Development and Preclinical Evaluation of Fixed-Dose Capsules Containing Nicergoline, Piracetam, and Hawthorn Extract for Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Evaluation of API–Excipient Thermal Compatibility
2.3. Detection of API–Excipient Interactions
2.4. Solid-State Characterization and Compatibility
2.5. Evaluation of Powder Flow and Compressibility Parameters
2.6. Quantification of NIC, PIR, and HE Flavonoids
2.7. In Vitro Dissolution Profiling
2.8. Stability Studies
2.9. Antioxidant Capacity Assessment
2.10. Acute Toxicity (AT) Evaluation
2.11. Assessment of Ototoxicity (OT) Potential
2.12. Ethical Considerations
3. Results and Discussion
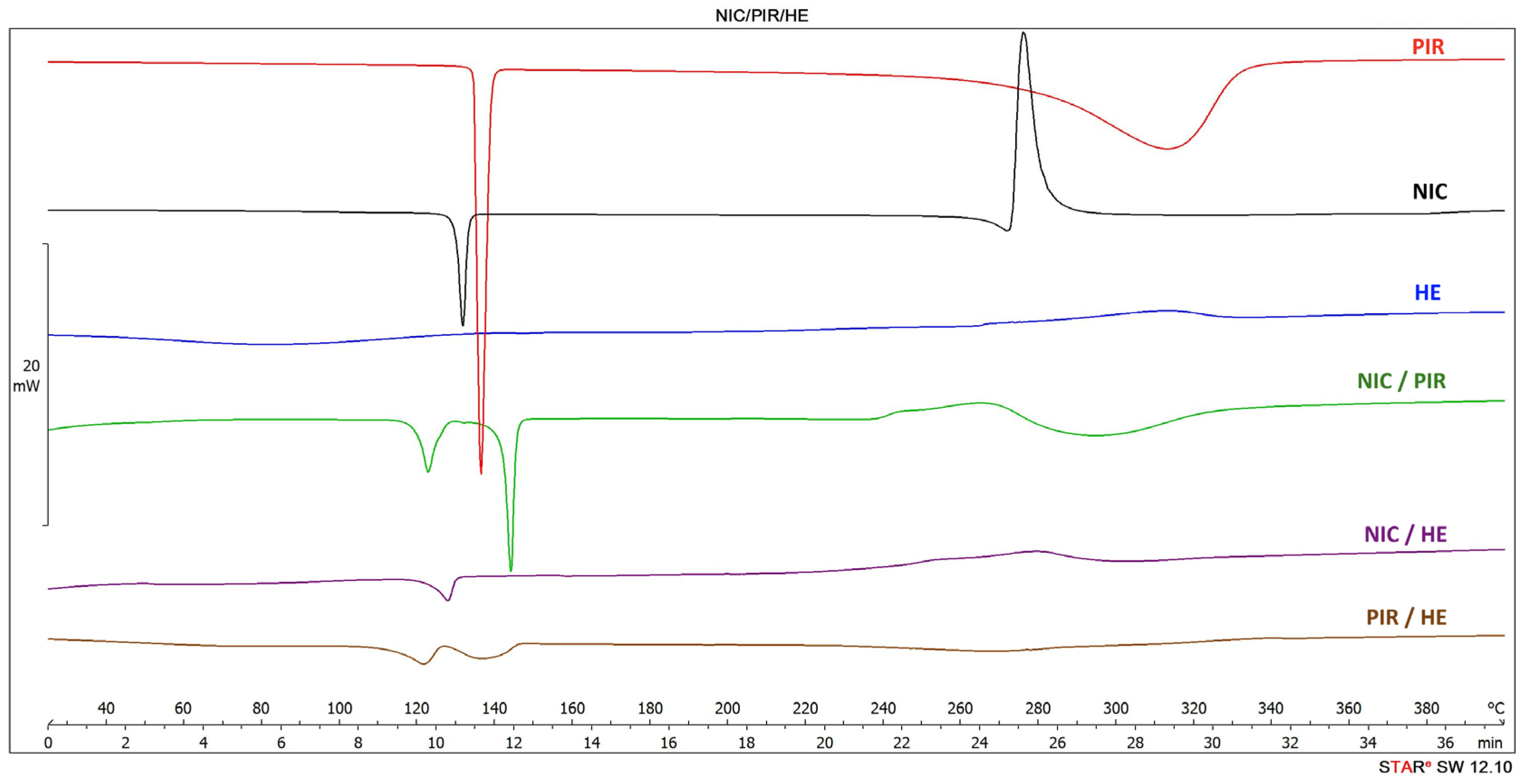
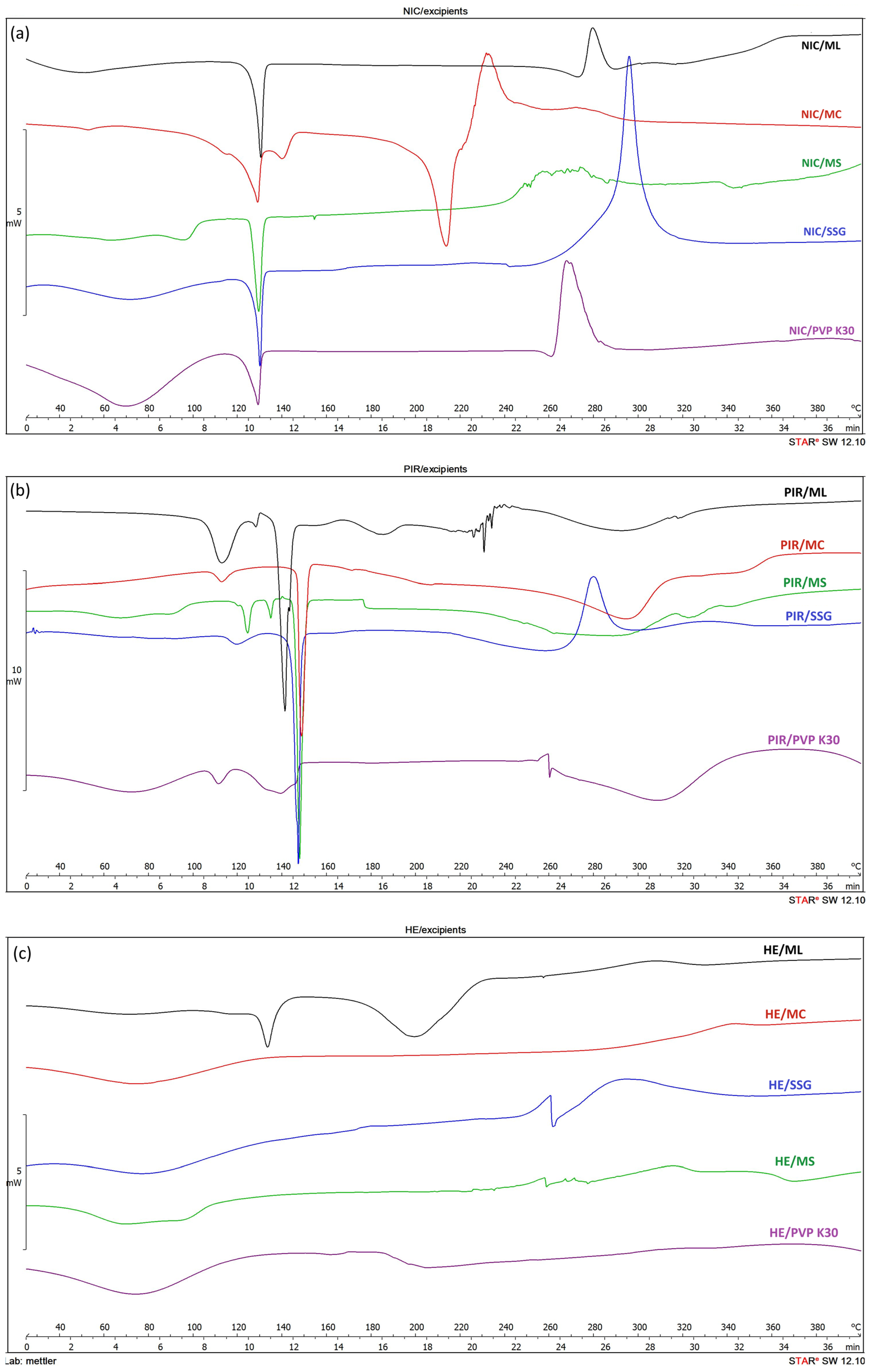
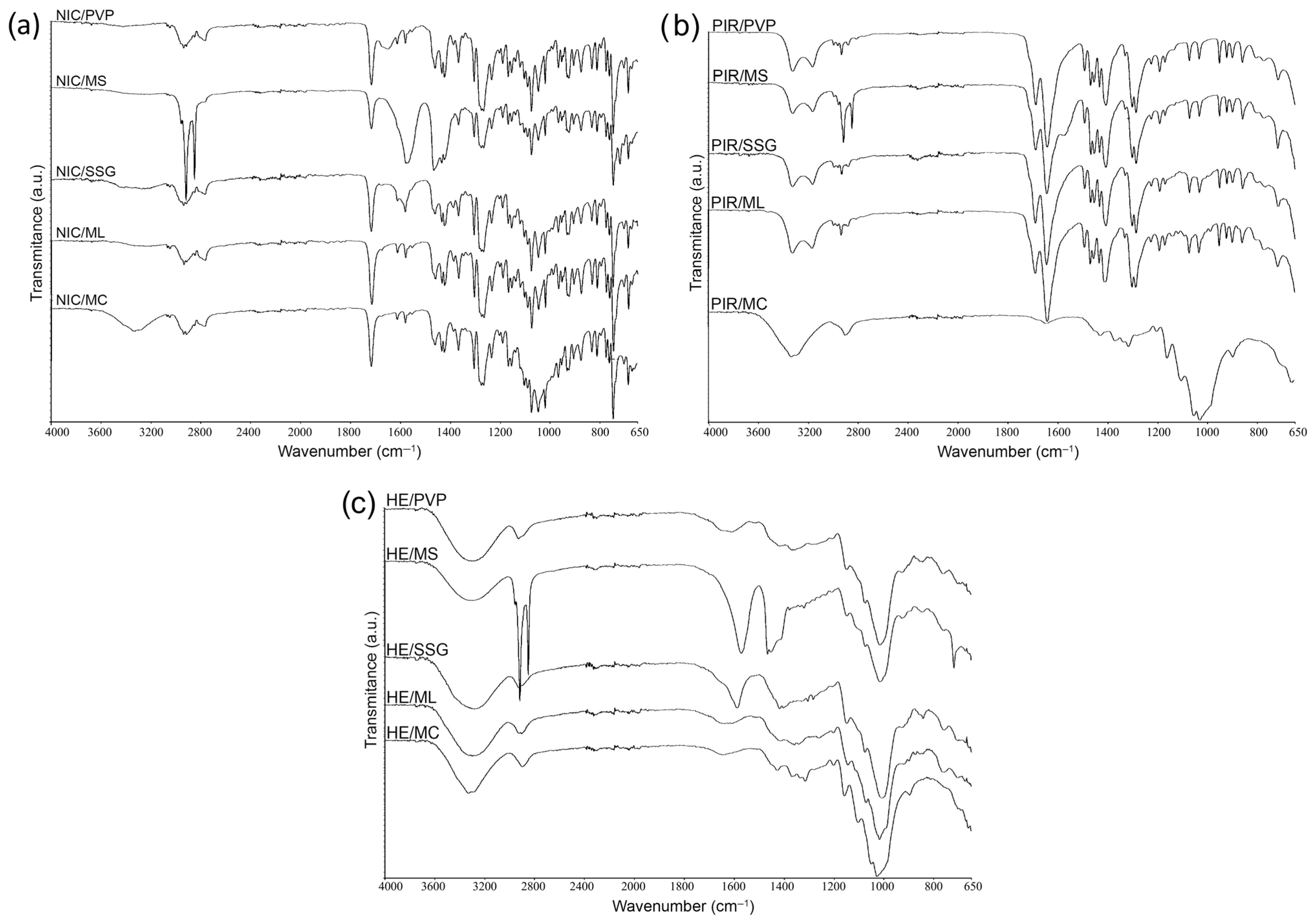
3.1. Physicochemical Compatibility Results
3.1.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.1.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
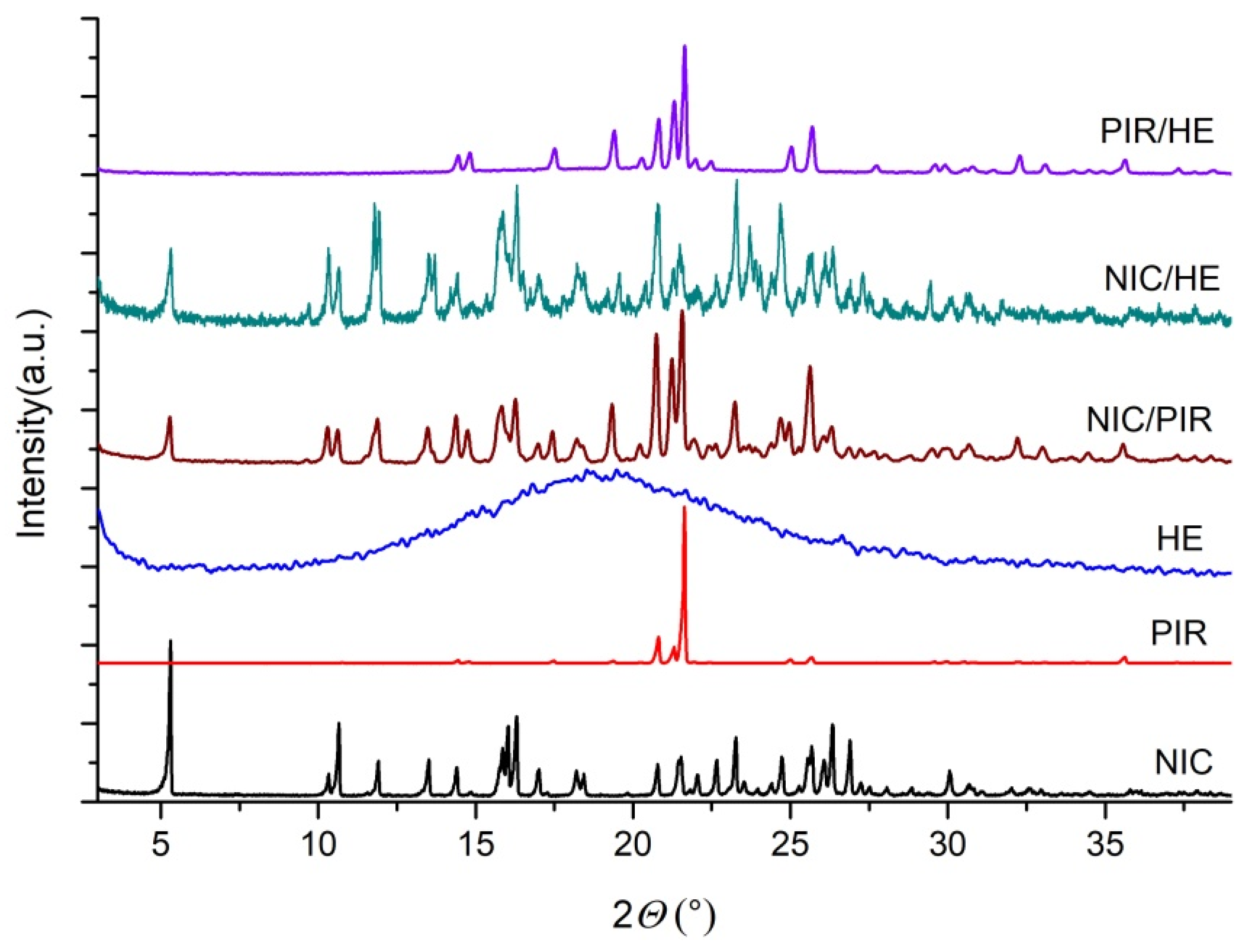
3.1.3. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3.2. Pharmaceutical Formulation Development and Stability Evaluation
3.2.1. Pharmaco-Technological Parameters of Capsule Formulations
3.2.2. Quantification of Active Substances and Flavonoids
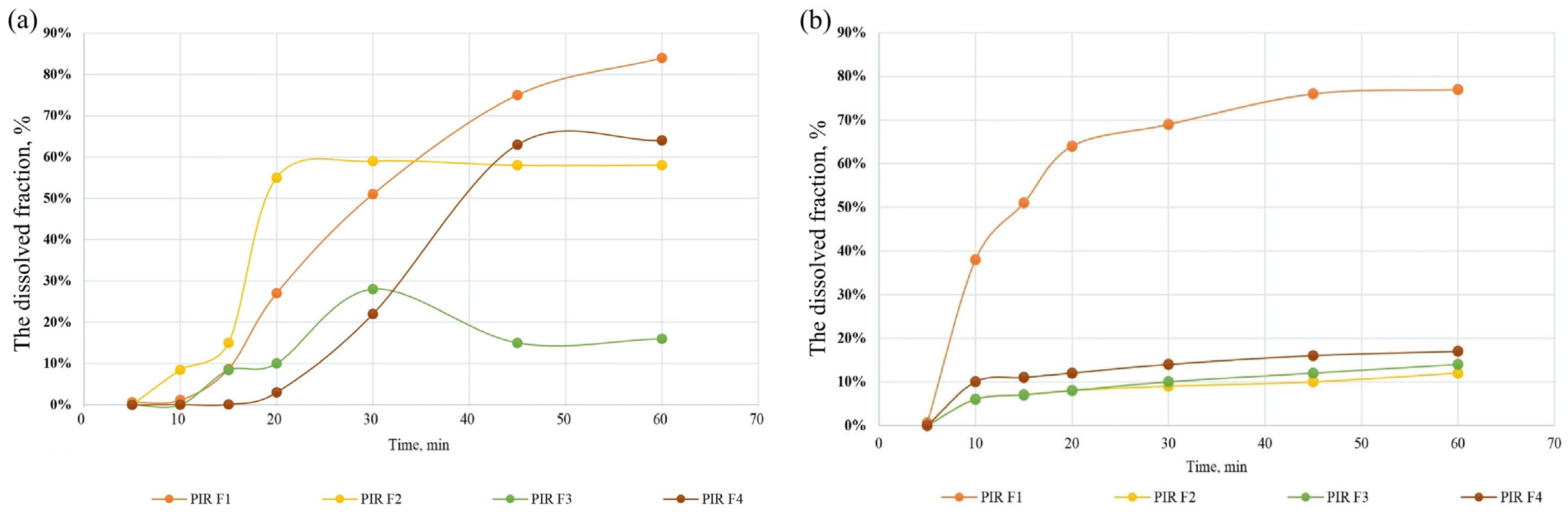
3.2.3. Dissolution Profiles of NIC and PIR in Capsule Formulations
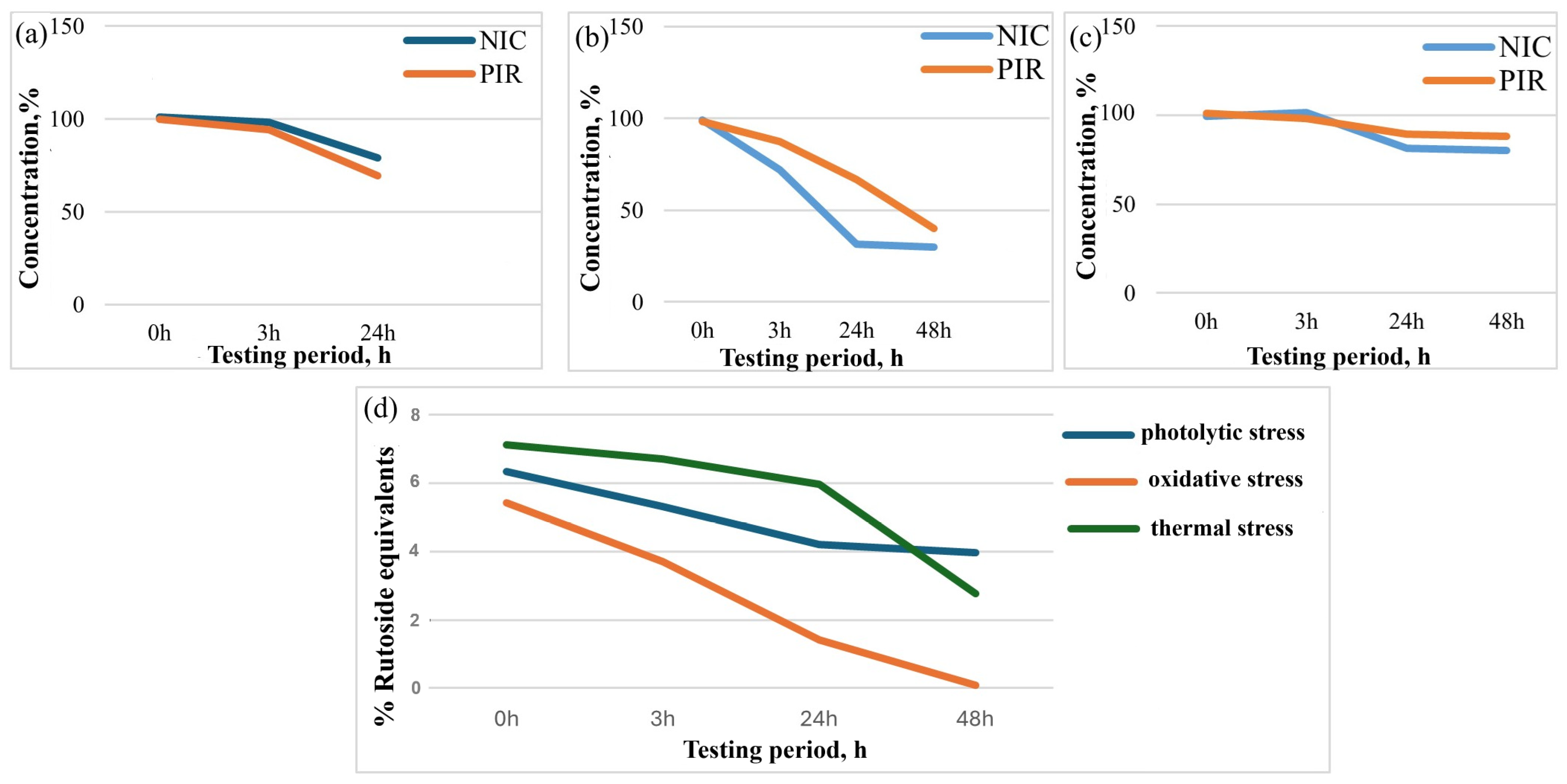
3.2.4. Stability Studies Under Stress Conditions
3.3. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity and Safety
3.3.1. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
3.3.2. Determination of Acute Toxicity
3.3.3. Ototoxicity Studies
3.4. Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snell, E.S. Pharmacological Appraisal of Fixed-Dose Combination Medicines: Discussion Paper. J. R. Soc. Med. 1982, 75, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A. Fixed-Dose Combinations. In Introduction to Basics of Pharmacology and Toxicology Volume 1: General and Molecular Pharmacology: Principles of Drug Action; Marshall, R.G., Ramasamy, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Growth Plus Reports. Fixed-Dose Combination Drugs Market Forecast. 2023–2031. Available online: https://www.growthplusreports.com/report/fixeddose-combination-drugs-market/8498 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Sawicki-Wrzask, D.; Thomsen, M.; Bjerrum, O.J. An Analysis of the Fixed-Dose Combinations Authorized by the European Union, 2009-2014: A Focus on Benefit-Risk and Clinical Development Conditions. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2015, 49, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Deafness and Hearing Loss Fact Sheet. 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Singh, A.; Irugu, D.V. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss–A contemporary review of management issues. J. Otol. 2020, 15, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Xu, B.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y. Intrinsic Mechanism and Pharmacologic Treatments of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Theranostics 2023, 13, 3524–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Hungerford, M.; Luxmore, R.; Ding, D.; Qiu, Z.; Lei, D.; Yang, A.; Liang, R.; Ohlemiller, K.K. Prophylactic and Therapeutic Functions of Drug Combinations against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Hear. Res. 2013, 304, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Fernández, M.A.; Montero-Zeledón, E.; Abdala-Saiz, A.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; Araya-Sibaja, A.M. Interaction and Compatibility Studies in the Development of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide Formulations under a Real Manufacturing Process. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozon, E.A.; Iuga, I.D.M.; Mititelu, M.; Musuc, A.M.; Manolescu, B.N.; Petrescu, S.; Cusu, J.P.; Rusu, A.; Surdu, V.A.; Oprea, E.; et al. Pharmacotechnical, Physico-Chemical, and Antioxidant Evaluation of Newly Developed Capsule Formulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaydo, R.H.; Al Zakri, D.J.; Sakur, A.A.; Lotfy, H.M. Ultraviolet Spectrophotometric Methods for the Determination of the Minor Component Presented in Fixed-Dose Pharmaceutical Combinations through the Last Two Decades (2000–2020). Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharanon, W.; Guo, Y.; Peerapattana, J.; Sun, C.C. A Systematic Comparison of Four Pharmacopoeial Methods for Measuring Powder Flowability. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 661, 124454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.B.; Tawakkul, M.A.; Khan, M.A. Comparative Evaluation of Flow for Pharmaceutical Powders and Granules. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2008, 9, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uncu, L.; Evtodienco, V.; Mazur, E.; Donici, E.; Valica, V. Validation of the Spectrophotometric Method for the Dosing of Some Combined Capsule. Mold. Med. J. 2021, 64, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChemSpider. Royal Society of Chemistry. Available online: https://www.Chemspider.Com (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Fornea, D.; Cereniuc, A.; Uncu, L. Evaluation of the Stability of Nicergoline in Monocomponent Pharmaceuticals and in Combinations. In Proceedings of the Direcții de Reformare a Sistemului Farmaceutic din Perspectiva Cursului European al Republicii Moldova, Ediția a 2-a, Chişinău, Moldova, 28 April 2023; pp. 144–145. [Google Scholar]
- Klamkam, P.; Pagcharoenpol, R.; Treesaranuwattana, T.; Silpsrikul, P.; Jaruchinda, P.; Wasuwat, P. Effectiveness of Nicergoline in Preventing Acoustic Trauma. Res. Sq. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamkam, P.; Pagcharoenpol, R.; Treesaranuwattana, T.; Silpsrikul, P.; Jaruchinda, P.; Wasuwat, P.; Suwannahitatorn, P. A Clinical Trial of Nicergoline to Prevent Temporary Threshold Shift. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, K.; Shaharyar, M.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Sahu, S. Establishment of Inherent Stability on Piracetam by UPLC/HPLC and Development of a Validated Stability-Indicating Method. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S576–S582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, N.Y.; Yilmaz, Y.F.; Gurgen, S.G.; Kum, R.O.; Ozcan, M.; Unal, A. Effects of Parenteral Papaverine and Piracetam Administration on Cochlea Following Acoustic Trauma. Noise Health 2018, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fu, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Yang, S.; et al. Biological Properties and Potential Application of Hawthorn and Its Major Functional Components: A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafakou, M.-E.; Szikora, Z.; Olga Mátyus, R.; Vargáné Szabó, B.; Tóth, B. Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Clinically Significantly Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1027. [Google Scholar]
- Lenarz, T.; Schwieger, J.; Matsunaga, M.; Nakagawa, T. Future Pharmacotherapy for Sensorineural Hearing Loss by Protection and Regeneration of Auditory Hair Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, L.; Gibaja, A.; Scheper, V.; Alvarado, J.C.; Almodovar, C.; Lenarz, T.; Juiz, J.M. Efficacy and Mechanisms of Antioxidant Compounds and Combinations Thereof against Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss in a Rat Model. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Melgar-Rojas, P.; Valero, M.L.; Gabaldón-Ull, M.C.; Miller, J.M.; Juiz, J.M. Synergistic Effects of Free Radical Scavengers and Cochlear Vasodilators: A New Otoprotective Strategy for Age-Related Hearing Loss. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Juiz, J.M. Antioxidants and Vasodilators for the Treatment of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Are They Really Effective? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Stability Testing for New Dosage Forms. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q1C%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products Q1A(R2). Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q1A%28R2%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay. Processes 2023, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Chen, W.; Weng, Y.M.; Tseng, C.Y. Chemical Composition, Physical Properties, and Antioxidant Activities of Yam Flours as Affected by Different Drying Methods. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, Test No. 420: Acute Oral Toxicity—Fixed Dose Procedure. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/test-no-420-acute-oral-toxicity-fixed-dose-procedure_9789264070943-en.html (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Le Prell, C.G.; Ojano-Dirain, C.; Rudnick, E.W.; Nelson, M.A.; DeRemer, S.J.; Prieskorn, D.M.; Miller, J.M. Assessment of Nutrient Supplement to Reduce Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2014, 15, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Martena, V.; Hoti, E.; Malaj, L.; Di Martino, P. Preformulation Study of Nicergoline Solid Dispersions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martena, V.; Censi, R.; Hoti, E.; Malaj, L.; Di Martino, P. Physicochemical Characterization of Nicergoline and Cabergoline in Its Amorphous State. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 108, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, S.; Klukkert, M.; Löbmann, K.A.M.; Strachan, C.J.; Sakmann, A.; Gordon, K.; Rades, T.; Leopold, C.S. Investigation of the Formation Process of Two Piracetam Cocrystals during Grinding. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 706–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiko, B.N.; Kolpakov, I.M. DSC Monitoring of Piracetam Concentration Stability during Experimental Storage. Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Gopalkrishna, B.; Shukla, P. Isolation of Rutin from Phyllanthus Amarus. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, E.; Martínez, E.M.; Cogordán, J.A.; Delgado, G. Triterpenes, Phenols, and Other Constituents from the Leaves of Ochroma Pyramidale (Balsa Wood, Bombacaceae). Preferred Conformations of 8-C-β β-D-Glucopyranosyl-Apigenin (Vitexin). Rev. De La Soc. Química De México 2001, 45, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Pubchem. Compound Summary for CID 1130, Thiamine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Thiamine (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Fernandes, F.H.A.; Santana, C.P.; Santos, R.L.; Correia, L.P.; Conceição, M.M.; MacÊdo, R.O.; Medeiros, A.C.D. Thermal Characterization of Dried Extract of Medicinal Plant by DSC and Analytical Techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 113, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciochi, R.; Diogo, H.P.; Minas Da Piedade, M.E. Thermodynamic Characterization of Three Polymorphic Forms of Piracetam. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Mittal, A.; Ikram, S.; Tyagi, L.; Gupta, C. Solubility Enhancement of Nicergoline Poorly Water Soluble Drug by Novel Melt Sonocrystallization Technique. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2020, 9, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourehab, M.A.S.; Khames, A.; Genedy, S.; Mostafa, S.; Khaleel, M.A.; Omar, M.M.; El Sisi, A.M. Sesame Oil-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Nicergoline, Intranasal Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Synergistic Cerebrovascular Protection. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamancheva, I.; Staneva, T. Determination of Possible Impurities in Piracetam Using FTIR Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 21, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, K.A.M.; El-Olemy, A.; Serag, A.; Abbas, A.E.F.; Eid, S.M. Environmentally Sustainable DRS-FTIR Probe Assisted by Chemometric Tools for Quality Control Analysis of Cinnarizine and Piracetam Having Diverged Concentration Ranges: Validation, Greenness, and Whiteness Studies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 302, 123161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabiazar, R.; Qadir, G.S.; Faqe, Z.A.; Khalid, K.M.; Othman, K.I.; Rasool, N.F.; saeed, H.F. Green Biosynthesis of CdS NPs and CdS/Fe3O4 NCs by Hawthorn Plant Extract for Photodegradation of Methyl Orange Dye and Antibacterial Applications. J. Clust. Sci. 2022, 33, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, M.; Pascu, D.E.; Traistaru, G.A.; Cretu, G.; Nechifor, A.C.; Bunaciu, A.A.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Membrane Separation and Concentration Study of Biological Active Compounds. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2013, 3, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, A.I. Preformulation: The Use of FTIR in Compatibility Studies. J. Innov. Appl. Pharm. Sci. (JIAPS) 2019, 4, 01–06. [Google Scholar]
- Chadha, R.; Bhandari, S. Drug–Excipient Compatibility Screening—Role of Thermoanalytical and Spectroscopic Techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.H.M.; Depaifve, S.; Neveu, A.; Francqui, F.; Dickhoff, B.H.J. Impact of Powder Properties on the Rheological Behavior of Excipients. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Rehman, Z.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Albratty, M.M.; Majrashi, N.H.; Hakami, K.M.; Najmi, N.A.; Mobarki, A.A. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions with QbD for Method Development and Validation of Bosutinib by HPLC: Applications in Dosage Forms and Rat Plasma Analysis. Separations 2023, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Li, F.; Yeh, S.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Xin, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Ling, B. Recent Advances in Enhancement of Dissolution and Supersaturation of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug in Amorphous Pharmaceutical Solids: A Review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ye, M.; Yang, G. The Opposed Effects of Polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 on Dissolution and Precipitation for Indomethacin Supersaturating Drug Delivery Systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Labu, Z.K.; Khan, S.; Ritu, S.M.; Mim, S.; Sarker, M.A.; Rahman, M.T. Optimization of Super Disintegrants in Clonazepam Orally Fast Disintegrating Tablets: Impact on Dissolution, Drug Release and Stability. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shen, L. A Comprehensive Understanding of Disintegrants and Disintegration Quantification Techniques: From the Perspective of Tablet Microstructure. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukaram, N.B.; Rajagopalan, I.V.; Shartchandra, P.S.I. The Effects of Lactose, Microcrystalline Cellulose and Dicalcium Phosphate on Swelling and Erosion of Compressed HPMC Matrix Tablets: Texture Analyzer. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 4, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- González-González, O.; Ramirez, I.O.; Ramirez, B.I.; O’Connell, P.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Torrado, J.J.; Serrano, D.R. Drug Stability: ICH versus Accelerated Predictive Stability Studies. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Liang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, M. Protective Effect of Hawthorn Extract against Genotoxicity Induced by Benzo(<alpha>)Pyrene in C57BL/6 Mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110761. [Google Scholar]
- Lenucci, S.; Papazidou, V.; Makrygiannis, I.; Mantiniotou, M.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Isolation of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Crataegus Monogyna Leaves via Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Extraction. Plants 2025, 14, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezalu, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Salehi, P.; Sonboli, A.; Alirezalu, K.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Barba, F.J.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Physicochemical Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and Phenolic Compounds of Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Fruits Species for Potential Use in Food Applications. Foods 2020, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, F.Z.; Bencheikh, N.; Bouhrim, M.; Saleh, A.; Al kamaly, O.; Parvez, M.K.; Elbouzidi, A.; Bnouham, M.; Zair, T. Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant, and Antihyperglycemic Activities of Crataegus Monogyna Jacq Aqueous Extract. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Park, S.K.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, M.G.; Chung, W.H. Gentamicin Induced Nitric Oxide-Related Oxidative Damages on Vestibular Afferents in the Guinea Pig. Hear. Res. 2006, 211, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjea, D.; Rybak, L.P.; Sheehan, K.E.; Kaur, T.; Ramkumar, V.; Jajoo, S.; Sheth, S. The Design and Screening of Drugs to Prevent Acquired Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2011, 6, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloud, A.; Vilcins, D.; McEwen, B. The Effect of Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review. Adv. Integr. Med. 2020, 7, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, I.; Nam, Y.H.; Shin, S.W.; Seo, G.J.; Kim, N.W.; Nuankaew, W.; Kim, D.H.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Peng, X.H.; et al. Effects of Castanopsis Echinocarpa on Sensorineural Hearing Loss via Neuronal Gene Regulation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.N.; Shin, S.W.; Nam, Y.H.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, N.W.; Kim, M.C.; Nuankaew, W.; Kwak, J.H.; Kang, T.H. Amelioration of Sensorineural Hearing Loss through Regulation of Trpv1, Cacna1h, and Ngf Gene Expression by a Combination of Cuscutae Semen and Rehmanniae Radix Preparata. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharm Sci, P.J.; Wang, B.; Zhong, L.; Qiao, P.; Ma, Z. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Nicergoline Combined with Oxiracetam in the Treatment of Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
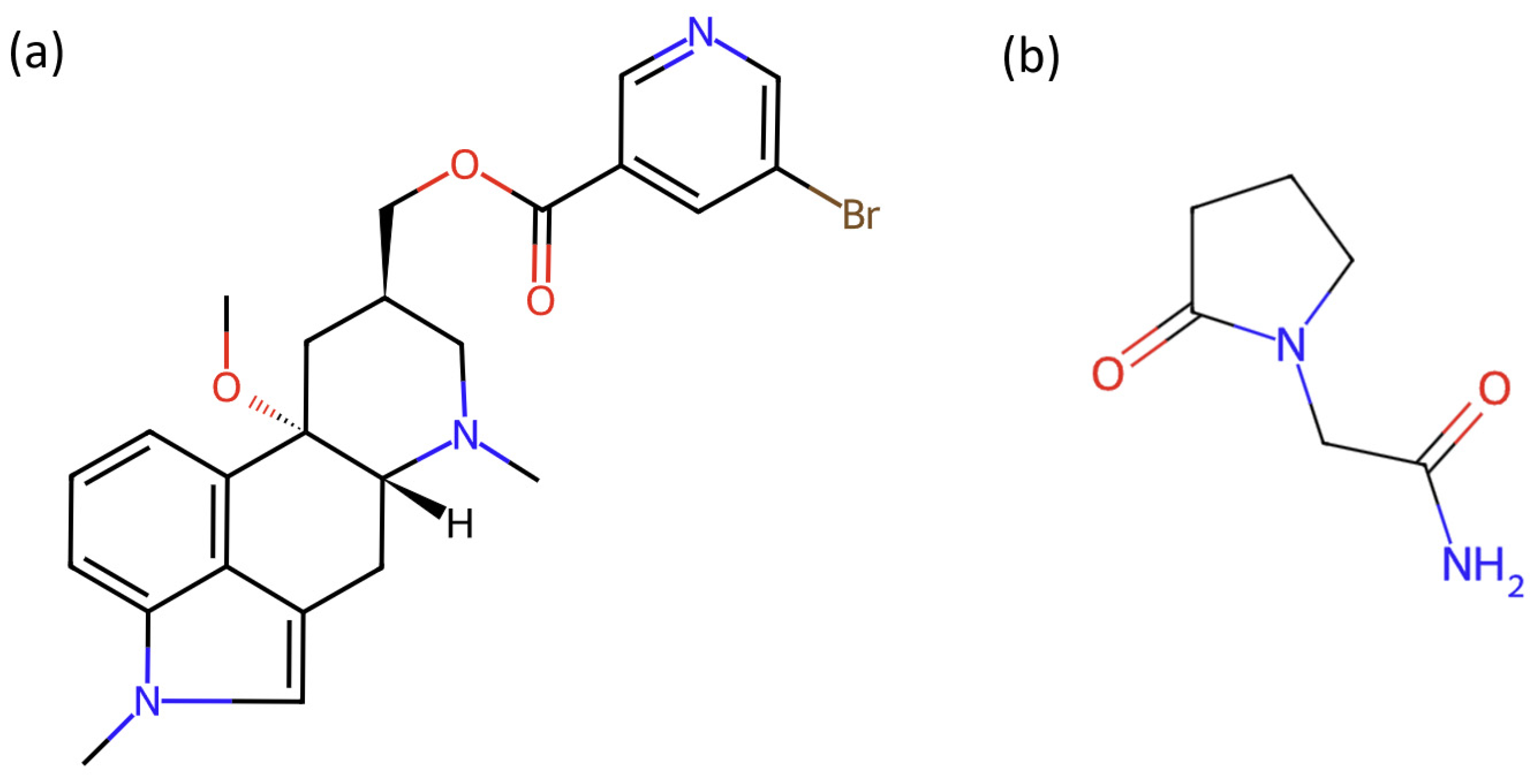




| Component | Role | Formula Code/ Amount Expressed in mg Per Capsule | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | ||
| NIC | API | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| PIR | API | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| HE | API | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| MS | Lubricant | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| MC | Filler/dry binder | - | 140.5 | - | 141.5 |
| SSG | Superdisintegrant | 2.5 | - | - | 2.0 |
| PVP K30 | Binder | - | 2.5 | 2.0 | - |
| ML | Filler | 240.5 | 100.0 | 241.5 | 100.0 |
| Total | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | |
| Formulations | Tilting Angle (°) | Angle of Repose (°) | Initial Bulk Volume, V0 (cm3) | Tapped Volume, Vt (cm3) | Initial Bulk Density, dvi (g/cm3) | Tapped Density, dvt (g/cm3) | Carr’s Index, % | Hausner Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excipients mixtures | ||||||||
| ML/MS/SSG (F1) | 36 | 23 | 32 | 28 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 12.5 | 1.14 |
| MC/MS/PVP (F2) | 45 | 41 | 49 | 34 | 0.50 | 0.73 | 30.6 | 1.44 |
| ML/MS/PVP (F3) | 26 | 30 | 31 | 27 | 0.73 | 0.84 | 12.90 | 1.15 |
| MC/MS/SSG (F4) | 50 | 48 | 59 | 49 | 0.39 | 0.47 | 16.95 | 1.20 |
| Excipients with active substances | ||||||||
| F1 | 31 | 20 | 30 | 25 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 16.67 | 1.21 |
| F2 | 48 | 45 | 35 | 25 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 28.57 | 1.38 |
| F3 | 21 | 25 | 30 | 23 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 23.33 | 1.30 |
| F4 | 45 | 45 | 55 | 45 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 18.18 | 1.22 |
| Sample | Flavonoid Content (% Rutoside Equivalents) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Rutoside trihydrate (standard) | 91,8602 | 5.65 |
| Hawthorn extract | 0.58662 | 5.67 |
| Capsules | 0.52041 | 5.41 |
| Samples | DPPH, IC50 (µg/mL) | ABTS (μM TE/g Dry Mass) | Iron-Chelating Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry hawthorn extract | 88.43 (5.581) | 20.84 (1.221) | 77.19 (0.015) |
| Combined capsules (F1) | 99.16 (2.421) | 19.33 (0.349) | 59.87 (0.618) |
| Trolox (reference) | 3.7100 (1.84) | - | |
| EDTA (reference) | - | - | 93.54 (0.8475) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rus, L.M.; Uncu, A.; Parii, S.; Uifălean, A.; Hegheș, S.C.; Iuga, C.A.; Tomuță, I.; Mazur, E.; Șepeli, D.; Kacso, I.; et al. Development and Preclinical Evaluation of Fixed-Dose Capsules Containing Nicergoline, Piracetam, and Hawthorn Extract for Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081017
Rus LM, Uncu A, Parii S, Uifălean A, Hegheș SC, Iuga CA, Tomuță I, Mazur E, Șepeli D, Kacso I, et al. Development and Preclinical Evaluation of Fixed-Dose Capsules Containing Nicergoline, Piracetam, and Hawthorn Extract for Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081017
Chicago/Turabian StyleRus, Lucia Maria, Andrei Uncu, Sergiu Parii, Alina Uifălean, Simona Codruța Hegheș, Cristina Adela Iuga, Ioan Tomuță, Ecaterina Mazur, Diana Șepeli, Irina Kacso, and et al. 2025. "Development and Preclinical Evaluation of Fixed-Dose Capsules Containing Nicergoline, Piracetam, and Hawthorn Extract for Sensorineural Hearing Loss" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081017
APA StyleRus, L. M., Uncu, A., Parii, S., Uifălean, A., Hegheș, S. C., Iuga, C. A., Tomuță, I., Mazur, E., Șepeli, D., Kacso, I., Macaev, F., Valica, V., & Uncu, L. (2025). Development and Preclinical Evaluation of Fixed-Dose Capsules Containing Nicergoline, Piracetam, and Hawthorn Extract for Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081017












