Dual pH- and Temperature-Responsive Performance and Cytotoxicity of N-Isopropylacrylamide and Acrylic Acid Functionalized Bimodal Mesoporous Silicas with Core–Shell Structure and Fluorescent Feature for Hela Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PxAN@M-BMMs
2.2.1. Synthesis of t-BMMs and Surface Modification
2.2.2. Synthesis of PxAN@M-t-BMMs
2.2.3. Removing CTAB
2.3. Loading and Releasing of IBU
2.3.1. IBU Loading
2.3.2. In Vitro Release of IBU
2.4. Computational Methods
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Cell Uptake Study
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Cellular Internalization
2.10. Hemocompatibility Test of PxAN@M-BMMs
2.11. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
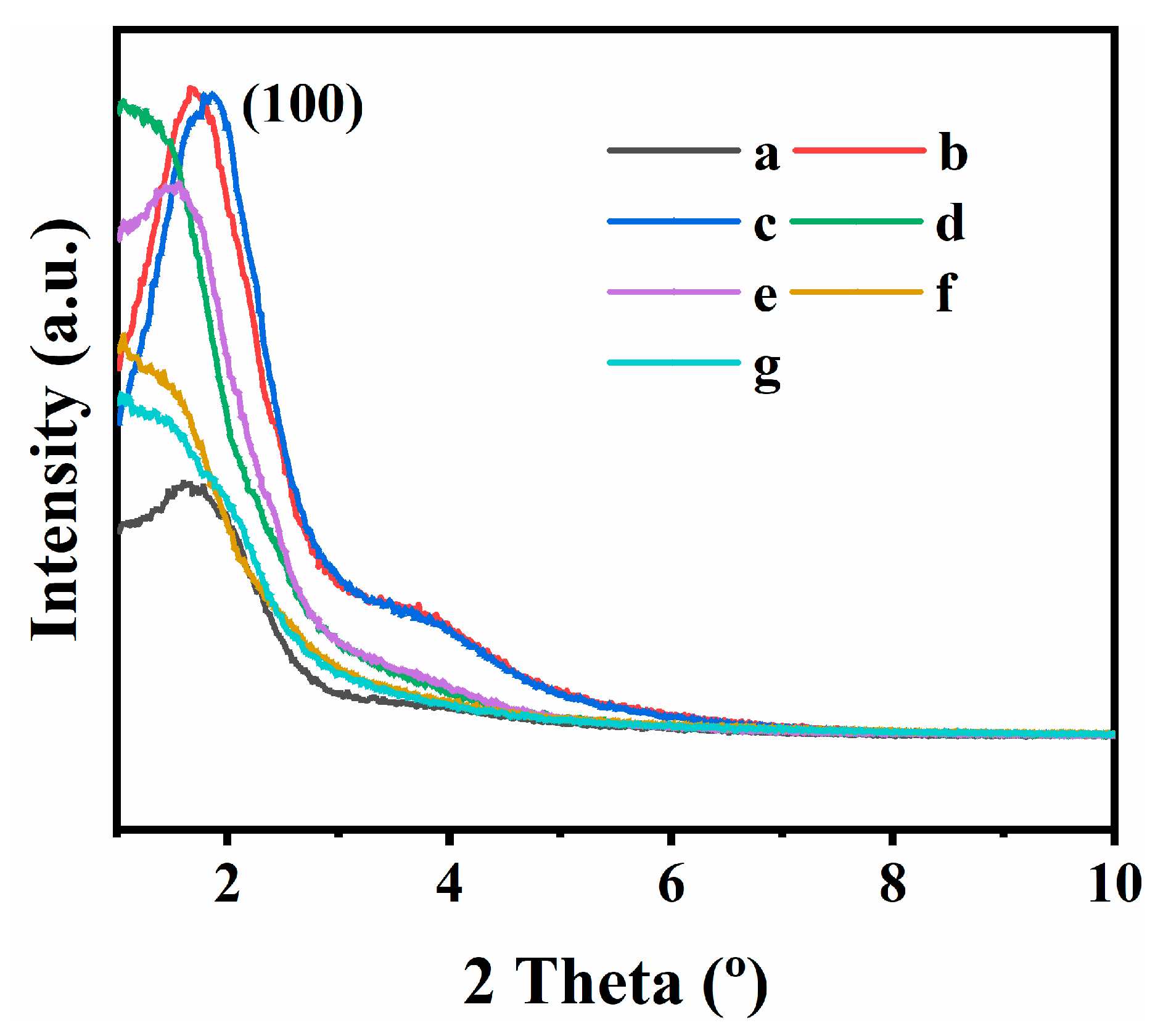
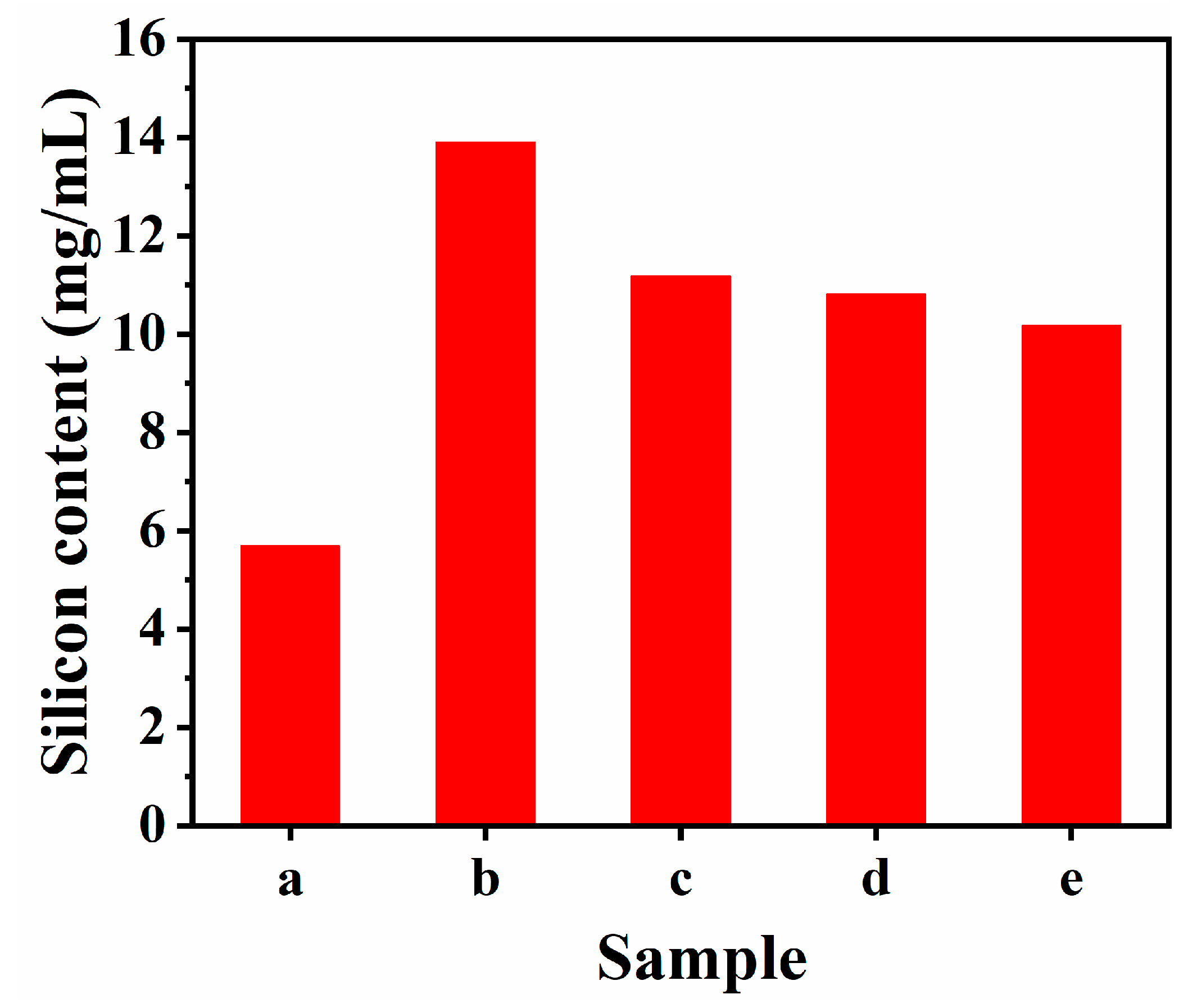
3.1. Structural and Textural Characterizations
3.2. Fractal Features
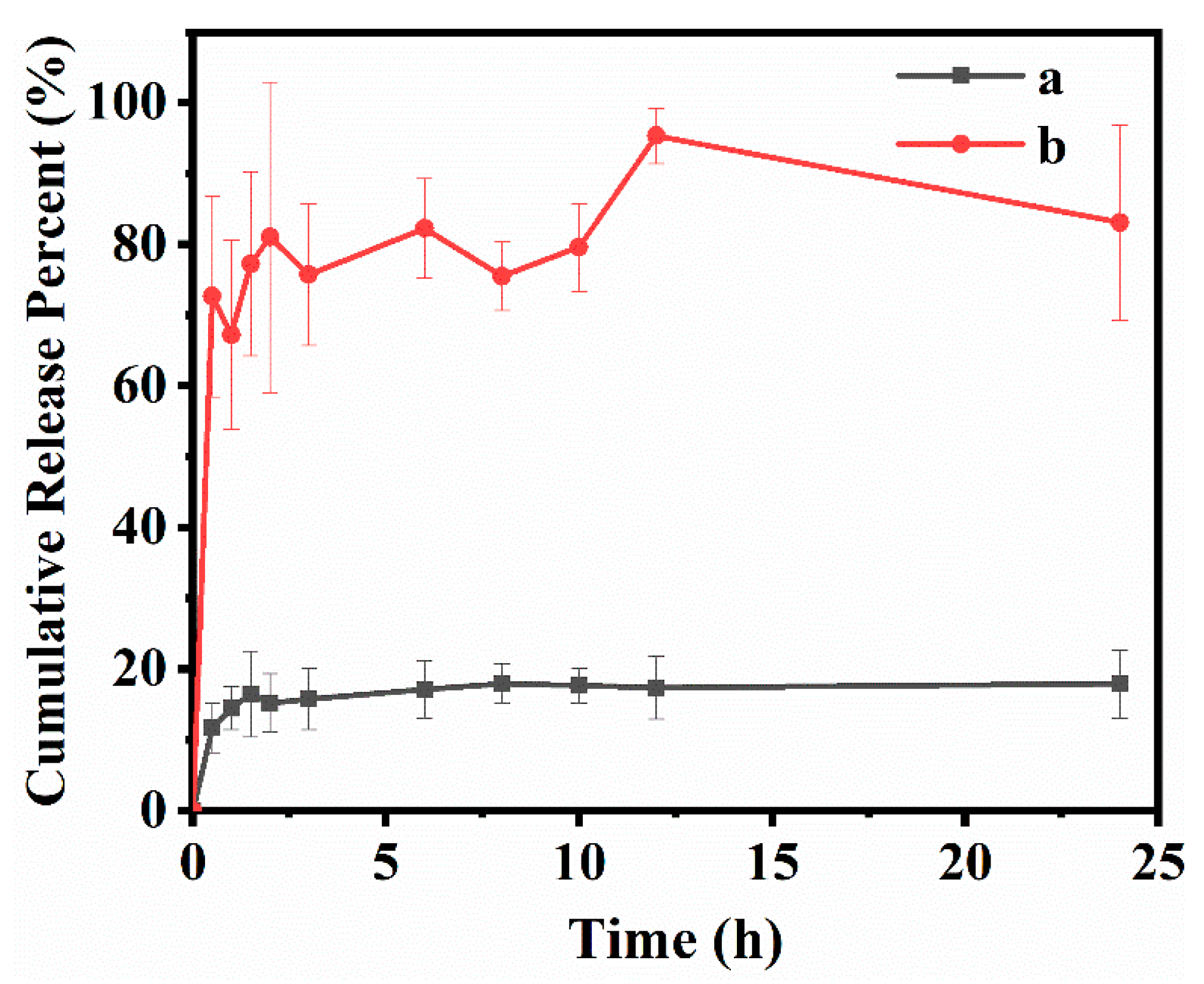
3.3. In Vitro Drug Loading and Release
3.4. Simulations for IBU-Adsorption Energy in PAN@M-BMMs
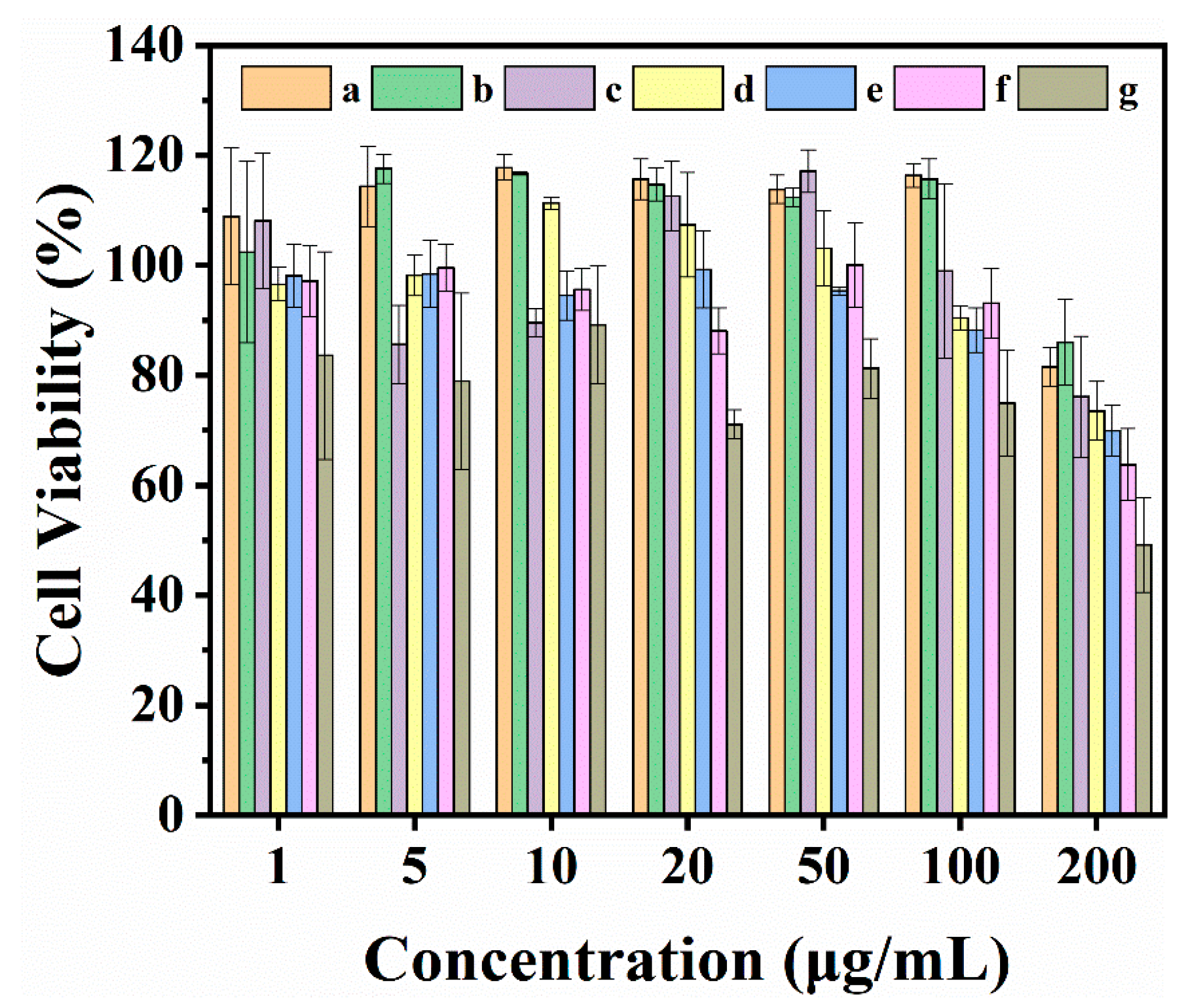
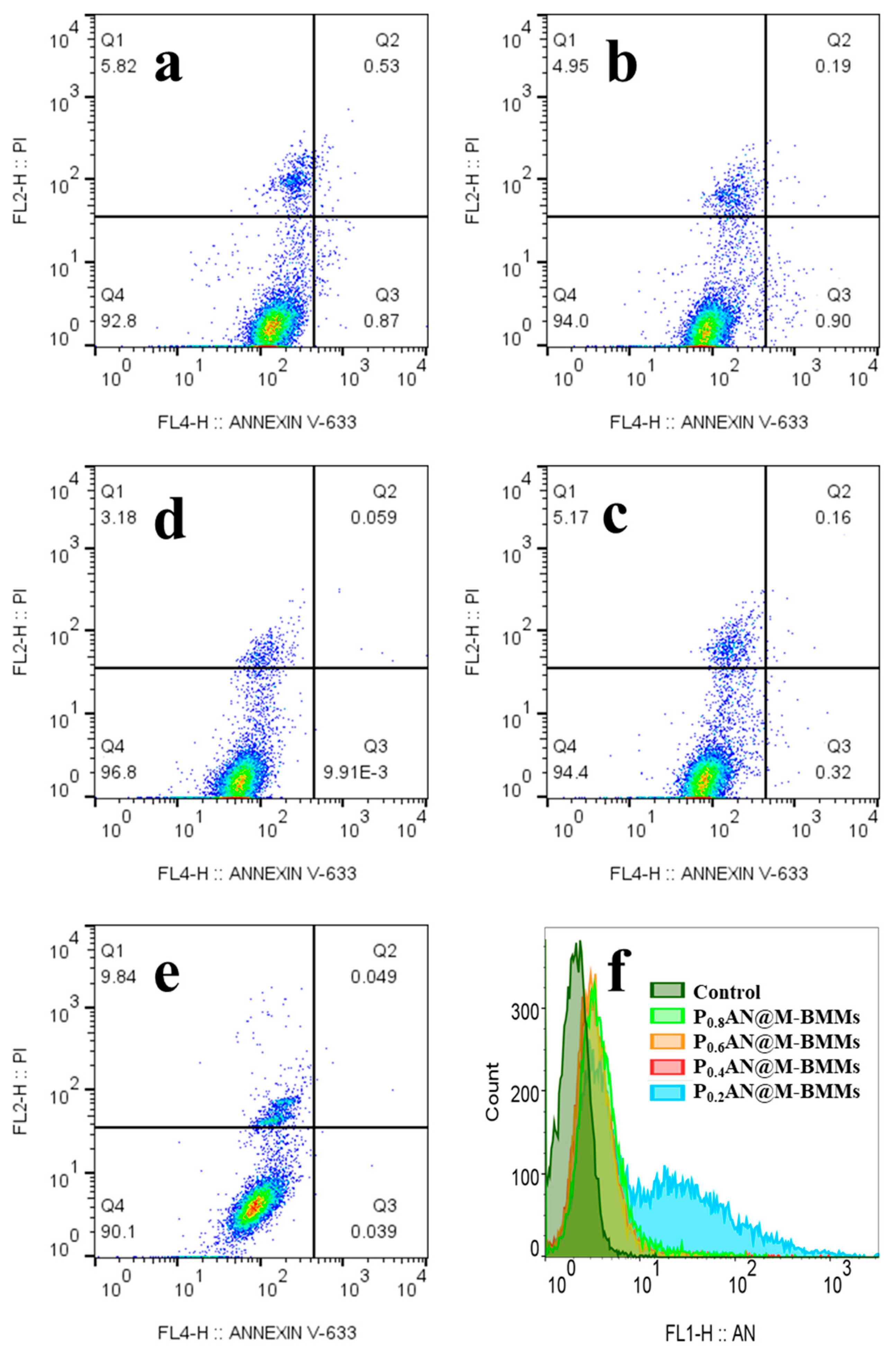
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assessment
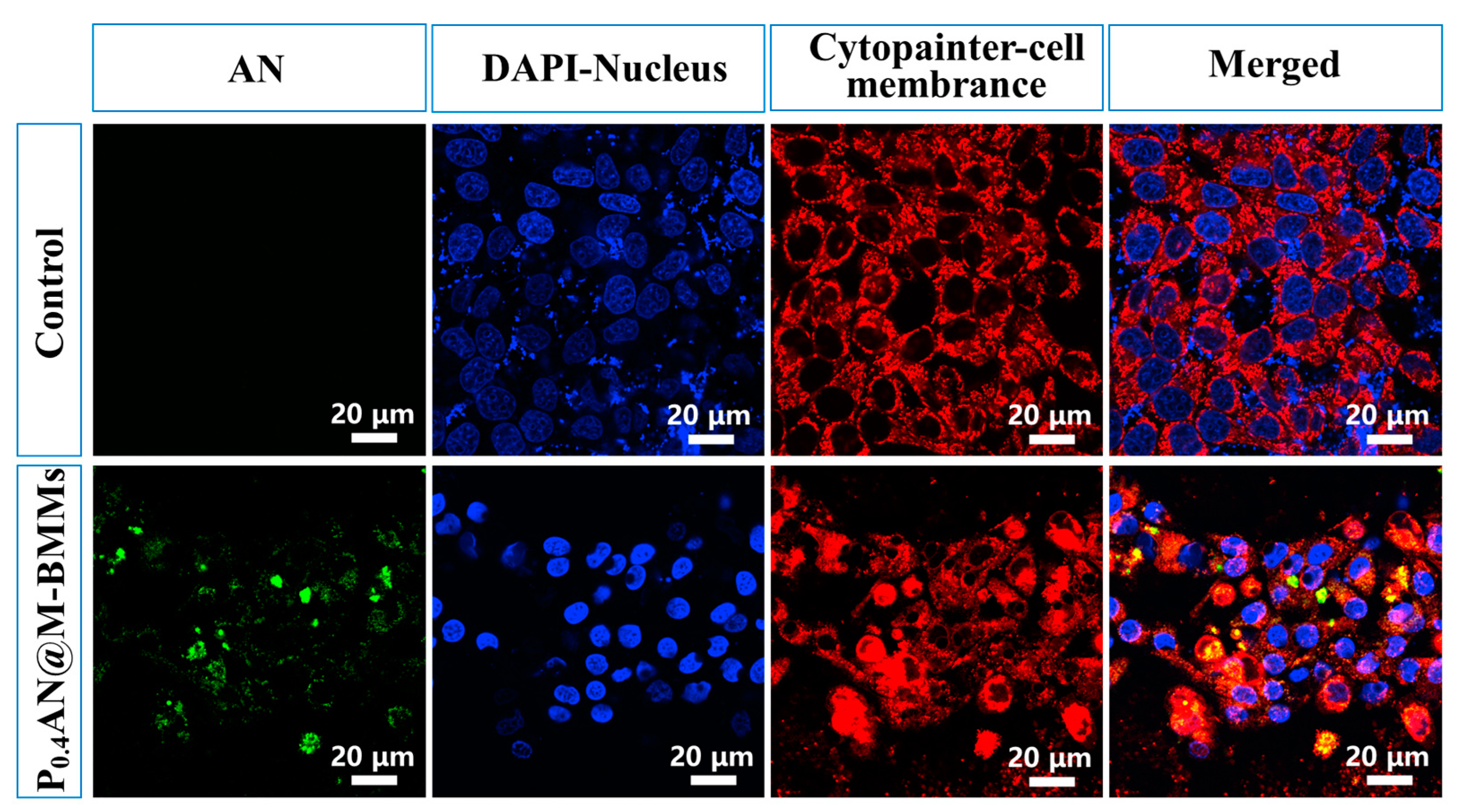
3.6. Cell Uptake Behaviors
3.7. Cellular Internalization
3.8. Hemocompatibility Test of PXAN@M-BMMs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Link, H.; Martin, R. New drugs may improve, complicate treatment for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chao, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, G.; Yi, X.; Song, G.; Cheng, L. Bottom-Up Preparation of Uniform Ultrathin Rhenium Disulfide Nanosheets for Image-Guided Photothermal Radiotherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Coimbra, R.N.; Escapa, C.; Figueiredo, S.A.; Freitas, O.M.; Otero, M. Green microalgae scenedesmus obliquus utilization for the adsorptive removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from water samples. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3707–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sádecká, J.; Cakrt, M.; Hercegová, A.; Polonský, J.; Skacáni, I. Determination of ibuprofen and naproxen in tablets. J Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 25, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Searle, S.; Muse, D.; Paluch, E.; Leyva, R.; DePadova, E.; Cruz-Rivera, M.; Kellstein, D. Efficacy and safety of single and multiple doses of a fixed-dose combination of ibuprofen and acetaminophen in the treatment of postsurgical dental pain: Results from 2 phase 3, randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Clin. J. Pain 2020, 36, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, N.; Singh, A.; Singh, M.; Das, D. Efficient MoS2 Exfoliation by Cross-β-Amyloid Nanotubes for Multistimuli-Responsive and Biodegradable Aqueous Dispersions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7772–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dai, W.; Zhang, K.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Fabricating aptamer-conjugated pegylated-MoS2/Cu1.8S theranostic nanoplatform for multiplexed imaging diagnosis and chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 160559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Schüth, F.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M. Engineering mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Where are we after two decades? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5365–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Shi, R.; Liu, H. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Cai, K.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Shen, X. Biocompatible magnetic liposomes for temperature triggered drug delivery. Nanoscale 2014, 4, 6289–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bimbo, L.M.; Mäkilä, E.; Villanova, F.; Kaasalainen, M.; Herranz-Blanco, B.; Santos, H.A. Co-delivery of a hydrophobic small molecule and a hydrophilic peptide by porous silicon nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yin, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Biomineralization inspired surface engineering of nanocarriers for pH-responsive, targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, E.; Bernardos, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Maquieira, A.; Marcos, M.D.; Pastor-Navarro, N.; Amorós, P. Controlled delivery systems using antibody-capped mesoporous nanocontainers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14075–14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cai, K.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y. Intracellular redox-activated anticancer drug delivery by functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoreservoirs with tumor specificity. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7951–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Li, X.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, X.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S.Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with organo-bridged silsesquioxane framework as innovative platforms for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 90–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Cao, S. Hydroxyapatite/mesoporous silica coated gold nanorods with improved degradability as a multi-responsive drug delivery platform. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 83, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Mao, L.; Xu, D.; Wan, Q.; Zeng, G.; Wei, Y. Preparation and controlled drug delivery applications of mesoporous silica polymer nanocomposites through the visible light induced surface-initiated ATRP. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, M.; Mao, L.; Huang, H.; Wan, Q.; Wei, Y. Direct surface grafting of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with phospholipid choline-containing copolymers through chain transfer free radical polymerization and their controlled drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Choi, E.S.; Cheon, J.Y.; Joo, S.H.; Ryu, J.H. Noncovalent polymer-gatekeeper in mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery platform. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.; Park, J.; Singha, K.; Park, H.; Kim, W.J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based cisplatin prodrug delivery and anticancer effect under reductive cellular environment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lai, S.; Shang, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X. Synthesis and performance of temperature/pH dual stimulus responsive drug carriers based on core-shell structure. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 629, 127396–127409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Jin, C.; Song, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G. A dual responsive targeted drug delivery system based on smart polymer coated mesoporous silica for laryngeal carcinoma treatment. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4830–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Panezai, H.; Bai, S.; Wu, X. Dual (pH- and temperature-) stimuli responsive nanocarrier with bimodal mesoporous silica nanoparticles core and copolymer shell for controlled ibuprofen-releasing: Fractal feature and diffusion mechanism. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2017, 254, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Panezai, H.; Bai, S.; Wu, X. P(NIPAM-co-AA)@BMMs with mesoporous silica core and controlled copolymer shell and its fractal characteristics for dual pH- and temperature-responsive performance of ibuprofen release. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2018, 67, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Panezai, H.; Bai, S.; Wu, X. Regulating dual temperature- and pH-responsibility constructed from core-shell mesoporous hybrid silica (P(NIPAM-co-AA)@BMMs) via adjusting AA incorporation onto NIPAM. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2019, 68, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Lin, L.; Gao, L. Post-treatment and characterization of novel luminescent hybrid bimodal mesoporous silicas. J. Solid State Chem. 2010, 183, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Gao, L.; Wu, X.; Yang, B. Novel luminescent hybrid materials by covalently anchoring 2-[3-(triethoxysilyl) propyl-1H-Benz [de]isoquinoline-1, 3(2H)-dione to bimodal mesoporous materials. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Wu, X. Preparation of hybrid bimodal mesoporous silicas loaded with various capacity of 1,8-naphthalic anhydride and their luminescent properties. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2012, 258, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sheng, M.; Wei, T.; Sun, J.; Bai, S.; Wu, X. Core-shell structured assembly strategy of naphthalene anhydride derivatives and MPS-modified mesoporous SiO2 with temperature-responsive property for controlled drug delivery with strong fluorescence. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2021, 70, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Sheng, M.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Bai, S. Fluorescent pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles with core-shell feature as a traceable delivery carrier for ibuprofen. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 6123–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision D.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühne, T.D.; Iannuzzi, M.; Del Ben, M.; Rybkin, V.V.; Seewald, P.; Stein, F.; Hutter, J. CP2K: An electronic structure and molecular dynamics software package-Quickstep: Efficient and accurate electronic structure calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 194103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VandeVondele, J.; Hutter, J. An efficient orbital transformation method for electronic structure calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 4365–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicki, J.D.; Sofo, J.O.; Skelton, A.A.; Bandura, A. A new hypothesis for the dissolution mechanism of silicates. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2012, 116, 17479–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shan, Z.; Maschmeyer, T.; Coppens, M.O. Synthesis of bimodal nanostructured silicas with independently controlled small and large mesopore sizes. Langmuir 2003, 19, 8395–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Jia, B.; Xu, B.; Bai, S.; Sun, J.; Munir, T. Fractal features of pH-sensitive bimodal mesoporous silica-supported bipyridine-proline organocatalysts with core-shell structure and their application in asymmetric aldol reaction. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bai, S.; Sun, J.; Han, J.; Guo, Y. pH-responsive ibuprofen delivery in silane-modified poly (methylacrylic acid) coated bimodal mesoporous silicas. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 53, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. Functionalized bimodal mesoporous silicas as carriers for controlled aspirin delivery. J. Solid. State. Chem. 2011, 184, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sun, J.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Structural characterization and surface heterogeneity of bimodal mesoporous silicas functionalized with aminopropyl groups and loaded aspirin. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Jung, M.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ha, C.S. Functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles with excellent cytotoxicity against various cancer cells for pH-responsive and controlled drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108187–108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Shang, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Z. Structure evolution of aluminosilicate sol and its structure-directing effect on the synthesis of NaY zeolite. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, D.A.; Trewhella, J. Small-angle scattering for structural biology-Expanding the frontier while avoiding the pitfalls. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Jia, B.; Xu, B.; Sun, J. Dispersion Performances of Naphthalimides Doped in Dual Temperature-and pH-Sensitive Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic Acid) Shell Assembled with Vinyl-Modified Mesoporous SiO2 Core for Fluorescence Cell Imaging. Polymers 2023, 15, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Liu, S.; Wu, S.; Lu, W.; Wang, D.; Jin, L.; Quan, Z. pH-responsive poly (acrylic acid)-gated mesoporous silica and its application in oral colon targeted drug delivery for doxorubicin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 154, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, C.; Gineste, S.; Coutelier, O.; Tourrette, A.; Marty, J.D.; Destarac, M. A deeper insight into the dual temperature-and pH-responsiveness of poly (vinylamine)-b-poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) double hydrophilic block copolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 641, 128502–128512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H. Fractal Features of Stimulus-Responsive and Fluorescent Mesoporous SiO2 for Controlled Drug Delivery. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing University of Technology (D), Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, C.; Cai, K. Reasonable design of a V2O5-x/TiO2 active interface structure with high polysulfide adsorption energy for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 403, 139723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, Q. Independent gradient model based on Hirshfeld partition: A new method for visual study of interactions in chemical systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2022, 43, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Han, Y.H.; Xia, H.Y.; Wang, S.B.; Chen, A.Z. Nanoarchitectured prototypes of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for innovative biomedical applications. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.H.; Ma, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, W.T.; Zhang, M.Q.; Meng, F.N.; Gong, Y.K. Smart MSN-drug-delivery system for tumor cell targeting and tumor microenvironment release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 42522–42532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennick, J.J.; Johnston, A.P.; Parton, R.G. Key principles and methods for studying the endocytosis of biological and nanoparticle therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, H.; Wang, X.; Bai, S.; Bi, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Fu, W.; Xu, D. Dual pH- and Temperature-Responsive Performance and Cytotoxicity of N-Isopropylacrylamide and Acrylic Acid Functionalized Bimodal Mesoporous Silicas with Core–Shell Structure and Fluorescent Feature for Hela Cell. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020206
Ge H, Wang X, Bai S, Bi Y, Liu F, Sun J, Fu W, Xu D. Dual pH- and Temperature-Responsive Performance and Cytotoxicity of N-Isopropylacrylamide and Acrylic Acid Functionalized Bimodal Mesoporous Silicas with Core–Shell Structure and Fluorescent Feature for Hela Cell. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Huijie, Xiaoli Wang, Shiyang Bai, Yuhua Bi, Fei Liu, Jihong Sun, Wenliang Fu, and Donggang Xu. 2025. "Dual pH- and Temperature-Responsive Performance and Cytotoxicity of N-Isopropylacrylamide and Acrylic Acid Functionalized Bimodal Mesoporous Silicas with Core–Shell Structure and Fluorescent Feature for Hela Cell" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020206
APA StyleGe, H., Wang, X., Bai, S., Bi, Y., Liu, F., Sun, J., Fu, W., & Xu, D. (2025). Dual pH- and Temperature-Responsive Performance and Cytotoxicity of N-Isopropylacrylamide and Acrylic Acid Functionalized Bimodal Mesoporous Silicas with Core–Shell Structure and Fluorescent Feature for Hela Cell. Pharmaceutics, 17(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020206







