Prediction of Postoperative Infection for Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery: Findings from Electronic Health Records
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
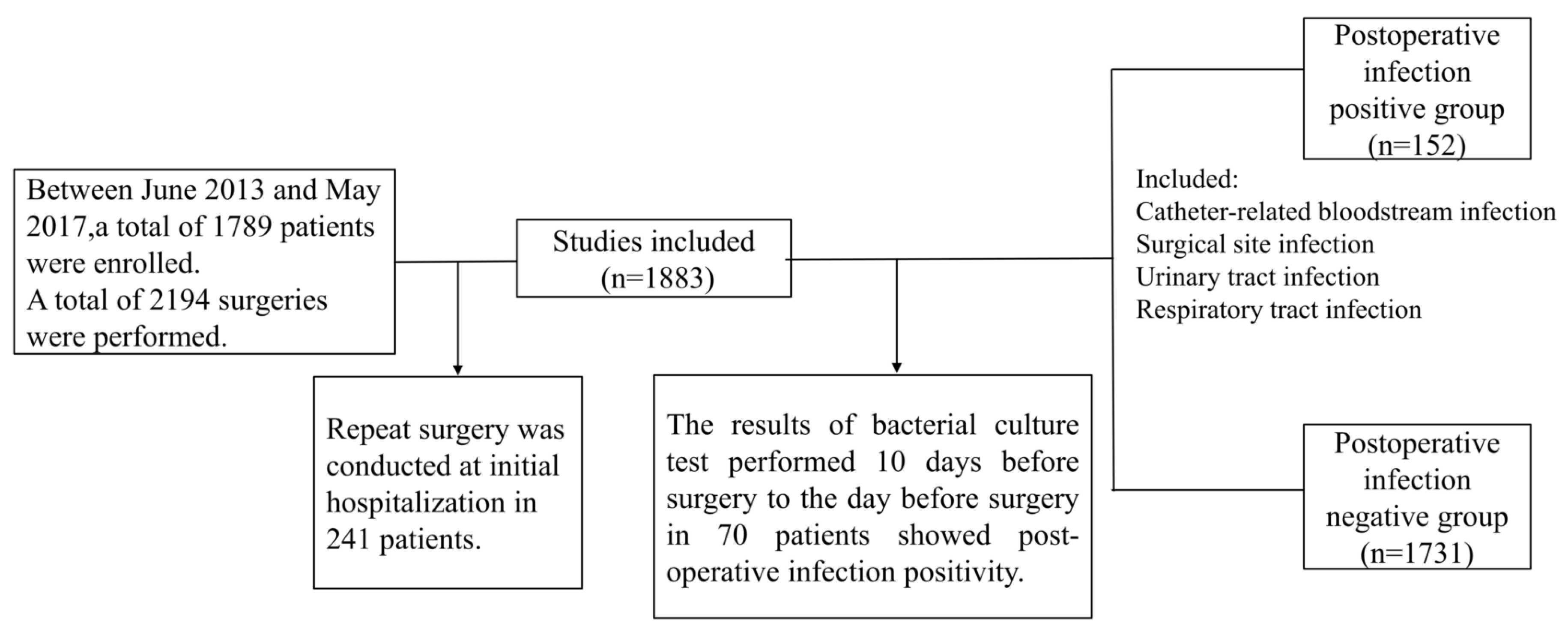
2.1. Patients
2.2. Variables
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Incidence of Postoperative Infections
3.2. Generalized Estimating Equation Analysis in Patients Who Had Several Readmissions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niitsuma, T.; Kusachi, S.; Takesue, Y.; Mikamo, H.; Asai, K.; Watanabe, M. Current status of postoperative infections after digestive surgery in Japan: The Japan Postoperative Infectious Complications Survey in 2015. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2019, 3, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Shimada, Y.; Satoh, M.; Kojima, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Hori, S. Evaluation of economic burden of colonic surgical site infection at a Japanese hospital. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Daiko, H. Optimal duration of prophylactic antimicrobial administration and risk of postoperative infectious events in thoracic esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection: Short-course versus pro-longed antimicrobial administration. Esophagus 2015, 12, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.R.; Gladman, E.; Barbateskovic, M. Antimicrobial prophylaxis for colorectal surgery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 5, CD001181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Jiang, B.; Manne, S.; Lissoos, T.; Bennett, D.; Dolin, P. Risk factors for postoperative infection after gastrointestinal surgery among adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Findings from a large observational US cohort study. JGH Open 2018, 2, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torpy, M.J.; Burke, E.A.; Glass, M.R. Postoperative infections. JAMA 2010, 303, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.B.; Rivers, P.E.; Abrahamian, M.F.; Moran, J.G.; Abraham, E.; Trzeciak, S.; Huang, T.D.; Osborn, T.; Stevens, D.; Talan, A.D. Severe sepsis and septic shock: Review of the literature and emergency department management guidelines. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2006, 48, 28–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelcuta, R.M.; Baleanu, V.D.; Davitoiu, D.V.; Tenea Cojan, T.S.; Pascal, A.; Socea, B.; Ciora, C.A.; Calin, G. Group A Streptococcal infection—Biochemical and pharmacological aspects. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 3857–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National and State Healthcare—Associated Infections Progress Report, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2017. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/hai/data/portal/progress-report.html (accessed on 6 October 2019).
- Weiner, M.L.; Webb, K.A.; Limbago, B.; Dudeck, A.M.; Patel, J.; Kallen, J.A.; Edwards, R.J.; Sievert, M.D. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2011–2014. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Bischoff, T.; Tallent, M.S.; Seifert, H.; Wenzel, P.R.; Edmond, B.M. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/BMI/bmi-m.htm (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_40 (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Ichihara, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hotta, T.; Hosogaya, S.; Miyachi, H.; Itoh, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Kang, D. Collaborative derivation of reference intervals for major clinical laboratory tests in Japan. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 53, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratzler, W.D.; Dellinger, P.E.; Olsen, M.K.; Perl, M.T.; Auwaerter, G.P.; Bolon, K.M.; Fish, N.D.; Napolitano, M.L.; Sawyer, G.R.; Slain, D.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery. Surg. Infect. 2013, 14, 73–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Insurance Price List Japan; Jihou Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2016. (In Japanese)
- Enders, C.K. Applied Missing Data Analysis; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 217–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbe, M.J. Logistic Regression Models, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 441–480. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, S.; Miyata, H.; Konno, H.; Gotoh, M.; Motoi, F.; Kumamaru, H.; Wakabayashi, G.; Kakeji, Y.; Mori, M.; Seto, Y.; et al. Risk factors of serious postoperative complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy and risk calculators for predicting postoperative complications: A nationwide study of 17,564 patients in Japan. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2017, 24, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, A.K.; Minei, P.J.; Laronga, C.; Harbrecht, G.B.; Jensen, H.E.; Fry, E.D.; Itani, M.K.; Dellinger, E.P.; Ko, Y.C.; Duane, M.T. American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines, 2016 Update. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 224, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zywot, A.; Lau, S.M.C.; Fletcher, H.S.; Paul, S. Bundles prevent surgical site infections after colorectal surgery: Meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Gastrointest Surg. 2017, 21, 1915–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, E.J.; Speicher, J.P.; Thacker, K.M.J.; Walter, M.; Kuchibhatla, M.; Mantyh, R.C. The preventive surgical site infection bundle in colorectal surgery: An effective approach to surgical site infection reduction and health care cost savings. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socea, B.; Halau, O.; Diaconu, C.; Bratu, O.G.; Neagu, P.; Dimitriu, M. Clostridium difficile infections in surgical patients (literature review). Rom. J. Med. Pract. 2019, 14, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, C.J.; Keller, S.D.; Baldini, G.; Bordeianou, L.; Weiss, E.; Lee, L.; Boutros, M.; McClane, J.; Feldman, S.L.; Steele, R.S. Clinical practice guidelines for enhanced recovery after colon and rectal surgery from the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. Dis. Colon Rectum 2017, 60, 761–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total (%) | Postoperative Infection | Chi-Square Test p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n = 135) | Negative (n = 1502) | |||
| Sex | 0.014 | |||
| Female | 673 (41.1) | 42 (6.2) | 631 (93.8) | |
| Male | 964 (58.9) | 93 (9.6) | 871 (90.4) | |
| Age at hospitalization | 0.002 | |||
| 60 years | 476 (29.0) | 23 (4.8) | 453 (95.2) | |
| 61–70 years | 518 (31.6) | 40 (7.7) | 478 (92.3) | |
| 71–80 years | 467 (28.5) | 50 (10.7) | 417 (89.3) | |
| ≥81 years | 176 (10.8) | 22 (12.5) | 154 (87.5) | |
| History of smoking | 0.003 | |||
| No | 776 (48.1) | 46 (5.9) | 730 (94.1) | |
| Yes | 836 (51.9) | 83 (9.9) | 753 (90.1) | |
| Missing | 26 | 5 (24.0) | 21 (76.0) | |
| Alcohol habit | 0.924 | |||
| Absence | 1050 (65.2) | 84 (8.0) | 966 (92.0) | |
| Presence | 561 (34.8) | 46 (8.2) | 515 (91.8) | |
| Missing | 26 | 6 (24.0) | 19 (76.0) | |
| Body mass index at hospitalization | 0.671 | |||
| <18.5 kg/m2 | 202 (12.3) | 19 (9.4) | 183 (90.6) | |
| 18.5–24.9 kg/m2 | 1089 (66.5) | 91 (8.4) | 998 (91.6) | |
| ≥25 kg/m2 | 346 (21.1) | 25 (7.2) | 321 (92.8) | |
| Drainage | <0.001 | |||
| Absence | 439 (26.8) | 16 (3.6) | 423 (96.4) | |
| Presence | 1198 (73.2) | 119 (9.9) | 1079 (90.1) | |
| Variables | Total (%) | Postoperative Infection | Chi-Square Test p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n = 135) | Negative (n = 1502) | |||
| Temperature | 0.001 | |||
| Normal (<38.0 °C) | 1598 (97.6) | 125 (7.8) | 1473 (92.2) | |
| Abnormal (≥38.0 °C) | 39 (2.4) | 10 (25.6) | 29 (74.4) | |
| White blood cell | 0.019 | |||
| Normal (<10,000/per μL) | 1440 (88.0) | 110 (7.6) | 1330 (92.4) | |
| Abnormal (≥10,000 per μL) | 197 (12.0) | 25 (12.7) | 172 (87.3) | |
| Albumin | 0.005 | |||
| Normal (≥3.0 g/dL) | 1521 (92.9) | 117 (7.7) | 1404 (92.3) | |
| Abnormal (<3.0 g/dL) | 116 (7.1) | 18 (15.5) 1 | 98 (84.5) | |
| Hemoglobin | 0.100 | |||
| Normal (≥10.0 g/dL) | 972 (59.4) | 71 (7.3) | 901 (92.7) | |
| Abnormal (<10.0 g/dL) | 665 (40.6) | 64 (9.6) | 601 (90.4) | |
| Red blood cell | 0.061 | |||
| Normal (≥10.0 × 104/μL) | 1048 (64.0) | 76 (7.3) | 972 (92.7) | |
| Abnormal (<10.0 104/μL) | 589 (36.0) | 59 (10.0) | 530 (90.0) | |
| International normalized ratio | 0.008 | |||
| Normal (<1.15) | 1451 (88.6) | 110 (7.6) | 1341 (92.4) | |
| Abnormal (≥1.15) | 186 (11.4) | 25 (13.4) | 161 (86.6) | |
| Platelet count | 0.738 | |||
| Normal (>75,000/μL) | 1509 (92.2) | 123 (8.2) | 1386 (91.8) | |
| Abnormal (<75,000/μL) | 128 (7.8) | 12 (9.4) | 116 (90.6) | |
| Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase | 0.548 | |||
| Normal (<47/L) | 1181 (72.1) | 94 (8.0) | 1087 (92.0) | |
| Abnormal (≥47/L) | 456 (27.9) | 41 (9.0) | 415 (91.0) | |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 0.237 | |||
| Normal (<47/L) | 1415 (86.4) | 112 (7.9) | 1303 (92.1) | |
| Abnormal (≥47/L) | 222 (13.6) | 23 (10.4) | 199 (89.6) | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 0.129 | |||
| Normal (Male < 42, Female < 23/L) | 1395 (85.2) | 109 (7.8) | 1286 (92.2) | |
| Abnormal (Male ≥ 42, Female ≥ 23/L) | 242 (14.8) | 26 (10.7) | 216 (89.3) | |
| Potassium | 0.344 | |||
| Normal (3.0–5.5 mmol/L) | 1429 (87.3) | 114 (8.0) | 1315 (92.0) | |
| Abnormal (<3.0, ≥5.5 mmol/L) | 208 (12.7) | 21 (10.1) | 187 (89.9) | |
| Sodium | 0.008 | |||
| Normal (130–150 mmol/L) | 1371 (83.8) | 102 (7.4) | 1269 (92.6) | |
| Abnormal (<130, ≥150 mmol/L) | 266 (16.2) | 33 (12.4) | 233 (87.6) | |
| Creatinine | 0.162 | |||
| Normal 1 | 1445 (88.3) | 114 (7.9) | 1331 (92.1) | |
| Abnormal 2 | 192 (11.7) | 21 (10.9) | 171 (89.1) | |
| Variables | Total (%) | Postoperative Infection | Chi-Square Test p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n = 135) | Negative (n = 1502) | |||
| Operation time (hour) | <0.001 | |||
| <3 | 674 (41.2) | 37 (5.5) | 637 (94.5) | |
| 3–6 | 614 (37.5) | 52 (8.5) | 562 (91.5) | |
| 6–9 | 249 (15.2) | 29 (11.6) | 220 (88.4) | |
| ≥9 | 100 (6.10) | 17 (17.0) | 83 (83.0) | |
| Type of surgery | <0.001 | |||
| Endoscopic | 448 (27.4) | 14 (3.1) | 434 (96.9) | |
| Non-endoscopic | 1189 (72.6) | 121 (10.2) | 1068 (89.8) | |
| Site of surgery | ||||
| Thoracic | <0.001 | |||
| Absence | 1572 (96.0) | 117 (7.4) | 1455 (92.6) | |
| Presence | 65 (4.0) | 18 (27.7) | 47 (72.3) | |
| Body surface | 0.434 | |||
| Absence | 1550 (94.7) | 130 (8.4) | 1420 (91.6) | |
| Presence | 87 (5.3) | 5 (5.7) | 82 (94.3) | |
| Peritonitis, abdominal wall | 0.004 | |||
| Absence | 1222 (74.6) | 115 (9.4) | 1107 (90.6) | |
| Presence | 415 (25.4) | 20 (4.8) | 395 (95.2) | |
| Liver, pancreas, biliary tract, spleen | 0.616 | |||
| Absence | 1183 (72.3) | 95 (8.0) | 1088 (92.0) | |
| Presence | 454 (27.7) | 40 (8.8) | 414 (91.2) | |
| Lower gastrointestinal tract | 0.172 | |||
| Absence | 954 (58.3) | 71 (7.4) | 883 (92.6) | |
| Presence | 683 (41.7) | 64 (9.4) | 619 (90.6) | |
| Others (urinary tract, generative organ) | 0.816 | |||
| Absence | 1581 (96.6) | 131 (8.3) | 1450 (91.7) | |
| Presence | 56 (3.4) | 4 (7.1) | 52 (92.9) | |
| Variables | Total (%) | Postoperative Infection | Chi-Square Test p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n = 135) | Negative (n = 1502) | |||
| Cardiovascular agents | <0.001 | |||
| Absence | 405 (24.7) | 11 (2.7) | 394 (97.3) | |
| Presence | 1232 (75.3) | 124 (10.1) | 1108 (89.9) | |
| Immunosuppressive agents | <0.001 | |||
| Absence | 168 (10.3) | 6 (3.6) | 162 (96.4) | |
| 1–3 drugs | 922 (56.3) | 45 (4.9) | 877 (95.1) | |
| ≥4 drugs | 547 (33.4) | 84 (15.4) | 463 (84.6) | |
| Lifestyle disease agents | 0.006 | |||
| Absence | 1627 (99.2) | 131 (8.1) | 1416 (91.9) | |
| Presence | 10 (0.6) | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | |
| Hematopoietic stem cell mobilizer | 0.109 | |||
| Absence | 1104 (67.4) | 85 (7.7) | 1019 (92.3) | |
| 1–3 drugs | 348 (21.3) | 38 (10.9) | 310 (89.1) | |
| ≥4 drugs | 185 (11.3) | 12 (6.5) | 173 (93.5) | |
| Antibiotics | 0.481 | |||
| Absence | 138 (8.4) | 15 (10.9) | 123 (89.1) | |
| 1–3 drugs | 1297 (79.2) | 105 (8.1) | 1192 (91.9) | |
| ≥4 drugs | 202 (12.3) | 15 (7.4) | 187 (92.6) | |
| Medical nutritional products | 0.662 | |||
| Absence | 945 (57.7) | 83 (8.8) | 862 (91.2) | |
| 1–3 drugs | 435 (26.6) | 33 (7.6) | 402 (92.4) | |
| ≥4 drugs | 257 (15.7) | 19 (7.4) | 238 (92.6) | |
| Gastrointestinal agents | 0.736 | |||
| Absence | 520 (31.8) | 42 (8.1) | 478 (91.9) | |
| 1–3 drugs | 583 (35.6) | 45 (7.7) | 538 (92.3) | |
| ≥4 drugs | 534 (32.6) | 48 (9.0) | 486 (91.0) | |
| Analgesics | 0.516 | |||
| Absence | 338 (20.6) | 33 (9.8) | 305 (90.2) | |
| 1–3 drugs | 701 (42.8) | 54 (7.7) | 647 (92.3) | |
| ≥4 drugs | 598 (36.5) | 48 (8.0) | 550 (92.0) | |
| Antipsychotics | 1.00 | |||
| Absence | 1495 (91.3) | 123 (8.2) | 1372 (91.8) | |
| Presence | 142 (8.7) | 12 (8.5) | 130 (91.5) | |
| Respiratory agents | 0.907 | |||
| Absence | 290 (17.7) | 23 (7.9) | 267 (92.1) | |
| Presence | 1347 (82.3) | 112 (8.3) | 1235 (91.7) | |
| Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at hospitalization | |||
| 60 years | Ref | ||
| 61–70 years | 1.52 | 0.89–2.61 | 0.133 |
| 71–80 years | 2.10 | 1.22–3.56 | 0.007 |
| ≥81 years | 2.69 | 1.40–5.10 | 0.003 |
| History of smoking | |||
| No | Ref | ||
| Yes | 2.09 | 1.41–3.10 | <0.001 |
| Drainage | |||
| Absence | Ref | ||
| Presence | 2.41 | 1.38–4.22 | 0.002 |
| Temperature | |||
| Normal (<38.0 °C) | Ref | ||
| Abnormal (≥38.0 °C) | 2.83 | 1.27–6.23 | 0.011 |
| White blood cell | |||
| Normal (<10,000/μL) | Ref | ||
| Abnormal (≥10,000/μL) | 2.01 | 1.23–3.29 | 0.005 |
| Hemoglobin | |||
| Normal (≥10.0 g/dL) | Ref | ||
| Abnormal (<10.0 g/dL) | 0.71 | 0.48–1.06 | 0.092 |
| Type of surgery | |||
| Endoscopic | Ref | ||
| Non-endoscopic | 2.75 | 1.53–4.85 | 0.001 |
| Surgical site | |||
| Thoracic | |||
| Absence | Ref | ||
| Presence | 5.37 | 2.77–10.38 | <0.001 |
| Lower gastrointestinal tract | |||
| Absence | Ref | ||
| Presence | 1.63 | 1.12–2.41 | 0.011 |
| Medical nutritional products | |||
| Absence | Ref | ||
| 1–3 drugs | 2.18 | 1.40–3.39 | 0.001 |
| ≥4 drugs | 4.06 | 2.55–6.42 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakazawa, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Toyama, A.; Wakai, T.; Akazawa, K. Prediction of Postoperative Infection for Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery: Findings from Electronic Health Records. Gastroenterol. Insights 2020, 11, 36-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent11020007
Nakazawa K, Ishikawa T, Toyama A, Wakai T, Akazawa K. Prediction of Postoperative Infection for Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery: Findings from Electronic Health Records. Gastroenterology Insights. 2020; 11(2):36-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent11020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakazawa, Kyoko, Takashi Ishikawa, Akira Toyama, Toshifumi Wakai, and Kohei Akazawa. 2020. "Prediction of Postoperative Infection for Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery: Findings from Electronic Health Records" Gastroenterology Insights 11, no. 2: 36-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent11020007
APA StyleNakazawa, K., Ishikawa, T., Toyama, A., Wakai, T., & Akazawa, K. (2020). Prediction of Postoperative Infection for Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery: Findings from Electronic Health Records. Gastroenterology Insights, 11(2), 36-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent11020007





