammad, E.N.; Ahmad, A.; Hashim, M.H.; Muhamad, N.A. Environmental risk factors of leptospirosis in urban settings: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e023359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, D.I.; Roess, A.A.; Pereira, S.V.C.; Schneider, M.C. Epidemiology of human leptospirosis in urban and rural areas of Brazil, 2000–2015. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupouey, J.; Faucher, B.; Edouard, S.; Richet, H.; Kodjo, A.; Drancount, M.; Davoust, B. Human leptospirosis: An emerging risk in Europe? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 37, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
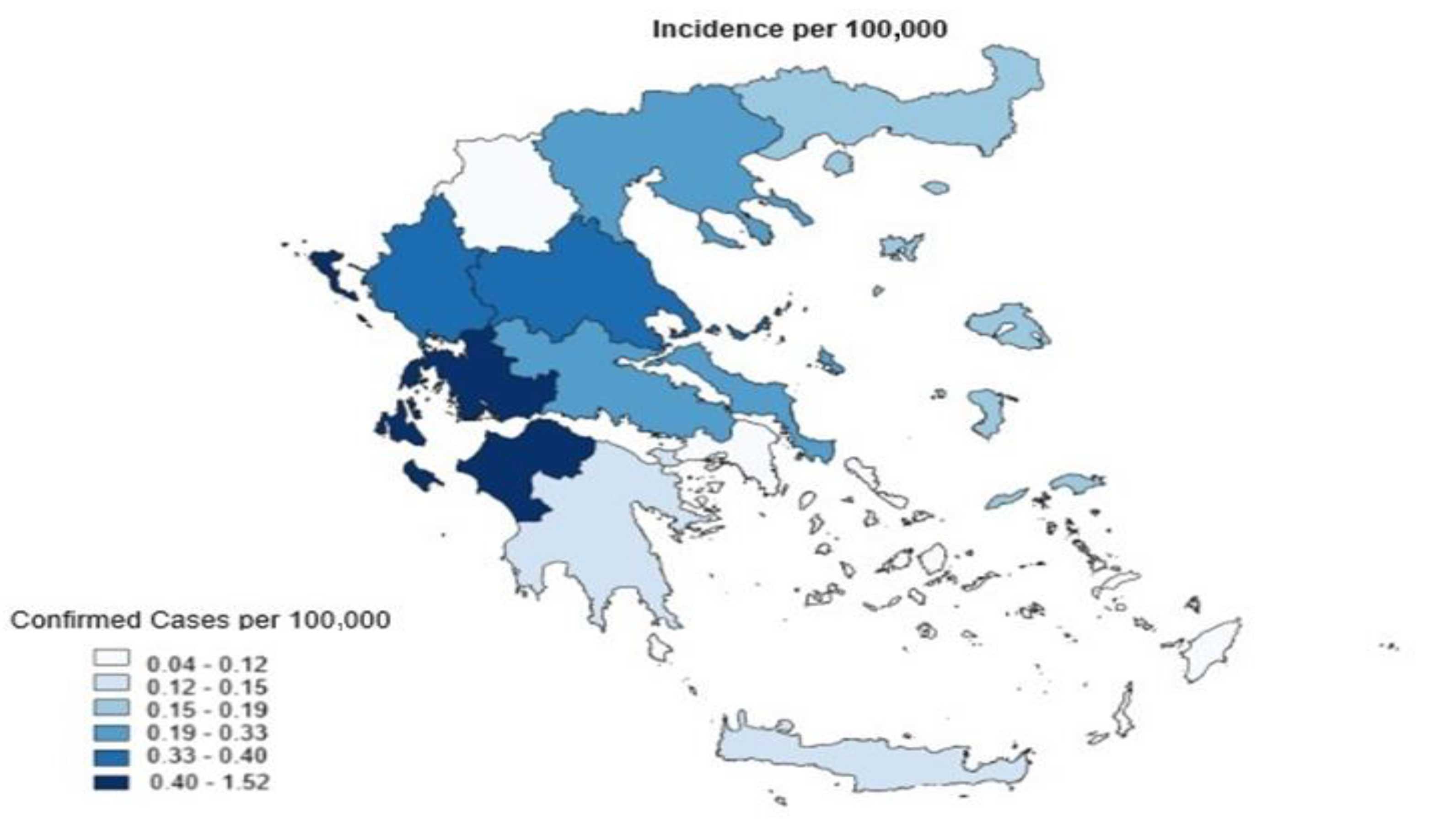
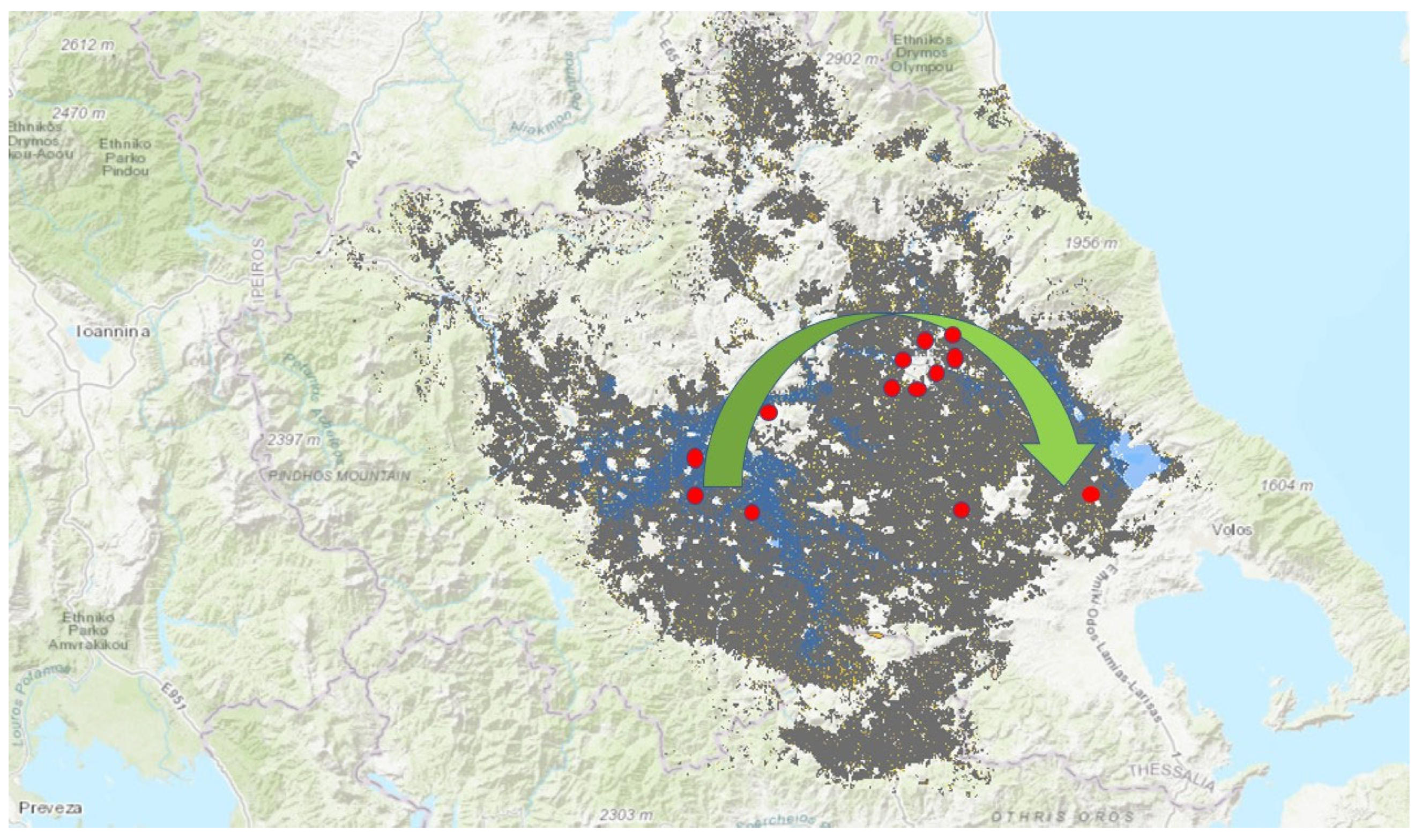
| Cases | Sex | Resident | Age | Symptoms | Laboratory Confirmation RT-PCR, IgM, IgG | Diagnosis | Exposure | Date | Region | Hospitalisation, Treatment with Antibiotics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | Rural | 43 | Myalgia, fever, rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 26 September 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 2 | Female | Rural | 47 | Fever, jaundice, rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 24 September 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 3 | Female | Urban | 26 | Fever, rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 26 September 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 4 | Female | Rural | 22 | Skin rash, myalgia | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 28 September 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 5 | Female | Rural | 76 | Fever, rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 21 September 2024 | Karditsa | Rocephin, 5 days of hospitalisation |
| 6 | Male | Urban | 61 | Rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 28 September 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 7 | Female | Urban | 36 | Myalgia, kidney failure | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 10 October 2023 | Larissa | Rocephin, 11 days of hospitalisation |
| 8 | Male | Urban | 26 | Skin rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Occupation | 10 October 2023 | Karditsa | Vibramycin |
| 9 | Male | Urban | 53 | Rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 10 October 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 10 | Male | Urban | 32 | Fever, increasing CPK | Yes | Leptospirosis | Occupation | 12 October 2023 | Trikala | Vibramycin |
| 11 | Male | Rural | 49 | Fever, rash | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 16 October 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
| 12 | Female | Rural | 27 | Hematoma, fever | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 14 October 2023 | Magnesia | Vibramycin |
| 13 | Male | Urban | 25 | Fever, myalgia | Yes | Leptospirosis | Work outdoors | 18 October 2023 | Larissa | Vibramycin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulakida, I.; Kotsiou, O.S.; Boutlas, S.; Stergioula, D.; Papadamou, G.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Papagiannis, D. Leptospirosis Incidence Post-Flooding Following Storm Daniel: The First Case Series in Greece. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16, 880-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16050069
Poulakida I, Kotsiou OS, Boutlas S, Stergioula D, Papadamou G, Gourgoulianis KI, Papagiannis D. Leptospirosis Incidence Post-Flooding Following Storm Daniel: The First Case Series in Greece. Infectious Disease Reports. 2024; 16(5):880-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16050069
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulakida, Irene, Ourania S. Kotsiou, Stylianos Boutlas, Despoina Stergioula, Georgia Papadamou, Konstantinos I. Gourgoulianis, and Dimitrios Papagiannis. 2024. "Leptospirosis Incidence Post-Flooding Following Storm Daniel: The First Case Series in Greece" Infectious Disease Reports 16, no. 5: 880-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16050069
APA StylePoulakida, I., Kotsiou, O. S., Boutlas, S., Stergioula, D., Papadamou, G., Gourgoulianis, K. I., & Papagiannis, D. (2024). Leptospirosis Incidence Post-Flooding Following Storm Daniel: The First Case Series in Greece. Infectious Disease Reports, 16(5), 880-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16050069









