IoT-Based Patient Movement Monitoring: The Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- This paper enhances the post-operative hip fracture recovery model that we published in our conference paper [2];
- This paper suggests an IoT-based movement monitoring system that supports the model’s implementation;
- This paper analyzes the data collected on the core rehabilitation movement and offers approaches that improve the movement’s recognition;
- This paper attempts to utilize the available computational resources in the Cloud, at the gateway edge, and at the wearable sensor edge to support the system’s performance.
2. Related Work
3. Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model
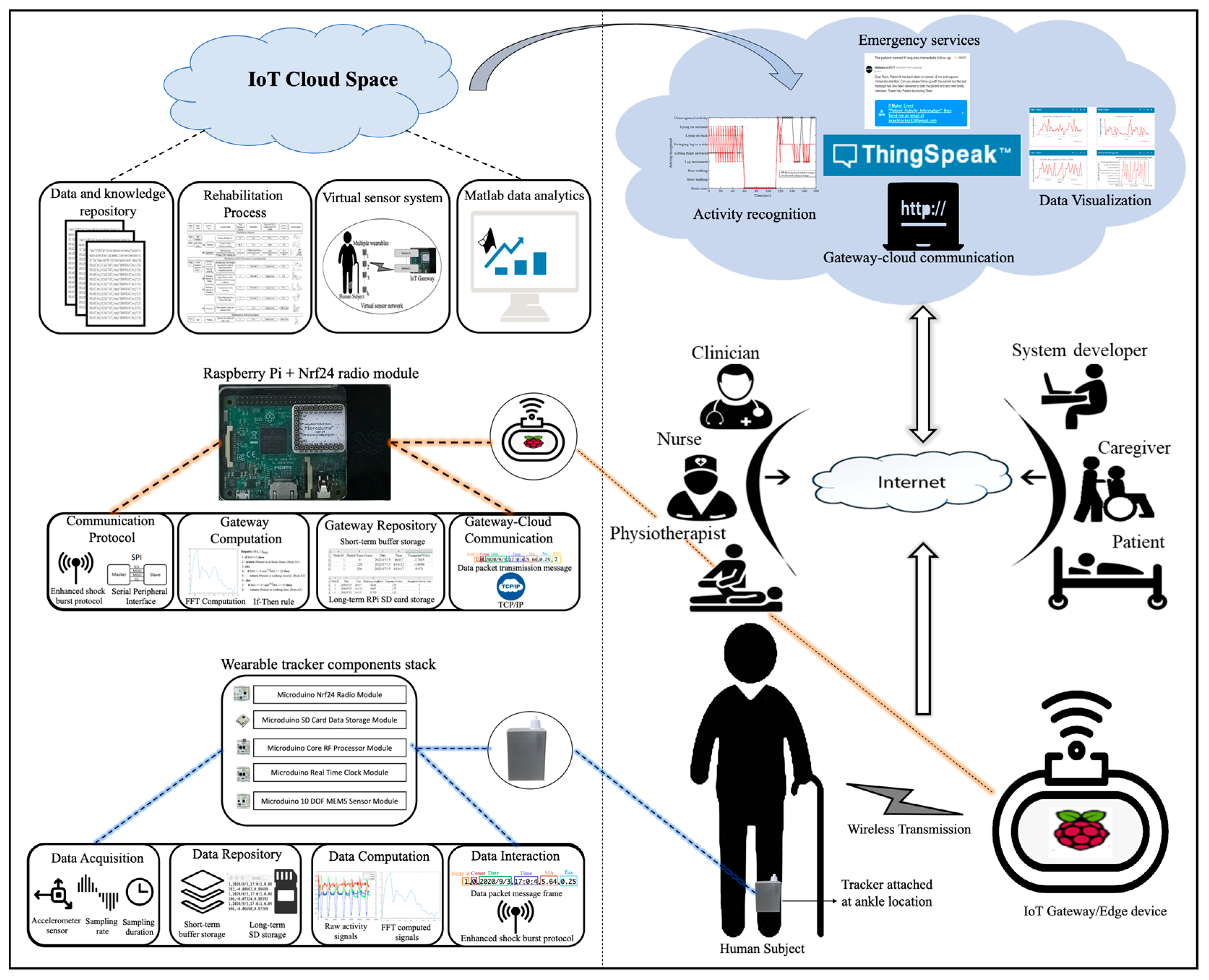
4. Movement Monitoring System Architecture
5. IoT System Performance
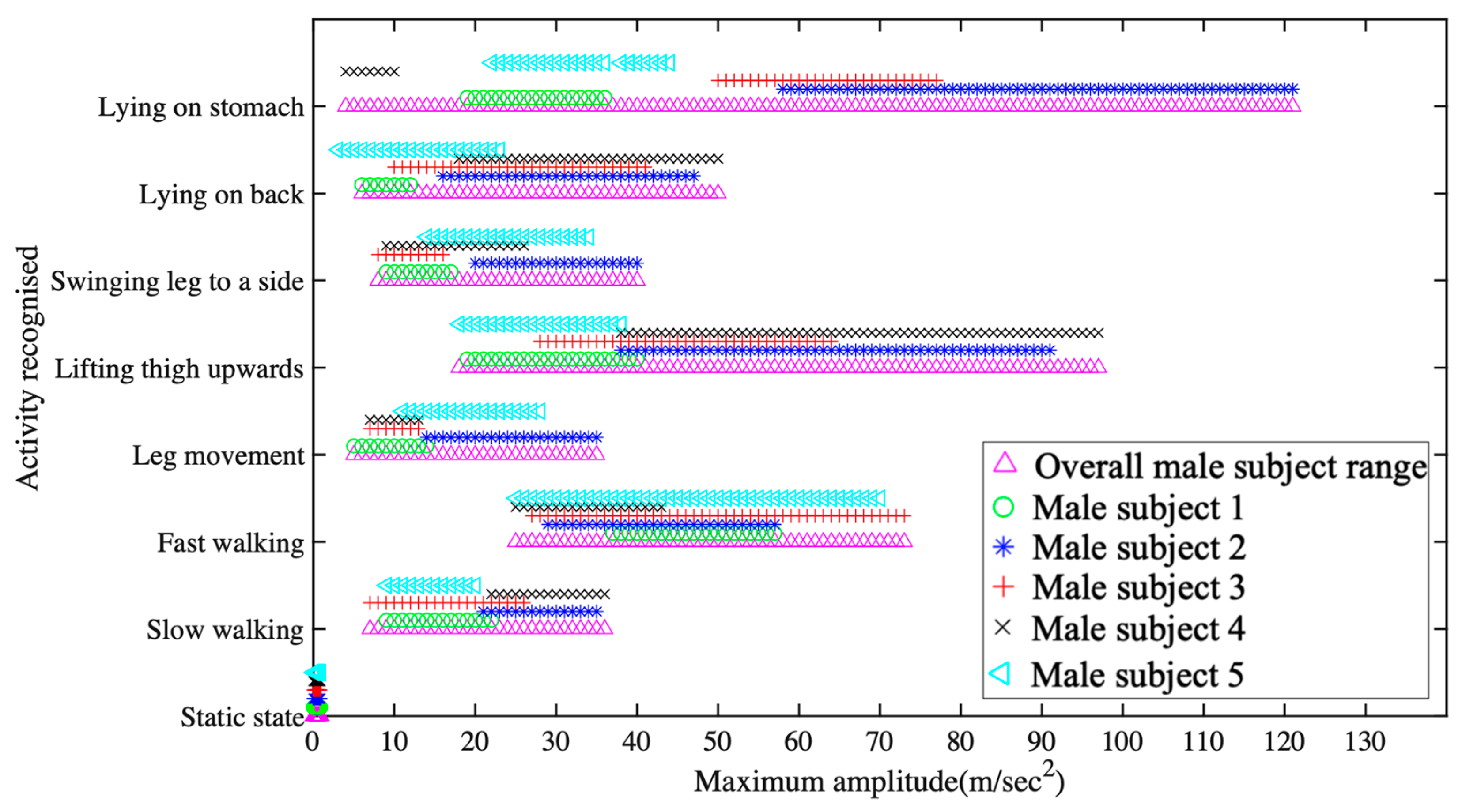
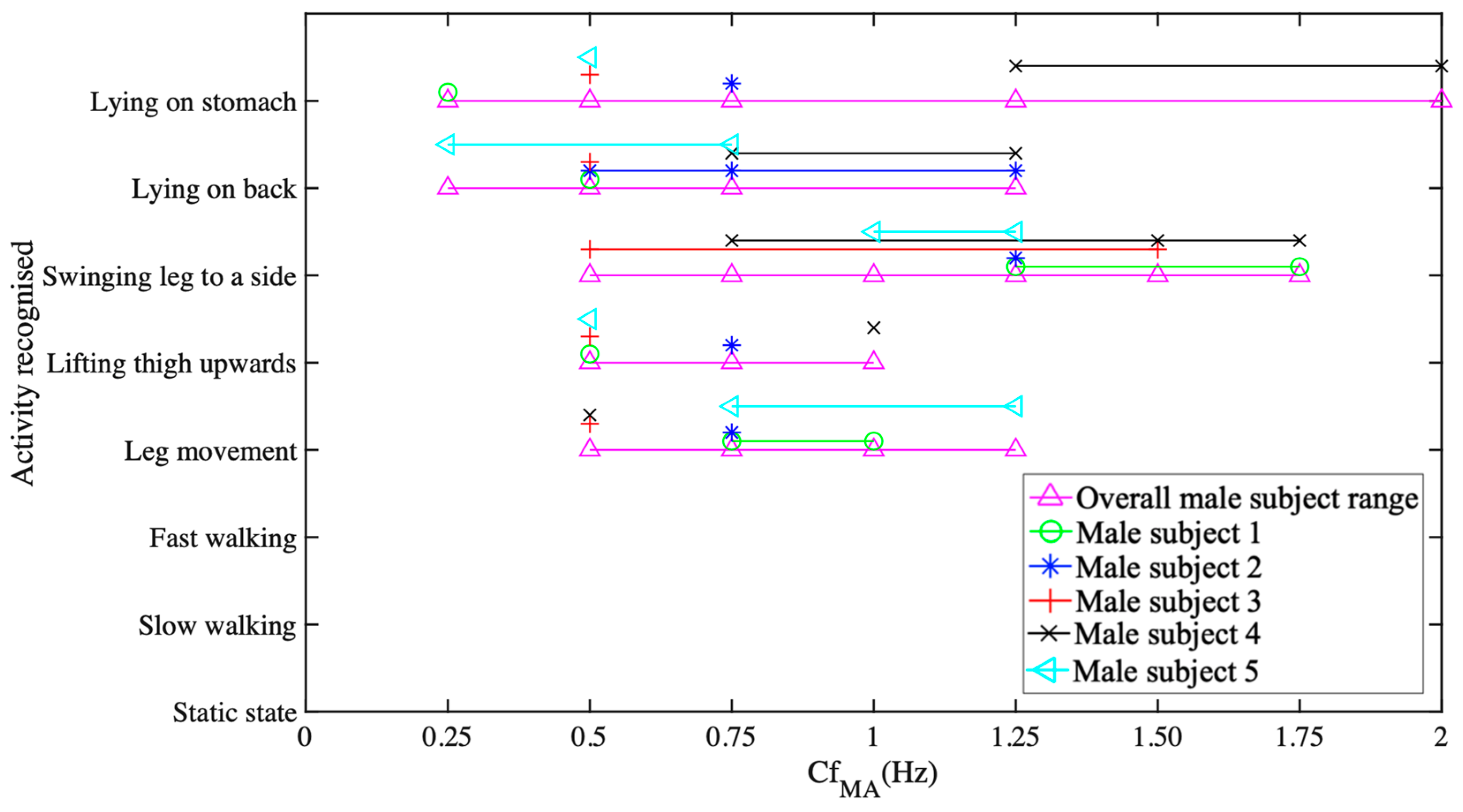
5.1. Data Collection and Activity Recognition
- Raw data acquisition and calibration of 518 samples at a sampling rate of 128 sample/second;
- FFT processing for identifying the dominant spectrum identification over four seconds of acquisition time;
- Finite time movement classification over 4-second window.
5.2. IoT System Performance Testing
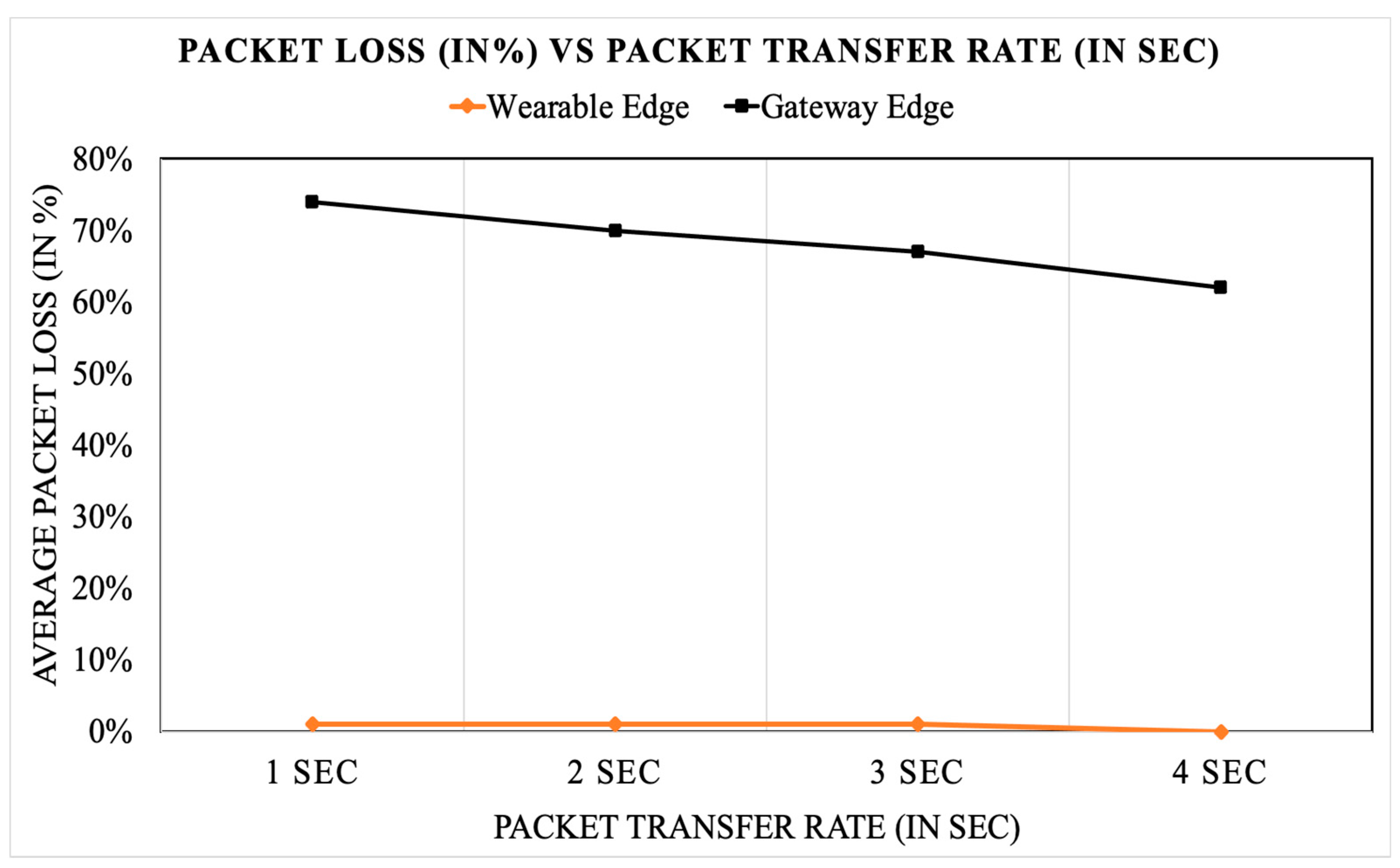
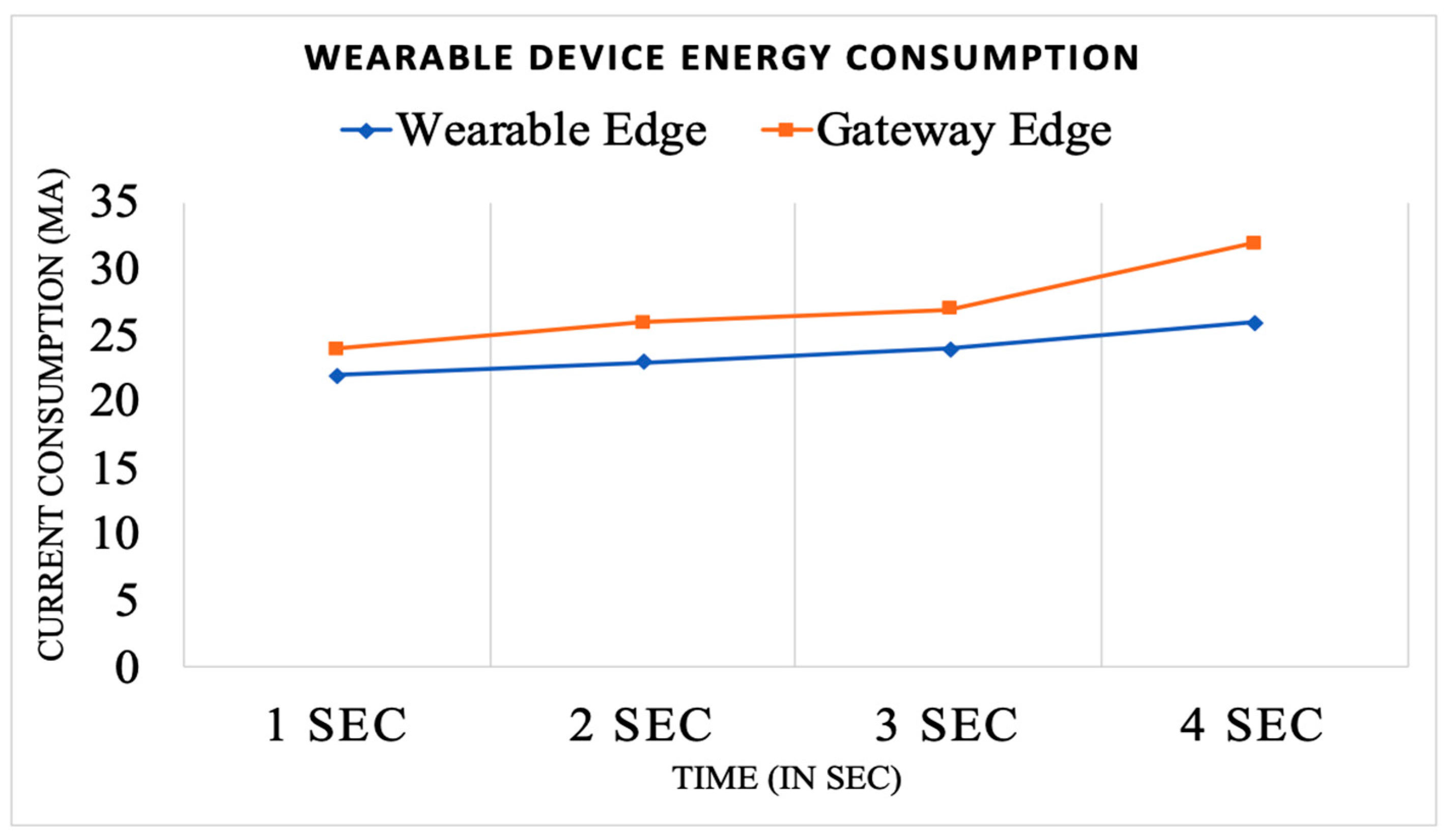
Wireless Sensor Edge vs. Gateway Edge Analysis
5.3. Long-Term Data Presentation and Cloud Role
- Investigating the role of and impact of machine learning techniques on the subject’s big movement data analysis and movement pattern personalization to further improve the classification precision.
- Long-term data collection and analysis of the elderly patients who have undergone hip fracture surgery operation. In doing so, extending the proposed concept for offering communal elderly home care monitoring.
- Investigation of further computational and interaction involvement will be performed to make full sense of the proposed rehabilitation model. A cloud-based environment such as ThingSpeak could offer resources in addressing such an issue.
- Looking into the system compliance with Industry 4.0 direction and for a software-defined infrastructure.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.; Al-Naime, K.; Al-Anbuky, A. IoT Environment for Monitoring Human Movements: Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Case. In Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 44–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Al-Naime, K.; Al-Anbuky, A. Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Health Informatics & Medical Systems (HIMS 2020), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Al-Anbuky, A.; McNair, P. Activity Classification Feasibility Using Wearables: Considerations for Hip Fracture. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2018, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Hu, N.; Tan, J.H. Efficacy of home-based exercise programme on physical function after hip fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, D.; Gibertoni, D.; Rucci, P.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Rosa, S.; Bianciardi, L.; Rolli, M.; Fantini, M.P. Impact of rehabilitation on mortality and readmissions after surgery for hip fracture. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, M.C.; Riet, G.T.; van Hartingsveldt, M.; Kröse, B.; Buurman, B.M. Effectiveness of sensor monitoring in a rehabilitation programme for older patients after hip fracture: A three-arm stepped wedge randomised trial. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, G.; Bickenbach, J.; Gutenbrunner, C.; Melvin, J. Rehabilitation: The health strategy of the 21st century. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Al-Naime, K.; Al-Anbuky, A. IoT based Testbed for Human Movement Activity Monitoring and Presentation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health, Prague, Czech Republic, 3–5 May 2020; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.; Lee, K. The Internet of Things (IoT): Applications, investments, and challenges for enterprises. Bus. Horiz. 2015, 58, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, F.J.; Vahidnia, R.; Rahmati, A. Wearables and the Internet of Things (IoT), applications, opportunities, and challenges: A Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69200–69211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciuncula, F.; Roto, A.V.; Kumar, D.; Davis, I.; Roy, S.; Walsh, C.J.; Awad, L.N. Wearable movement sensors for rehabilitation: A focused review of technological and clinical advances. PM&R 2018, 10, S220–S232. [Google Scholar]
- Cirani, S.; Picone, M. Wearable Computing for the Internet of Things. IT Prof. 2015, 17, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, M.; Zordan, D.; del Testa, D.; Grisan, E.; Rossi, M. Boosting the battery life of wearables for health monitoring through the compression of biosignals. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1647–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloi, G.; Fortino, G.; Gravina, R.; Pace, P.; Savaglio, C. Simulation-Driven Platform for Edge-Based AAL Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 39, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R.; Segal, S. A Review of Internet of Things Technologies for Ambient Assisted Living Environments. Future Internet 2019, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awais, M.; Raza, M.; Ali, K.; Ali, Z.; Irfan, M.; Chughtai, O.; Khan, I.; Kim, S.; Rehman, M.U. An Internet of Things Based Bed-Egress Alerting Paradigm Using Wearable Sensors in Elderly Care Environment. Sensors 2019, 19, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Roy, S.; Alsentzer, E.; McDermott, M.B.; Falck, F.; Bica, I.; Adams, G.; Pfohl, S.; Hyland, S.L. Machine Learning for Health (ML4H) 2020: Advancing Healthcare for All. In Machine Learning for Health; PMLR: Brookline, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, F.; El-Sappagh, S.; Islam, S.R.; Ali, A.; Attique, M.; Imran, M.; Kwak, K.-S. An intelligent healthcare monitoring framework using wearable sensors and social networking data. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 114, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; El-Sappagh, S.; Islam, S.R.; Kwak, D.; Ali, A.; Imran, M.; Kwak, K.-S. A smart healthcare monitoring system for heart disease prediction based on ensemble deep learning and feature fusion. Inf. Fusion 2020, 63, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, S.L.; Faltys, M.; Hüser, M.; Lyu, X.; Gumbsch, T.; Esteban, C.; Bock, C.; Horn, M.; Moor, M.; Rieck, B.; et al. Early prediction of circulatory failure in the intensive care unit using machine learning. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Q.; Hernando, A.B.G.; la Cruz, D.; Pau, I. The elderly’s independent living in smart homes: A characterization of activities and sensing infrastructure survey to facilitate services development. Sensors 2015, 15, 11312–11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania-Richmond, A.; Werle, J.; Robert, J. Bone and Joint Health Strategic Clinical Network: Keeping Albertans moving. CMAJ 2019, 191, S10–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magaziner, J.; Hawkes, W.; Hebel, J.R.; Zimmerman, S.I.; Fox, K.M.; Dolan, M.; Felsenthal, G.; Kenzora, J. Recovery From Hip Fracture in Eight Areas of Function. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2000, 55, M498–M507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidani, A.S.; Sabzwari, S.; Ahmad, K.; Mohammed, A.; Noordin, S. Effectiveness of home-based rehabilitation program in minimizing disability and secondary falls after a hip fracture: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Surg. Protoc. 2020, 22, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sheng, M.; Ruan, W.; Gu, T.; Li, X.; Falkner, N.; Yang, Z. RF-Care: Device-Free Posture Recognition for Elderly People Using A Passive RFID Tag Array. In Proceedings of the 12th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, Coimbra, Portugal, 22–24 July 2015; pp. 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Ni, L.M. Wifall: Device-free fall detection by wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 16, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gia, T.N.; Tcarenko, I.; Sarker, V.K.; Rahmani, A.M.; Westerlund, T.; Liljeberg, P.; Tenhunen, H. IoT-based fall detection system with energy efficient sensor nodes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Nordic Circuits and Systems Conference (NORCAS), Copenhagen, Denmark, 1–2 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, W.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Yao, L.; Li, X.; Falkner, N.J.; Yang, L. Device-free human localization and tracking with UHF passive RFID tags: A data-driven approach. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 104, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Xiao, J.; Han, J.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Ni, L.M. GRfid: A Device-Free RFID-Based Gesture Recognition System. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 16, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, N.; Diethe, T.; Fafoutis, X.; Elsts, A.; McConville, R.; Flach, P.; Craddock, I. A Comprehensive Study of Activity Recognition Using Accelerometers. Informatics 2018, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dargie, W. Analysis of Time and Frequency Domain Features of Accelerometer Measurements. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–6 August 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, Y.; Park, J.W. Physical activity recognition using a single triaxial accelerometer and a barometric sensor for baby and child care in a home environment. J. Ambient. Intell. Smart Environ. 2013, 5, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütő, J.; Oniga, S.; Buchman, A. Real time human activity monitoring. In Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae; Eszterházy Károly University: Eger, Hungary, 2015; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Karantonis, D.; Narayanan, M.; Mathie, M.; Lovell, N.; Celler, B. Implementation of a Real-Time Human Movement Classifier Using a Triaxial Accelerometer for Ambulatory Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2006, 10, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibzadeh, H.; Dinesh, K.; Shishvan, O.R.; Boggio-Dandry, A.; Sharma, G.; Soyata, T. A Survey of Healthcare Internet of Things (HIoT): A Clinical Perspective. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Deng, J.; Pang, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Deng, B.; Pang, Z.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M.; Liljeberg, P.; et al. An IoT-enabled stroke rehabilitation system based on smart wearable armband and machine learning. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacchirema, D.C.; Sarabia, D.; Palau, C.E.; Esteve, M. A Smart System for Sleep Monitoring by Integrating IoT with Big Data Analytics. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35988–36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.T.U.; Badshah, F.; Dad, F.; Amin, N.; Jan, M.A. Cloud-assisted IoT-based smart respiratory monitoring system for asthma patients. In Applications of Intelligent Technologies in Healthcare; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. The IoT-based heart disease monitoring system for pervasive healthcare service. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, F.; García, A.; Vázquez, M.; Cortez, J.; Espinoza, A. An IoT-Based Glucose Monitoring Algorithm to Prevent Diabetes Complications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, P.; Lopez-Benitez, M.; Lee, G.M.; Kim, T.-S.; Minhas, A.S. Wearable Internet of Things—from human activity tracking to clinical integration. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2361–2364. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, S.; Aghayi, E.; Noferesti, M.; Memarzadeh-Tehran, H.; Mondal, T.; Pang, Z.; Deen, M.J. Smart Homes for Elderly Healthcare—Recent Advances and Research Challenges. Sensors 2017, 17, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Diethe, T.; Camplani, M.; Tao, L.; Burrows, A.; Twomey, N.; Kaleshi, D.; Mirmehdi, M.; Flach, P.; Craddock, I.J. Bridging e-Health and the Internet of Things: The SPHERE Project. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2015, 30, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, P.P. Home Health Hub Internet of Things (H 3 IoT): An architectural framework for monitoring health of elderly people. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Science Engineering and Management Research (ICSEMR), Chennai, India, 27–29 November 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]


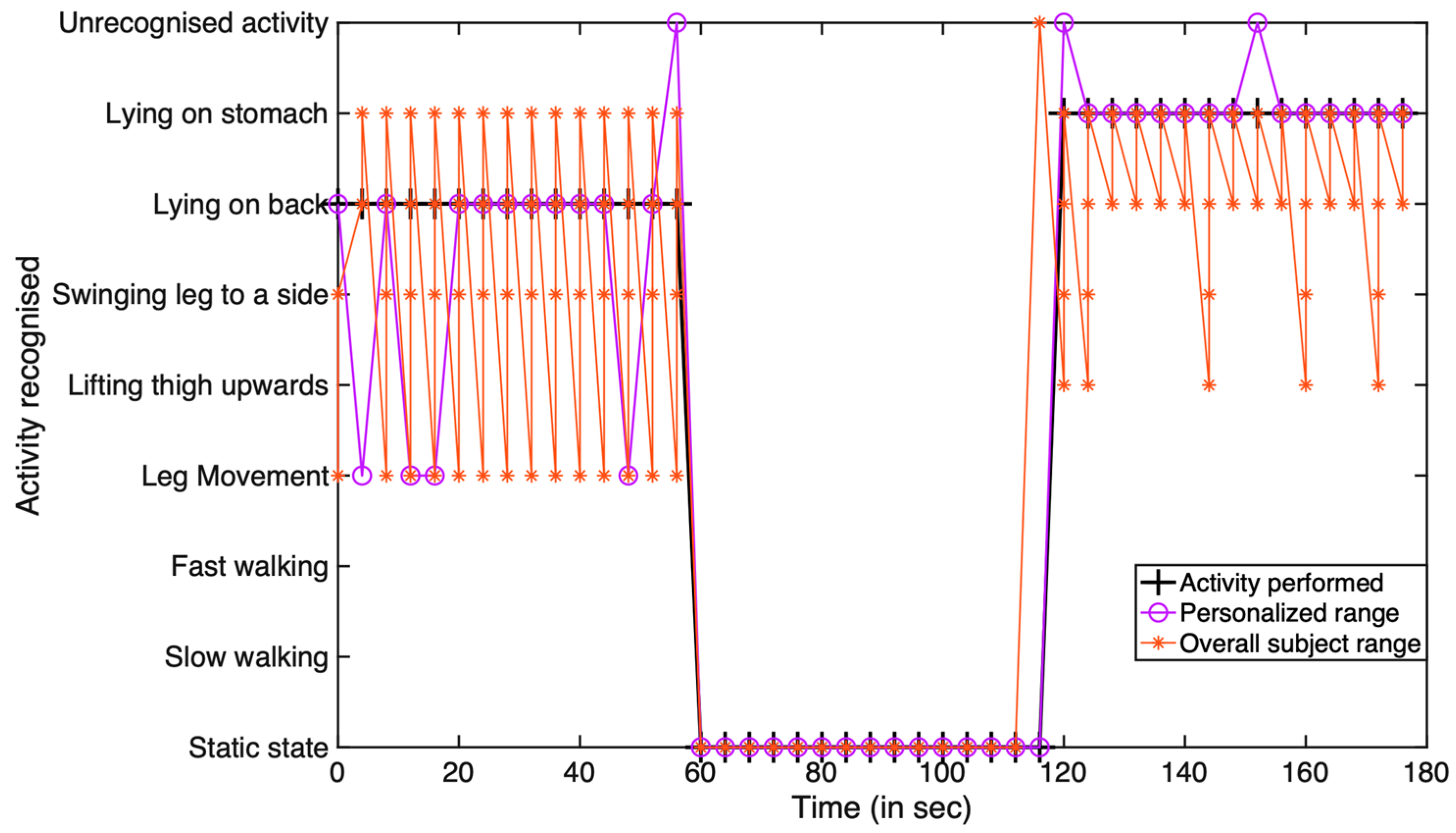



| Activity Performed | Overlap Activity | Correct Recognition | Incorrect Recognition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1: LTU | LOS | 13/15 times | 2/15 times |
| Case 1: Static | None | 15/15 times | None |
| Case 1: SLTS | LM | 11/15 times | 4/15 times |
| Case 2: LOB | LM | 11/15 times | 4/15 times |
| Case 2: Static | None | 15/15 times | None |
| Case 2: LOS | None | 13/15 times | 2/15 times |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, A.; Al-Anbuky, A. IoT-Based Patient Movement Monitoring: The Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model. Future Internet 2021, 13, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080195
Gupta A, Al-Anbuky A. IoT-Based Patient Movement Monitoring: The Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model. Future Internet. 2021; 13(8):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080195
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Akash, and Adnan Al-Anbuky. 2021. "IoT-Based Patient Movement Monitoring: The Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model" Future Internet 13, no. 8: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080195
APA StyleGupta, A., & Al-Anbuky, A. (2021). IoT-Based Patient Movement Monitoring: The Post-Operative Hip Fracture Rehabilitation Model. Future Internet, 13(8), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080195






