Pristimerin Dampens Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity; The Role of NF-κB/iNOS/COX-II/Cytokines, PI3K/AKT, and BAX/BCL-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Study Design
2.2. Drugs and Chemicals
2.3. Histopathology
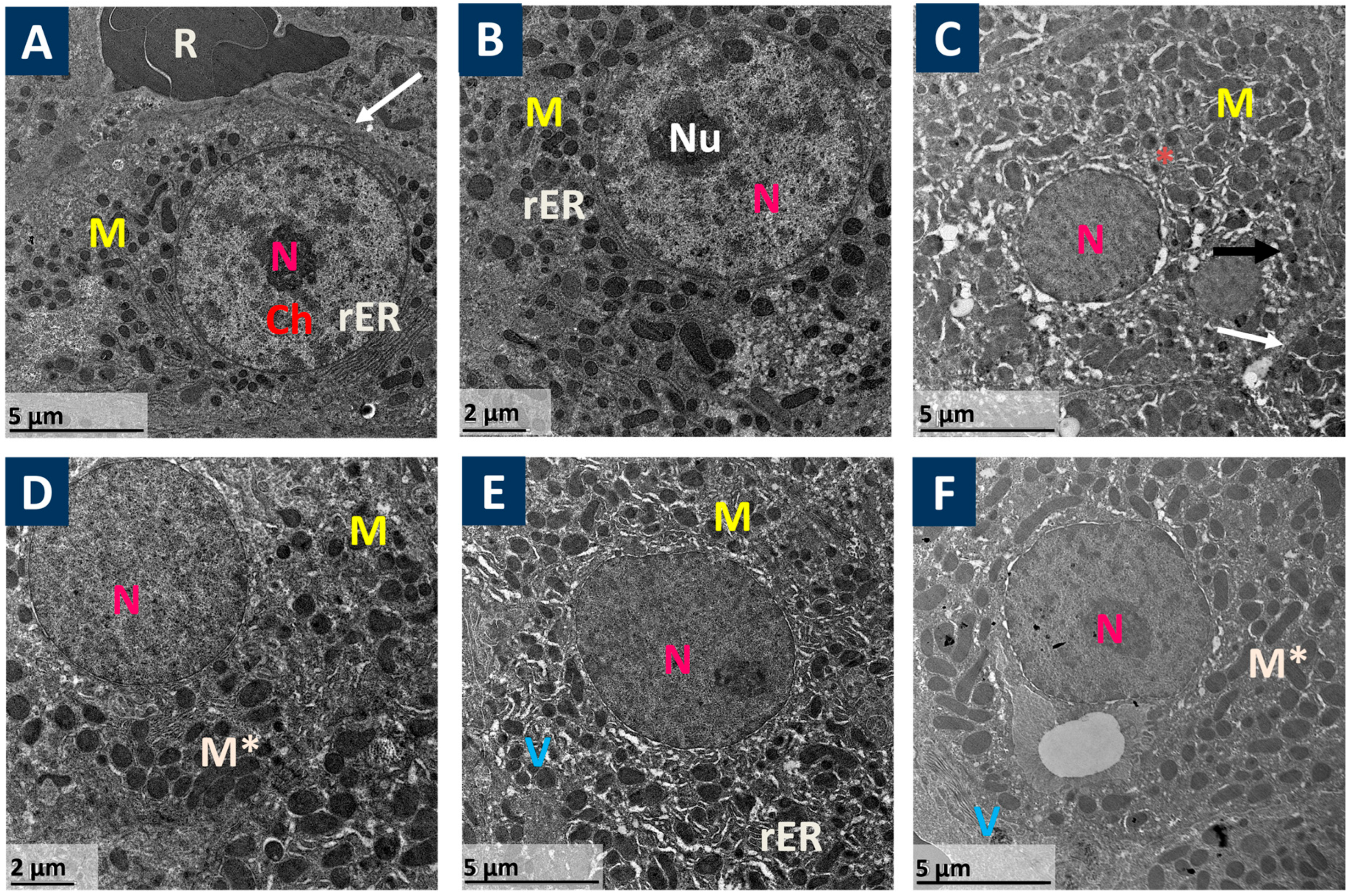
2.4. Ultra-Structure Examination of Liver by Electron Microscope
2.5. Immunohistochemical Examination
2.6. Liver Function Biomarkers
2.7. Oxidative Status Biomarkers
2.8. Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
| Gene | Sequence at Annealing Temperature (60 °C) | Product Size (bp) | RefSeq | References |
| iNOS | F: CAGCTGGGCTGTACAAACCTT R: CATTGGAAGTGAAGCGTTTCG | 95 | NM_001313921.1 | [38] |
| COX-II | F: ACACACTCTATCACTGGCACC R: TTCAGGGAGAAGCGTTTGC | 274 | NM_011198.5 | [39] |
| TNF-α | F: TGAACTTCGGGGTGATCGGT R: GGTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAGGG | 99 | NM_001278601.1 | [40] |
| IL-6 | F: TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGC R: CTGCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTC | 116 | NM_001314054.1 | [41] |
| IL-1β | F: GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT R: GGGTCCGTCAACTTCAAAGA | 81 | NM_008361.4 | [40] |
| BCL-2 | F: CCTGTGGATGACTGAGTACCTG R: AGCCAGGAGAAATCAAACAGAGG | 123 | NM_009741.5 | [40] |
| BAX | F: TGAAGACAGGGGCCTTTTTG R: AATTCGCCGGAGACACTCG | 140 | NM_007527.3 | [40] |
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
Protein Extraction Procedure
2.10. Determination of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Markers by ELISA
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prist Improved APAP-Induced Hepatic Histopathological Lesions
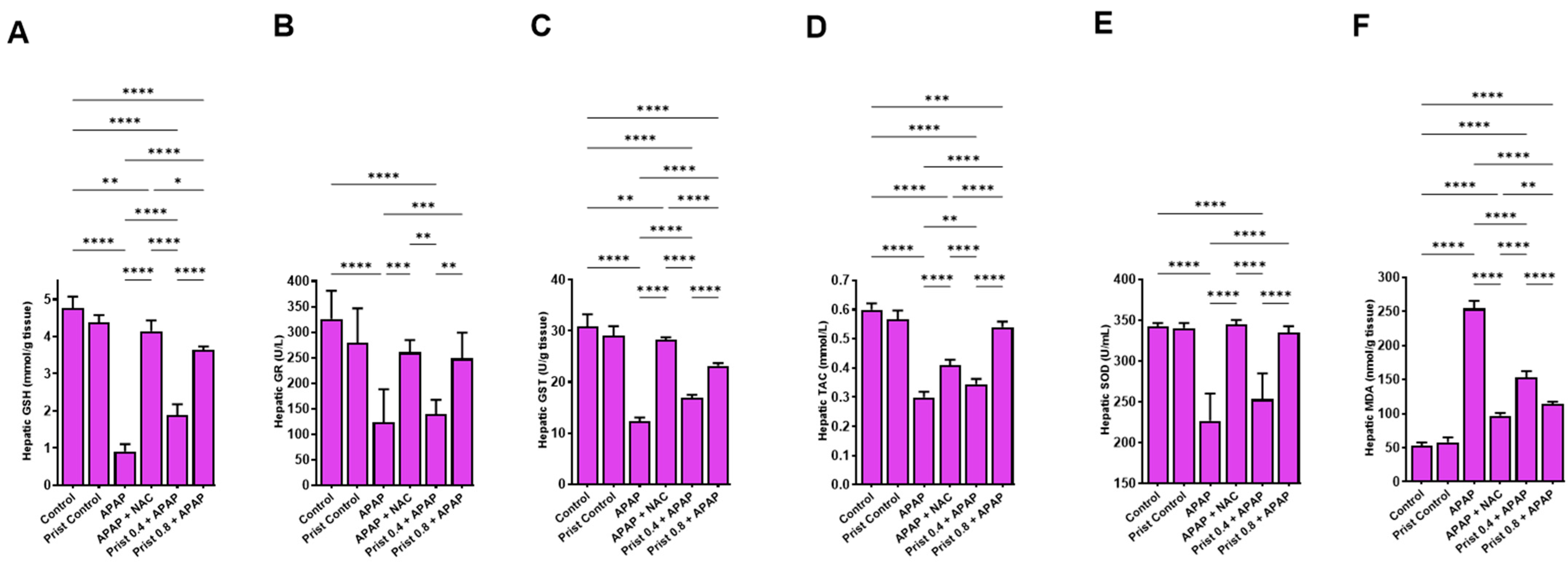
3.2. Prist Ameliorated Serum Biomarkers of APAP-Induced Hepatic Intoxication
3.3. Prist Augmented Hepatic Antioxidants and Counteracted APAP-Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress
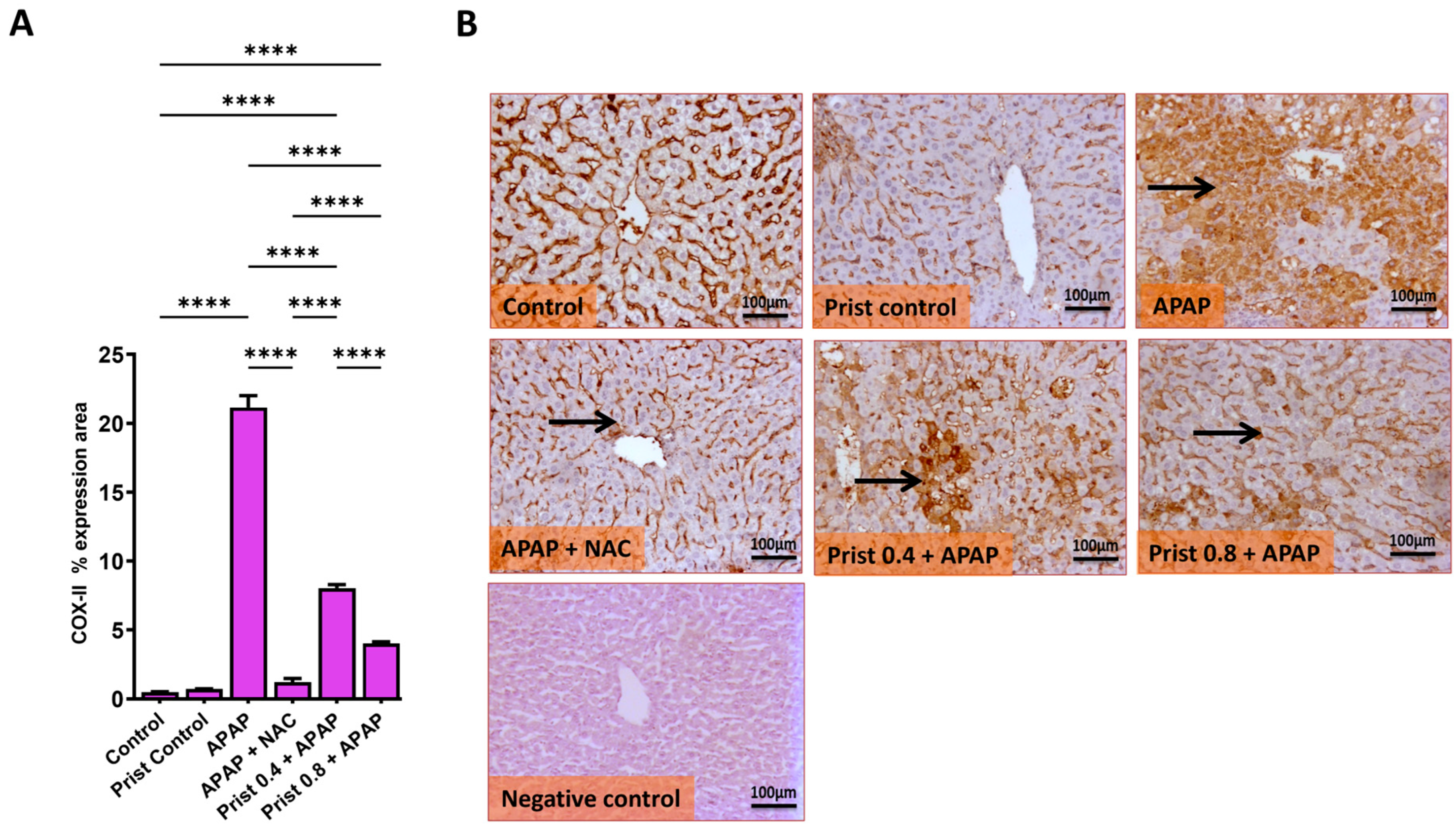
3.4. Prist Attenuated Hepatic iNOS and COX-II Expression
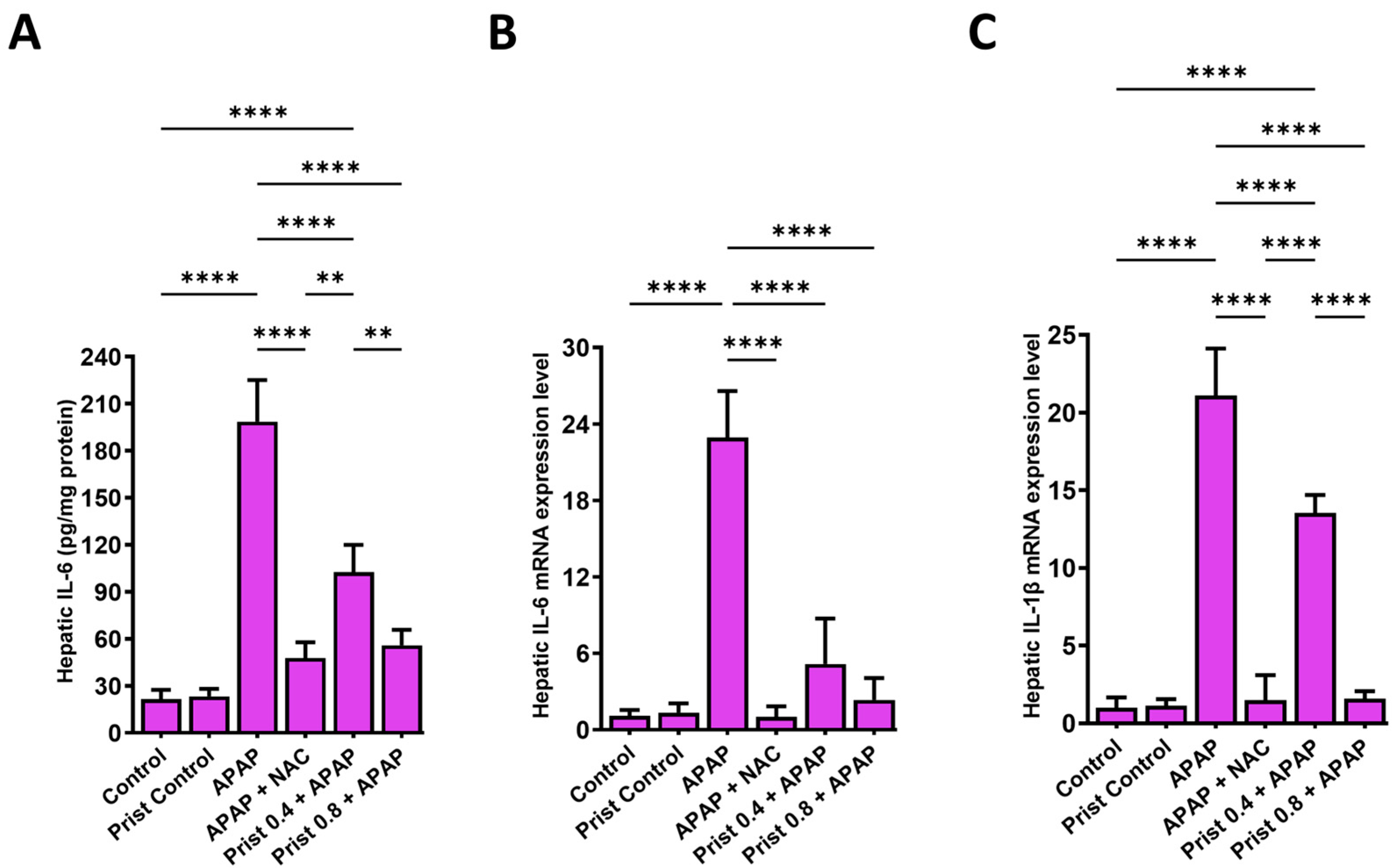
3.5. Prist Restrained APAP-Induced Activation of NFκB and Downstream Cytokines
3.6. Prist Ameliorated APAP-Induced Change in p-PI3K and p-AKT Expression in Hepatic Tissues
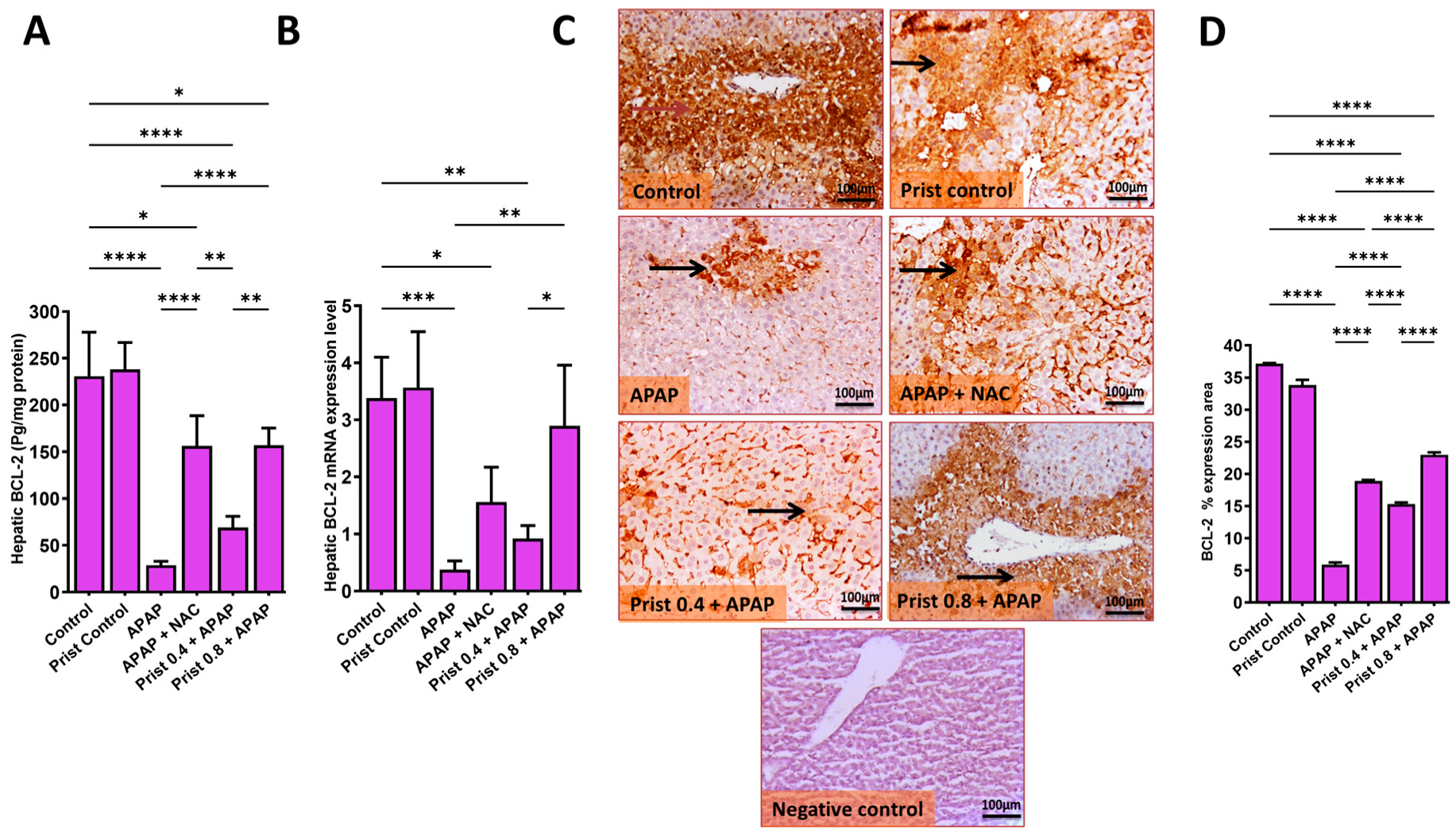
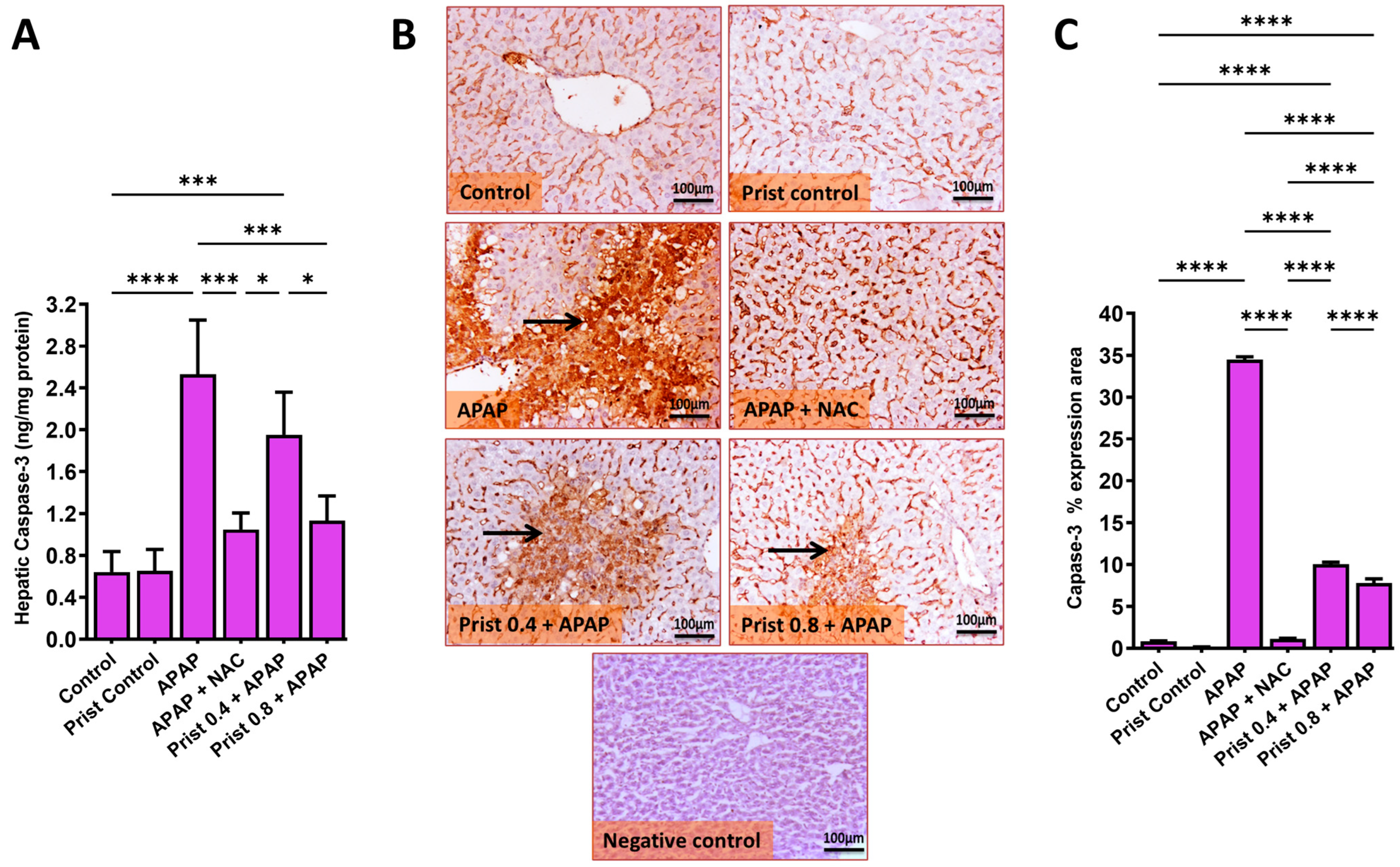
3.7. Prist Attenuated APAP-Induced Apoptosis in Hepatic Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fathelrahman, A.I. Ten challenges associated with management of paracetamol overdose: An update on current practice and relevant evidence from epidemiological and clinical studies. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2021, 15, FE01–FE06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, A.S.; Buckley, N.A.; Noghrehchi, F.; Cairns, R. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose and hepatotoxicity: Mechanism, treatment, prevention measures, and estimates of burden of disease. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Xie, Y.; McGill, M.R. Acetaminophen-induced liver injury: From animal models to humans. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2014, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.; Srivastava, D.; Madhuri, S. A standard hepatotoxic model produced by paracetamol in rat. Toxicol. Int. 2008, 15, 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenović, D.; Radosavljević, T.; Ninković, M.; Vučević, D.; Ješić-Vukićević, R.; Todorović, V. Liver antioxidant capacity in the early phase of acute paracetamol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.L.; McLean, A.E. Comparison of paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat in vivo with progression of cell injury in vitro in rat liver slices. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 21, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossanen, J.; Tacke, F. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canayakin, D.; Bayir, Y.; Kilic Baygutalp, N.; Sezen Karaoglan, E.; Atmaca, H.T.; Kocak Ozgeris, F.B.; Keles, M.S.; Halici, Z. Paracetamol-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats: The protective role of Nigella sativa. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, M.R.; Jafari, R.; Yousefi, K.; Zolbanin, N.M. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic interventions. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2022, 127, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarneshan, S.N.; Fakhri, S.; Farzaei, M.H.; Khan, H.; Saso, L. Astaxanthin targets PI3K/Akt signaling pathway toward potential therapeutic applications. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.-P.; Deng, J.-S.; Huang, S.-S.; Wu, S.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Liao, J.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, H.-Y.; Huang, G.-J. Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelium prevents paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity through regulating the MAPK/NF-κB, Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1, TLR4/PI3K/Akt, and CaMKKβ/LKB1/AMPK pathways and suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.-P.; Chuang, Y.-T.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Tang, J.-Y.; Hou, M.-F.; Yen, C.-Y.; Chang, H.-W. Impacts of oxidative stress and PI3K/AKT/mTOR on metabolism and the future direction of investigating fucoidan-modulated metabolism. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Jin, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xin, Y.; Duan, Z. The protective effect of heme oxygenase-1 against intestinal barrier dysfunction in cholestatic liver injury is associated with NF-κB inhibition. Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X. Noncanonical NF-κB signaling pathway in liver diseases. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, A.H.; Lee, H.C.; Liao, C.C.; Yu, H.P.; Liu, F.C. ERK/NF-kB/COX-2 Signaling Pathway Plays a Key Role in Curcumin Protection against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Life 2023, 13, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, T.; et al. Febuxostat ameliorates APAP-induced acute liver injury by activating Keap1/Nrf2 and inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathways. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 1864–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, C.L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S.; Hu, J.N.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, C.; Li, W. NF-κB and AMPK/PI3K/Akt signaling pathways are involved in the protective effects of Platycodon grandiflorum saponins against acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity in mice. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, D.T.L.; Son, N.T. Pristimerin: Natural Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Pharmacology, and Pharmacokinetics. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2024, 34, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, N.; Ferro, E.A. Bioactive triterpenes and related compounds from celastraceae. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2005, 30, 635–702. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Hu, R.; Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Li, Z. Beneficial effect of pristimerin against the development of osteoporosis in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis rats by the RANKL/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2022, 18, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Hui, L. Pristimerin inhibits LPS-triggered neurotoxicity in BV-2 microglia cells through modulating IRAK1/TRAF6/TAK1-mediated NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways in vitro. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 33, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.-G.; Zhang, N. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pristimerin in cancer therapy: Recent advances. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 671548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Tian, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, S.; Wang, M. Pristimerin Exerts Pharmacological Effects Through Multiple Signaling Pathways: A Comprehensive Review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 1673–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agamy, D.S.; Shaaban, A.A.; Almaramhy, H.H.; Elkablawy, S.; Elkablawy, M.A. Pristimerin as a Novel Hepatoprotective Agent Against Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, E. Pristimerin ameliorates colitis-induced intestinal mucosal injury by inhibiting intestinal epithelial necroptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, A.A.; El-Kashef, D.H.; Hamed, M.F.; El-Agamy, D.S. Protective effect of pristimerin against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 59, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, P.; Shao, X.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.-J.; Ma, X.; Manautou, J.E.; et al. Acetaminophen-induced liver injury alters expression and activities of cytochrome P450 enzymes in an age-dependent manner in mouse liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2020, 48, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falach-Malik, A.; Rozenfeld, H.; Chetboun, M.; Rozenberg, K.; Elyasiyan, U.; Sampson, S.R.; Rosenzweig, T. N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine inhibits the development of glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis in diabetes-prone mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3744–3756. [Google Scholar]
- Elshal, M.; Abdelmageed, M.E. Diacerein counteracts acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via targeting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-4/MCP-1 signaling pathways. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2022, 45, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, R.S.; Abdel-Rahman, N. Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury in mice dependent of Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, K.M.; Shaker, M.E.; Shaaban, A.A.; Abdelrahman, R.S.; Said, E. The c-Met inhibitor capmatinib alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.A.; Ragab, M.A.; Shazly, S.A.; Ahmed, M.E.; El-Kholany, M.E.; El-Raghi, A.A. Feasible feeding strategies for sustainable management of serve heat stress conditions: Effect of Milk Thistle extract on growth performance and health status of newly weaned rabbits. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 108, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.; Elazab, S.T.; Saati, A.A.; Ahmed, G.S.; Baokbah, T.A.; Fathy, K.; El-Shenbaby, I.; Abdelbagi, O.; Hassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.M. Zamzam Water Ameliorates Gentamicin-Induced Testicular Toxicity in a Rat Model via Targeting Sperm Parameters, Testicular Tissue Oxidative Insult, Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Pituitary-Gonadal Axis. Toxics 2023, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesdon, J.-L.; Ternynck, T.; Avrameas, S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1979, 27, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helps, S.C.; Thornton, E.; Kleinig, T.J.; Manavis, J.; Vink, R. Automatic nonsubjective estimation of antigen content visualized by immunohistochemistry using color deconvolution. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2012, 20, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lou, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Oxysophocarpine reduces oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced microglial activation and injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar]
- Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Colucci, R.; Antonioli, L.; Bernardini, N.; Segnani, C.; Baragatti, B.; Barogi, S.; Berti, P.; Spisni, R.; et al. Role of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 in the modulation of neuromuscular functions in the distal colon of humans and mice. Gut 2005, 54, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.; ElKaffas, M.; Metwally, K.; Abdelfattah, M.; Elsery, E.A.; Elshazly, A.; Gomaa, H.E.; Alsayed, A.; El-Desouky, S.; El-Gamal, R.; et al. Impairment of Nrf2 signaling in the hippocampus of P301S tauopathy mice model aligns with the cognitive impairment and the associated neuroinflammation. J. Inflamm. 2024, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. MiR-152 may silence translation of CaMK II and induce spontaneous immune tolerance in mouse liver transplantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, W.M. Acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity-Isn’t it time for APAP to go away? J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.S.; Curry, S.C. Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity. Adv. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, M.R. The past and present of serum aminotransferases and the future of liver injury biomarkers. EXCLI J. 2016, 15, 817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kisaoglu, A.; Ozogul, B.; Turan, M.I.; Yilmaz, I.; Demiryilmaz, I.; Atamanalp, S.S.; Bakan, E.; Suleyman, H. Damage induced by paracetamol compared with N-acetylcysteine. J. Chin. Med Assoc. 2014, 77, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baali, N.; Belloum, Z.; Baali, S.; Chabi, B.; Pessemesse, L.; Fouret, G.; Ameddah, S.; Benayache, F.; Benayache, S.; Feillet-Coudray, C. Protective activity of total polyphenols from Genista quadriflora Munby and Teucrium polium geyrii Maire in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, A.; Anadón, A.; Rodríguez, J.-L.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Yuan, Z.; Martínez, M.-A. Paracetamol: Overdose-induced oxidative stress toxicity, metabolism, and protective effects of various compounds in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 395–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Peng, S.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Shen, L. Pristimerin reduces dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting microRNA-155. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 94, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen toxicity: Novel insights into mechanisms and future perspectives. Gene Expr. 2018, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambach, D.M.; Durham, S.K.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Distinct roles of NF-κB p50 in the regulation of acetaminophen-induced inflammatory mediator production and hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 211, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehner, S.P.; Heinrich, M.; Bork, P.M.; Vogt, M.; Ratter, F.; Lehmann, V.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Droge, W.; Schmitz, M.L. Sesquiterpene lactones specifically inhibit activation of NF-κB by preventing the degradation of IκB-α and IκB-β. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, J.A.; Roberts, D.W.; James, L.P. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver necrosis. Advers. Drug React. 2010, 196, 369–405. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; McGill, M.R.; Dorko, K.; Kumer, S.C.; Schmitt, T.M.; Forster, J.; Jaeschke, H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced cell death in primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 279, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Su, L.; He, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, D.; Peng, J.; Yang, F.; Cao, Y.; Luo, X. Pristimerin alleviates cigarette smoke-induced inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via inhibiting NF-κB pathway. Biochem. Cell Biol 2022, 100, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, G.M.; Kim, J.-K. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Pristimerin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Murine Macrophages. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 36, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agamy, D.S.; El-Harbi, K.M.; Khoshhal, S.; Ahmed, N.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Shaaban, A.A.; Abo-Haded, H.M. Pristimerin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and fibrosis through modulation of Nrf2 and MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gong, N. Role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: A narrative review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 80617–80817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, X.; Qu, M.; Yang, X.; Fang, Y.; Ying, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, J.; Pan, Y. Exploring the potential of treating chronic liver disease targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway and polarization mechanism of macrophages. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Song, F.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Gu, Y.; Yuan, Y. Salvianolic acid A attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR, Bcl-2/Bax and caspase-3/cleaved caspase-3 signaling pathways. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jing, Z.T.; Xue, C.R.; Wu, S.X.; Chen, W.N.; Lin, X.J.; Lin, X. PI3K/AKT inhibitors aggravate death receptor-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 381, 114729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, W. Hesperetin ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE pathway in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and a rat model of high-fat diet-induced NAFLD. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3898–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cui, H.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Chen, K.; Deng, J. Modulation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway and Bcl-2 Family Proteins Involved in Chicken’s Tubular Apoptosis Induced by Nickel Chloride (NiCl2). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22989–23011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.M.; Wu, Y.T.; Chen, L.; Tan, Z.B.; Fan, H.J.; Xie, L.P.; Zhang, W.T.; Chen, H.M.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; et al. 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid protects H9C2 cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 10–29219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, M.; Tang, M.; Song, X.; Zheng, K.; Meng, T.; Li, C.; Du, L. Mechanism of PI3K/Akt-mediated mitochondrial pathway in obesity-induced apoptosis (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2025, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, W.; Hu, J.; Mi, X.; Han, Y.; Ren, S.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W. Maltol Improves APAP-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Response via NF-κB and PI3K/Akt Signal Pathways. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Hu, J. Tempol Protects Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Quan, X.-B.; Zeng, W.-J.; Yang, X.-O.; Wang, M.-J. Mechanism of hepatocyte apoptosis. J. Cell Death 2016, 9, JCD.S39824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-L.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Liu, X.-J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Tao, L.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.-X. Melatonin protects against apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF)-dependent cell death during acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; McGill, M.R.; Xie, Y.; Ni, H.M.; Ding, W.X.; Jaeschke, H. Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte necrosis in mice. Hepatology 2013, 58, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiang, G.T.; Yu, Y.L.; Lin, K.T.; Chen, J.N.; Chang, W.J.; Wei, C.W. Acetaminophen induces JNK/p38 signaling and activates the caspase-9-3-dependent cell death pathway in human mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R. Caspase activation and inhibition. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2022, 14, a041020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Ella, E.; El-Kott, A.F.; El-Kenawy, A.; Khalifa, H.; Bin-Meferij, M.M.; Alramlawy, A. Dehydroepiandrosterone protects against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in rats by upregulation of bcl-2 and activation of sirt signaling. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71, 781–792. [Google Scholar]
- Edlich, F. BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: Recent insights and unknowns. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Kou, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, N.; Zeng, T.; Xie, K. Diallyl sulfide treatment protects against acetaminophen-/carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.P.; Cheng, L.; Ju, C. Identification and characterization of infiltrating macrophages in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, E.; Samia-Grinberg, S.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Brazowski, E.; Shibolet, O.; Halpern, Z.; Varol, C. Infiltrating monocyte-derived macrophages and resident kupffer cells display different ontogeny and functions in acute liver injury. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
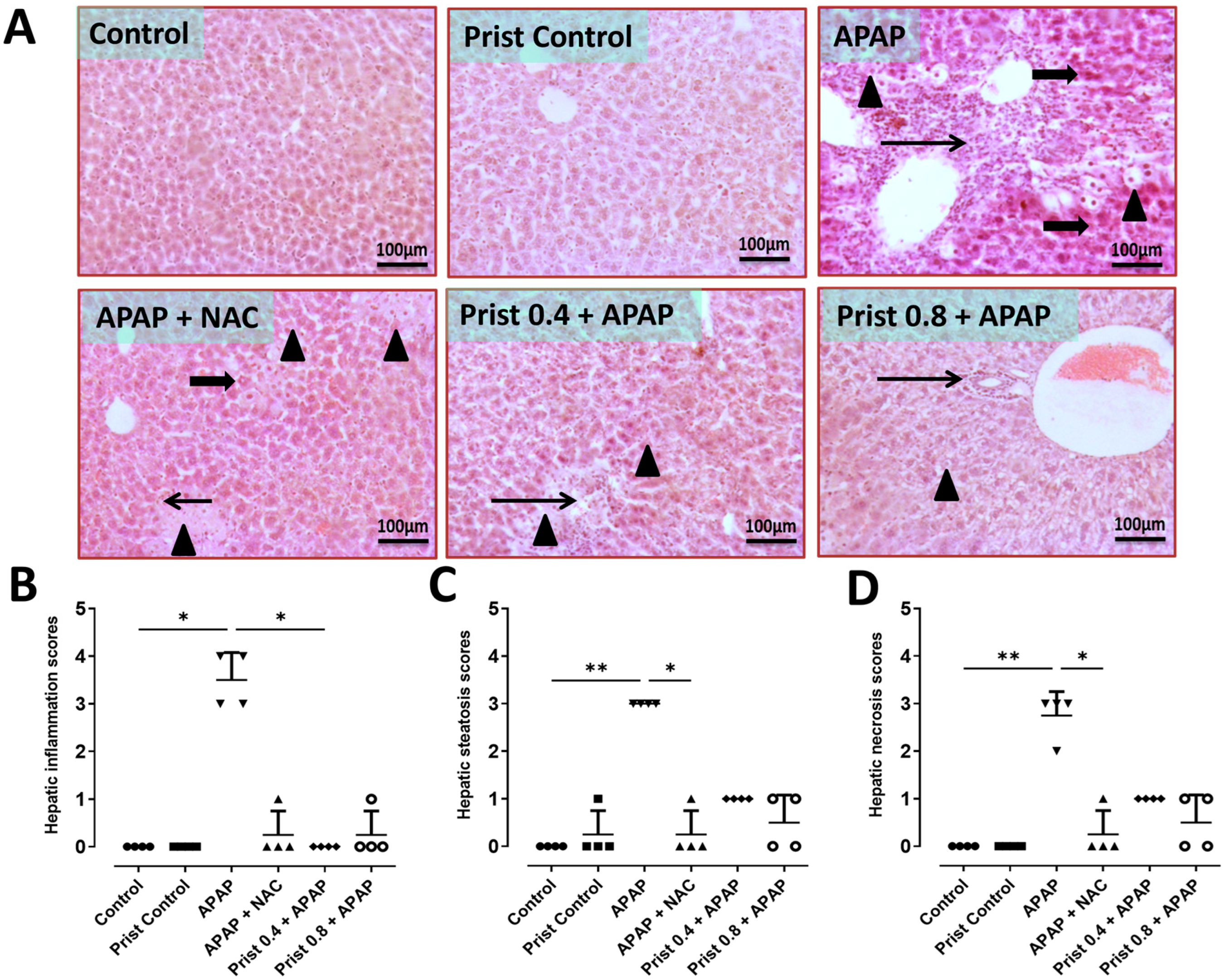






| Score | Steatosis | Necrosis | Inflammation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | None | None |
| 1 | Less than 5% of tissue affected | Minimal, few | 1 focus/5 field examined |
| 2 | More than 5–50% of tissue affected | Mild to moderate, multifocal to coalescing necrotic area | 2-3 foci/5 field examined |
| 3 | More than 50% of tissue exhibited steatosis | Diffuse, many | More than 3 foci/5 field examined |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altowijri, M.A.; Abdelmageed, M.E.; El-Gamal, R.; Saeedi, T.; El-Agamy, D.S. Pristimerin Dampens Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity; The Role of NF-κB/iNOS/COX-II/Cytokines, PI3K/AKT, and BAX/BCL-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081003
Altowijri MA, Abdelmageed ME, El-Gamal R, Saeedi T, El-Agamy DS. Pristimerin Dampens Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity; The Role of NF-κB/iNOS/COX-II/Cytokines, PI3K/AKT, and BAX/BCL-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081003
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltowijri, Mohammed A., Marwa E. Abdelmageed, Randa El-Gamal, Tahani Saeedi, and Dina S. El-Agamy. 2025. "Pristimerin Dampens Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity; The Role of NF-κB/iNOS/COX-II/Cytokines, PI3K/AKT, and BAX/BCL-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081003
APA StyleAltowijri, M. A., Abdelmageed, M. E., El-Gamal, R., Saeedi, T., & El-Agamy, D. S. (2025). Pristimerin Dampens Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity; The Role of NF-κB/iNOS/COX-II/Cytokines, PI3K/AKT, and BAX/BCL-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081003






