Study of the Acidic, Basic, and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Three Antihypertensive Drugs—Individually and in Combination
Abstract
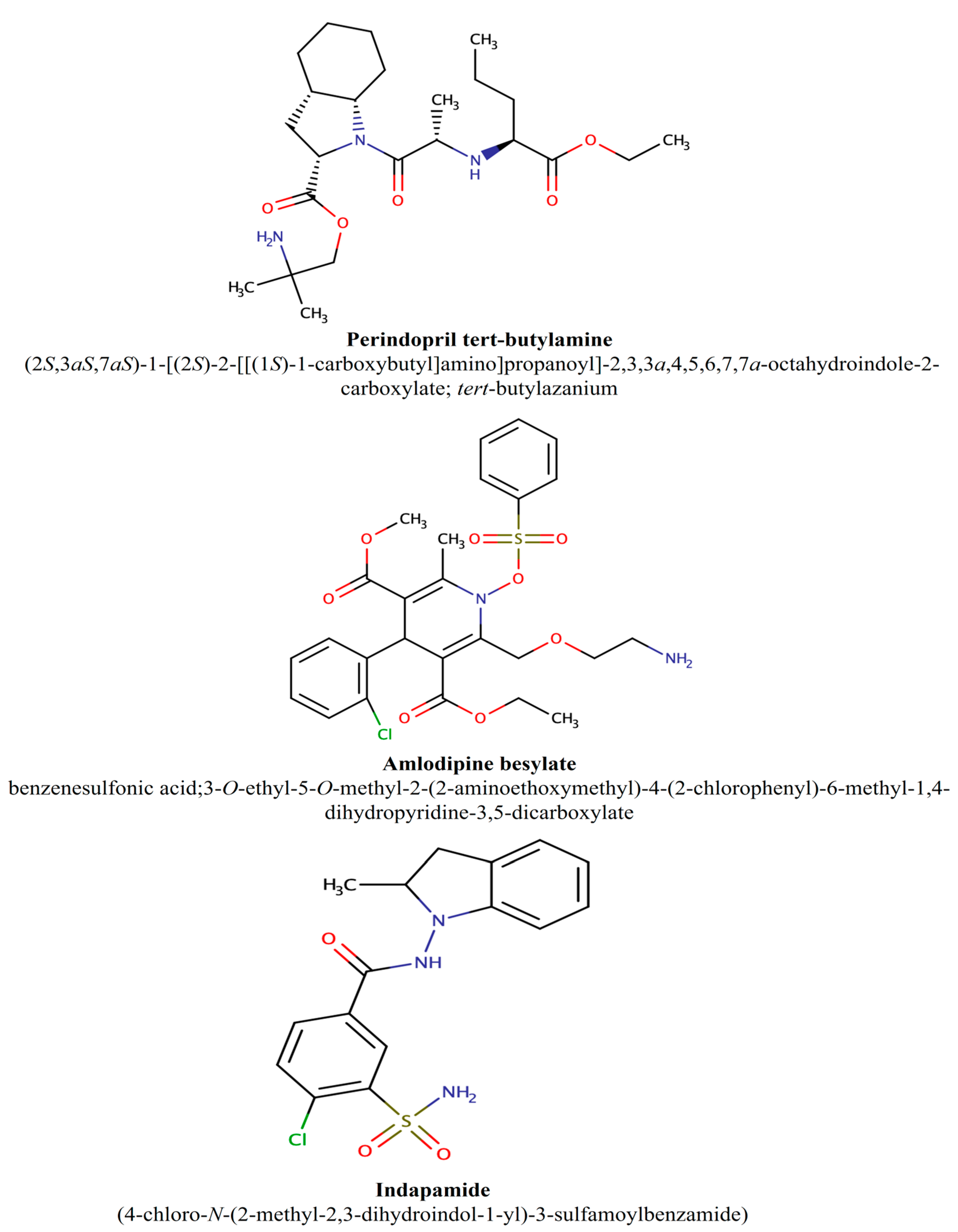
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Kinetic Studies
2.2.1. Sample Preparation for Degradation Kinetic Studies
2.2.2. Drug Stability Testing
2.2.3. Kinetic Calculations
2.3. HPLC Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Drug Stability
3.1.1. Oxidation-Induced Drug Degradation
3.1.2. Light-Induced Drug Degradation
3.2. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Parameters Determination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ICH Q1A (R2) Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Drug Products—Scientific Guideline|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q1a-r2-stability-testing-new-drug-substances-drug-products-scientific-guideline (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Farrag, S.A.; Rageh, A.H.; Askal, H.F.; Saleh, G.A. HPTLC/MS and HPTLC/UV for Monitoring of Degradation Behavior of Some β-Lactam Antibiotics Mixtures under Ambient Storage Conditions. Microchem. J. 2023, 185, 108241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-K.; Jee, J.-P.; Jang, D.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-E. Quality by Design (QbD) Application for the Pharmaceutical Development Process. J. Pharm. Investig. 2022, 52, 649–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, S.N.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; Rekkas, D.M. Design of Experiments (DoE) in Pharmaceutical Development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeia, H.B.; Silva, C.; Simões, S.P.; Reis, M.S. Quality by Design in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: A Systematic Review of Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 147, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhangare, D.; Rajput, N.; Jadav, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Tekade, R.K.; Sengupta, P. Systematic Strategies for Degradation Kinetic Study of Pharmaceuticals: An Issue of Utmost Importance Concerning Current Stability Analysis Practices. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokar, D.; Rajput, N.; Sengupta, P. Industrial Approaches and Consideration of Clinical Relevance in Setting Impurity Level Specification for Drug Substances and Drug Products. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 119018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, O.; Ramirez, I.O.; Ramirez, B.I.; O’Connell, P.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Torrado, J.J.; Serrano, D.R. Drug Stability: ICH versus Accelerated Predictive Stability Studies. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, A.L.; Colgan, S.T.; Kochling, J.D.; Alasandro, M.S. AAPS Workshop: Accelerating Pharmaceutical Development through Predictive Stability Approaches, April 4–5, 2016. AAPS Open 2017, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Colgan, S.; Hofer, J.; Timpano, R.; Vukovinsky, K.; Waterman, K.; Norris, K. Lean Stability. AAPS News Mag. 2015, 2015, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Irshad, K.; Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Imran, I. Principles of Pharmaceutical Analysis in Drug Stability and Chemical Kinetics. In Drug Stability and Chemical Kinetics; Akash, M.S.H., Rehman, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–18. ISBN 9789811564260. [Google Scholar]
- Sica, D.A. Rationale for Fixed-Dose Combinations in the Treatment of Hypertension. Drugs 2002, 62, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison, H.C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerenberg, K.A.; Zarnke, K.B.; Leung, A.A.; Dasgupta, K.; Butalia, S.; McBrien, K.; Harris, K.C.; Nakhla, M.; Cloutier, L.; Gelfer, M.; et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2018 Guidelines for Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, Prevention, and Treatment of Hypertension in Adults and Children. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 506–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Task Force of the Latin American Society of Hypertension Guidelines on the Management of Arterial Hypertension and Related Comorbidities in Latin America. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 1529–1545. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK). Hypertension: The Clinical Management of Primary Hypertension in Adults: Update of Clinical Guidelines 18 and 34; National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: Guidance; Royal College of Physicians: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.A.; Nerenberg, K.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; McBrien, K.; Zarnke, K.B.; Dasgupta, K.; Cloutier, L.; Gelfer, M.; Lamarre-Cliche, M.; Milot, A.; et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2016 Canadian Hypertension Education Program Guidelines for Blood Pressure Measurement, Diagnosis, Assessment of Risk, Prevention, and Treatment of Hypertension. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, S.; Arima, H.; Arima, S.; Asayama, K.; Dohi, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Horio, T.; Hoshide, S.; Ikeda, S.; Ishimitsu, T.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1235–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Kieble, M.; Enners, S.; Kintscher, U.; Laufs, U.; Böhm, M.; Schulz, M. Use of Fixed-Dose Combination Antihypertensives in Germany between 2016 and 2020: An Example of Guideline Inertia. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2023, 112, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, M.G.; Lee, G.A.; Young, J.D.; Sidney, S.; Go, A.S. Improved Blood Pressure Control Associated With a Large-Scale Hypertension Program. JAMA 2013, 310, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandić-Kovačević, N.; Kasagić-Vujanović, I.; Popović Bijelić, A. Analysis of Fixed-Dose Combination of Three Antihypertensive Drugs by a Green and Quality by Design Approach. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2023, 61, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wzgarda, A.; Dettlaff, K.; Rostalska, M.; Pabian, E.; Regulska, K.; Stanisz, B.J. Thermo-, Radio- and Photostability of Perindopril Tert-Butyloamine in The Solid State. Comparison to Other Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2017, 16, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczak, A.; Stanisz, B.J.; Szczołko, W.; Pieszak, M.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Impact of Hydrochlorothiazide on the Stability of Two Perindopril Salts. Evaluation of the Interaction with HPLC and ESI LC/MS Methods. Acta Pol. Pharm.-Drug Res. 2018, 75, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buda, V.; Andor, M.; Ledeti, A.; Ledeti, I.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Cristescu, C.; Voicu, M.; Suciu, L.; Tomescu, M.C. Comparative Solid-State Stability of Perindopril Active Substance vs. Pharmaceutical Formulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simončič, Z.; Roškar, R.; Gartner, A.; Kogej, K.; Kmetec, V. The Use of Microcalorimetry and HPLC for the Determination of Degradation Kinetics and Thermodynamic Parameters of Perindopril Erbumine in Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 356, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumieniczek, A.; Galeza, J.; Berecka, A.; Mroczek, T.; Wojtanowski, K.; Lipska, K.; Skarbek, J. Chemical Stability and Interactions in a New Antihypertensive Mixture Containing Indapamide and Dihydralazine Using FT-IR, HPLC and LC-MS Methods. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 36076–36089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda-Seiman, C.; Vlase, T.; Vlase, G.; Duda-Seiman, D.; Albu, P.; Doca, N. Thermal Analysis Study of Amlodipine as Pure Compound and in Binary Mixture. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Q1B Photostability Testing of New Active Substances and Medicinal Products—Scientific Guideline|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q1b-photostability-testing-new-active-substances-medicinal-products-scientific-guideline (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Loftsson, T. Drug Stability for Pharmaceutical Scientists; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 0-12-411562-4. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.W.; De Paula, J.; Keeler, J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; ISBN 0-19-884781-5. [Google Scholar]
- Physical Stability of Salts of Weak Bases in the Solid-State—Stephenson—2011—Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jps.22405 (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection, and Use, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Pharmaceutical+Salts%3A+Properties%2C+Selection%2C+and+Use%2C+2nd+Revised+Edition-p-9783906390512 (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Ioele, G.; Chieffallo, M.; Occhiuzzi, M.A.; De Luca, M.; Garofalo, A.; Ragno, G.; Grande, F. Anticancer Drugs: Recent Strategies to Improve Stability Profile, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodapati, K.; Vaidya, J.R.; Siddiraju, S.; Gowrisankar, D. Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Studies for the Estimation of Irbesartan and Amlodipine Besylate in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Identification and Characterization of Degradants Using LC-MS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugga, H.H.T.; Peraman, R.; Nayakanti, D. Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Perindopril Erbumine in Tablet Dosage Form. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.10 |
| 1 | 1.04 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.07 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.07 |
| 24 | 5.17 ± 0.02 | 2.96 ± 0.01 | 1.15 ± 0.14 | 1.44 ± 0.08 |
| 48 | 8.93 ± 0.02 | 6.89 ± 0.11 | 3.46 ± 0.09 | 2.53 ± 0.13 |
| 72 | 11.37 ± 0.08 | 10.41 ± 0.09 | 4.58 ± 0.08 | 4.03 ± 0.05 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0078 | 0.0065 | 0.0027 | 0.0023 |
| t1/2 (h) | 561.91 | 630.44 | 1460.85 | 1803.46 |
| t90 (h) | 62.37 | 69.98 | 162.15 | 200.18 |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 1.69 ±0.07 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | 0.65 ± 0.11 | 0.83 ± 0.05 |
| 1 | 3.27 ± 0.03 | 1.49 ± 0.06 | 2.42 ± 0.14 | 1.64 ± 0.05 |
| 24 | 17.36 ± 0.64 | 12.37 ± 0.65 | 11.29 ± 0.15 | 9.50 ± 0.51 |
| 48 | 27.60 ± 0.51 | 19.58 ± 0.43 | 19.59 ± 0.50 | 14.69 ± 0.35 |
| 72 | 35.72 ± 0.18 | 26.94 ± 0.95 | 26.82 ± 0.39 | 20.53 ± 0.66 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.043 | 0.0286 | 0.0275 | 0.019 |
| t1/2 (h) | 131.89 | 198.87 | 200.94 | 282.25 |
| t90 (h) | 14.64 | 22.07 | 22.30 | 31.33 |
| INDAPAMIDE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.09 |
| 1 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.08 | 0.60 ± 0.04 |
| 24 | 0.85 ± 0.07 | 0.93 ± 0.16 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 1.21 ± 0.12 |
| 48 | 1.52 ± 0.03 | 1.28 ± 0.04 | 1.05 ± 0.24 | 1.51 ± 0.05 |
| 72 | 2.34 ± 0.20 | 1.70 ± 0.16 | 1.43 ± 0.14 | 1.53 ± 0.03 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0012 | 0.0009 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 |
| t1/2 (h) | 3243.23 | 4343.95 | 4879.55 | 4854.71 |
| t90 (h) | 92.50 | 482.18 | 541.63 | 538.88 |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.01 ± 0.007* | 0.74 ± 0.12 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 0.46 ± 0.10 |
| 1 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 1.17 ± 0.16 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 1.32 ± 0.03 |
| 24 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 1.31 ± 0.13 | 0.76 ± 0.23 | 1.86 ± 0.14 |
| 48 | 0.87 ± 0.07 | 10.80 ± 0.20 | 0.86 ± 0.02 | 3.00 ± 0.05 |
| 72 | 0.93 ± 0.09 | 14.53 ± 0.48 | 1.30 ± 0.15 | 3.16 ± 0.10 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0006 | 0.0098 | 0.0007 | 0.0019 |
| t1/2 (h) | 7572.10 | 434.38 | 6945.15 | 2394.29 |
| t90 (h) | 840.50 | 48.22 | 770.91 | 265.77 |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 2.54 ± 0.16 | 2.80 ± 0.19 | 0.72 ± 0.11 | 2.09 ± 0.08 |
| 1 | 2.76 ± 0.09 | 3.25 ± 0.20 | 3.13 ± 0.03 | 2.96 ± 0.14 |
| 24 | 11.85 ± 0.30 | 11.93 ± 0.62 | 14.34 ± 0.89 | 31.31 ± 1.18 |
| 48 | 20.78 ± 0.81 | 23.05 ± 1.51 | 27.66 ± 1.11 | 48.35 ± 2.18 |
| 72 | 27.32 ± 0.97 | 28.75 ± 1.26 | 39.77 ± 1.10 | 57.18 ± 0.21 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0295 | 0.0301 | 0.0501 | 0.1055 |
| t1/2 (h) | 196.80 | 193.15 | 117.39 | 53.92 |
| t90 (h) | 21.84 | 20.41 | 13.03 | 5.99 |
| INDAPAMIDE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 0.005 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| 1 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| 24 | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 7.19 ± 0.75 |
| 48 | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.07 | 1.49 ± 0.06 | 12.60 ± 0.42 |
| 72 | 0.82 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 1.86 ± 0.08 | 15.48 ± 0.55 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0002 | 0.00009 | 0.001 | 0.0097 |
| t1/2 (h) | 17,844.12 | 43,047.10 | 3779.39 | 376.70 |
| t90 (h) | 1980.70 | 4778.23 | 419.51 | 41.81 |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.01 ± 0.006 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.28 ± 0.03 |
| 1 | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.07 | 0.55 ± 0.03 |
| 24 | 0.39 ± 0.10 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.82 ± 0.09 |
| 48 | 0.52 ± 0.12 | 7.41 ± 0.41 | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 1.05 ± 0.07 |
| 72 | 0.72 ± 0.12 | 7.64 ± 0.31 | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 1.13 ± 0.09 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0004 | 0.0055 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 |
| t1/2 (h) | 10,786.97 | 788.54 | 21,131.51 | 10,950.41 |
| t90 (h) | 1197.35 | 87.33 | 2345.60 | 1215.50 |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 1.05 ± 0.06 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.45 ± 0.13 | 0.74 ± 0.08 |
| 1 | 1.15 ± 0.07 | 0.36 ± 0.08 | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 1.29 ± 0.06 |
| 24 | 1.42 ± 0.15 | 0.75 ± 0.09 | 1.66 ± 0.11 | 7.67 ± 0.39 |
| 48 | 1.49 ± 0.21 | 7.17 ± 0.70 | 12.21 ± 0.12 | 11.20 ± 0.81 |
| 72 | 1.91 ± 0.12 | 9.81 ± 0.24 | 13.09 ± 0.36 | 14.68 ± 0.36 |
| n | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| k (mM h−1) | 0.00002 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 |
| t1/2 (h) | 4393.31 | 445.02 | 238.62 | 286.11 |
| t90 (h) | 878.62 | 89.00 | 47.72 | 57.22 |
| INDAPAMIDE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.01 ± 0.001 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.09 |
| 1 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.05 |
| 24 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.10 |
| 48 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 2.38 ± 0.40 | 1.23 ± 0.70 |
| 72 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 2.51 ± 0.48 | 2.86 ± 0.12 |
| n | II | II | II | 0 |
| k | 0.0001 mM−1h−1 | 0.0002 mM−1h−1 | 0.0014 mM−1h−1 | 0.00009 mM h−1 |
| t1/2 (h) | 36,043.88 | 17,307.17 | 2550.09 | 1490.27 |
| t90 (h) | 4000.87 | 1921.10 | 283.06 | 298.05 |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 2.92 ± 0.13 | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.01 |
| 1 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 2.96 ± 0.19 | 0.59 ± 0.20 | 0.65 ± 0.02 |
| 24 | 0.74 ± 0.16 | 3.50 ± 0.25 | 1.87 ± 0.13 | 0.69 ± 0.06 |
| 48 | 1.27 ± 0.12 | 8.20 ± 0.30 | 3.23 ± 0.16 | 1.59 ± 0.12 |
| 72 | 2.86 ± 0.14 | 9.78 ± 008 | 3.87 ± 0.14 | 2.65 ± 0.13 |
| n | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| k (mM h−1) | 0.00008 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.00007 |
| t1/2 (h) | 1451.27 | 402.87 | 1268.95 | 1689.27 |
| t90 (h) | 290.25 | 80.57 | 253.79 | 337.85 |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.40 ± 0.09 | 1.250.09 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| 1 | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 1.60 ± 0.17 | 0.85 ± 0.15 | 0.33 ± 0.07 |
| 24 | 8.97 ± 0.58 | 7.05 ± 0.50 | 9.20 ± 0.52 | 4.80 ± 0.41 |
| 48 | 16.75 ± 0.27 | 14.04 ± 0.03 | 14.13 ± 0.24 | 10.20 ± 1.58 |
| 72 | 23.33 ± 2.20 | 19.81 ± 0.72 | 20.27 ± 1.20 | 14.72 ± 0.60 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0238 | 0.0186 | 0.0386 | 0.0137 |
| t1/2 (h) | 238.03 | 302.56 | 290.79 | 424.32 |
| t90 (h) | 26.42 | 33.58 | 32.28 | 47.10 |
| INDAPAMIDE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| 1 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.08 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.11 |
| 24 | 1.05 ± 0.06 | 1.49 ± 0.10 | 0.78 ± 0.05 | 1.27 ± 0.09 |
| 48 | 1.85 ± 0.10 | 7.46 ± 0.11 | 1.27 ± 0.21 | 2.44 ± 0.44 |
| 72 | 2.38 ± 0.05 | 9.40 ± 0.05 | 1.49 ± 0.04 | 3.52 ± 0.49 |
| n | II | II | II | II |
| k (mM−1h−1) | 0.0013 | 0.0065 | 0.0008 | 0.0018 |
| t1/2 (h) | 2777.76 | 554.54 | 4748.47 | 2095.57 |
| t90 (h) | 308.33 | 61.55 | 527.08 | 232.61 |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.01 ± 0.005 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.01 ± 0.005 | 0.02 ± 0.006 |
| 1 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.16 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.03 |
| 24 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.70 ± 0.0.08 |
| 48 | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 0.32 ± 0.07 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 1.39 ± 0.05 |
| 72 | 0.58 ± 0.12 | 0.81 ± 0.19 | 1.68 ±0.21 | 6.83 ± 0.10 |
| n | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| k (mM h−1) | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00005 | 0.0002 |
| t1/2 (h) | 6275.00 | 6240.07 | 2473.44 | 634.15 |
| t90 (h) | 1207.30 | 1248.01 | 494.69 | 126.83 |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.015 | 0.01 ± 0.003 |
| 1 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.03 ± 0.015 | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| 24 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.25 ± 0.08 | 1.54 ± 0.19 | 2.23 ± 0.09 |
| 48 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 3.76 ± 0.25 | 7.55 ± 0.40 |
| 72 | 0.50 ± 0.11 | 0.52 ± 0.05 | 7.90 ± 0.14 | 13.84 ± 0.16 |
| n | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| k (mM h−1) | 0.00001 | 0.000009 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 |
| t1/2 (h) | 8360.54 | 9180.00 | 418.46 | 287.62 |
| t90 (h) | 1672.11 | 1836.00 | 83.69 | 57.52 |
| INDAPAMIDE * | ||||
| Time of degradation (h) | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.003 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| 1 | 0.39 ± 0.17 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| 24 | 0.50 ± 0.05 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 1.05 ± 0.09 | 0.37 ± 0.20 |
| 48 | 7.14 ± 0.43 | 7.94 ± 0.39 | 1.69 ± 0.10 | 0.76 ± 0.22 |
| 72 | 26.18 ± 0.40 | 27.54 ± 0.59 | 4.45 ± 0.34 | 1.50 ± 0.15 |
| n | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| k (mM h−1) | 0.0008 | 0.0009 | 0.0001 | 0.00005 |
| t1/2 (h) | 174.79 | 144.10 | 1315.21 | 2717.94 |
| t90 (h) | 34.96 | 28.82 | 263.04 | 543.59 |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 50.33 | 57.88 | 64.56 | 78.16 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 47.69 | 55.23 | 61.91 | 75.51 |
| 65 °C | 47.52 | 55.07 | 61.75 | 75.35 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 91.13 | 92.28 | 87.52 | 94.48 |
| 65 °C | 93.87 | 94.62 | 89.14 | 95.68 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.137 | −0.117 | −0.081 | −0.060 |
| 65 °C | −0.137 | −0.117 | −0.081 | −0.060 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0071 | 0.0046 | 0.0278 | 0.002 |
| 65 °C | 0.0219 | 0.0168 | 0.1179 | 0.0115 | |
| n | 45 °C | I | I | II | I |
| 65 °C | I | I | II | I | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 97.61 | 150.65 | 148.69 | 319.5 |
| 65 °C | 31.64 | 41.25 | 34.89 | 55.56 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 14.79 | 22.83 | 16.50 | 52.50 |
| 65 °C | 4.79 | 6.25 | 3.87 | 9.13 | |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 22.77 | 3.80 | 16.25 | 5.57 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 20.13 | 1.16 | 13.61 | 2.92 |
| 65 °C | 19.96 | 0.993 | 13.44 | 2.76 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 85.03 | 85.22 | 84.99 | 85.79 |
| 65 °C | 89.12 | 90.51 | 89.48 | 91.01 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.204 | −0.264 | −0.224 | −0.261 |
| 65 °C | −0.205 | −0.265 | −0.225 | −0.261 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0713 | 0.0664 | 0.0725 | 0.0535 |
| 65 °C | 0.1187 | 0.0723 | 0.1043 | 0.0606 | |
| n | 45 °C | II | II | II | II |
| 65 °C | II | II | II | II | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 80.48 | 85.91 | 77.44 | 105.13 |
| 65 °C | 49.44 | 77.12 | 54.82 | 90.97 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 8.93 | 9.54 | 8.59 | 11.67 |
| 65 °C | 5.49 | 8.56 | 6.08 | 10.10 | |
| INDAPAMIDE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 44.75 | 65.94 | 54.45 | 17.82 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 42.11 | 63.30 | 51.83 | 15.17 |
| 65 °C | 41.94 | 63.13 | 51.67 | 15.01 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 90.20 | 90.12 | 93.79 | 89.17 |
| 65 °C | 93.23 | 91.82 | 96.43 | 93.83 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.151 | −0.084 | −0.132 | −0.233 |
| 65 °C | −0.152 | −0.085 | −0.132 | −0.233 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0101 | 0.0104 | 0.0026 | 0.0149 |
| 65 °C | 0.0275 | 0.0455 | 0.0088 | 0.0222 | |
| n | 45 °C | II | II | II | II |
| 65 °C | II | II | II | II | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 348.52 | 346.10 | 1391.95 | 243.73 |
| 65 °C | 130.45 | 78.70 | 409.36 | 160.49 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 38.69 | 38.42 | 154.51 | 27.05 |
| 65 °C | 14.48 | 8.74 | 45.44 | 17.81 | |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 54.68 | 34.68 | 46.00 | 28.15 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 52.04 | 32.04 | 43.36 | 25.51 |
| 65 °C | 51.87 | 31.87 | 43.19 | 25.34 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 93.00 | 88.29 | 93.41 | 87.52 |
| 65 °C | 95.42 | 91.83 | 96.56 | 91.43 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.129 | −0.177 | −0.157 | −0.195 |
| 65 °C | −0.129 | −0.177 | −0.158 | −0.196 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0035 | 0.0208 | 0.003 | 0.0278 |
| 65 °C | 0.0119 | 0.0452 | 0.0084 | 0.0522 | |
| n | 45 °C | I | II | I | II |
| 65 °C | I | II | I | II | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 198 | 197.83 | 231.00 | 146.37 |
| 65 °C | 58.23 | 79.86 | 82.50 | 80.73 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 30.00 | 21.96 | 35.00 | 16.25 |
| 65 °C | 8.82 | 8.86 | 12.50 | 8.96 | |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 28.93 | 41.85 | 66.17 | 68.07 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 26.29 | 39.21 | 63.53 | 65.42 |
| 65 °C | 26.12 | 39.04 | 63.36 | 65.26 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 72.79 | 85.20 | 74.08 | 75.01 |
| 65 °C | 75.72 | 88.10 | 74.75 | 75.62 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.146 | −0.145 | −0.033 | −0.030 |
| 65 °C | −0.147 | −0.145 | −0.034 | −0.031 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 7.3077 | 0.0669 | 4.4853 | 3.1626 |
| 65 °C | 13.963 | 0.1707 | 19.723 | 14.509 | |
| n | 45 °C | II | I | II | II |
| 65 °C | II | I | II | II | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 0.75 | 10.36 | 1.26 | 1.78 |
| 65 °C | 0.41 | 4.06 | 0.29 | 0.38 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 0.08 | 1.57 | 0.14 | 0.20 |
| 65 °C | 0.05 | 0.61 | 0.03 | 0.04 | |
| INDAPAMIDE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 62.24 | 11.92 | 52.75 | 65.82 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 59.60 | 9.28 | 50.11 | 63.18 |
| 65 °C | 59.43 | 9.11 | 49.94 | 63.01 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 92.86 | 89.72 | 92.72 | 89.23 |
| 65 °C | 94.95 | 94.79 | 95.40 | 90.87 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.105 | −0.253 | −0.134 | −0.082 |
| 65 °C | −0.105 | −0.253 | −0.134 | −0.082 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0037 | 0.0121 | 0.0037 | 0.0146 |
| 65 °C | 0.0149 | 0.0158 | 0.0127 | 0.0637 | |
| n | 45 °C. | I | I | I | II |
| 65 °C | I | I | I | II | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 187.30 | 57.27 | 177.69 | 237.76 |
| 65 °C | 46.51 | 43.86 | 54.57 | 56.19 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 28.38 | 8.68 | 26.92 | 26.39 |
| 65 °C | 7.05 | 6.65 | 8.27 | 6.24 | |
| PERINDOPRIL TERT-BUTYLAMINE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | PER | PER + AML | PER + IND | PER + AML + IND | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 45.92 | 40.17 | 30.97 | 49.09 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 43.28 | 37.52 | 28.33 | 46.44 |
| 65 °C | 43.11 | 37.36 | 28.16 | 46.28 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 92.72 | 93.00 | 96.90 | 98.15 |
| 65 °C | 95.83 | 96.50 | 101.22 | 101.40 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.155 | −0.174 | −0.216 | −0.163 |
| 65 °C | −0.156 | −0.175 | −0.216 | −0.163 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0039 | 0.0035 | 0.0008 | 0.0005 |
| 65 °C | 0.0109 | 0.0086 | 0.0016 | 0.0015 | |
| n | 45 °C | I | I | 0 | 0 |
| 65 °C | I | I | 0 | 0 | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 177.69 | 198.00 | 165.79 | 238.78 |
| 65 °C | 63.58 | 80.58 | 74.22 | 77.81 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 26.92 | 30.00 | 33.16 | 47.76 |
| 65 °C | 9.63 | 12.21 | 14.84 | 15.56 | |
| AMLODIPINE BESYLATE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | AML | AML + PER | AML + IND | AML + PER + IND | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 57.91 | 34.05 | 76.62 | 71.91 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 55.27 | 31.41 | 73.98 | 69.27 |
| 65 °C | 55.10 | 31.24 | 73.81 | 69.10 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 93.50 | 95.43 | 102.68 | 102.40 |
| 65 °C | 95.91 | 99.46 | 104.49 | 104.49 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.120 | −0.201 | −0.090 | −0.104 |
| 65 °C | −0.121 | −0.202 | −0.091 | −0.105 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.0029 | 0.0014 | 0.00009 | 0.0001 |
| 65 °C | 0.0106 | 0.003 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | |
| n | 45 °C | I | I | 0 | 0 |
| 65 °C | I | I | 0 | 0 | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 238.97 | 495.00 | 982.54 | 855.78 |
| 65 °C | 65.38 | 231.00 | 170.54 | 170.16 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 36.21 | 75.08 | 196.51 | 171.16 |
| 65 °C | 9.91 | 32.84 | 34.11 | 34.03 | |
| INDAPAMIDE | |||||
| Thermodynamic parameters | IND | IND + PER | IND + AML | IND + PER + AML | |
| Ea (kJ mol−1) | 35.68 | 71.91 | 54.68 | 102.88 | |
| ΔH‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 33.03 | 69.27 | 52.04 | 100.24 |
| 65 °C | 32.87 | 69.10 | 51.87 | 100.07 | |
| ΔG‡ (kJ mol−1) | 45 °C | 102.68 | 102.40 | 98.15 | 106.66 |
| 65 °C | 107.07 | 104.50 | 101.05 | 107.07 | |
| ΔS‡ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | 45 °C | −0.219 | −0.104 | −0.145 | −0.020 |
| 65 °C | −0.220 | −0.105 | −0.146 | −0.021 | |
| Kinetic parameters | |||||
| k * | 45 °C | 0.00005 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.00002 |
| 65 °C | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | 0.0017 | 0.0002 | |
| n | 45 °C | 0 | 0 | II | 0 |
| 65 °C | 0 | 0 | II | 0 | |
| t1/2 (h) | 45 °C | 2734.72 | 2713.21 | 7004.85 | 6896.66 |
| 65 °C | 697.00 | 553.58 | 2152.00 | 687.57 | |
| t90 (h) | 45 °C | 546.94 | 271.32 | 777.54 | 1379.33 |
| 65 °C | 139.40 | 55.36 | 238.87 | 137.51 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandić-Kovacević, N.; Kasagić-Vujanović, I.; Gatarić, B.; Škrbić, R.; Popović Bijelić, A. Study of the Acidic, Basic, and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Three Antihypertensive Drugs—Individually and in Combination. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111410
Mandić-Kovacević N, Kasagić-Vujanović I, Gatarić B, Škrbić R, Popović Bijelić A. Study of the Acidic, Basic, and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Three Antihypertensive Drugs—Individually and in Combination. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(11):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111410
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandić-Kovacević, Nebojša, Irena Kasagić-Vujanović, Biljana Gatarić, Ranko Škrbić, and Ana Popović Bijelić. 2024. "Study of the Acidic, Basic, and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Three Antihypertensive Drugs—Individually and in Combination" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 11: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111410
APA StyleMandić-Kovacević, N., Kasagić-Vujanović, I., Gatarić, B., Škrbić, R., & Popović Bijelić, A. (2024). Study of the Acidic, Basic, and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Three Antihypertensive Drugs—Individually and in Combination. Pharmaceutics, 16(11), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111410







