Esophageal Food Impaction and Foreign Object Ingestion in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of Clinical and Endoscopic Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis
3. Management
4. Specific Foreign Bodies
4.1. Food Bolus Impaction
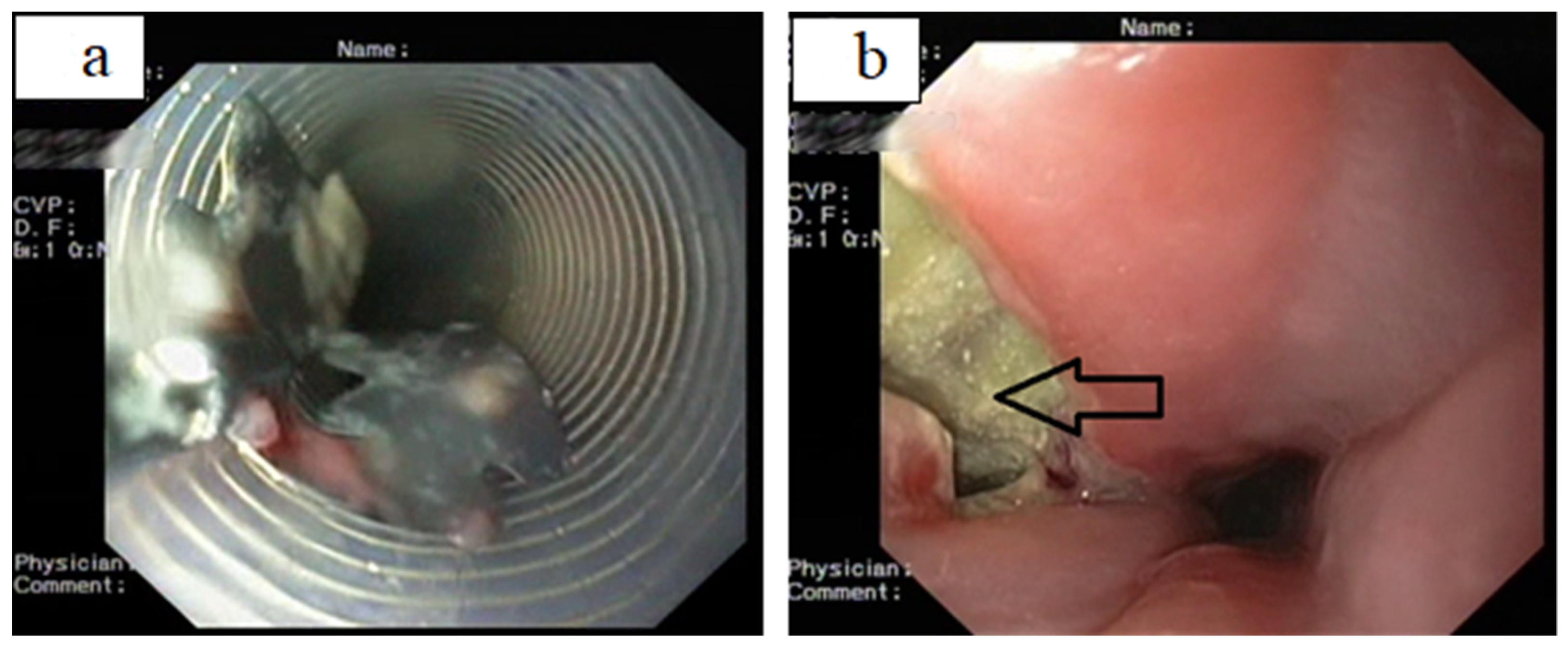
4.2. Sharp-Pointed Object
4.3. Blunt Objects: Coins, Batteries, and Magnets
4.4. Long Object
4.5. Illegal Drug Packages
4.6. Small Bowel Foreign Objects
4.7. Colorectal Foreign Objects
5. Endoscopic Procedure-Related Complications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gurala, D.; Polavarapu, A.; Philipose, J.; Amarnath, S.; Avula, A.; Idiculla, P.S.; Demissie, S.; Gumaste, V. Esophageal Food Impaction: A Retrospective Chart Review. Gastroenterol. Res. 2021, 14, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birk, M.; Bauerfeind, P.; Deprez, P.H.; Häfner, M.; Hartmann, D.; Hassan, C.; Hucl, T.; Lesur, G.; Aabakken, L.; Meining, A. Removal of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract in adults: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy 2016, 48, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storm, A.C.; Fishman, D.S.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Coelho-Prabhu, N.; Al-Haddad, M.A.; Amateau, S.K.; Calderwood, A.H.; DiMaio, C.J.; Elhanafi, S.E.; Forbes, N.; et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on informed consent for GI endoscopic procedures. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 207–215.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, B.M.; Sweetser, S.; Song, L.M.W.K.; Tabibian, J.H. Foreign object ingestion and esophageal food impaction: An update and review on endoscopic management. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 11, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstreth, G.F.; Longstreth, K.J.; Yao, J.F. Esophageal food impaction: Epidemiology and therapy. A retrospective, observational study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 53, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães-Costa, P.; Carvalho, L.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Túlio, M.A.; Marques, S.; Carmo, J.; Bispo, M.; Chagas, C. Endoscopic Management of Foreign Bodies in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract: An Evidence-Based Review Article. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 23, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Sharma, P. Foreign Bodies in Esophagus: An Experience with Rigid Esophagoscope in ENT Practice. Int. J. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becq, A.; Camus, M.; Dray, X. Foreign body ingestion: Dos and don’ts. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawa, C. Endoscopic management of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 6, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, S.S.; Nimmo, A.; Chin, G.A. Ingestion of a unilateral removable partial denture causing serious complications. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1988, 66, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, C.; Oprea, A.; Ştefan, O.; Lupu, V.V.; Mircea Drăghici, M.T. Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal foregin bodies in children. Rom. Med. J. 2016, 63, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, O. Foreign body in the esophagus: A review. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2006, 124, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.H.; Enns, R. Review of food bolus management. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 22, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreiro-Iglesias, R.; Blanco Freire, M.N.; Paz Novo, M.; Domínguez Muñoz, J.E. Boerhaave’s syndrome: Diagnostic gastroscopy. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2017, 109, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erbil, B.; Karaca, M.A.; Aslaner, M.A.; Ibrahimov, Z.; Kunt, M.M.; Akpinar, E.; Özmen, M.M. Emergency admissions due to swallowed foreign bodies in adults. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6447–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Aiolfi, A.; Bonitta, G.; Riva, C.G.; Rausa, E.; Siboni, S.; Toti, F.; Bonavina, L. Flexible versus rigid endoscopy in the management of esophageal foreign body impaction: Systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2018, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, W.S.; Li, Y.N.; Feng, M.X.; Lu, Y.Q. Retrospective observational analysis of esophageal foreign bodies: A novel characterization based on shape. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.; Han, J.I.; Choi, A.L.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, M. Adverse events of conscious sedation using midazolam for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 14, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, G.M.; Baron, T.H.; Dominitz, J.A.; Faigel, D.O.; Goldstein, J.L.; Johanson, J.F.; Mallery, J.S.; Raddawi, H.M.; Vargo, J.J.; Waring, J.P.; et al. Guideline for the management of ingested foreign bodies. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 55, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurling, T.J.; Zaloga, G.P.; Richter, J.E. Fiberendoscopic removal of a gastric foreign body with overtube technique. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1983, 29, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, W.A. Management of foreign bodies of the upper gastrointestinal tract: Update. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 41, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, C.T.; Engel, J.; Schlesinger, P. Foreign body ingestion: Review and suggested guidelines for management. Endoscopy 1987, 19, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, G.; Stan-Ilie, M.; Oprita, R. Gastroenterologie; II. Editura Niculescu: Bucharest, Romania, 2022; ISBN 978-606-38-0775-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg, G.G. Management of ingested foreign objects and food bolus impactions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 41, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, N.; Niikura, R.; Yamada, A.; Sakurai, T.; Shimbo, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Mitsuno, Y.; Ogura, K.; Hirata, Y.; et al. Acute middle gastrointestinal bleeding risk associated with NSAIDs, antithrombotic drugs, and PPIs: A multicenter case-control study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, W.M.; Adler, D.G.; Conway, J.D.; Diehl, D.L.; Farraye, F.A.; Kantsevoy, S.V.; Kaul, V.; Kethu, S.R.; Kwon, R.S.; Mamula, P.; et al. Overtube use in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, T.; Ishihara, S.; Okada, M.; Kusunoki, R.; Moriyama, I.; Amano, Y.; Kinoshita, Y. Double-alloon endoscopy for treatment of small bowel penetration by fish bone. Dig. Endosc. 2012, 24, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faigel, D.O.; Stotland, B.R.; Kochman, M.L.; Hoops, T.; Judge, T.; Kroser, J.; Lewis, J.; Long, W.B.; Metz, D.C.; O’Brien, C.; et al. Device choice and experience level in endoscopic foreign object retrieval: An in vivo study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1996, 43, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.E.; Leech, M.H.; Carr, M.G. A safe and cost-effective protocol for the management of esophageal coins in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1993, 28, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaradi, O.; Bartholomew, M.; Barkin, J.S.; Bolondi, L. Upper endoscopy and glucagon: A new technique in the management of acute esophageal food impaction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, V.; Grade, A.; Pulliam, G.; Johnson, C.; Fass, R. Effect of doses of glucagon used to treat food impaction on esophageal motor function of normal subjects. Dysphagia 1999, 14, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanjia, N.D.; Rees, M. The use of Coca-Cola in the management of bolus obstruction in benign oesophageal stricture. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1993, 75, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thimmapuram, J.; Oosterveen, S.; Grim, R. Use of Glucagon in Relieving Esophageal Food Bolus Impaction in the Era of Eosinophilic Esophageal Infiltration. Dysphagia 2013, 28, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, H.A.; de Lange, E.E. Gastrointestinal foreign bodies and strictures: Radiologic interventions. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 1994, 23, 207–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schunk, J.E.; Harrison, A.M.; Corneli, H.M.; Nixon, G.W. Fluoroscopic foley catheter removal of esophageal foreign bodies in children: Experience with 415 episodes. Pediatrics 1994, 94, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikino, K.; Ikusaka, M. Steakhouse syndrome. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, G.I.; Zuber-Jerger, I.; Endlicher, E.; Gelbmann, C.; Ott, C.; Ruemmele, P.; Schölmerich, J.; Klebl, F. Causes of bolus impaction in the esophagus. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 3170–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.P.; Dwivedi, M. Entrapment of guide-wire during oesophageal dilation. Trop. Gastroenterol. 1997, 18, 117–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin, P.; Jones, D.; Remedios, M.; Campbell, C. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults with food bolus obstruction of the esophagus. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Pinto, E.; Pereira, P.; Macedo, G. Endoscopic management of a delayed diagnosed foreign body esophageal perforation. GE J. Port. Gastrenterologia 2014, 21, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koito, Y.; Asano, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Mashima, H. Endoscopic Mucosal Incision to Remove a Fish Bone Completely Embedded Under the Esophageal Mucosa: A Case Report and Literature Review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 23, e936773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Tam, P.Y.H.; Kwong, K.H.; Lau, J.W.Y. “Blister pack”-induced gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikenberry, S.O.; Jue, T.L.; Anderson, M.A.; Appalaneni, V.; Banerjee, S.; Ben-Menachem, T.; Decker, G.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Fisher, L.R.; Fukami, N.; et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahshan, A. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children. J. Okla. State Med. Assoc. 2001, 94, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Du, B.; Huang, L. Multiple magnetic foreign bodies causing severe digestive tract injuries in a child. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2016, 10, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltzman, M.L.; Baskin, M.; Wypij, D.; Mooney, D.; Jones, D.; Fleisher, G. A randomized clinical trial of the management of esophageal coins in children. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inayat, F.; Zafar, F.; Lodhi, H.T.; Hayat, M.; Saleem, H.M.K.; Afzal, A.; Sohail, C.S. Endoscopic Removal of Large Sharp-edged Foreign Bodies in the Gastrointestinal Tract Using an Innovative Modification of the Overtube. Cureus 2018, 10, e3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, A.R.; Veltri, J.C. One year’s experience in a regional poison control center: The intermountain regional poison control center. Clin. Toxicol. 1978, 12, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, R.; Sahota, A.; Bemarki, A.; Salama, P.; Simpson, N.; Laine, L. Foreign-body ingestion: Characteristics and outcomes in a lower socioeconomic population with predominantly intentional ingestion. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 69, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulstrode, N.; Banks, F.; Shrotria, S. The outcome of drug smuggling by “body packers”—The British experience. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2002, 84, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, J.M.; Scott, H.J. “Surgical mules”: The smuggling of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. J. R. Soc. Med. 1995, 88, 450–453. [Google Scholar]
- Booker, R.J.; Smith, J.E.; Rodger, M.P. Packers, pushers and stuffers-managing patients with concealed drugs in UK emergency departments: A clinical and medicolegal review. Emerg. Med. J. 2009, 26, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, R.; Aks, S.E.; Keys, N.; Wahl, M. Medical outcome of cocaine bodystuffers. J. Emerg. Med. 2000, 18, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandava, N.; Chang, R.S.; Wang, J.H.; Bertocchi, M.; Yrad, J.; Allamaneni, S.; Aboian, E.; Lall, M.H.; Mariano, R.; Richards, N. Establishment of a definitive protocol for the diagnosis and management of body packers (drug mules). Emerg. Med. J. 2011, 28, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.I.; Choi, H.; Choi, K.Y.; Ji, J.S.; Kim, B.W.; Cho, S.H.; Park, J.M.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, M.G.; Chung, I.S. Retrieval of a retained capsule endoscope by double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 62, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.; Nachbar, L.; Ell, C. Extraction of entrapped capsules from the small bowel by means of push-and-pull enteroscopy with the double-balloon technique. Endoscopy 2005, 37, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhanafi, S.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Tabibian, J.H. Endoscopic Removal of Shattered Glass from the Cecum. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, G.; Satsangi, B.; Raikwar, R.; Shukla, S.; Mathur, R. Unusual rectal foreign body presenting as intestinal obstruction: A case report. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011, 17, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.L.; Buccimazza, I.; Anderson, F.A.; Thomson, S.R. Colorectal foreign bodies. Color. Dis. 2005, 7, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, M.; Swanström, L.L.; Halvax, P.; Lègner, A.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Alzaga, A.; D’Urso, A.; Marescaux, J. Esophageal covered stent fixation using an endoscopic over-the-scope clip. Mechanical proof of the concept and first clinical experience. Surg. Endosc. 2015, 29, 3367–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.Y.; Fang, C.X.; Tam, P.K.H. Selective upper endoscopy for foreign body ingestion in children: An evaluation of management protocol after 282 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokar, B.; Cevik, A.A.; Ilhan, H. Ingested gastrointestinal foreign bodies: Predisposing factors for complications in children having surgical or endoscopic removal. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2007, 23, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

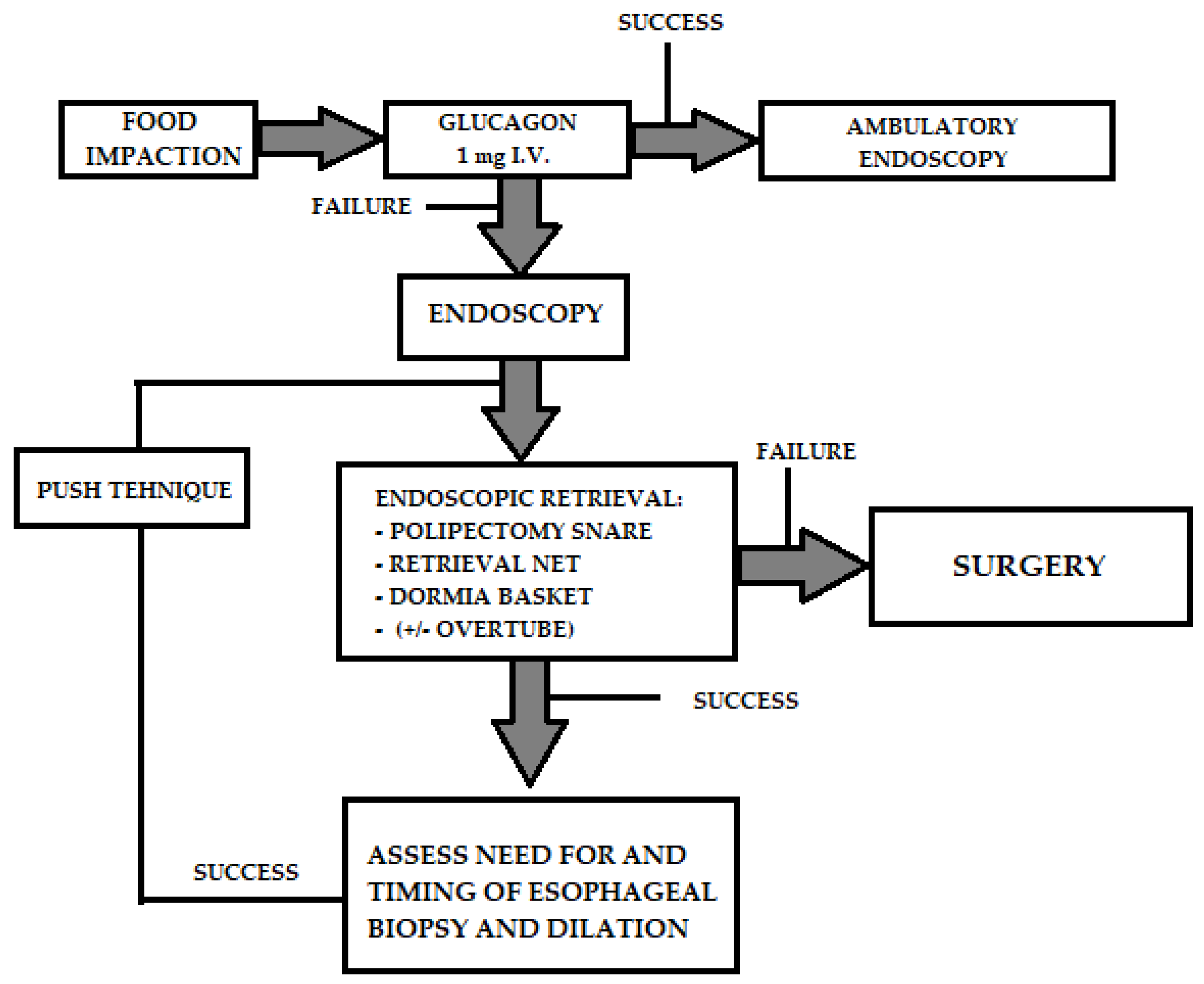
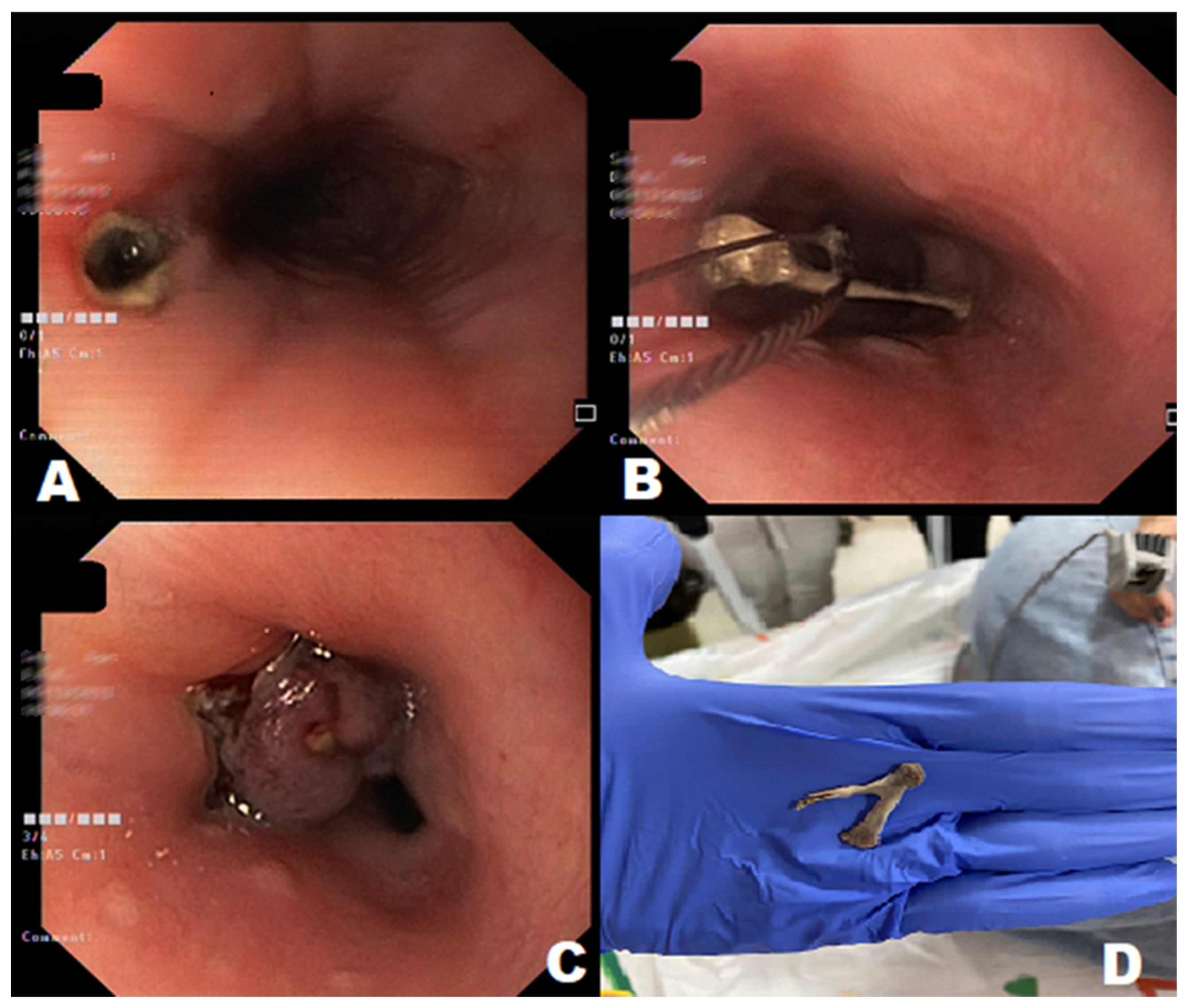
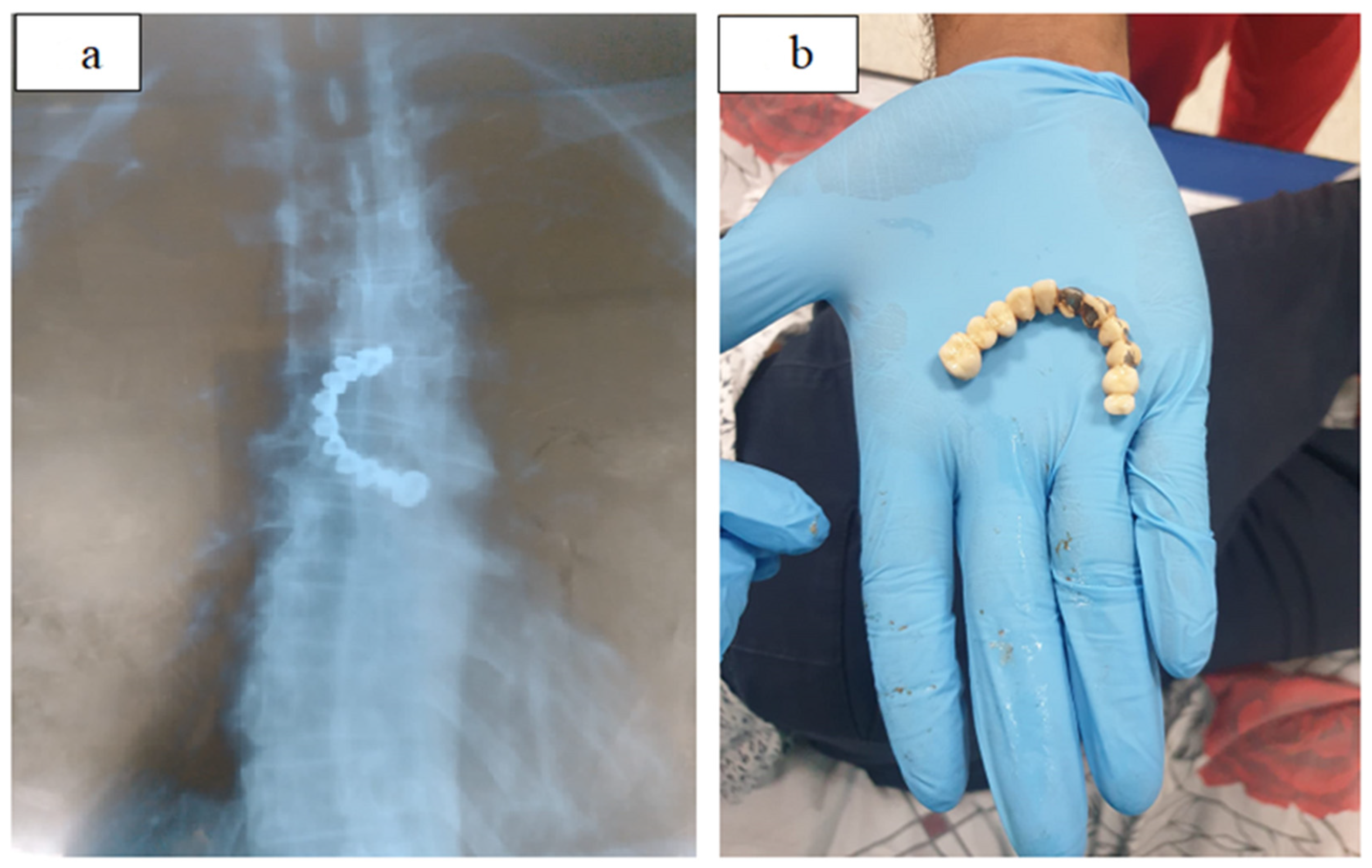
| Category (Sort) | Example |
|---|---|
| Blunt bodies | Round bodies: coins, buttons, batteries and magnets |
| Cutting objects | Thin objects: needles, toothpicks, pins, razor blades, crushed glass, partial dental plaque |
| Impacted food (bolus) | With or without bones |
| Long objects | Turnscrew, toothbrush, fork, pen or pencil |
| Others | Packets of illegal drugs |
| Foreign Body | Endoscopic Retrieval Devices |
|---|---|
| Blunt bodies | Polypectomy snare, Dormia basket, retrieval net, grasping forceps |
| Cutting objects | Grasping forceps, polypectomy snare, Dormia basket, retrieval net, clear latex cap, overtube |
| Long objects | Polypectomy snare, Dormia basket |
| Impacted food (bolus) | Polypectomy snare, grasping forceps, retrieval forceps, Dormia basket |
| Examples of Underlying Disorders Implied in Esophageal Obstruction | |
|---|---|
| Eosinophilic esophagitis | Schatzki ring |
| Peptic stricture | Radiation-induced stricture |
| Esophageal neoplasia | Diverticulum |
| Achalasia and other spastic dysmotility | Post-surgical (fundoplication) |
| Object Type | Location | Timing |
|---|---|---|
| Batteries | Esophagus | Immediate (<2 h) |
| Stomach/small intestine | Urgent | |
| Magnets | Esophagus | Urgent |
| Stomach/small intestine | Urgent | |
| Cutting objects | Esophagus | Immediate (<2 h) |
| Stomach/small intestine | Urgent | |
| Blunt and small foreign body < 2.5 cm size | Esophagus | Urgent |
| Stomach/small intestine | Non-urgent | |
| Blunt and medium-sized foreign body > 2.5 cm size | Esophagus | Urgent |
| Stomach/small intestine | Non-urgent | |
| Large object > 5 cm | Esophagus | Urgent |
| Stomach/small intestine | Urgent | |
| Impacted food (bolus) | Esophagus | Immediate (urgent if obstruction is not complete) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negoita, L.M.; Ghenea, C.S.; Constantinescu, G.; Sandru, V.; Stan-Ilie, M.; Plotogea, O.-M.; Shamim, U.; Dumbrava, B.F.; Mihaila, M. Esophageal Food Impaction and Foreign Object Ingestion in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of Clinical and Endoscopic Management. Gastroenterol. Insights 2023, 14, 131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14010010
Negoita LM, Ghenea CS, Constantinescu G, Sandru V, Stan-Ilie M, Plotogea O-M, Shamim U, Dumbrava BF, Mihaila M. Esophageal Food Impaction and Foreign Object Ingestion in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of Clinical and Endoscopic Management. Gastroenterology Insights. 2023; 14(1):131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegoita, Livia Marieta, Catalin Stefan Ghenea, Gabriel Constantinescu, Vasile Sandru, Madalina Stan-Ilie, Oana-Mihaela Plotogea, Umar Shamim, Bogdan Florin Dumbrava, and Mariana Mihaila. 2023. "Esophageal Food Impaction and Foreign Object Ingestion in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of Clinical and Endoscopic Management" Gastroenterology Insights 14, no. 1: 131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14010010
APA StyleNegoita, L. M., Ghenea, C. S., Constantinescu, G., Sandru, V., Stan-Ilie, M., Plotogea, O.-M., Shamim, U., Dumbrava, B. F., & Mihaila, M. (2023). Esophageal Food Impaction and Foreign Object Ingestion in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of Clinical and Endoscopic Management. Gastroenterology Insights, 14(1), 131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent14010010





