Assessment of the In Vitro Biological Activities of Schiff Base-Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles as an Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer, and Anti-Cancer Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of SB and SB-CuO-NPs
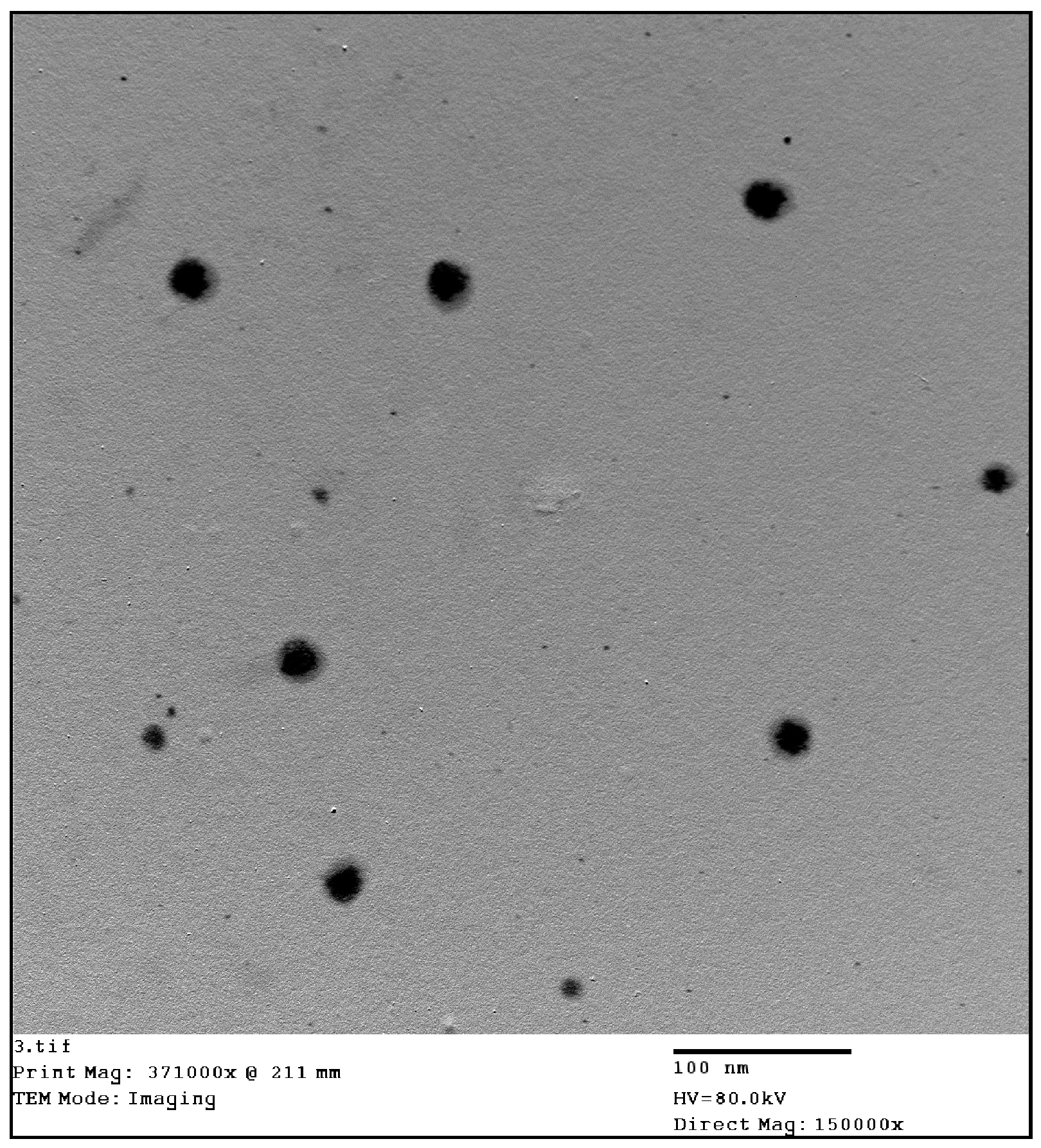
2.2. Characterization of SB-CuO-NPs
2.3. In Vitro Biological Activities
3. Results and Discussion
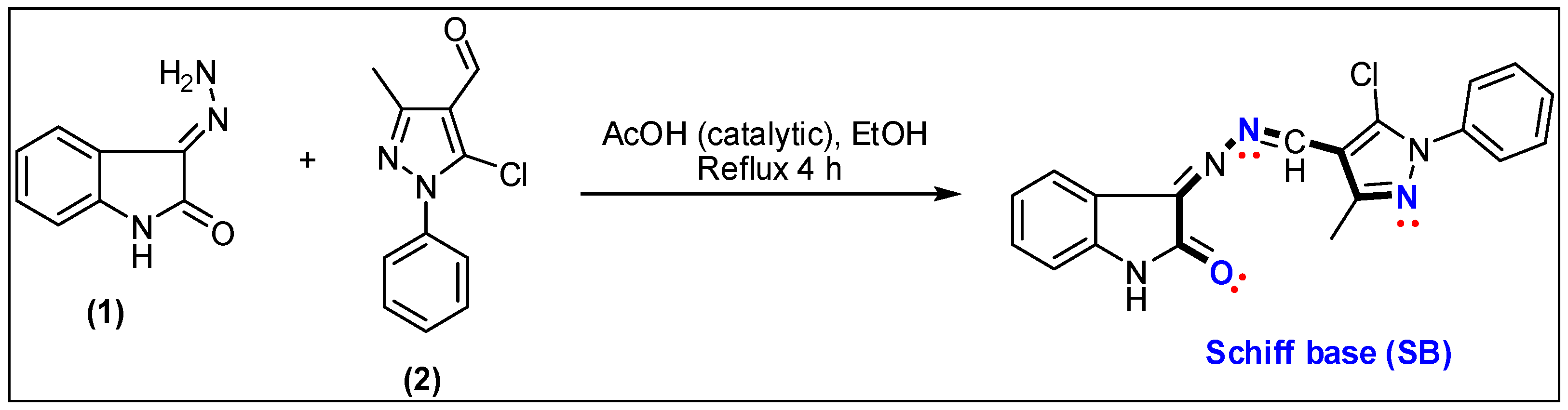
3.1. Preparation of the Schiff Base (SB)
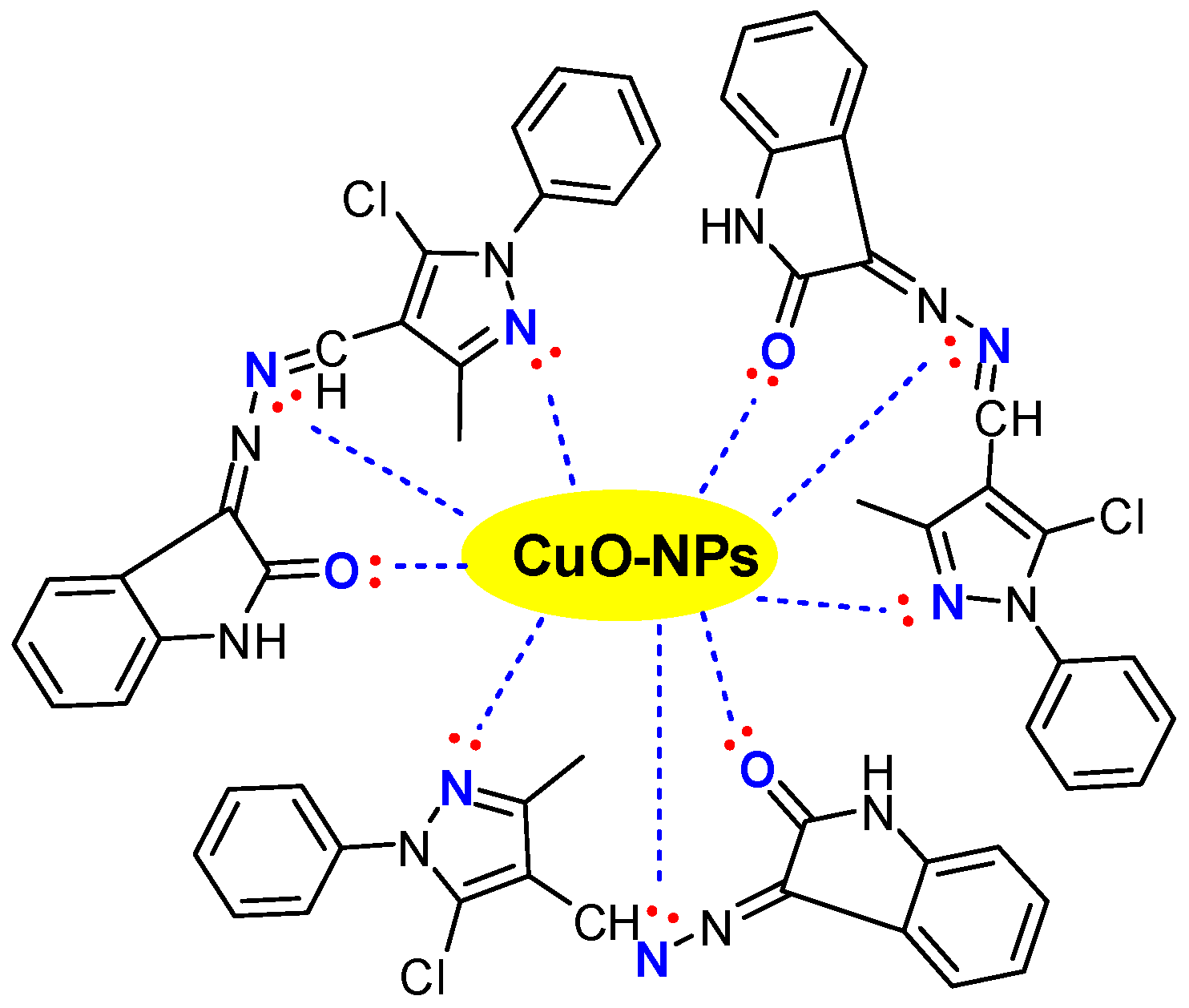
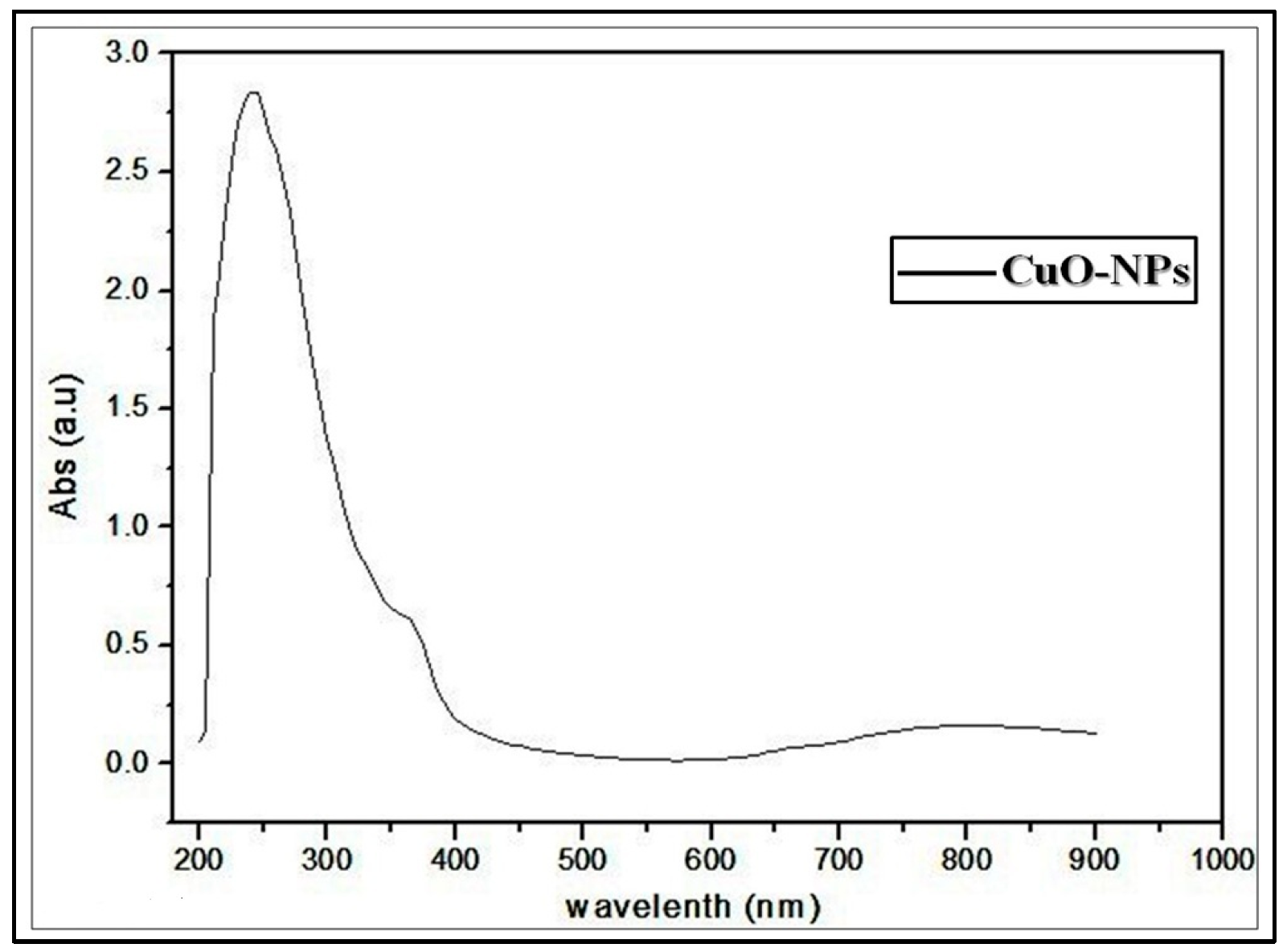
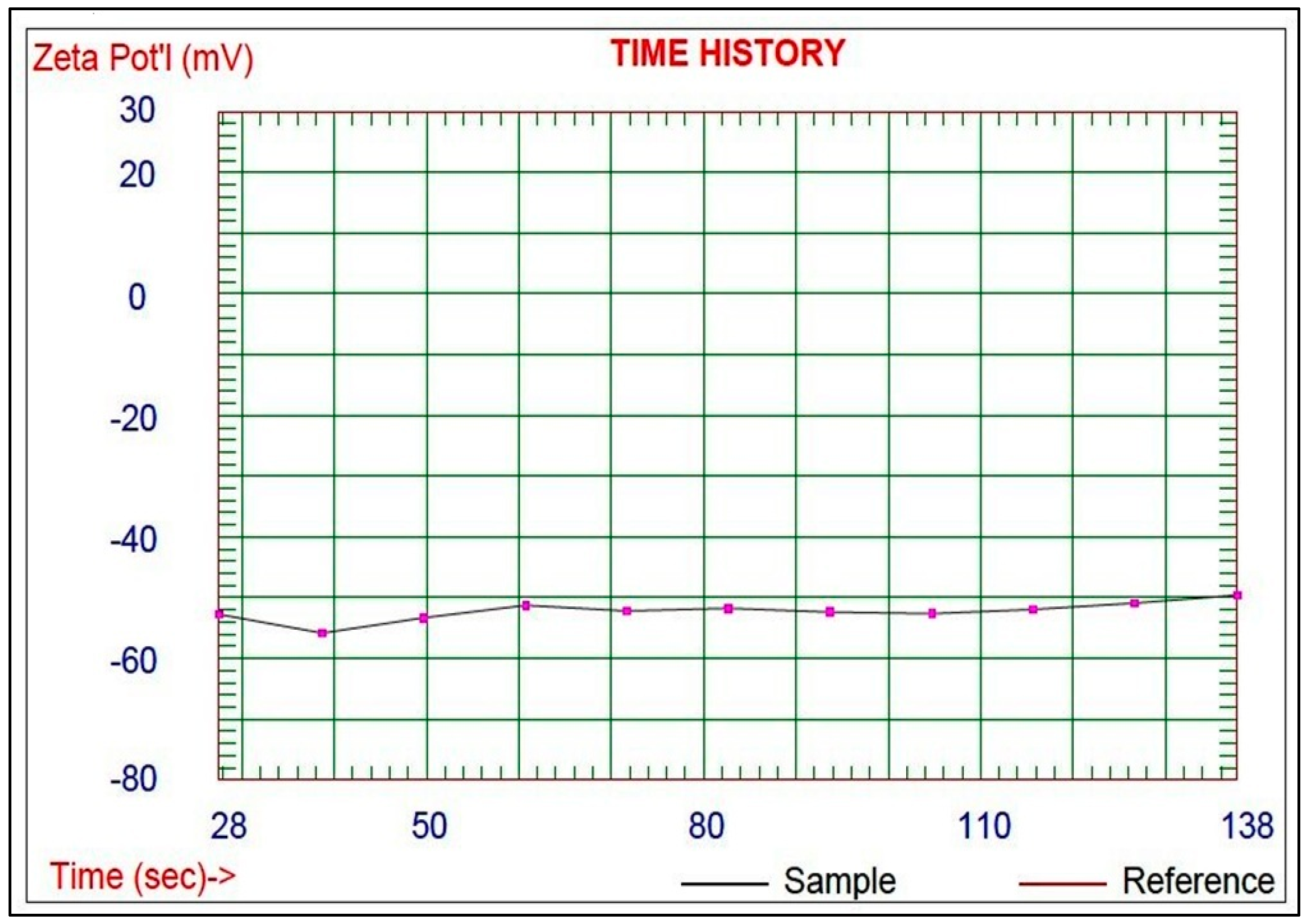
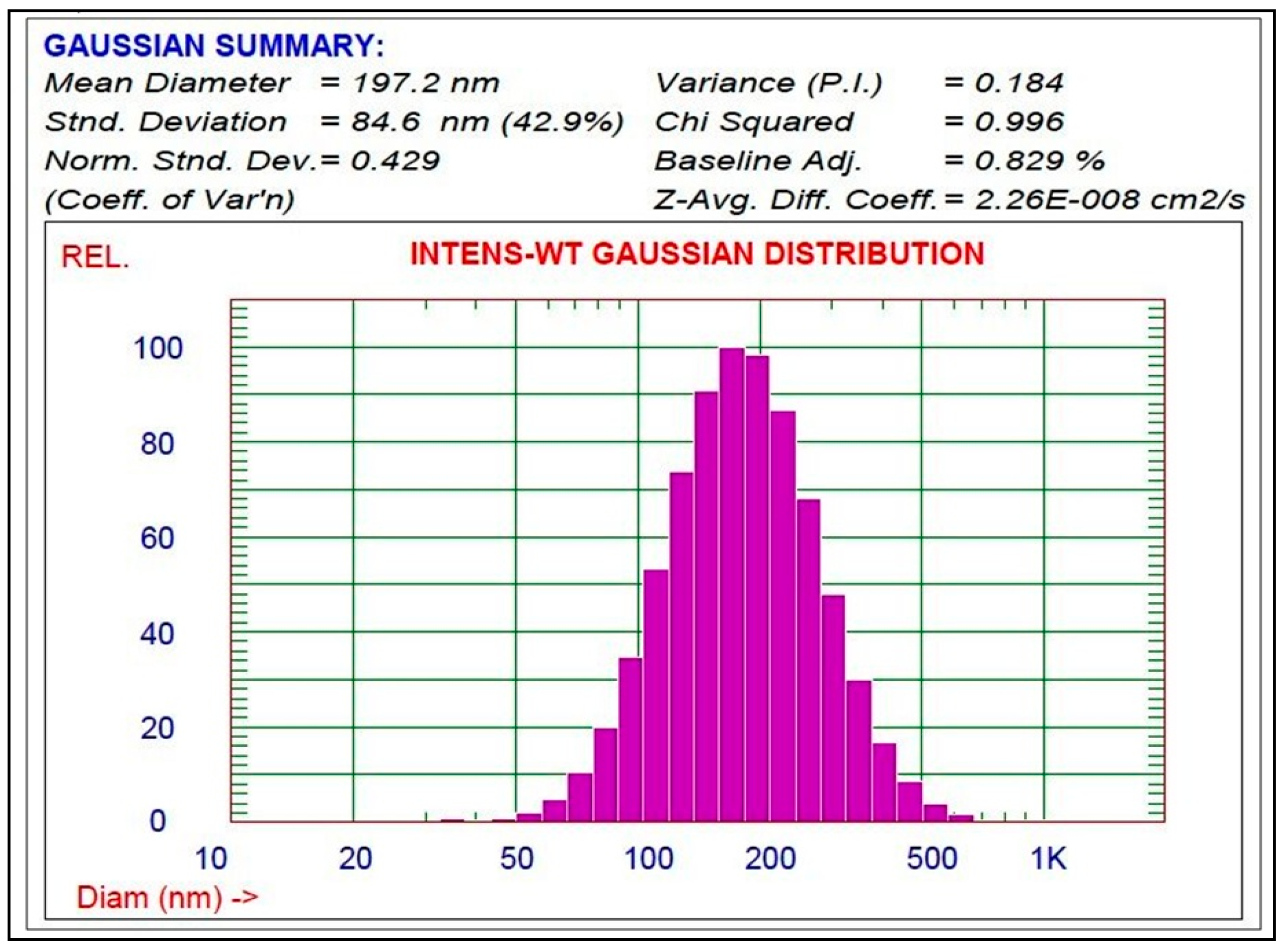
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of the Schiff Base-Copper Oxide Nanoparticles (SB-CuO-NPs)
3.3. In Vitro Biological Activities
3.3.1. Antioxidant and Scavenging Activity
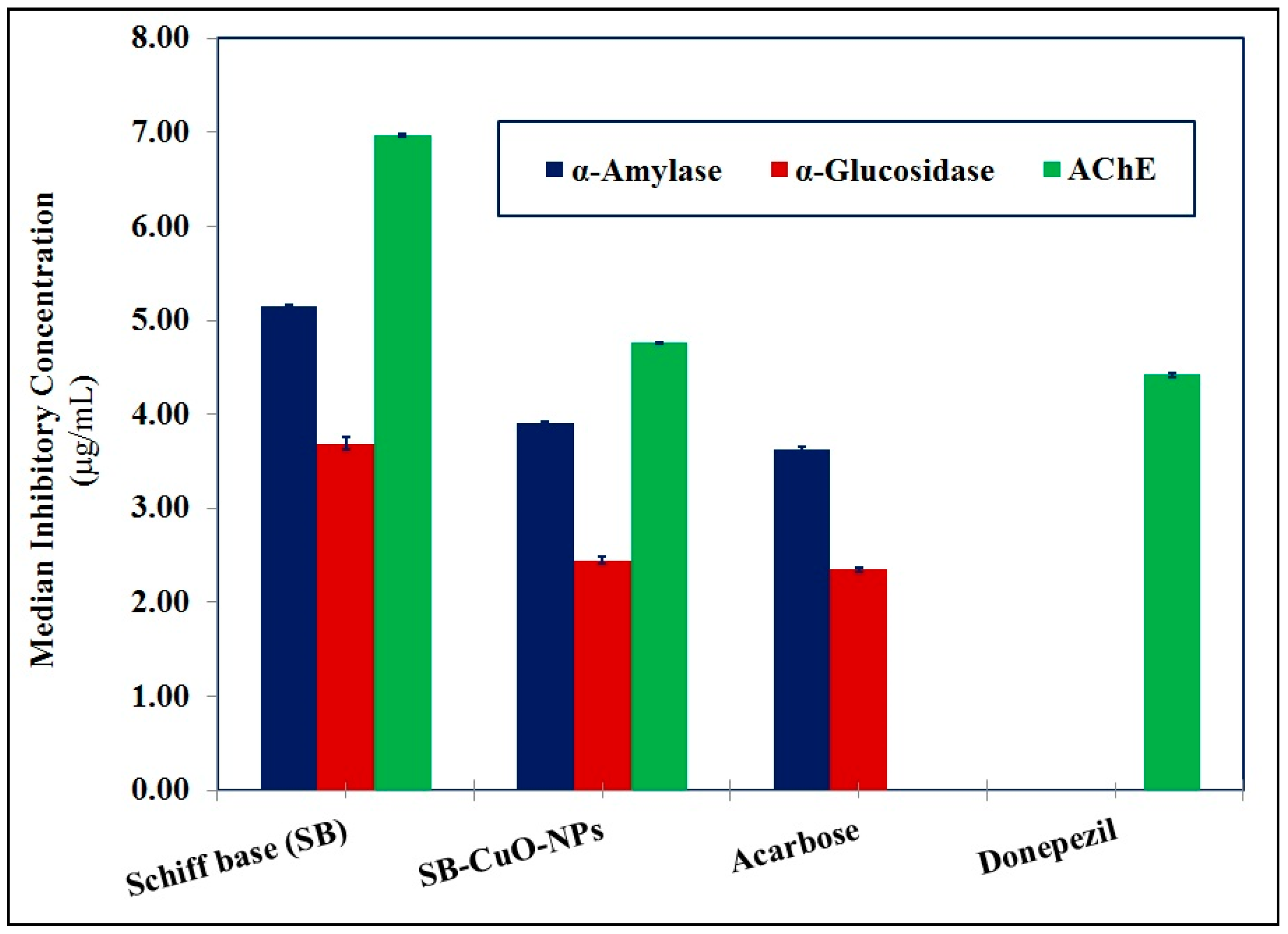
3.3.2. Anti-Diabetic and Anti-Alzheimer’s Activities
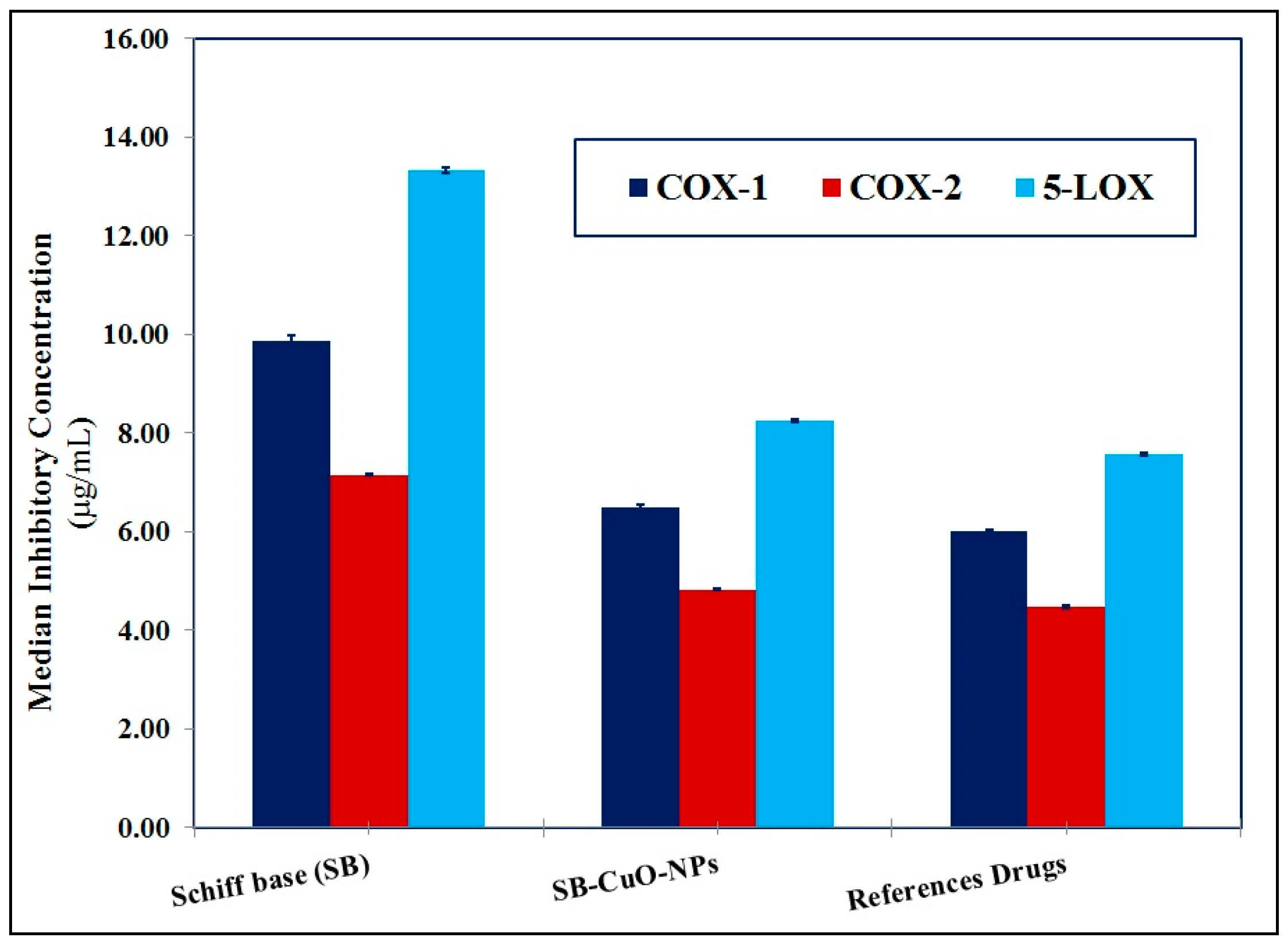
3.3.3. Anti-Arthritic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
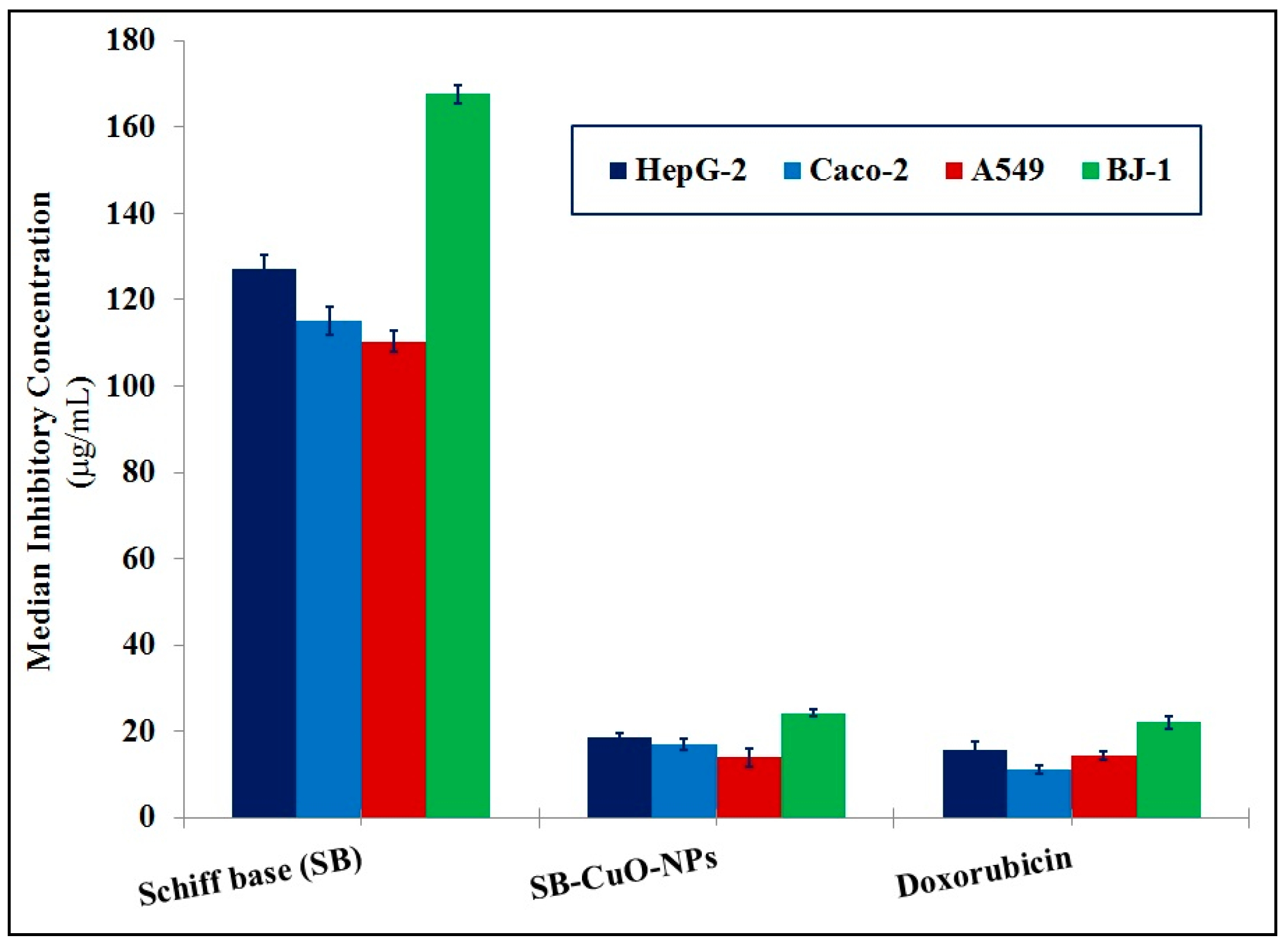
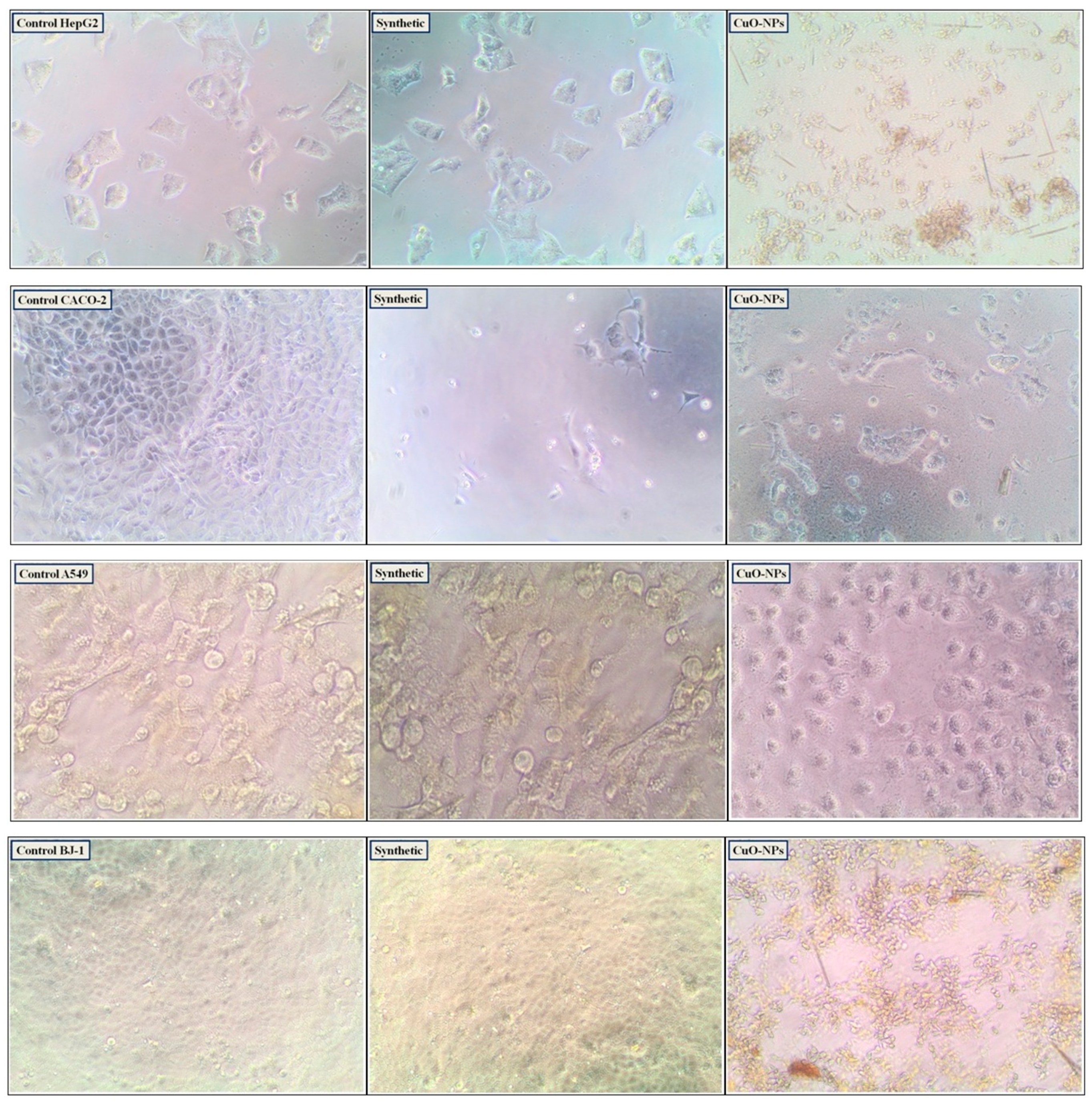
3.3.4. Cytotoxic Activity and Enzymatic Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Thani, H.F.; Ahmad, M.N.; Younes, S.; Zayed, H. Genetic variants associated with Alzheimer disease in the 22 Arab countries: A systematic review. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2021, 35, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, H.S. Cancer status in the Occupied Palestinian Territories: Types; incidence; mortality; sex, age, and geography distribution; and possible causes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 5139–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Emerging applications of nanotechnology in healthcare and medicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krsek, A.; Baticic, L. Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Innovations in Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Focus on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4, 352–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzari-Tavakoli, A.; Babajani, A.; Tavakoli, M.M.; Safaeinejad, F.; Jafari, A. Integrating natural compounds and nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems: A novel strategy for enhanced efficacy and selectivity in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panova, I.G.; Tatikolov, A.S. Endogenous and Exogenous Antioxidants as Agents Preventing the Negative Effects of Contrast Media (Contrast-Induced Nephropathy). Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almehizia, A.A.; Aboulthana, W.M.; Naglah, A.M.; Hassan, A.S. In vitro biological studies and computational prediction-based analyses of pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 8397–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.S.; Hidayathulla, S.; Rehman, M.T.; ElGamal, A.A.; Al-Massarani, S.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Alqahtani, M.S.; El Dib, R.A.; AlAjmi, M.F. Alpha-Amylase and Alpha-Glucosidase Enzyme Inhibition and Antioxidant Potential of 3-Oxolupenal and Katononic Acid Isolated from Nuxia oppositifolia. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglah, A.M.; Almehizia, A.A.; Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Alharbi, A.S.; Alqarni, M.H.; Hassan, A.S.; Aboulthana, W.M. Exploring the Potential Biological Activities of Pyrazole-Based Schiff Bases as Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer’s, Anti-Inflammatory, and Cytotoxic Agents: In Vitro Studies with Computational Predictions. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyzueta-Mamani, L.D.; Ccahuana, H.L.B.; Chávez-Fumagalli, M.A.; Alvarez, K.L.; Aguilar-Pineda, J.A.; Vera-Lopez, K.J.; Cardenas, C.L.L. In Silico Analysis of Metabolites from Peruvian Native Plants as Potential Therapeutics against Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmik, M.; Ullmann, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Haan, S.; Letellier, E. In search of definitions: Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their markers. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepis, T.; De Lucia, S.S.; Pellegrino, A.; del Gaudio, A.; Maresca, R.; Coppola, G.; Chiappetta, M.F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F.; Candelli, M.; et al. State-of-the-Art and Upcoming Innovations in Pancreatic Cancer Care: A Step Forward to Precision Medicine. Cancers 2023, 15, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Thangaraj, P.; Wang, L.; Cao, Q.; Kim, J.H. Nanovaccines: An effective therapeutic approach for cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 15992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayman, R.; Radwan, A.M.; Elmetwally, A.M.; Ammar, Y.A.; Ragab, A. Discovery of novel pyrazole and pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as cyclooxygenase inhibitors (COX-1 and COX-2) using molecular modeling simulation. Arch. Pharm. 2023, 356, 2200395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yue, T.; Ding, Y.; Tan, H.; Weng, J.; Luo, S.; Zheng, X. Nanotechnology translation in vascular diseases: From design to the bench. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Naveed, M.; Aziz, T.; Shabbir, M.A.; Mubeen, H.; Khan, A.A.; Alsmari, A.F. In-vitro and in-vivo assessments of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles from Cascabela thevetia plant extract for the treatment of ventricular septal defect. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2025, 177, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamus-Grabicka, A.A.; Hikisz, P.; Sikora, J. Nanotechnology as a Promising Method in the Treatment of Skin Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, N.K.; Dutta, D.; Biswas, J. A review on synthesis and biological activity of Schiff Bases. Indian J. Chem. Sect. B 2021, 60, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczuk, E.; Dmochowska, B.; Samaszko-Fiertek, J.; Madaj, J. Different Schiff bases-structure, importance and classification. Molecules 2022, 27, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vchislo, N.V.; Adamovich, S.N.; Fedoseeva, V.G.; Oborina, E.N.; Rozentsveig, I.B.; Verpoort, F. Schiff Base of 3-Aminopropylalkoxysilanes and 3-Aminopropylsilatranes: Importance of Investigations and the Potential Applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, e7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Bitu, N.A.; Chaki, B.M.; Hossain, M.J.; Asraf, M.A.; Hossen, M.F.; Kudrat-E-Zahan, M.; Latif, M.A. Water-soluble Schiff base ligands and metal complexes: An overview considering green solvent. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 25256–25272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akitsu, T.; Nakane, D.; Miroslaw, B. Viewpoints Concerning Crystal Structure from Recent Reports on Schiff Base Compounds and Their Metal Complexes. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.A.; Ain, Q.U.; Qadir, T.; Malik, A.Q.; Jan, S.; Shahverdi, S.; Nabi, S.A. A review of semicarbazone-derived metal complexes for application in biomedicine and related fields. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1295, 136216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.S. Mixed isatin with 3-(2-(aryl)hydrazono)acetylacetone Mn(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) complexes: Antibacterial evaluation and molecular properties prediction. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2020, 34, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.K.; Yadav, R.K.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S. Recent developments in the biological activities of 3d-metal complexes with salicylaldehyde-based N, O-donor Schiff base ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 505, 215663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.; Ganguly, M.; Sharma, P. Recent applications of coinage metal nanoparticles passivated with salicylaldehyde and salicylaldehyde-based Schiff bases. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 4545–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Chandra, R.; Dutta, S.; Sahu, D.; Patra, G.K. Schiff base and organic ligand stabilized metal nanoparticles as potential chemosensors for hazardous metal ions: Design, principle, optical signaling mechanism and application. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2024, 573, 122321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.R.; Habib, M.A.; Naime, J.; Rumon, M.M.H.; Al Mamun, M.S.; Islam, A.N.; Mahiuddin, M.; Karim, K.M.R.; Ara, M.H. A review on synthesis, characterizations, and applications of Schiff base functionalized nanoparticles. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamillapalli, V.; Atmakuri, A.M.; Khantamneni, P. Nanoparticles for Herbal Extracts. Asian J. Pharm. 2016, 10, S54–S60. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yuhong, J.; Xin, P.; Han, J.L.; Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Sagboye, P.A.; Umenweke, G.; Ajala, O.J.; Omoarukhe, F.O.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Ogunniyi, S.; Adeniyi, A.G. CuO nanoparticles (CuO NPs) for water treatment: A review of recent advances. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Gul, A.; Zia, M.; Javed, R. Synthesis, biomedical applications, and toxicity of CuO nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1039–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringu, T.; Das, A.; Ghosh, S.; Pramanik, N. Exploring the potential of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) for sustainable environmental bioengineering applications. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 679–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaningini, A.G.; Motlhalamme, T.; More, G.K.; Mohale, K.C.; Maaza, M. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic properties of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) using Athrixia phylicoides DC. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreslassie, Y.T.; Gebremeskel, F.G. Green and cost-effective biofabrication of copper oxide nanoparticles: Exploring antimicrobial and anticancer applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 41, e00828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigl, G. The impact of copper oxide nanoparticles on plant growth: A comprehensive review. J. Plant Interact. 2023, 18, 2243098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulthana, W.M.; Omar, N.I.; El-Feky, A.M.; Hassan, A.K.; Hasan, E.A.; Seif, M.; Youssef, A.M. Phyto- and biochemical study on cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana L.) extract incorporated with metal nanoparticles against hepatic injury induced in rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.S.; Hafez, T.S. Antimicrobial Activities of Ferrocenyl Complexes: A Review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almehizia, A.A.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Al-Obaid, A.M.; Naglah, A.M.; Bhat, M.A.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Khatab, T.K.; Hassan, A.S. Synthesis and characterization of curcumin-encapsulated loaded on carboxymethyl cellulose with docking validation as α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitors. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2024, 26, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almehizia, A.A.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Naglah, A.M.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Hassan, A.S.; Khatab, T.K. Green preparation of argentum tungstate and characterization as nanorod with catalytic evaluation for synthesizing tetracyclic xanthenes and validation as anti-TB. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2024, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.S. Antimicrobial evaluation, in silico ADMET prediction, molecular docking, and molecular electrostatic potential of pyrazole-isatin and pyrazole-indole hybrid molecules. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 3577–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.S.; Morsy, N.M.; Aboulthana, W.M.; Ragab, A. Exploring novel derivatives of isatin-based Schiff bases as multi-target agents: Design, synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation, and in silico ADMET analysis with molecular modeling simulations. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9281–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.R.; Khan, F. Green approach for biofabrication of CuO nanoparticles from Prunus amygdalus pericarp extract and characterization. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2019, 49, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndrez, M.F.; Cárdenas, G.; Arbiol, J. Synthesis and characterization of gallium colloidal nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 346, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, R.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.; Schrand, A.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M. Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to in vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboulthana, W.M.K.; Refaat, E.; Khaled, S.E.; Ibrahim, N.E.S.; Youssef, A.M. Metabolite profiling and biological activity assessment of Casuarina equisetifolia bark after incorporating gold nanoparticles. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 3457–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Pineda, M.; Aguilar, M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: Specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 269, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyaizu, M. Studies on product of browning reaction prepared from glucose amine. Jpn. J. Nutr. Diet. 1986, 44, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.B.; Biswas, M.; Alam, A.K. In vitro antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of different parts of Tabebuia pallida growing in Bangladesh. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Cano, A.; Acosta, M. The hydrophilic and lipophilic contribution to total antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborthy, G.S. Free radical scavenging activity of Costus speciosus leaves. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2009, 43, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wickramaratne, M.N.; Punchihewa, J.; Wickramaratne, D. In-vitro alpha amylase inhibitory activity of the leaf extracts of Adenanthera pavonina. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistia-Brueggeman, G.; Hollingsworth, R.I. A preparation and screening strategy for glycosidase inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 8773–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.J.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Sureshkumar, P. Effect of methanolic root extract of Blepharispermum subsesssile DC in controlling arthritic activity. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 11, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Oyedapo, O.O.; Famurewa, A.J. Antiprotease and Membrane Stabilizing Activities of Extracts of Fagara Zanthoxyloides, Olax Subscorpioides and Tetrapleura Tetraptera. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 1995, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meera, S.; Ramaiah, N.; Kalidindi, N. Illustration of anti-rheumatic mechanism of rheumavedic capsule. Saudi Pharm. J. 2011, 19, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaa, A.M.; El-Azab, A.S.; Abou-Zeid, L.A.; ElTahir, K.E.; Abdel-Aziz, N.I.; Ayyad, R.R.; Al-Obaid, A.M. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and COX-1/2 inhibition activities of anilides based on 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine-2, 4-dione scaffold: Molecular docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 115, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and docking study of novel indole-2-amide as anti-inflammatory agents with dual inhibition of COX and 5-LOX. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.S.; Hafez, T.S.; Ali, M.M.; Khatab, T.K. Design, synthesis and cytotoxic activity of some new pyrazolines bearing benzofuran and pyrazole moieties. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 417–429. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Qari, H.A.; Oves, M. A Novel Approach to Unraveling the Apoptotic Potential of Rutin (Bioflavonoid) via Targeting Jab1 in Cervical Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.S.; Awad, H.M.; Magd-El-Din, A.A.; Hafez, T.S. Synthesis and in vitro antitumor evaluation of novel Schiff bases. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwin Jose, P.; Sankarganesh, M.; Dhaveethu Raja, J.; Arumugam, S. DNA/BSA interaction, anticancer, antimicrobial and catalytic applications of synthesis of nitro substituted pyrimidine-based Schiff base ligand capped nickel nanoparticles. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 5931–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boshra, M.; Adly, O.M.; Abdelrhman, E.M.; Eid, M.F.; Samy, F. Novel Cu (II) and Zn (II) Nanocomplexes Based on 5, 6-Diphenyl-1, 2, 4-Triazine: Preparation, Spectroscopic, TD-DFT Calculations, Molecular Docking and Solvatochromic Studies. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, e7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R. Antioxidant and Catalytic Activity of Biosynthesized CuO Nanoparticles Using Extract of Galeopsidis herba. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2018, 28, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naika, H.R.; Lingaraju, K.; Manjunath, K.; Kumar, D.; Nagaraju, G.; Suresh, D.; Nagabhushana, H. Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. extract and their antibacterial activity. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Smita, K.; Debut, A.; Cumbal, L. Andean Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia Volubilis L.) leaf-mediated synthesis of Cu2O nanoparticles: A low-cost approach. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahalam, L.A.; Prasad, K.R.S.; Krishna, P.M.; Supraja, N.; Shanmugan, S. The exploration of bio-inspired copper oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and in-vitro biological investigations. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzilu, D.M.; Madivoli, E.S.; Makhanu, D.S.; Wanakai, S.I.; Kiprono, G.K.; Kareru, P.G. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its efficiency in degradation of rifampicin antibiotic. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamila, B.; Eddine, L.S.; Abderrhmane, B.; Nassiba, A.; Barhoum, A. In vitro antioxidant activities of copper mixed oxide (CuO/Cu2O) nanoparticles produced from the leaves of Phoenix dactylifera L. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 6567–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, F.; Shahid, S.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, W.; Zaman, S. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Abutilon indicum leaf extract: Antimicrobial, antioxidant and photocatalytic dye degradation activities. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouidad, A.; Sara, C.; Samir, D. Biological properties and acute toxicity study of copper oxide nanoparticles prepared by aqueous leaves extract of Portulaca oleracea (L). Asian J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 10, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bighetti, A.E.; Sampaio, P.G.; De gusmão, C.P. Study of the antioxidant activity of a cosmetic formulation. Rev. Uningá 2018, 55, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, G.K.; Makola, R.T. In-vitro analysis of free radical scavenging activities and suppression of LPS-induced ROS production in macrophage cells by Solanum sisymbriifolium extracts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Feky, A.M.; Aboulthana, W.M. Chemical composition of lipoidal and flavonoidal extracts from Egyptian olive leaves with in vitro biological activities. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainat; Khan, M.A.; Ali, F.; Faisal, S.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, Z.; Zaman, N.; Afsheen, Z.; Uddin, M.N.; Bibi, N. Exploring the therapeutic potential of Hibiscus rosa sinensis synthesized cobalt oxide (Co3O4-NPs) and magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5157–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelazeem, N.M.; Aboulthana, W.M.; Hassan, A.S.; Almehizia, A.A.; Naglah, A.M.; Alkahtani, H.M. Synthesis, in silico ADMET prediction analysis, and pharmacological evaluation of sulfonamide derivatives tethered with pyrazole or pyridine as anti-diabetic and anti-Alzheimer’s agents. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarimov, R.M.; Matveyeva, T.A.; Binhi, V.N. Laser interferometry of the hydrolytic changes in protein solutions: The refractive index and hydration shells. J. Biol. Phys. 2018, 44, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.S.; Morsy, N.M.; Aboulthana, W.M.; Ragab, A. In vitro enzymatic evaluation of some pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives: Design, synthesis, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-Alzheimer, and anti-arthritic activities with molecular modeling simulation. Drug Dev. Res. 2023, 84, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Feky, A.M.; El-Rashedy, A.A. Sterols and flavonoids in strawberry calyx with free radical scavenging, anti-inflammatory, and molecular dynamic study. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.; Shukla, A.; Makhal, P.N.; Kaki, V.R. Natural product-driven dual COX-LOX inhibitors: Overview of recent studies on the development of novel anti-inflammatory agents. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, H.; Ali, W.; Khan, N.Z.; Aasim, M.; Khan, T.; Khan, A.A. Delphinium uncinatum mediated biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and in-vitro evaluation of their antioxidant, cytotoxic, antimicrobial, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging activities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.-H.; Hong, J.; McGuffie, M.; Yeom, B.; VanEpps, J.S.; Kotov, N.A. Shape-Dependent Biomimetic Inhibition of Enzyme by Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Activity. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9097–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.M.; Hameed, P.; Rao, R.P.; Shrivastava, N.; Mittal, J.; Mohapatra, S. Biosynthesis of Highly Stable Fluorescent Selenium Nanoparticles and the Evaluation of Their Photocatalytic Degradation of Dye. BioNanoSci 2020, 10, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, F.; Jiang, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H. Berberine hydrochloride inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer via the suppression of the MMP2 and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7409–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Yadav, R.; Jain, S.; Vaidya, A. Caspase-3: A Primary Target for Natural and Synthetic Compounds for Cancer Therapy. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 144–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, A.M.; Othman, M.S.; Obeidat, S.T.; Aleid, G.M.; Aboelnaga, S.M.; Fehaid, A.; Hathout, H.M.R.; Bakkar, A.A.; Moneim, A.E.A.; El-Garawani, I.M.; et al. Green-Synthesized Silver and Selenium Nanoparticles Using Berberine: A Comparative Assessment of In Vitro Anticancer Potential on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line (HepG2). Cells 2024, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, M.S.; Obeidat, S.T.; Al-Bagawi, A.H.; Fareid, M.A.; Fehaid, A.; Abdel Moneim, A.E. Green-synthetized selenium nanoparticles using berberine as a promising anticancer agent. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 20, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Activities | Units | SB | SB-CuO-NPs | Ascorbic Acid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Antioxidant activity | TAC | mg gallic acid/g | 65.41 ± 0.19 | 76.53 ± 0.22 | 83.75 ± 0.13 |
| IRP | µg/mL | 47.66 ± 0.19 | 58.78 ± 0.22 | 66.00 ± 0.13 | |
|
Scavenging activity | DPPH | Inhib. (%) | 44.54 ± 0.18 | 54.93 ± 0.21 | 61.68 ± 0.12 |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 6.24 ± 0.01 | 5.06 ± 0.01 | 4.50 ± 0.03 | ||
| ABTS | Inhib. (%) | 48.29 ± 0.18 | 58.68 ± 0.21 | 65.43 ± 0.12 | |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 5.40 ± 0.06 | 4.45 ± 0.05 | 3.99 ± 0.04 | ||
| NO | Inhib. (%) | 36.79 ± 0.18 | 47.18 ± 0.21 | 53.93 ± 0.12 | |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 7.69 ± 0.04 | 5.99 ± 0.03 | 5.24 ± 0.02 | ||
| Activities | Units | SB | SB-CuO-NPs | Standard Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anti-diabetic activity | α-Amylase | Inhib. (%) | 38.63 ± 0.14 | 51.03 ± 0.18 | 54.96 ± 0.10 Acarbose |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 5.15 ± 0.02 | 3.90 ± 0.02 | 3.62 ± 0.03 Acarbose | ||
| α-Glucosidase | Inhib. (%) | 28.38 ± 0.14 | 42.82 ± 0.19 | 44.71 ± 0.10 Acarbose | |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 3.69 ± 0.06 | 2.45 ± 0.04 | 2.35 ± 0.02 Acarbose | ||
| Anti-Alzheimer activity | Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) | Inhib. (%) | 32.64 ± 0.16 | 47.83 ± 0.21 | 51.42 ± 0.12 Donepezil |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 6.97 ± 0.02 | 4.76 ± 0.01 | 4.42 ± 0.02 Donepezil | ||
| Activities | Units | SB | SB-CuO-NPs | Standard Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-arthritic activity | Protein Denaturation | Inhib. (%) | 26.11 ± 0.13 | 38.27 ± 0.17 | 41.14 ± 0.09 Diclofenac Sodium |
| Proteinase | Inhib. (%) | 23.41 ± 0.13 | 35.57 ± 0.17 | 38.44 ± 0.09 Diclofenac Sodium | |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 10.84 ± 0.06 | 7.13 ± 0.03 | 6.60 ± 0.02 Diclofenac Sodium | ||
| Anti-inflammatory activity | COX-1 | Inhib. (%) | 31.61 ± 0.18 | 48.02 ± 0.23 | 51.89 ± 0.13 Indomethacin |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 9.86 ± 0.11 | 6.49 ± 0.07 | 6.01 ± 0.02 Indomethacin | ||
| COX-2 | Inhib. (%) | 33.86 ± 0.18 | 50.27 ± 0.23 | 54.14 ± 0.13 Indomethacin | |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 7.15 ± 0.01 | 4.83 ± 0.02 | 4.47 ± 0.03 Indomethacin | ||
| 5-LOX | Inhib. (%) | 26.71 ± 0.18 | 43.12 ± 0.23 | 46.99 ± 0.13 Zileuton | |
| IC50 (µg/mL) | 13.33 ± 0.07 | 8.25 ± 0.03 | 7.57 ± 0.03 Zileuton | ||
| Activities | Units | SB | SB-CuO-NPs | Doxorubicin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) | HepG-2 | IC50 (µg/mL) | 127.16 ± 3.13 | 18.68 ± 0.83 | 15.49 ± 1.98 |
| Caco-2 | IC50 (µg/mL) | 115.16 ± 3.25 | 17.08 ± 1.30 | 11.13 ± 1.09 | |
| A549 | IC50 (µg/mL) | 110.37 ± 2.49 | 13.87 ± 2.25 | 14.36 ± 1.12 | |
| BJ-1 | IC50 (µg/mL) | 167.65 ± 2.22 | 24.23 ± 0.76 | 22.00 ± 1.51 | |
| Activities | Units | DMSO | SB | SB-CuO-NPs | Doxorubicin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG-2 | Caspase-3 | Pg/mL | 94.60 ± 0.74 | 165.55 ± 1.29 | 291.00 ± 1.34 | 306.04 ± 1.23 |
| Bcl-2 | ng/mL | 12.82 ± 0.17 | 7.32 ± 0.10 | 4.17 ± 0.05 | 4.00 ± 0.02 | |
| Caco-2 | Caspase-3 | Pg/mL | 82.44 ± 0.12 | 144.28 ± 0.22 | 252.31 ± 0.30 | 265.13 ± 0.12 |
| Bcl-2 | ng/mL | 6.60 ± 0.09 | 3.77 ± 0.05 | 2.14 ± 0.01 | 2.04 ± 0.01 | |
| A549 | Caspase-3 | Pg/mL | 77.11 ± 0.10 | 134.94 ± 0.18 | 236.30 ± 0.22 | 247.96 ± 0.08 |
| Bcl-2 | ng/mL | 14.46 ± 0.05 | 8.26 ± 0.03 | 4.72 ± 0.02 | 4.51 ± 0.01 | |
| BJ-1 | Caspase-3 | Pg/mL | 62.32 ± 0.10 | 109.07 ± 0.18 | 191.03 ± 0.22 | 200.43 ± 0.08 |
| Bcl-2 | ng/mL | 8.71 ± 0.05 | 4.98 ± 0.03 | 2.85 ± 0.02 | 2.72 ± 0.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almehizia, A.A.; Naglah, A.M.; Aljafen, S.S.; Hassan, A.S.; Aboulthana, W.M. Assessment of the In Vitro Biological Activities of Schiff Base-Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles as an Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer, and Anti-Cancer Agent. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020180
Almehizia AA, Naglah AM, Aljafen SS, Hassan AS, Aboulthana WM. Assessment of the In Vitro Biological Activities of Schiff Base-Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles as an Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer, and Anti-Cancer Agent. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmehizia, Abdulrahman A., Ahmed M. Naglah, Sadeem S. Aljafen, Ashraf S. Hassan, and Wael M. Aboulthana. 2025. "Assessment of the In Vitro Biological Activities of Schiff Base-Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles as an Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer, and Anti-Cancer Agent" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020180
APA StyleAlmehizia, A. A., Naglah, A. M., Aljafen, S. S., Hassan, A. S., & Aboulthana, W. M. (2025). Assessment of the In Vitro Biological Activities of Schiff Base-Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles as an Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer, and Anti-Cancer Agent. Pharmaceutics, 17(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020180






