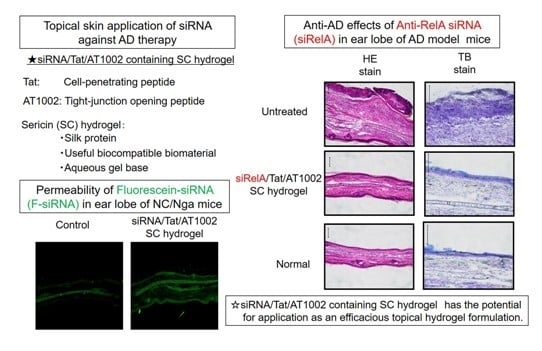
Topical Anti-Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Small Interfering RNA with Functional Peptides Containing Sericin-Based Hydrogel for Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. RNAs, Peptides, and Animals
2.2. Preparation of siRNA Complex and SC Based Hydrogels
2.3. FAM-siRNA Distribution in Tape-Stripped Mouse Skin
2.4. Topical Induction of AD-Like Skin in Ears of NC/Nga Mice
2.5. Distribution of FAM-siRNA in AD-Like Mouse Ear Skin
2.6. Evaluation of AD-Induced Mice Treated with siRelA-Containing SC Hydrogels
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Intradermal siRNA Distribution in Tape-Stripped Back Skin of Mice
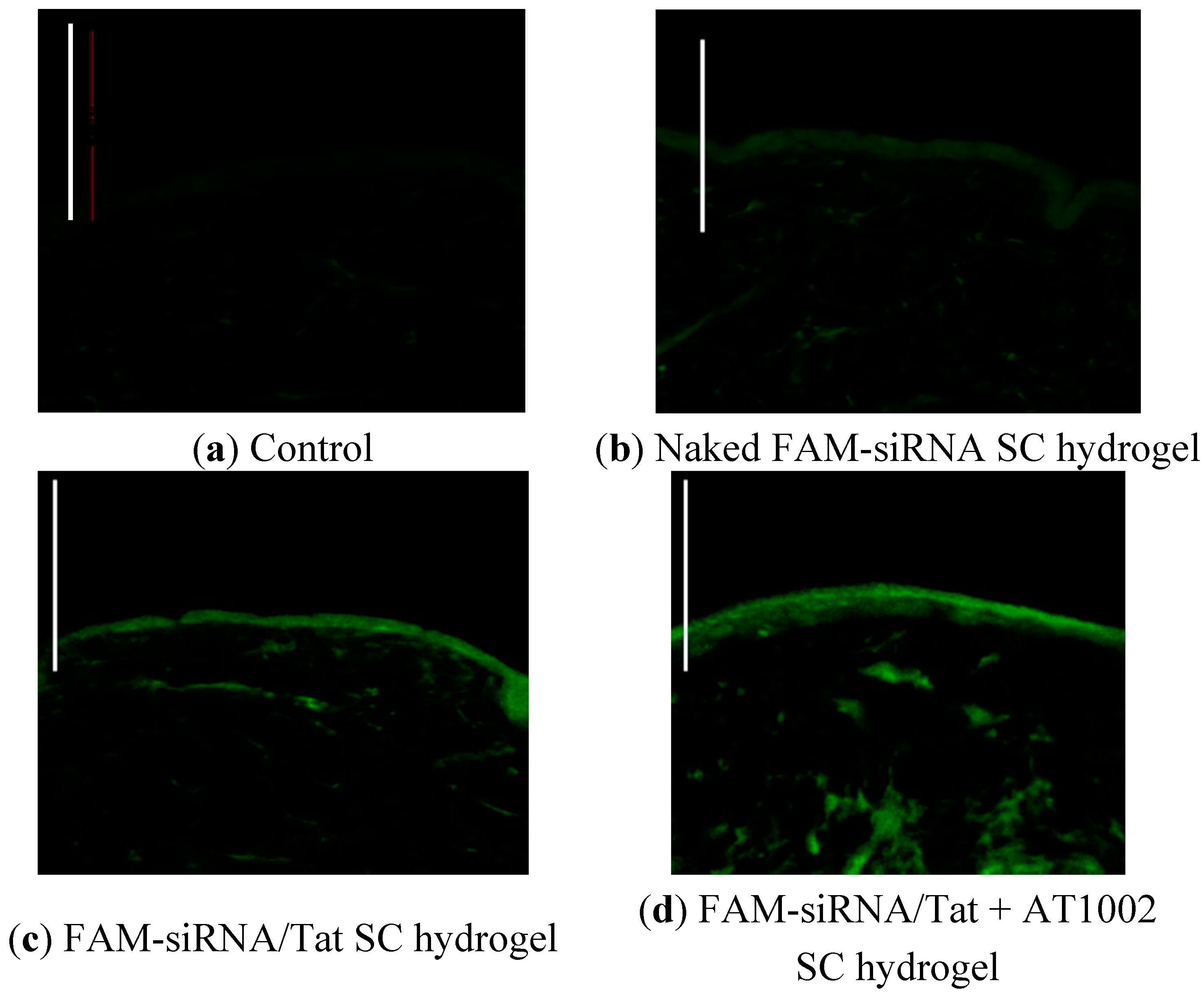
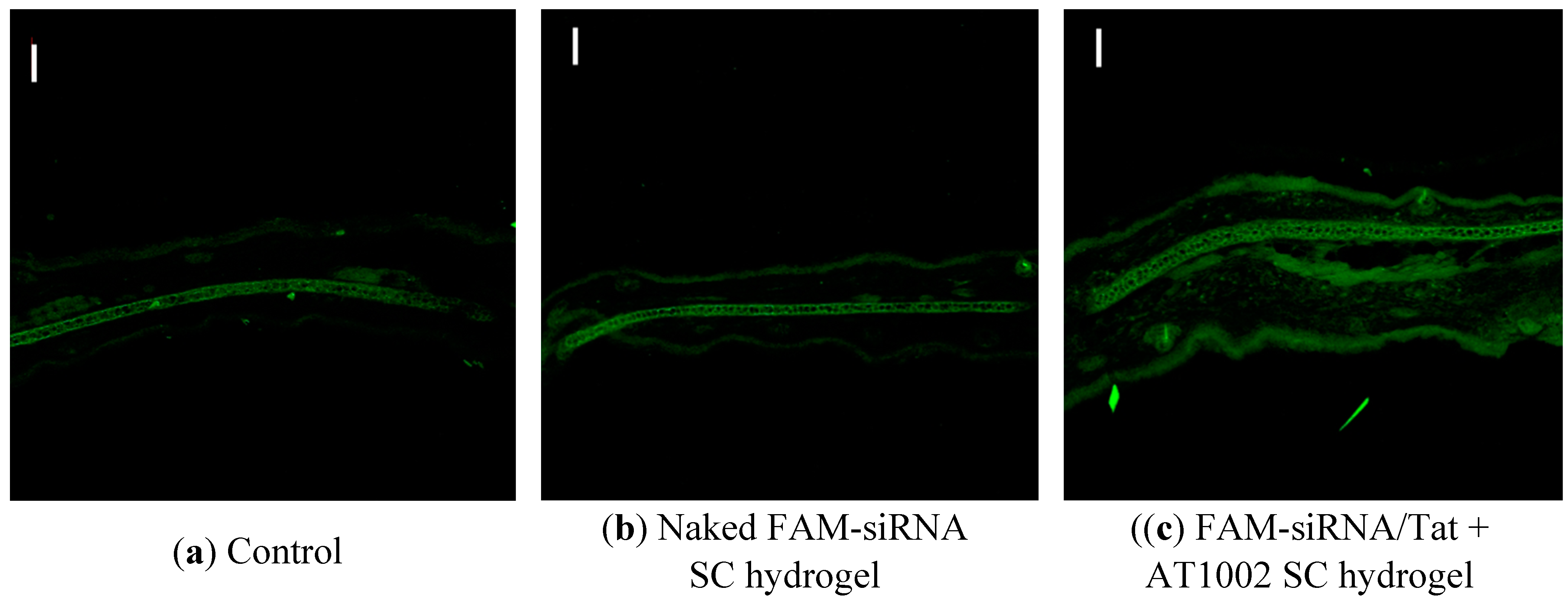
3.2. Intradermal siRNA Distribution in AD-Like Mouse Ear Skin
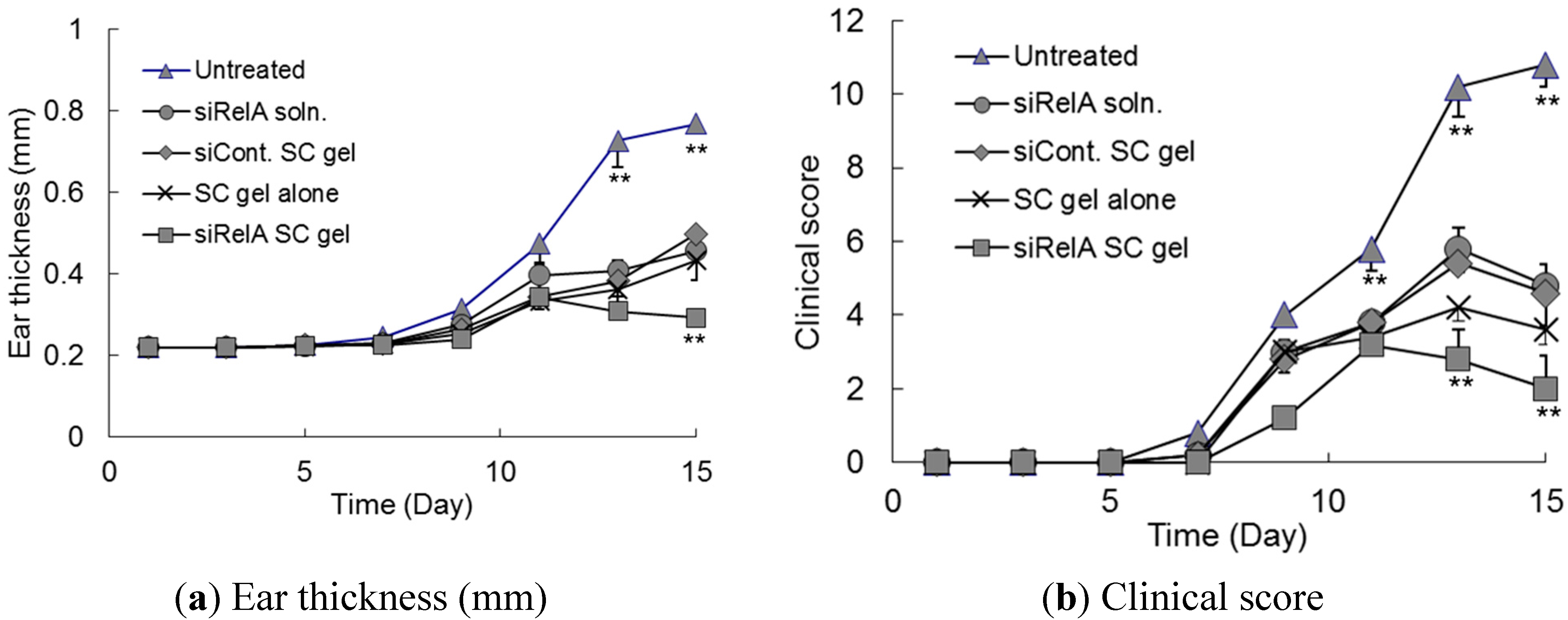
3.3. Effects of Anti-siRelA on Ear Thickness and Clinical Score in NC/Nga AD Mice
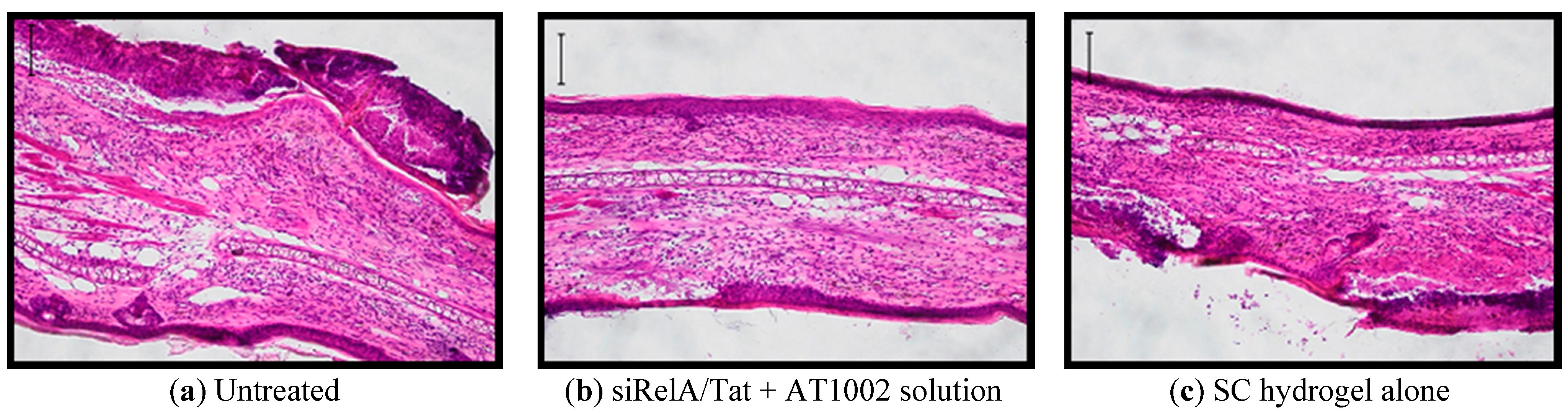
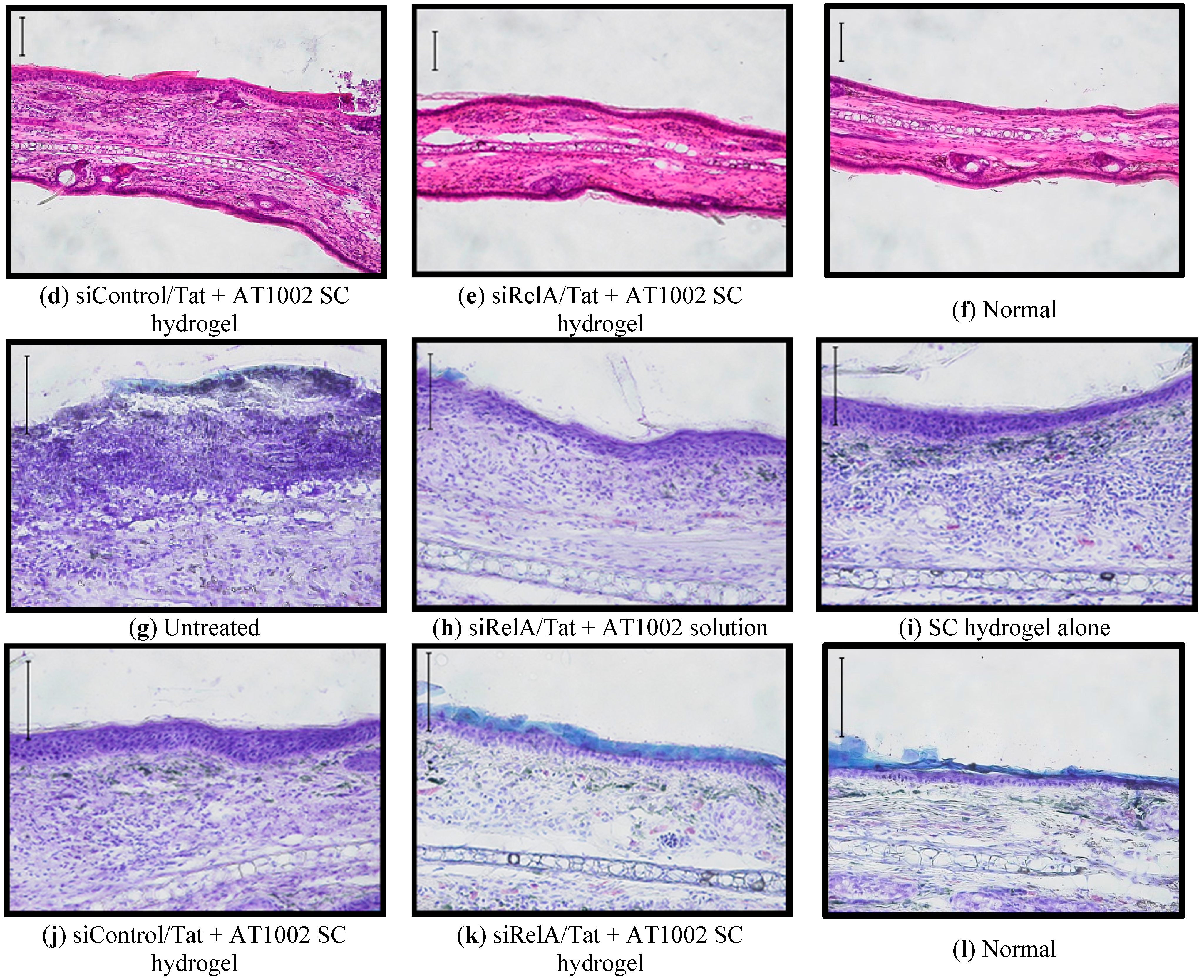
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, D.Y. Atopic dermatitis: New insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheer, S.M.; Plosker, G.L. Tacrolimus ointment. A review of its therapeutic potential as a topical therapy in atopic dermatitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2001, 2, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, R.; Sugimoto, T.; Aoki, M.; Kida, I.; Tomita, N.; Moriguchi, A.; Maeda, K.; Sawa, Y.; Kaneda, Y.; Higaki, J.; et al. In vivo transfection of cis element “decoy” against nuclear factor-kappaB binding site prevents myocardial infarction. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajee, M.; Muchamuel, T.; Schryver, B.; Oo, A.; Alleman-Sposeto, J.; De Vry, C.G.; Prasad, S.; Ruhrmund, D.; Shamsunder, R.; Mutnick, D.; et al. Blockade of experimental atopic dermatitis via topical NF-κB decoy oligonucleotide. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Aoki, M.; Tamai, K.; Oishi, M.; Ogihara, T.; Kaneda, Y.; Morishita, R. Prevention and regression of atopic dermatitis by ointment containing NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides in NC/Nga atopic mouse model. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Kanazawa, T.; Kawai, M.; Takashima, Y.; Okada, H. Therapeutic effects on atopic dermatitis by anti-RelA short interfering RNA combined with functional peptides Tat and AT1002. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, T.; Hamasaki, T.; Endo, T.; Tamano, K.; Sogabe, K.; Seta, Y.; Ohgi, T.; Okada, H. Functional peptide nanocarriers for delivery of novel anti-RelA RNA interference agents as a topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partidos, C.D.; Beignon, A.S.; Mawas, F.; Belliard, G.; Briand, J.P.; Muller, S. Immunity under the skin: Potential application for topical delivery of vaccines. Vaccine 2003, 21, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.B.; Brophy, C.M.; Furnich, E.; Flynn, C.R.; Sparks, O.; Komalavilas, P.; Joshi, L.; Panitch, A.; Bentley, M.V. Comparative study of the skin penetration of protein transduction domains and a conjugated peptide. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.M. The skin: An indispensable barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmush, M.L.; Golberg, A.; Serša, G.; Kotnik, T.; Miklavčič, D. Electroporation-based technologies for medicine: Principles, applications, and challenges. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 16, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liang, Z. A pliable electroporation patch (ep-Patch) for efficient delivery of nucleic acid molecules into animal tissues with irregular surface shapes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, R.; Bu, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Li, Z. A flexible microneedle array as low-voltage electroporation electrodes for in vivo DNA and siRNA delivery. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kigasawa, K.; Kajimoto, K.; Hama, S.; Saito, A.; Kanamura, K.; Kogure, K. Noninvasive delivery of siRNA into the epidermis by iontophoresis using an atopic dermatitis-like model rat. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 383, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, O.; Depelsenaire, A.C.; Meliga, S.C.; Yukiko, S.R.; McMillan, N.A.; Frazer, I.H.; Kendall, M.A. CXCL1 gene silencing in skin using liposome-encapsulated siRNA delivered by microprojection array. J. Control. Release 2014, 194, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.R.; Marepally, S.; Patel, A.R.; Voshavar, C.; Chaudhuri, A.; Singh, M. Topical delivery of anti-TNFα siRNA and capsaicin via novel lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles efficiently inhibits skin inflammation in vivo. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, K.S.; Chen, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Johnston, N.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, K.; Koropatnick, J.; Gillies, E.R.; Min, W.P. Non-covalently functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube for topical siRNA delivery into melanoma. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3435–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothbard, J.B.; Garlington, S.; Lin, Q.; Kirschberg, T.; Kreider, E.; McGrane, P.L.; Wender, P.A.; Khavari, P.A. Conjugation of arginine oligomers to cyclosporin A facilitates topical delivery and inhibition of inflammation. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.W.; Chan, M.H.; Hsu, H.R.; Liu, B.R.; Chen, C.P.; Chen, H.H.; Lee, H.J. Transdermal delivery of proteins mediated by non-covalently associated arginine-rich intracellular delivery peptides. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, P.B.; Oliver, S.F.; Sheu, S.M.; Goodnough, J.B.; Wender, P.; Khavari, P.A. Peptide delivery to tissue via reversibly linked protein transduction sequences. BioTechniques 2002, 33, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zakrewsky, M.; Gupta, V.; Anselmo, A.C.; Slee, D.H.; Muraski, J.A.; Mitragotri, S. Topical delivery of siRNA into skin using SPACE-peptide carriers. J. Control. Release 2014, 179, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.; Mitragotri, S. Delivery of siRNA and other macromolecules into skin and cells using a peptide enhancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15816–15821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahi, S.A.; Taghibiglou, C.; Azizi, E.; Farboud, E.S. Cell-penetrating peptides as a novel transdermal drug delivery system. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 80, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Kanazawa, T.; Kawai, M.; Takashima, Y.; Okada, H. Development of an efficient siRNA transdermal delivery system using functional peptides, Tat and AT1002. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Yamada, M.; Kanazawa, T.; Takashima, Y.; Ouchi, K.; Okada, H. Use of silk protein, sericin, as a sustained-release material in the form of a gel, sponge and film. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, A.; Yamada, M.; Kanazawa, T.; Takashima, Y.; Ouchi, K.; Okada, H. Sustained-release of protein from biodegradable sericin film, gel and sponge. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 407, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Q. Applications of natural silk protein sericin in biomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2002, 20, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Sato, S.; Yamanaka, A.; Yamada, H.; Fuwa, N.; Nomura, M. Silk protein, sericin, inhibits lipid peroxidation and tyrosinase activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, R.; Mandal, M.; Ghosh, S.K.; Kundu, S.C. Silk sericin protein of tropical tasar silkworm inhibits UVB-induced apoptosis in human skin keratinocytes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2008, 311, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanazawa, T.; Shizawa, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Tamano, K.; Ibaraki, H.; Seta, Y.; Takashima, Y.; Okada, H. Topical Anti-Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Small Interfering RNA with Functional Peptides Containing Sericin-Based Hydrogel for Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 294-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030294
Kanazawa T, Shizawa Y, Takeuchi M, Tamano K, Ibaraki H, Seta Y, Takashima Y, Okada H. Topical Anti-Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Small Interfering RNA with Functional Peptides Containing Sericin-Based Hydrogel for Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(3):294-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030294
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanazawa, Takanori, Yuki Shizawa, Mayu Takeuchi, Kuniko Tamano, Hisako Ibaraki, Yasuo Seta, Yuki Takashima, and Hiroaki Okada. 2015. "Topical Anti-Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Small Interfering RNA with Functional Peptides Containing Sericin-Based Hydrogel for Atopic Dermatitis" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 3: 294-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030294
APA StyleKanazawa, T., Shizawa, Y., Takeuchi, M., Tamano, K., Ibaraki, H., Seta, Y., Takashima, Y., & Okada, H. (2015). Topical Anti-Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Small Interfering RNA with Functional Peptides Containing Sericin-Based Hydrogel for Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics, 7(3), 294-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030294