Enhancing the Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Trimethoprim Through PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
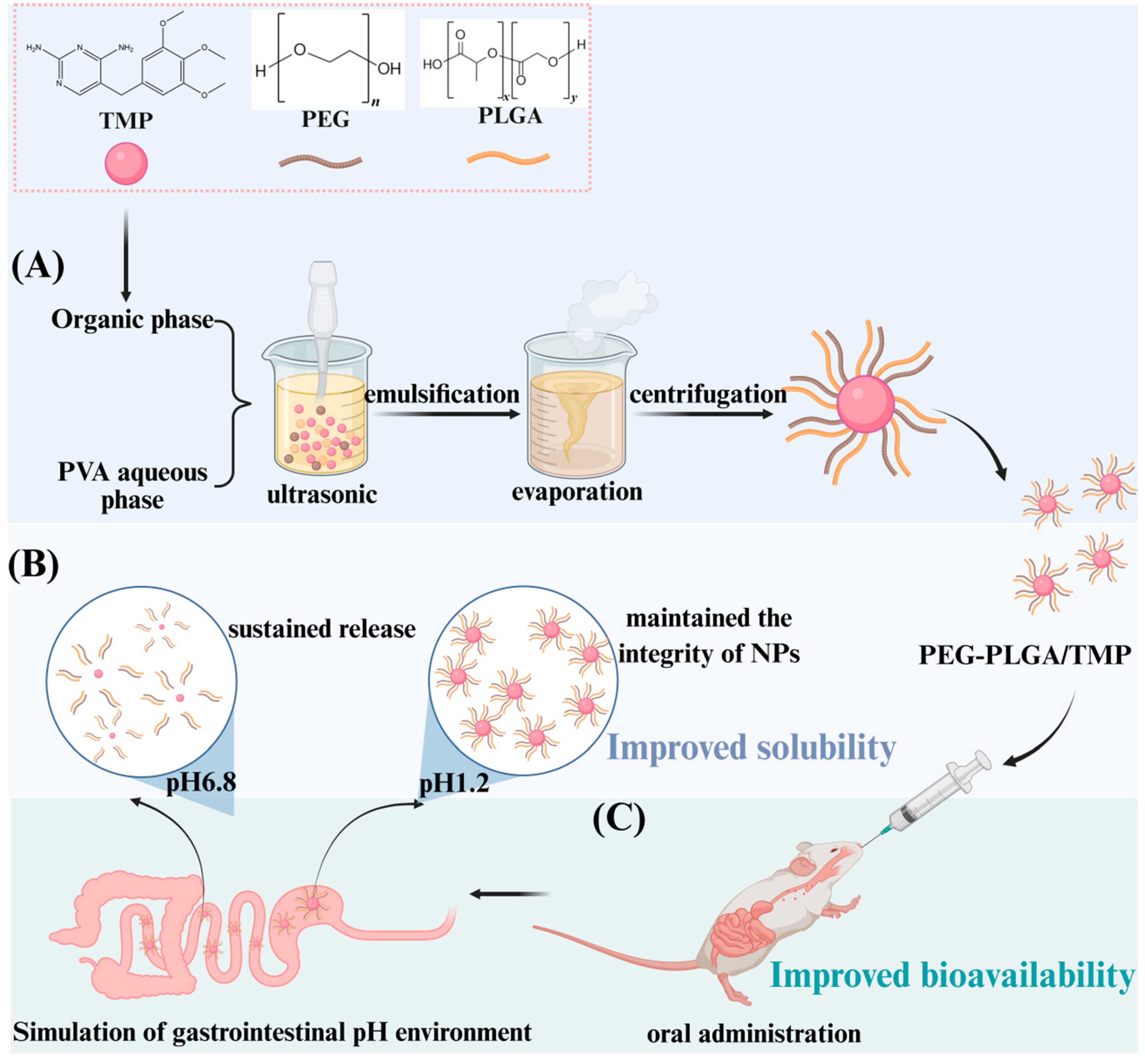
2.2. Preparation of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs by Emulsification Method
2.3. Characterization of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs
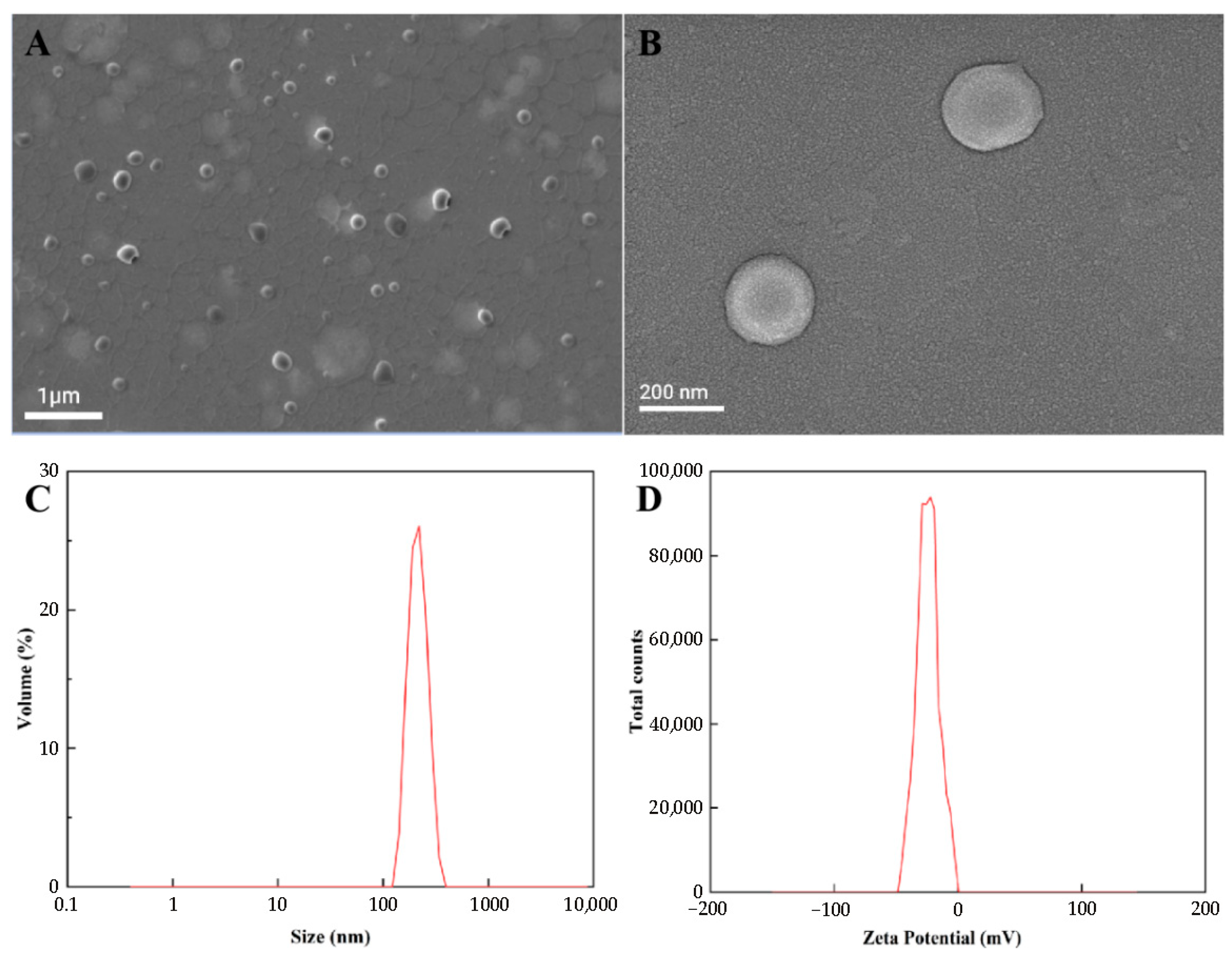
2.3.1. Particle Size, PDI, Zeta Potential, and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
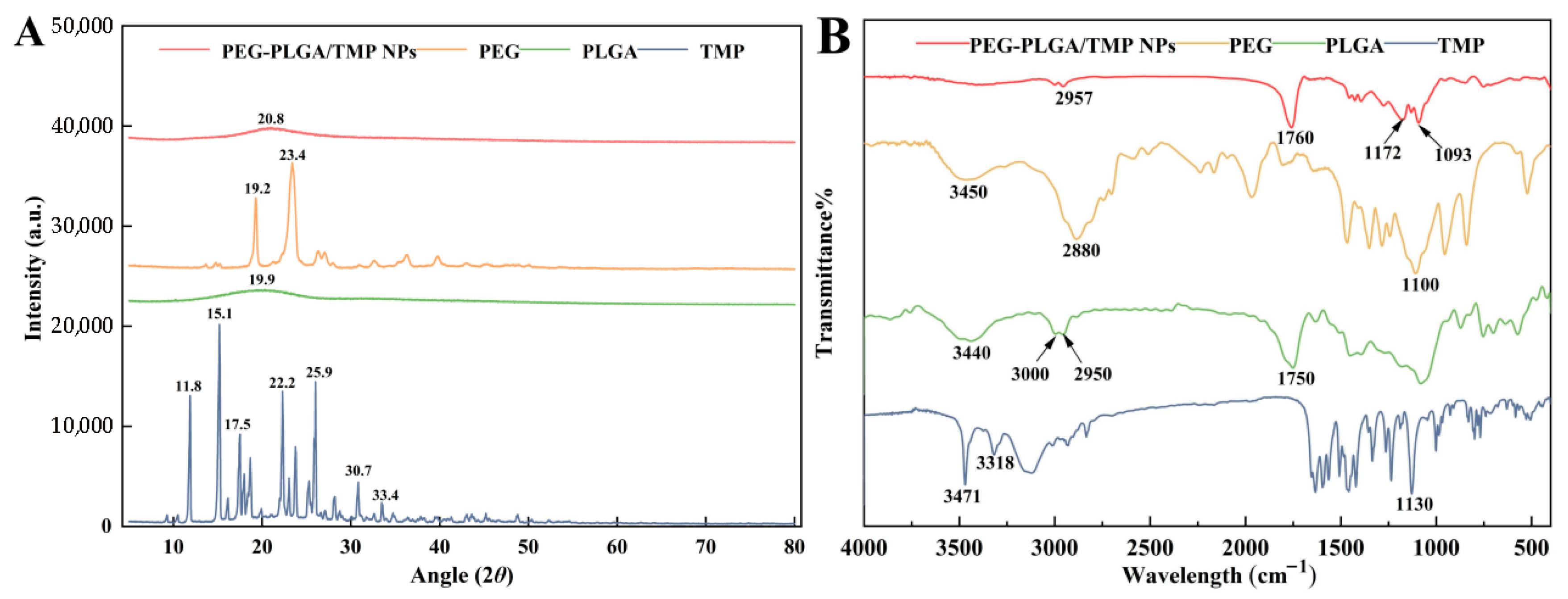
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.3.4. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
2.4. LC and EE of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs
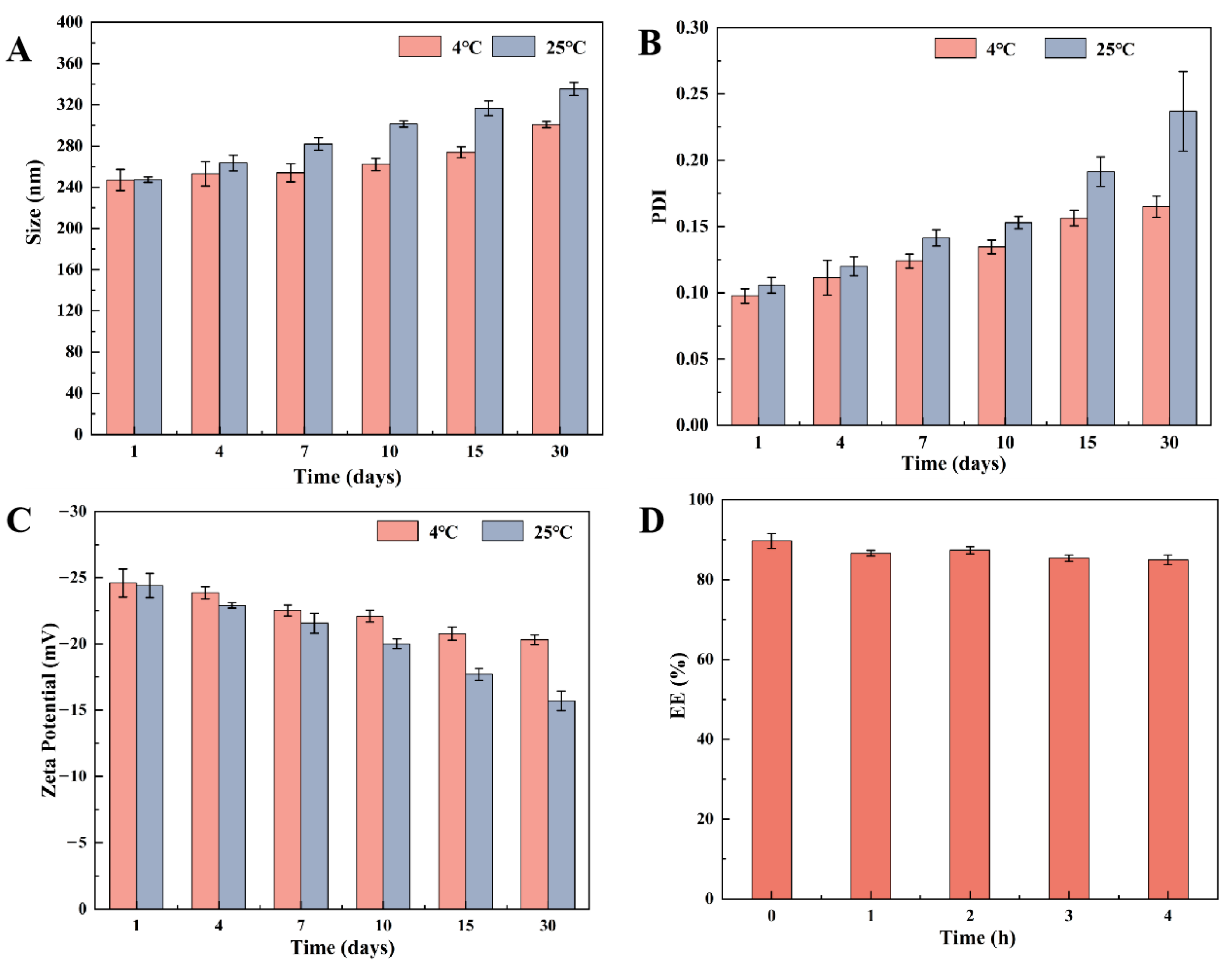
2.5. Stability of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs
2.6. In Vitro Release of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs
2.7. Evaluation of the Ex Vivo and In Vivo Relevance of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs
2.8. Animals
2.9. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.10. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.10.1. Pharmacokinetic Assay
2.10.2. Sample Preparation
2.10.3. Data Preparation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs
3.2. Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Static Stability and Stability in Acidic Media
3.4. In Vitro Release
3.5. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
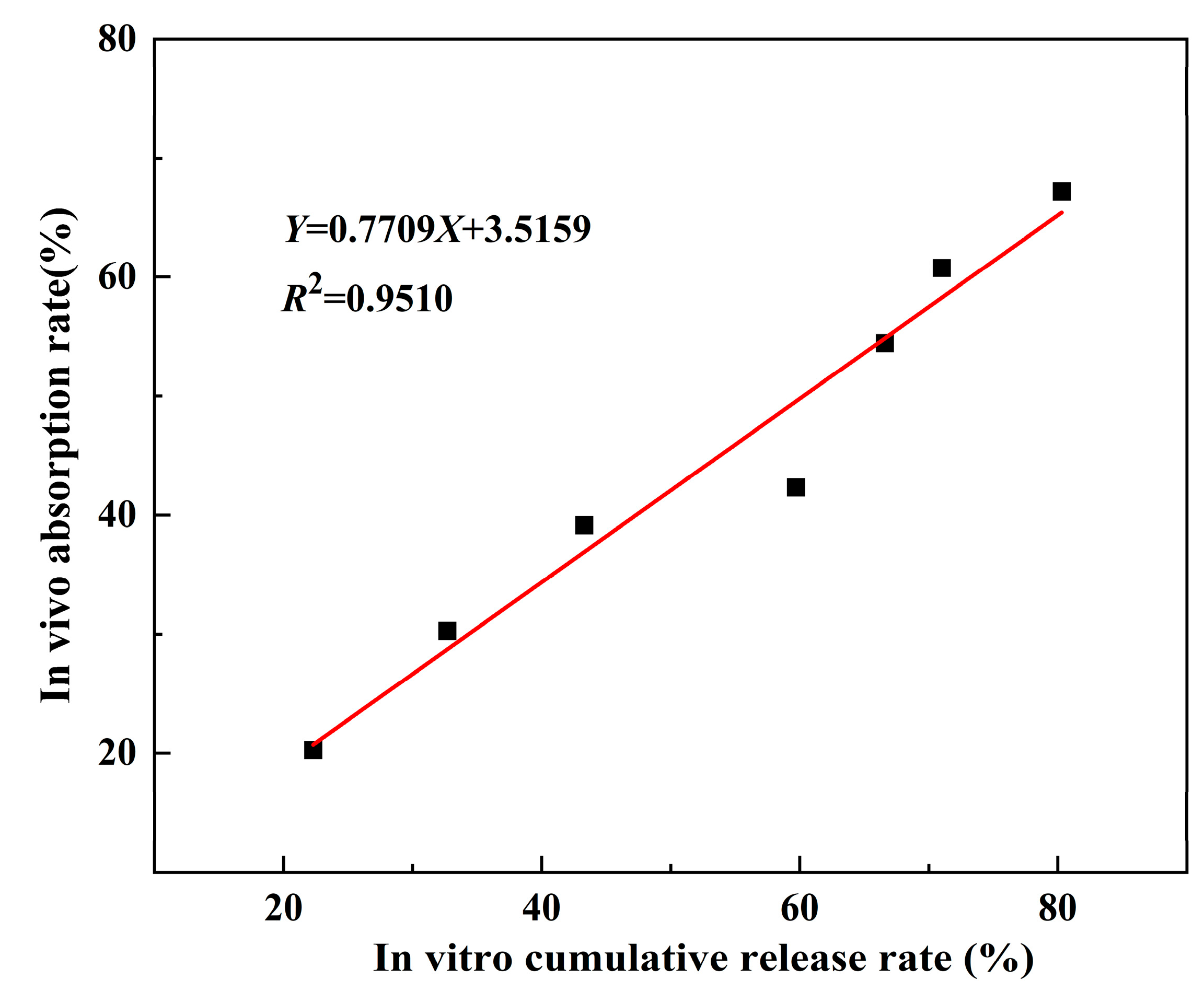
3.6. Evaluation of Ex Vivo and In Vivo Relevance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bodro, M.; Paterson, D.L. Has the Time Come for Routine Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Prophylaxis in Patients Taking Biologic Therapies? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, M.S.; Tamer, Y.T.; Gaszek, I.; Poulides, N.; Ahmed, A.; Wang, X.; Toprak, F.C.R.; Woodard, D.R.; Koh, A.Y.; Williams, N.S.; et al. A Trimethoprim Derivative Impedes Antibiotic Resistance Evolution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilchik, M.W.; Morris, A.S.; Reeves, D.S. Immunosuppressive Powers of the Antibacterial Agent Trimethoprim. Nature 1970, 227, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klugman, K.P.; Madhi, S.A.; Huebner, R.E.; Kohberger, R.; Mbelle, N.; Pierce, N. A Trial of a 9-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Children with and Those without HIV Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; Clark, A.B.; Cahn, T.; Chilvers, E.R.; Fraser, W.; Hammond, M.; Livermore, D.M.; Maher, T.M.; Parfrey, H.; Swart, A.M.; et al. Effect of Co-Trimoxazole (Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole) vs. Placebo on Death, Lung Transplant, or Hospital Admission in Patients With Moderate and Severe Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The EME-TIPAC Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feurle, G.E.; Moos, V.; Blker, H.; Loddenkemper, C.; Moter, A.; Stroux, A.; Marth, T.; Schneider, T. Intravenous Ceftriaxone, Followed by 12 or Three Months of Oral Treatment with Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole in Whipple’s Disease. J. Infect. 2013, 66, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Reid, C.J.; Kudinha, T.; Jarocki, V.M.; Djordjevic, S.P. Genomic Analysis of Trimethoprim-Resistant Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanthavong, V.; Vigad, N.; Pelyuntha, W.; Yamik, D.Y.; Vongkamjan, K.; Yingkajorn, M.; Chaisowwong, W.; Tippaya, K.; Tadee, P.; Chukiatsiri, K. Effectiveness of a Single-Dose Phage Cocktail on the Reduction of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli in Suckling Piglets. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 302, 110395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.-H.; Sun, B.-B.; Zuo, B.-X.-Z.; Chen, X.-Q.; Du, A.-F. Prevalence and Drug Resistance of Avian Eimeria Species in Broiler Chicken Farms of Zhejiang Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Bakht, U.; Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Adelnia, H.; Abdollahi, S.H.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H.; Raza, A. A PEGylated Nanostructured Lipid Carrier for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Antibiotics. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlan, R.; Mcdonald, C.; Sunderland, V.B. Solubilities and Intrinsic Dissolution Rates of Sulphamethoxazole and Trimethoprim. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnero, C.; Zoppi, A.; Genovese, D.; Longhi, M. Studies on Trimethoprim:Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin: Aggregate and Complex Formation. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2550–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-N.; Xiong, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-H. Inclusion Complex of Trimethoprim with β-Cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Hong, M.; Xie, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, S. Progress and Prospects of Nanomaterials against Resistant Bacteria. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ding, L.; Liu, G. Nanoparticle Formulations for Therapeutic Delivery, Pathogen Imaging and Theranostic Applications in Bacterial Infections. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1545–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauner, B.; Schwarz, P.; Wirth, M.; Gabor, F. Micro vs. Nano: PLGA Particles Loaded with Trimethoprim for Instillative Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Tang, G.; Yao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, C.; Fu, Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. Formulation of pH-Responsive PEGylated Nanoparticles with High Drug Loading Capacity and Programmable Drug Release for Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadani, C.M.; Dasanayake, G.S.; Gorniak, M.E.; Pride, M.C.; Monroe, W.; Chism, C.M.; Heintz, R.; Jarrett, E.; Singh, G.; Edgecomb, S.X.; et al. Development of Ionic Liquid-Coated PLGA Nanoparticles for Applications in Intravenous Drug Delivery. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 2509–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X. Macrophage-Evading and Tumor-Specific Apoptosis Inducing Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; Russo, D.; Prévost, S.; Teixeira, J.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Based Surfactant Reduces the Conformational Change of Adsorbed Proteins on Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4282–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in Drug Delivery: Pros and Cons as Well as Potential Alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheffey, V.V.; Siew, E.B.; Tanner, E.E.L.; Eniola-Adefeso, O. PLGA’s Plight and the Role of Stealth Surface Modification Strategies in Its Use for Intravenous Particulate Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-B.; Chen, Z.-X.; Gao, F.; Zhang, C.; Zou, M.-Z.; Ye, J.-J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Remodeling Extracellular Matrix Based on Functional Covalent Organic Framework to Enhance Tumor Photodynamic Therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 234, 119772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Wu, M.; Yuan, M.; Wu, M.; Shen, A.; Chen, Y.; Lian, D.; Liu, X.; Peng, J. Enhancing the Therapeutic Potential of Isoliensinine for Hypertension through PEG-PLGA Nanoparticle Delivery: A Comprehensive in Vivo and in Vitro Study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Pillay, V. Comparative Nanofabrication of PLGA-Chitosan-PEG Systems Employing Microfluidics and Emulsification Solvent Evaporation Techniques. Polymers 2020, 12, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Tao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Meng, K.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; et al. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Enteric Coating for Improving Stability, Palatability, and Oral Bioavailability of Enrofloxacin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.; Peña-Bahamonde, J.; Shakiba, S.; Astete, C.E.; Louie, S.M.; Sabliov, C.M.; Rodrigues, D.F. Prevention of Infection Caused by Enteropathogenic E. coli O157:H7 in Intestinal Cells Using Enrofloxacin Entrapped in Polymer Based Nanocarriers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; Tan, D.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, F.; Yang, Z. Preparation, Characterization, and Ex Vivo Evaluation of Isoxanthohumol Nanosuspension. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 667, 124909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, S.R.; Gao, X. Monodisperse Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biodetection, Imaging, and Drug Delivery: A Versatile and Evolving Technology. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 583–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, K.; Kaplan, M.; Çalış, S. Effects of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Zeta Potential on Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoustafa, H.A.; Alshawsh, M.A.; Chik, Z. Technical Aspects of Preparing PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles as Carrier for Chemotherapeutic agents by Nanoprecipitation Method. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Shu, B.; Deng, X.; Qian, K.; Pan, R.; Qiu, S.; Yang, J.; Fu, Q.; Ma, Y. Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity, Acute Toxicity, and Solubility of Co-Crystals of 5-Fluorouracil and Trimethoprim. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21522–21530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollaeva, M.R.; Yabbarov, N.; Sokol, M.; Chirkina, M.; Mollaev, M.D.; Zabolotskii, A.; Seregina, I.; Bolshov, M.; Kaplun, A.; Nikolskaya, E. Optimization, Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Study of Meso-Tetraphenylporphyrin Metal Complex-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, M.S.; Thangam, R.; Sundarraj, S.; Sheena, T.S.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Kulandaivel, J.; Thirumurugan, R. Co-Delivery of Diverse Therapeutic Compounds Using PEG–PLGA Nanoparticle Cargo against Drug-Resistant Bacteria: An Improved Anti-Biofilm Strategy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djellouli, F.; Dahmani, A.; Hassani, A. Characterization of the Polymorph Changes in Trimethoprim. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.A.; Tawfeek, H.M.; Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A.; Harashima, H. Clinical Translation of Nanomedicines: Challenges, Opportunities, and Keys. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 181, 114083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, F.; Duan, W.; Mu, X.; Fang, S.; Lu, N.; Zhou, X.; Kong, W. Engineering a “PEG-g-PEI/DNA Nanoparticle-in- PLGA Microsphere” Hybrid Controlled Release System to Enhance Immunogenicity of DNA Vaccine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yang, S.; Fang, S.; Li, L.; Jing, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Lu, Y. PLGA Nanoparticles Enhanced Cardio-Protection of Scutellarin and Paeoniflorin against Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Ischemia in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 648, 123567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalba, S.; Ten Hagen, T.L.M.; Burgui, C.; Garrido, M.J. Stealth Nanoparticles in Oncology: Facing the PEG Dilemma. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Time (min) | Mobile Phase A | Mobile Phase B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80 | 20 |
| 1 | 80 | 20 |
| 7 | 20 | 80 |
| 8 | 20 | 80 |
| 9 | 80 | 20 |
| 13 | 80 | 20 |
| Levels | Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (TMP, mg/mL) | Concentration (PVA, %) | Sonication Power (W) | Centrifugation Speed (rcf) | |
| 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 200 | 14,000 |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | 250 | 16,000 |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 300 | 20,000 |
| Sample | Concentration (TMP, mg/mL) | Concentration (PVA, %) | Sonication Power (W) | Centrifugal Speed (rcf) | LC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10.4 ± 0.2 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10.9 ± 0.3 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 17.5 ± 0.6 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 34.0 ± 1.6 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 26.3 ± 1.1 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 15.6 ± 0.4 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 22.8 ± 1.3 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 14.6 ± 0.4 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 20.0 ± 1.2 |
| K1 | 38.8 | 67.2 | 40.6 | 56.7 | |
| K2 | 75.9 | 51.8 | 64.9 | 49.3 | |
| K3 | 57.4 | 53.1 | 66.6 | 66.1 | |
| k1 | 12.9 | 22.4 | 13.5 | 18.9 | |
| k2 | 25.3 | 17.3 | 21.6 | 16.4 | |
| k3 | 19.1 | 17.7 | 22.2 | 22.0 | |
| R | 12.4 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 5.6 | |
| Optimum | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | LC (%) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 245 ± 40 | 0.103 ± 0.019 | −23.8 ± 1.2 | 34.0 ± 1.6 | 88.2 ± 4.3 |
| pH 1.2 | pH 6.8 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | R2 | Equation | R2 | |
| Zero order | 0.8048 | 0.5150 | ||
| First order | 0.9886 | 0.9623 | ||
| Higuchi | 0.9408 | 0.7785 | ||
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | 0.9534 | 0.9106 | ||
| Parameter | Unit | TMP | PEG-PLGA/TMP NPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0−t | h·ng/mL | 802 ± 104 | 2134 ± 188 * |
| AUC0−∞ | h·ng/mL | 814 ± 99 | 2298 ± 227 * |
| Cmax | 417.51 ± 23.34 | ||
| Tmax | 0.33 ± 0.13 | ||
| t1/2 | 0.72 ± 0.08 | ||
| MRT | h | 1.27 ± 0.11 | 3.10 ± 0.11 * |
| Vd | L/kg | 25.65 ± 3.29 | 31.97 ± 2.51 * |
| CL | L/h/kg | 24.87 ± 3.26 | 9.03 ± 0.85 * |
| F (%) | / | / | 282.31% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Dai, G.; Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Li, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J. Enhancing the Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Trimethoprim Through PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Performance. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080957
Zhou Y, Dai G, Xu J, Xu W, Li B, Chen S, Zhang J. Enhancing the Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Trimethoprim Through PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Performance. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080957
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yaxin, Guonian Dai, Jing Xu, Weibing Xu, Bing Li, Shulin Chen, and Jiyu Zhang. 2025. "Enhancing the Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Trimethoprim Through PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Performance" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080957
APA StyleZhou, Y., Dai, G., Xu, J., Xu, W., Li, B., Chen, S., & Zhang, J. (2025). Enhancing the Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Trimethoprim Through PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Performance. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080957






