Use of Transient Transfection for cGMP Manufacturing of eOD-GT8 60mer, a Self-Assembling Nanoparticle Germline-Targeting HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transient Transfection and Upstream Process Development
2.2. Downstream Process Development
2.3. Analytical Characterization
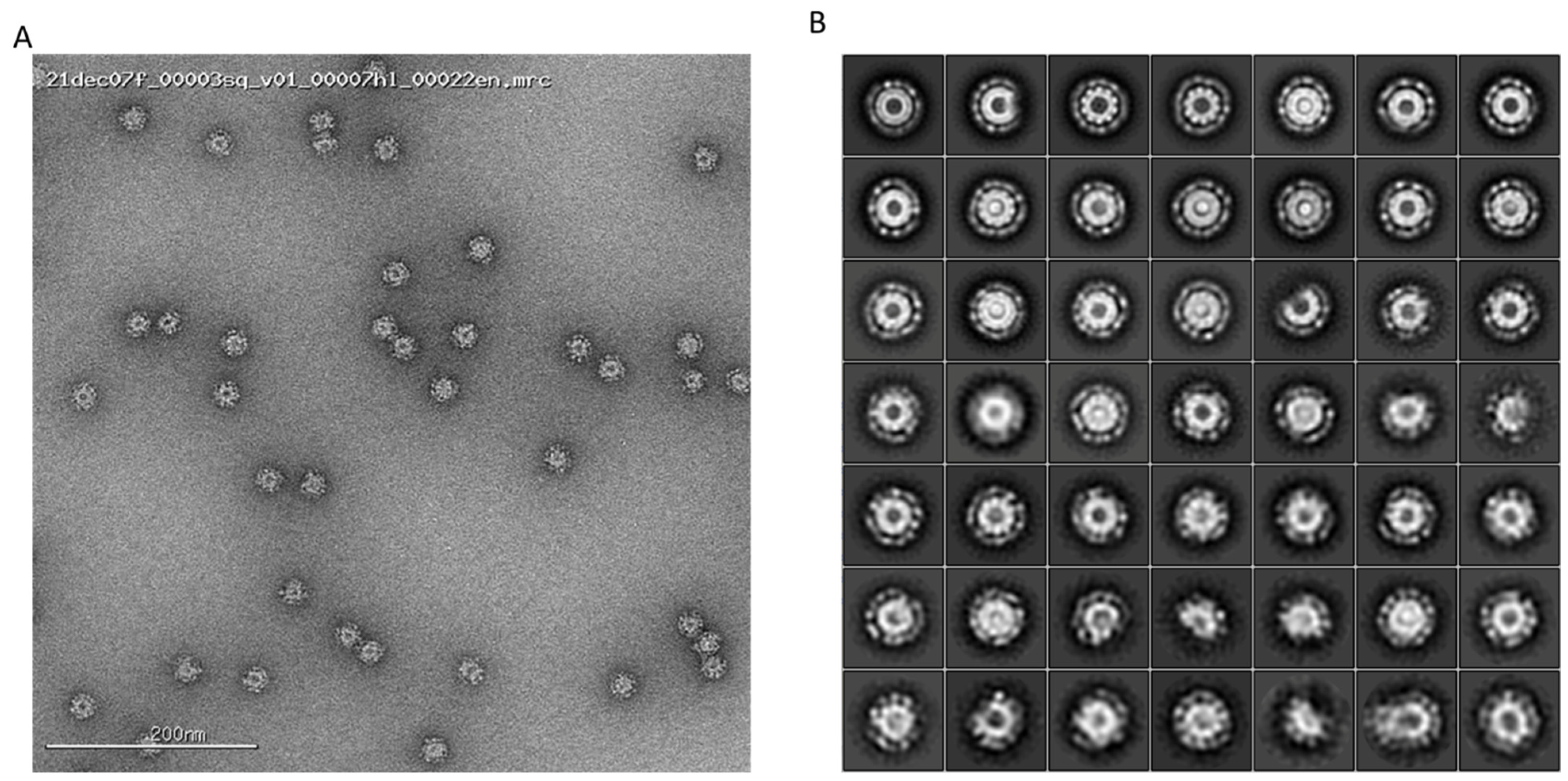
3. Results
Nonclinical Safety Assessment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNAIDS. The Aids Epidemic Can Be Ended by 2030. 2016. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_with-your-help_en.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2016).
- UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS Statistics. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Corey, L.; Gilbert, P.B.; Juraska, M.; Montefiori, D.C.; Morris, L.; Karuna, S.T.; Edupuganti, S.; Mgodi, N.M.; deCamp, A.C.; Rudnicki, E.; et al. Two Randomized Trials of Neutralizing Antibodies to Prevent HIV-1 Acquisition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Huang, Y.; deCamp, A.C.; Karuna, S.; Zhang, Y.; Magaret, C.A.; Giorgi, E.E.; Korber, B.; Edlefsen, P.T.; Rossenkhan, R.; et al. Neutralization titer biomarker for antibody-mediated prevention of HIV-1 acquisition. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; Borate, B.; Huang, Y.; Pauthner, M.G.; Hessell, A.J.; Julg, B.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Schmidt, S.D.; Carpp, L.N.; Cully, M.D.; et al. A Meta-analysis of Passive Immunization Studies Shows that Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Titer Associates with Protection against SHIV Challenge. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 336–346.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatatos, L.; Pancera, M.; McGuire, A.T. Germline-targeting immunogens. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrabi, R.; Bhiman, J.N.; Burton, D.R. Strategies for a multi-stage neutralizing antibody-based HIV vaccine. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Crotty, S. HIV vaccinology: 2021 update. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 51, 101470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggat, D.J.; Cohen, K.W.; Willis, J.R.; Fulp, W.J.; Decamp, A.C.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Cottrell, C.A.; Menis, S.; Finak, G.; Ballweber-Fleming, L.; et al. Vaccination induces HIV broadly neutralizing antibody precursors in humans. Science 2022, 378, eadd6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolano, A.; Steichen, J.M.; Dosenovic, P.; Kulp, D.W.; Golijanin, J.; Sok, D.; Freund, N.T.; Gitlin, A.D.; Oliveira, T.; Araki, T.; et al. Sequential Immunization Elicits Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies in Ig Knockin Mice. Cell 2016, 166, 1445–1458.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, J.M.; Kulp, D.W.; Tokatlian, T.; Escolano, A.; Dosenovic, P.; Stanfield, R.L.; McCoy, L.E.; Ozorowski, G.; Hu, X.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; et al. HIV Vaccine Design to Target Germline Precursors of Glycan-Dependent Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. Immunity 2016, 45, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, S.D.; Duan, H.; Cheng, C.; Chuang, G.Y.; Gu, Y.; Louder, M.K.; Lin, B.C.; Shen, C.H.; et al. Vaccination induces maturation in a mouse model of diverse unmutated VRC01-class precursors to HIV-neutralizing antibodies with >50% breadth. Immunity 2021, 54, 324–339.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, J.; Julien, J.P.; Menis, S.; Ota, T.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; McGuire, A.; Sok, D.; Huang, P.S.; MacPherson, S.; Jones, M.; et al. Rational HIV immunogen design to target specific germline B cell receptors. Science 2013, 340, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosenovic, P.; von Boehmer, L.; Escolano, A.; Jardine, J.; Freund, N.T.; Gitlin, A.D.; McGuire, A.T.; Kulp, D.W.; Oliveira, T.; Scharf, L.; et al. Immunization for HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies in Human Ig Knockin Mice. Cell 2015, 161, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardine, J.G.; Ota, T.; Sok, D.; Pauthner, M.; Kulp, D.W.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Skog, P.D.; Thinnes, T.C.; Bhullar, D.; Briney, B.; et al. HIV-1 VACCINES. Priming a broadly neutralizing antibody response to HIV-1 using a germline-targeting immunogen. Science 2015, 349, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardine, J.G.; Kulp, D.W.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Sarkar, A.; Briney, B.; Sok, D.; Sesterhenn, F.; Ereno-Orbea, J.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Deresa, I.; et al. HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody precursor B cells revealed by germline-targeting immunogen. Science 2016, 351, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, D.; Briney, B.; Jardine, J.G.; Kulp, D.W.; Menis, S.; Pauthner, M.; Wood, A.; Lee, E.C.; Le, K.M.; Jones, M.; et al. Priming HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody precursors in human Ig loci transgenic mice. Science 2016, 353, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.K.; Lee, J.H.; Menis, S.; Skog, P.; Rossi, M.; Ota, T.; Kulp, D.W.; Bhullar, D.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; et al. Precursor Frequency and Affinity Determine B Cell Competitive Fitness in Germinal Centers, Tested with Germline-Targeting HIV Vaccine Immunogens. Immunity 2018, 48, 133–146.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Sarkar, A.; Kulp, D.W.; Toy, L.; Hu, X.; Deresa, I.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Kaushik, K.; Upadhyay, A.A.; Menis, S.; et al. The human naive B cell repertoire contains distinct subclasses for a germline-targeting HIV-1 vaccine immunogen. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat0381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Abbott, R.K.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Skog, P.D.; Al-Kolla, R.; Groschel, B.; Blane, T.R.; Menis, S.; Tran, J.T.; Thinnes, T.C.; et al. B cells expressing authentic naive human VRC01-class BCRs can be recruited to germinal centers and affinity mature in multiple independent mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22920–22931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ray, R.; Kratochvil, S.; Melzi, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Giguere, S.; Xu, L.; Warner, J.; Cheon, D.; Liguori, A.; et al. Multiplexed CRISPR/CAS9-mediated engineering of pre-clinical mouse models bearing native human B cell receptors. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, K.R.; MacCamy, A.J.; Trichka, J.; Gray, M.; Weidle, C.; Borst, A.J.; Khechaduri, A.; Takushi, B.; Agrawal, P.; Guenaga, J.; et al. Overcoming Steric Restrictions of VRC01 HIV-1 Neutralizing Antibodies through Immunization. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3060–3072.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, A.T.; Gray, M.D.; Dosenovic, P.; Gitlin, A.D.; Freund, N.T.; Petersen, J.; Correnti, C.; Johnsen, W.; Kegel, R.; Stuart, A.B.; et al. Specifically modified Env immunogens activate B-cell precursors of broadly neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in transgenic mice. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, N.; Hickey, J.M.; Kaur, K.; Xiong, J.; Sawant, N.; Cupo, A.; Lee, W.-H.; Ozorowski, G.; Medina-Ramírez, M.; Ward, A.B. Developability assessment of physicochemical properties and stability profiles of HIV-1 BG505 SOSIP. 664 and BG505 SOSIP. v4. 1-GT1. 1 gp140 envelope glycoprotein trimers as candidate vaccine antigens. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2264–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Ramirez, M.; Garces, F.; Escolano, A.; Skog, P.; de Taeye, S.W.; Del Moral-Sanchez, I.; McGuire, A.T.; Yasmeen, A.; Behrens, A.J.; Ozorowski, G.; et al. Design and crystal structure of a native-like HIV-1 envelope trimer that engages multiple broadly neutralizing antibody precursors in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2573–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, K.J. The Future of Antibody-Based HIV Prevention. Available online: https://www.iavi.org/iavi-report/the-future-of-antibody-based-hiv-prevention/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Rajendra, Y.; Hougland, M.D.; Alam, R.; Morehead, T.A.; Barnard, G.C. A high cell density transient transfection system for therapeutic protein expression based on a CHO GS-knockout cell line: Process development and product quality assessment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, P.A.; Kavran, J.M.; Kim, M.-S.; Leahy, D.J. Transient mammalian cell transfection with polyethylenimine (PEI). Methods Enzymol. 2013, 529, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, M. An FDA Perspective on the Implementation of State-of-the-Art Analytical Methods for Therapeutic Proteins. Available online: https://www.casss.org/docs/default-source/wcbp/2018-speaker-presentations/shapiro-marjie-fda-2018.pdf?sfvrsn=282065fc_6 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Berkowitz, S.A.; Engen, J.R.; Mazzeo, J.R.; Jones, G.B. Analytical tools for characterizing biopharmaceuticals and the implications for biosimilars. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnick, R.; Solli, N.; Papa, P. The role of quality control in biotechnology: An analytical perspective. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.J.; Dowd, K.A.; Mendoza, F.H.; Saunders, J.G.; Sitar, S.; Plummer, S.H.; Yamshchikov, G.; Sarwar, U.N.; Hu, Z.; Enama, M.E.; et al. Safety and tolerability of chikungunya virus-like particle vaccine in healthy adults: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Trozado, C.; Lee, J.; Schwartz, R.M. Development of a mammalian cell culture process for rapid Clinical-Scale production of novel Influenza Nanoparticle vaccines. BMC Proc. 2015, 9, O12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzel, Y.; Rödig, J.; Rapp, E.; Reichl, U. Vaccine production: Upstream processing with adherent or suspension cell lines. In Animal Cell Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 371–393. [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer, P.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. Trends in upstream and downstream process development for antibody manufacturing. Bioengineering 2014, 1, 188–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbein, A.D.; Tropea, J.E.; Mitchell, M.; Kaushal, G.P. Kifunensine, a potent inhibitor of the glycoprotein processing mannosidase I. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 15599–15605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallee, F.; Karaveg, K.; Herscovics, A.; Moremen, K.W.; Howell, P.L. Structural basis for catalysis and inhibition of N-glycan processing class I alpha 1,2-mannosidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 41287–41298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, A.T.; Ottens, M. Purifying biopharmaceuticals: Knowledge-based chromatographic process development. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, S.M.; Holstein, M.A. Downstream bioprocessing: Recent advances and future promise. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2011, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, B.; Lazo, A.; Grossberg, H.; Page, G.; Lippin, A.; Swan, G. Virus inactivation by solvent/detergent treatment and the manufacture of SD-plasma. Vox Sang 1998, 74 (Suppl. 1), 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempst, P.; Riviere, L. Examination of automated polypeptide sequencing using standard phenyl isothiocyanate reagent and subpicomole high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 183, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.L.; Lary, J.W.; Moody, T.P.; Laue, T.M. Analytical ultracentrifugation: Sedimentation velocity and sedimentation equilibrium. Methods Cell Biol. 2008, 84, 143–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential–what they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Vouros, P.; Glick, J. Mass spectrometric based analysis, characterization and applications of circulating cell free DNA isolated from human body fluids. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2011, 304, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.K.; Cupo, A.; Ozorowski, G.; Sharma, V.K.; Behrens, A.J.; Go, E.P.; Ketas, T.J.; Yasmeen, A.; Klasse, P.J.; Sayeed, E.; et al. cGMP production and analysis of BG505 SOSIP.664, an extensively glycosylated, trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein vaccine candidate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geigert, J. The Challenge of CMC Regulatory Compliance for Biopharmaceuticals and Other Biologics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guidance for Industry. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Q2 (R1). 2005; pp. 2–15. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/q2r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-and-methodology-guidance-industry (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Crommelin, D.J.; Storm, G.; Verrijk, R.; de Leede, L.; Jiskoot, W.; Hennink, W.E. Shifting paradigms: Biopharmaceuticals versus low molecular weight drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 266, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Diedrich, J.K.; Kulp, D.W.; Pauthner, M.; He, L.; Park, S.R.; Sok, D.; Su, C.Y.; Delahunty, C.M.; Menis, S.; et al. Global site-specific N-glycosylation analysis of HIV envelope glycoprotein. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Pauthner, M.; Andrabi, R.; Rantalainen, K.; Berndsen, Z.; Diedrich, J.K.; Menis, S.; Sok, D.; Bastidas, R.; Park, S.R.; et al. Differential processing of HIV envelope glycans on the virus and soluble recombinant trimer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baboo, S.; Diedrich, J.K.; Martinez-Bartolome, S.; Wang, X.; Schiffner, T.; Groschel, B.; Schief, W.R.; Paulson, J.C.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. DeGlyPHER: An Ultrasensitive Method for the Analysis of Viral Spike N-Glycoforms. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13651–13657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, L. Separation of glycans and monosaccharides. In Liquid Chromatography, 2nd ed.; Fanali, S., Haddad, P.R., Poole, C., Riekkola, M.-L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Briney, B.; Sok, D.; Jardine, J.G.; Kulp, D.W.; Skog, P.; Menis, S.; Jacak, R.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; de Val, N.; Sesterhenn, F.; et al. Tailored Immunogens Direct Affinity Maturation toward HIV Neutralizing Antibodies. Cell 2016, 166, 1459–1470.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokatlian, T.; Read, B.J.; Jones, C.A.; Kulp, D.W.; Menis, S.; Chang, J.Y.H.; Steichen, J.M.; Kumari, S.; Allen, J.D.; Dane, E.L.; et al. Innate immune recognition of glycans targets HIV nanoparticle immunogens to germinal centers. Science 2019, 363, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zuo, T.; Wen, Z. First clinical study of germline-targeting strategy: One step closer to a successful bnAb-based HIV vaccine. Innovation 2023, 4, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

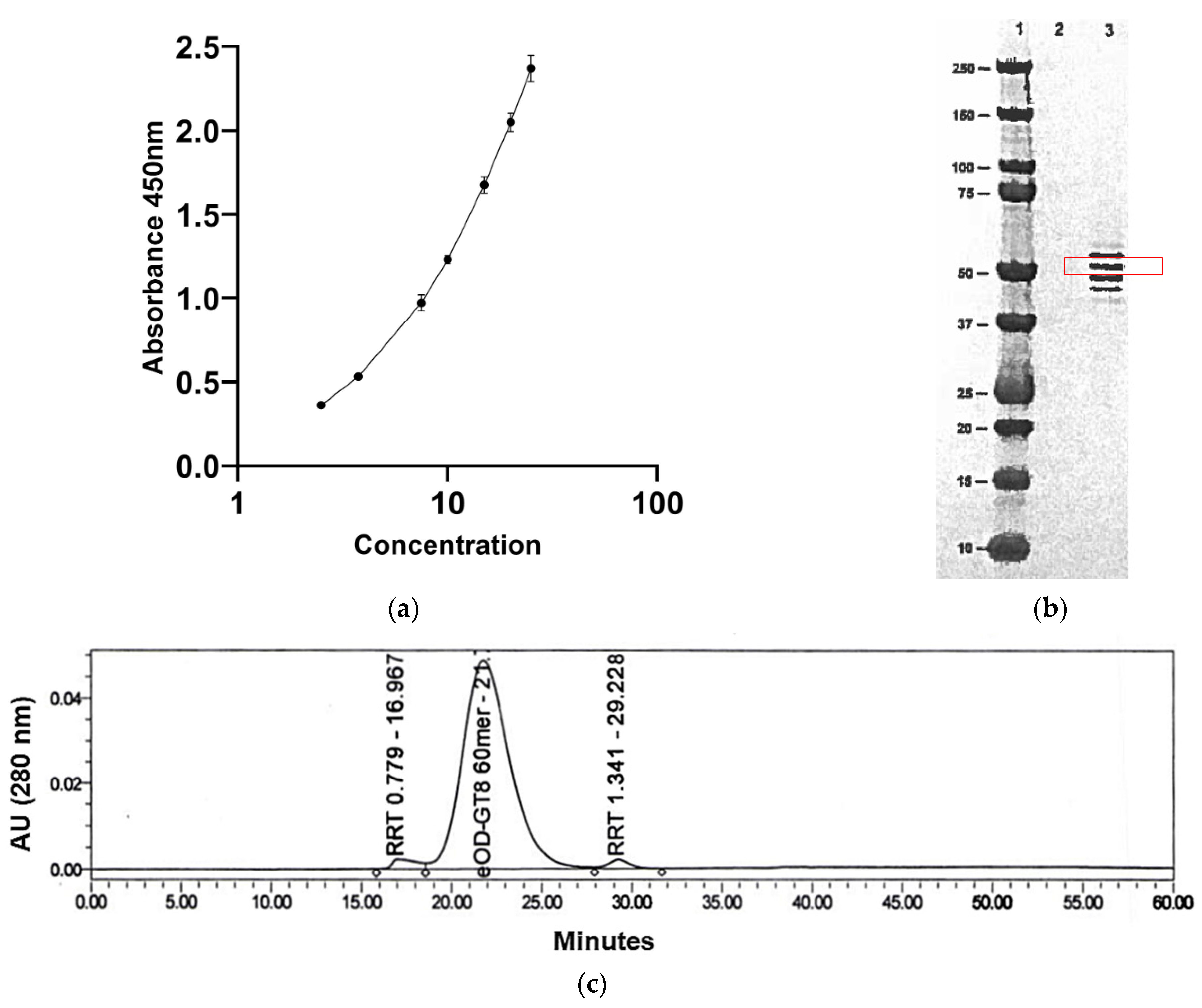
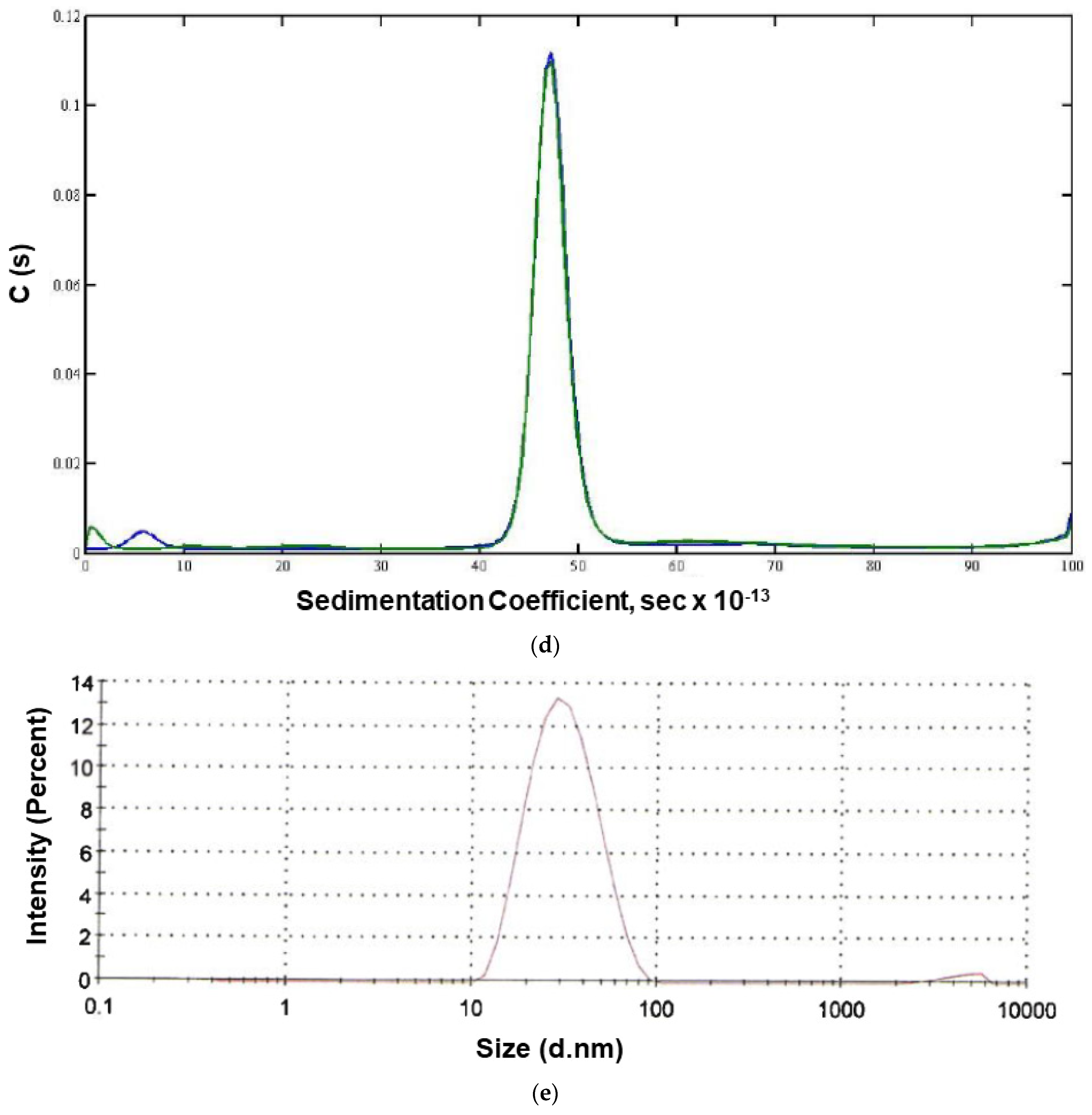
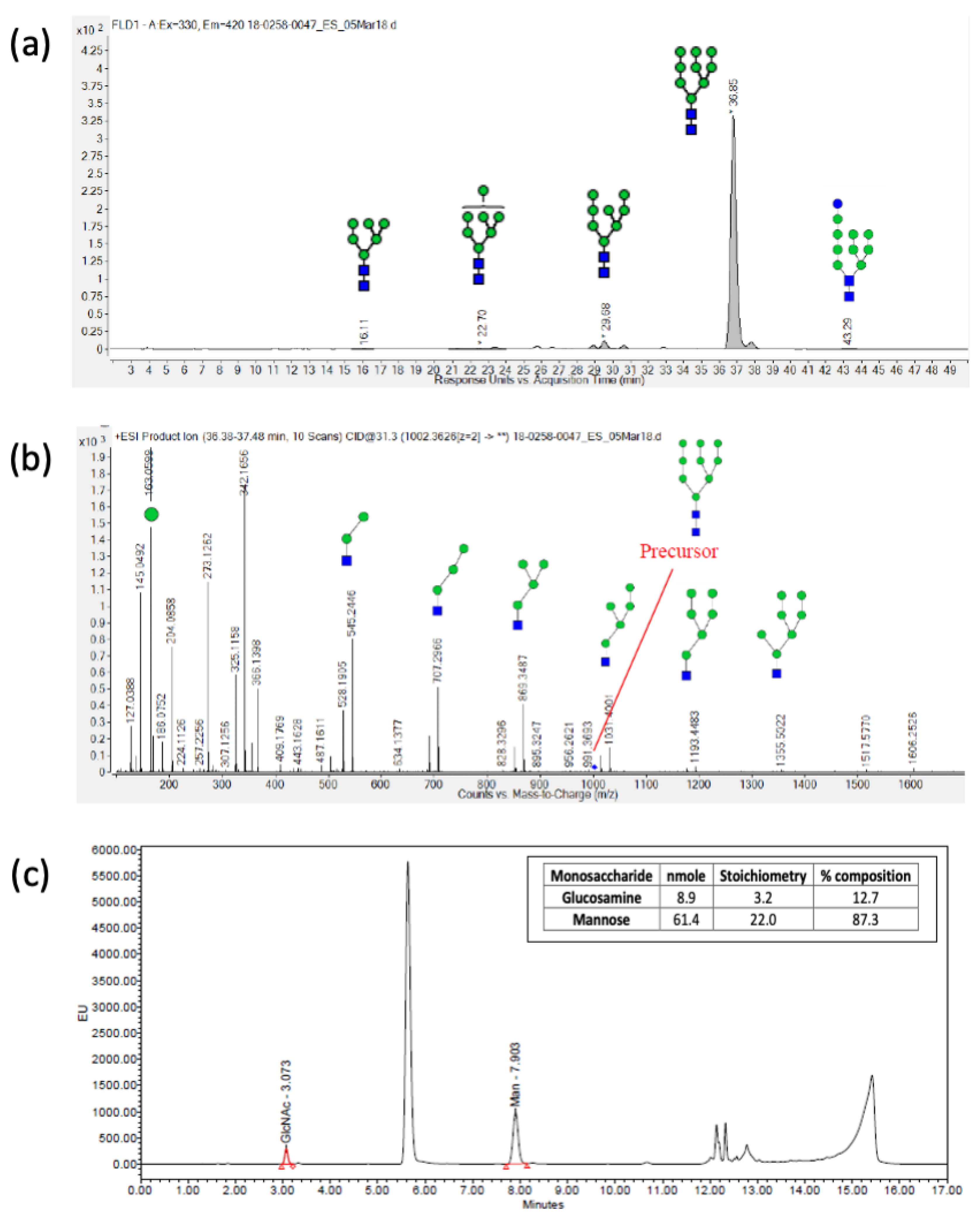
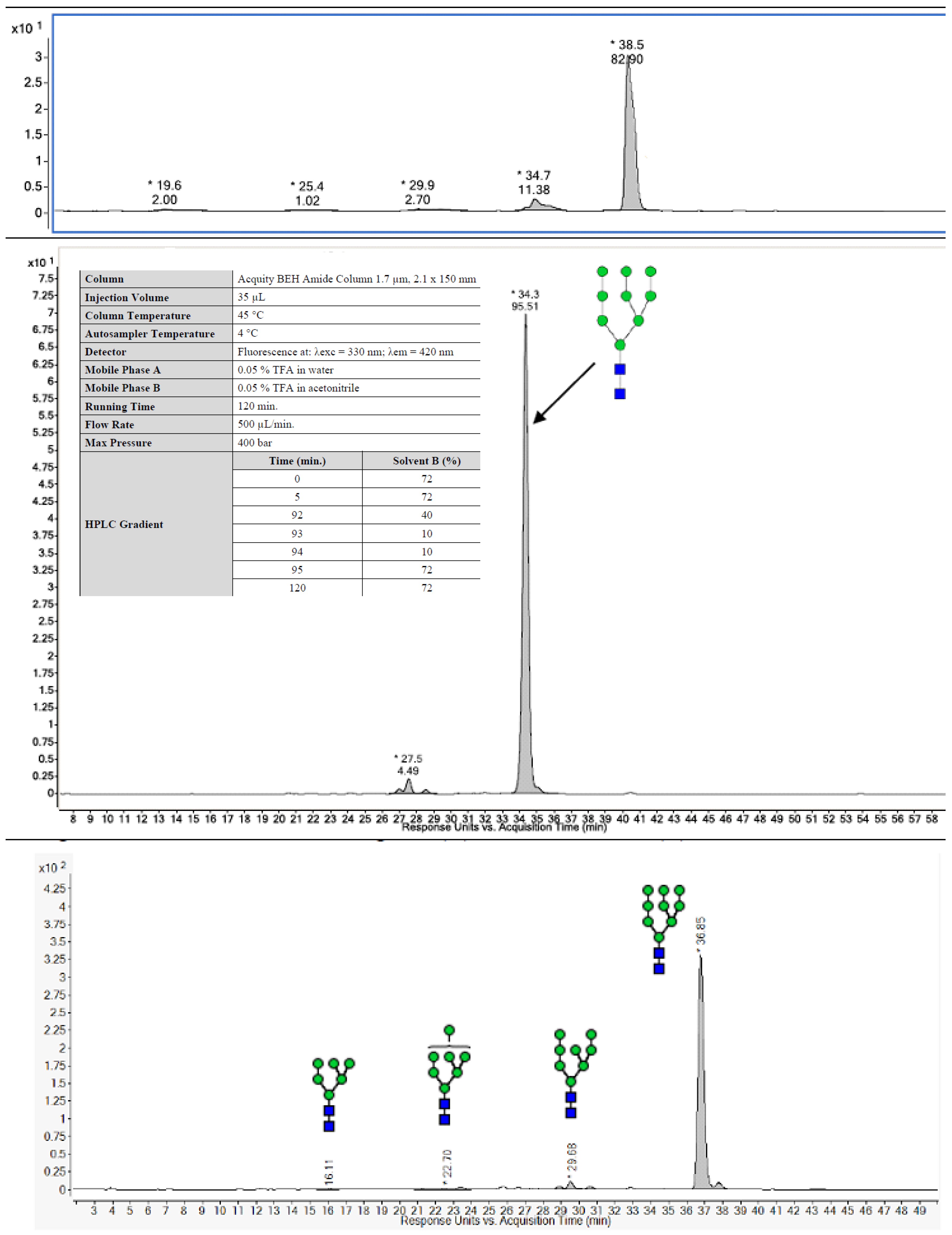
| Method | Research Run (2.0 L) | Process Batch (2 × 10 L) | Non-Clinical Batch (200 L) | cGMP Batch (200 L Scale) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 7.2 | |
| UV280-content | 1.0 mg/mL | 1.0 mg/mL | 1.1 mg/mL | 1.0 mg/mL | |
| ELISA | 100% | 60% | 90% | 89% | |
| SE-HPLC | >95% | >92.8% | 95.35% | 95.81% | |
| DLS | n.d. | n.d. | 29.85 nm | 26.46 nm | |
| qPCR Residual Host cell DNA | n.d. | n.d. | ≤90 ng/mL | ≤90 ng/mL | |
| SDS-PAGE (Non-reduced and Reduced) | Four bands ~50 KDa | Four bands ~50 KDa | Four bands ~50 KDa | Four bands ~50 KDa | |
| AUC-Sedimentation Velocity | One main peak (97.8%) | n.d. | One main peak (>95%) | One main peak (>90%) | |
| N-Terminal Edman Sequencing | MQIYEGKLTA * | MQIYEGKLTA * | ETGMQIYEGK † | ETGMQIYEGK † | |
| LC-MS/MS ‡ | Sequence coverage | 97.9% | 98% | 99.7% | 98% † |
| Fully occupied N-glycan site | 187, 234 | 187, 234, 267 | 187, 234, 298 | 187, 234, 261, 267, 298 | |
| Partially occupied N-glycan site | 261, 267, 275, 298, 334 | 298, 334 | 261, 267, 282, 315, 334, 339 | 315, 334, 339 | |
| Fully unoccupied N-glycan site | 282, 315, 339 | 261, 275, 282, 315, 339 | 275 | 275, 282 | |
| HILIC-FLD-MS/MS | High mannose; 82.9% Man9 | High mannose; 90% Man9 | High mannose; 95.5% Man9 | High mannose; 91.9% Man9 | |
| RP-UPLC | Mannose: 89.1% Glucosamine: 10.9% | Mannose: 94.7% Glucosamine: 5.3% | Mannose: 87.3% Glucosamine: 12.7% | Mannose: 92.4% Glucosamine: 7.6% | |
| Endotoxin | n.d. | ≤100 EU/mL | ≤100 EU/mL | ≤100 EU/mL | |
| Bioburden | n.d. | ≤1 CFU per 10 mL (TSA) ≤1 CFU per 10 mL (SDA) | ≤1 CFU per 10 mL (TSA) ≤1 CFU per 10 mL (SDA) | ≤1 CFU per 10 mL (TSA) ≤1 CFU per 10 mL (SDA) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, V.K.; Menis, S.; Brower, E.T.; Sayeed, E.; Ackland, J.; Lombardo, A.; Cottrell, C.A.; Torres, J.L.; Hassell, T.; Ward, A.B.; et al. Use of Transient Transfection for cGMP Manufacturing of eOD-GT8 60mer, a Self-Assembling Nanoparticle Germline-Targeting HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060742
Sharma VK, Menis S, Brower ET, Sayeed E, Ackland J, Lombardo A, Cottrell CA, Torres JL, Hassell T, Ward AB, et al. Use of Transient Transfection for cGMP Manufacturing of eOD-GT8 60mer, a Self-Assembling Nanoparticle Germline-Targeting HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(6):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Vaneet K., Sergey Menis, Evan T. Brower, Eddy Sayeed, Jim Ackland, Angela Lombardo, Christopher A. Cottrell, Jonathan L. Torres, Thomas Hassell, Andrew B. Ward, and et al. 2024. "Use of Transient Transfection for cGMP Manufacturing of eOD-GT8 60mer, a Self-Assembling Nanoparticle Germline-Targeting HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 6: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060742
APA StyleSharma, V. K., Menis, S., Brower, E. T., Sayeed, E., Ackland, J., Lombardo, A., Cottrell, C. A., Torres, J. L., Hassell, T., Ward, A. B., Tsvetnitsky, V., & Schief, W. R. (2024). Use of Transient Transfection for cGMP Manufacturing of eOD-GT8 60mer, a Self-Assembling Nanoparticle Germline-Targeting HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate. Pharmaceutics, 16(6), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060742







