Development of Low-Dose Disulfiram Rectal Suppository Intended for Application in Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Inclusion Complexes and the Respective Physical Mixtures
2.3. Preparation of the Suppositories
2.4. Dissolution of Suppositories
2.5. Dissolution Profile Comparison—Statistics and Analysis of the Similarity Factor, f2
2.6. Small Volume Dissolution–Permeation Analysis
2.7. Quality Control of Selected Suppository Composition
2.7.1. Weight Uniformity
2.7.2. Content Uniformity
2.7.3. Disintegration
2.7.4. Hardness
2.7.5. One-Month Drug Content Stability Monitoring with UV/VIS Method
2.7.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7.7. X-ray Diffraction Study (XRD)
2.7.8. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
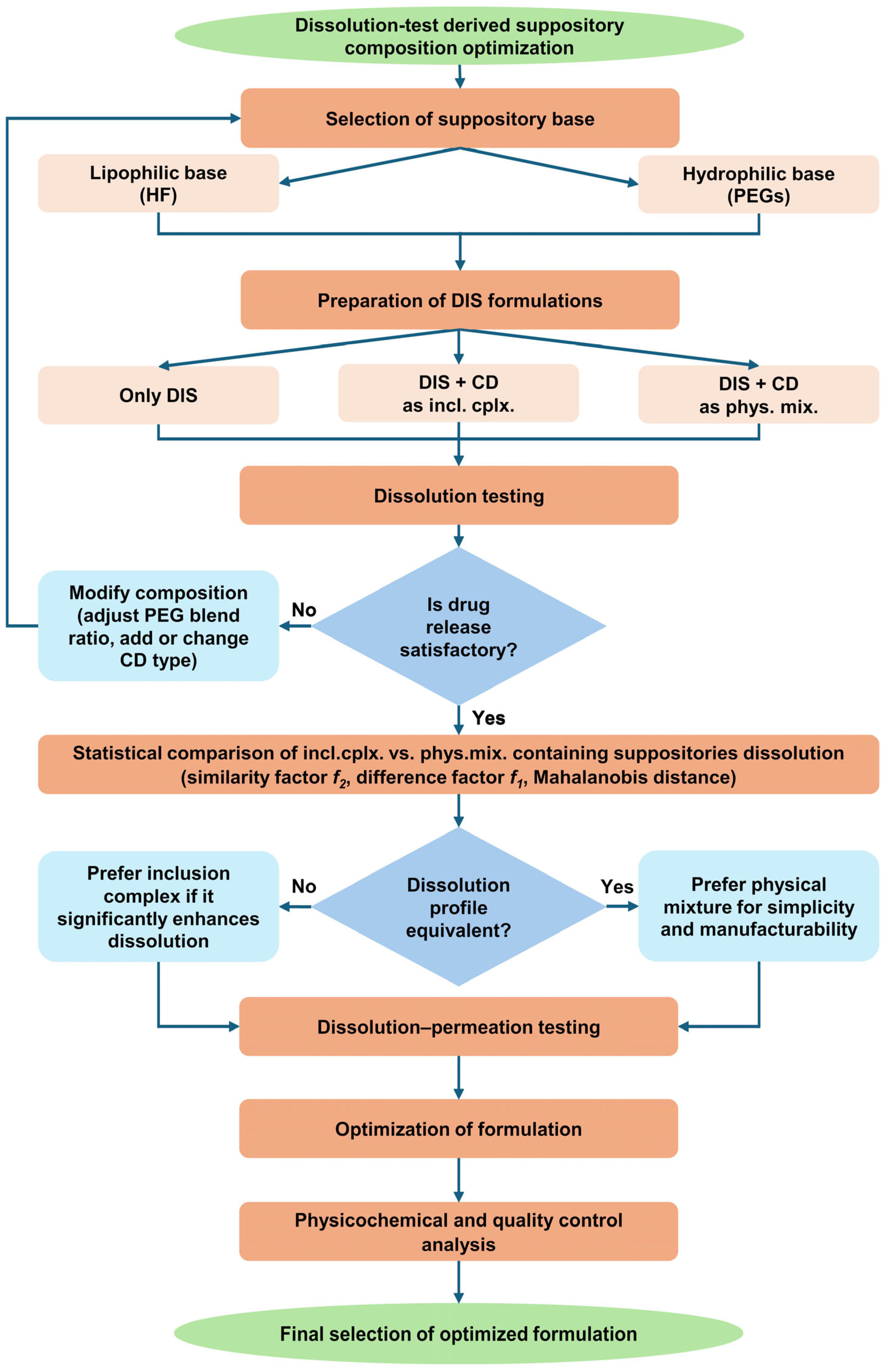
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of Suppositories
3.2. Dissolution Test-Driven Composition Optimization
3.2.1. Suppository Base Selection
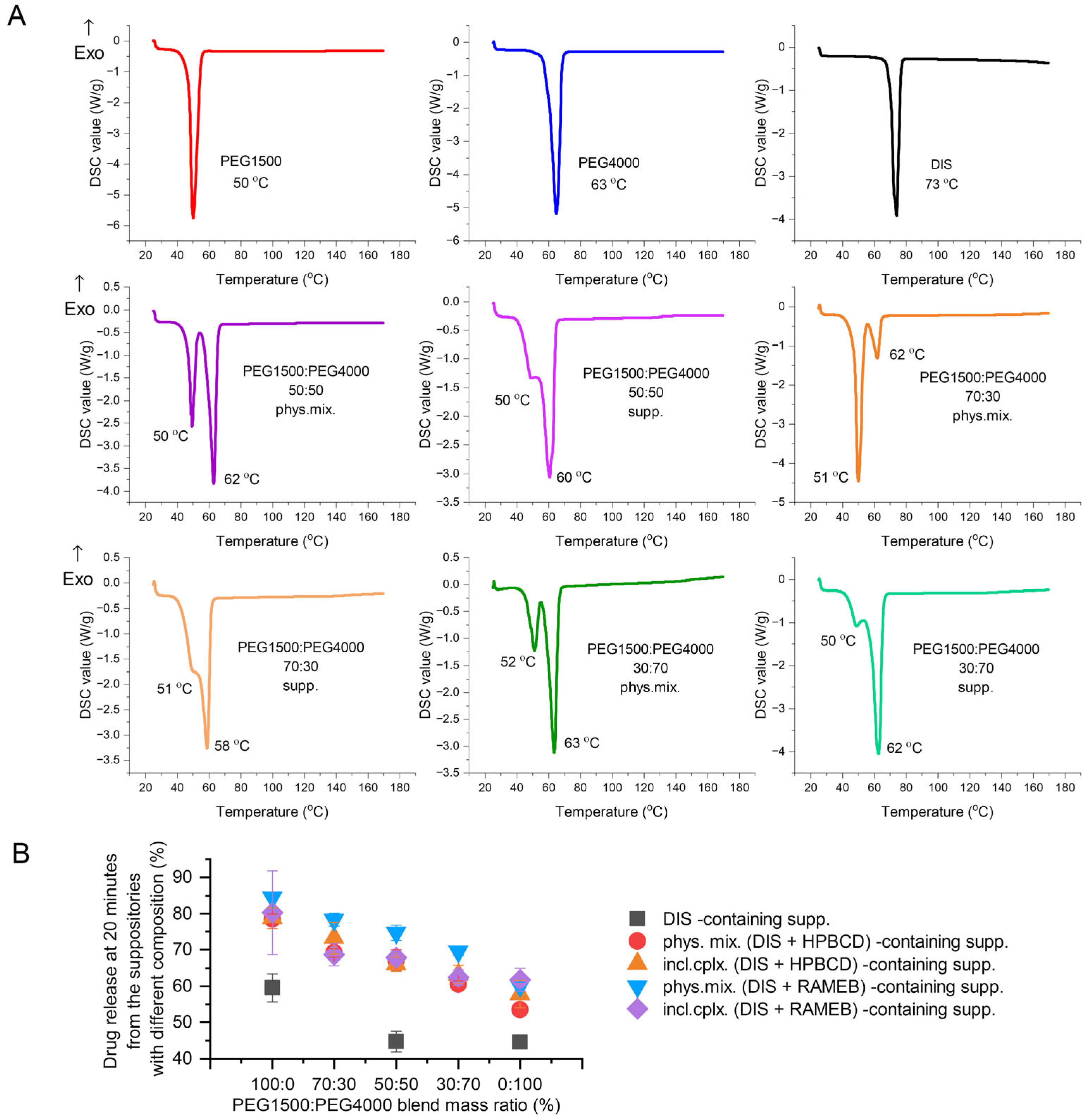
3.2.2. Investigating the Effect of Different PEG Blends on Formulation
3.2.3. Dissolution-Driven Justification of the Preliminary Inclusion Complex Preparation Step in the Suppository Formulation Process
3.2.4. CD Type Selection
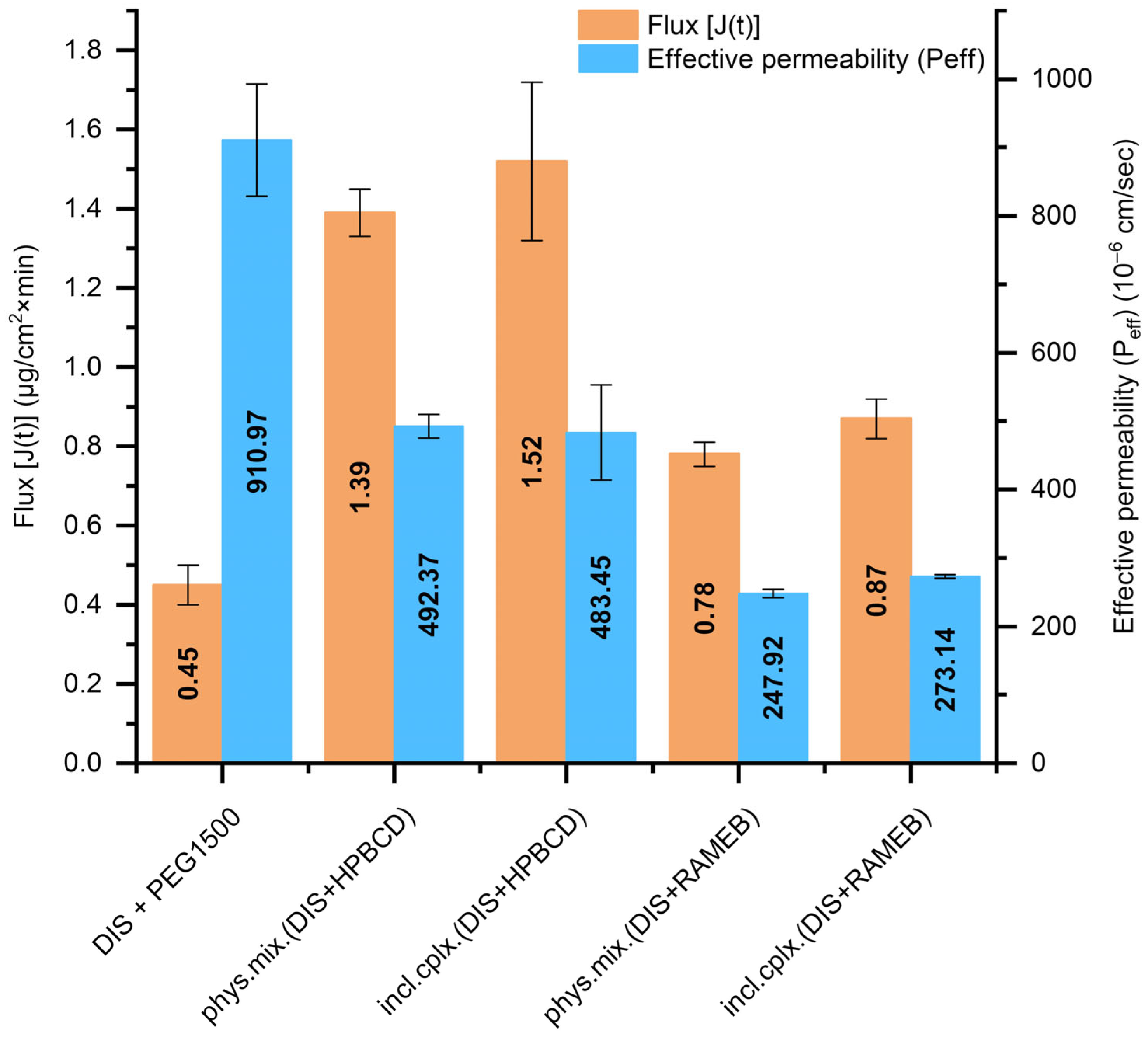
3.3. Results of Small Volume Dissolution–Permeation Analysis
3.4. Results of Quality Control on Selected Suppository Composition
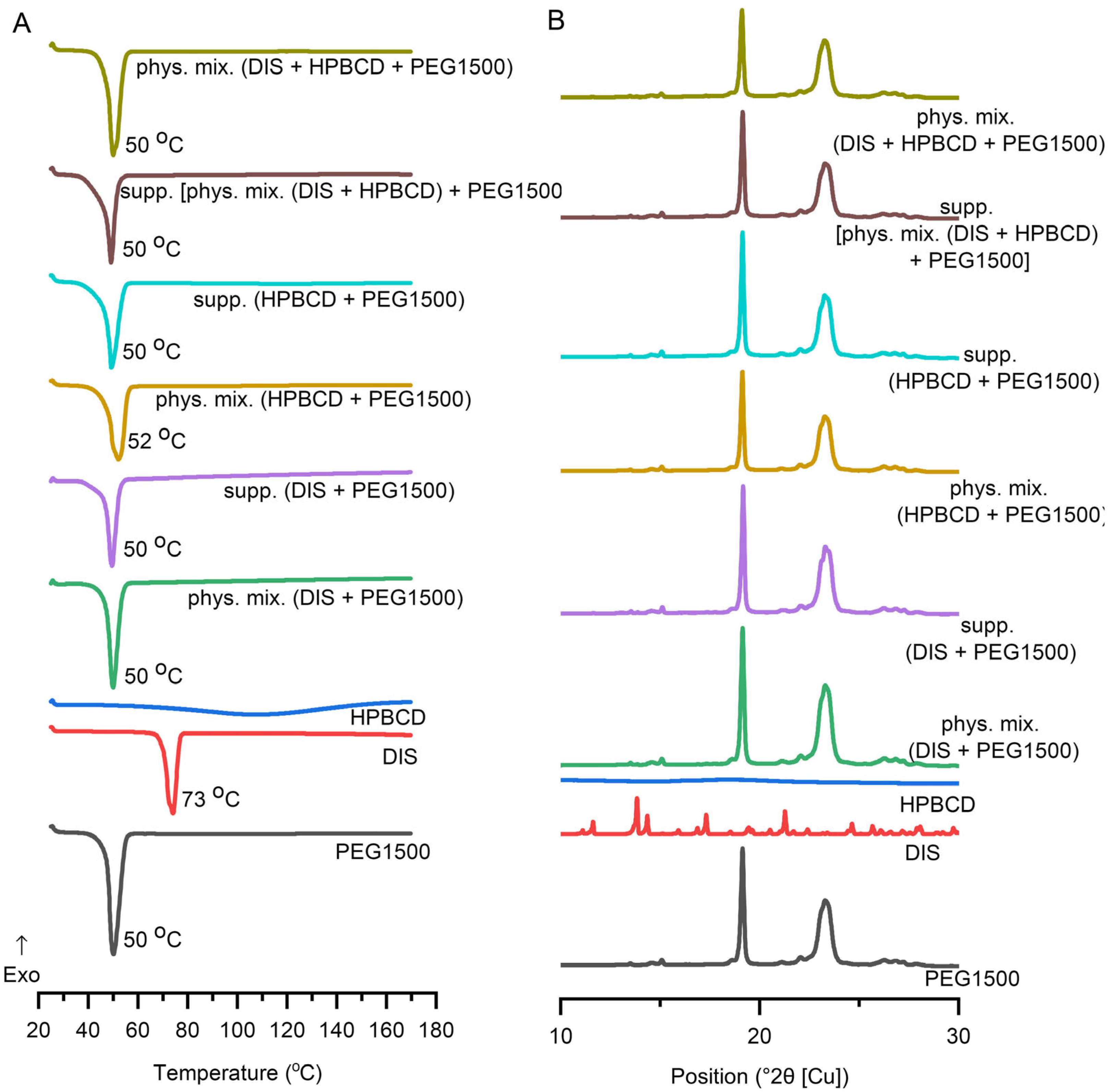
3.4.1. DSC
3.4.2. XRD
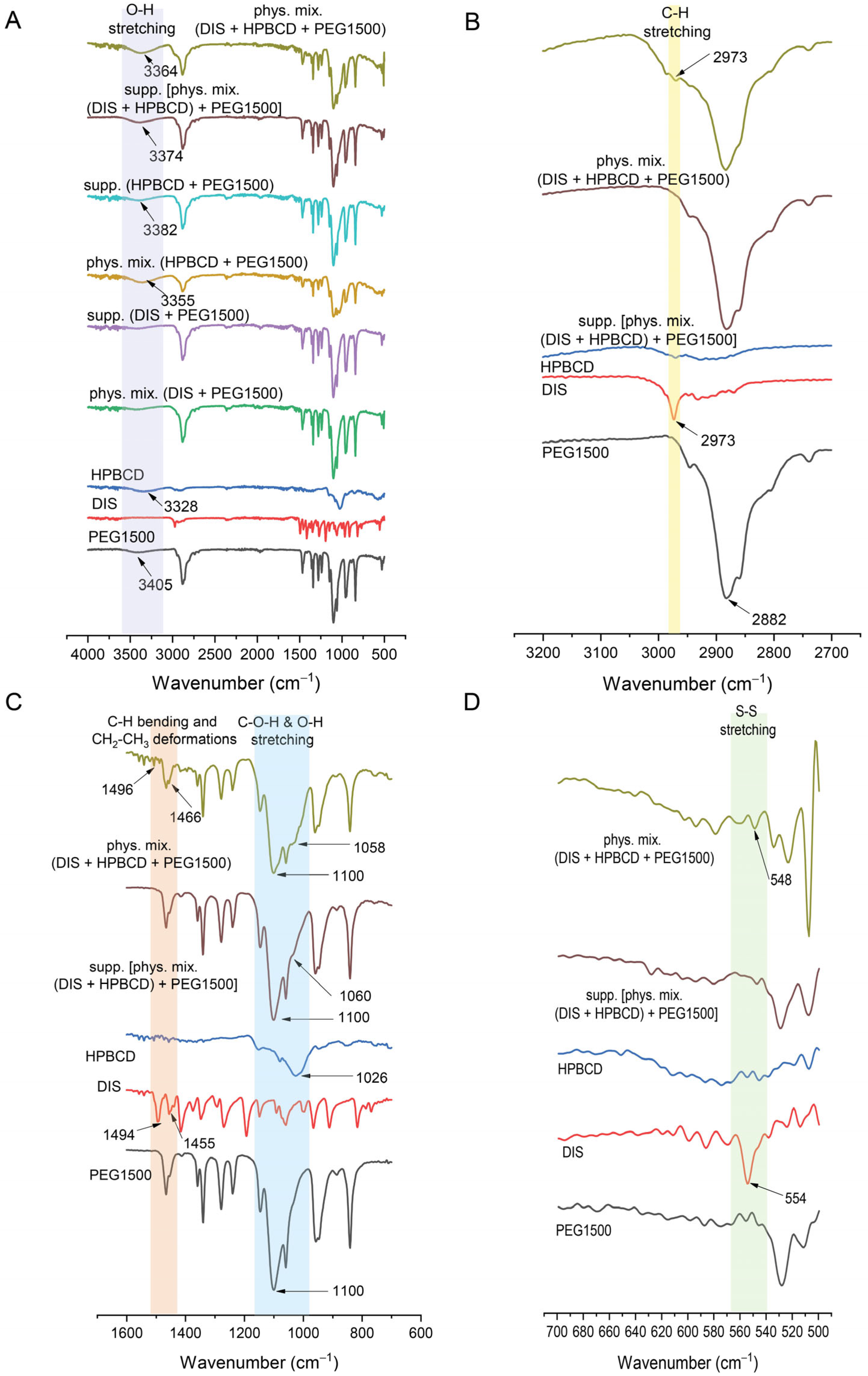
3.4.3. FTIR
4. Discussion
4.1. Low-Dose DIS in the Treatment of Lyme Disease
4.2. Role of Suppository Matrix
4.3. Applicability of DIS-Containing Rectal Suppositories in Lyme Disease
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALDH | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase |
| ATR-FTIR | Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| CD | Cyclodextrin |
| DIS | Disulfiram |
| DS | Degrees of Substitution |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| f1 | Difference Factor |
| f2 | Similarity Factor |
| HF | Hard Fat |
| HPBCD | Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin |
| incl.cplx. | Inclusion Complex |
| J(t) | Flux |
| Peff | Effective Permeability |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| phys.mix. | Physical Mixture |
| PTLDS | Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome |
| RAMEB | Randomly Methylated-β-Cyclodextrin |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
References
- Das, A.; Pathak, K.; Pathak, M.P.; Gogoi, U.; Saikia, R. Lyme Disease Management. In Rising Contagious Diseases; Amponsah, S.K., Shegokar, R., Pathak, Y.V., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimyan, S.; Syed, M.S.; Soti, V. Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome: Need for Diagnosis and Treatment. Cureus 2021, 13, e18703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, A.; Skufca, J.; Vyse, A.; Pilz, A.; Begier, E.; Riera-Montes, M.; Gessner, B.D.; Stark, J.H. The Landscape of Lyme Borreliosis Surveillance in Europe. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, P.; Hinckley, A.; Kugeler, K. Lyme Disease Surveillance and Epidemiology in the United States: A Historical Perspective. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230 (Suppl. 1), S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowska, K.; Janocha, A.; Jerzak, A.; Ziemba, P. Diagnosis, Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Lyme Disease. Qual. Sport 2024, 18, 53283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothineni, V.R.; Wagh, D.; Babar, M.M.; Inayathullah, M.; Solow-Cordero, D.; Kim, K.M.; Samineni, A.V.; Parekh, M.B.; Tayebi, L.; Rajadas, J. Identification of new drug candidates against Borrelia burgdorferi using high-throughput screening. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1307–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, M.M.; Sparks, J.; Long, T.E. Disulfiram: A Repurposed Drug in Preclinical and Clinical Development for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Anti Infect. Agents 2022, 20, e040122199856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinderlehrer, D.A. Recovery from Lyme Disease: The Integrative Medicine Guide to Diagnosing and Treating Tick-Borne Illness; Skyhorse Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Gong, Z.; Montesano, D.; Glazer, E.; Liegner, K. “Repurposing” Disulfiram in the Treatment of Lyme Disease and Babesiosis: Retrospective Review of First 3 Years’ Experience in One Medical Practice. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liegner, K.B. Disulfiram (Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide) in the Treatment of Lyme Disease and Babesiosis: Report of Experience in Three Cases. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, D.S. Disulfiram (Antabuse) Neurotoxicity: Implications of Painful Small Fiber Sensory Polyneuropathy for Lyme Disease and Addiction. World J. Neurosci. 2020, 10, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schardt, F.W. Different Treatments in Patients with Neuroborreliosis and Coinfections. Med. Res. Arch. 2023, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potula, H.-H.S.K.; Shahryari, J.; Inayathullah, M.; Malkovskiy, A.V.; Kim, K.-M.; Rajadas, J. Repurposing Disulfiram (Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide) as a Potential Drug Candidate against Borrelia burgdorferi In Vitro and In Vivo. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Manzo, H.S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of Disulfiram Drug Combinations and Identification of Other More Effective Combinations against Stationary Phase Borrelia burgdorferi. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, L.; Süss, R.; Zannettino, A.; Richter, K. The revival of dithiocarbamates: From pesticides to innovative medical treatments. iScience 2021, 24, 102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, Y.; Jacobs, M.B.; Hasenkampf, N.R.; Tardo, A.C.; McDaniel, C.E.; Embers, M.E. Superior efficacy of combination antibiotic therapy versus monotherapy in a mouse model of Lyme disease. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1293300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautmann, A.; Gascan, H.; Ghozzi, R. Potential Patient-Reported Toxicities with Disulfiram Treatment in Late Disseminated Lyme Disease. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkő, B.M.; Lamprou, D.A.; Sebestyén, A.; Zelkó, R.; Sebe, I. Clinical, pharmacological, and formulation evaluation of disulfiram in the treatment of glioblastoma—A systematic literature review. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, J.; Biniaz-Harris, N.; Kuvaldina, M.; Jain, S.; Lewis, K.; Fallon, B.A. Disulfiram: Mechanisms, Applications, and Challenges. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Gao, W.; Pu, Y.; Luo, K.; He, B.; Gu, Z. Leveraging disulfiram to treat cancer: Mechanisms of action, delivery strategies, and treatment regimens. Biomaterials 2022, 281, 121335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allensworth, J.L.; Evans, M.K.; Bertucci, F.; Aldrich, A.J.; Festa, R.A.; Finetti, P.; Ueno, N.T.; Safi, R.; McDonnell, D.P.; Thiele, D.J.; et al. Disulfiram (DSF) acts as a copper ionophore to induce copper-dependent oxidative stress and mediate anti-tumor efficacy in inflammatory breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Schneider, J.M.; Schneider, E.M. Disulfiram Inhibits Opsonin-Independent Phagocytosis and Migration of Human Long-Lived In Vitro Cultured Phagocytes from Multiple Inflammatory Diseases. Cells 2024, 13, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, R.I.; Freeman, P.R. Efficacy of Short-Term High Dose Pulsed Dapsone Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Lyme Disease/Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS) and Associated Co-Infections: A Report of Three Cases and Literature Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, R.I.; Fallon, J.; Freeman, P.R. Combining Double-Dose and High-Dose Pulsed Dapsone Combination Therapy for Chronic Lyme Disease/Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome and Co-Infections, Including Bartonella: A Report of 3 Cases and a Literature Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, K.R.; Moore, J.A.; Long, T.E. Antibacterial activity of disulfiram and its metabolites. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, B. The Promiscuity of Disulfiram in Medicinal Research. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, D.S.; Murphy, B.F. Antabuse for Lyme Disease: The Way Forward. World J. Neurosci. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grout, M.M.; Mitchell, K.B. Disulfiram—Mitigating Unintended Effects. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, S.M.; Schweig, S.K. The Use of Natural Bioactive Nutraceuticals in the Management of Tick-Borne Illnesses. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkő, B.M.; Tóth, G.; Moldvai, D.; Kádár, S.; Szabó, E.; Szabó, Z.I.; Kraszni, M.; Szente, L.; Fiser, B.; Sebestyén, A.; et al. Cyclodextrin encapsulation enabling the anticancer repositioning of disulfiram: Preparation, analytical and in vitro biological characterization of the inclusion complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 657, 124187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, D.A.; Colgan, S.T.; Langer, C.S.; Bandi, N.T.; Likar, M.D.; Van Alstine, L. Dissolution Similarity Requirements: How Similar or Dissimilar Are the Global Regulatory Expectations? AAPS J. 2016, 18, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kádár, S.; Tőzsér, P.; Nagy, B.; Farkas, A.; Nagy, Z.K.; Tsinman, O.; Tsinman, K.; Csicsák, D.; Völgyi, G.; Takács-Novák, K.; et al. Flux-Based Formulation Development-A Proof of Concept Study. AAPS J. 2022, 24, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoli, A.; Favoni, O. Particle size, size distribution and morphological evaluation of airborne dust particles of diverse woods by scanning electron microscopy and image processing program. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S. Physiological and Pharmaceutical Considerations for Rectal Drug Formulations. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, R.; Sanshita; Kumar, A.; Vishvakarma, V.; Huanbutta, K.; Singh, I.; Sangnim, T. Advancements in Rectal Drug Delivery Systems: Clinical Trials, and Patents Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P. Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations I: Structure and physicochemical properties, formation of complexes, and types of complex. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, G.; Yarnykh, T.; Herasymova, I. Analytical Review of the Modern Range of Suppository Bases. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, W.M.; Lide, D.R.; Bruno, T.J. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data, 97th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tyukova, V.S.; Kedik, S.A.; Panov, A.V.; Zhavoronok, E.S.; Mendeleev, D.I.; Senchikhin, I.N.; Fursova, A.Z.; Rumyantseva, Y.V.; Kolosova, N.G. Synthesis of a Disulfuram Inclusion Complex with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Its Effect on Cataract Development in Rats. Pharm. Chem. J. 2020, 53, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, D.; Ito, Y.; Nabekura, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C. Bioavailability and anticataract effects of a topical ocular drug delivery system containing disulfiram and hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin on selenite-treated rats. Curr. Eye Res. 2004, 29, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, L.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, D. Therapeutic effect of disulfiram inclusion complex embedded in hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on intracranial glioma-bearing male rats via intranasal route. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 156, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Kaya, A.; Alves, D.; Ansari-Fard, N.; Tolaymat, I.; Arafat, B.; Najlah, M. Preparation and Characterization of Disulfiram and Beta Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Potential Application in the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 via Nebulization. Molecules 2022, 27, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebukuro, T.; Arima, T.; Kasamatsu, M.; Nakano, Y.; Tobita, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; Terashima, Y.; Toda, E.; Shimizu, A.; Takahashi, H. Disulfiram Ophthalmic Solution Inhibited Macrophage Infiltration by Suppressing Macrophage Pseudopodia Formation in a Rat Corneal Alkali Burn Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.K.; Branton, A.; Trivedi, D.; Nayak, G.; Bairwa, K.; Jana, S. Spectroscopic Characterization of Disulfiram and Nicotinic Acid after Biofield Treatment. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2015, 6, 1000265. [Google Scholar]
- Butnariu, M.; Peana, M.; Sarac, I.; Chirumbolo, S.; Tzoupis, H.; Chasapis, C.T.; Bjørklund, G. Analytical and in silico study of the inclusion complexes between tropane alkaloids atropine and scopolamine with cyclodextrins. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 5523–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, K. Morphology, compatibility, physical and thermo-regulated properties of the electrospinning polyamide 6 and polyethylene glycol blended nanofibers. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 45, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajarin-Reinares, M.; Martinez-Esteve, E.; Pena-Rodríguez, E.; Cañellas-Santos, M.; Bulut, S.; Karabelas, K.; Clauss, A.; Nieto, C.; Mallandrich, M.; Fernandez-Campos, F. The Efficacy and Biopharmaceutical Properties of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Disulfiram and Benzyl Benzoate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, R.I.; Freeman, P.R. Efficacy of Double-Dose Dapsone Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Lyme Disease/Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS) and Associated Co-infections: A Report of Three Cases and Retrospective Chart Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuvaldina, M.; Preston, J.; Mcclellan, D.; Pavlicova, M.; Brannagan, T.H.; Fallon, B.A. A pilot study of disulfiram for individuals with persistent symptoms despite prior antibiotic treatment for Lyme disease. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1549324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Aquib, M.; Khan, D.H.; Hussain, Z.; Ahsan, A.; Baig, M.M.F.A.; Wande, D.P.; Ahmad, M.M.; Ahsan, H.M.; Jiajie, J.; et al. Recent advances in the delivery of disulfiram: A critical analysis of promising approaches to improve its pharmacokinetic profile and anticancer efficacy. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P. Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations II: Solubilization, binding constant, and complexation efficiency. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Martínez, B.; Dávila-Pousa, C.; Merino-Bohórquez, V.; García-Palomo, M.; Flox-Benítez, M.P. Use of cyclodextrins as excipients in pharmaceutical products: Why not in extemporaneous preparations? Farm. Hosp. 2021, 46, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Justen, A.; Schaldach, G.; Thommes, M. Insights into the Mechanism of Enhanced Dissolution in Solid Crystalline Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, M.; Aldén, M. Solid state studies of drug-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in PEG 6000 prepared by a new method. Eur J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kamachi, M. Complex formation between poly(ethylene glycol) and α-cyclodextrin. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 2821–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Pérez-Revuelta, B.I.; Rodríguez, L.J. Effect of PVP K-25 on the formation of the naproxen:β-ciclodextrin complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 253, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirlekar, R.S.; Sonawane, S.N.; Kadam, V.J. Studies on the effect of water-soluble polymers on drug-cyclodextrin complex solubility. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, I.; Bateson, M.; Bari, M.; Joshi, H.N. Synergistic effect of PEG-400 and cyclodextrin to enhance solubility of progesterone. AAPS PharmSciTech 2003, 4, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, B. Multiple deadlocks in the development of nonprofit drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2411–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

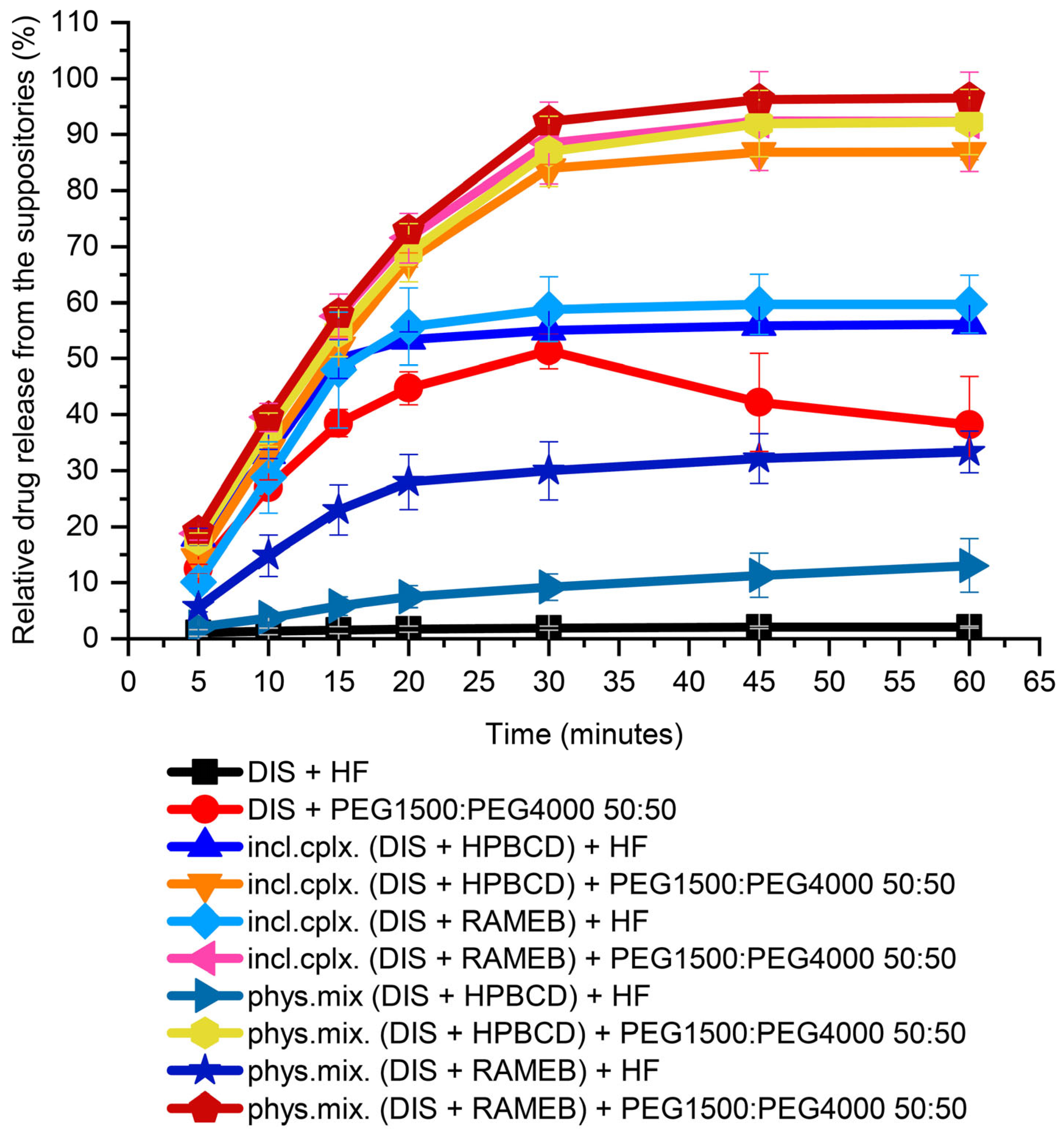
| Compared Samples | TEST: phys. mix. (DIS + HPBCD) + PEG1500:PEG4000 50:50 Versus REFERENCE: incl. cplx. (DIS + HPBCD) + PEG1500:PEG4000 50:50 | TEST: phys. mix. (DIS + RAMEB) + PEG1500:PEG4000 50:50 Versus REFERENCE: incl. cplx. (DIS + RAMEB) + PEG1500:PEG4000 50:50 |
|---|---|---|
| f1 ± Standard Error | 4.59 ± 1.09 | 12.48 ± 2.61 |
| f2 ± Standard Error | 80.88 ± 3.36 | 61.43 ± 4.78 |
| Mahalanobis distance 1 | 2.11 | 1.16 |
| Time | DIS Content (mg) [±SD] | DIS Content (%) [±SD] | Δ (Weekn-Initial) (mg) | Δ (Weekn-Initial) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 29 [±1.49] | 96.66 [±4.98] | 0 | 0 |
| Week1 | 30.24 [±1.52] | 100.79 [±5.07] | 1.24 | 4.13 |
| Week2 | 28.94 [±0.70] | 96.46 [±2.32] | −0.06 | −0.20 |
| Week3 | 30.14 [±0.64] | 100.48 [±2.14] | 1.15 | 3.82 |
| Week4 | 29.48 [±2.73] | 98.26 [±9.11] | 0.48 | 1.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benkő, B.-M.; Szabó, B.-I.; Kádár, S.; Szabó, E.; Tóth, G.; Szente, L.; Tonka-Nagy, P.; Zelkó, R.; Sebe, I. Development of Low-Dose Disulfiram Rectal Suppository Intended for Application in Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070849
Benkő B-M, Szabó B-I, Kádár S, Szabó E, Tóth G, Szente L, Tonka-Nagy P, Zelkó R, Sebe I. Development of Low-Dose Disulfiram Rectal Suppository Intended for Application in Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070849
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenkő, Beáta-Mária, Bálint-Imre Szabó, Szabina Kádár, Edina Szabó, Gergő Tóth, Lajos Szente, Péter Tonka-Nagy, Romána Zelkó, and István Sebe. 2025. "Development of Low-Dose Disulfiram Rectal Suppository Intended for Application in Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070849
APA StyleBenkő, B.-M., Szabó, B.-I., Kádár, S., Szabó, E., Tóth, G., Szente, L., Tonka-Nagy, P., Zelkó, R., & Sebe, I. (2025). Development of Low-Dose Disulfiram Rectal Suppository Intended for Application in Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070849







