Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Pure Substances
2.2.2. Physical Mixtures
2.2.3. smartFilms Loaded with Norfloxacin
2.2.4. Granulation of Norfloxacin-Loaded smartFilms
2.2.5. Production of Tablets
2.3. Solid-State Characterization
2.3.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction
2.3.2. Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy
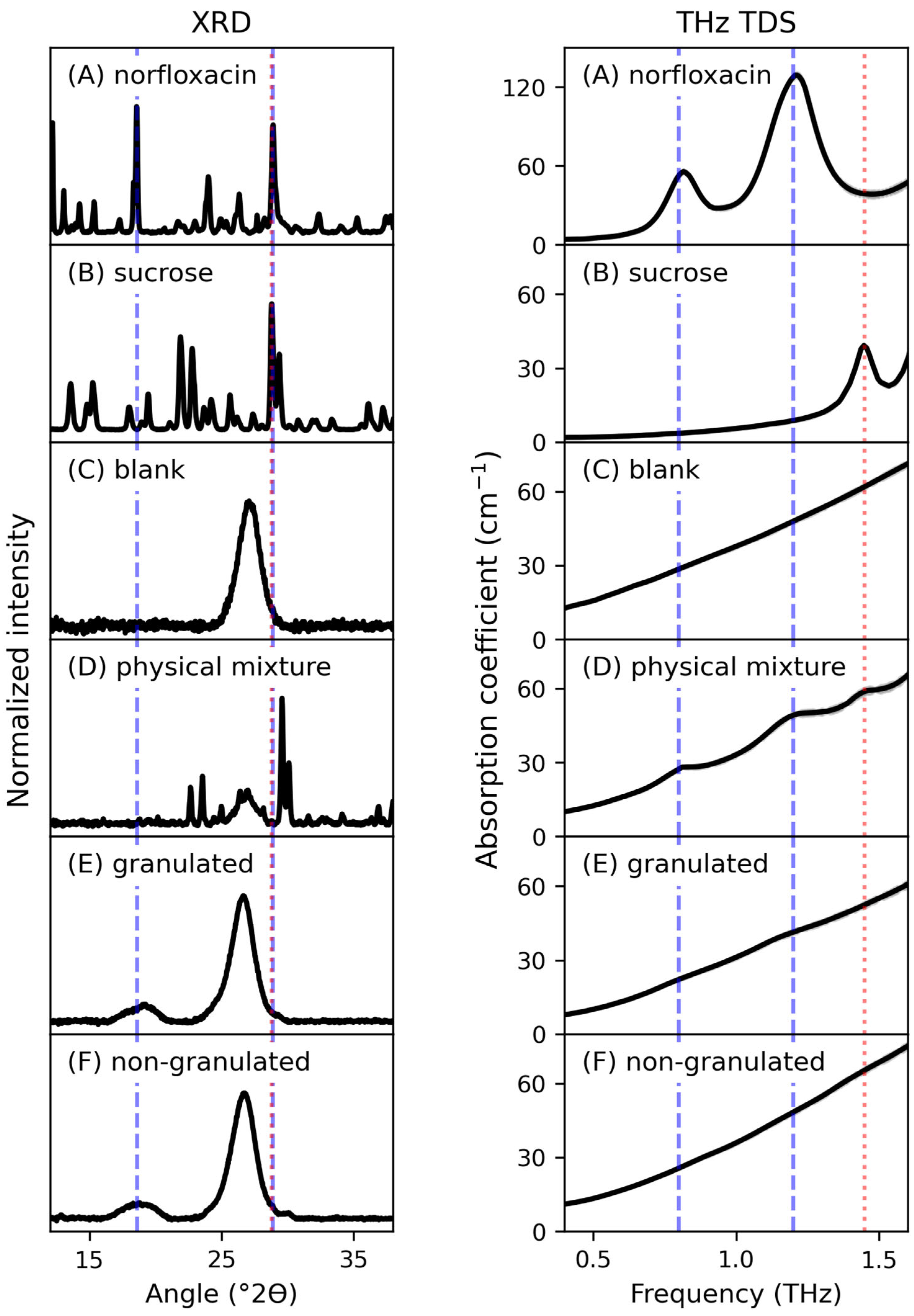
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sastry, S.V.; Nyshadham, J.R.; Fix, J.A. Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery—A review. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug solubility: Importance and enhancement techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, F.L.O.; Marques, M.B.D.F.; Kato, K.C.; Carneiro, G. Nanonization techniques to overcome poor water-solubility with drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, B.J.; Bergström, C.A.S.; Vinarov, Z.; Kuentz, M.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P.; Brandl, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; et al. Successful oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs both depends on the intraluminal behavior of drugs and of appropriate advanced drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, H.A.; Allam, A.; Elsabahy, M.; Fetih, G.; El-Badry, M. Nanostructured lipid carriers for improved oral delivery and prolonged antihyperlipidemic effect of simvastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, S.; Strätling, E.-J.; Hans-Peter; Keck, C.M. Cellulose fibre based support matrices for layered products for oral and peroral application and their preparation. European Patent Office EP3192499A1, 14 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, B.C.; Parks, M. What is the true solubility advantage for amorphous pharmaceuticals? Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornik, J.; Knoth, D.; Koch, M.; Keck, C.M. Terahertz-spectroscopy for non-destructive determination of crystallinity of L-tartaric acid in smartFilms® and tablets made from paper. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, F.; Keck, C.M. Tablets made from paper. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyeswari, C.D.; Prasanth, Y.; Sameeda, R. Formulation and development of efavirenz tablets by paper technique using co-solvency method. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2019, 11, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornik, J.; Heidrich, L.; Schesny, R.; Castro-Camus, E.; Keck, C.M.; Koch, M. Non-destructive crystallinity assessment of indomethacin in tablets made from smartFilms® using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.; Moos, C.; Pelloux, A.; Pfeiffer, M.; Alter, C.; Kolling, S.; Keck, C.M. Tablets made from paper—An industrially feasible approach. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.; Nallbati, L.; Keck, C.M. Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, F. Tablets Made from Paper for Oral Administration of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Ph.D. Thesis, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Marburg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, N.F.; Daniels, R.; Fernandes, A.I.; Pinto, J.F. Amorphous and Co-Amorphous Olanzapine Stability in Formulations Intended for Wet Granulation and Pelletization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, D.; Karan, K.; Gajera, B.Y.; Dave, R.H. Investigate the effect of solvents on wet granulation of microcrystalline cellulose using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as a binder and evaluation of rheological and thermal characteristics of granules. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdešič, P.; Sovány, T.; German Ilić, I. High-shear granulation of high-molecular weight hypromellose: Effects of scale-up and process parameters on flow and compaction properties. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. Solid Form and Phase Transformation Properties of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride during Wet Granulation Process. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.A.; Zografi, G.; Gao, P.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Modeling Physical Stability of Amorphous Solids Based on Temperature and Moisture Stresses. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, L. Practical guidelines for the characterization and quality control of pure drug nanoparticles and nano-cocrystals in the pharmaceutical industry. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 131, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitler, J.A.; Taday, P.F.; Newnham, D.A.; Pepper, M.; Gordon, K.C.; Rades, T. Terahertz pulsed spectroscopy and imaging in the pharmaceutical setting—A review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, J.C.; Saraceno, C.J.; Koch, M.; Kaurav, P.; Pfeiffer, U.R.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Kurner, T.; Stohr, A.; El-Absi, M.; Abbas, A.A.-H.; et al. THz Systems Exploiting Photonics and Communications Technologies. IEEE J. Microw. 2023, 3, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Cardoso, G.G.; Rojas-Landeros, S.C.; Alfaro-Gomez, M.; Hernandez-Serrano, A.I.; Salas-Gutierrez, I.; Lemus-Bedolla, E.; Castillo-Guzman, A.R.; Lopez-Lemus, H.L.; Castro-Camus, E. Terahertz imaging for early screening of diabetic foot syndrome: A proof of concept. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittleman, D.M. Perspective: Terahertz science and technology. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 230901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.V.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Forysenkova, A.A.; Davydova, G.A.; Fosca, M.; Filippov, Y.Y.; Antoniac, I.V.; Antoniac, A.; D’Arco, A.; Di Fabrizio, M.; et al. Strontium Substituted Tricalcium Phosphate Bone Cement: Short and Long-Term Time-Resolved Studies and In Vitro Properties. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitenstorfer, A.; Moskalenko, A.S.; Kampfrath, T.; Kono, J.; Castro-Camus, E.; Peng, K.; Qureshi, N.; Turchinovich, D.; Tanaka, K.; Markelz, A.; et al. The 2023 Terahertz Science and Technology Roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 223001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.U.; Cooke, D.G.; Koch, M. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging—Modern techniques and applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 5, 124–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Ostmann, T.; Wilk, R.; Rutz, F.; Koch, M.; Niemann, H.; Güttler, B.; Brandhorst, K.; Grunenberg, J. Probing noncovalent interactions in biomolecular crystals with terahertz spectroscopy. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, M.; Fischer, B.M.; Uhd Jepsen, P. Noncovalent intermolecular forces in polycrystalline and amorphous saccharides in the far infrared. Chem. Phys. 2003, 288, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, C.J.; Rades, T.; Newnham, D.A.; Gordon, K.C.; Pepper, M.; Taday, P.F. Using terahertz pulsed spectroscopy to study crystallinity of pharmaceutical materials. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 390, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibik, J.; Zeitler, J.A. Direct measurement of molecular mobility and crystallisation of amorphous pharmaceuticals using terahertz spectroscopy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Gebauer, D.; Duschek, L.; Fischer, B.M.; Cölfen, H.; Koch, M. Crystallization Caught in the Act with Terahertz Spectroscopy: Non-Classical Pathway for l-(+)-Tartaric Acid. Chemistry 2017, 23, 14128–14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajito, K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ueno, Y.; Song, H.-J.; Ueda, K.; Limwikrant, W.; Yamamoto, K.; Moribe, K. Nondestructive Multicomponent Terahertz Chemical Imaging of Medicine in Tablets. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B171–B175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, C.J.; Taday, P.F.; Newnham, D.A.; Gordon, K.C.; Zeitler, J.A.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T. Using terahertz pulsed spectroscopy to quantify pharmaceutical polymorphism and crystallinity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, X.; Ochani, A.; Shen, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ruggiero, M.T. Low-frequency vibrational spectroscopy: A new tool for revealing crystalline magnetic structures in iron phosphate crystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 22241–22245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santitewagun, S.; Thakkar, R.; Zeitler, J.A.; Maniruzzaman, M. Detecting Crystallinity Using Terahertz Spectroscopy in 3D Printed Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2380–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuel, C. Norfloxacin. Anal. Profiles Drug Subst. 1991, 20, 557–600. [Google Scholar]
- Breda, S.A.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F.; Manzo, R.H.; Olivera, M.E. Solubility behavior and biopharmaceutical classification of novel high-solubility ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin pharmaceutical derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieweg, N.; Rettich, F.; Deninger, A.; Roehle, H.; Dietz, R.; Göbel, T.; Schell, M. Terahertz-time domain spectrometer with 90 dB peak dynamic range. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Mittleman, D.M.; Ornik, J.; Castro-Camus, E. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Menlo Systems GmbH. TeraLyzer Terahertz Software. Available online: https://www.menlosystems.com/products/thz-time-domain-solutions/teralyzer-single/ (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Pupeza, I.; Wilk, R.; Koch, M. Highly accurate optical material parameter determination with THz time-domain spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 4335–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, M.; Jansen, C.; Koch, M. Analyzing sub-100-μm samples with transmission terahertz time domain spectroscopy. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahvenainen, P.; Kontro, I.; Svedström, K. Comparison of sample crystallinity determination methods by X-ray diffraction for challenging cellulose I materials. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, B.H.; Li, D.Y.; Hunter, B.A. The importance of the specimen displacement correction in Rietveld pattern fitting with symmetric reflection-optics diffraction data. Adv. X-Ray Anal. 2001, 44, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-K.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, T.; Son, J.-H.; Park, Q.-H.; Seo, M. Highly sensitive and selective sugar detection by terahertz nano-antennas. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, L.; Ornik, J.; Keck, C.M.; Castro-Camus, E.; Koch, M. Polyvinylpyrrolidone as co-inhibitor of crystallization of nifedipine in paper tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisazumi, J.; Suzuki, T.; Nakagami, H.; Terada, K. Quantification of pharmaceutical polymorphs and prediction of dissolution rate using theophylline tablet by terahertz spectroscopy. Chem. Pharm. Bull. Tokyo 2011, 59, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Reyes, E.S.; Carriles-Jaimes, R.; Castro-Camus, E. Algorithm for Determination of Cutoff Frequency of Noise Floor Level for Terahertz Time-Domain Signals. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2022, 43, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, C.-Y.; Richter, C. Sample Thickness Measurement with THz-TDS: Resolution and Implications. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 840–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: ICH Topic Q 2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Step 5: Note for Guidance on Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology (CPMP/ICH/381/95). Validation of Analytical Procedures: Definitions and Methodology, London. 2006. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Lee, S.L.; O’Connor, T.F.; Yang, X.; Cruz, C.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Madurawe, R.D.; Moore, C.M.V.; Yu, L.X.; Woodcock, J. Modernizing Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: From Batch to Continuous Production. J. Pharm. Innov. 2015, 10, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Authelin, J.-R.; Leveder, C.; Segalini, A. A practical method to predict physical stability of amorphous solid dispersions. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2792–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmkemper, K.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Heinzerling, O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Impact of Polymer Type and Relative Humidity on the Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4374–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.; Zografi, G. What We Need to Know about Solid-State Isothermal Crystallization of Organic Molecules from the Amorphous State below the Glass Transition Temperature. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1761–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, E.P.J.; Zeitler, J.A.; Friščić, T.; Pepper, M.; Jones, W.; Day, G.M.; Gladden, L.F. Testing the Sensitivity of Terahertz Spectroscopy to Changes in Molecular and Supramolecular Structure: A Study of Structurally Similar Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
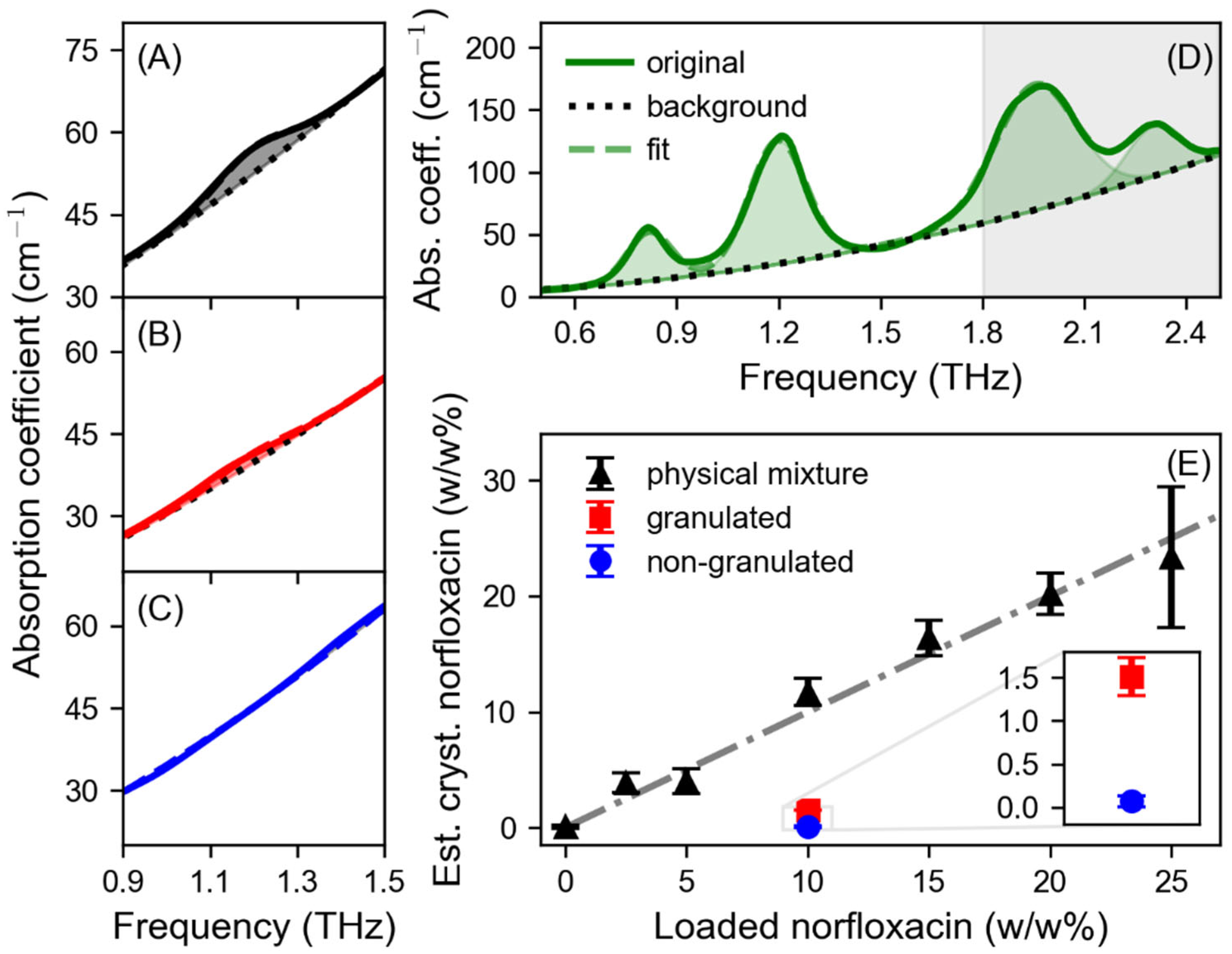

| Peak | G (cm−1) | v0 (THz) | Δv (THz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.32 | 0.82 | 0.06 |
| 2 | 99.11 | 1.20 | 0.08 |
| 3 | 100.56 | 1.96 | 0.12 |
| 4 | 40.00 | 2.30 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heidrich, L.; Abdelkader, A.; Ornik, J.; Castro-Camus, E.; Keck, C.M.; Koch, M. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786
Heidrich L, Abdelkader A, Ornik J, Castro-Camus E, Keck CM, Koch M. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeidrich, Lara, Ayat Abdelkader, Jan Ornik, Enrique Castro-Camus, Cornelia M. Keck, and Martin Koch. 2023. "Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786
APA StyleHeidrich, L., Abdelkader, A., Ornik, J., Castro-Camus, E., Keck, C. M., & Koch, M. (2023). Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786






