Risk Factors Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: An Italian Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
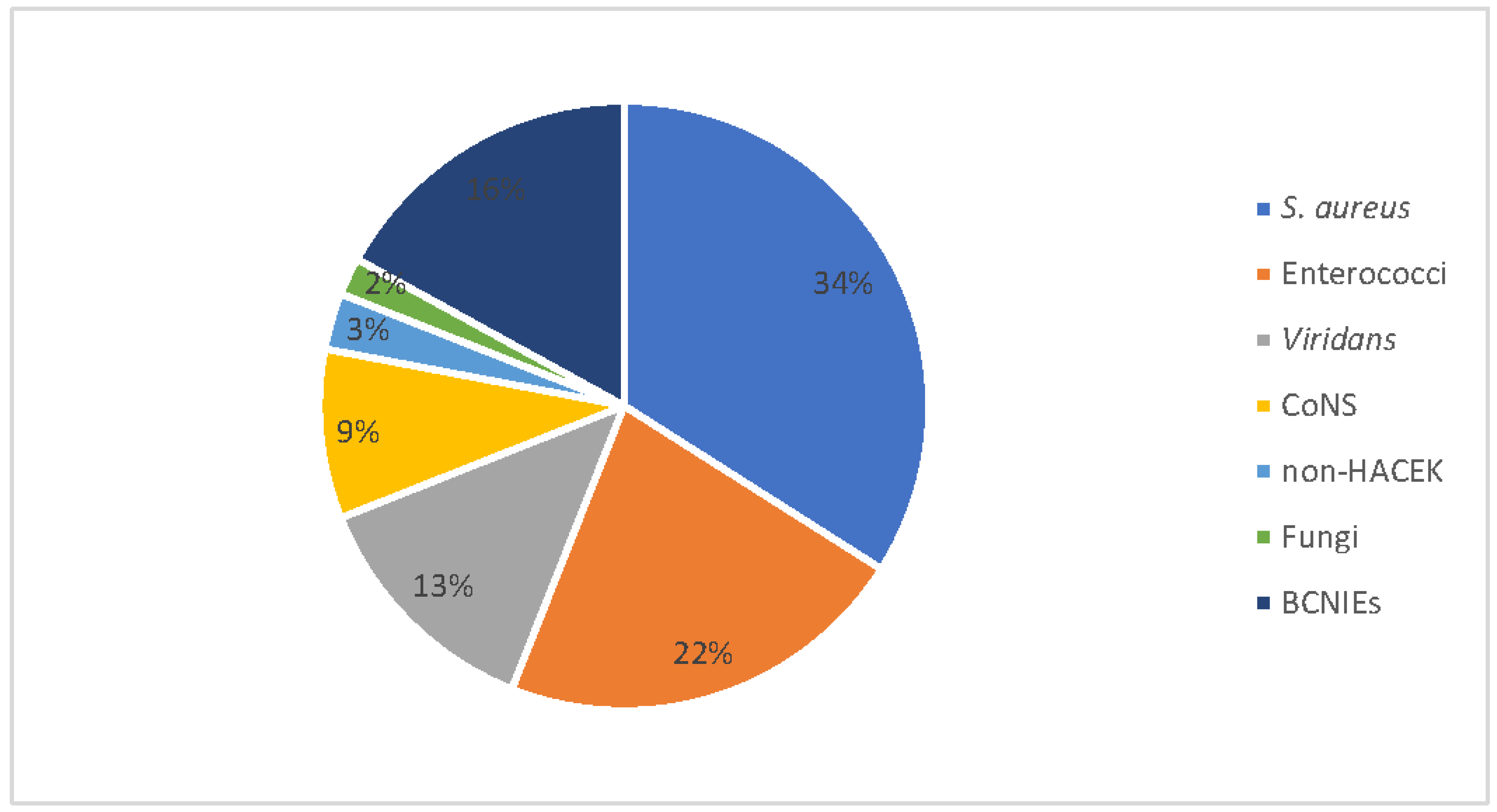
3. Results
Study Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 9th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3036–3037. [CrossRef]
- Iversen, K.; Ihlemann, N.; Gill, S.U.; Madsen, T.; Elming, H.; Jensen, K.T.; Bruun, N.E.; Høfsten, D.E.; Fursted, K.; Christensen, J.J.; et al. Partial Oral versus Intravenous Antibiotic Treatment of Endocarditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancino, P.; Ucciferri, C.; Falasca, K.; Pizzigallo, E.; Vecchiet, J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) endocarditis treated with linezolid. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 40, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeager, S.D.; Oliver, J.E.; Shorman, M.A.; Wright, L.R.; Veve, M.P. Comparison of linezolid step-down therapy to standard parenteral therapy in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezar, R.; Jirak, P.; Lichtenauer, M.; Jung, C.; Lauten, A.; Hoppe, U.C.; Wernly, B. Partial oral antibiotic therapy is non-inferior to intravenous therapy in non-critically ill patients with infective endocarditis. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 132, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí-Carvajal, A.J.; Dayer, M.; O Conterno, L.; Garay, A.G.G.; Martí-Amarista, C.E. A comparison of different antibiotic regimens for the treatment of infective endocarditis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD009880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, D.L.; Lakbar, I.; Tattevin, P. A review of current treatment strategies for infective endocarditis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infective Ther. 2020, 19, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, D.R.; Corey, G.R.; Hoen, B.; Miro, J.M.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Bayer, A.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; Olaison, L.; Pappas, P.A.; Moreillon, P.; et al. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: The International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, V.G.; Miro, J.M.; Hoen, B.; Cabell, C.H.; Abrutyn, E.; Rubinstein, E.; Corey, G.R.; Spelman, D.; Bradley, S.F.; Barsic, B.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis. JAMA 2005, 293, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemberger, I.; Biffi, M.; Lorenzetti, S.; Martignani, C.; Raffaelli, E.; Ziacchi, M.; Rapezzi, C.; Pacini, D.; Boriani, G. Predictors of long-term survival free from relapses after extraction of infected CIED. Europace 2017, 20, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, N.; Mossuto, E.; Ricci, D.; Luciani, M.; Russo, M.; Salsano, A.; Pozzoli, A.; Pierri, M.D.; D’Onofrio, A.; Chiariello, G.A.; et al. Prosthetic valve endocarditis: Predictors of early outcome of surgical therapy. A multicentric study. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, S.; Yuan, J.; Yu, D.; Bei, W.; Chen, R.; Qin, H. Accuracy and Prognosis Value of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score Combined With C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Complicated Infective Endocarditis. Front. Med. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.G.; Júnior, F.P.; Filippini, F.B.; Dannenhauer, G.P.; Miglioranza, M.H. SHARPEN score accurately predicts in-hospital mortality in infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 92, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.; Cruz, I.; Caldeira, D.; Alegria, S.; Gomes, A.C.; Broa, A.L.; João, I.; Pereira, H. Fatores de Risco para Mortalidade Hospitalar na Endocardite Infecciosa. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2019, 114, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoc, A.; Kessels, J.; Roosens, B.; Lacor, P.; Van de Veire, N.; De Sutter, J.; Magne, J.; Droogmans, S.; Cosyns, B. Impact of the initial clinical presentation on the outcome of patients with infective endocarditis. Cardiol. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iung, B.; Erba, P.A.; Petrosillo, N.; Lazzeri, E. Common diagnostic flowcharts in infective endocarditis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 58, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Giuffrè, G.; Ursi, M.P.; Iossa, D.; Bertolino, L.; Senese, A.; Pafundi, P.C.; D’Amico, F.; Albisinni, R.; Zampino, R. Predictors of long-term mortality in left-sided infective endocarditis: An historical cohort study in 414 patients. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 94, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Almirante, B.; Tornos, P.; González-Alujas, M.; Planes, A.; Larrosa, M.N.; Sambola, A.; Igual, A.; Pahissa, A. Prognosis of left-sided infective endocarditis in patients transferred to a tertiary-care hospital—prospective analysis of referral bias and influence of inadequate antimicrobial treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buburuz, A.-M.; Petris, A.; Costache, I.; Jelihovschi, I.; Arsenescu-Georgescu, C.; Iancu, L. Evaluation of Laboratory Predictors for In-Hospital Mortality in Infective Endocarditis and Negative Blood Culture Pattern Characteristics. Pathogens 2021, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Q.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, H.; Qian, Z.; Peng, J. Nomogram based on neutrophil-to-platelet ratio to predict in-hospital mortality in infective endocarditis. Biomarkers Med. 2021, 15, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arregle, F.; Martel, H.; Philip, M.; Gouriet, F.; Casalta, J.P.; Riberi, A.; Torras, O.; Casalta, A.-C.; Camoin-Jau, L.; Lavagna, F.; et al. Infective endocarditis with neurological complications: Delaying cardiac surgery is associated with worse outcome. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 114, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurological Sequelae of Endocarditis–PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31194361/ (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Alegria, S.; Marques, A.; Cruz, I.; Broa, A.L.; Pereira, A.R.F.; João, I.; Simões, O.; Pereira, H. Complicações Neurológicas em Pacientes com Endocardite Infecciosa: Perspectivas de um Centro Terciário. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2021, 116, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, T.; Rabinstein, A.; Wijdicks, E. Neurologic complications of infective endocarditis. Neurol. Clin. 2021, 177, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, R.O.M.; Zollinger, E.; Seiler, C.; Cerny, A. Infective endocarditis: Clinical spectrum, presentation and outcome. An analysis of 212 cases 1980–1995. Heart 2000, 84, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, J.T.; Schranz, A.J.; Strassle, P.D.; Agala, C.B.; Mody, G.N.; Ikonomidis, J.S.; Long, J.M. Pulmonary complications observed in patients with infective endocarditis with and without injection drug use: An analysis of the National Inpatient Sample. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-W.; Juan, L.-I.; Hsu, S.-C.; Chen, C.-K.; Wu, C.-W.; Lee, C.-C.; Wu, J.-Y. Role of procalcitonin in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primus, C.P.; A Clay, T.; McCue, M.S.; Wong, K.; Uppal, R.; Ambekar, S.; Das, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Davies, L.C.; Woldman, S.; et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT improves diagnostic certainty in native and prosthetic valve Infective Endocarditis over the modified Duke Criteria. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoen, B.; Selton-Suty, C.; Lacassin, F.; Etienne, J.; Briançon, S.; Leport, C.; Canton, P. Infective Endocarditis in Patients with Negative Blood Cultures: Analysis of 88 Cases from a One-Year Nationwide Survey in France. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 20, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age, Year | 65.6 ± 17.4 |
|---|---|
| Sex: | |
| M | 46 (67.6%) |
| F | 22 (32.4%) |
| Drug addiction | 10 (14.7%) |
| Duration of hospitalization, d | 23.9 ± 15 |
| Heart Valve: | |
| • Native valve; | 44 (64.7%) |
| • Mechanical valve; | 24 (35.3%) |
| • Early onset; | 3 (12.5%) |
| • Late onset. | 21 (87.5%) |
| Comorbidities: | |
| • Diabetes mellitus; | 23 (33.8%) |
| • Hypertension; | 42 (61.8%) |
| • Heart failure; | 7 (10.3%) |
| • Ischemic heart disease; | 11 (16.2%) |
| • Chronic renal failure; | 11 (16.2%) |
| • Immunosuppression. | 4 (5.9%) |
| Hb, g/dL | 11.10 ± 2.04 |
| WBC, cell/mm3 | 12,390 ± 6430 |
| PLT, cell/mm3 | 205,560 ± 110,800 |
| INR | 1.34 ± 0.49 |
| ERS, mm/h | 40.6 ± 35.21 |
| PCR, mg/dL | 12.2 ± 14.85 |
| PCT, ng/mL | |
| - Basal | 7.43 ± 20.27 |
| - 48–72 h | 3.59 ± 13.10 |
| 48–72 h | |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 76.7 ± 38.2 |
| Troponin, U/L | 0.74 ± 2.60 |
| LDH, U/L | 630 ± 470 |
| NT-Pro-BNP, pg/mL | 3653.3 ± 848 |
| Ejection fraction, % | 59.4 ± 8.01 |
| Clinical Manifestation | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Fever (with or without chills) | 50 (73.6) |
| Cutaneous manifestations | 14 (20.6) |
| Focal neurologic deficits | 7 (10.3) |
| Asthenia and non-specific symptoms | 17 (25.1) |
| New-onset heart murmur | 42 (61.8) |
| Embolization | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Splenic | 7 (10.3) |
| Pulmonary | 8 (11.7) |
| Mixed (splenic ± renal, ± lower limbs, ± mesenteric) | 5 (7.3) |
| Cerebral embolization | 7 (10.3) |
| Total embolic events | 27 (39.6) |
| Pearson R | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | 30 Days | 6 Months | Discharge | 30 Days | 6 Months | |
| Age | 0.346 | 0.386 | 0.386 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| eGFR | −0.343 | −0.437 | −0.425 | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Basal PCT | 0.266 | 0.337 | 0.339 | 0.029 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| 48–72 h PCT | 0.222 | 0.308 | 0.305 | 0.049 | 0.011 | 0.011 |
| New-onset heart murmur | 0.311 | 0.273 | 0.294 | 0.010 | 0.025 | 0.015 |
| Non-continued antibiotic therapy | 0.232 | 0.239 | 0.283 | 0.050 | 0.05 | 0.019 |
| Neurological manifestations | - | - | 0.284 | - | - | 0.019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ucciferri, C.; Auricchio, A.; Cutone, C.; Di Gasbarro, A.; Vecchiet, J.; Falasca, K. Risk Factors Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: An Italian Single-Center Experience. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14020026
Ucciferri C, Auricchio A, Cutone C, Di Gasbarro A, Vecchiet J, Falasca K. Risk Factors Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: An Italian Single-Center Experience. Infectious Disease Reports. 2022; 14(2):213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleUcciferri, Claudio, Antonio Auricchio, Carmine Cutone, Alessandro Di Gasbarro, Jacopo Vecchiet, and Katia Falasca. 2022. "Risk Factors Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: An Italian Single-Center Experience" Infectious Disease Reports 14, no. 2: 213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14020026
APA StyleUcciferri, C., Auricchio, A., Cutone, C., Di Gasbarro, A., Vecchiet, J., & Falasca, K. (2022). Risk Factors Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: An Italian Single-Center Experience. Infectious Disease Reports, 14(2), 213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14020026






