Optimization of Salbutamol Sulfate Dissolution from Sustained Release Matrix Formulations Using an Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental design
| Formulation | Methocel® K100M (mg) | Xanthan gum (mg) | Carbopol® 974P (mg) | Surelease® (% w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAL001 | 120 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL002 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL003 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 4 |
| SAL004 | 60 | 50 | 20 | 12 |
| SAL005 | 90 | 75 | 15 | 16 |
| SAL006 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 20 |
| SAL007 | 90 | 25 | 15 | 16 |
| SAL008 | 30 | 75 | 15 | 16 |
| SAL009 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL010 | 90 | 75 | 5 | 8 |
| SAL011 | 0 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL012 | 30 | 25 | 5 | 16 |
| SAL013 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL014 | 30 | 25 | 15 | 8 |
| SAL015 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL016 | 60 | 100 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL017 | 90 | 75 | 5 | 16 |
| SAL018 | 30 | 25 | 15 | 16 |
| SAL019 | 90 | 25 | 5 | 8 |
| SAL020 | 90 | 75 | 15 | 8 |
| SAL021 | 30 | 75 | 5 | 16 |
| SAL022 | 30 | 25 | 5 | 8 |
| SAL023 | 30 | 75 | 5 | 8 |
| SAL024 | 90 | 25 | 15 | 8 |
| SAL025 | 60 | 50 | 0 | 12 |
| SAL026 | 90 | 25 | 5 | 16 |
| SAL027 | 60 | 0 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL028 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL029 | 60 | 50 | 10 | 12 |
| SAL030 | 30 | 75 | 15 | 8 |
2.3. Manufacture of sustained release matrix tablets
2.4. In vitro dissolution studies
2.5. Artificial neural network

2.6. Optimization procedure

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In vitro dissolution testing
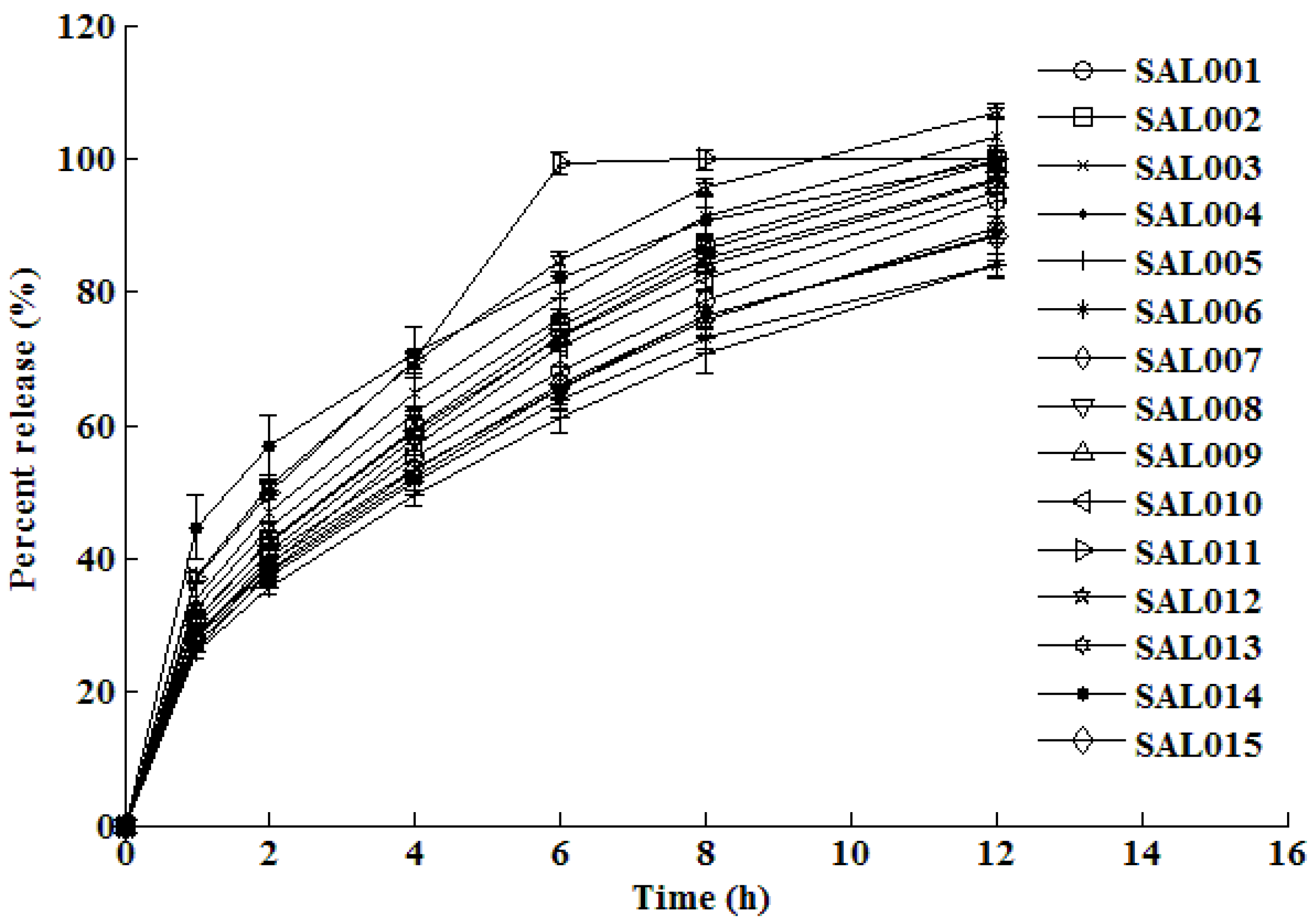
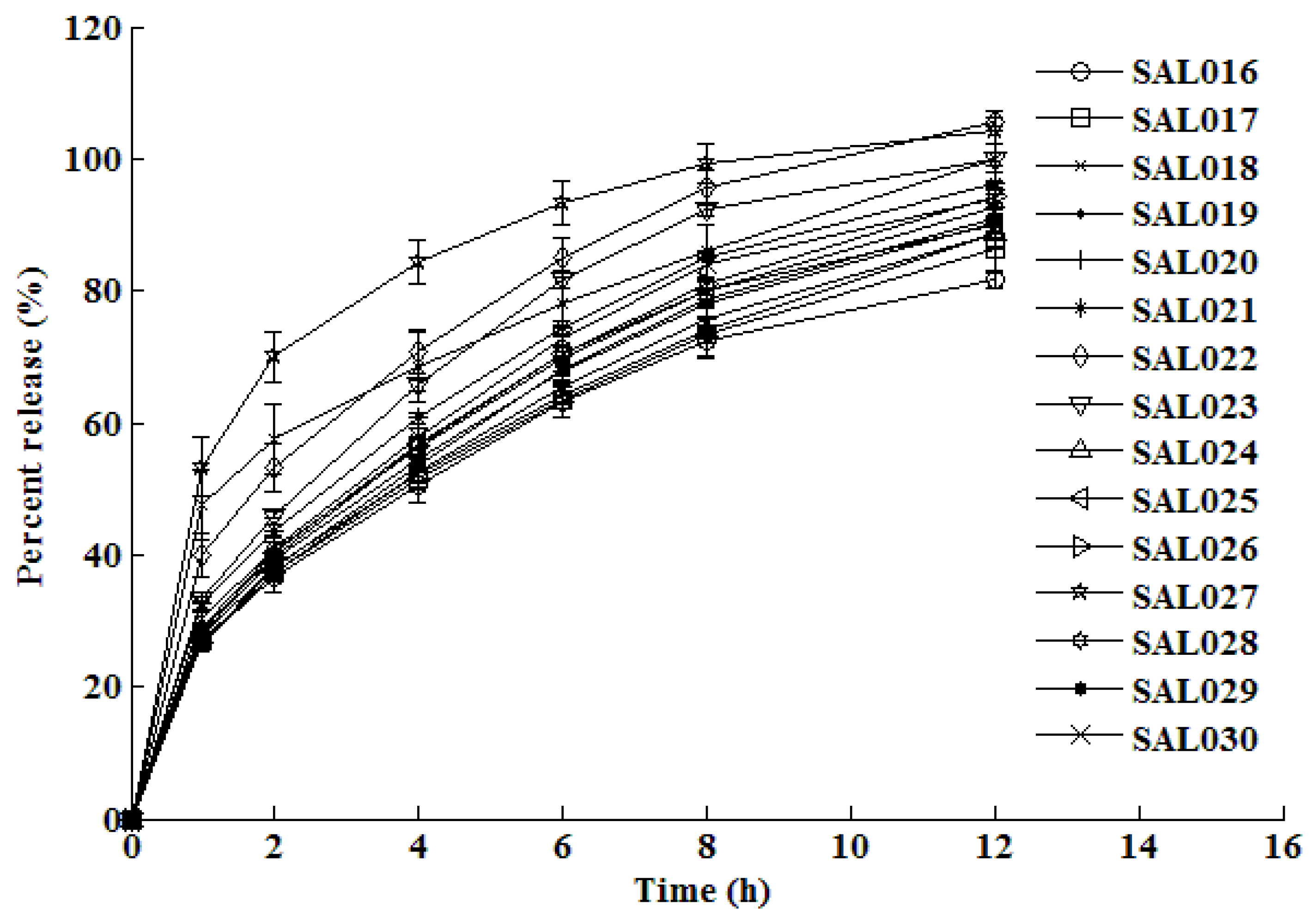
3.2. Training and testing ANN

| Output factor | R2 |
|---|---|
| % Release after 1 h | 0.9366 |
| % Release after 2 h | 0.9501 |
| % Release after 4 h | 0.9366 |
| % Release after 6 h | 0.9508 |
| % Release after 8 h | 0.9181 |
| % Release after 12 h | 0.8323 |

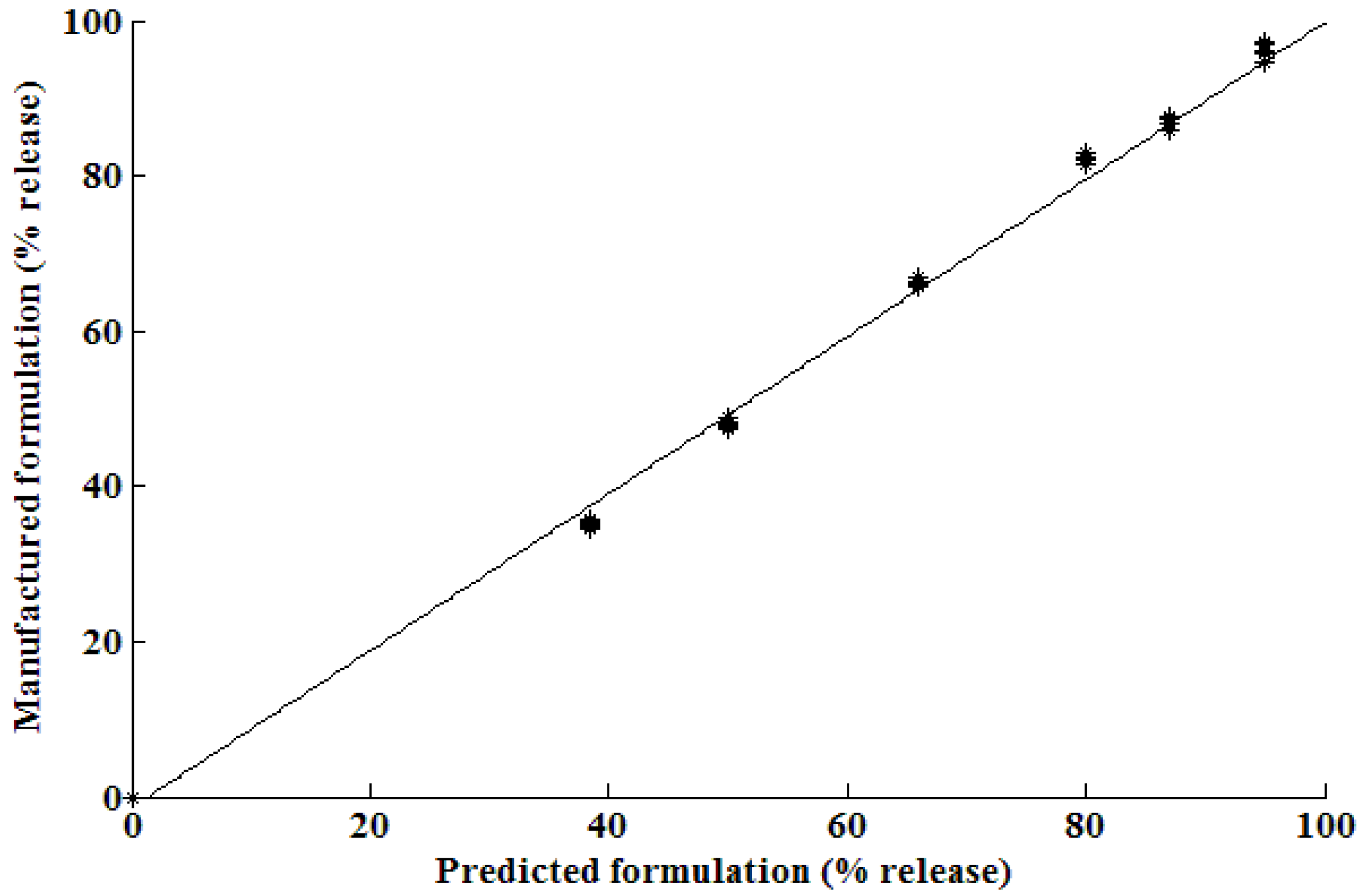
3.3. Simulation ability of the neural network
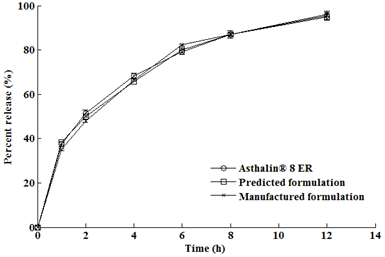
3.4. Optimization results
| Formulation | Predicted dissolution profile | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Methocel® K100M | 45 mg | y1h | 38.38% |
| Xanthan gum | 30 mg | y2h | 49.95% |
| Carbopol® 974P | 5 mg | y4h | 65.87% |
| Surelease® | 10% w/w | y6h | 80.00% |
| Avicel® PH101 | 105.1 mg | y8h | 87.00% |
| Colloidal silica | 0.5% w/w | y12h | 95.00% |
| Magnesium stearate | 1% w/w | f2 factor | 90.5 |

4. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- My Singh, B.; Kumar, R.; Ahuja, N. Optimizing drug delivery systems using systematic "Design of Experiments." Part I: Fundamental aspects. Critical Rev. in Ther. Drug Carrier Systems 2004, 22, 27–105. [Google Scholar]
- Colbourn, E.A. Neural computing in pharmaceutical formulation. Latest Reviews. 2004. Available online: http://www.pharmainfo.net/reviews/neural-computing-pharmaceutical-formulation/ accessed on 21 April 2009.
- Wu, P.C.; Obata, Y.; Fujikawa, M.; Li, C.J.; Higashiyama, K.; Takayama, K. Simultaneous optimization based on artificial neural networks in ketoprofen hydrogel formula containing O-ethyl-3-butylcyclohexanol as percutaneous absorption enhancer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Fujikawa, M.; Obata, Y.; Morishita, M. Neural network based optimization of drug formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 12, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Morva, A.; Fujikawa, M.; Hattori, Y.; Obata, Y.; Nagai, T. Formula optimization of theophylline controlled-release tablet based on artificial neural networks. J. Control. Release 2000, 68, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shukla, A.J. Application of artificial neural networks in the design of controlled release drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourquin, J.; Schmidli, H.; van Hoogevest, P.; Leuenberger, H. Comparison of artificial neural networks (ANN) with classical modelling techniques using different experimental designs and data from a galenical study on a solid dosage form. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 6, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.S.; Yu, X.Q.; Johnson, R.D. Application of neural computing in pharmaceutical product development. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebube, N.K. Intelligent preformulation design and predictions using artificial neural networks. In Preformulation solid dosage form development; Adeyeye, M.C., Brittain, H.G., Eds.; Informa Healthcare: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 81–114. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, R.J. Introduction to backpropagation neural network computation. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, A.S.; Kowalski, J.G.; Rhodes, C.T. Artificial neural Networks - Implications for pharmaceutical sciences. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1995, 21, 119–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Takahara, J.; Fujikawa, M.; Ichikawa, H.; Nagai, T. Formula optimization based on artificial neural networks in transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 1999, 62, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibric, S.; Jovanovic, M.; Djuric, Z.; Parojcic, J.; Petrovic, S.D.; Solomun, L.; et al. Artificial neural networks in the modeling and optimization of aspirin extended release tablets with Eudragit L 100 as matrix substance. AAPS PharmSciTech 2003, 4, E9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; McCall, T.W.; Baichwal, A.R.; Meyer, M.C. The application of an artificial neural network and pharmacokinetic simulations in the design of controlled-release dosage forms. J. Control. Release 1999, 59, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupancic Bozic, D.; Vrecer, F.; Kozjek, F. Optimization of diclofenac sodium dissolution from sustained release formulations using an artificial neural network. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibric, S.; Jovanovic, M.; Djuric, Z.; Parojcic, J.; Solomun, L. The application of generalized regression neural network in the modeling and optimization of aspirin extended release tablets with Eudragit® RS PO as matrix substance. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, J.; Takayama, K.; Nagai, T. Multi-objective simultaneous optimization technique based on an artificial neural network in sustained release formulations. J. Control. Release 1997, 49, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, M.M.; Michoel, A.; Rombaut, P.; Kinget, R. Comparative study on xanthan gum and hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose as matrices for controlled-release drug delivery I. Compaction and in vitro drug release behaviour. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 129, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha Roy, D.; Rohera, B.D. Comparative evaluation of rate of hydration and matrix erosion of HEC and HPC and study of drug release from their matrices. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 16, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Hydrophilic matrices for controlled drug delivery: An improved mathematical model to predict the resulting drug release kinetics (the "Sequential Layer" Model). Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudan Rao, Y.; Krishna Veni, J.; Jayasagar, G. Formulation and evaluation of diclofenac sodium using hydrophilic matrices. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2001, 27, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P. Modelling of drug diffusion through swellable polymeric systems. J. Memb. Sci. 1980, 7, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.I. Diffusional release of a solute from a polymeric matrix -- approximate analytical solutions. J. Memb. Sci. 1980, 7, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujja-areevath, J.; Munday, D.L.; Cox, P.J.; Khan, K.A. Relationship between swelling, erosion and drug release in hydrophilic natural gum mini-matrix formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 6, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vueba, M.L.; de Carvalho, L.A.E.B.; Veiga, F.; Sousa, J.J.; Pina, M.E. Role of cellulose ether polymers on ibuprofen release from matrix tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinís, M.A.; Lugará, S.; Calvo, B.; Hernández, R.M.; Gascón, A.R.; Pedraz, J.L. Release of salbutamol sulfate enantiomers from hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrices. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 161, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.N.; Hiremath, S.R.R. Formulation and evaluation of controlled-release transdermal patches of theophylline-salbutamol sulfate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2001, 27, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, J.J.; Ferrero, C.; Jiménez-Castellanos, M.R. Compaction properties, drug release kinetics and fronts movement studies from matrices combining mixtures of swellable and inert polymers: Effect of HPMC of different viscosity grades. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 351, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Maggi, L.; Segale, L.; Ochoa Machiste, E.; Conte, U.; Grenier, P.; Vergnault, G. Matrices containing NaCMC and HPMC: 2. Swelling and release mechanism study. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 333, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baveja, S.K.; Rao, K.V.R. Sustained release tablet formulation of centperazine. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 31, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baveja, S.K.; Ranga Rao, K.V.; Padmalatha Devi, K. Zero-order release hydrophilic matrix tablets of [beta]-adrenergic blockers. Int. J. Pharm. 1987, 39, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.M.; Jiabi, Z. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of ibuprofen-carbopol® 974P-NF controlled release matrix tablets III: influence of co-excipients on release rate of the drug. J. Control. Rel. 1998, 54, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, M.J.; Andrews, A.; Whiteker, R.; Banner, S.C. Studies on drug release kinetics from carbomer matrices. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1994, 20, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Schwartz, J.B. Studies on drug release from a carbomer tablet matrix. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1995, 21, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid Khan, G.; Bi Zhu, J. Ibuprofen release kinetics from controlled-release tablets granulated with aqueous polymeric dispersion of ethylcellulose II: Influence of several parameters and coexcipients. J. Control. Release 1998, 56, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.; San, Y.P.; Ho, H.O.; Wu, J.S.; Sheu, M.T. Film-forming polymer-granulated excipients as the matrix materials for controlled release dosage forms. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salbutamol. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, Electronic Version 2009; Available online: http://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/martindale/current/ms-2104-z.htm/ accessed 21 February 2009.
- Calverley, P.M.A. Modern treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Resp. J. 2001, 18, 60s–66s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Flanner, H.H. Mathematical comparison of dissolution profiles. Pharm. Tech. 1996, 20, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht-Nielsen, R. Kolmogorov's mapping neural network existence theorem. In Proceedings of the first IEEE international conference on neural networks, San Diego CA, USA, 1987; pp. 11–14.
- Carpenter, W.C.; Hoffman, M.E. Understanding neural network approximation and polynomial approximations helps neural network performance. AI Expert 1995, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Plumb, A.P.; Rowe, R.C.; York, P.; Brown, M. Optimisation of the predictive ability of artificial neural network (ANN) models: A comparison of three ANN programs and four classes of training algorithm. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 25, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaibva, F.; Burton, M.; Walker, R.B. Optimization of Salbutamol Sulfate Dissolution from Sustained Release Matrix Formulations Using an Artificial Neural Network. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 182-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020182
Chaibva F, Burton M, Walker RB. Optimization of Salbutamol Sulfate Dissolution from Sustained Release Matrix Formulations Using an Artificial Neural Network. Pharmaceutics. 2010; 2(2):182-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020182
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaibva, Faith, Michael Burton, and Roderick B. Walker. 2010. "Optimization of Salbutamol Sulfate Dissolution from Sustained Release Matrix Formulations Using an Artificial Neural Network" Pharmaceutics 2, no. 2: 182-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020182
APA StyleChaibva, F., Burton, M., & Walker, R. B. (2010). Optimization of Salbutamol Sulfate Dissolution from Sustained Release Matrix Formulations Using an Artificial Neural Network. Pharmaceutics, 2(2), 182-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020182