Using Ion-Selective Electrodes to Study the Drug Release from Porous Cellulose Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Working Principle of Electrodes
2.3. Preparation of ISEs

2.4. Preparation of the Drug-Containing Solid Dosage Forms
2.5. Potentiometric and UV Spectrophotometric Measurements

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Quality of ISEs
3.1.1. Calibration Curves
 ) and lidocaine hydrochloride (
) and lidocaine hydrochloride (  ). Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
). Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
 ) and lidocaine hydrochloride (
) and lidocaine hydrochloride (  ). Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
). Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).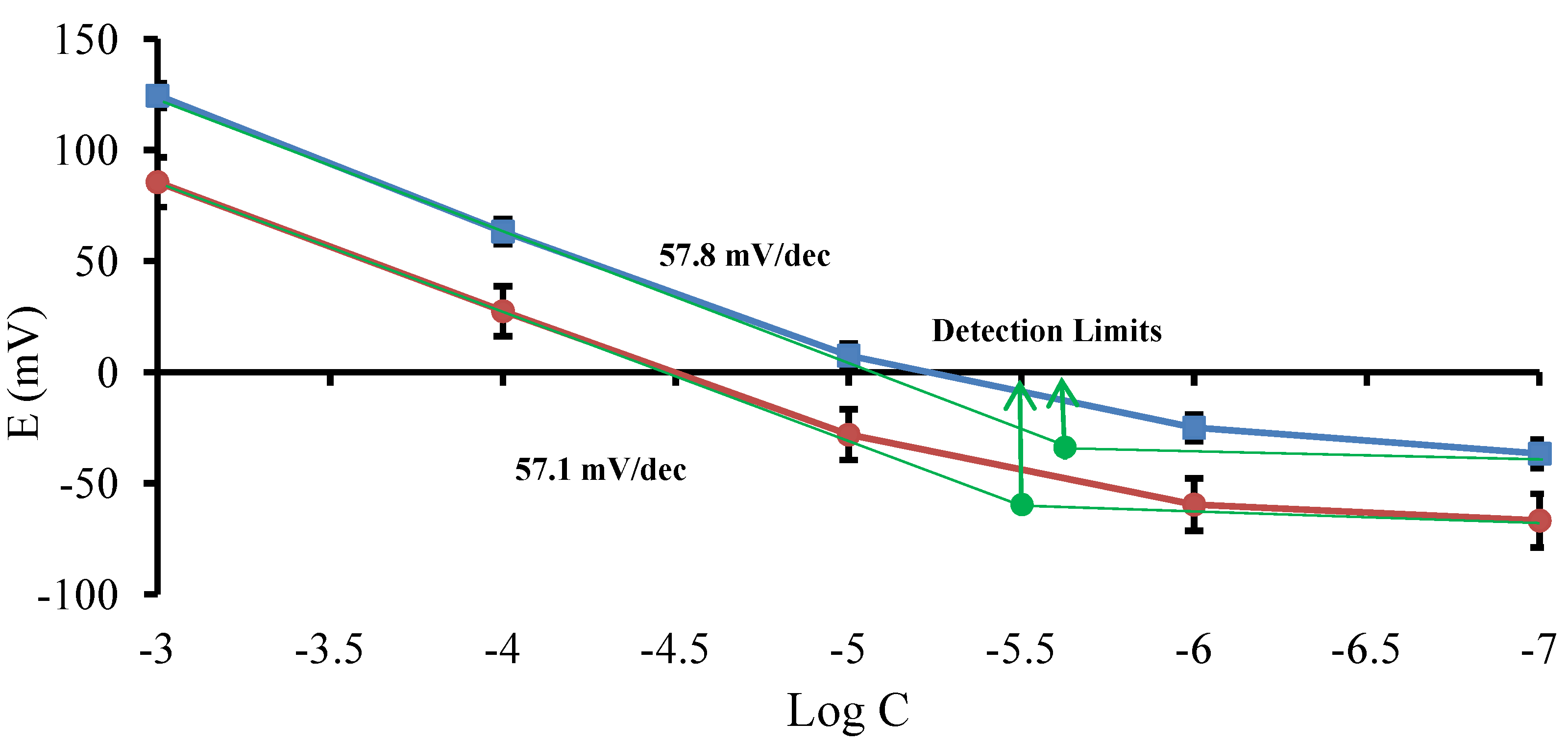
3.1.2. Response Time
 ) and lidocaine hydrochloride (
) and lidocaine hydrochloride (  ). (a) 1.0×10−3 M; (b) 1.0×10−3.5 M; (c) 1.0×10−4 M; (d) 1.0×10−4.5 M; (e) 1.0×10−5 M; (f) 1.0×10−5.5 M; (g) 1.0×10−6 M and (h) 1.0×10−7 M.
). (a) 1.0×10−3 M; (b) 1.0×10−3.5 M; (c) 1.0×10−4 M; (d) 1.0×10−4.5 M; (e) 1.0×10−5 M; (f) 1.0×10−5.5 M; (g) 1.0×10−6 M and (h) 1.0×10−7 M.
 ) and lidocaine hydrochloride (
) and lidocaine hydrochloride (  ). (a) 1.0×10−3 M; (b) 1.0×10−3.5 M; (c) 1.0×10−4 M; (d) 1.0×10−4.5 M; (e) 1.0×10−5 M; (f) 1.0×10−5.5 M; (g) 1.0×10−6 M and (h) 1.0×10−7 M.
). (a) 1.0×10−3 M; (b) 1.0×10−3.5 M; (c) 1.0×10−4 M; (d) 1.0×10−4.5 M; (e) 1.0×10−5 M; (f) 1.0×10−5.5 M; (g) 1.0×10−6 M and (h) 1.0×10−7 M.
3.1.3. Effect of pH
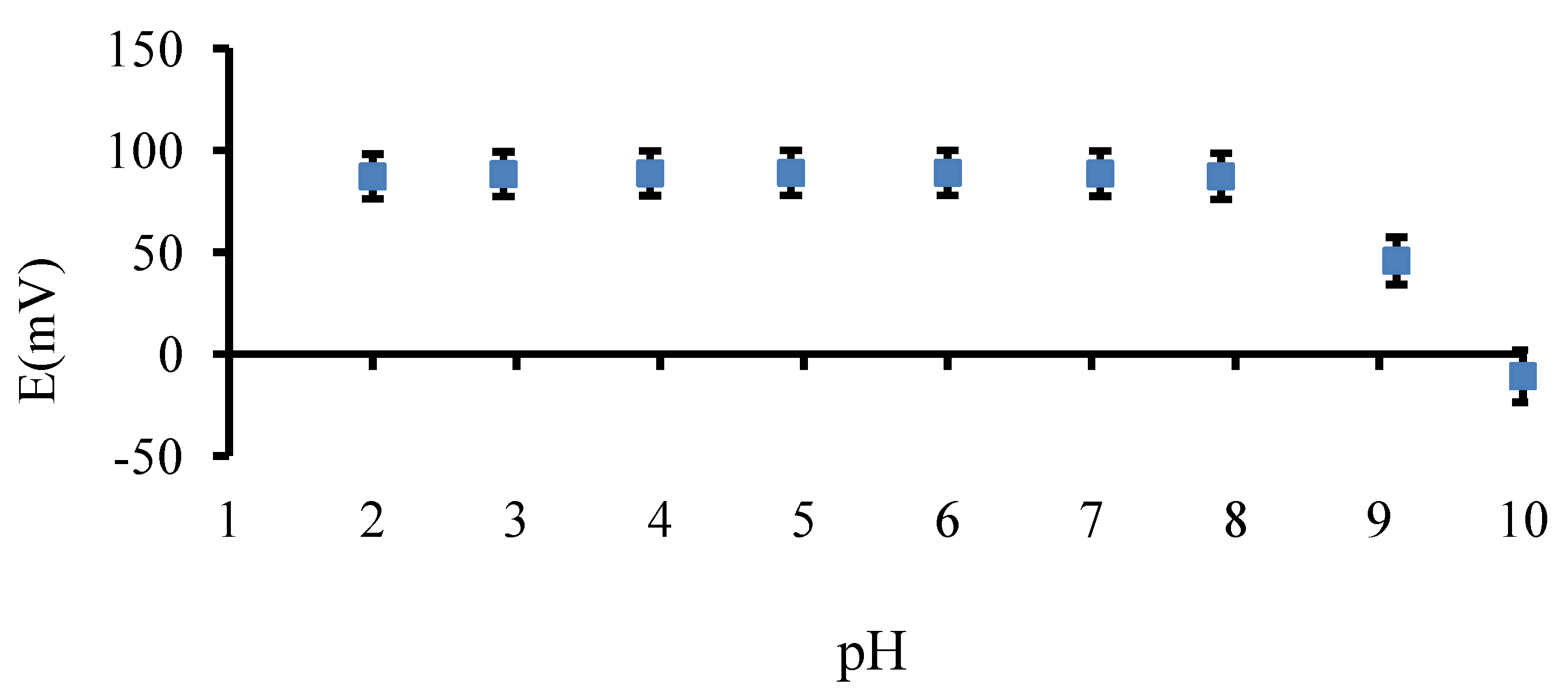
3.1.4. Potentiometric Selectivity
| Mn+ | KpotLid,M |
|---|---|
| K+ | 5.00 × 10−4 |
| Na+ | 7.94 × 10−5 |
| Ca2+ | 3.98 × 10−6 |
| Mg2+ | 3.16 × 10−6 |
3.2. Comparison of Potentiometric and UV Spectrophotometry Methods
3.2.1. Polymer Films
 ) and potentiometric method (
) and potentiometric method (  ). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
 ) and potentiometric method (
) and potentiometric method (  ). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).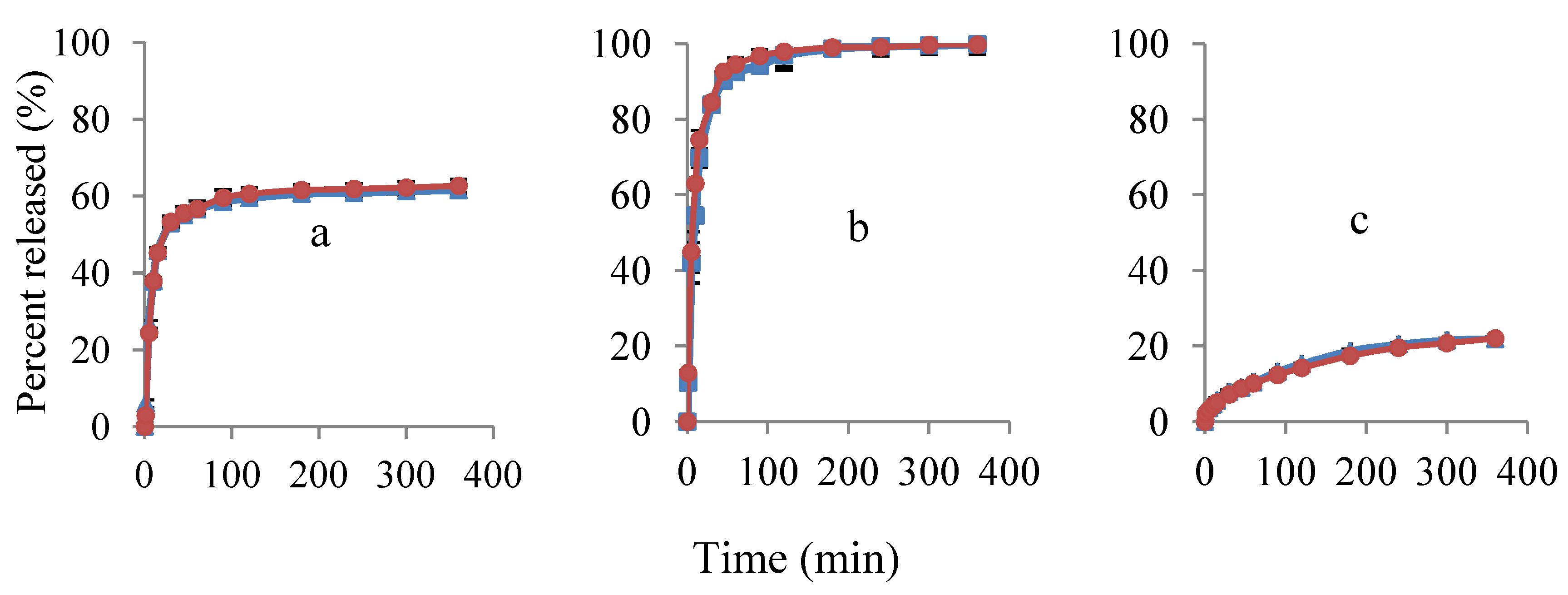
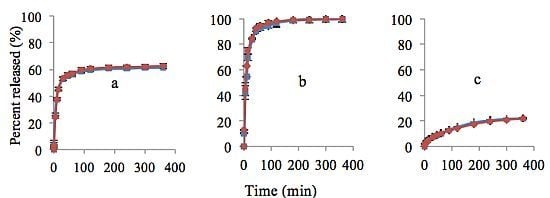
3.2.2. Porous Filter Paper Substrates
 ) and potentiometric method (
) and potentiometric method (  ). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
 ) and potentiometric method (
) and potentiometric method (  ). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
). Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).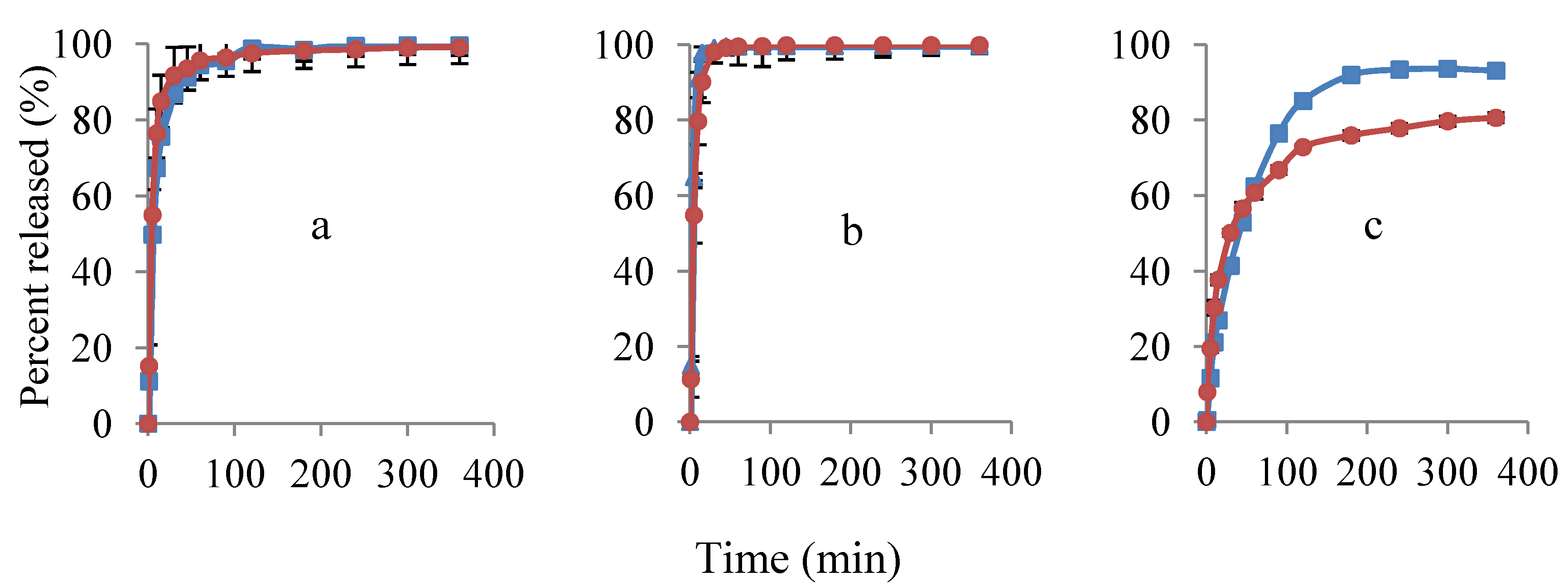
3.3. Study of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Release
 ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) lidocaine in drug-polymer solutions. Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
) lidocaine in drug-polymer solutions. Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
 ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) lidocaine in drug-polymer solutions. Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).
) lidocaine in drug-polymer solutions. Ratios of EC:HPC in the polymer component are (a) 1:1; (b) 0:1 and (c) 1:0. Mean ± SD values are shown (n = 3).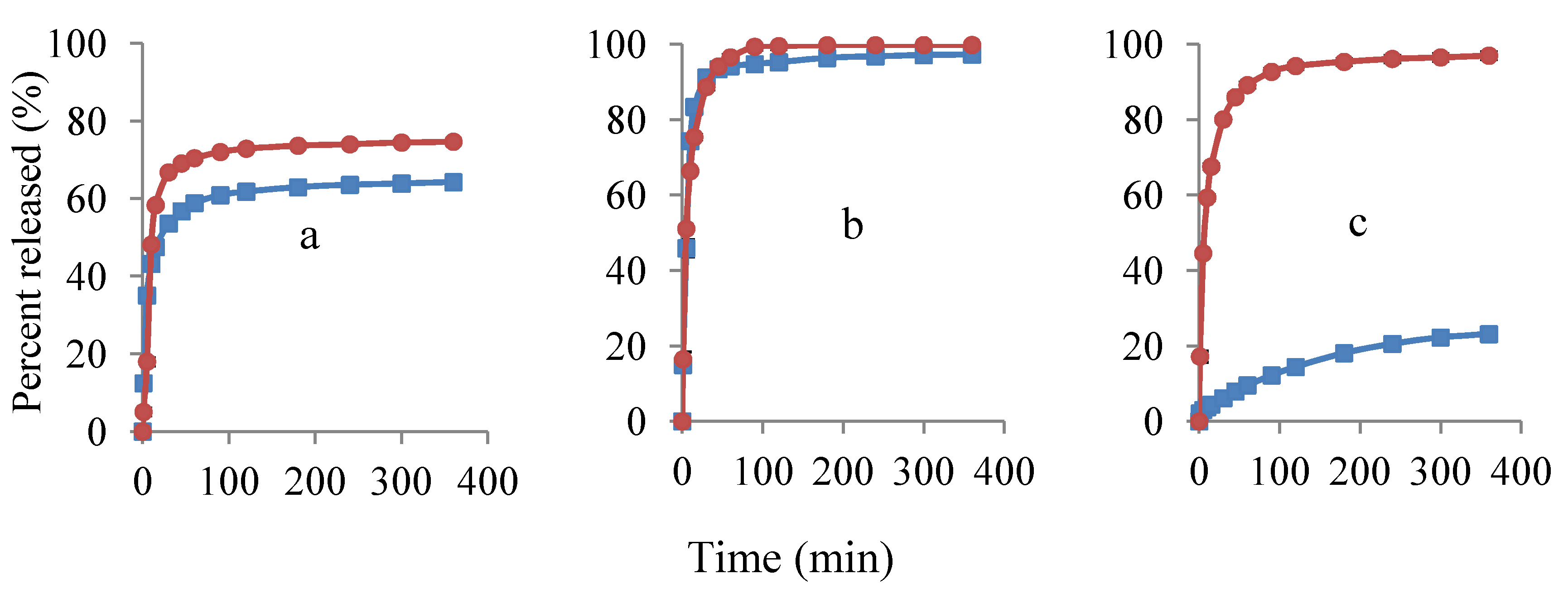
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Amman, D.; Morf, W.E.; Anker, P.; Meier, P.C.; Pretsch, E.; Simon, W. Neutral carrier based ion-selective electrodes. Ion. Sel. Electrode. R. 1983, 5, 3–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, E.; Diamond, D.; Lewenstam, A; Pretsch, E. Ion sensors: Current limits and new trends. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1999, 393, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, G. An organic cation-selective electrode: Potentiometric determination of acetylcholine activity. Anal. Lett. 1970, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, G.; Ward, F.B. General enzyme studies with a substrate selective electrode: Characterization of cholinesterases. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 42, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, G. Determination of cholinesterase by an organic substrate selective electrode. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 39, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Coşofreţ, V.V. Drug membrane sensors and their pharmaceutical applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 1991, 10, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Borham, N. Phenothiazine drug poly(vinyl chloride) matrix membrane electrodes and their use in pharmaceutical analysis. Microchem. J. 1999, 63, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Sun, X.X. Anovel ion selective PVC membrane electrode for determination of propranolol in pharmaceutical formulation. Analusis. 2000, 28, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giahi, M.; Mirzaei, M.; Veghar Lahijani, G. Potentiometric PVC membrane sensors for the determination of phenylephrine hydrochloride in some pharmaceutical products. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşofreţ, V.V.; Buck, R.P. A poly (vinylchloride) membrane electrode for determination of phenytoin in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 1986, 6, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Coşofreţ, V.V.; Buck, R.P. A chloroquine membrane electrode with low detection limit. Anal. Chim. Acta 1985, 174, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, K.; De Maesschalck, R.; Bohets, H.; Vanhoutte, K.; Nagels, L. In situ dissolution testing using potentiometric sensors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Bohets, H.; Vanhoutte, K.; de Maesschalck, R.; Cockaerts, P.; Vissers, B; Nagels, J.L. Development of in situ ion selective sensors for dissolution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 581, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheubel, E.; Lindenberg, M.; Beyssac, E.; Cardot, J.M. Small volume dissolution testing as a powerful method during pharmaceutical development. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffner, C. Regulatory aspects of drug dissolution from a European perspective. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Analytical electrochemistry, 3rd ed; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, N.J. USA, 2006; p. 189. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sundfors, F. Solid-contact ion Sensors: Materials and properties. Ph.D. Thesis, Åbo Akademi University, Finland, June 2010. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Coşofreţ, V.V.; Buck, R.P. Recent advances in pharmaceutical analysis with potentiometric membrane sensors. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1993, 24, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaviuhkola, T.; Bobacka, J.; Nissinen, M.; Rissanen, K.; Ivaska, A.; Pursiainen, J. Synthesis characterization and complexation of tetraarylborates with aromatic cations and their use in chemical sensors. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Mattinen, U.; Rabiej, S.; Lewenstam, A.; Bobacka, J. Impedance study of the ion-to-electron transduction process for carbon cloth as solid-contact material in potentiometric ion sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 10683–10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Buhlmann, P.; Pretsch, E. Carrier-based ion-selective electrodes and bulk optodes. 1. General characteristics. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 3083–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa, Y.; Umezawa, K.; Sato, H. Selectivity coefficients for ion-selective electrodes: Recommended methods for reporting KpotA,B values. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadrashta, S.M.; Katikaneni, P.R.; Hileman, G.A.; Keshary, P.R. Direct compression controlled release tablets using ethylcellulose. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1993, 19, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikaneni, P.R.; Upadrashta, S.M.; Neau, S.H.; Mitra, A.K. Ethyl cellulose matrix controlled-release tablets of water soluble. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 123, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, F.; Hoffmann, A.; Leclercq, B.; Carlin, B.; Siepmann, J. How to adjust desired drug release patterns from ethylcellulose-coated dosage forms. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kohda, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Baba, Y.; Yuasa, H.; Ozeki, T.; Kanaya, Y.; Sagara, E. Controlled release of lidocaine hydrochloride from buccal mucosa-adhesive films with solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 158, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vakili, H.; Genina, N.; Ehlers, H.; Bobacka, J.; Sandler, N. Using Ion-Selective Electrodes to Study the Drug Release from Porous Cellulose Matrices. Pharmaceutics 2012, 4, 366-376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics4030366
Vakili H, Genina N, Ehlers H, Bobacka J, Sandler N. Using Ion-Selective Electrodes to Study the Drug Release from Porous Cellulose Matrices. Pharmaceutics. 2012; 4(3):366-376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics4030366
Chicago/Turabian StyleVakili, Hossein, Natalja Genina, Henrik Ehlers, Johan Bobacka, and Niklas Sandler. 2012. "Using Ion-Selective Electrodes to Study the Drug Release from Porous Cellulose Matrices" Pharmaceutics 4, no. 3: 366-376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics4030366
APA StyleVakili, H., Genina, N., Ehlers, H., Bobacka, J., & Sandler, N. (2012). Using Ion-Selective Electrodes to Study the Drug Release from Porous Cellulose Matrices. Pharmaceutics, 4(3), 366-376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics4030366