Tunable Intranasal Polymersome Nanocarriers Triggered Olanzapine Brain Delivery and Improved In Vivo Antipsychotic Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Formulation of Olanzapine-Loaded Polymersomes
2.2.2. Optimization of Olanzapine-Loaded Polymersomes
2.2.3. In Vitro Characterization of Olanzapine-Loaded Polymersomes
Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurement
Determination of Olanzapine Entrapment Efficiency and Loading Efficiency
Transmission Electron Microscopy
In Vitro Serum Stability
In Vitro Drug Release
2.2.4. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamic Studies
Animals
Pharmacokinetics Study
Pharmacodynamics Study
- Paw placement test
- Open-field tests in schizophrenia-like rat model
2.2.5. Comparative Effects of Oral and Intranasal Olanzapine on Metabolic and Oxidative Stress Markers in Rats
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Optimization of Olanzapine-Loaded Polymersomes
3.2. Design Space for Optimized PolyOla Formulation
3.3. Characterization of the Prepared PolyOla
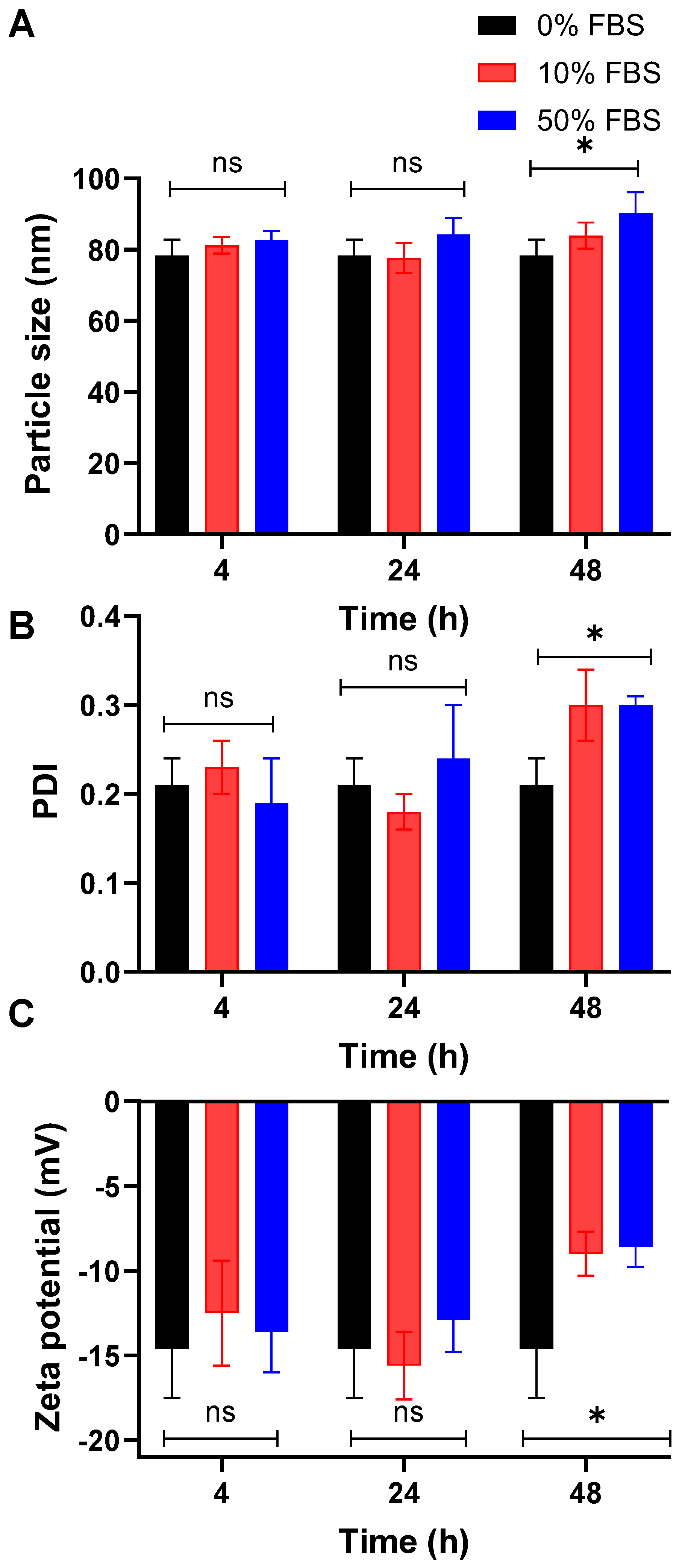
3.4. The Optimized PolyOla Serum Stability
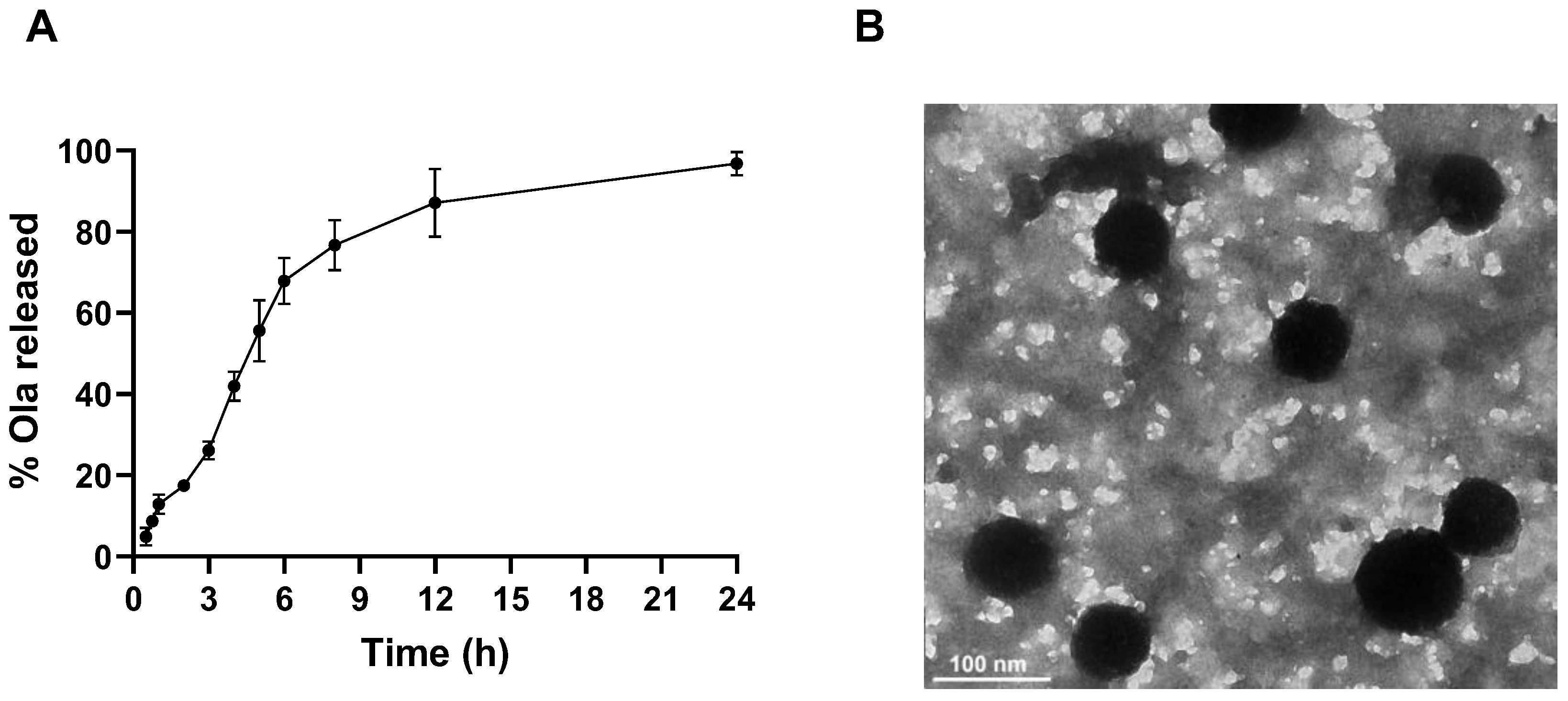
3.5. In Vitro Release Profile of Ola from PolyOla
3.6. The Transmission Electron Micrograph of PolyOla
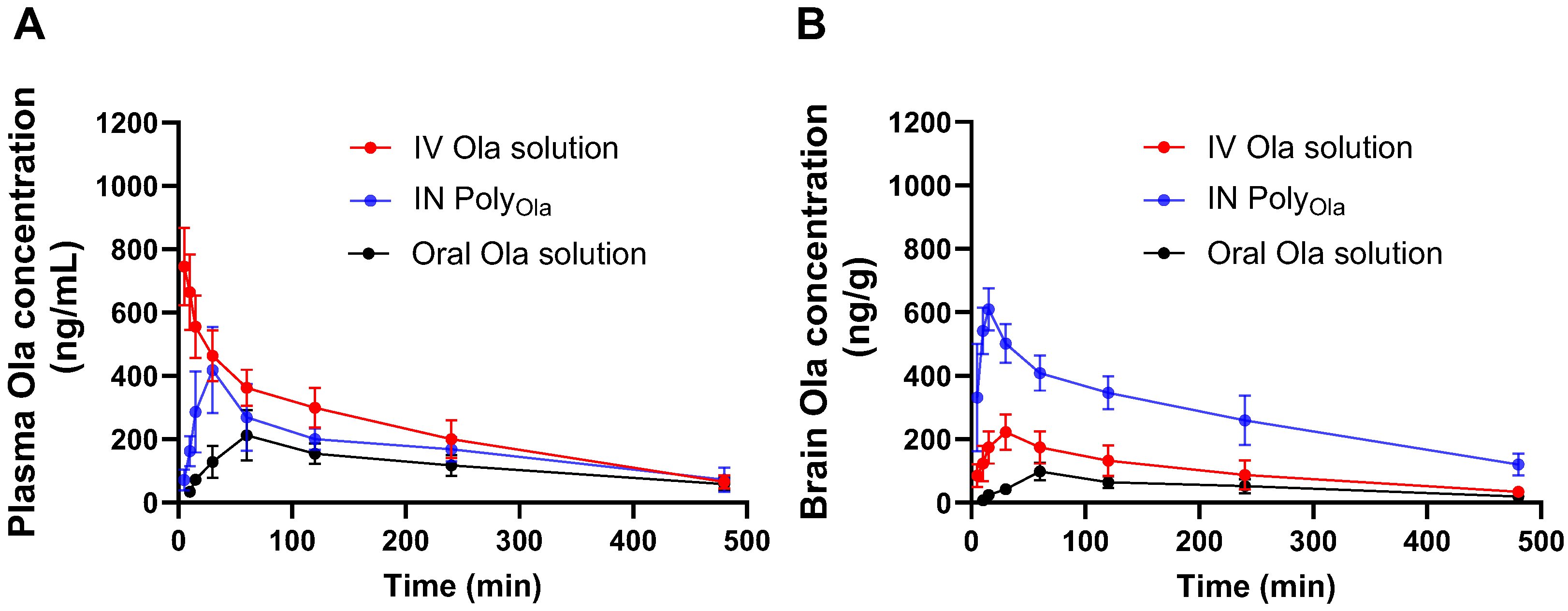
3.7. Pharmacokinetics Profile of Ola from the Prepared Nasal PolyOla Formulation
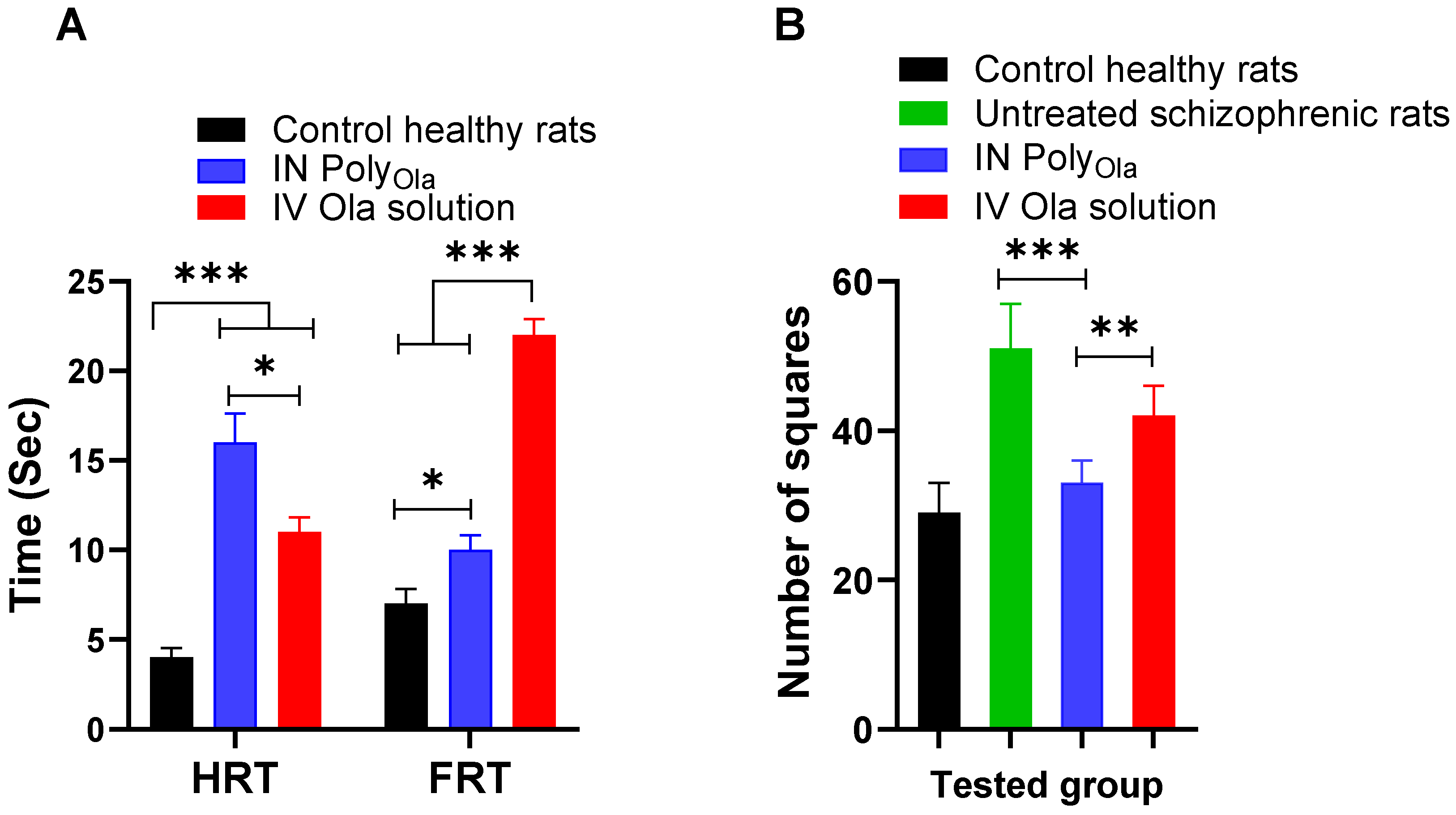
3.8. Pharmacodynamic Assessment of PolyOla in Schizophrenia’s Model Rats
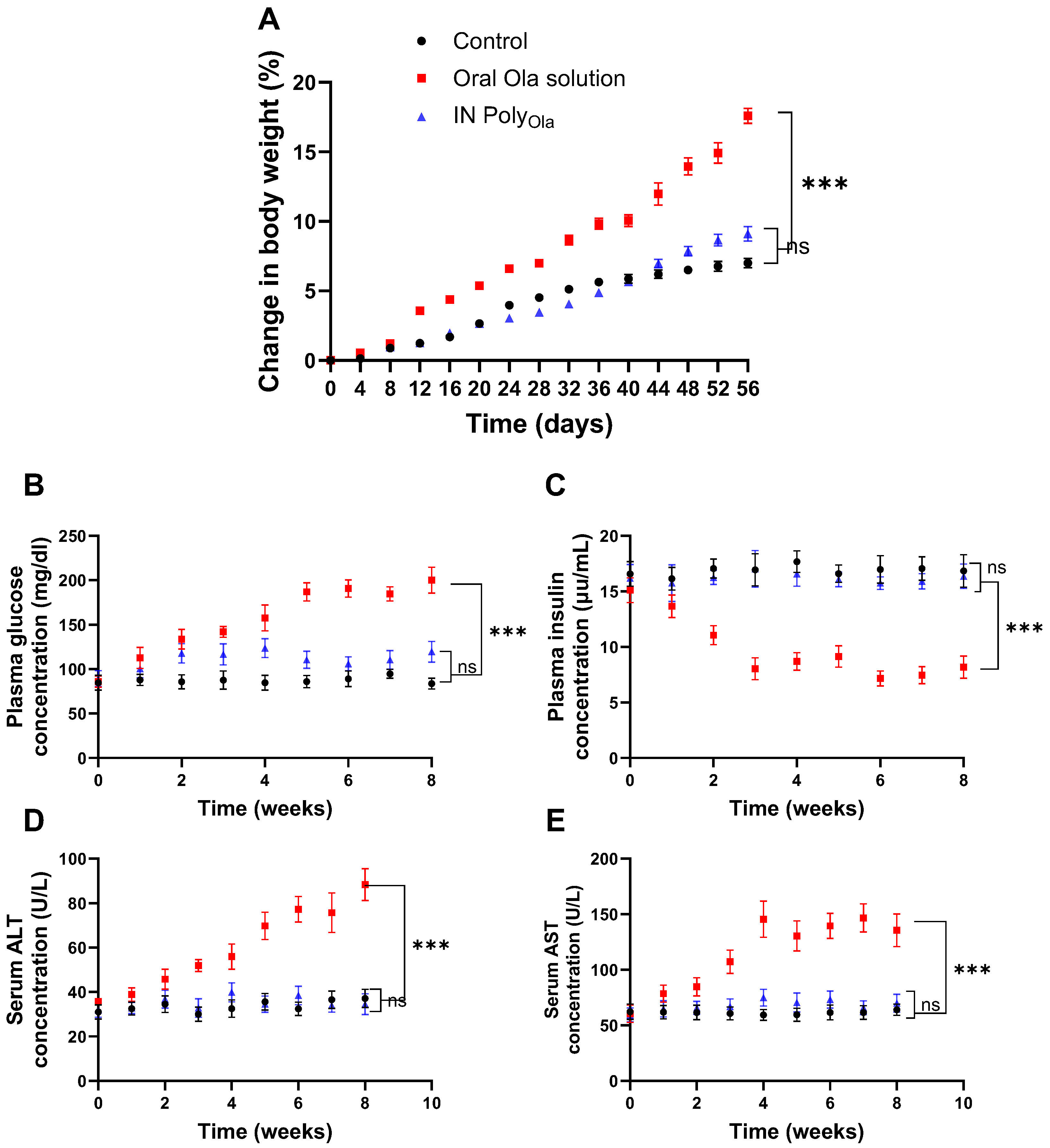
3.9. Evaluation of Metabolic and Hepatic Safety Profiles
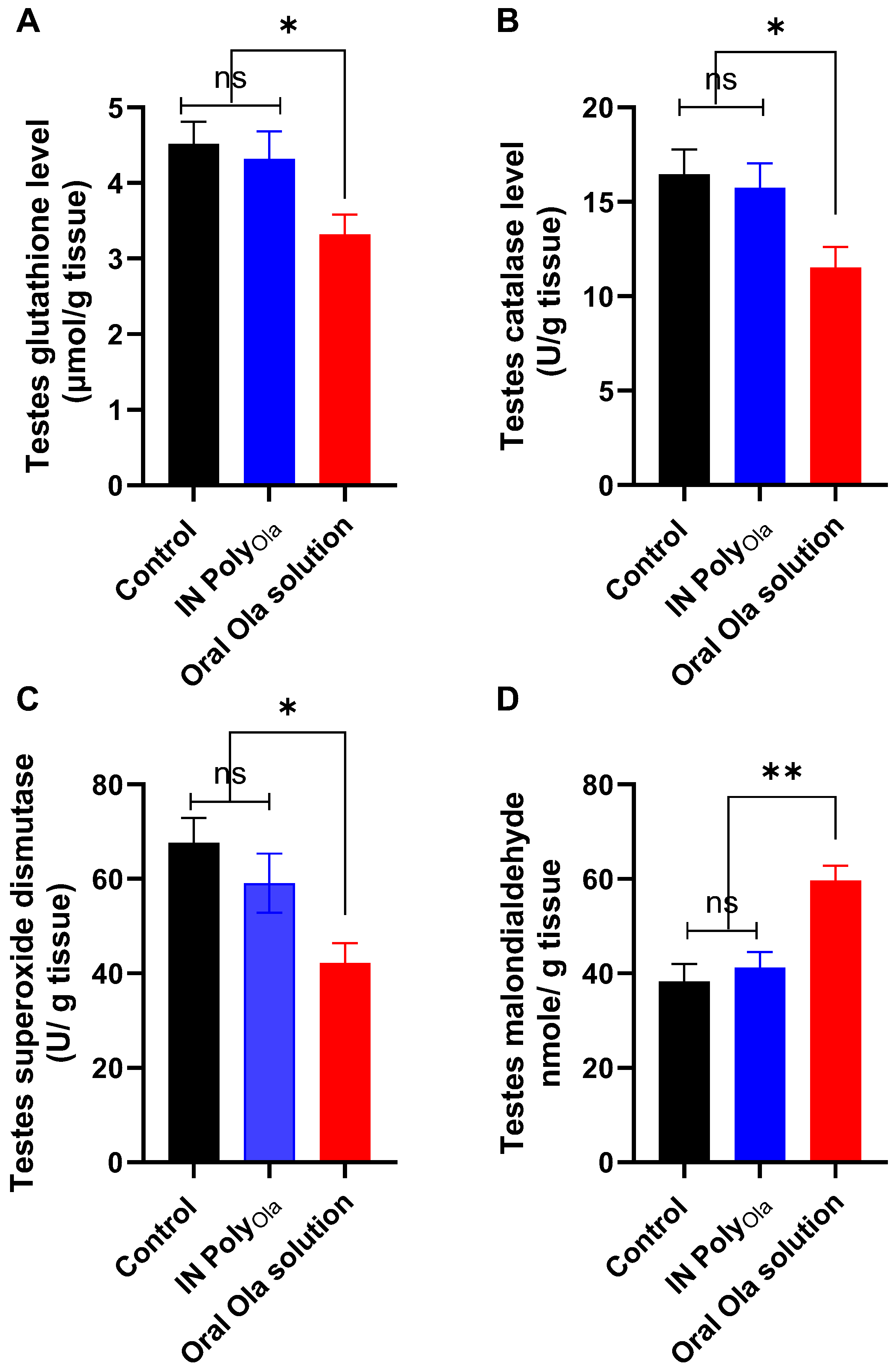
3.10. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Markers in Testicular Tissue
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayano, G. Schizophrenia: A concise overview of etiology, epidemiology diagnosis and management: Review of literatures. J. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 3, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mosolov, S.N.; Yaltonskaya, P.A. Primary and secondary negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 766692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvsannyam, E.; Jain, M.S.; Pormento, M.K.L.; Siddiqui, H.; Balagtas, A.R.A.; Emuze, B.O.; Poprawski, T. Neurobiology of Schizophrenia: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e23959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, S.; Halimi, S.M.A.; Khan, I. Olanzapine Use in Schizophrenia and the Modulation of Its Response by Genetic Variations. Mol. Med. Commun. 2022, 2, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, S.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Yang, N.; Yu, L.; Deng, Y.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Chronic olanzapine administration causes metabolic syndrome through inflammatory cytokines in rodent models of insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Chacartegui, P.; Villapalos-García, G.; Zubiaur, P.; Abad-Santos, F.; Koller, D. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated With the Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Adverse Effects of Olanzapine, Aripiprazole and Risperidone. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 711940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, C.U.; Kim, E.; Sliwa, J.K.; Hamm, W.; Gopal, S.; Mathews, M.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Saklad, S.R. Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics for Schizophrenia: An Overview. CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detke, H.C.; Zhao, F.; Witte, M.M. Efficacy of olanzapine long-acting injection in patients with acutely exacerbated schizophrenia: An insight from effect size comparison with historical oral data. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorkina, Y.; Abramova, O.; Ushakova, V.; Morozova, A.; Zubkov, E.; Valikhov, M.; Melnikov, P.; Majouga, A.; Chekhonin, V. Nano carrier drug delivery systems for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders: Advantages and limitations. Molecules 2020, 25, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.D.; Duarte, J.; Veiga, F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Pires, P.C. Nanosystems for brain targeting of antipsychotic drugs: An update on the most promising nanocarriers for increased bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, J.; Baskaran, M.; Humtsoe, L.C.; Vadivelan, R.; Justin, A. Enhanced brain targeting efficacy of Olanzapine through solid lipid nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, A.L.; Nandi, U.; Galli, M.; Trivedi, V. Olanzapine Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via High Shear Homogenization and Ultrasonication. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo El-Enin, H.A.; Ahmed, M.F.; Naguib, I.A.; El-Far, S.W.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alsalahat, I.; Abdel-Bar, H.M. Utilization of Polymeric Micelles as a Lucrative Platform for Efficient Brain Deposition of Olanzapine as an Antischizophrenic Drug via Intranasal Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veragten, A.; Contri, R.V.; Betti, A.H.; Herzfeldt, V.; Frank, L.A.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Rates, S.M.K.; Guterres, S.S. Chitosan-coated nanocapsules ameliorates the effect of olanzapine in prepulse inhibition of startle response (PPI) in rats following oral administration. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 148, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahar, N.; Hingarh, P.K.; Arun, R.; Selvaraj, J.; Anbarasan, A.; Sathianarayanan, S.; Nagaraju, G. Enhanced oral bioavailability of an antipsychotic drug through nanostructured lipid carriers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seju, U.; Kumar, A.; Sawant, K.K. Development and evaluation of olanzapine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhadri, A.; Dommeti, M.D.; Sana, J. A Comprehensive Review on the Nanotechnology-based Intranasal Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Targeting. J. Pharma Insights Res. 2024, 2, 015–023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cao, S.; Huo, M.; van Hest, J.C.; Che, H. Recent advances in permeable polymersomes: Fabrication, responsiveness, and applications. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7411–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefley, J.; Waldron, C.; Becer, C.R. Macromolecular design and preparation of polymersomes. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 7124–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobde, S.S. Polymersomes for targeting to brain tumors. In Nanocarriers for Drug-Targeting Brain Tumors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 451–481. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.; Kuperkar, K.; Yusa, S.-I.; Bahadur, P. Nanoscale Self-Assemblies from Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Proficient Templates in Drug Delivery. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 898–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghibhela, B.; Mishra, A.; Sharma, D. Chapter-3 Brahmi: A Memory Booster Medicinal Herb. ITS Benefits 2022, 5, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Kotha, R.; Kara, D.D. Polymersomes Based Versatile Nanoplatforms for Controlled Drug Delivery and Imaging. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 13, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.-J.; Xu, D.; Tian, M.-L.; Zhou, J.-F.; Wang, Q.-S.; Cui, Y.-L. Thermosensitive hydrogel designed for improving the antidepressant activities of genipin via intranasal delivery. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, J. Design and application in delivery system of intranasal antidepressants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 626882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Moreira, J.; Amaral, M.; Lobo, J.S.; Silva, A.C. Nose-to-brain delivery of lipid-based nanosystems for epileptic seizures and anxiety crisis. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, K.; Patel, S.; Singh, R.; Patel, K.; Sawant, K. Hyaluronic acid tethered pH-responsive alloy-drug nanoconjugates for multimodal therapy of glioblastoma: An intranasal route approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-B.; Xu, D.; Bai, L.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y.-L. A Review of Non-Invasive Drug Delivery through Respiratory Routes. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, D.; Shi, A.; Long, Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Hu, Y.; He, X. Multidrug-loaded liposomes prevent ischemic stroke through intranasal administration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muso-Cachumba, J.J.; Feng, S.; Belaid, M.; Zhang, Y.; de Oliveira Rangel-Yagui, C.; Vllasaliu, D. Polymersomes for protein drug delivery across intestinal mucosa. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 648, 123613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusci, L.J.; Peter Hackett, L.; Fellows, L.M.; Ilett, K.F. Determination of olanzapine in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography using ultraviolet absorbance detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 773, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehate, C.; Nayal, A.; Koul, V. Redox Responsive Polymersomes for Enhanced Doxorubicin Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katamesh, A.A.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Break, M.K.B.; Hassoun, S.M.; Subaiea, G.; Radwan, A.; Abo El-Enin, H.A. Manipulation of Lipid Nanocapsules as an Efficient Intranasal Platform for Brain Deposition of Clozapine as an Antipsychotic Drug. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek, B.A.; Peeters, B.; Honig, W.; Cools, A. The paw test: A behavioural paradigm for differentiating between classical and atypical neuroleptic drugs. Psychopharmacology 1987, 93, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Tulbah, A.S.; Darwish, H.W.; Salama, R.; Naguib, I.A.; Yassin, H.A.; Abo El-Enin, H.A. Quetiapine Albumin Nanoparticles as an Efficacious Platform for Brain Deposition and Potentially Improved Antipsychotic Activity. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsikas, N.; Georgiadou, G.; Delis, F.; Antoniou, K. Effects of anesthetic ketamine on anxiety-like behaviour in rats. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutub, M.; Tatode, A.; Premchandani, T.; Taksande, J.; Mane, D.; Umekar, M. Blending induced variations in Poloxamer’s/Pluronic’s® gelation: Thermodynamic and rheological perspectives. JCIS Open 2024, 16, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.; Jarak, I.; Victor, F.; Domingues, C.; Veiga, F.; Figueiras, A. Polymersomes as the Next Attractive Generation of Drug Delivery Systems: Definition, Synthesis and Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Walters, A.A.; Wang, J.T.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Combinatory Delivery of Etoposide and siCD47 in a Lipid Polymer Hybrid Delays Lung Tumor Growth in an Experimental Melanoma Lung Metastatic Model. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2001853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, P.; Dey, J.; Ghosh, S.K. Spontaneously formed redox-and pH-sensitive polymersomes by mPEG based cytocompatible random copolymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 501, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Sadeghi, F.; Atyabi, F.; Asouri, M.; Ahmadi, A.A.; Hadizadeh, F. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of therapy targeting epithelial-cell adhesion-molecule aptamers for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Control. Release 2015, 209, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muso-Cachumba, J.J.; Ruiz-Lara, G.; Monteiro, G.; Rangel-Yagui, C.D.O. Challenges in estimating the encapsulation efficiency of proteins in polymersomes-Which is the best method? Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 59, e23365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Owen, S.C.; Shoichet, M.S. Stability of Self-Assembled Polymeric Micelles in Serum. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6002–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kao, W.J. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Abdel-Reheem, A.Y.; Awad, G.A.; Mortada, N.D. Evaluation of brain targeting and mucosal integrity of nasally administrated nanostructured carriers of a CNS active drug, clonazepam. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 16, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotoudegan, F.; Amini, M.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Samadi, N.; Sotoudegan, F. Poloxamer®s anchored with TAT enhance blood–brain barrier penetration of carbamazepine for the treatment of epilepsy: An in vivo study. AAPS Open 2024, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltzley, S.; Mohammad, A.; Malkawi, A.H.; Al-Ghananeem, A.M. Intranasal drug delivery of olanzapine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, H.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Kamel, A.O.; Mayssa, A.H.; Awad, G.A.S. Brain delivery of olanzapine by intranasal administration of transfersomal vesicles. J. Liposome Res. 2012, 22, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo El-Enin, H.A.; Tulbah, A.S.; Darwish, H.W.; Salama, R.; Naguib, I.A.; Yassin, H.A.; Abdel-Bar, H.M. Evaluation of Brain Targeting and Antipsychotic Activity of Nasally Administrated Ziprasidone Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanocarriers. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, L.; Zoabi, A.; Yakobi, R.; Natsheh, H.; Touitou, E.; Margulis, K. Evaluation of nasal delivery systems of olanzapine by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, I.; O’Dwyer, S.; Brooks, M.; Sahm, L.; Crowley, E.; Ní Dhubhlaing, C. Worth the Weight? Olanzapine Prescribing in Schizophrenia. A Review of Weight Gain and Other Cardiometabolic Side Effects of Olanzapine. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 730769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Shah, A.; Bhat, G. Olanzapine-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Reversible Etiology Overlooked in Psychiatric Patients. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 10, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grajales, D.; Vázquez, P.; Alén, R.; Hitos, A.B.; Valverde, Á.M. Attenuation of Olanzapine-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Improves Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Metabolites 2022, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Ding, C.; Huang, P.; Ran, J.; Lian, P.; Tang, Y.; Dai, W.; Huang, X. Metformin Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis induced by olanzapine through inhibiting LXRα/PCSK9 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebaid, H.; Bashandy, S.A.E.; Hassan, I.; Al-Tamimi, J.; Haredy, S.A.; Imbabi, T.; Omara, E.A.; Bashandy, Y.S.; Awad, E.M. The Preventive Effect of Zinc Sulfate against Olanzapine-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Male Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 203, 3764–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factors | Levels | |
|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |
| A: P401 concentration (mg/mL) a | 30 | 50 |
| B: Ola concentration (mg/mL) b | 1 | 3 |
| C: Stirring speed (rpm) | 500 | 1000 |
| Responses | Constraints | |
| Y1: Particle size (nm) | Minimize | |
| Y2: EE (%) | Maximize | |
| Y3: LE (%) | Maximize | |
| Formula | Particle Size (nm) b,f | PDI b,f | Zeta Potential (mV) c,f | EE% d,f | LE% e,f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyOla | 78.3 ± 4.5 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | −14.64 ± 2.9 | 91.36 ± 3.55 | 9.11 ± 1.59 |
| Parameter | Plasma | Brain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV Ola Solution | Oral Ola Solution | IN PolyOla | IV Ola Solution | Oral Ola Solution | IN PolyOla | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | - | 212.38 ± 24.36 | 418.21 ± 45.69 | 222.65 ± 25.32 | 98.21 ± 12.11 | 609.46 ± 65.98 |
| Tmax (min) | - | 60 | 30 | 30 | 60 | 15 |
| AUC 0–480 min (µg/mL.h) | 108.34 ± 9.69 | 55.34 ± 6.12 | 82.53 ± 8.14 | 47.31± 7.33 | 23.21 ± 3.55 | 131.68 ± 11.96 |
| MRT (h) | 2.62 ± 0.27 | 3.24 ± 0.39 | 2.96 ± 0.34 | 2.766± | 3.15± | 2.96± |
| Kel (h−1) | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.28± | 0.2± | 0.17± |
| DTE (%) | - | - | - | - | - | 365.38 |
| DTP (%) | - | - | - | - | - | 72.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katamesh, A.A.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Mahafdeh, R.; Bin Break, M.K.; Hassoun, S.M.; Subaiea, G.M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Almansour, K.; Abo El-Enin, H.A.; Yassin, H.A. Tunable Intranasal Polymersome Nanocarriers Triggered Olanzapine Brain Delivery and Improved In Vivo Antipsychotic Activity. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070811
Katamesh AA, Abdel-Bar HM, Mahafdeh R, Bin Break MK, Hassoun SM, Subaiea GM, El-Naggar ME, Almansour K, Abo El-Enin HA, Yassin HA. Tunable Intranasal Polymersome Nanocarriers Triggered Olanzapine Brain Delivery and Improved In Vivo Antipsychotic Activity. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070811
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatamesh, Ahmed A., Hend Mohamed Abdel-Bar, Rania Mahafdeh, Mohammed Khaled Bin Break, Shimaa M. Hassoun, Gehad M. Subaiea, Mostafa E. El-Naggar, Khaled Almansour, Hadel A. Abo El-Enin, and Heba A Yassin. 2025. "Tunable Intranasal Polymersome Nanocarriers Triggered Olanzapine Brain Delivery and Improved In Vivo Antipsychotic Activity" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070811
APA StyleKatamesh, A. A., Abdel-Bar, H. M., Mahafdeh, R., Bin Break, M. K., Hassoun, S. M., Subaiea, G. M., El-Naggar, M. E., Almansour, K., Abo El-Enin, H. A., & Yassin, H. A. (2025). Tunable Intranasal Polymersome Nanocarriers Triggered Olanzapine Brain Delivery and Improved In Vivo Antipsychotic Activity. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070811






