Long-Term Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Levobupivacaine Wound Infiltration or Diclofenac for Postoperative Pain Relief
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Postoperative Analgesia
2.2. Long-Term Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
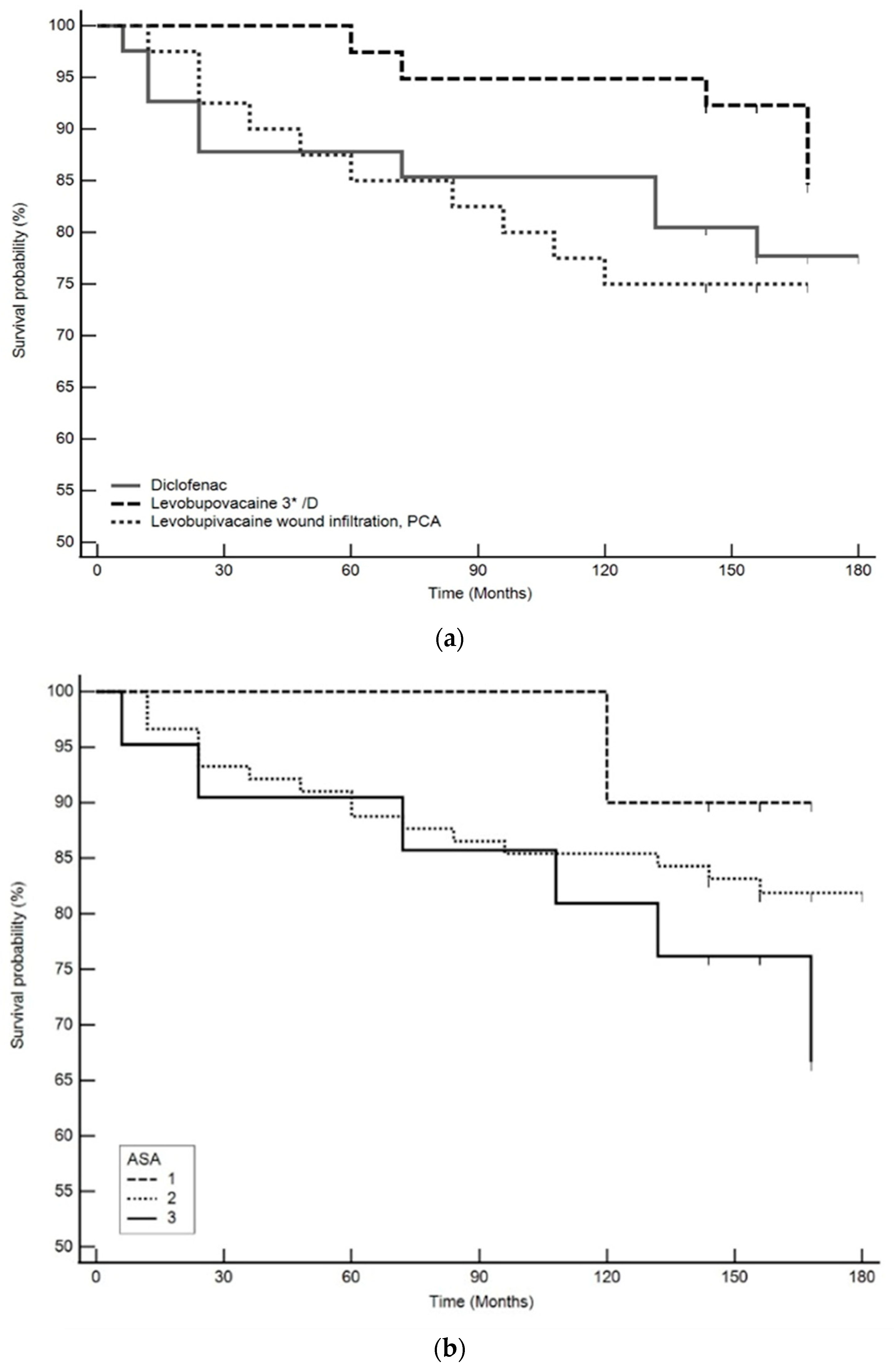
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bundred, J.R.; Michael, S.; Stuart, B.; Cutress, R.I.; Beckmann, K.; Holleczek, B.; Dahlstrom, J.E.; Gath, J.; Dodwell, D.; Bundred, N.J. Margin status and survival outcomes after breast cancer conservation surgery: Prospectively registered systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 378, e070346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beguinot, M.; Monrigal, E.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Ginzac, A.; Joly, D.; Gayraud, G.; Le Bouedec, G.; Gimbergues, P. Continuous Wound Infiltration with Ropivacaine After Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 254, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, U.; Shamshery, C.; Agarwal, A.; Prakash, N.; Valiveru, R.C.; Mishra, P. Evaluation of postoperative pain in patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy with pectoralis or serratus-intercostal fascial plane blocks. Korean J. Anesth. 2020, 73, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.E.; Greenberger, B.A.; Shi, Z.; Gajjar, S.; Shi, W.; Mourad, W.F.; Yan, W. Post-mastectomy and post-breast conservation surgery pain syndrome: A review of etiologies, risk prediction, and trends in management. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9 (Suppl. S1), S77–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, J.; Choi, J.W.; Bang, Y.J.; Oh, E.J.; Park, J.; Hong, K.Y.; Sim, W.S. The efficacy of ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with a tissue expander: A randomized clinical trial. Korean J. Pain 2021, 34, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabeeny, W.Y.; Shehab, N.N.; Wadod, M.A.; Elkady, M.A. Perioperative Analgesic Modalities for Breast Cancer Surgeries: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 2885–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Effects of local anesthetics on breast cancer cell viability and migration. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Liu, S.T.; Huang, S.M.; Wu, Z.F. Apoptosis, Proliferation, and Autophagy Are Involved in Local Anesthetic-Induced Cytotoxicity of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, V.; Piroli, A.; Marinangeli, F.; d’Angelo, M.; Benedetti, E.; Ippoliti, R.; Zis, P.; Varrassi, G.; Giordano, A.; Paladini, A.; et al. Local anesthetics counteract cell proliferation and migration of human triple-negative breast cancer and melanoma cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 3474–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakye, A.K.; Kampo, S.; Lv, J.; Ramzan, M.N.; Richard, S.A.; Falagán, A.A.; Agudogo, J.; Atito-Narh, E.; Yan, Q.; Wen, Q.P. Levobupivacaine inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of breast cancer cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, I.; Kalichman, L.; Chen, N.; Susmallian, S. Effect of physical activity levels on oncological breast surgery recovery: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savioli, F.; Edwards, J.; McMillan, D.; Stallard, S.; Doughty, J.; Romics, L. The effect of postoperative complications on survival and recurrence after surgery for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 155, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.; Kawai, A.; Wakisaka, M.; Sawada, S.; Shimoyama, M.; Yasuda, N.; Kin, T.; Arihiro, K. Outpatient breast-conserving surgery for breast cancer: Use of local and intravenous anesthesia and/or sedation may reduce recurrence and improve survival. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 60, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legeby, M.; Sandelin, K.; Wickman, M.; Olofsson, C. Analgesic efficacy of diclofenac in combination with morphine and paracetamol after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2005, 49, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslić Sersić, D.; Vuletić, G. Psychometric evaluation and establishing norms of Croatian SF-36 health survey: Framework for subjective health research. Croat. Med. J. 2006, 47, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- van der Windt, D.A.; van der Heijden, G.J.; de Winter, A.F.; Koes, B.W.; Devillé, W.; Bouter, L.M. The responsiveness of the Shoulder Disability Questionnaire. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Clarke, C.A.; Lichtensztajn, D.Y.; Hunt, K.K.; Giordano, S.H. Incorporating Tumor Characteristics to the American Joint Committee on Cancer Breast Cancer Staging System. Oncologist 2017, 22, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerkerk, C.D.A.; Chargi, N.; de Jong, P.A.; van den Bos, F.; de Bree, R. Sarcopenia measured with handgrip strength and skeletal muscle mass to assess frailty in older patients with head and neck cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2021, 12, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallet, J.; Tillman, B.; Zuckerman, J.; Guttman, M.P.; Chesney, T.; Mahar, A.L.; Chan, W.C.; Coburn, N.; Haas, B. Association Between Frailty and Time Alive and At Home After Cancer Surgery Among Older Adults: A Population-Based Analysis. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 1223–1232.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewertz, M.; Jensen, A.B. Late effects of breast cancer treatment and potentials for rehabilitation. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, U.G.; Mazzola, A.; Carotti, S.; Francesconi, M.; Catapano, S.; Magrì, F.; Perrone, G.; Morini, S.; De Salvatore, S.; Denaro, V. The role of estrogen and progesterone receptors in the rotator cuff disease: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.L.; Cartmel, B.; Gross, C.P.; Ercolano, E.; Li, F.; Yao, X.; Fiellin, M.; Capozza, S.; Rothbard, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Randomized exercise trial of aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia in breast cancer survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, H.; Easson, A. Age at diagnosis of breast cancer in Arab nations. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.K.; Li, J.; Huang, R.; Fan, J.H.; Zheng, R.S.; Zhang, B.N.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Z.H.; Xie, X.M.; Yang, H.J.; et al. Age of diagnosis of breast cancer in China: Almost 10 years earlier than in the United States and the European union. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 10021–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.; George, P.S.; Kunnambath, R.; Mathew, B.S.; Kumar, A.; Syampramod, R.; Booth, C.M. Educational Status, Cancer Stage, and Survival in South India: A Population-Based Study. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Sui, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, D.; Jiang, J. Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer following Breast Conservation Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3877984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joaquim, A.; Leão, I.; Antunes, P.; Capela, A.; Viamonte, S.; Alves, A.J.; Helguero, L.A.; Macedo, A. Impact of physical exercise programs in breast cancer survivors on health-related quality of life, physical fitness, and body composition: Evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 955505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, H.; Lauche, R.; Klose, P.; Lange, S.; Langhorst, J.; Dobos, G.J. Yoga for improving health-related quality of life, mental health and cancer-related symptoms in women diagnosed with breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1, Cd010802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.H.; Shu, X.O.; Ruan, Z.X.; Gao, Y.T.; Zheng, W. Association of overweight with breast cancer survival. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riondino, S.; Formica, V.; Valenzi, E.; Morelli, C.; Flaminio, V.; Portarena, I.; Torino, F.; Roselli, M. Obesity and Breast Cancer: Interaction or Interference with the Response to Therapy? Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano Dos Santos, F.L.; Michalek, I.M.; Wojciechowska, U.; Didkowska, J. Changes in the survival of patients with breast cancer: Poland, 2000-2019. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 197, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.E.; Akbari, A.; Khayamzadeh, M.; Salmanian, R.; Akbari, M. Ten-Year Survival of Breast Cancer in Iran: A National Study (Retrospective Cohort Study). Breast Care 2023, 18, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepp, K.P.; Björk, J.; Kontis, V.; Parks, R.M.; Bæk, K.T.; Emilsson, L.; Lallukka, T. Estimates of excess mortality for the five Nordic countries during the COVID-19 pandemic 2020–2021. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaubrun-Renard, M.M.; Veronique-Baudin, J.; Macni, J.; Ulric-Gervaise, S.; Almont, T.; Aline-Fardin, A.; Grossat, N.; Furtos, C.; Escarmant, P.; Vinh-Hung, V.; et al. Overall survival of triple negative breast cancer in French Caribbean women. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamaraux-Tran, T.-N.; Mathelin, C.; Aprahamian, M.; Joshi, G.P.; Tomasetto, C.; Diemunsch, P.; Akladios, C. Antitumor Effects of Lidocaine on Human Breast Cancer Cells: An In Vitro and In Vivo Experimental Trial. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Y.; Wang, P.; Fan, L. Bupivacaine inhibits the malignant biological behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting the activation of ERK1/2 and STAT3. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.; Crowley, P.D.; Foley, A.G.; Gallagher, H.C.; Iwasaki, M.; Ma, D.; Buggy, D.J. Effect of Perioperative Lidocaine, Propofol and Steroids on Pulmonary Metastasis in a Murine Model of Breast Cancer Surgery. Cancers 2019, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Chen, D.T.; Pan, J.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Xue, R.F.; Yuan, Y.F.; Zeng, W.A. Lidocaine Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses Tumor Growth in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and in a Xenograft Model In Vivo. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, W.; Guan, H.; Yan, N.; Cai, X.; Zhu, L. Local anesthetic bupivacaine inhibits proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Diclofenac (N = 41) | Levobupivacaine Bolus (N = 39) | Levobupivacaine PCA (N = 40) | P† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 57 (49.5–65.5) | 56 (52–65) | 55.5 (49.5–60.5) | 0.522 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 29 (23–31.4) | 27.8 (24.8–30.6) | 26 (22.7–30.8) | 0.639 |
| ASA status | 2 (2–2) | 2 (2–2) | 2 (2–2) | 0.716 |
| Hand grip strength (bar) | 0.38 (0.34–0.44) | 0.37 (0.31–0.44) | 0.40 (0.34–0.47) | 0.452 |
| Stage of disease | 4 (2–6) | 4 (2.5–4.5) | 4.5 (2.75–6.25) | 0.214 |
| Five-Year Survival Bivariate Regression Analysis | ß | Wald | P Value | HR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | 0.04 | 1.35 | 0.25 | 104 | 0.97 do 1.11 |
| BMI | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.88 do 1.11 |
| ASA | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 1.46 | 0.46 do 4.65 |
| Hand grip strength | −6.92 | 4.89 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.001 do 0.45 |
| Stage of disease | 0.28 | 2.62 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.94 do 1.86 |
| Groups (diclofenac *) | |||||
| Levobupivacaine bolus | −1.63 | 2.21 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.02 do 1.68 |
| Levobupivacaine PCA | −0.005 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.29 do 3.44 |
| Drugs (diclofenac *) | |||||
| Any levobupivacaine group | −0.52 | 0.75 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 0.18 do 1.94 |
| Multivariate regression analysis | |||||
| Hand grip strength | −8.964 | 5.81 | 0.02 | 0.0002 | 0 do 0.20 |
| Constant | 0.44 | 4.45 | 0.03 | 1.56 | 1.03 do 2.36 |
| Time from Surgery to Outcome | Diseases Stage at Diagnosis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median (IQR) | P * | n | Median (IQR) | P * | |
| Current status | ||||||
| Died | 23 | 60 (24–120) | <0.001 † | 23 | 5 (3–7) | 0.03 ‡ |
| Active disease, current treatment | 10 | 156 (155–168) (min 144–max 168) | 10 | 6 (4–7) | ||
| No signs of disease | 87 | 156 (156–168) (min 144–max 180) | 87 | 4 (2–5) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glavas Tahtler, J.; Djapic, D.; Neferanovic, M.; Miletic, J.; Milosevic, M.; Kralik, K.; Neskovic, N.; Tomas, I.; Mesaric, D.; Marjanovic, K.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Levobupivacaine Wound Infiltration or Diclofenac for Postoperative Pain Relief. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092183
Glavas Tahtler J, Djapic D, Neferanovic M, Miletic J, Milosevic M, Kralik K, Neskovic N, Tomas I, Mesaric D, Marjanovic K, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Levobupivacaine Wound Infiltration or Diclofenac for Postoperative Pain Relief. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(9):2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092183
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlavas Tahtler, Josipa, Dajana Djapic, Marina Neferanovic, Jelena Miletic, Marta Milosevic, Kristina Kralik, Nenad Neskovic, Ilijan Tomas, Dora Mesaric, Ksenija Marjanovic, and et al. 2023. "Long-Term Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Levobupivacaine Wound Infiltration or Diclofenac for Postoperative Pain Relief" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 9: 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092183
APA StyleGlavas Tahtler, J., Djapic, D., Neferanovic, M., Miletic, J., Milosevic, M., Kralik, K., Neskovic, N., Tomas, I., Mesaric, D., Marjanovic, K., Rajc, J., Orkic, Z., Cicvaric, A., & Kvolik, S. (2023). Long-Term Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Levobupivacaine Wound Infiltration or Diclofenac for Postoperative Pain Relief. Pharmaceutics, 15(9), 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092183






