Longitudinal Projection of Herd Prevalence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infection in the Norwegian Pig Population by Discrete-Time Markov Chain Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Norwegian Pig Population H1N1pdm09 Active Serosurveillance
2.2. Laboratory Analyses and Herd Diagnoses
2.3. Surveillance Data 2009 to 2020 and Parameter Selection for DTMC Model
2.3.1. Initial Herd Prevalence in 2009 (State X0)
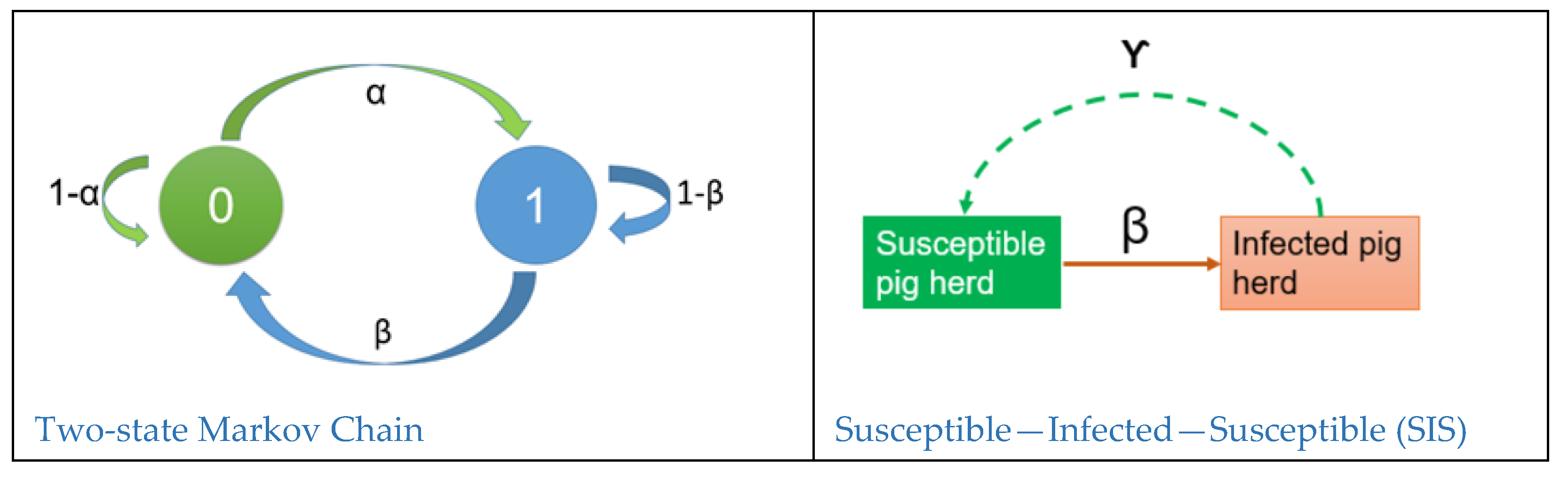
2.3.2. Four Transition Probabilities for the Transition Matrix
2.3.3. Equations for Discrete-Time Markov Chain Binomial Model
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zipkin, E.F.; Jennelle, C.S.; Cooch, E.G. A primer on the application of Markov chains to the study of wildlife disease dynamics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuli, N.P.; Bean, N.G.; Ross, J.V. Hybrid Markov chain models of S-I-R disease dynamics. J. Math. Biol. 2017, 75, 521–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lium, B.; Er, C.; Zerihun, A. The Surveillance and Control Programme for Specific Virus Infections in Swine Herd in Norway 2013; Norwegian Veterinary Institute: Oslo, Norway, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hofshagen, M.; Gjerset, B.; Er, C.; Tarpai, A.; Brun, E.; Dannevig, B.; Bruheim, T.; Fostad, I.G.; Iversen, B.; Hungnes, O.; et al. Pandemic influenza A(H1N1)v: Human to pig transmission in Norway? Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Les Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2009, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pourbohloul, B.; Ahued, A.; Davoudi, B.; Meza, R.; Meyers, L.A.; Skowronski, D.M.; Villasenor, I.; Galvan, F.; Cravioto, P.; Earn, D.J.; et al. Initial human transmission dynamics of the pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus in North America. Influenza Respir. Viruses 2009, 3, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajardi, P.; Poletto, C.; Ramasco, J.J.; Tizzoni, M.; Colizza, V.; Vespignani, A. Human mobility networks, travel restrictions, and the global spread of 2009 H1N1 pandemic. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Tu, W.W.; Yen, H.L. A novel H1N1 virus causes the first pandemic of the 21(st) century. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2946–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, C.; Donnelly, C.A.; Cauchemez, S.; Hanage, W.P.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; Griffin, J.; Baggaley, R.F.; Jenkins, H.E.; Lyons, E.J.; et al. Pandemic Potential of a Strain of Influenza A (H1N1): Early Findings. Science 2009, 324, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torne, A.N.; Cassini, A.; Ammon, A.; Amato-Gauci, A.; Nicoll, A.; Jansson, A.; Magiorakos, A.; Lenglet, A.; Ciancio, B.; Santos, C.V.; et al. Initial Epidemiological Findings in the European Union Following the Declaration of Pandemic Alert Level 5 Due to Influenza a (H1n1). Eurosurveillance 2009, 14, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.; Enserink, M. Swine flu. After delays, WHO agrees: The 2009 pandemic has begun. Science 2009, 324, 1496–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, A. WHO raises level of alert on flu pandemic. BMJ 2009, 338, b1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappaioanou, M.; Gramer, M. Lessons from Pandemic H1N1 2009 to Improve Prevention, Detection, and Response to Influenza Pandemics from a One Health Perspective. Ilar J. 2010, 51, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DSB. New Influenza A Virus (H1N1), A Summary of A Study on the National Response in Norway; DSB: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerset, B.; Er, C.; Lotvedt, S.; Jorgensen, A.; Hungnes, O.; Lium, B.; Germundsson, A. Experiences after Twenty Months with Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Infection in the Naive Norwegian Pig Population. Influenza Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 206975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grontvedt, C.A.; Er, C.; Gjerset, B.; Germundsson, A.; Framstad, T.; Brun, E.; Jorgensen, A.; Lium, B. Clinical Impact of Infection with Pandemic Influenza (H1N1) 2009 Virus in Naive Nucleus and Multiplier Pig Herds in Norway. Influenza Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 163745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, C.; Skjerve, E.; Brun, E.; Framstad, T.; Lium, B. Occurrence and spread of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection in Norwegian pig herds based on active serosurveillance from 2010 to 2014. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3148–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grontvedt, C.A.; Er, C.; Gjerset, B.; Hauge, A.G.; Brun, E.; Jorgensen, A.; Lium, B.; Framstad, T. Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection in Norwegian swine herds 2009/10: The risk of human to swine transmission. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 110, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, C.; Lium, B.; Tavornpanich, S.; Hofmo, P.O.; Forberg, H.; Hauge, A.G.; Grontvedt, C.A.; Framstad, T.; Brun, E. Adverse effects of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection on growth performance of Norwegian pigs—A longitudinal study at a boar testing station. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, C.; Skjerve, E.; Brun, E.; Hofmo, P.O.; Framstad, T.; Lium, B. Production impact of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection on fattening pigs in Norway. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalin, A.M.; Gidlund, K.; Eliasson-Selling, L. Post-mortem examination of genital organs from sows with reproductive disturbances in a sow-pool. Acta Vet. Scand 1997, 38, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engblom, L.; Lundeheim, N.; Strandberg, E.; Schneider Mdel, P.; Dalin, A.M.; Andersson, K. Factors affecting length of productive life in Swedish commercial sows. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. Available online: https://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.03.04_AI.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- NVI. Norwegian Veterinary Institute Surveillance Programmes. Available online: https://www.vetinst.no/rapporter-og-publikasjoner/rapporter/2020/surveillance-programmes-2019-summary-of-results (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Er, J.C.; Lium, B.; Framstad, T. Antibodies of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus in pigs’ sera cross-react with other influenza A virus subtypes. A retrospective epidemiological interpretation of Norway’s serosurveillance data from 2009–2017. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanders, W.D.; Kleinbaum, D.G. Basic models for disease occurrence in epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omey, E.; Santos, J.; Van Gulck, S. A Markov-Binomial Distribution. Appl. Anal. Discr. Math. 2008, 2, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PLOS. Two-State Markov Chain Approach. Available online: https://storage.googleapis.com/plos-corpus-prod/10.1371/journal.pone.0098001/1/pone.0098001.s006.pdf?X-Goog-Algorithm=GOOG4-RSA-SHA256&X-Goog-Credential=wombat-sa%40plos-prod.iam.gserviceaccount.com%2F20210824%2Fauto%2Fstorage%2Fgoog4_request&X-Goog-Date=20210824T072804Z&X-Goog-Expires=86400&X-Goog-SignedHeaders=host&X-Goog-Signature=6f76968491af9730e5b2a529e27144b9a6bb4b5460535c7ab232a4b086427bc0aebcf281daacb2dd79b6b500ab685df1dfcf9819491552516f26d961719f968b8104b59e08774797659ff35edd8332e5a28e44fbc8c9d3db05f103dfa992fd5da842f00ad99bc2c79c15474f7af13f9d97021227c3c202d4c49a70a10dce1b0168cb8432a2081919e07ce5dd0fdb29c0546b2343c6ace4ad6cf296d4baafb002c834fbc79200ea2febd1afa80d97a78084d04756edd62a04f88e47ebf06a878c17e53f14784612d7e9b73b61917af9f7cafdcd9c7777b140ee5a167b9874c1cb2c5eed17aac3a496d544de8bfbd4fe1a100671a4d8dcdf5aa406aa4ac961d9c6 (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- FHI. Influensa in Norway, Season 2016-17. Available online: https://www.fhi.no/globalassets/dokumenterfiler/rapporter/2017/influensasesongen-i-norge-2016-2017.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- FHI. Influensa in Norway, Season 2015-16. Available online: https://www.fhi.no/globalassets/dokumenterfiler/influensa/sesongrapport-influensa-2015-16.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2020).
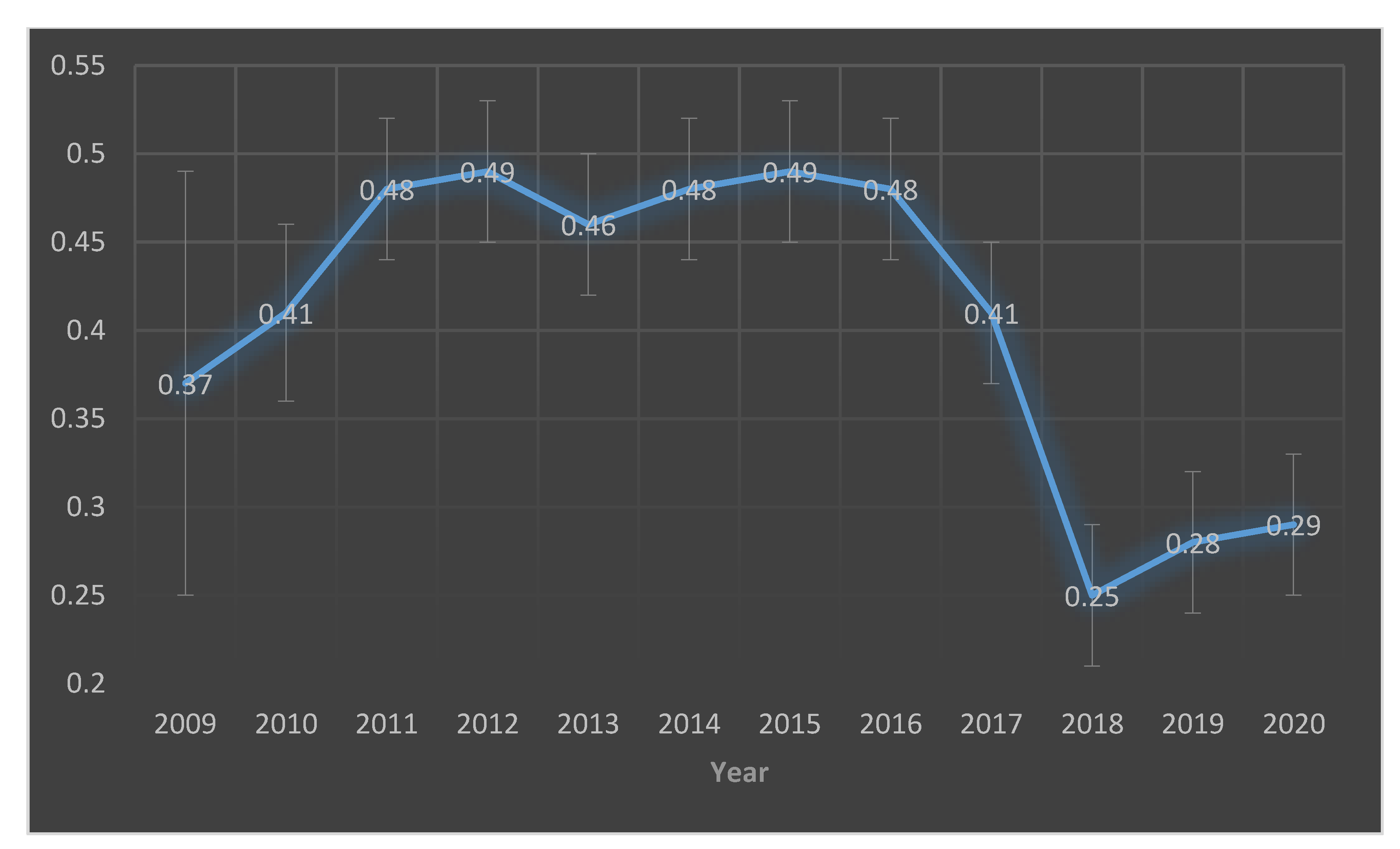
| Year | Total Pig Herds | Herds Tested | Population Proportion | Herds Positive | Prevalence | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2546 | 452 (54 *) | 2% | 20 | 0.37 | (25–52) |
| 2010 | 2441 | 459 | 19% | 189 | 0.41 | (37–46) |
| 2011 | 2346 | 730 | 31% | 353 | 0.48 | (45–52) |
| 2012 | 2213 | 764 | 35% | 378 | 0.49 | (46–53) |
| 2013 | 2178 | 737 | 34% | 338 | 0.46 | (42–50) |
| 2014 | 2117 | 622 | 29% | 296 | 0.48 | (44–52) |
| 2015 | 2141 | 568 | 27% | 280 | 0.49 | (45–53) |
| 2016 | 2180 | 564 | 26% | 271 | 0.48 | (44–52) |
| 2017 | 1955 | 548 | 28% | 225 | 0.41 | (37–45) |
| 2018 | 2038 | 533 | 26% | 134 | 0.25 | (22–29) |
| 2019 | 1853 | 545 | 29% | 153 | 0.28 | (24–32) |
| 2020 | 535 | 154 | 0.29 | (25–33) |
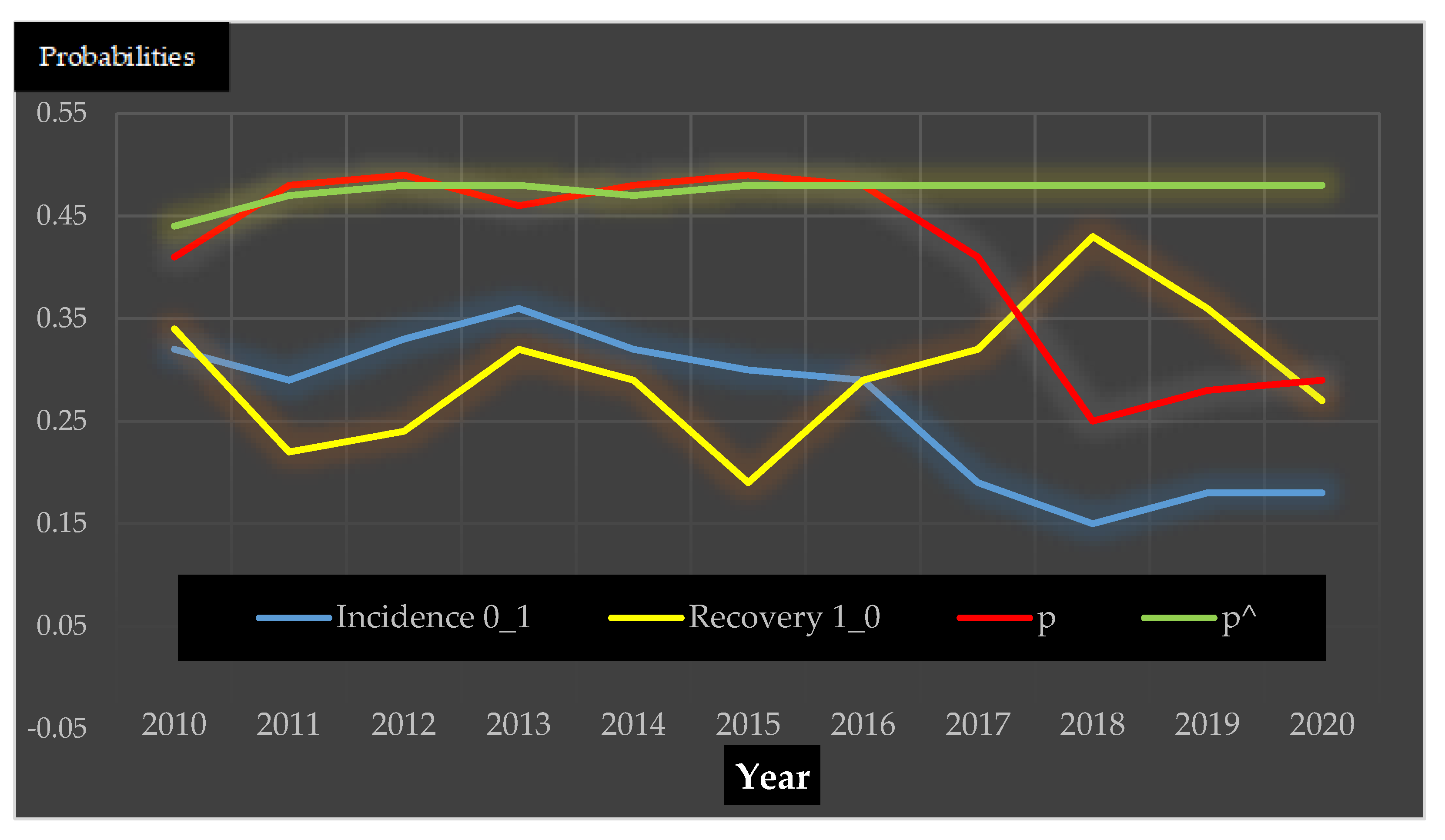
| Transition Probabilities (n = Pig Herds) | DTMC Projected Prevalence | Surveillance Prevalence | DTMC— Observed | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | No. of Pig Herds | 0_0 | Incidence 0_1 | 1_1 | Recovery 1_0 | p^ | p (95 CI) | p^ − p |
| 2009 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 37% | 37% (25–52) | 0% |
| 2010 | 113 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 44% | 41% (37–46) | 3% |
| 2011 | 241 | 0.71 | 0.29 | 0.78 | 0.22 | 47% | 48% (45–52) | −1% |
| 2012 | 447 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.76 | 0.24 | 48% | 49% (46–53) | −1% |
| 2013 | 461 | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 48% | 46% (42–50) | 2% |
| 2014 | 433 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 0.71 | 0.29 | 47% | 48% (44–52) | −1% |
| 2015 | 348 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.81 | 0.19 | 48% | 49% (45–53) | −1% |
| 2016 | 348 | 0.71 | 0.29 | 0.71 | 0.29 | 48% | 48% (44–52) | 0% |
| 2017 | 332 | 0.81 | 0.19 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 48% | 41% (37–45) | 7% |
| 2018 | 237 | 0.85 | 0.15 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 48% | 25% (22–29) | 23% |
| 2019 | 315 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.64 | 0.36 | 48% | 28% (24–32) | 20% |
| 2020 | 188 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.73 | 0.27 | 48% | 29% (25–33) | 19% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Er, J.C. Longitudinal Projection of Herd Prevalence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infection in the Norwegian Pig Population by Discrete-Time Markov Chain Modelling. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 13, 748-756. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr13030070
Er JC. Longitudinal Projection of Herd Prevalence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infection in the Norwegian Pig Population by Discrete-Time Markov Chain Modelling. Infectious Disease Reports. 2021; 13(3):748-756. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr13030070
Chicago/Turabian StyleEr, Jwee Chiek. 2021. "Longitudinal Projection of Herd Prevalence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infection in the Norwegian Pig Population by Discrete-Time Markov Chain Modelling" Infectious Disease Reports 13, no. 3: 748-756. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr13030070
APA StyleEr, J. C. (2021). Longitudinal Projection of Herd Prevalence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infection in the Norwegian Pig Population by Discrete-Time Markov Chain Modelling. Infectious Disease Reports, 13(3), 748-756. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr13030070






