The Potential Relationship between Gastric and Small Intestinal-Derived Endotoxin on Serum Testosterone in Men
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- Recovery of lactulose (%) = plasma lactulose concentration/5 g of administered lactulose × 100
- (2)
- Recovery of rhamnose (%) = plasma rhamnose concentration/0.5 g of administered rhamnose × 100
- (3)
- L/R ratio = plasma concentration of lactulose large probe/plasma concentration of rhamnose
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Questionnaires
3.2.1. Physical Activity
3.2.2. Sleep Quality
3.2.3. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
3.3. Serology
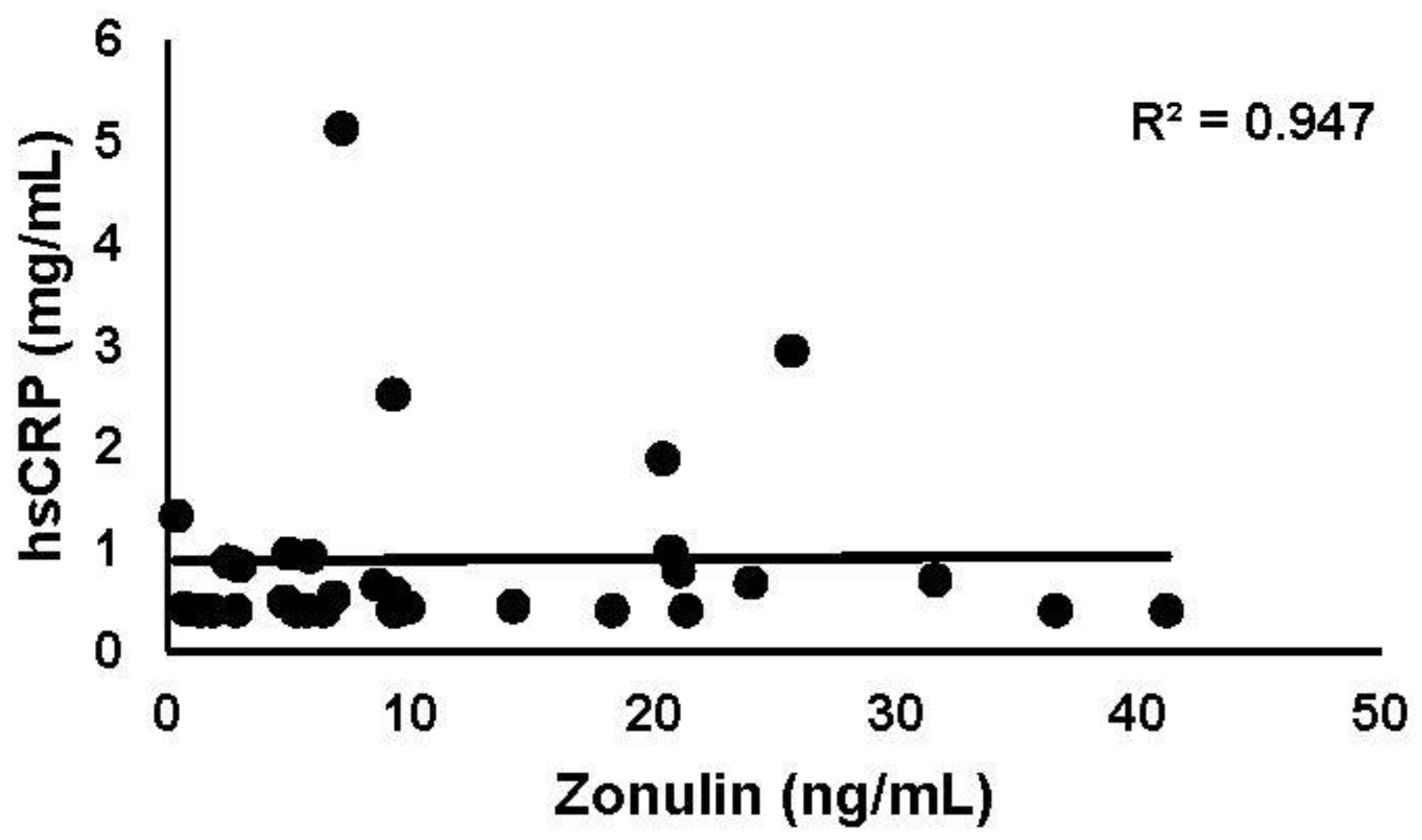
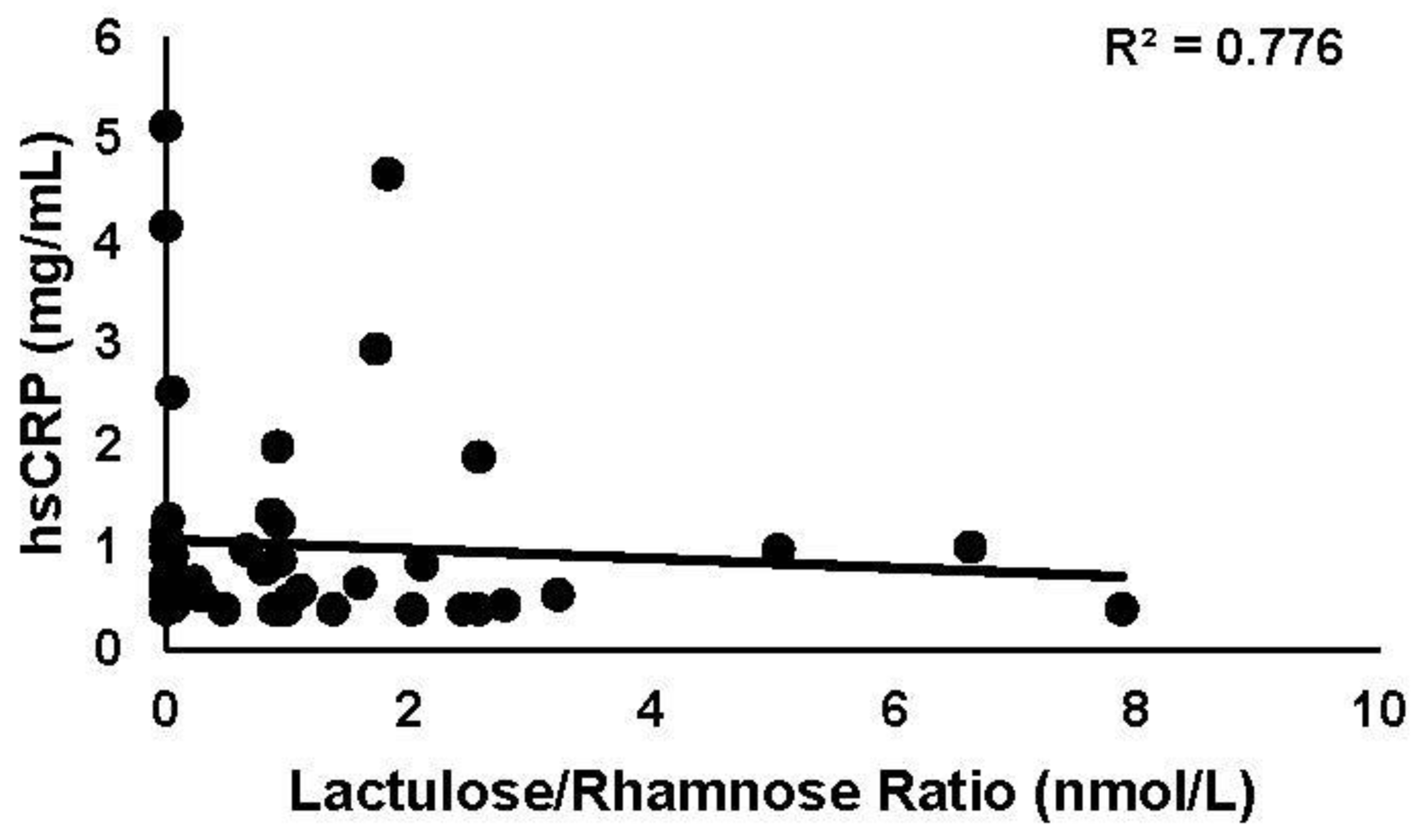
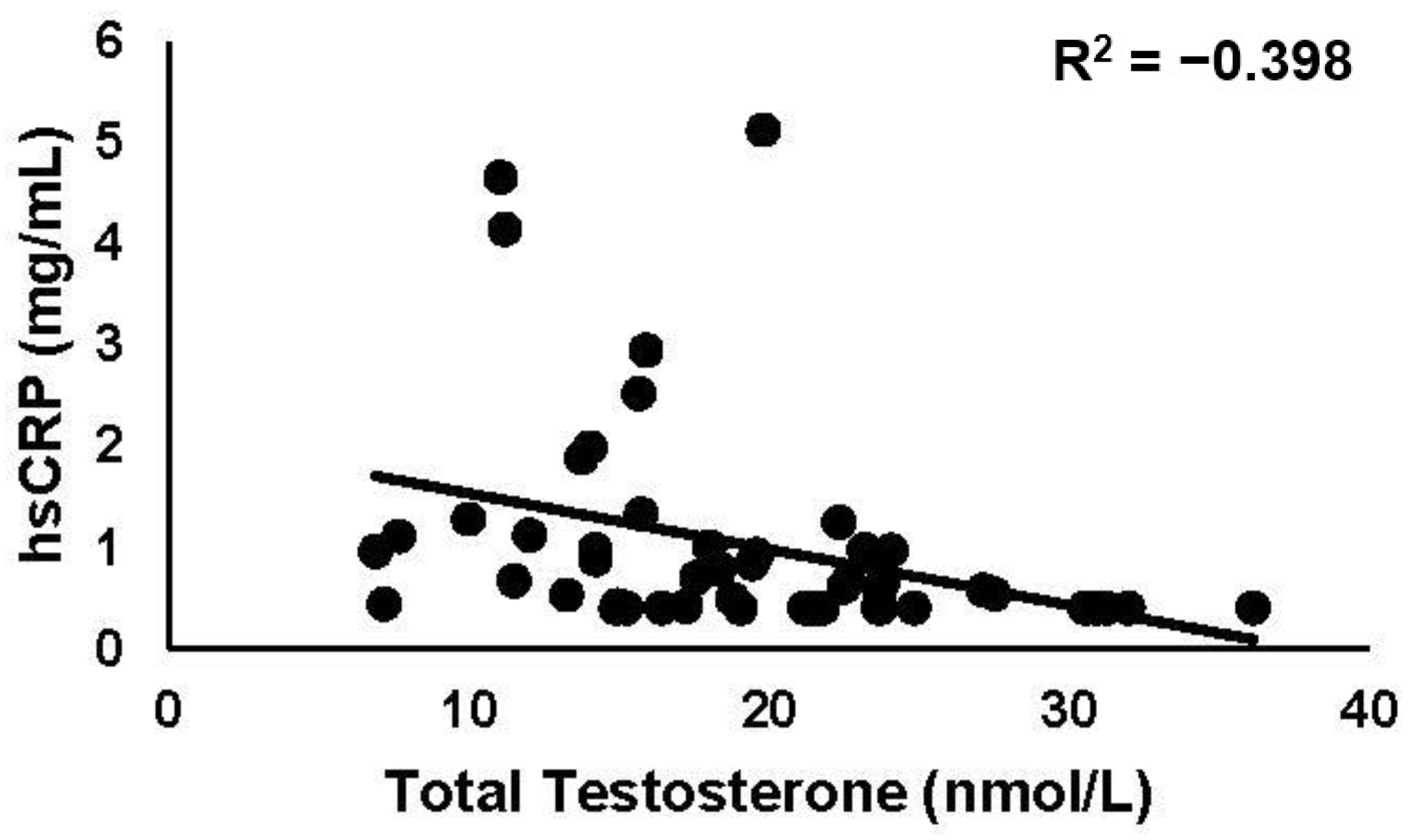
3.3.1. hsCRP
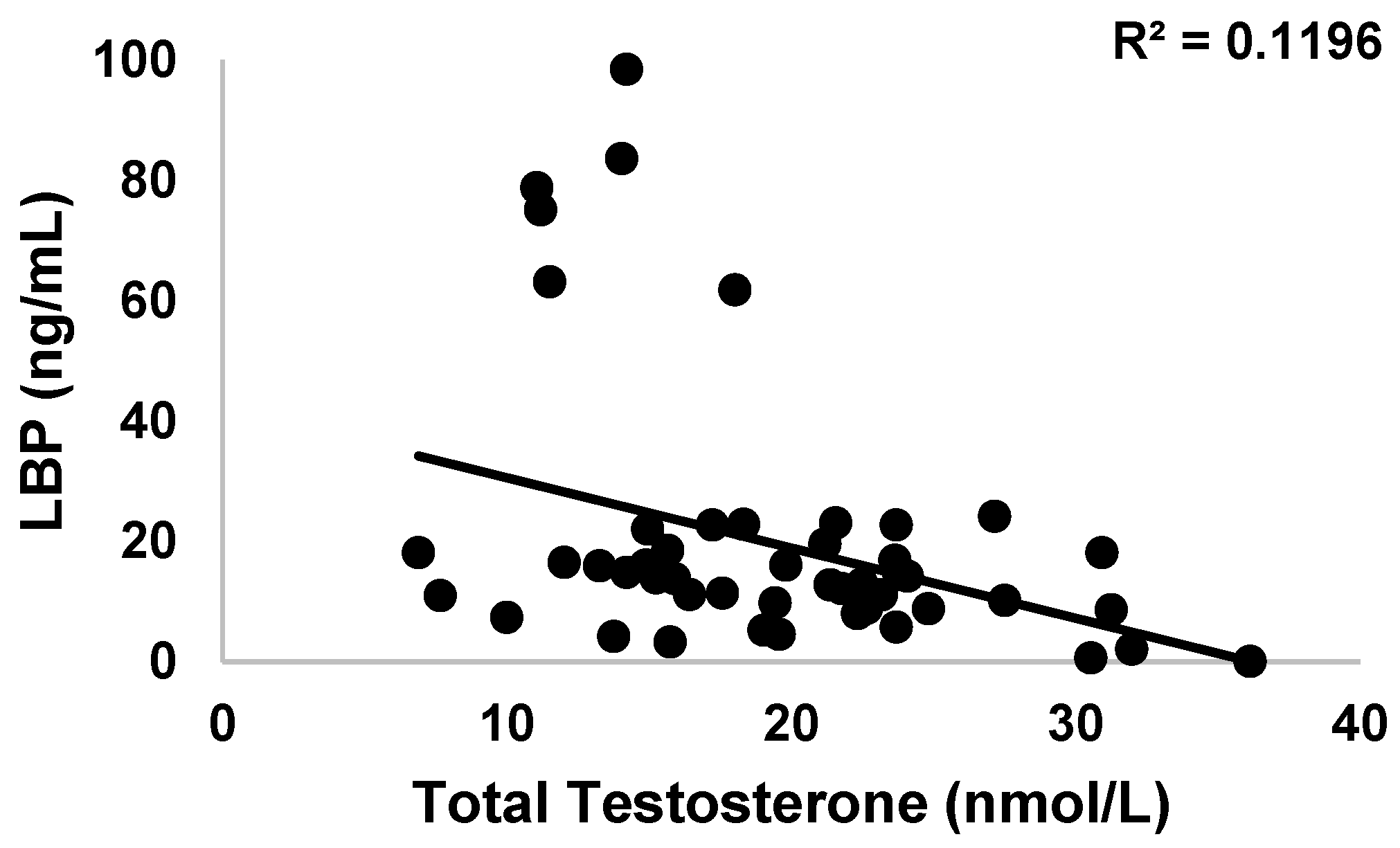
3.3.2. LBP
3.3.3. H. pylori
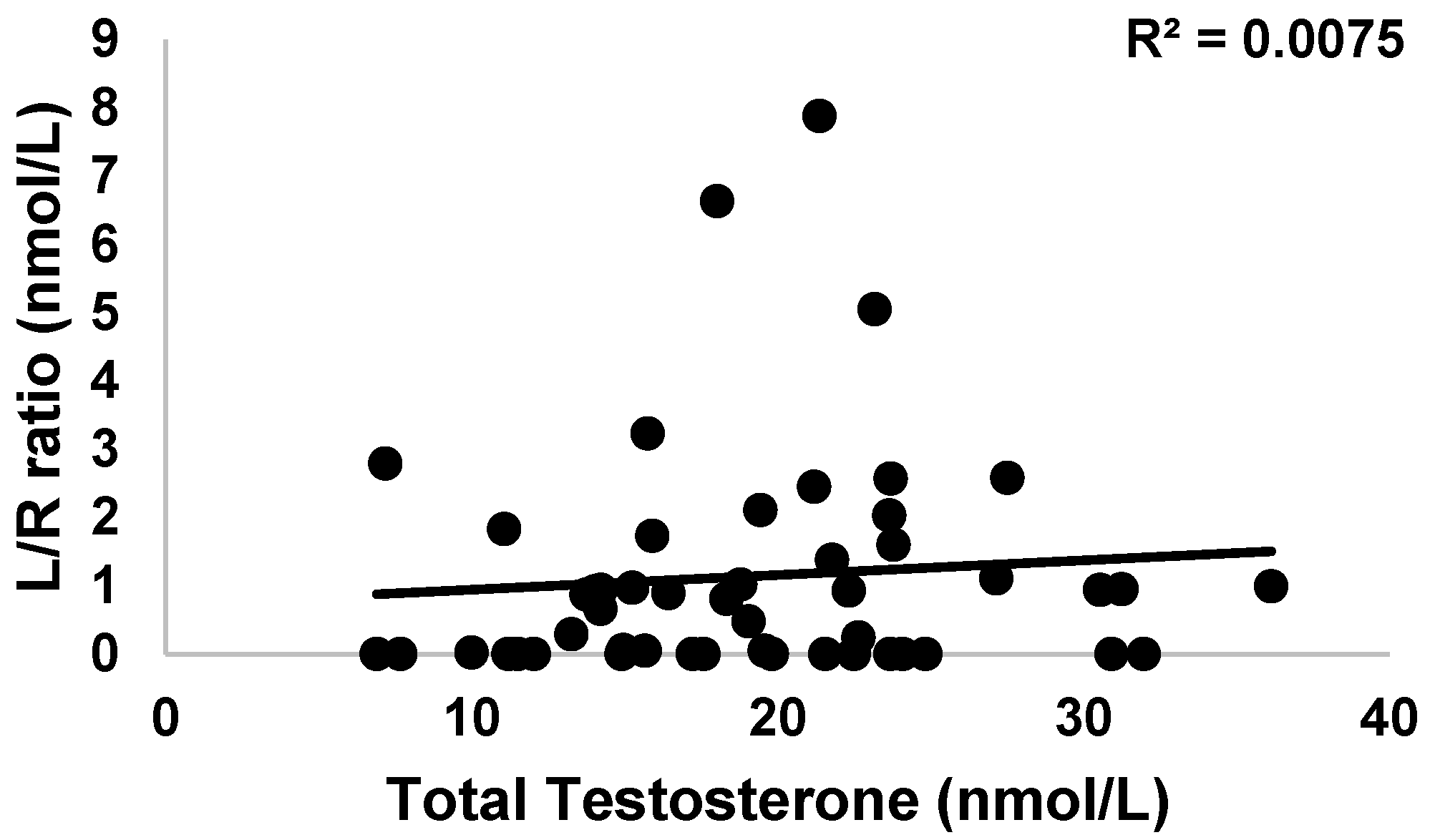
3.3.4. Intestinal Permeability
3.4. Endocrinology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nassar, G.N.; Leslie, S.W. Physiology, Testosterone. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Behre, H.M. Male Reproductive Function. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health; Heggenhougen, H.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 187–195. ISBN 978-0-12-373960-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, I.; Fui, M.N.T.; Zajac, J.D.; Grossmann, M. Assessment and Management of Male Androgen Disorders: An Update. Aust. Fam. Physician 2014, 43, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dandona, P.; Rosenberg, M.T. A Practical Guide to Male Hypogonadism in the Primary Care Setting. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2010, 64, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Gavini, S.; Dobs, A.S. Male Hypogonadism in Systemic Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Mulgund, A.; Hamada, A.; Chyatte, M.R. A Unique View on Male Infertility around the Globe. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaria, S. Male Hypogonadism. Lancet 2014, 383, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zotova, N.V.; Chereshnev, V.A.; Gusev, E.Y. Systemic Inflammation: Methodological Approaches to Identification of the Common Pathological Process. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutagy, N.E.; McMillan, R.P.; Frisard, M.I.; Hulver, M.W. Metabolic Endotoxemia with Obesity: Is It Real and Is It Relevant? Biochimie 2016, 124, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y. Effect of Bacterial Endotoxin Lipopolysaccharide Treatment on Duck Leydig Cells. Anim. Reprod. 2019, 16, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremellen, K. Gut Endotoxin Leading to a Decline IN Gonadal Function (GELDING)—A Novel Theory for the Development of Late Onset Hypogonadism in Obese Men. Basic Clin. Androl. 2016, 26, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held Hales, K.; Diemer, T.; Ginde, S.; Shankar, B.K.; Roberts, M.; Bosmann, H.B.; Hales, D.B. Diametric Effects of Bacterial Endotoxin Lipopolysaccharide on Adrenal and Leydig Cell Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4000–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.; Abrams, M.S.; De Souza, L.; Wagner, C.G.; Whitlock, B.; Sartin, J.L. Endotoxin Inhibition of Luteinizing Hormone in Sheep. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2003, 25, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Bing, G. Lipopolysaccharide Animal Models for Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2011, 2011, 327089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, R.R.; Leong, S.R.; Flaggs, G.W.; Gray, P.W.; Wright, S.D.; Mathison, J.C.; Tobias, P.S.; Ulevitch, R.J. Structure and Function of Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein. Science 1990, 249, 1429–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremellen, K.; Pearce, K. Probiotics to Improve Testicular Function (Andrology 5:439–444, 2017)—A Comment on Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Potential of Probiotics beyond Reproduction. Andrology 2017, 5, 1052–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opal, S.M.; Scannon, P.J.; Vincent, J.-L.; White, M.; Carroll, S.F.; Palardy, J.E.; Parejo, N.A.; Pribble, J.P.; Lemke, J.H. Relationship between Plasma Levels of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS-Binding Protein in Patients with Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Bistritz, L.; Meddings, J.B. Alterations in Intestinal Permeability. Gut 2006, 55, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D. Human Gut Microbiome: Hopes, Threats and Promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Lee, S.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut Biogeography of the Bacterial Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Wang, J.; Darzi, Y.; Faust, K.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Vandeputte, D.; et al. Population-Level Analysis of Gut Microbiome Variation. Science 2016, 352, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Rodríguez, R.; Godínez-Victoria, M.; Abarca-Rojano, E.; Pacheco-Yépez, J.; Reyna-Garfias, H.; Barbosa-Cabrera, R.E.; Drago-Serrano, M.E. Stress Modulates Intestinal Secretory Immunoglobulin A. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Punder, K.; Pruimboom, L. Stress Induces Endotoxemia and Low-Grade Inflammation by Increasing Barrier Permeability. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlavaty, T.; Krajcovicova, A.; Kollerova, J.; Koller, T.; Leskova, Z.; Sturdik, I.; Payer, J. P567 Cross-Sectional Study of the Low Serum Concentrations of Testosterone in IBD and the Influence on Disease Activity. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, S369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Riordan, S.M.; McIver, C.J.; Thomas, D.H.; Duncombe, V.M.; Bolin, T.D.; Thomas, M.C. Luminal Bacteria and Small-Intestinal Permeability. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losurdo, G.; D’Abramo, F.S.; Indellicati, G.; Lillo, C.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. The Influence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Digestive and Extra-Intestinal Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, M.; Donaldson, J. Effect of Bile Salts on the DNA and Membrane Integrity of Enteric Bacteria. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, E.C.; Valenza, V.; Sparano, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Gabrielli, M.; Cazzato, A.; Ferraro, P.M.; Gasbarrini, A. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Intestinal Permeability. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 1131–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusiak, A.; Chałubiński, M.; Broncel, M.; Rechciński, T.; Rudnicka, K.; Miszczyk, E.; Walencka, M.; Strapagiel, D.; Gajewski, A.; Chmiela, M. Putative Consequences of Exposure to Helicobacter pylori Infection in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease in Terms of Humoral Immune Response and Inflammation. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.J.; Lamichhane, B.; Webberley, K.M. A Longitudinal, Population-Level, Big-Data Study of Helicobacter Pylori-Related Disease across Western Australia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, T.J.; Scott, K.E.; Fox, J.G.; Hagen, S.J. Tight Junction Disruption: Helicobacter pylori and Dysregulation of the Gastric Mucosal Barrier. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11411–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedwick, J.P.; Lapointe, T.K.; Meddings, J.B.; Sherman, P.M.; Buret, A.G. Helicobacter pylori Activates Myosin Light-Chain Kinase to Disrupt Claudin-4 and Claudin-5 and Increase Epithelial Permeability. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 7844–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schooling, C.M.; Dowd, J.B.; Jones, H.E. Helicobacter pylori Is Associated with Lower Androgen Activity among Men in NHANES III. Gut 2013, 62, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baecke, J.A.; Burema, J.; Frijters, J.E. A Short Questionnaire for the Measurement of Habitual Physical Activity in Epidemiological Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A New Instrument for Psychiatric Practice and Research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, C.Y.; Morris, J.; Whorwell, P.J. The Irritable Bowel Severity Scoring System: A Simple Method of Monitoring Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Progress. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, J.N.; Impey, S.G.; Doran, D.A.; Fleming, S.C.; Morton, J.P.; Close, G.L. Acute High-Intensity Interval Running Increases Markers of Gastrointestinal Damage and Permeability but Not Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, J.N.; Sparks, A.S.; Doran, D.A.; Fleming, S.C.; Langan-Evans, C.; Kirk, B.; Fearn, R.; Morton, J.P.; Close, G.L. Four Weeks of Probiotic Supplementation Reduces GI Symptoms during a Marathon Race. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.D.; Hawkes, J.; Graham, R.D.; Kitchen, J.L.; Symonds, E.L.; Davidson, G.P.; Butler, R.N. Zinc-Fortified Oral Rehydration Solution Improved Intestinal Permeability and Small Intestinal Mucosal Recovery. Clin. Pediatr. 2015, 54, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.; Howarth, G.S.; Kitessa, S.M.; Tran, C.D.; Forder, R.E.A.; Hughes, R.J. New Biomarkers for Increased Intestinal Permeability Induced by Dextran Sodium Sulphate and Fasting in Chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, e237–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.M.; Jadhav, S.R.; Phan, L.; Tremellen, K.; Tran, C.D.; Beale, D.J. Plasma Metabolic and Lipidomic Fingerprinting of Individuals with Increased Intestinal Permeability. Metabolites 2022, 12, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, C.R.; Laniado, N.; Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; Borrell, L.N.; Qi, Q.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Morse, D.E.; Singer, R.H.; Kaplan, R.C.; Badner, V.; et al. Better-Quality Diet Is Associated with Lower Odds of Severe Periodontitis in US Hispanics/Latinos. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Consultation on Obesity, 1999. In Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a WHO Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ness-Abramof, R.; Apovian, C.M. Waist Circumference Measurement in Clinical Practice. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-S.; Li, F.-Y.; Chang, F.-Y.; Lee, S.-D. Immunoglobulin G Antibody against Helicobacter Pylori: Clinical Implications of Levels Found in Serum. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gallay, P.; Barras, C.; Tobias, P.S.; Calandra, T.; Glauser, M.P.; Heumann, D. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Binding Protein in Human Serum Determines the Tumor Necrosis Factor Response of Monocytes to LPS. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fu, E.L.; Andersson Franko, M.; Obergfell, A.; Dekker, F.; Gabrielsen, A.; Jernberg, T.; Carrero, J. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease Progression or Acute Kidney Injury in Post-Myocardial Infarction Patients. Am. Heart J. 2019, 216, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patgiri, D.; Pathak, M.S.; Sharma, P.; Kutum, T.; Mattack, N. Serum hsCRP: A Novel Marker for Prediction of Cerebrovascular Accidents (Stroke). J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, CC08–CC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.E. Study Design Considerations for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Clinical Trials. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Quintela, A.; Alonso, M.; Campos, J.; Vizcaino, L.; Loidi, L.; Gude, F. Determinants of Serum Concentrations of Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein (LBP) in the Adult Population: The Role of Obesity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Brito, J.P.; Cunningham, G.R.; Hayes, F.J.; Hodis, H.N.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Snyder, P.J.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wu, F.C.; Yialamas, M.A. Testosterone Therapy in Men With Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1715–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.H.B. Tietz Clinical Guide to Laboratory Tests; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-1-4377-1987-1. [Google Scholar]
- Karkhah, A.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Rostamtabar, M.; Koppolu, V.; Darvish, S.; Vasigala, V.K.R.; Validi, M.; Nouri, H.R. Helicobacter Pylori Evasion Strategies of the Host Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Survive and Develop Gastrointestinal Diseases. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 218, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, G.; Reyes, V.E.; Beswick, E.J. Immune Response to H Pylori. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5593–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Perez, G.I.; Peek, R.M.; Legath, A.J.; Heine, P.R.; Graff, L.B. The Role of CagA Status in Gastric and Extragastric Complications of Helicobacter Pylori. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 50, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, X.; Guo, J.; Yu, D.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Helicobacter Pylori Infection Alters Gastric and Tongue Coating Microbial Communities. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.; Tavakkoli, H.; Habizadeh, M.R.; Emami, M.H. Diagnostic Values of Helicobacter Pylori Diagnostic Tests: Stool Antigen Test, Urea Breath Test, Rapid Urease Test, Serology and Histology. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Diagnostic Methods of Helicobacter Pylori Infection for Epidemiological Studies: Critical Importance of Indirect Test Validation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4819423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiho, H.; Ihara, E.; Nakamura, K. Low-Grade Inflammation Plays a Pivotal Role in Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. World J. Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Loke, W.; Lim, D.Y.; Yeo, W.-S. The Role of Inflammation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Nadeau, A.; Lamsam, J.; Nord, S.L.; Ryks, M.; Burton, D.; Sweetser, S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Singh, R. Understanding Measurements of Intestinal Permeability in Healthy Humans with Urine Lactulose and Mannitol Excretion. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, e15–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremellen, K.; Pearce, K.; Murphy, K.; Phan, L. Do Drugs and Supplements That Modify the Gut Microbiome Influence Testicular Function and Fertility? 2023; manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, K.L.; Hill, A.; Tremellen, K.P. Obesity Related Metabolic Endotoxemia Is Associated with Oxidative Stress and Impaired Sperm DNA Integrity. Basic Clin. Androl. 2019, 29, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamian, M.; Steer, D.; Rosella, G.; Gibson, P.R. Serum Zonulin as a Marker of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function: May Not Be What It Seems. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massier, L.; Chakaroun, R.; Kovacs, P.; Heiker, J.T. Blurring the Picture in Leaky Gut Research: How Shortcomings of Zonulin as a Biomarker Mislead the Field of Intestinal Permeability. Gut 2020, 70, 1801–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ahmeid, M. Metformin Effects on Zonulin Level in Polycystic Ovarian Women. ADMET DMPK 2021, 9, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, U.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose Tissue Regulates Insulin Sensitivity: Role of Adipogenesis, de Novo Lipogenesis and Novel Lipids. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Data Type | n | Variable | Mean | ± | SD | Cohort Range | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric | 50 | Age (years) | 36.2 | ± | 5.5 | 18.0–48.0 | - |
| 50 | Height (cm) | 174.6 | ± | 7.8 | 139.0–200.0 | - | |
| 50 | Weight (kg) | 78.8 | ± | 15.2 | 49.0–205.0 | - | |
| 50 | BMI (kg/m2) | 25.6 | ± | 4.5 | 19.1–40.0 | Underweight: 16.0–18.4; Normal weight: 18.5–24.9; Overweight: 25.0–29.9; Moderately Obese: 30.0–34.9; Severely Obese: 35.0–39.9; Morbidly Obese: ≥40.0 [43]). | |
| 50 | Waist circumference (cm) | 85.5 | ± | 13.5 | 63.1–130.00 | >102 cm in men: increased cardiometabolic risk [44]. | |
| 50 | Physical Activity (score) | 7.84 | ± | 1.74 | 4.3–11.9 | No published reference range, however, minimum–maximum scores range between 1–15 [34]. | |
| 50 | Sleep Quality (score) | 4.14 | ± | 2.18 | 1.0–12.0 | No published reference range, however, minimum–maximum scores range between 0–21 [35]. | |
| 50 | IBS symptoms (score) | 44.23 | ± | 24.37 | 0.9–2.1 | 75–175 mild; 175–300 moderate; >300 severe cases [36]. | |
| Serological | 50 | H. pylori igG antibodies (U/mL) | 0.98 | ± | 1.79 | 0.0–7.40 | <0.9 negative; 0.9–1.1 equivocal; >1.1 positive [45]. |
| 50 | L/R (mmol/L) | 1.16 | ± | 1.66 | 0.0–7.9 | Diagnostic data unpublished. | |
| 38 | Zonulin (ng/mL) | 12.23 | ± | 10.81 | 0.37–41.20 | 40.0 Cusabio Human Zonulin ELISA Kit upper limit of the standard (CUSABIO TECHNOLOGY LLC, Wuhan, China). | |
| 50 | LBP (mcg/mL) | 19.90 | ± | 22.57 | 0.04–98.4 | 18.1 control; 40.0–60.0 septic shock [46]. | |
| 50 | hsCRP (mg/L) | 1.01 | ± | 1.08 | 0.40–5.1 | 1.00–3.00 slightly increased relative risk of CHD [47,48]. | |
| Endocrine | 50 | T (nmol/L) | 19.18 | ± | 6.69 | 6.9–36.1 | <6.9 hypogonadism; 6.9–11.1 equivocal; >11.1 normal [1] |
| 50 | LH (IU/L) | 6.43 | ± | 2.87 | 2.12–13.17 | 1.8–8.6 normal [3]. | |
| 50 | FSH (IU/L) | 4.54 | ± | 3.31 | 0.94–20.13 | 1.0–5.0 normal [3]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan, L.N.; Murphy, K.J.; Pearce, K.L.; Tran, C.D.; Tremellen, K.P. The Potential Relationship between Gastric and Small Intestinal-Derived Endotoxin on Serum Testosterone in Men. Gastroenterol. Insights 2023, 14, 394-405. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14030029
Phan LN, Murphy KJ, Pearce KL, Tran CD, Tremellen KP. The Potential Relationship between Gastric and Small Intestinal-Derived Endotoxin on Serum Testosterone in Men. Gastroenterology Insights. 2023; 14(3):394-405. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14030029
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan, Laura N., Karen J. Murphy, Karma L. Pearce, Cuong D. Tran, and Kelton P. Tremellen. 2023. "The Potential Relationship between Gastric and Small Intestinal-Derived Endotoxin on Serum Testosterone in Men" Gastroenterology Insights 14, no. 3: 394-405. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14030029
APA StylePhan, L. N., Murphy, K. J., Pearce, K. L., Tran, C. D., & Tremellen, K. P. (2023). The Potential Relationship between Gastric and Small Intestinal-Derived Endotoxin on Serum Testosterone in Men. Gastroenterology Insights, 14(3), 394-405. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14030029






