Physical and Oxidative Stability of Uncoated and Chitosan-Coated Liposomes Containing Grape Seed Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Material
2.2. Preparation of Extract Solution
2.3. Preparation of Primary Liposomes
2.4. Preparation of Secondary Chitosan-Coated Liposomes
2.5. Particle Size Determination
2.6. ζ-Potential Measurements
2.7. Gas Chromatography (GC)
2.8. Folin-Ciocalteu Assay
2.9. Statistical Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Appearance of Liposomal Systems

3.2. Effect of Encapsulation of Grape Seed Extract and Coating with Chitosan on Particle Diameter and ζ-Potential of Liposomes
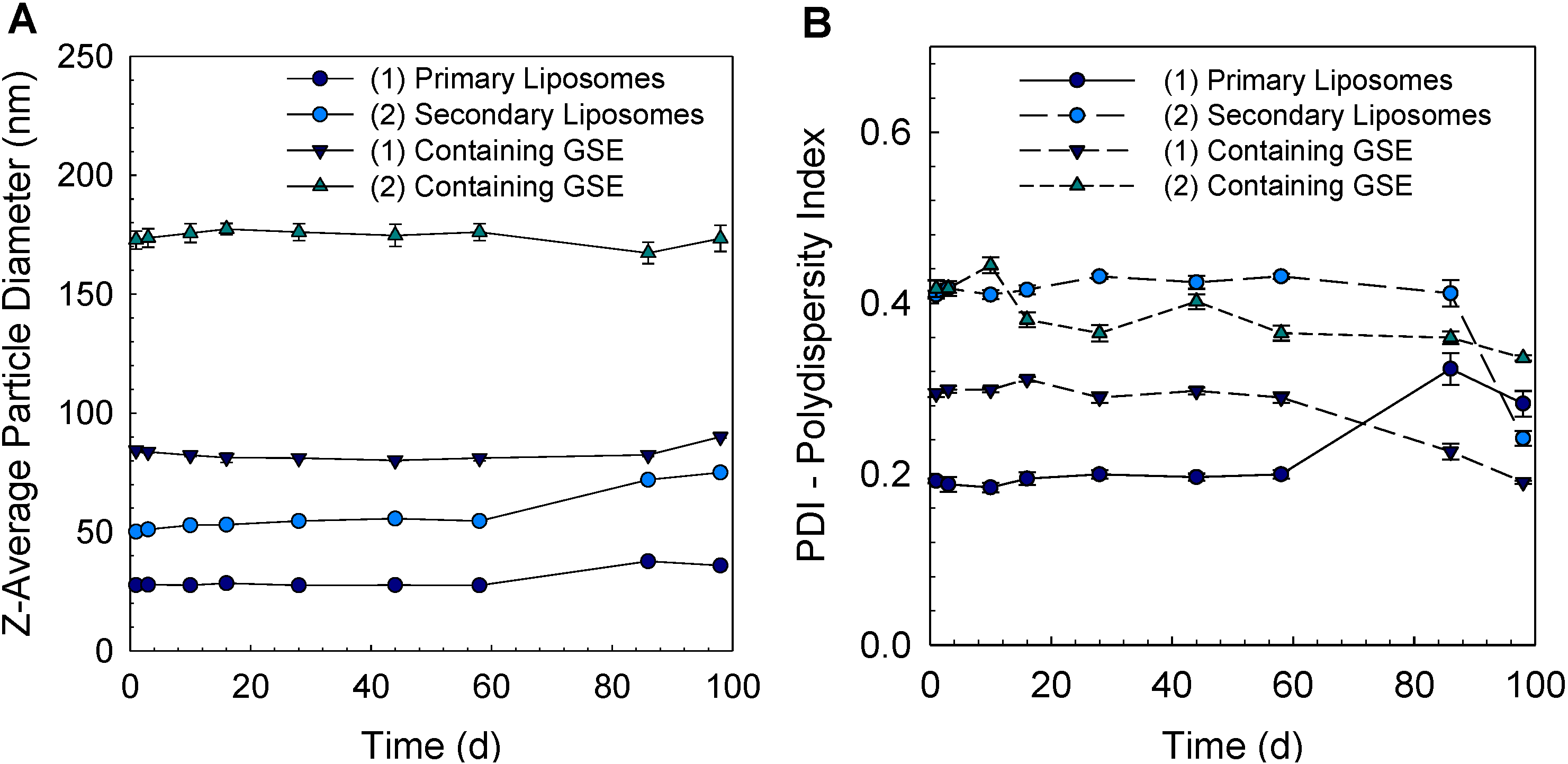
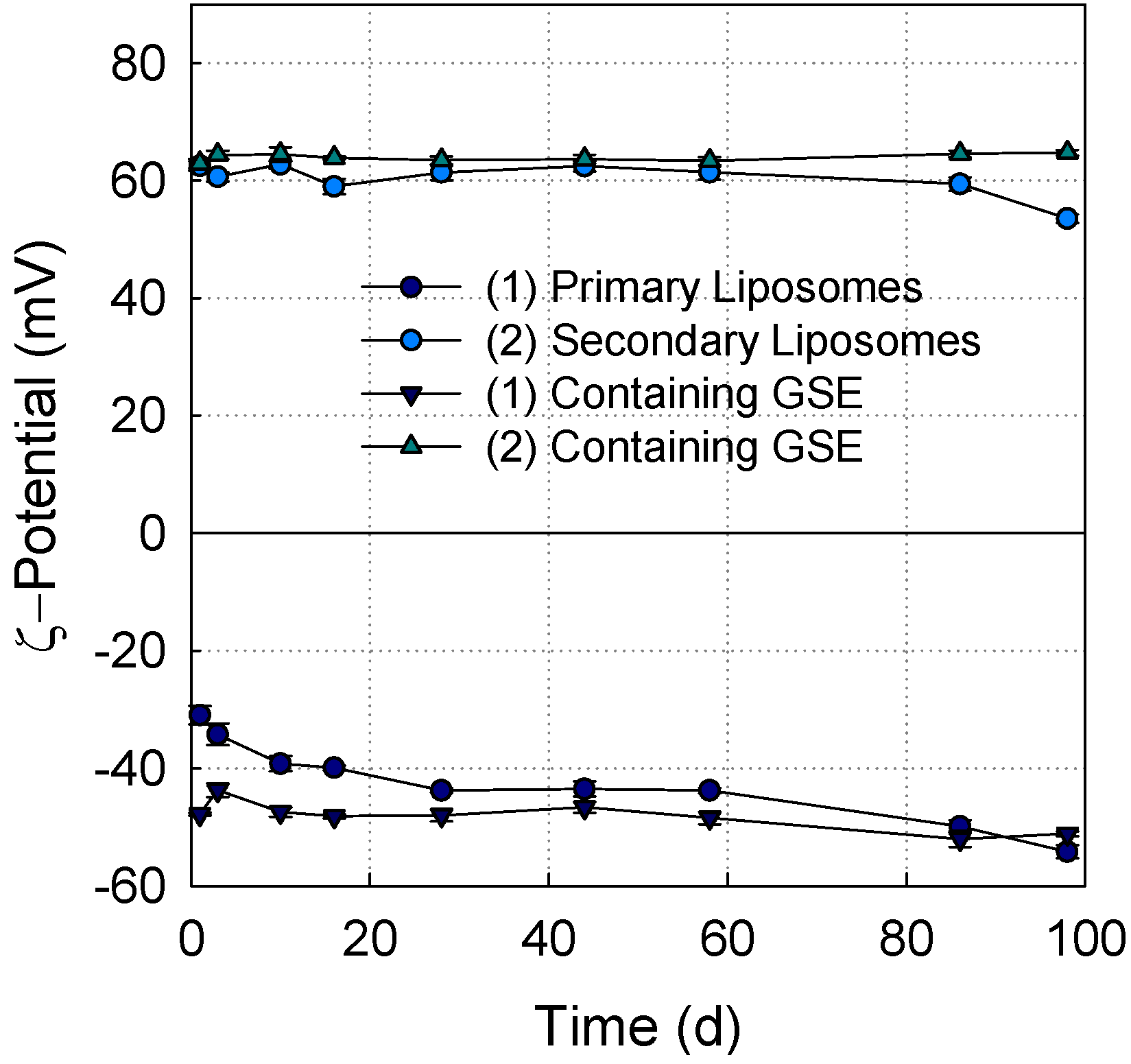
3.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds and Entrapment Efficiency

| Sample type | Concentration of phenolic compounds mg gallic acid/L | Difference between sample type phenolic compounds mg gallic acid/L |
|---|---|---|
| GSE | 406 ± 3 | na |
| GSE a | 1 ± 22 | na |
| Primary liposomes containing GSE b | 381 ± 17 | na |
| Free polyphenols c | na | 25 ± 20 c |
| Primary liposomes with GSE a | 350 ± 1 | na |
| Polyphenols in the core d | na | 31 ± 20 d |
| Secondary liposomes with GSE a | 292 ± 1 | na |
| Polyphenols in the core e | na | 63 ± 12 e |
| Secondary liposomes containing chitosan and GSE b | 355 ± 10 | na |
3.4. Lipid Oxidation of Liposomes
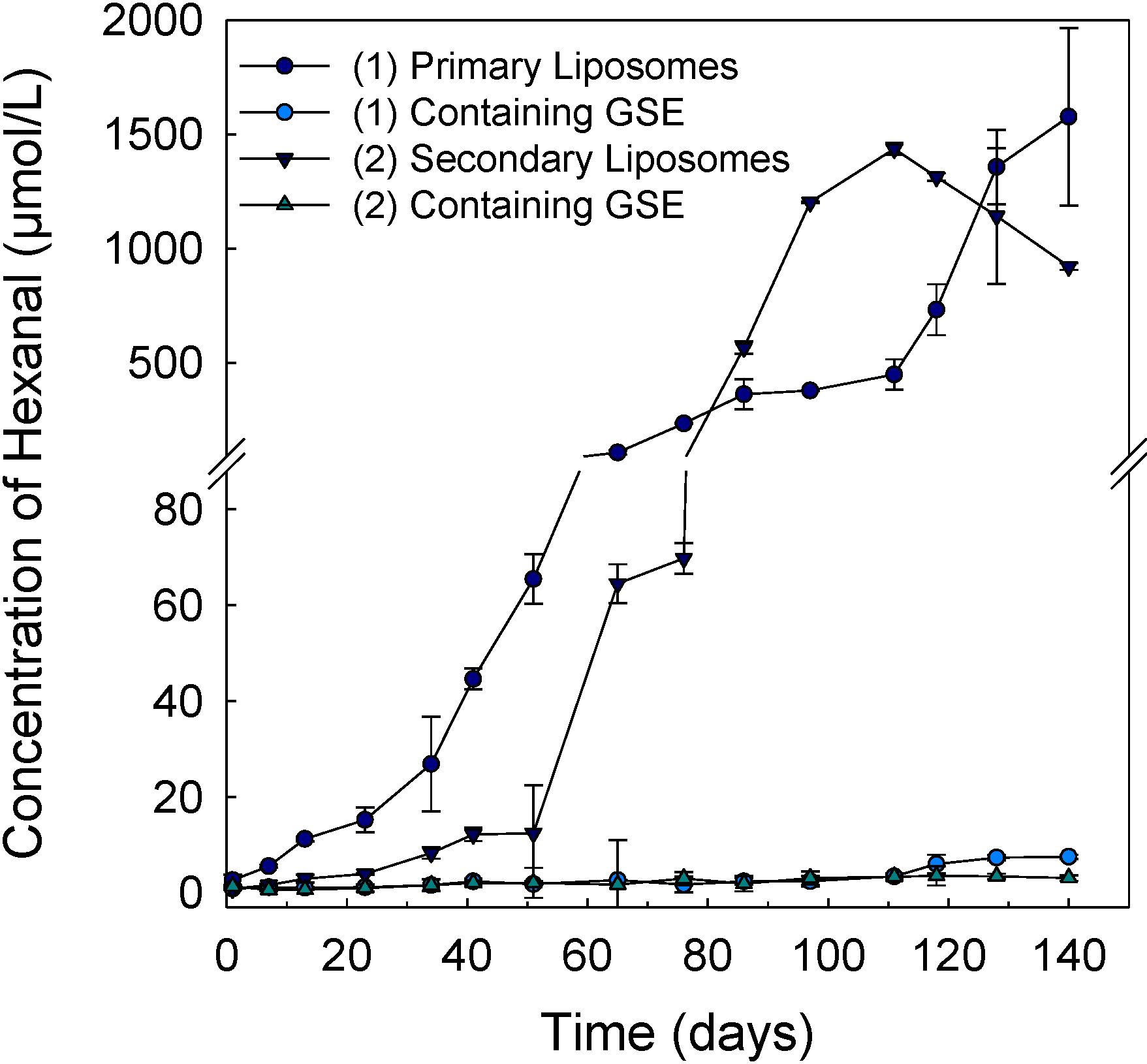
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, J.; Yu, J.; Pohorly, J.E.; Kakuda, Y. Polyphenolics in grape seeds—Biochemistry and functionality. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumalla, A.V.S.; Hettiarachchy, N.S. Green tea and grape seed extracts—Potential applications in food safety and quality. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterodt, H.; Slavin, M.; Whent, M.; Turner, E.; Yu, L.L. Fatty acid composition, oxidative stability, antioxidant and antiproliferative properties of selected cold-pressed grape seed oils and flours. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, P.; Laight, D.; Shaw, K.M.; Cummings, M.H. Flavonoid-rich grapeseed extracts: A new approach in high cardiovascular risk patients? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.G.; McClements, D.J. Functional biopolymer particles: Design, fabrication, and applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 374–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R.; Johnson, C.; Hatziantoniou, S.; Demetzos, C. Nanoliposomes and their applications in food nanotechnology. J. Liposome Res. 2008, 18, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R.; Flanagan, J.; Matia-Merino, L.; Awati, A.; Omri, A.; Suntres, Z.E.; Singh, H. Recent trends in the lipid-based nanoencapsulation of antioxidants and their role in foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibis, M.; Vogt, E.; Weiss, J. Encapsulation of polyphenolic grape seed extract in polymer-coated liposomes. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Kajiya, K.; Kumazawa, S. Interaction of plant polyphenols with liposomes. Adv. Planar Lipid Bilayers Liposomes 2006, 4, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.S.H.; Nielsen, N.S.; Timm-Heinrich, M.; Jacobsen, C. Oxidative stability of marine phospholipids in the liposomal form and their application. Lipids 2011, 46, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y.; Weiss, J. Structural design principles for delivery of bioactive components in nutraceuticals and functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 577–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, Y. Structured emulsion-based delivery systems: Controlling the digestion and release of lipophilic food components. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.M.; Davidson, P.M.; Bruce, B.D.; Weiss, J. Liposomal nanocapsules in Food Science and Agriculture. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzey, D.; McClements, J.D. Formation, stability and properties of multilayer emulsions for application in the food industry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128–130, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degim, Z.; Celebi, N.; Alemdaroglu, C.; Deveci, M.; Öztürk, S.; Özugul, C. Evaluation of chitosan gel containing liposome-loaded epidermal growth factor on burn wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2011, 8, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zeng, Z.W.; Xiao, R.Z.; Xie, T.; Zhou, G.L.; Zhan, X.R.; Wang, S.L. Recent advances of chitosan nanoparticles as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 765–774. [Google Scholar]
- Panya, A.; Laguerre, M.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Effects of chitosan and rosmarinate esters on the physical and oxidative stability of liposomes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of environmental conditions on the stability of oil in water emulsions containing droplets stabilized by lecithin-chitosan membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudipati, V.; Sandra, S.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Oxidative stability and in vitro digestability of fish oil-in-water emulsions containing multilayered membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8093–8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.-Q.; Peng, H.-L.; Xiong, H.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhao, L.-P.; Xiao, X.-N. Carboxymethylchitosan-coated proliposomes containing coix seed oil: Characterisation, stability and in vitro release evaluation. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Schieber, A.; Kammerer, D.R.; Carle, R. Residues of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) seed oil production as a valuable source of phenolic antioxidants. Food Chem. 2008, 112, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Gibis, M.; Weiss, J. Antioxidant capacity and inhibitory effect of grape seed and rosemary extract in marinades on the formation of heterocyclic amines in fried beef patties. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeu-Nadal, M.; Castellote, A.I.; López-Sabater, M.C. Headspace gas chromatographic method for determining volatile compounds in infant formulas. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1046, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laye, C.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Formation of biopolymer-coated liposomes by electrostatic deposition of chitosan. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, N7–N15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibis, M.; Rahn, N.; Weiss, J. Physical and Oxidative Stability of Uncoated and Chitosan-Coated Liposomes Containing Grape Seed Extract. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030421
Gibis M, Rahn N, Weiss J. Physical and Oxidative Stability of Uncoated and Chitosan-Coated Liposomes Containing Grape Seed Extract. Pharmaceutics. 2013; 5(3):421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030421
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibis, Monika, Nina Rahn, and Jochen Weiss. 2013. "Physical and Oxidative Stability of Uncoated and Chitosan-Coated Liposomes Containing Grape Seed Extract" Pharmaceutics 5, no. 3: 421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030421
APA StyleGibis, M., Rahn, N., & Weiss, J. (2013). Physical and Oxidative Stability of Uncoated and Chitosan-Coated Liposomes Containing Grape Seed Extract. Pharmaceutics, 5(3), 421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5030421






