The Impact of a Manufacturing Process on the Stability of Microcrystalline Long-Acting Injections: A Case Study on Aripiprazole Monohydrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Batch Preparation Processes
2.2.1. Preparation of Vehicle
2.2.2. Vehicle Autoclaving
2.2.3. Preparation of Primary Suspension
2.2.4. Preparation of Secondary Suspension
2.2.5. Freeze-Drying
2.2.6. Sampling
2.2.7. Batch Manufacturing Conditions and Naming
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Particle Size Distribution (PSD) Analysis
2.3.2. Viscosity Analysis
2.3.3. CMCNa Molecular Mass Determination
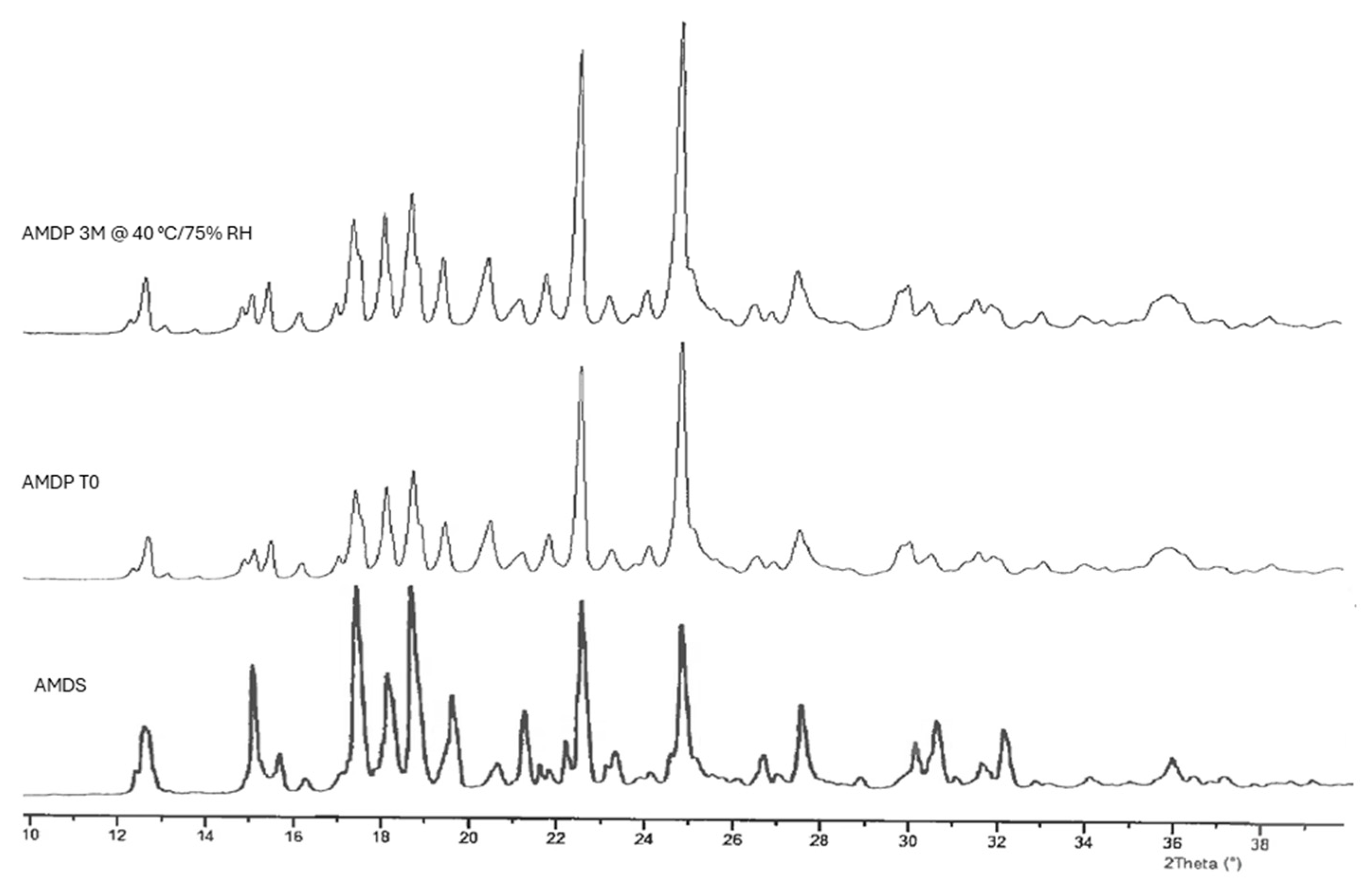
2.3.4. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) Analysis
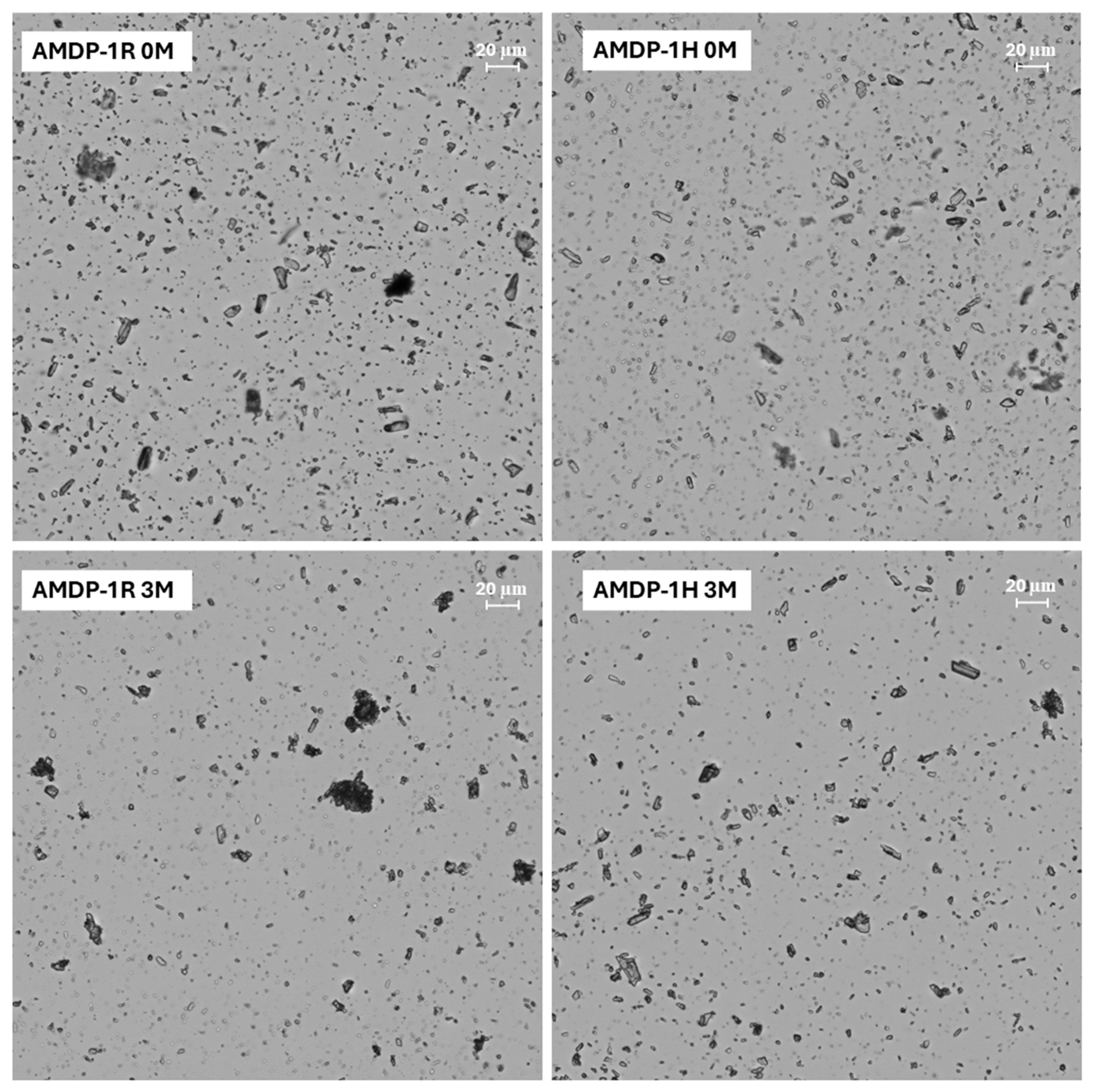
2.3.5. Optical Microscopy
2.3.6. Stability Study
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- tn—total time of milling for the n-th sample [min];
- ṁ—mass flow rate [g/min];
- msusp,n—mass of the remaining suspension at the n-th sample, accounting for the total mass of previous samples [g].
- N—theoretical passages;
- a, b—fitting parameters.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Citrome, L. Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics: What, When, and How. CNS Spectr. 2021, 26, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Kubisiak, M.; Asendrych-Wicik, K.; Kołodziejczyk, M.; Grzelińska, J.; Fabijańska, M.; Pietrzak, T. Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics—A Review on Formulation and In Vitro Dissolution. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Amatya, S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, J.H.; Seol, E.; Lee, H.; Shin, Y.-H.; Na, D.H. Long-Acting Injectable Formulations of Antipsychotic Drugs for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.S.; Velazquez, E.; Yuen, K.C.J. Long-Acting Growth Hormone Preparations—Current Status and Future Considerations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2121–e2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, J.; Lee, D.; Tice, T.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Clinical Translation of Long-Acting Drug Delivery Formulations. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.B.; Bhide, A.R.; Salave, S.; Rana, D.; Benival, D. Long-Acting Parenteral Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 198, 114862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, A.; Rannard, S. Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Challenges for Long Acting Injectable Therapies: Insights for Applications in HIV Therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 103, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulick, R.M.; Flexner, C. Long-Acting HIV Drugs for Treatment and Prevention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, C.L.; Rhodes, C.A.; Prestrelski, S.J. Long Acting Injections and Implants; Wright, J.C., Burgess, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4614-0553-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinow, B.E. Nanosuspensions in Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rifai, N.; Holm, R. Suspension-Based Long-Acting Injectables. In Biodegradable Long Acting Injectables and Implants; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 135–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnfeld, L.; Luciani, P. Injectable Lipid-Based Depot Formulations: Where Do We Stand? Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Roy, M.; Kwok, O.; Burgess, D.J. Long-Acting Injectable in Situ Forming Implants: Impact of Polymer Attributes and API. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 670, 125080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, A.K.; Vora, L.K.; Umeyor, C.; Surve, D.; Patel, A.; Biswas, S.; Patel, K.; Patravale, V.B. Polymeric in Situ Forming Depots for Long-Acting Drug Delivery Systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 200, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Burgess, D.J. Drug Release from in Situ Forming Implants and Advances in Release Testing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.N.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Loffredo, D.M. Challenges and Opportunities in the Development of Complex Generic Long-Acting Injectable Drug Products. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajora, A.; Nagpal, K. Suspensions: Theory, Formulation Considerations, Flocculated and Deflocculated Suspensions, and Evaluation of Suspension Stability. In Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 199–218. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.C.; Bae, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Wang, Y.; Kozak, D.; Ashraf, M.; Xu, X. Impact of Particle Flocculation on the Dissolution and Bioavailability of Injectable Suspensions. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 604, 120767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostwald, W. Studien Über Die Bildung Und Umwandlung Fester Körper. Z. Phys. Chem. 1897, 22, 289–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.A.; Franzén, A.; Carlert, S.; Skantze, U.; Lindfors, L.; Olsson, U. On the Ostwald Ripening of Crystalline and Amorphous Nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2025, 21, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Azad, M.; Davé, R.; Bilgili, E. Nanomilling of Drugs for Bioavailability Enhancement: A Holistic Formulation-Process Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Zheng, A. Progress in the Development of Stabilization Strategies for Nanocrystal Preparations. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakay, A.; Merwade, M.; Bilgili, E.; Dave, R.N. Novel Aspects of Wet Milling for the Production of Microsuspensions and Nanosuspensions of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.; Kimura, A.; Coffey, M.J.; Tyle, P. Pharmaceutical Development of Suspension Dosage Form. In Pharmaceutical Suspensions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 103–126. [Google Scholar]
- Breslin, J.C. Freeze-Drying/Lyophilization of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products; Rey, L., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 206, ISBN 9780429151859. [Google Scholar]
- Willmann, A.-C.; Berkenfeld, K.; Faber, T.; Wachtel, H.; Boeck, G.; Wagner, K.G. Itraconazole Nanosuspensions via Dual Centrifugation Media Milling: Impact of Formulation and Process Parameters on Particle Size and Solid-State Conversion as Well as Storage Stability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulbeari, N.; Holm, R. Wet Bead Milling by Dual Centrifugation—An Approach to Obtain Reproducible and Differentiable Suspensions. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 646, 123455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Burgess, D.J. Wet Milling Induced Physical and Chemical Instabilities of Naproxen Nano-Crystalline Suspensions. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 466, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Van den Mooter, G.; Augustijns, P. Top-down Production of Drug Nanocrystals: Nanosuspension Stabilization, Miniaturization and Transformation into Solid Products. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamatari, M.; Taylor, K.M.G.; Malamataris, S.; Douroumis, D.; Kachrimanis, K. Pharmaceutical Nanocrystals: Production by Wet Milling and Applications. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Monteagudo, S.I.; Yan, B.; Balasubramaniam, V.M. Engineering Process Characterization of High-Pressure Homogenization—From Laboratory to Industrial Scale. Food Eng. Rev. 2017, 9, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, C.; Muller, R. Drug Nanocrystals of Poorly Soluble Drugs Produced by High Pressure Homogenisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 62, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, Z.H.; Samanta, A.K.; Sia Heng, P.W. Overview of Milling Techniques for Improving the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guner, G.; Mehaj, M.; Seetharaman, N.; Elashri, S.; Yao, H.F.; Clancy, D.J.; Bilgili, E. Do Mixtures of Beads with Different Sizes Improve Wet Stirred Media Milling of Drug Suspensions? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, M.L.A.D.; Müller, R.H.; Möschwitzer, J.P. Systematic Screening of Different Surface Modifiers for the Production of Physically Stable Nanosuspensions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulbeari, N.; Holm, R. Is Roller Milling—The Low Energy Wet Bead Media Milling—A Reproducible and Robust Milling Method for Formulation Investigation of Aqueous Suspensions? Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 651, 123733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.P.; Honorato, S.B.; Filho, J.M.; Grillo, D.; Quintero, M.; Gilles, F.; Polla, G. Thermal Stability of Aripiprazole Monohydrate Investigated by Raman Spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 54, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.E.; Gelbrich, T.; Kahlenberg, V.; Tessadri, R.; Wieser, J.; Griesser, U.J. Stability of Solvates and Packing Systematics of Nine Crystal Forms of the Antipsychotic Drug Aripiprazole. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Chu, W.; Zhou, L.; Pan, W.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Ma, D.; Liang, X.; et al. Process Control and in Vitro/in Vivo Evaluation of Aripiprazole Sustained-Release Microcrystals for Intramuscular Injection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 125, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Zhong, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, G.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Tang, X. Morphological and Crystalline Transitions in Monohydrous and Anhydrous Aripiprazole for a Long-Acting Injectable Suspension. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Characteristic. ABILIFY MAINTENA (Aripiprazole) Extended-Release Injectable Suspension. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/202971s018,217006s001lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Varinot, C.; Berthiaux, H.; Dodds, J. Prediction of the Product Size Distribution in Associations of Stirred Bead Mills. Powder Technol. 1999, 105, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.C. Thermal Stability of Starch- and Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Polymers Used in Drilling Fluids. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1982, 22, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A.; Walter, R.H.; Cooley, H.J. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Flow Properties of Aqueous Guar Gum and Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) Solutions. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Recent Progress in the Viscosity Modeling of Concentrated Suspensions of Unimodal Hard Spheres. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostanski, J.W.; Matsuda, T.; Nerurkar, M.; Naringrekar, V.H. Controlled Release Sterile Injectable Aripiprazole Formulation and Method. US 2015/0024056 A1, 22 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Knieke, C.; Sommer, M.; Peukert, W. Identifying the Apparent and True Grinding Limit. Powder Technol. 2009, 195, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdeira, A.M.; Gander, B.; Mazzotti, M. Role of Milling Parameters and Particle Stabilization on Nanogrinding of Drug Substances of Similar Mechanical Properties. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, I.; Schenck, D.; Bose, S.; Ruegger, C. Optimization of Formulation and Process Parameters for the Production of Nanosuspension by Wet Media Milling Technique: Effect of Vitamin E TPGS and Nanocrystal Particle Size on Oral Absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| AMDS Batch Name 1 | AMDP Batch Name 2 | Vehicle Thermal Treatment | Homogenization During Bead Milling | Homogenization After Bead Milling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMDS-1 | AMDP-1R | N | N | N |
| AMDP-1H | Y | |||
| AMDS-2 | AMDP-2R | N | Y | N |
| AMDP-2H | Y | |||
| AMDS-2 | AMDP-3R | Y | N | N |
| AMDP-3H | Y | |||
| AMDS-3 | AMDP-4R | Y | Y | N |
| AMDP-4H | Y |
| AMDS Batch Name | Dv10 [µm] | Dv50 [µm] | Dv90 [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMDS-1 | 24 | 166 | 467 |
| AMDS-2 | 22 | 192 | 548 |
| AMDS-3 | 9 | 55 | 215 |
| Thermal Treatment Duration [min] | Mn [kDa] | Mw [kDa] | Mz [kDa] | PDI (Mw/Mn) | PDI (Mz/Mn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 40.5 (± 1.6) | 60.8 (±3.5) | 96.6 (±10.6) | 1.50 (±0.06) | 2.39 (±0.23) |
| 15 | 41.1 (±2.8) | 62.3 (±3.0) | 103.7 (±6.3) | 1.52 (±0.03) | 2.52 (±0.07) |
| 22 | 39.1 (±1.8) | 60.4 (±1.3) | 99.6 (±2.7) | 1.54 (±0.05) | 2.55 (±0.14) |
| 30 | 39.6 (±1.2) | 60.5 (±2.8) | 99.9 (±10.3) | 1.53 (±0.04) | 2.52 (±0.20) |
| 60 | 40.1 (±1.9) | 59.4 (±1.5) | 95.5 (±3.6) | 1.48 (±0.04) | 2.39 (±0.13) |
| Manufacturing Process | Dv10 [µm] | Dv50 [µm] | Dv90 [µm] | Dv99 [µm] | Dv100 [µm] | D[4;3] [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMDP-1 | 1.75 (±0.04) | 7.31 (±0.25) | 29.9 (±0.8) | 54.7 (±0.2) | 80.8 (±2.9) | 12.1 (±0.3) |
| AMDP-2 | 1.74 (±0.07) | 8.51 (±0.35) | 34.5 (±1.1) | 62.7 (±1.1) | 92.6 (±3.3) | 14.0 (±0.5) |
| AMDP-3 | 1.86 | 7.49 | 30.3 | 57.1 | 85.6 | 12.4 |
| AMDP-4 | 1.60 (±0.07) | 7.77 (±0.76) | 31.8 (±1.9) | 56.4 (±2.5) | 81.8 (±3.1) | 12.9 (±0.9) |
| Process | Stage | Dv10 [µm] | Dv50 [µm] | Dv90 [µm] | D[4;3] [µm] | Viscosity [mPa·s] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R 1 | H 1 | R 1 | H 1 | R 1 | H 1 | R 1 | H 1 | R 1 | H 1 | ||
| AMDP-1 | pre-lyo | 1.30 (±0.09) | 1.21 (±0.07) | 3.81 (±0.12) | 3.36 (±0.08) | 10.05 (±0.49) | 8.37 (±0.31) | 4.93 (±0.21) | 4.30 (±0.08) | - 3 | - 3 |
| post-lyo | 1.25 (±0.08) | 1.20 (±0.06) | 3.50 (±0.10) | 3.30 (±0.07) | 9.36 (±0.40) | 8.25 (±0.28) | 4.61 (±0.17) | 4.27 (±0.06) | 14.5 (±0.2) | 13.3 (±0.3) | |
| AMDP-2 | pre-lyo | 1.31 (±0.01) | 1.29 (±0.02) | 3.46 (±0.09) | 3.51 (±0.11) | 9.27 (±0.38) | 9.40 (±0.53) | 4.65 (±0.13) | 4.73 (±0.20) | - 3 | - 3 |
| post-lyo | - 2 | 1.30 (±0.02) | - 2 | 3.41 (±0.11) | - 2 | 9.34 (±0.61) | - 2 | 4.69 (±0.21) | - 2,3 | 12.5 (±0.4) | |
| AMDP-3 | pre-lyo | 1.46 | 1.37 | 3.62 | 3.39 | 9.06 | 8.58 | 4.63 | 4.49 | - 3 | - 3 |
| post-lyo | 1.40 | 1.35 | 3.42 | 3.31 | 8.81 | 8.42 | 4.53 | 4.42 | 11.7 | 11.1 | |
| AMDP-4 | pre-lyo | 1.18 (±0.03) | 1.16 (±0.05) | 3.33 (±0.10) | 3.36 (±0.11) | 9.19 (±0.44) | 9.46 (±0.46) | 4.73 (±0.18) | 4.76 (±0.13) | - 3 | - 3 |
| post-lyo | - 2 | 1.12 (±0.07) | - 2 | 3.21 (±0.15) | - 2 | 9.16 (±0.79) | - 2 | 4.49 (±0.31) | - 2,3 | 11.2 (±0.3) | |
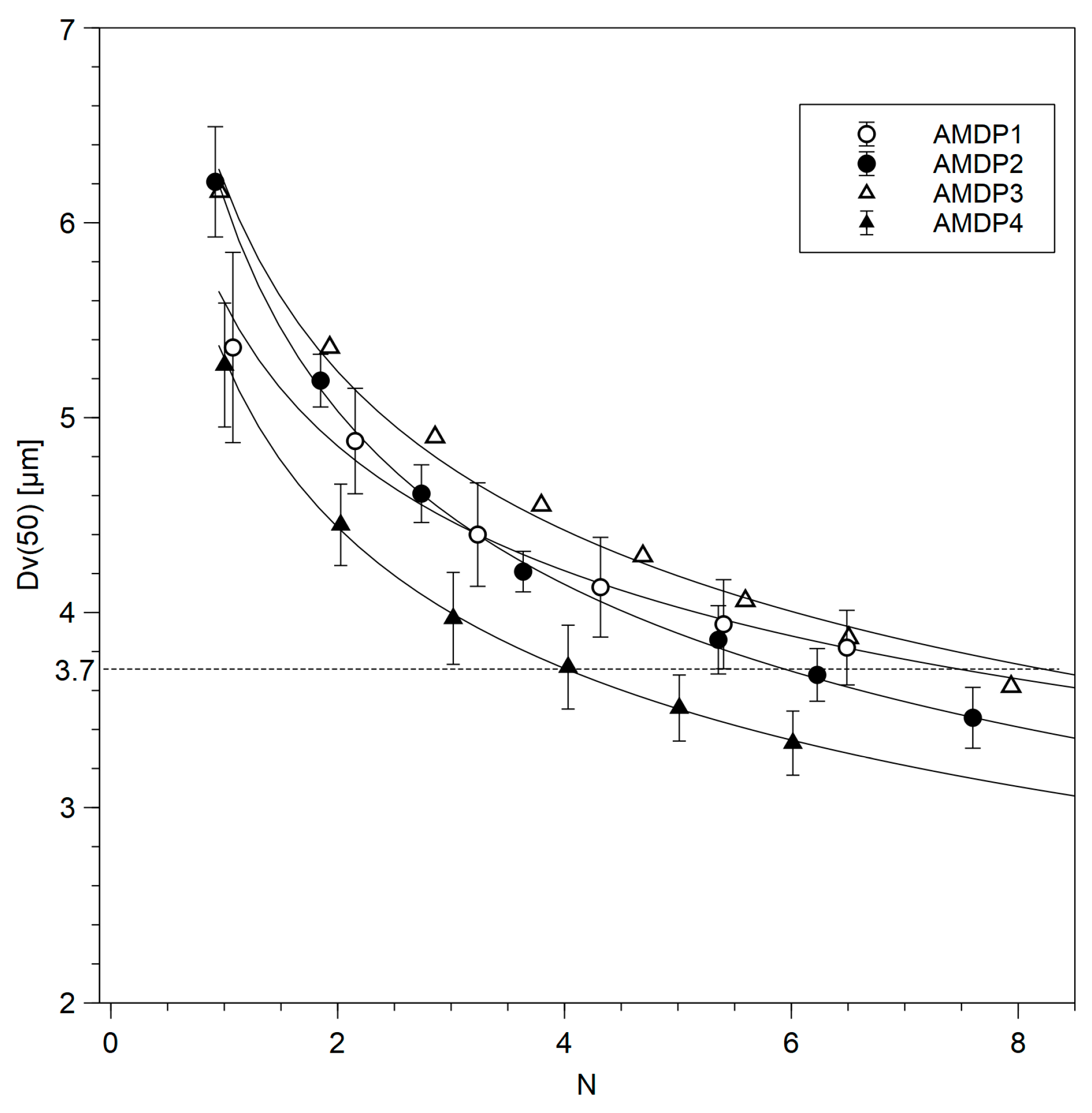
| Manufacturing Process | N |
|---|---|
| AMDP-1 | 8 |
| AMDP-2 | 6 |
| AMDP-3 | 7 |
| AMDP-4 | 4 |
| Manufacturing Process | Timepoint [months] | D[4;3] [µm] | Viscosity [mPa·s] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | H | R | H | ||
| AMDP-1 | 0 | 4.67 | 4.19 | 14.9 | 13.2 |
| 3 | 5.09 | 4.45 | 21.7 | 18.6 | |
| AMDP-2 | 0 | - 1 | 4.33 | - 1 | 11.7 |
| 3 | - 1 | 4.85 | - 1 | 12.1 | |
| AMDP-3 | 0 | 4.53 | 4.42 | 11.7 | 11.1 |
| 3 | 4.75 | 4.43 | 13.7 | 12.3 | |
| AMDP-4 | 0 | - 1 | 3.89 | - 1 | 10.7 |
| 3 | - 1 | 3.79 | - 1 | 11.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietrzak, T.; Szendzielorz, Z.; Borychowska, J.; Ratajczak, T.; Kubisiak, M. The Impact of a Manufacturing Process on the Stability of Microcrystalline Long-Acting Injections: A Case Study on Aripiprazole Monohydrate. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060735
Pietrzak T, Szendzielorz Z, Borychowska J, Ratajczak T, Kubisiak M. The Impact of a Manufacturing Process on the Stability of Microcrystalline Long-Acting Injections: A Case Study on Aripiprazole Monohydrate. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060735
Chicago/Turabian StylePietrzak, Tomasz, Ziemowit Szendzielorz, Joanna Borychowska, Tomasz Ratajczak, and Marcin Kubisiak. 2025. "The Impact of a Manufacturing Process on the Stability of Microcrystalline Long-Acting Injections: A Case Study on Aripiprazole Monohydrate" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060735
APA StylePietrzak, T., Szendzielorz, Z., Borychowska, J., Ratajczak, T., & Kubisiak, M. (2025). The Impact of a Manufacturing Process on the Stability of Microcrystalline Long-Acting Injections: A Case Study on Aripiprazole Monohydrate. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060735






