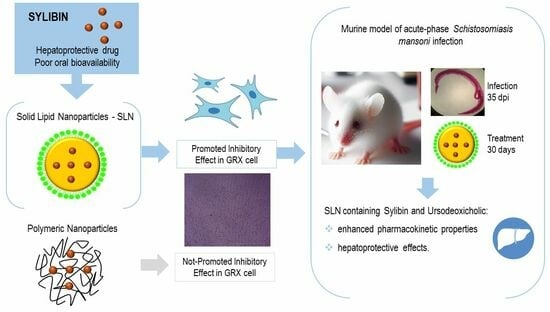
Evaluation of Silybin Nanoparticles against Liver Damage in Murine Schistosomiasis mansoni Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SLN
2.3. Preparation of PNs
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization of the Nanoparticles
2.4.1. Mean Diameter, Polydispersity Index, Zeta Potential, and Morphology
2.4.2. SIB and URSO Quantification
2.4.3. Process Yield and Encapsulation Efficiency (EE)
2.4.4. SIB Release Studies
2.4.5. Stability Study
2.5. In Vitro Studies in Cell Culture
2.5.1. Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays
2.5.2. Permeability Assay on Caco-2 Monolayer
2.6. In Vivo Studies
2.6.1. Animals and Experimental Model
2.6.2. Relative Liver Weight
2.6.3. Parasitological Evaluation
2.6.4. Dosage of Liver Enzymes Levels
2.6.5. Hydroxyproline Determination
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Preparation Method of SLNs Containing SIB
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of SLN and PN Containing SIB
3.2.1. Mean Diameter, Polydispersity Index, Zeta Potential, and Morphology
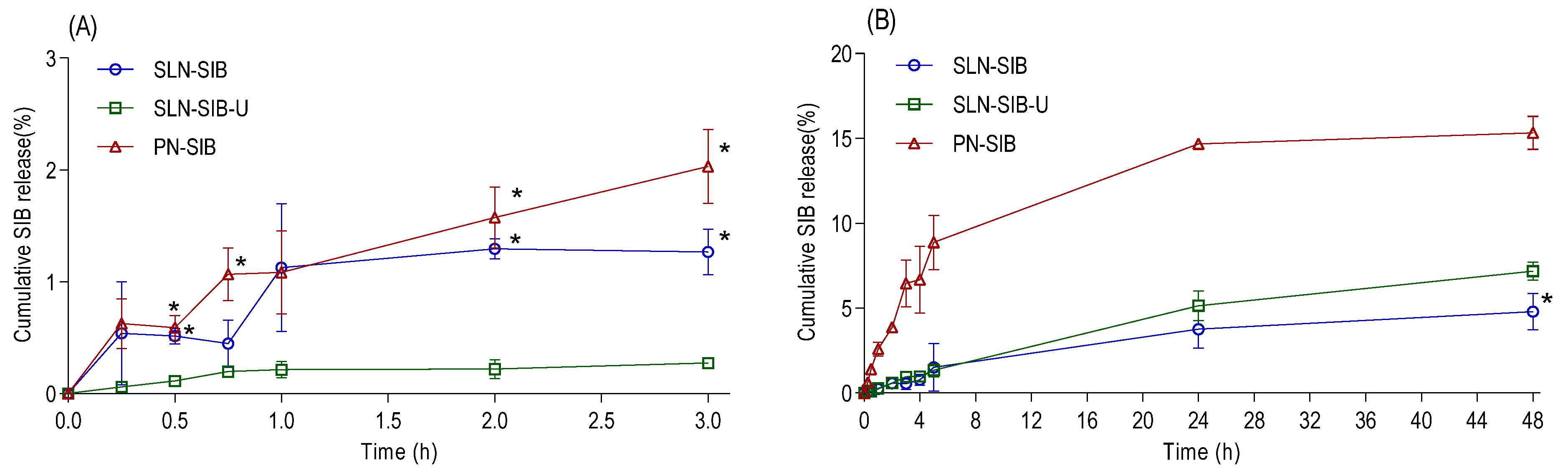
3.2.2. SIB Release Studies
3.3. In Vitro Studies in Cell Culture
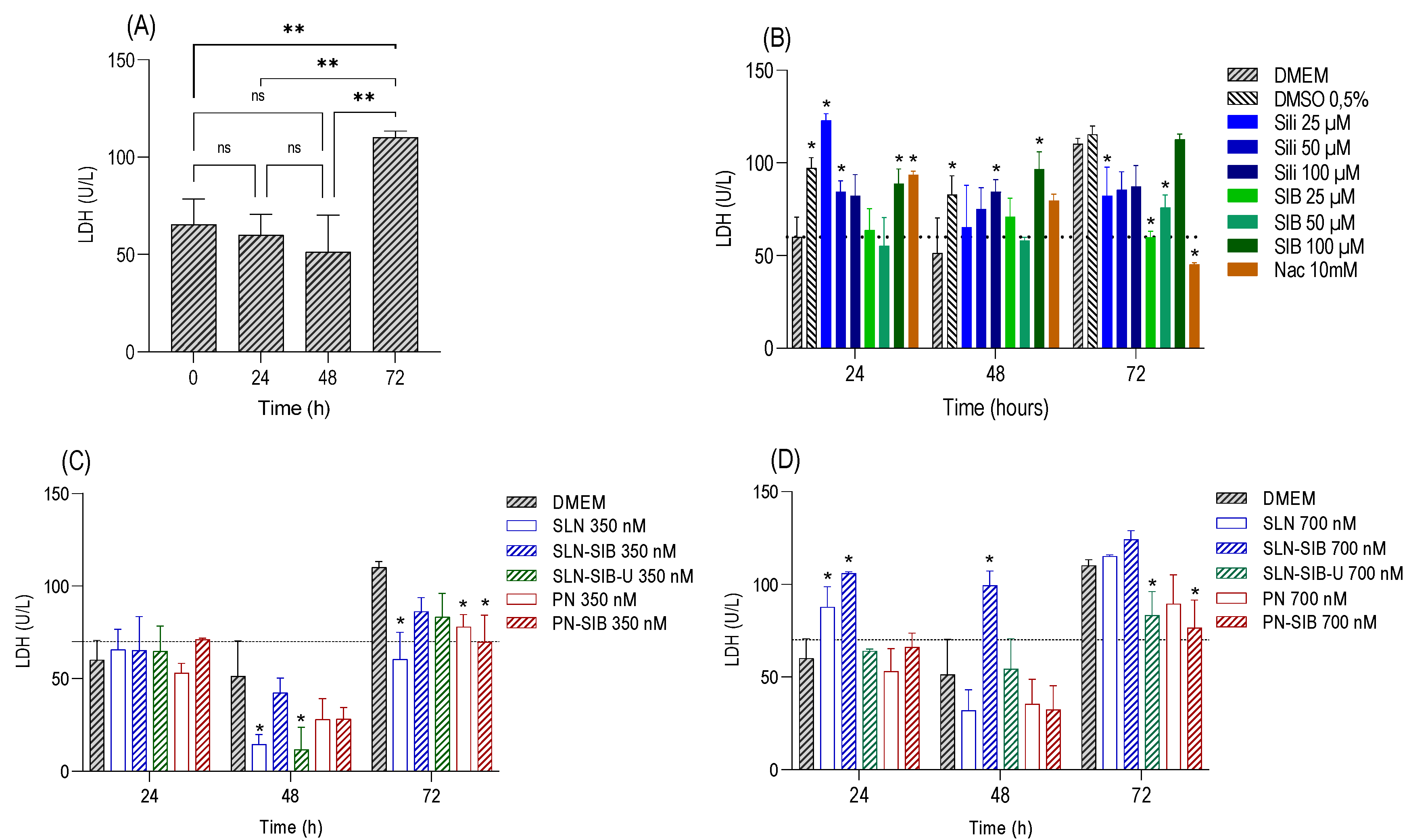
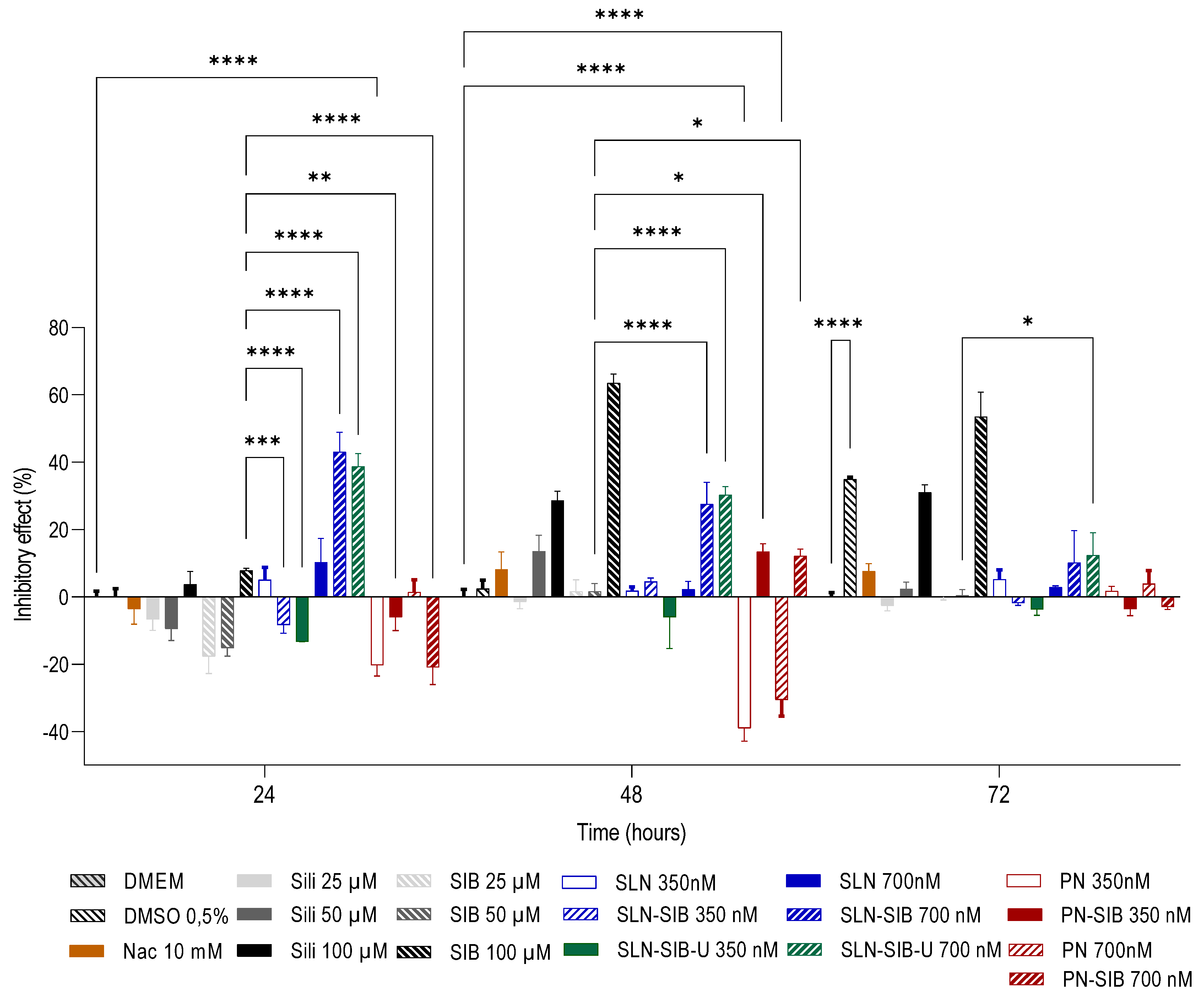
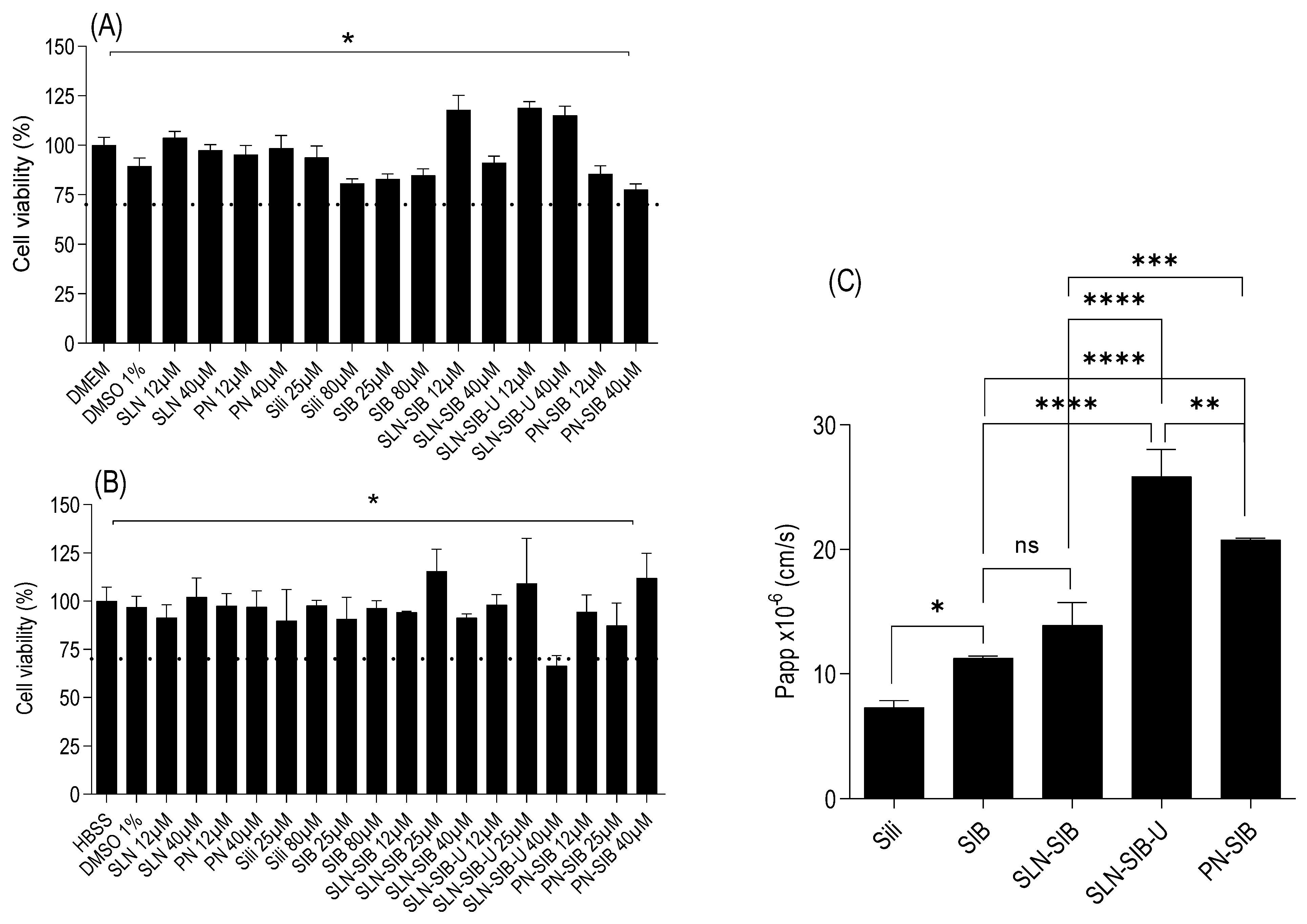
3.3.1. Cell Proliferation Assay and Viability Assays
3.3.2. Permeability Assay on Caco-2 Monolayer
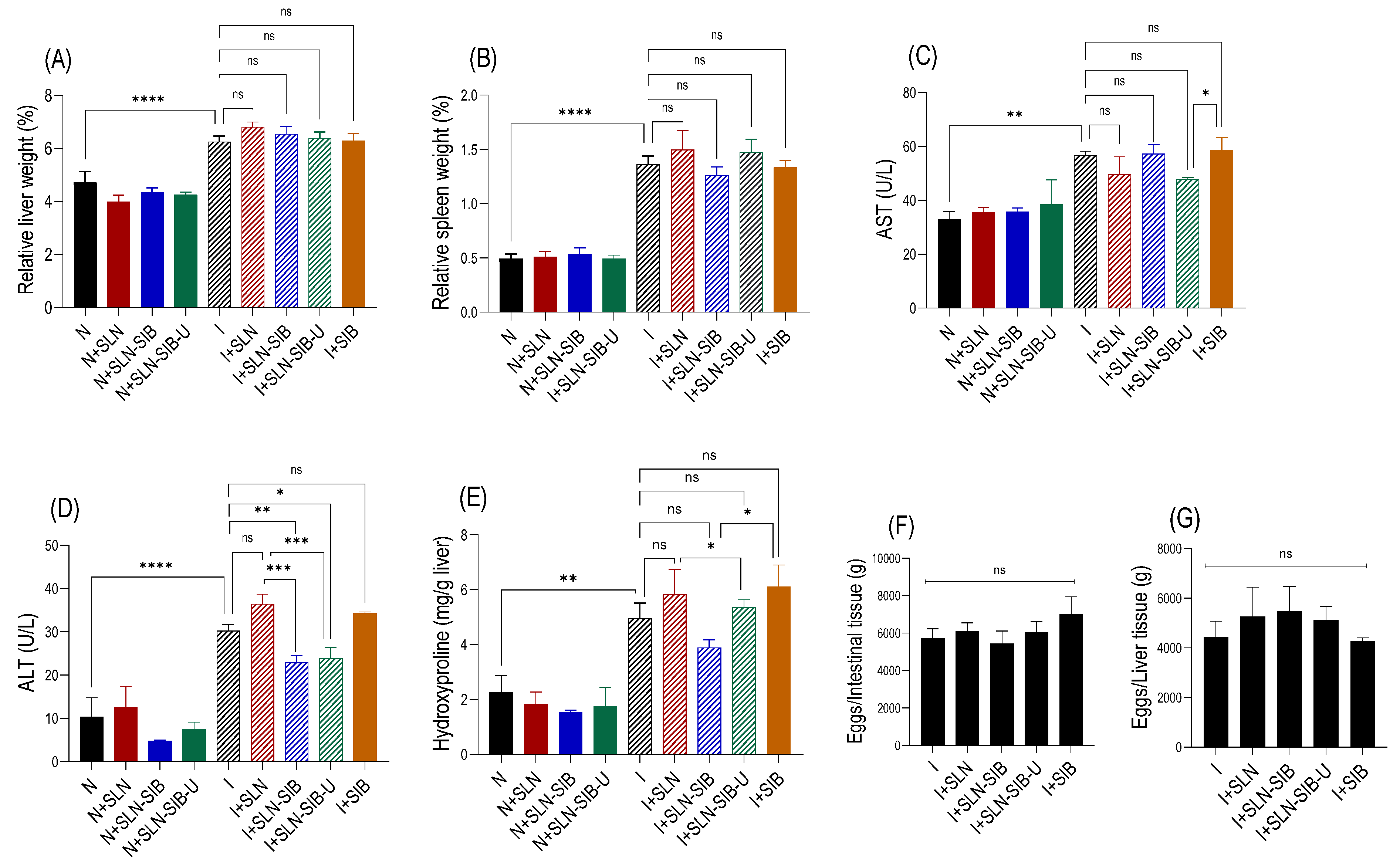
3.4. In Vivo Study
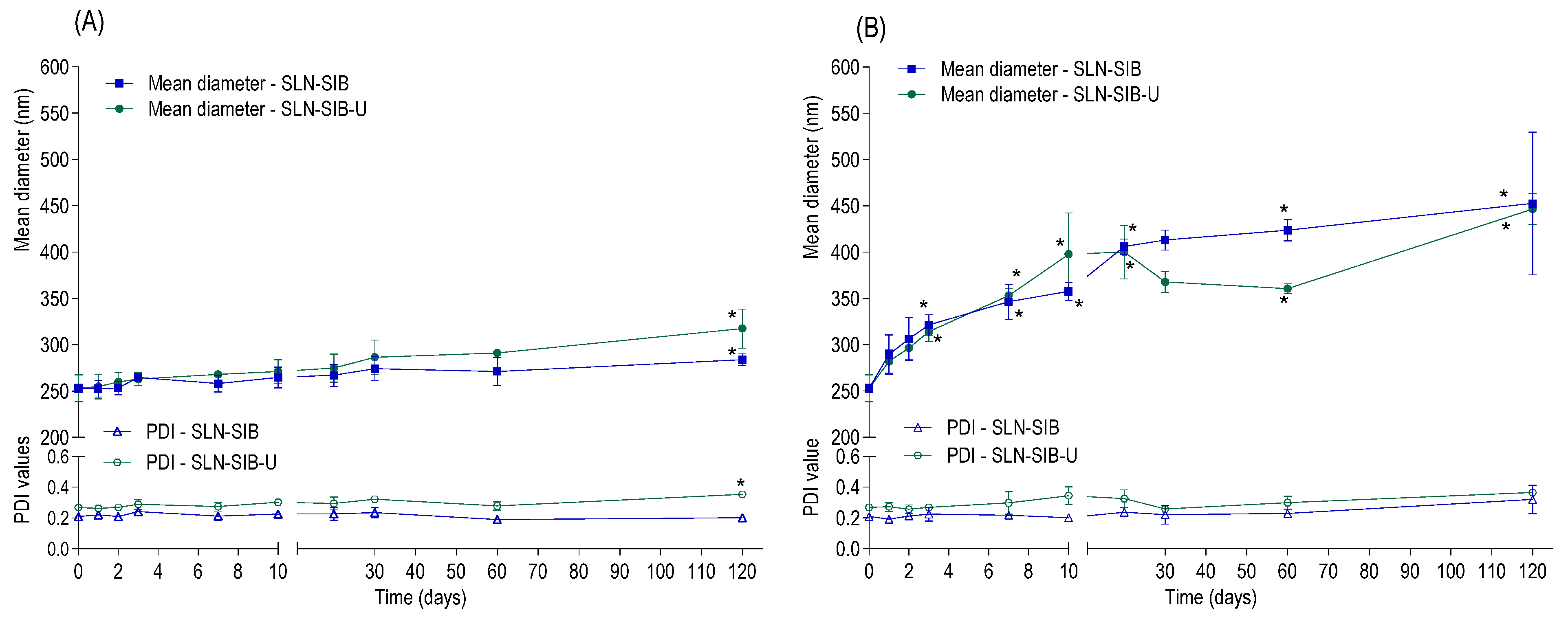
3.5. Stability Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Csupor, D.; Csorba, A.; Hohmann, J. Recent advances in the analysis of flavonolignans of Silybum marianum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipournazari, P.; Pourmadadi, M.; Abdouss, M.; Rahdar, A.; Pandey, S. Enhanced delivery of doxorubicin for breast cancer treatment using pH-sensitive starch/PVA/g-C3N4 hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Santos, H.A.; Dutra, F.F.; Rocha, C.C.; Lino, F.G.; Xavier, F.R.; Chinalia, L.A.; Hossy, B.H.; Castelo-Branco, M.T.; Teodoro, A.J.; Paiva, C.N.; et al. Silymarin reduces profibrogenic cytokines and reverses hepatic fibrosis in chronic murine schistosomiasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gür, F.M.; Bilgiç, S. Silymarin, an antioxidant flavonoid, protects the liver from the toxicity of the anticancer drug paclitaxel. Tissue Cell 2023, 83, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habotta, O.; Ateya, A.; Saleh, R.M.; El-Ashry, E.S. Thiamethoxam evoked neural oxido-inflammatory stress in male rats through modulation of Nrf2/NF-kB/iNOS signaling and inflammatory cytokines: Neuroprotective effect of Silymarin. NeuroToxicology 2023, 96, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Shukla, S.; Behl, T.; Gupta, S.; Anwer, M.K.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Bungau, S.G.; Brisc, C. Understanding the Potential Role of Nanotechnology in Liver Fibrosis: A Paradigm in Therapeutics. Molecules 2023, 28, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfuso, B.; Giraudi, P.J.; Tiribelli, C.; Rosso, N. Silybin Modulates Collagen Turnover in an In Vitro Model of NASH. Molecules 2019, 24, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hsu, M.-C.; Tsai, W.-L.; Chang, C.-y.; Chiu, C.-H. Effect of silymarin on lipid and alcohol metabolism in mice following long-term alcohol consumption. J. Food Biochem. 2012, 36, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Morales-González, A.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; García-Luna, Y.; González-Rubio, M.; Gayosso-de-Lucio, J.A.; Morales-González, J.A. Hepatoprotective effect of silymarin. World J. Hepatol. 2014, 6, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Wang, H. Silymarin attenuated hepatic steatosis through regulation of lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Vecchione, G.; Grasselli, E.; Voci, A.; Baldini, F.; Grattagliano, I.; Wang, D.Q.; Portincasa, P.; Vergani, L. Silybin counteracts lipid excess and oxidative stress in cultured steatotic hepatic cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6016–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, U.; Akhtar, J.; Singh, S.P.; Badruddeen; Ahmad, F.J.; Siddiqui, S.; Wahajuddin. Silymarin nanoemulsion against human hepatocellular carcinoma: Development and optimization. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Duan, W.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, N.; Feng, W.; Ding, M.; Nie, Y.; et al. Silybin-mediated inhibition of Notch signaling exerts antitumor activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagoner, J.; Negash, A.; Kane, O.J.; Martinez, L.E.; Nahmias, Y.; Bourne, N.; Owen, D.M.; Grove, J.; Brimacombe, C.; McKeating, J.A.; et al. Multiple effects of silymarin on the hepatitis C virus lifecycle. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Santos, H.A.; Lino, F.G.; Rocha, C.C.; Paiva, C.N.; Castelo Branco, M.T.; Pyrrho Ados, S. Silymarin treatment reduces granuloma and hepatic fibrosis in experimental schistosomiasis. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, J.P.; Ramm, G.A.; Robinson, M.W.; McManus, D.P.; Gobert, G.N. Schistosome-Induced Fibrotic Disease: The Role of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, D.P.; Dunne, D.W.; Sacko, M.; Utzinger, J.; Vennervald, B.J.; Zhou, X.N. Schistosomiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicoro, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borojevic, R.; Monteiro, A.N.A.; Vinhas, S.A.; Domont, G.B.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Emonard, H.; Grimaldi, G.; Grimaud, J.-A. Establishment of a continuous cell line from fibrotic schistosomal granulomas in mice livers. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 1985, 21, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzini, V.; Cinci, L.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Chitosan-coated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Tool for Silybin Delivery: Formulation, Characterization, and In vitro Evaluation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sornsuvit, C.; Hongwiset, D.; Yotsawimonwat, S.; Toonkum, M.; Thongsawat, S.; Taesotikul, W. The Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Silymarin SMEDDS Formulation Study in Healthy Thai Volunteers. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1507834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, R.; Jain, D.K. Nanotechnology Based Approaches for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Water Soluble Antihypertensive Drugs. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 8525679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Shegokar, R.; Souto, E.B. Chapter 30—Role of Excipients in formulation development and biocompatibility of lipid nanoparticles (SLNs/NLCs). In Nanostructures for Novel Therapy; Ficai, D., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 811–843. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinska, A.; Carreiro, F.; Oliveira, A.M.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization, Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Molecules 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.F.; de Oliveira Rezende, R.L.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Poly varepsilon-caprolactone nanoparticles loaded with Uncaria tomentosa extract: Preparation, characterization, and optimization using the Box-Behnken design. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and cytotoxicity of nanomaterials. Small 2011, 7, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.T.; Guo, J.; Presas, E.; Donovan, M.D.; Alonso, M.J.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and biodistribution following oral administration of nanocarriers containing peptide and protein drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Yin, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Size-dependent absorption mechanism of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of protein drugs. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8569–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.; Golocorbin-Kon, S.; Ethanic, M.; Stanimirov, B.; Al-Salami, H.; Stankov, K.; Mikov, M. Bile Acids and Their Derivatives as Potential Modifiers of Drug Release and Pharmacokinetic Profiles. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, C.Y.; Lin, L.J.; Kao, S.T.; Lo, H.Y.; Chou, S.T.; Ho, T.Y. Glycyrrhizin, silymarin, and ursodeoxycholic acid regulate a common hepatoprotective pathway in HepG2 cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2015, 22, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Chung, H.; Ji, S.C.; Lee, S.; Yu, K.S.; Jang, I.J.; Cho, J.Y. Ursodeoxycholic acid exerts hepatoprotective effects by regulating amino acid, flavonoid, and fatty acid metabolic pathways. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauner, M.; Graziadei, I.W. Review article: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications of ursodeoxycholic acid in chronic liver diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 13, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Chen, X.Z.; Wu, P.B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G. Ursodeoxycholic acid alleviates experimental liver fibrosis involving inhibition of autophagy. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuman, D.M.; Mills, A.S.; McCall, J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Pandak, W.M.; Vlahcevic, Z.R. Conjugates of ursodeoxycholate protect against cholestasis and hepatocellular necrosis caused by more hydrophobic bile salts. In vivo studies in the rat. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Yoon, S.; Ji, S.C.; Yang, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.; Yu, K.S.; Jang, I.J.; Chung, J.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Ursodeoxycholic acid improves liver function via phenylalanine/tyrosine pathway and microbiome remodelling in patients with liver dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.L.; Jasti, B.R. Preparation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles containing silibinin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paswan, S.K.; Saini, T.R. Purification of Drug Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Prepared by Emulsification Solvent Evaporation Using Stirred Cell Ultrafiltration Technique. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, R.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; Noronha, C.M.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Rosa, C.G.; Nunes, M.R.; Barreto, P.L.M. Development and Characterization of Poly-ε-caprolactone Nanocapsules Containing β-carotene Using the Nanoprecipitation Method and Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Furtado, P.; Agnes Silva Camargo de Oliveira, A.; Santiago Rodrigues, P.; Rita Santiago de Paula Gonçalves, A.; Raphaella Autran Colaço, A.; Pinheiro da Costa, S.; Muniz da Paz, M.; Wetler Meireles Carreiros Assumpção, P.; Pereira Rangel, L.; Simon, A.; et al. In vivo evaluation of time-dependent antithrombotic effect of rivaroxaban-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/sodium lauryl sulfate or didodecyl dimethylammonium bromide nanoparticles in Wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 190, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Moreira, M.L.A.; Costa, I.F.d.J.B.; de Sousa, V.P.; Rodrigues, C.R.; da Rocha e Lima, L.M.T.; Sisnande, T.; do Carmo, F.A.; Leal, I.C.R.; dos Santos, K.R.N.; et al. Vancomycin-loaded nanoparticles against vancomycin intermediate and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 375101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairy, M.A.; Mansour, F.R. Simultaneous Determination of Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Chenodeoxycholic Acid in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form by HPLC-UV Detection. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH. International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1). 2005. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-q2r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-and-methodology-step-5-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Baka, E.; Comer, J.E.A.; Takács-Novák, K. Study of equilibrium solubility measurement by saturation shake-flask method using hydrochlorothiazide as model compound. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, L.C.L.; Todaro, V.; Sathler, P.C.; da Silva, L.C.R.P.; do Carmo, F.A.; Costa, C.M.; Toma, H.K.; Castro, H.C.; Rodrigues, C.R.; de Sousa, V.P.; et al. Development and Characterization of Nisin Nanoparticles as Potential Alternative for the Recurrent Vaginal Candidiasis Treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Mundada, V.; Sawant, K. Enhanced intestinal absorption of asenapine maleate by fabricating solid lipid nanoparticles using TPGS: Elucidation of transport mechanism, permeability across Caco-2 cell line and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheever, A.W. Conditions affecting the accuracy of potassium hydroxide digestion techniques for counting Schistosoma mansoni eggs in tissues. Bull. World Health Organ. 1968, 39, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- El-Agamy, D.S.; Shebl, A.M.; Said, S.A. Prevention and treatment of Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Inflammopharmacology 2011, 19, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegemann, H.; Stalder, K. Determination of hydroxyproline. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1967, 18, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.; Li, W.; Zou, J.; Jiang, X.; Xu, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, L. Spermidine Prolongs Lifespan and Prevents Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating MAP1S-Mediated Autophagy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2938–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho Vieira, C.; Peltonen, L.; Karttunen, A.P.; Ribeiro, A.J. Is it advantageous to use quality by design (QbD) to develop nanoparticle-based dosage forms for parenteral drug administration? Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 657, 124163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawi, N.; El-Say, K.; Attia, D.; El-Nabarawi, M.; Elmazar, M.; Teaima, M. Development of Pomegranate Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Quality by Design Approach to Screen the Variables Affecting the Quality Attributes and Characterization. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 21712–21721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scioli Montoto, S.; Muraca, G.; Ruiz, M.E. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Pharmacological and Biopharmaceutical Aspects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samimi, S.; Maghsoudnia, N.; Eftekhari, R.B.; Dorkoosh, F. Chapter 3—Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Systems. In Characterization and Biology of Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 47–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shnoudeh, A.J.; Hamad, I.; Abdo, R.W.; Qadumii, L.; Jaber, A.Y.; Surchi, H.S.; Alkelany, S.Z. Chapter 15—Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Metal Nanoparticles. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 527–612. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Shin, K.H.; Jang, J. Plasmonic photocatalytic system using silver chloride/silver nanostructures under visible light. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, C.; Patrício, A.B.; Prata, J.M.; Nadhman, A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Fonte, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles vs. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Comparative Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvamani, V. Chapter 15—Stability Studies on Nanomaterials Used in Drugs. In Characterization and Biology of Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 425–444. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Pi, C.; Feng, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Y. The Influence of Nanoparticle Properties on Oral Bioavailability of Drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6295–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalpiaz, A.; Fogagnolo, M.; Ferraro, L.; Beggiato, S.; Hanuskova, M.; Maretti, E.; Sacchetti, F.; Leo, E.; Pavan, B. Bile salt-coating modulates the macrophage uptake of nanocores constituted by a zidovudine prodrug and enhances its nose-to-brain delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durymanov, M.; Permyakova, A.; Reineke, J. Pre-treatment With PLGA/Silibinin Nanoparticles Mitigates Dacarbazine-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanikumar, L.; Choi, E.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Park, S.A.; Choi, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, C.; Ryu, J.H. Importance of Encapsulation Stability of Nanocarriers with High Drug Loading Capacity for Increasing in Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3030–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Li, R.; Chen, W. The cellular mechanobiology of aging: From biology to mechanics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1491, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, M.O.; Vercesi, F. Polycaprolactone: How a Well-Known and Futuristic Polymer Has Become an Innovative Collagen-Stimulator in Esthetics. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyenberg, W.; Filev, P.; Van den Plas, D.; Vandervoort, J.; De Smet, K.; Sollie, P.; Ludwig, A. Cytotoxicity of submicron emulsions and solid lipid nanoparticles for dermal application. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO10993-5; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- El-Lakkany, N.M.; Hammam, O.A.; El-Maadawy, W.H.; Badawy, A.A.; Ain-Shoka, A.A.; Ebeid, F.A. Anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic effects of the hepatoprotective silymarin and the schistosomicide praziquantel against Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.; Boueri, B.; Oliveira, C.; Silveira, I.; Ribeiro, A.J. Lipoplexes and polyplexes as nucleic acids delivery nanosystems: The current state and future considerations. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Nanoparticle | Method | Preparation Conditions | Composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UF | US (min) | P20 (% w/v) 1 | Stearic Acid (mg) 2 | SIB (mg) 2 | URSO (mg) 2 | ||
| NP-1 | A | No | 30 | 1.30 | 210 | 10 | - |
| NP-2 | B | No | 30 | 1.67 | 210 | 10 | - |
| NP-3 | C | No | 40 | 1.67 | 210 | 10 | - |
| NP-4 | D | No | 50 | 1.67 | 210 | 10 | - |
| NP-5 | D | No | 50 | 1.67 | 200 | 10 | 10 |
| NP-6 | D | No | 50 | 1.67 | 190 | 10 | 20 |
| NP-7 | D | No | 50 | 1.67 | 180 | 10 | 30 |
| NP-8 | D | No | 50 | 1.67 | 160 | 10 | 50 |
| SLN | D | Yes | 50 | 1.67 | 210 | - | - |
| SLN-SIB | D | Yes | 50 | 1.67 | 210 | 10 | - |
| SLN-SIB-U | D | Yes | 50 | 1.67 | 160 | 10 | 50 |
| Animal Groups | Infection | Dose (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| N * | No | - |
| N + SLN | No | 1 |
| N + SLN-SIB | No | 1 |
| N + SLN-SIB-U | No | 1 |
| I * | Yes | - |
| I + SIB | Yes | 10 |
| I + SLN | Yes | 1 |
| I + SLN-SIB | Yes | 1 |
| I + SLN-SIB-U | Yes | 1 |
| Nanoparticle | Method | Mean Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP-1 | A | 426.7 ± 48.3 | 0.428 ± 0.01 | −12.1 ± 1.8 |
| NP-2 | B | 386.8 ± 19.0 | 0.258 ± 0.02 | −11.7 ± 1.7 |
| NP-3 | C | 291.8 ± 16.1 | 0.206 ± 0.03 | −12.6 ± 2.2 |
| NP-4 | D | 260.9 ± 4.5 | 0.197 ± 0.02 | −11.6 ± 0.9 |
| NP-5 | D | 242.1 ± 1.4 | 0.178 ± 0.01 | −11.1 ± 0.2 |
| NP-6 | D | 251.4 ± 14.5 | 0.209 ± 0.03 | −12.0 ± 0.8 |
| NP-7 | D | 288.8 ± 10.8 | 0.250 ± 0.03 | −11.0 ± 1.9 |
| NP-8 | D | 279.2 ± 14.0 | 0.252 ± 0.03 | −12.1 ± 2.1 |
| SLN | D | 221.2 ± 9.7 | 0.154 ± 0.01 | −30.9 ± 1.8 |
| SLN-SIB | D | 252.8 ± 4.4 | 0.209 ± 0.01 | −34.5 ± 2.3 |
| SLN-SIB-U | D | 252.9 ± 14.4 | 0.269 ± 0.01 | −27.3 ± 1.3 |
| Nanoparticle | Mean Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | EE (%) | Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIB | URSO | |||||
| SLN | 221.2 ± 9.7 | 0.154 ± 0.005 | −30.9 ± 1.8 | - | - | - |
| SLN-SIB | 252.8 ± 4.4 * | 0.209 ± 0.007 * | −34.5 ± 2.3 * | 90.3 ± 2.2 | - | 38.8 ± 6.0 |
| SLN-SIB-U | 252.9 ± 14.4 * | 0.269 ± 0.005 * | −27.3 ± 1.3 | 77.1 ± 2.8 | 92.55 ± 4.3 | 32.1 ± 4.8 |
| PN | 267.3 ± 4.6 | 0.178 ± 0.045 | −2.1 ± 0.4 | - | - | - |
| PN-SIB | 241.8 ± 4.1 ** | 0.139 ± 0.017 | −2.2 ± 0.2 | 98.0 ± 0.2 | - | 86.8 ± 5.5 |
| Nanosystems | SLN-SIB | SLN-SIB-U | PN-SIB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | SGF | PBS | SGF | PBS | SGF | PBS |
| Kinetic model * | ||||||
| Zero-order | 0.686 | 0.925 | 0.708 | 0.914 | 0.958 | 0.885 |
| First-order | 0.640 | 0.563 | 0.562 | 0.687 | 0.867 | 0.532 |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | 0.663 | 0.966 | 0.835 | 0.919 | 0.908 | 0.926 |
| Higuchi | 0.730 | 0.981 | 0.813 | 0.839 | 0.962 | 0.939 |
| J (µg/h−1) | 16.58 ± 3.79 | 4.65 ± 0.99 | 2.96 ± 0.74 | 5.88 ± 0.36 | 28.94 ± 4.90 | 11.49 ± 2.52 |
| tlag (h) | 0.95 ± 0.72 | 2.91 ± 1.65 | 0.93 ± 0.43 | 2.03 ± 1.32 | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 7.65 ± 2.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vanzan, D.F.; Goma, E.P.; Locatelli, F.R.; Honorio, T.d.S.; Furtado, P.d.S.; Rodrigues, C.R.; de Sousa, V.P.; Mata dos Santos, H.A.; do Carmo, F.A.; Simon, A.; et al. Evaluation of Silybin Nanoparticles against Liver Damage in Murine Schistosomiasis mansoni Infection. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050618
Vanzan DF, Goma EP, Locatelli FR, Honorio TdS, Furtado PdS, Rodrigues CR, de Sousa VP, Mata dos Santos HA, do Carmo FA, Simon A, et al. Evaluation of Silybin Nanoparticles against Liver Damage in Murine Schistosomiasis mansoni Infection. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(5):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050618
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanzan, Daniel Figueiredo, Ester Puna Goma, Fernanda Resende Locatelli, Thiago da Silva Honorio, Priscila de Souza Furtado, Carlos Rangel Rodrigues, Valeria Pereira de Sousa, Hilton Antônio Mata dos Santos, Flávia Almada do Carmo, Alice Simon, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of Silybin Nanoparticles against Liver Damage in Murine Schistosomiasis mansoni Infection" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 5: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050618
APA StyleVanzan, D. F., Goma, E. P., Locatelli, F. R., Honorio, T. d. S., Furtado, P. d. S., Rodrigues, C. R., de Sousa, V. P., Mata dos Santos, H. A., do Carmo, F. A., Simon, A., Pyrrho, A. d. S., Ribeiro, A. J., & Cabral, L. M. (2024). Evaluation of Silybin Nanoparticles against Liver Damage in Murine Schistosomiasis mansoni Infection. Pharmaceutics, 16(5), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050618