Treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease Using Injectable Biomaterials and Drug-Coated Balloons: Safety and Efficacy Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
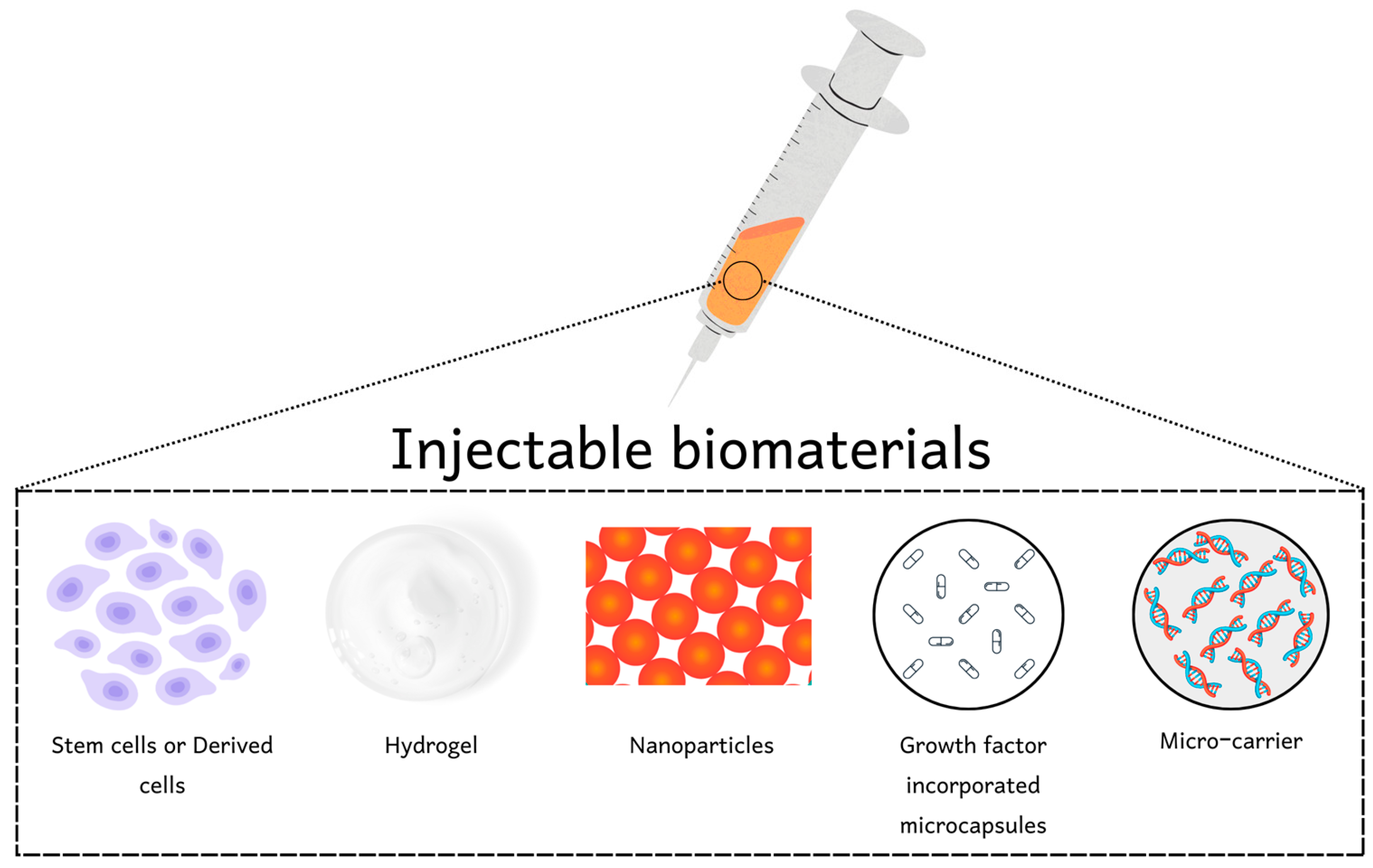
2. Injectable Biomaterials
3. Challenges in the Application of Injectable Biomaterials
4. Drug-Coated Balloon
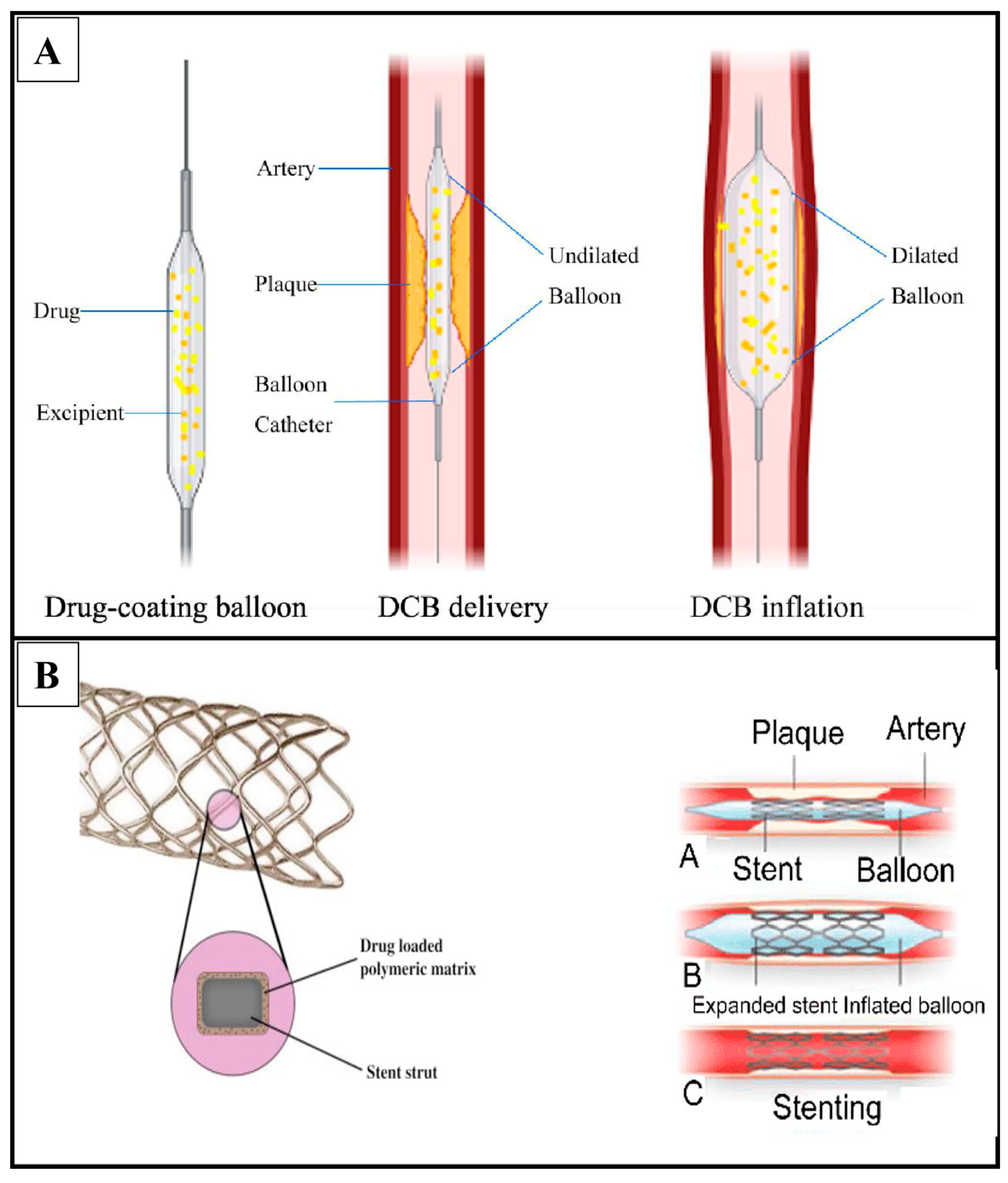
4.1. Types of Drug-Coated Balloon
4.1.1. Paclitaxel-Coated Balloons
- A.
- PaccocathTM
- B.
- NanoPac
- C.
- Pantera Lux
4.1.2. Limus-Coated Balloons
- A.
- MedAlliance SelutionTM Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon
- B.
- Magic Touch Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon
- C.
- Virtue Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon
| Type of DCB | Drug Excipient | Type of Study | Outcome | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paclitaxel-Coated Balloons | Paccocath TM | paclitaxel and iopromide | In vivo (pig coronary stent model) |
| [33] |
| Clinical trial (human) |
| [34] | |||
| Clinical trial (human) |
| [35] | |||
| NanoPac | paclitaxel on phospholipid nanocarrier | In vitro |
| [36] | |
| Pantera Lux | crystalline paclitaxel and butyryl-trihexyl citrate | In vivo (porcine arteries) and clinical trials (human) |
| [37,38,39,40] | |
| Limus-Coated Balloons | MedAlliance SelutionTM Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon | Sirolimus and poly (lactic-co-glycolic) microreservoir | In vivo (pig coronary stent model) |
| [43,44,45,46,47,48,49] |
| Magic Touch Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon | sirolimus and phospholipid nanocarrier | In vivo (white male rabbits and pigs) and clinical trial (humans) |
| [52,53,54] | |
| Virtue Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon | sirolimus packed in polyester-based polymers nanoparticle | In vivo (porcine arteries) and clinical trial (human) |
| [55] | |
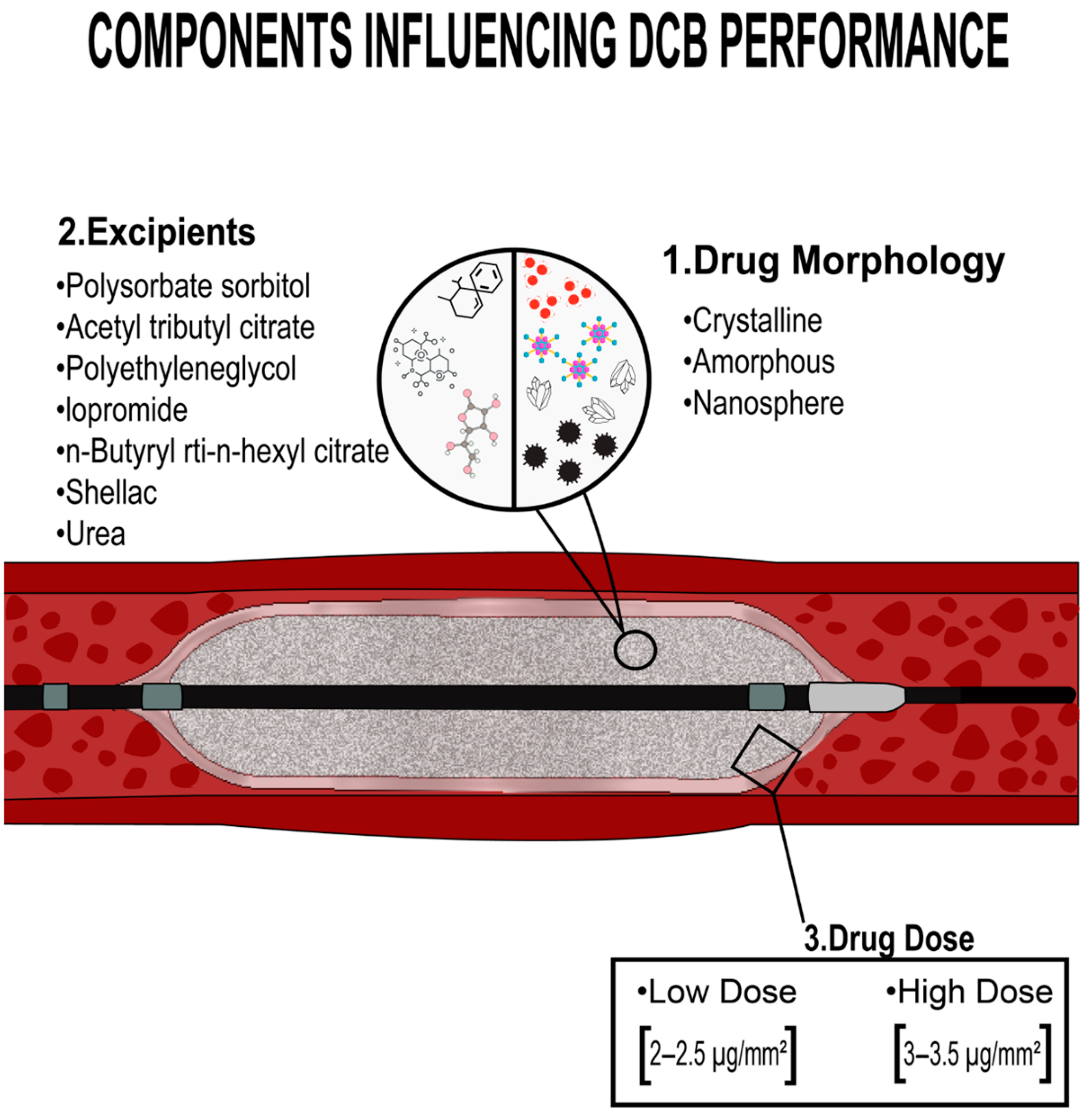
5. Challenges in the Application of Drug-Coated Balloons
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, X.; Su, X.; Zhang, W.; Yi, S.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xia, F. Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges of Troponin Analysis in the Early Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases. Anal. Chem. 2021, 94, 442–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullo, I.J.; Rooke, T.W. Peripheral artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglietto, A.; Manfredi, R.; Elia, E.; D’Ascenzo, F.; GM, D.F.; Munzel, T. Cardiovascular disease burden: Italian and global perspectives. Minerva Cardiol. Angiol. 2021, 69, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvoipati, T.; Kielhorn, C.E.; Armstrong, E.J. Peripheral artery disease in patients with diabetes: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and outcomes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Harper, Y.; Oliphant, C.S.; Morsy, M.; Skelton, M.; Askari, R.; Khouzam, R.N. Peripheral interventions and antiplatelet therapy: Role in current practice. World J. Cardiol. 2017, 9, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atturu, G.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Russell, D.A. Pharmacology in peripheral arterial disease: What the interventional radiologist needs to know. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 31, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Gao, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Mao, C.; Zhou, M.; Wan, M.; Shen, J. Platelet-derived nanomotor coated balloon for atherosclerosis combination therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5765–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gui, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. In Vitro evaluation of nanoparticle drug-coated balloons: A pectin-RGDS-OC8H17-paclitaxel solution. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Watanabe, S.; Bao, B.; Watanabe, H.; Nakatsuma, K.; Izuhara, M.; Ono, K.; Nakazawa, G.; Kimura, T.; Saito, N. Preclinical evaluation of a paclitaxel-incorporated nanoparticle-coated balloon in rabbit and porcine models. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2018, 19, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.C.; Liao, W.Y.; Tang, A.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Hsieh, P.C. The enhancement of endothelial cell therapy for angiogenesis in hindlimb ischemia using hyaluronan. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, W.; Ye, J.; Ji, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y. A cellular delivery system fabricated with autologous BMSCs and collagen scaffold enhances angiogenesis and perfusion in ischemic hind limb. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mima, Y.; Fukumoto, S.; Koyama, H.; Okada, M.; Tanaka, S.; Shoji, T.; Emoto, M.; Furuzono, T.; Nishizawa, Y.; Inaba, M. Enhancement of Cell-Based Therapeutic Angiogenesis Using a Novel Type of Injectable Scaffolds of Hydroxyapatite-Polymer Nanocomposite Microspheres. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marui, A.; Tabata, Y.; Kojima, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Tambara, K.; Nishina, T.; Saji, Y.; Inui, K.-i.; Hashida, T.; Yokoyama, S.; et al. A Novel Approach to Therapeutic Angiogenesis for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia by Sustained Release of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Using Biodegradable Gelatin Hydrogel. An Initial Report of the Phase I-IIa Study. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pan, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X. Preparation of gelatin microspheres encapsulated with bFGF for therapeutic angiogenesis in a canine ischemic hind limb. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2011, 22, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ren, F.; Yi, W.; Zhao, K.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; et al. Induction of Angiogenesis by Controlled Delivery of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Using Nanoparticles. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 31, e12–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, Y.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.H. Stem cell recruitment and angiogenesis of neuropeptide substance P coupled with self-assembling peptide nanofiber in a mouse hind limb ischemia model. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeQuach, J.A.; Lin, J.E.; Cam, C.; Hu, D.; Salvatore, M.A.; Sheikh, F.; Christman, K.L. Injectable skeletal muscle matrix hydrogel promotes neovascularization and muscle cell infiltration in a hindlimb ischemia model. Eur. Cell Mater. 2012, 23, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.L.; Gao, P.J.; Gu, Y.J.; Tang, X.F.; Liu, J.J.; Wei, J.; Inoue, K.; Zhu, D.L. Therapeutic angiogenesis by intramuscular injection of fibrin particles into ischaemic hindlimbs. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2006, 33, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, N.; Linke, A.; Süselbeck, T.; Müller-Ehmsen, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Schoors, D.; Rosenberg, M.; Bea, F.; Tuvia, S.; Leor, J. Intracoronary delivery of injectable bioabsorbable scaffold (IK-5001) to treat left ventricular remodeling after ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A first-in-man study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoneStar Heart. Safety and Feasibility of Algisyl-LVR as a Method of Left Ventricular Restoration in Patients with DCM Undergoing Open-Heart Surgery; LoneStar Heart: Irvine, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Classification of Products as Drugs and Devices and Additional Product Classification Issues, FDA-2011-D-0429; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017.
- Johnson, T.D.; Christman, K.L. Injectable hydrogel therapies and their delivery strategies for treating myocardial infarction. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axel, D.I.; Kunert, W.; Göggelmann, C.; Oberhoff, M.; Herdeg, C.; Küttner, A.; Wild, D.H.; Brehm, B.R.; Riessen, R.; Köveker, G. Paclitaxel inhibits arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration In Vitro and In Vivo using local drug delivery. Circulation 1997, 96, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, B.; Blanke, H.; Wolinsky, H. Influence of pressure on permeability of normal and diseased muscular arteries to horseradish peroxidase: A new catheter approach. Atherosclerosis 1987, 65, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangas, G.D.; Serruys, P.W.; Kereiakes, D.J.; Hermiller, J.; Rizvi, A.; Newman, W.; Sudhir, K.; Smith, R.S.; Cao, S.; Theodoropoulos, K. Meta-analysis of everolimus-eluting versus paclitaxel-eluting stents in coronary artery disease: Final 3-year results of the SPIRIT clinical trials program (Clinical Evaluation of the Xience V Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System in the Treatment of Patients With De Novo Native Coronary Artery Lesions). JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edelman, E.R.; Adams, D.H.; Karnovsky, M.J. Effect of controlled adventitial heparin delivery on smooth muscle cell proliferation following endothelial injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3773–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, B.; Speck, U.; Schmitt, A.; Clauss, W.; Sovak, M.; Böhm, M.; Stoll, H.-P. Acute cardiac tolerance of current contrast media and the new taxane protaxel using iopromide as carrier during porcine coronary angiography and stenting. Investig. Radiol. 2002, 37, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, B.; Speck, U.; Abramjuk, C.; Bernhardt, U.; Böhm, M.; Nickenig, G. Paclitaxel balloon coating, a novel method for prevention and therapy of restenosis. Circulation 2004, 110, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowinsky, E.K.; Donehower, R.C. Paclitaxel (taxol). N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; Kokaz, S.F.; Abed, S.N.; Paradkar, A.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 6—Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Polymers. In Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 203–267. [Google Scholar]
- Thangavel, P.; Muthukumar, S.; Karthekeyan, B.R.; Vakamudi, M.; Nayagam, H. Anaesthetic challenges in cardiac interventional procedures. World J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 4, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Feierkaiti, Y.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, X. The factors influencing the efficiency of drug-coated balloons. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 947776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; Bertoletti, A. Paclitaxel coated balloons for coronary artery interventions: A comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical data. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 161, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.; Schnorr, B.; Kutschera, M.; Waliszewski, M.W. Two-Year Mortality After Angioplasty of the Femoro-Popliteal Artery with Uncoated Balloons and Paclitaxel-Coated Balloons—A Pooled Analysis of Four Randomized Controlled Multicenter Trials. CardioVascular Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, K.; Schwefer, M.; Yusof, A.K.M.; Waliszewski, M.; Krackhardt, F.; Steen, P.; Ocaranza, R.; Zuhdi, A.S.; Bang, L.H.; Graf, K.; et al. Systematic Scoring Balloon Lesion Preparation for Drug-Coated Balloon Angioplasty in Clinical Routine: Results of the PASSWORD Observational Study. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 2210–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Shibuya, M.; McGregor, J.; Conditt, G.B.; Yi, G.-H.; Kaluza, G.L.; Gray, W.; Doshi, M.; Sojitra, P.; Granada, J.F. Biological effect on restenosis and vascular healing of encapsulated paclitaxel nanocrystals delivered via coated balloon technology in the familial hypercholesterolaemic swine model of in-stent restenosis. EuroIntervention 2016, 12, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, P.W.; Joner, M.; Joost, A.; Byrne, R.A.; Hartwig, S.; Bayer, G.; Steigerwald, K.; Wittchow, E. Vascular effects of paclitaxel following drug-eluting balloon angioplasty in a porcine coronary model: The importance of excipients. EuroIntervention 2011, 7, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, T.; Cassese, S.; Xhepa, E.; Mayer, K.; Tölg, R.; Hoppmann, P.; Laugwitz, K.-L.; Byrne, R.A.; Kastrati, A.; Kufner, S. Efficacy of drug-coated balloon angioplasty in early versus late occurring drug-eluting stent restenosis: A pooled analysis from the randomized ISAR DESIRE 3 and DESIRE 4 trials. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 96, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cho, Y.K.; Kim, S.W.; Hong, Y.J.; Koo, B.K.; Bae, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, T.H.; Park, H.S.; Choi, S.W.; et al. Clinical Results of Drug-Coated Balloon Treatment in a Large-Scale Multicenter Korean Registry Study. Korean Circ. J. 2022, 52, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthley, S.; Hendriks, R.; Worthley, M.; Whelan, A.; Walters, D.L.; Whitbourn, R.; Meredith, I. Paclitaxel-eluting balloon and everolimus-eluting stent for provisional stenting of coronary bifurcations: 12-month results of the multicenter BIOLUX-I study. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2015, 16, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assadi-Schmidt, A.; Mohring, A.; Liebsch, E.; Dannenberg, L.; Achilles, A.; Pöhl, M.; Afzal, S.; Veulemans, V.; Horn, P.; Sansone, R.; et al. SeQuent Please vs. Pantera Lux drug coated balloon angioplasty in real life: Results from the Düsseldorf DCB registry. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 231, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersin, R. Update on sirolimus coated balloon technologies. Cardiovasc. Res. Technol. (CRT 17) Wash. DC 2017, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding, C.; Krackhardt, F.; Bogaerts, K.; Urban, P.; Meis, S.; Morice, M.-C.; Eccleshall, S. Comparing a strategy of sirolimus-eluting balloon treatment to drug-eluting stent implantation in de novo coronary lesions in all-comers: Design and rationale of the SELUTION DeNovo Trial. Am. Heart J. 2023, 258, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.Y.; Chong, T.-T.; Yap, C.J.Q.; Soon, S.X.Y.; Chan, S.L.; Tan, R.Y.; Yap, H.Y.; Tay, H.T.u.; Tan, C.-S.; Barnhill, S.; et al. Intervention with selution SLRTM Agent Balloon for Endovascular Latent Limus therapy for failing AV Fistulas (ISABELLA) Trial: Protocol for a pilot clinical study and pre-clinical results. J. Vasc. Access 2023, 24, 11297298211020867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bong, T.S.; Yap, C.J.; Soon, S.X.; Tang, T.Y. Combination therapy using scoring and sirolimus drug-coated balloons during lower limb endovascular revascularization for chronic limb threatening ischaemia: A case series. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2022, 10, 2050313X221085859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, T.; Brechtel, K.; Meyer, D.-R.; Noory, E.; Beschorner, U.; Albrecht, T. Six-Month Outcomes From the First-in-Human, Single-Arm SELUTION Sustained-Limus-Release Drug-Eluting Balloon Trial in Femoropopliteal Lesions. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2020, 27, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.Y.; Soon, S.X.; Yap, C.J.; Tan, R.Y.; Pang, S.C.; Patel, A.; Gogna, A.; Tan, C.S.; Chong, T.T. Endovascular salvage of failing arterio-venous fistulas utilising sirolimus eluting balloons: Six months results from the ISABELLA trial. J. Vasc. Access 2021, 11297298211067059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.Y.; Yap, C.J.Q.; Soon, S.X.Y.; Tan, R.Y.; Pang, S.C.; Patel, A.; Gogna, A.; Tan, C.S.; Chong, T.T. Utility of the selution SLRTM sirolimus eluting balloon to rescue failing arterio-venous fistulas—12 month results of the ISABELLA Registry from Singapore. CVIR Endovasc. 2022, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.Y.; Yap, C.; Soon, S.X.Y.; Chan, S.L.; Lee, Q.S.; Yap, H.Y.; Tay, H.T.u.L.; Chong, T.T. World’s First Experience Treating TASC II C and D Tibial Occlusive Disease Using the Selution SLR Sirolimus-Eluting Balloon: Six-Month Results from the PRESTIGE Study. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2021, 28, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.Y.; Yap, C.J.Q.; Soon, S.X.Y.; Chan, S.L.; Khoo, V.B.X.; Chong, T.T. 12-Months Results From the PRESTIGE Study Using Sirolimus Drug-Eluting Balloons in the Treatment of Complex BTK Tibial Atherosclerotic Lesions in CLTI Patients. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2022, 43, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, P.A.; Farooq, V.; Takimura, C.K.; Gutierrez, P.S.; Virmani, R.; Kolodgie, F.; Christians, U.; Kharlamov, A.; Doshi, M.; Sojitra, P. Emerging technologies: Polymer-free phospholipid encapsulated sirolimus nanocarriers for the controlled release of drug from a stent-plus-balloon or a stand-alone balloon catheter. EuroIntervention 2013, 9, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takimura, C.K.; Galon, M.Z.; Sojitra, P.; Doshi, M.; Aiello, V.; Gutierrez, P.S.; Carvalho, J.; Ferreira, S.K.; Chaves, M.J.F.; Laurindo, F.R.M. Excipient: Drug dose determination for neointimal hyperplasia as assessed by optical coherence tomography and histopathology in porcine coronary arteries after sirolimus-eluting balloon employment. Rev. Bras. Cardiol. Invasiva (Engl. Ed.) 2012, 20, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Dani, S.; Shah, D.; Sojitra, P.; Parikh, K.; Shetty, R.; di Palma, G.; Cortese, B. A novel nanocarrier sirolimus-coated balloon for coronary interventions: 12-Month data from the Nanoluté Registry. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2019, 20, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, G.; De Michele, M.; Golino, L.; Manganiello, V.; Fattore, L. Sirolimus-Eluting balloon for the treatment of coronary lesions in complex ACS patients: The SELFIE registry. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2020, 2020, 8865223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheye, S.; Vrolix, M.; Kumsars, I.; Erglis, A.; Sondore, D.; Agostoni, P.; Cornelis, K.; Janssens, L.; Maeng, M.; Slagboom, T. The SABRE Trial (Sirolimus Angioplasty Balloon for Coronary In-Stent Restenosis) Angiographic Results and 1-Year Clinical Outcomes. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 10, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalta, K.; Yetkın, E.; Yalta, T. Harnessing drug-coated balloons for the management of left main coronary disease: A promising strategy? Kardiol. Pol. (Pol. Heart J.) 2022, 80, 717–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda-Zuniga, W.; Formanek, A.; Tadavarthy, M.; Vlodaver, Z.; Edwards, J.; Zollikofer, C.; Amplatz, K. The mechanism of balloon angioplasty. Radiology 1980, 135, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.W.; Roubin, G.; King, S., 3rd. Restenosis after coronary angioplasty. Potential biologic determinants and role of intimal hyperplasia. Circulation 1989, 79, 1374–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faxon, D.P.; Sanborn, T.A.; Haudenschild, C.C. Mechanism of angioplasty and its relation to restenosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 60, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, G.; Zeller, T.; Schnorr, B.; Claussen, C.D.; Beschorner, U.; Brechtel, K.; Scheller, B.; Speck, U. High-grade, non-flow-limiting dissections do not negatively impact long-term outcome after paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty: An additional analysis from the THUNDER study. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2013, 20, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, M.; Burzotta, F.; Srdanovic, I.; Petrovic, M.; Trani, C. Percutaneous coronary intervention to treat unprotected left main: Common (un-answered) challenges. Kardiol. Pol. (Pol. Heart J.) 2022, 80, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdoğan, E.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Tufaro, V.; Feng, S.-L.; Li, Q.; Liang, L.; Chang, S.; Bu, L.-T.; Liu, B. DCB combined with provisional DES implantation in the treatment of De Novo Medina 0, 1, 0 or 0, 0, 1 left main coronary bifurcation lesions: A proof-of-concept study. Anatol. J. Cardiol./Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 2022, 26, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Material for Biomaterial Formation | Cell Line Used for Biomaterial Formation | Test Environment | Conclusion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hyaluronan | human umbilical vein endothelial cells | in vitro (cell lines) in vivo (nude mouse model) |
| [10] |
| collagen scaffold | bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells | in vivo (hindlimb ischemic rabbit model) |
| [11] |
| NPs system with synthetic hydroxyapatite | bone marrow mononuclear cells | in vivo (ischemic limb murine model) |
| [12] |
| bFGF-incorporated gelatin hydrogel microspheres | clinical trial |
| [13] | |
| bFGF-incorporated glutaraldehyde-cross-linked gelatin microspheres | in vivo (canine ischemic hind limb) |
| [14] | |
| VEGF-incorporated dextran-co-gelatin NPs | in vivo (ischemic rabbit model) |
| [15] | |
| neuropeptide substance P-coupled with peptide nanofiber | in vivo (mouse hind limb ischemia model) |
| [16] | |
| hydrogel from decellularized skeletal muscle extracellular matrix | in vivo (ischemic hindlimb rat model) |
| [17] | |
| fibrin particles | in vivo (hindlimb ischemic rabbit model) |
| [18] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qamar, S.U.R.; Spahić, L.; Benolić, L.; Zivanovic, M.; Filipović, N. Treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease Using Injectable Biomaterials and Drug-Coated Balloons: Safety and Efficacy Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071813
Qamar SUR, Spahić L, Benolić L, Zivanovic M, Filipović N. Treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease Using Injectable Biomaterials and Drug-Coated Balloons: Safety and Efficacy Perspective. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071813
Chicago/Turabian StyleQamar, Safi Ur Rehman, Lemana Spahić, Leo Benolić, Marko Zivanovic, and Nenad Filipović. 2023. "Treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease Using Injectable Biomaterials and Drug-Coated Balloons: Safety and Efficacy Perspective" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071813
APA StyleQamar, S. U. R., Spahić, L., Benolić, L., Zivanovic, M., & Filipović, N. (2023). Treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease Using Injectable Biomaterials and Drug-Coated Balloons: Safety and Efficacy Perspective. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071813









