Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based High-Performance Positive and Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
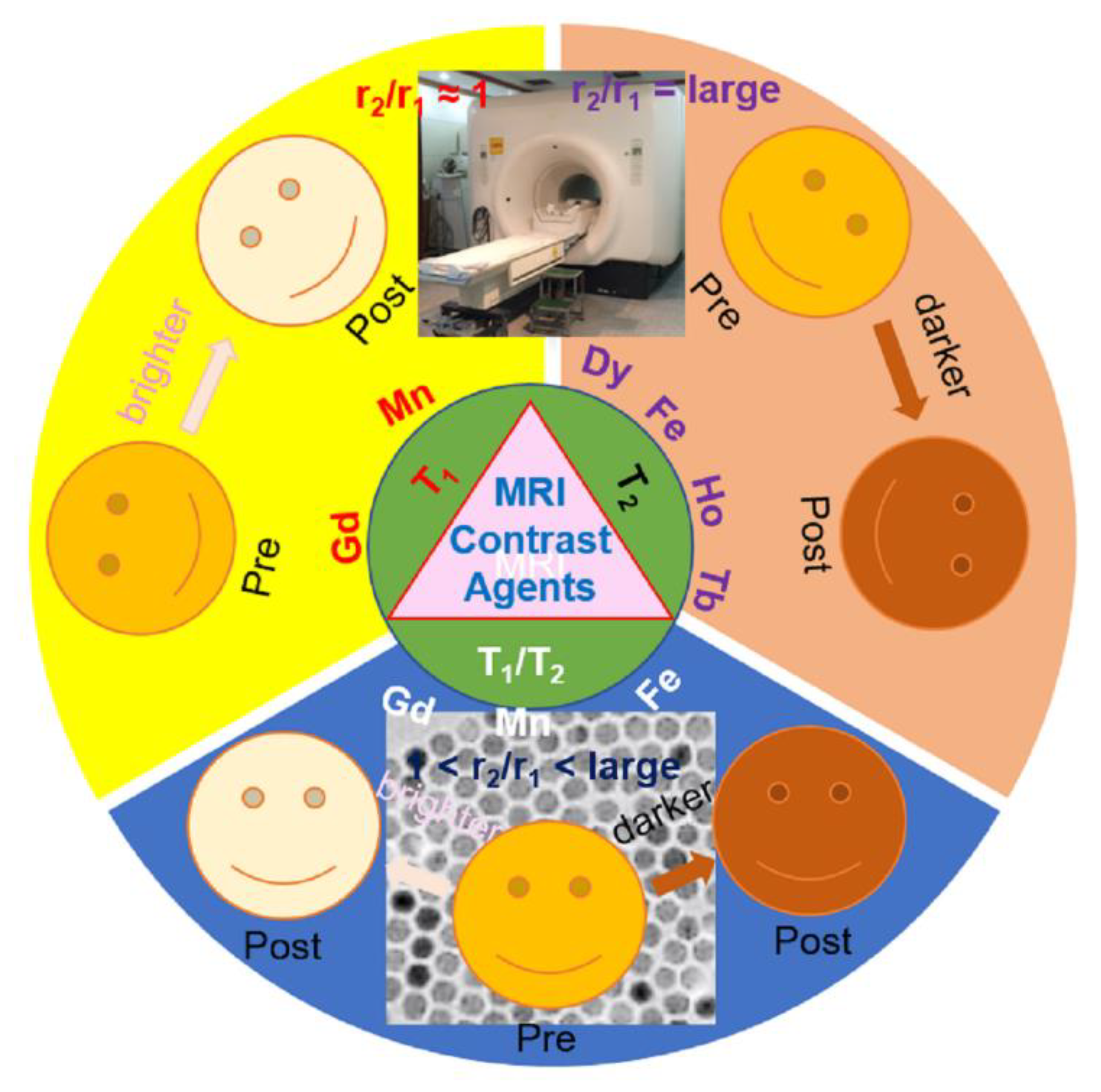
2. The Principle of Imaging Mode (T1 or T2 or Both)
2.1. T1 Imaging Mode
2.2. T2 Imaging Mode
2.3. T1 and T2 Dual-Imaging Mode
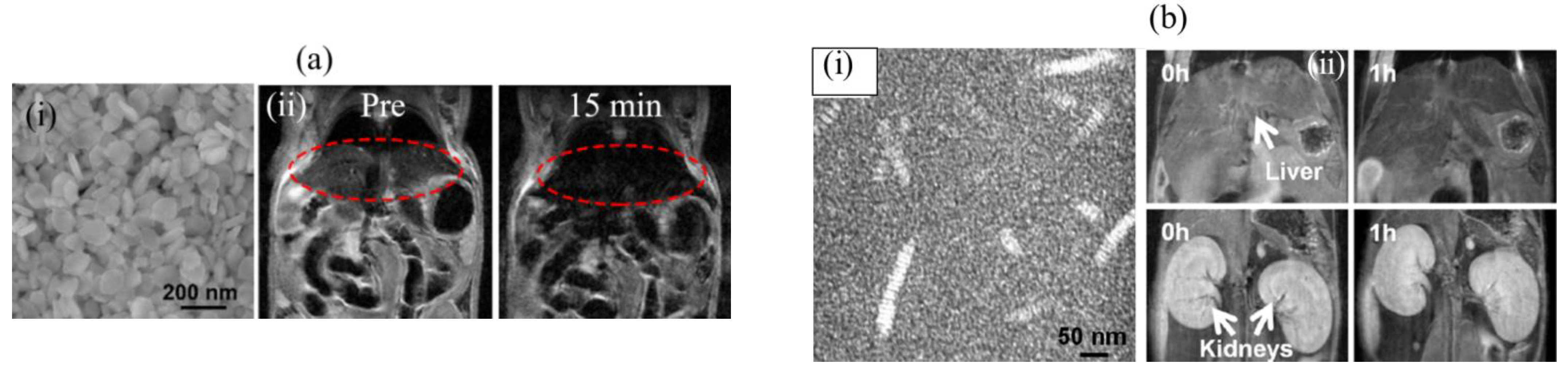
3. Examples of MNP-Based MRI Contrast Agents
3.1. T1 MRI Contrast Agents
3.1.1. Gd-Based NPs

3.1.2. Mn-Based NPs
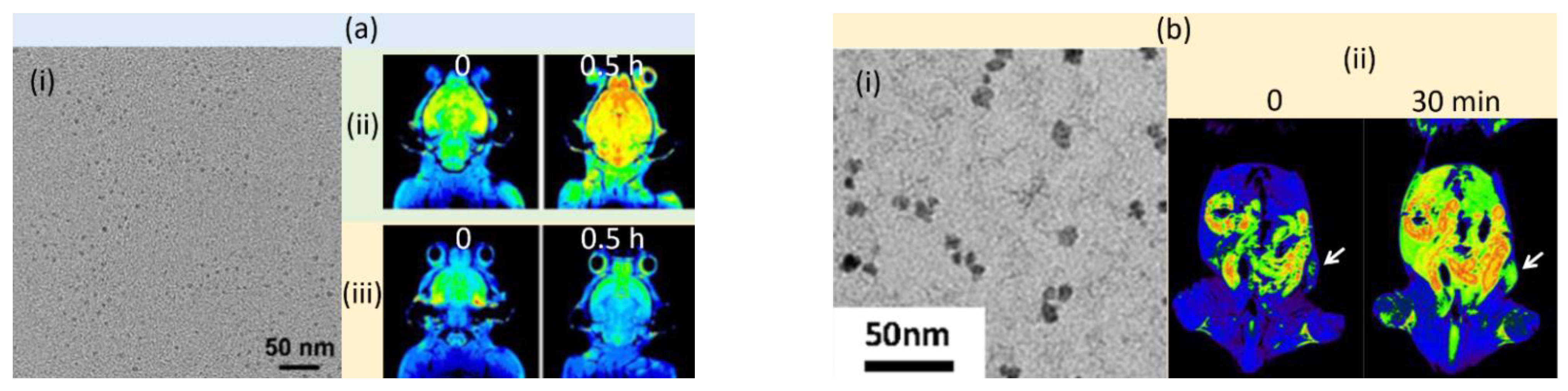
3.2. T2 MRI Contrast Agents
3.2.1. Fe-Based NPs
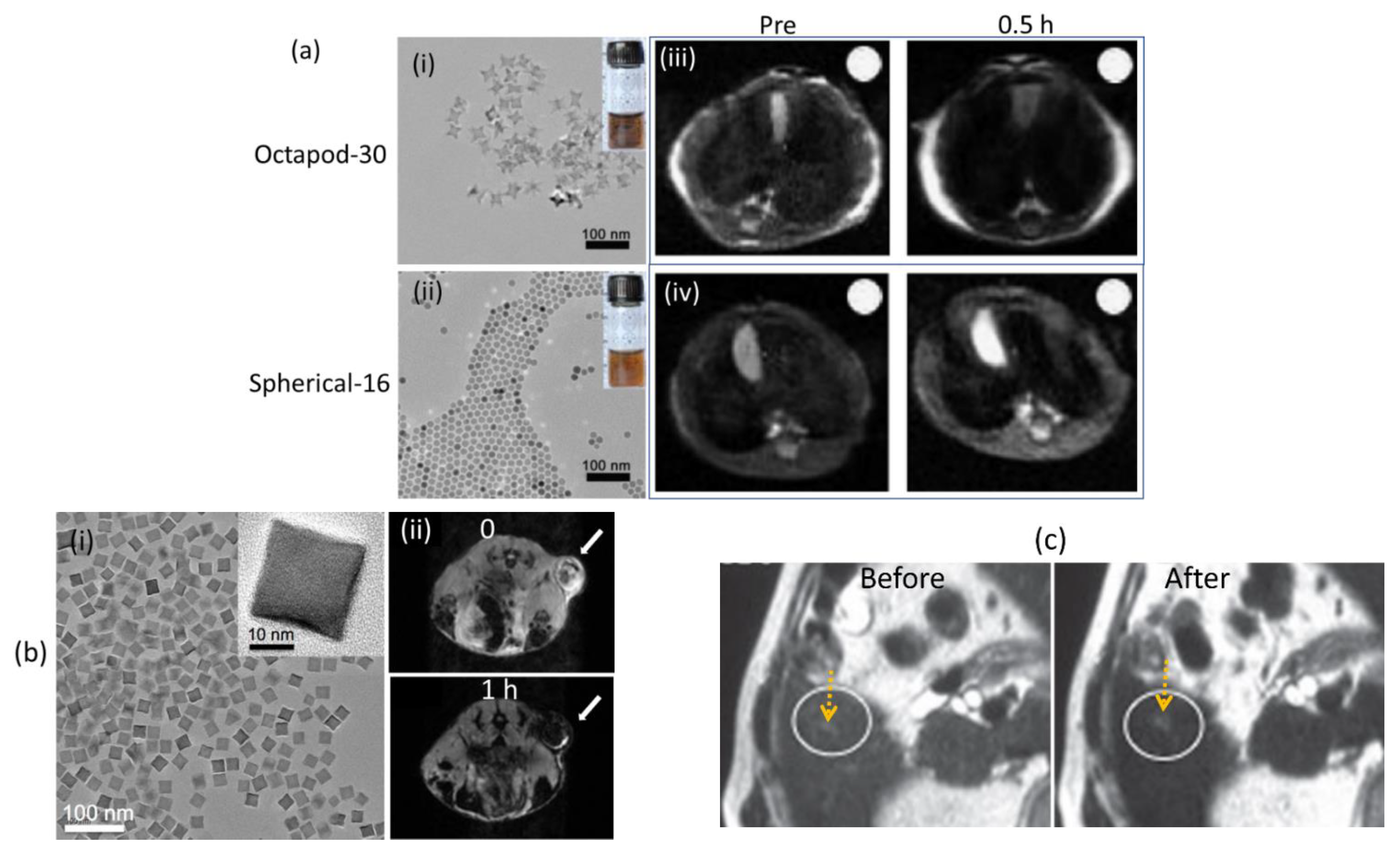
3.2.2. Dy-Based NPs

3.2.3. Ho-Based NPs
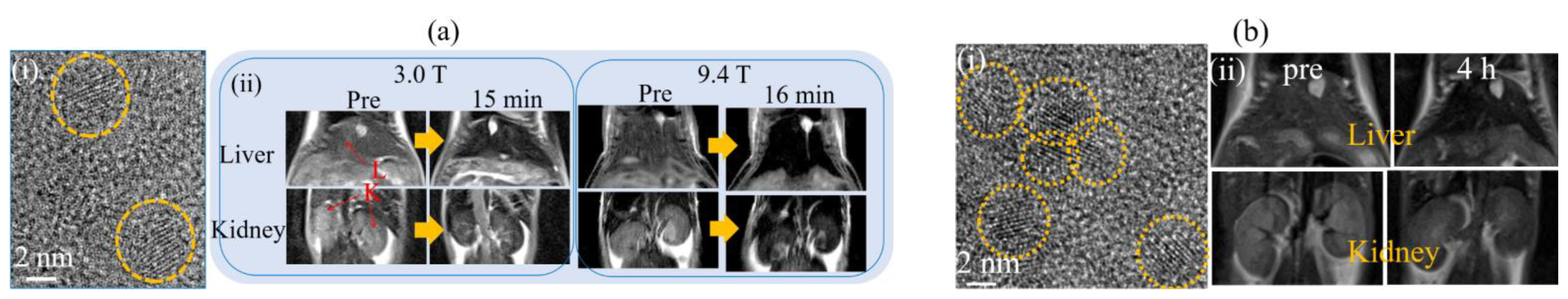
3.2.4. Tb-Based NPs
3.3. T1 and T2 Dual-Modal MNPs
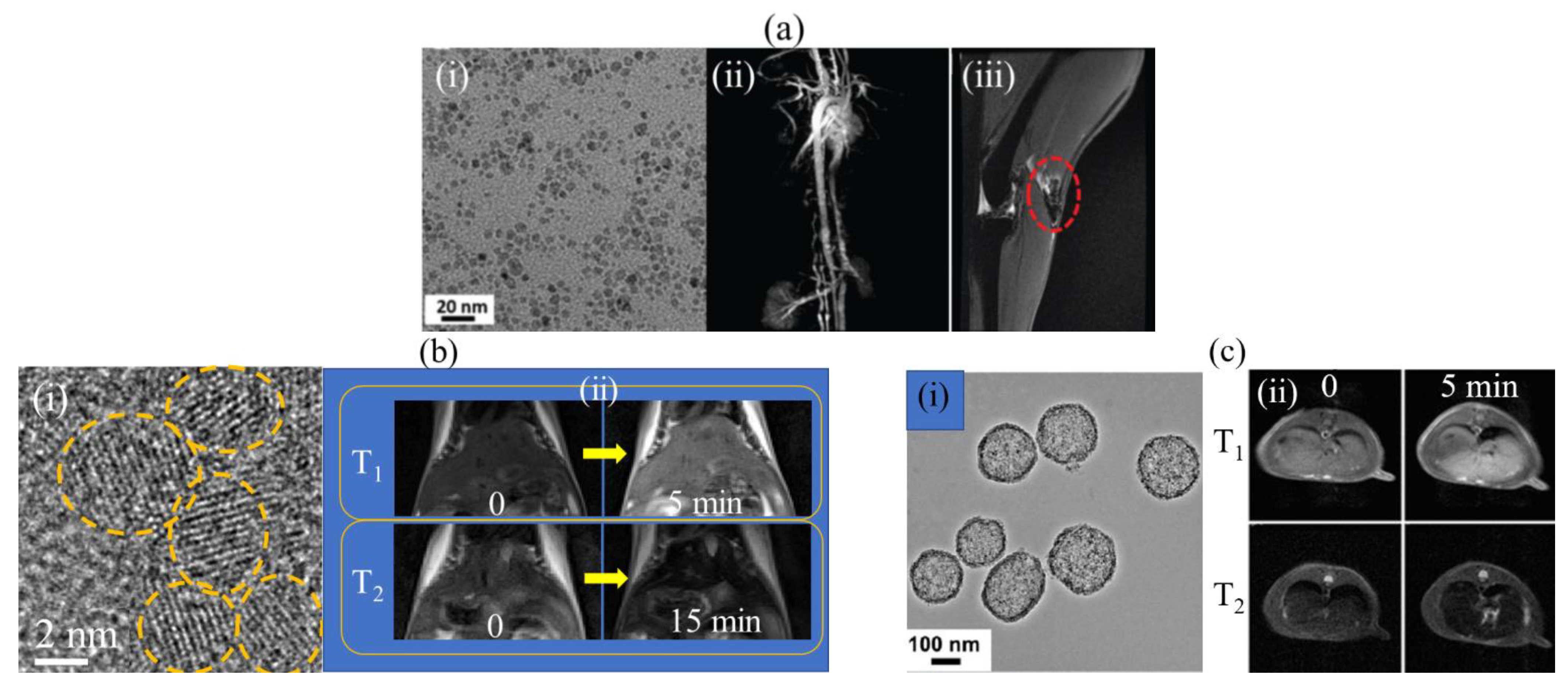
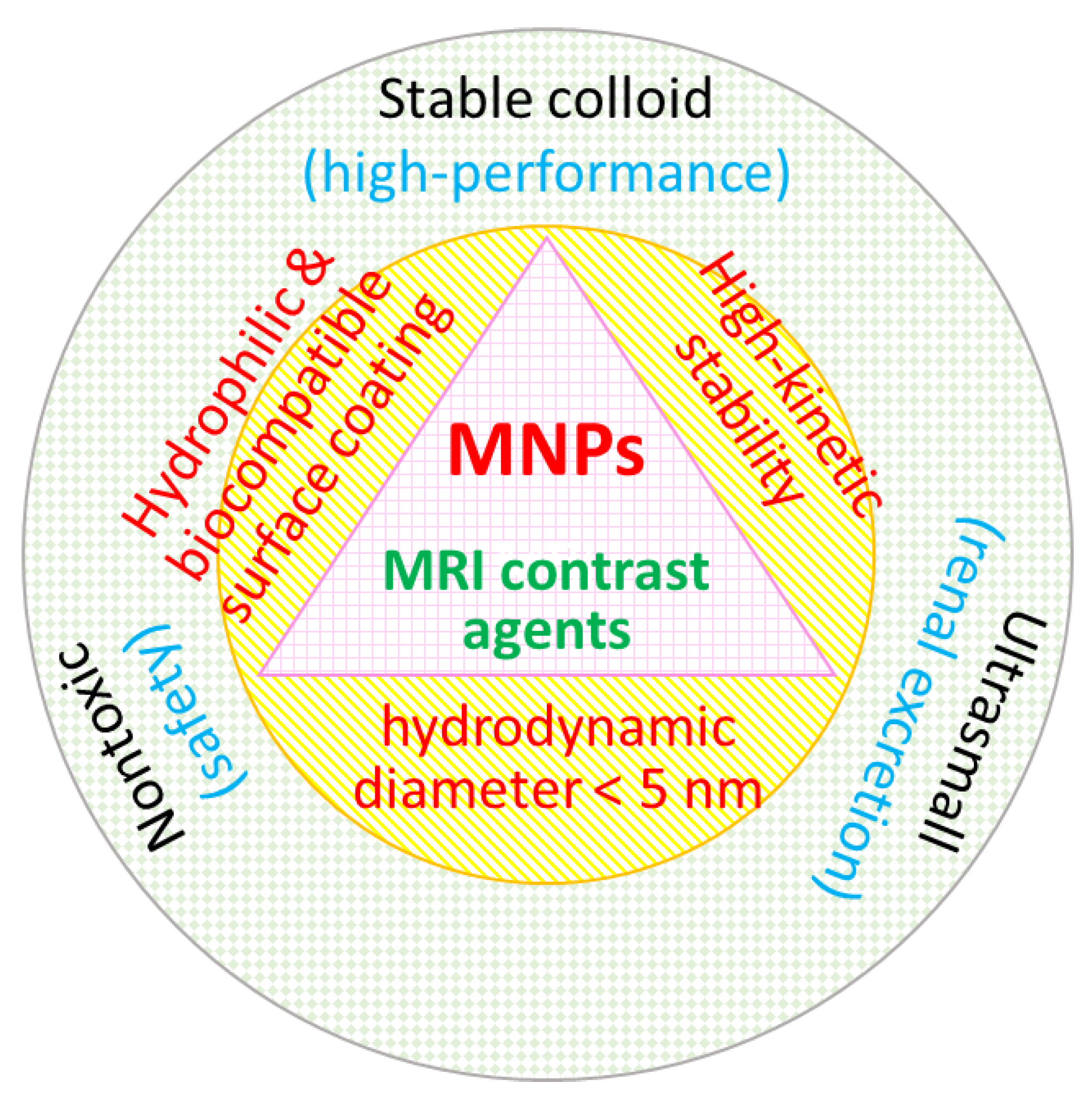
4. Colloidal Stability, Biocompatibility, and Renal Excretion
5. Conclusions
6. Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Beek, E.J.R.; Kuhl, C.; Anzai, Y.; Desmond, P.; Ehman, R.L.; Gong, Q.; Gold, G.; Gulani, V.; Hall-Craggs, M.; Leiner, T.; et al. Value of MRI in medicine: More than just another test? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e14–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, S.; Hoggard, N.; Craven, I.J.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Wilkinson, I.D. Understanding MRI: Basic MR physics for physicians. Postgrad. Med. J. 2013, 89, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzinger, A.L.; Hendee, W.R. Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-An Update. West. J. Med. 1985, 143, 782–792. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, V.P.B.; Tognarelli, J.M.; Crossey, M.M.E.; Cox, I.J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; McPhail, M.J.W. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Principles and Techniques: Lessons for Clinicians. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paeng, J.C.; Lee, D.S. Multimodal Molecular Imaging In Vivo. Open Nucl. Med. J. 2010, 2, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissleder, R.; Mahmood, U. Molecular imaging. Radiology 2001, 219, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.; Miranda, R.; Doyle, A.J. MRI imaging of soft tissue tumours of the foot and ankle. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Yoon, Y.C.; Seo, S.W.; Cha, M.J.; Jin, W.; Cha, J.G. Characterization of small, deeply located soft-tissue tumors: Conventional magnetic resonance imaging features and apparent diffusion coefficient for differentiation between non-malignancy and malignancy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrogiacomo, S.; Dou, W.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Hard Tissues and Hard Tissue Engineered Bio-substitutes. Mol. Imaging. Biol. 2019, 21, 1003–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellenberger, C.J.; Epelman, M.; Miller, S.F.; Babyn, P.S. Fast STIR whole-body MR imaging in children. Radiographics 2004, 24, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Atalar, E. MRI-guided gene therapy. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2958–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Grezia, G.D.; Cuccurullo, V.; Sardu, C.; Iovino, F.; Comune, R.; Ruggiero, A.; Chirico, M.; Forgia, D.L.; Fanizzi, A.; et al. MRI in Pregnancy and Precision Medicine: A Review from Literature. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, J.G.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Bharatha, A.; Montanera, W.J.; Park, A.L. Association Between MRI Exposure During Pregnancy and Fetal and Childhood Outcomes. JAMA 2016, 316, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, K.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Min, H.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; et al. A Bioinspired Nanoprobe with Multilevel Responsive T1 -Weighted MR Signal-Amplification Illuminates Ultrasmall Metastases. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, R.; Lu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Zou, L.; Wang, Z. A novel clustered SPIO nanoplatform with enhanced magnetic resonance T2 relaxation rate for micro-tumor detection and photothermal synergistic therapy. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2216–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coroiu, I.; Darabont, A.; Demco, D.E. Potential contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Appl. Magn. Reson. 1998, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Laurent, S. Classification and basic properties of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2009, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijkers, G.J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; van Tilborg, G.A.F.; Nicolay, K. MRI contrast agents: Current status and future perspectives. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.B.; Song, I.C.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic Nanoparticles for MRI Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, C.; Karmakar, A.; Gartia, Y.; Ramidi, P.; Biris, A.S.; Ghosh, A. Magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agents in biomedical imaging: Recent advances in iron- and manganese-based magnetic nanoparticles. Drug Metab. Rev. 2014, 46, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.S.; Hedgire, S.S.; Li, W.; Ganguli, S.; Prabhakar, A.M. Blood pool contrast agents for venous magnetic resonance imaging. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 6, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, H.S.; Morcos, S.K.; Almén, T.; Bellin, M.-F.; Bertolotto, M.; Bongartz, G.; Clement, O.; Leander, P.; Heinz-Peer, G.; Reimer, P.; et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-based contrast media: Updated ESUR Contrast Medium Safety Committee guidelines. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattel, K.; Park, J.Y.; Chang, Y.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, G.H. Paramagnetic nanoparticle T1 and T2 MRI contrast agents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 12687–12700. [Google Scholar]
- Caro, C.; Paez-Muñoz, J.M.; Beltrán, A.M.; Leal, M.P.; García-Martín, M.L. PEGylated Terbium-Based Nanorods as Multimodal Bioimaging Contrast Agents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4199–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shukla, S.; Gu, Y.; Yu, X.; Steinmetz, N.F. Dysprosium-Modified Tobacco Mosaic Virus Nanoparticles for Ultra-High-Field Magnetic Resonance and Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging of Prostate Cancer. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9249–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-Y.; Pellico, J.; Khrapitchev, A.A.; Sibson, N.R.; Davis, J.J. Dy-DOTA integrated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as promising ultrahigh field magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21041–21045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norek, M.; Peters, J.A. MRI contrast agents based on dysprosium or holmium. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2011, 59, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Zhang, J.; Bu, W.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Z.; Xing, H.; Wang, J.; Duan, F.; Liu, Y.; Fan, W.; et al. PEGylated NaHoF4 nanoparticles as contrast agents for both X-ray computed tomography and ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, H.S. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: History and Epidemiology. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 47, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berstein, E.J.; Schmidt-Lauber, C.; Kay, J. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: A systemic fibrosing disease resulting from gadolinium exposure. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 26, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, N.; Murata, K.; Gonzalez-Cuyar, L.F.; Maravilla, K.R. Gadolinium tissue deposition in brain and bone. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 34, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairinisa, M.A.; Ariyani, W.; Tsushima, Y.; Koibuchi, N. Effects of gadolinium deposits in the cerebellum: Reviewing the literature from in vitro laboratory studies to in vivo human investigations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, N.; Hurrell, R.; Kelishadi, R. Review on iron and its importance for human health. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wáng, Y.X.J.; Idée, J.-M. A comprehensive literatures update of clinical researches of superparamagnetic resonance iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2017, 7, 88–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: Current status of clinical application. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2011, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-X.J. Current status of superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents for liver magnetic resonance imaging. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 13400–13402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geppert, M.; Himly, M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Bioimaging—An Immune Perspective. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurea, S.; Mainenti, P.P.; Tambasco, A.; Imbriaco, M.; Mollica, C.; Laccetti, E.; Camera, L.; Liuzzi, R.; Salvatore, M. Diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging to identify and characterize focal liver lesions: Comparison between gadolinium and superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast media. Quant. Imaging. Med. Surg. 2014, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doane, T.L.; Burda, C. The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2885–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Baek, M.J.; Choi, E.S.; Woo, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.J.; Jung, J.C.; Chae, K.S.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Paramagnetic ultrasmall gadolinium oxide nanoparticles as advanced T1 MRI contrast agent: Account for large longitudinal relaxivity, optimal particle diameter, and in vivo T1 MR images. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3663–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrén, M.; Selegård, L.; Klasson, A.; Söderlind, F.; Abrikossova, N.; Skoglund, C.; Bengtsson, T.; Engström, M.; Käll, P.-O.; Uvdal, K. Synthesis and characterization of PEGylated Gd2O3 nanoparticles for MRI contrast enhancement. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5753–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Choi, E.S.; Baek, M.J.; Lee, G.H.; Woo, S.; Chang, Y. Water-Soluble Ultra Small Paramagnetic or Superparamagnetic Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Molecular MR Imaging. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 2477–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Y.; Ahmad, M.W.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Park, J.A.; Jung, K.-H.; Cha, H.; Marasini, S.; Ghazanfari, A.; Liu, S.; et al. In Vivo Positive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications of Poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic acid)-coated Ultra-small Paramagnetic Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridot, J.-L.; Faure, A.-C.; Laurent, S.; Rivière, C.; Billotey, C.; Hiba, B.; Janier, M.; Josserand, V.; Coll, J.-L.; Elst, L.V.; et al. Hybrid Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles: Multimodal Contrast Agents for In Vivo Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5076–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hifumi, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Tanimoto, A.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Gadolinium-Based Hybrid Nanoparticles as a Positive MR Contrast Agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15090–15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estelrich, J.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Busquets, M.A. Nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging: From simple to dual contrast agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Bony, B.A.; Baeck, J.S.; Chang, Y.; Bae, J.E.; Chae, K.S.; Lee, G.H. A Highly Efficient New T1 MRI Contrast Agent with r2/r1≈1.0: Mixed Cu(II)/Gd(III) Oxide Nanoparticle. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2015, 36, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer, R.B. Paramagnetic metal complexes as water proton relaxation agents for NMR imaging: Theory and design. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 901–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, A.; Muller, R.N.; Gillis, P. Theory of proton relaxation induced by superparamagnetic particles. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 5403–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravan, P.; Ellison, J.J.; McMurry, T.J.; Lauffer, R.B. Gadolinium(III) chelates as MRI contrast agents: Structure, dynamics, and applications. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2293–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1998; p. 1243. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Bruns, O.T.; Kaul, M.G.; Hansen, E.C.; Barch, M.; Wiśniowska, A.; Chen, O.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Okada, S.; et al. Exceedingly small iron oxide nanoparticles as positive MRI contrast agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Zheng, Q.; An, L.; He, M.; Lin, J.; Tian, Q.; Yang, S. T1-Weight Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performances of Iron Oxide Nanopart.icles Modified with a Natural Protein Macromolecule and an Artificial Macromolecule. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besenhard, M.O.; Panariello, L.; Kiefer, C.; LaGrow, A.P.; Storozhuk, L.; Perton, F.; Begin, S.; Mertz, D.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Gavriilidis, A. Small iron oxide nanoparticles as MRI T1 contrast agent: Scalable inexpensive water-based synthesis using a flow reactor. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8795–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromsdorf, U.I.; Bruns, O.T.; Salmen, S.C.; Beisiegel, U.; Weller, H. A highly effective, nontoxic T1 MR contrast agent based on ultrasmall PEGylated iron oxide nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4434–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; An, K.; Park, Y.I.; Choi, Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S.G.; Na, H.B.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of uniform and extremely small-sized iron oxide nanoparticles for high-resolution T1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12624–12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, Y.-P.; Liang, B.; Hu, F.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.-F.; Yin, P.-H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gu, H. Ultra-large-scale production of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for T1-weighted MRI. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22575–22585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Mignani, S.; Shi, X. RGD-functionalized ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted T1-weighted MR imaging of gliomas. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14538–14546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.H.; Keller, K.E. Theory of l/Tl and 1/T2 NMRD Profiles of Solutions of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Hu, K.; Delahunty, I.; Gao, S.; Xie, J. Surface impact on nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2521–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostevšek, N. A Review on the Optimal Design of Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based T2 MRI Contrast Agents. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norek, M.; Kampert, E.; Zeitler, U.; Peters, J.A. Tuning of the size of Dy2O3 nanoparticles for optimal performance as an MRI contrast agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5335–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norek, M.; Pereira, G.A.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Denkova, A.; Zhou, W.; Peters, J.A. NMR transversal relaxivity of suspensions of lanthanide oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10240–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Blasiak, B.; Merenco, A.J.; Trudel, S.; Tomanek, B.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Design and regulation of NaHoF4 and NaDyF4 nanoparticles for high field magnetic resonance imaging. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegafaw, T.; Xu, W.; Ahmad, M.W.; Baeck, J.S.; Chang, Y.; Bae, J.E.; Chae, K.S.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, G.H. Dual-mode T1 and T2 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent based on ultrasmall mixed gadolinium-dysprosium oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo application. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 365102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, B. Controlled synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles and Gd complex-based nanocomposites as tunable and enhanced T1/T2-weighted MRI contrast agents. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4748–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Chi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, J. Tunable T1 and T2 contrast abilities of manganese-engineered iron oxide nanoparticles through size control. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10404–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, D.-G.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, I.S. Fe3O4/MnO hybrid nanocrystals as a dual contrast agent for both T1- and T2-weighted liver MRI. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, L.; Liu, K.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Peng, H.; Zhang, W. Characterization of Fe3O4/SiO2/Gd2O(CO3)2 core/shell/shell nanoparticles as T1 and T2 dual mode MRI contrast agent. Talanta 2015, 131, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Choi, J.S.; Yun, S.; Kim, I.S.; Song, H.T.; Kim, Y.; Park, K.I.; Cheon, J. T1 and T2 dual-mode MRI contrast agent for enhancing accuracy by engineered nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3393–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Yang, M.; Zhang, R.; Qin, C.; Su, X.; Cheng, Z. Hybrid nanotrimers for dual T1 and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9884–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegafaw, T.; Xu, W.; Lee, S.H.; Chae, K.S.; Cha, H.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Ligand-size and ligand-chain hydrophilicity effects on the relaxometric properties of ultrasmall Gd2O3 nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 065114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Xu, W.; Cha, H.; Chang, Y.; Oh, I.T.; Chae, K.S.; Tegafaw, T.; Ho, S.L.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, G.H. Ultrasmall Gd2O3 nanoparticles surface-coated by polyacrylic acid (PAA) and their PAA-size dependent relaxometric properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 477, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, A.; Löwa, N.; Wiekhorst, F.; Gleich, B.; Haase, A. Size-dependent MR relaxivities of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, J.N.; Albanese, C.; Rodriguez, O.; Le, Y.-C.; Ackun-Farmmer, M.; Keuren, E.V. The effects of particle shape and size on T2 relaxation in magnetic resonance imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3392–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangville, C.; Gallois, M.; Li, Y.; Nguyen, H.H.; Lauth-de Viguerie, N.; Talham, D.R.; Mingotaud, C.; Marty, J.-D. Hyperbranched polymer mediated size-controlled synthesis of gadolinium phosphate nanoparticles: Colloidal properties and particle size-dependence on MRI relaxivity. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4252–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shan, P.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. A design strategy of ultrasmall Gd2O3 nanoparticles for T1 MRI with high performance. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 7270–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Xu, K. Comparative study on in vivo behavior of PEGylated gadolinium oxide nanoparticles and Magnevist as MRI contrast agent. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, K.; Fan, Y.; Lin, H.; Gao, J. Zwitterion-Coated Ultrasmall MnO Nanoparticles Enable Highly Sensitive T1-Weighted Contrast-Enhanced Brain Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3784–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, C.; Hou, P.; Zhang, M.; Xu, K. One-pot preparation of hydrophilic manganese oxide nanoparticles as T1 nano-contrast agent for molecular magnetic resonance imaging of renal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Tian, X.M.; Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Luo, N.Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.B.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, C.X.; Li, L.; et al. Ultrahigh relaxivity and safe probes of manganese oxide nanoparticles for in vivo imaging. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Chi, X.; Ni, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Octapod iron oxide nanoparticles as high-performance T2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, F.; Gao, X. Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle for T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28959–28966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, M.P.; Muñoz-Hernández, C.; Berry, C.C.; García-Martín, M.L. In vivo pharmacokinetics of T2 contrast agents based on iron oxide nanoparticles: Optimization of blood circulation times. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 76883–76891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, M.; Moon, W.K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T. Water-dispersible ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanocubes with extremely high r2 relaxivity for highly sensitive in vivo MRI of tumors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueron, M. Nuclear relaxation in macromolecules by paramagnetic ions: A novel mechanism. J. Magn. Reson. 1975, 19, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravan, P.; Greenfield, M.T.; Bulte, J.W.M. Molecular factors that determine Curie spin relaxation in dysprosium complexes. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 46, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mancebo, D.; Becerro, A.I.; Rojas, T.C.; García-Martín, M.L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Ocaña, M. HoF3 and DyF3 Nanoparticles as Contrast Agents for High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2017, 34, 1700116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, K.; Park, J.Y.; Xu, W.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, E.J.; Bony, B.A.; Heo, W.C.; Jin, S.; Baeck, J.S.; Chang, Y.; et al. Paramagnetic dysprosium oxide nanoparticles and dysprosium hydroxide nanorods as T2 MRI contrast agents. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3254–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Park, J.A.; Ho, S.L.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Cha, H.; Liu, S.; Tegafaw, T.; Marasini, S.; Ghazanfari, A.; Kim, S.; et al. New Class of Efficient T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent: Carbon-Coated Paramagnetic Dysprosium Oxide Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasini, S.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Cha, H.; Park, J.A.; Jung, K.H.; Ghazanfari, A.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Liu, S.; Chae, K.S.; et al. A Novel Paramagnetic Nanoparticle T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent with High Colloidal Stability: Polyacrylic Acid-Coated Ultrafine Dysprosium Oxide Nanoparticles. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2020, 41, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-González, E.; Caro, C.; García-Martín, M.L.; Becerro, A.I.; Ocaña, M. Outstanding MRI contrast with dysprosium phosphate nanoparticles of tuneable size. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11461–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-González, E.; Caro, C.; Martínez-Guterrez, D.; García-Martín, M.L.; Ocaña, M.; Becerro, A.I. Holmium phosphate nanoparticles as negative contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging: Synthesis, magnetic relaxivity study and in vivo evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabaev, T.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Song, S.-J.; Han, D.-W.; Hong, N.H. Toxicity and T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Potentials of Holmium Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Gong, T.; Yuan, Q. Facile Synthesis of Holmium-Based Nanoparticles as a CT and MRI Dual-Modal Imaging for Cancer Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 741383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasini, S.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Park, J.A.; Kim, S.; Jung, K.-H.; Cha, H.; Liu, S.; Tegafaw, T.; Ahmad, M.Y.; et al. Synthesis, Characterizations, and 9.4 Tesla T2 MR Images of Polyacrylic Acid-Coated Terbium(III) and Holmium(III) Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Kim, S.; Park, J.A.; Tegafaw, T.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Kim, S.; Saidi, A.K.A.A.; Zhao, D.; et al. Polyethylenimine-Coated Ultrasmall Holmium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicities, and Water Proton Spin Relaxivities. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tegafaw, T.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Kim, S.; Park, J.A.; Baek, A.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Hwang, D.W.; et al. Paramagnetic ultrasmall Ho2O3 and Tm2O3 nanoparticles: Characterization of r2 values and in vivo T2 MR images at a 3.0 T MR field. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 5857–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, N.; Li, L.; Shi, S.; Malaisamy, S.; Yan, C. TbF3 nanoparticles as dual-mode contrast agents for ultrahigh field magnetic resonance imaging and X-ray computed tomography. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasini, S.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Jung, K.H.; Park, J.A.; Cha, H.; Ghazanfari, A.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Liu, S.; Jang, Y.J.; et al. D-Glucuronic Acid-Coated Ultrasmall Paramagnetic Ln2O3 (Ln = Tb, Dy, and Ho) Nanoparticles: Magnetic Properties, Water Proton Relaxivities, and Fluorescence Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3832–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. Interplay between longitudinal and transverse contrasts in Fe3O4 nanoplates with (111) exposed surfaces. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7976–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Skallberg, A.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Mei, X.; Uvdal, K. One-step synthesis of water-dispersible ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles as contrast agents for T1 and T2 magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2953–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Hapuarachchige, S.; Artemov, D. Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Development and In Vivo Characterization. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 9625–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yi, P.W.; Sun, Q.; Lei, H.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Smith, S.C.; Lan, M.B.; Lu, G.Q. Ultrasmall Water-Soluble and Biocompatible Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Positive and Negative Dual Contrast Agents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2387–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Alipour, A.; Soran-Erdem, Z.; Aykut, Z.G.; Demir, H.V. Highly monodisperse low-magnetization magnetite nanocubes as simultaneous T1-T2 MRI contrast agents. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10519–10526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, B.; Diaz-Diestra, D.; Santiago-Medina, C.; Kumar, N.; Tu, K.; Beltran-Huarac, J.; Jadwisienczak, W.M.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. T1- and T2-weighted Magnetic Resonance Dual Contrast by Single Core Truncated Cubic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Abrupt Cellular Internalization and Immune Evasion. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2018, 1, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, C.; Qian, C.; Qiao, H.; Sun, M. Dual-Mode Avocado-like All-Iron Nanoplatform for Enhanced T1/T2 MRI-Guided Cancer Theranostic Therapy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4842–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F.; Duan, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Shuai, X.; et al. Manganese-doped mesoporous polydopamine nanoagent for T1–T2 magnetic resonance imaging and tumor therapy. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2991–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Hu, F.; Rui, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gu, H. A T1/T2 dual functional iron oxide MRI contrast agent with super stability and low hypersensitivity benefited by ultrahigh carboxyl group density. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekuria, S.L.; Debele, T.A.; Tsai, H.-C. Encapsulation of Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticle (Gd2O3) Contrasting Agents in PAMAM Dendrimer Templates for Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6782–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasini, S.; Yue, H.; Ghazanfari, A.; Ho, S.L.; Park, J.A.; Kim, S.; Cha, H.; Liu, S.; Tegafaw, T.; Ahmad, M.Y.; et al. Polyaspartic Acid-Coated Paramagnetic Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles as a Dual-Modal T1 and T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, J. Manganese-loaded dual-mesoporous silica spheres for efficient T1- and T2-weighted dual mode magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9942–9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alromi, D.A.; Madani, S.Y.; Seifalian, A. Emerging application of magnetic nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Polymers 2021, 13, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.Y.; Yue, H.; Tegafaw, T.; Liu, S.; Ho, S.L.; Lee, G.H.; Nam, S.-W.; Chang, Y. Functionalized lanthanide oxide nanoparticles for tumor targeting, medical imaging, and therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longmire, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: Considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Ipe, B.I.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal clearance of nanoparticles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peng, C.; Yu, M.; Zheng, J. Renal clearable nobel metal nanoparticles: Photoluminescence, elimination, and biomedical applications. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Imagind Mode | Fe-Based MNP | Mn-Based MNP | Gd-Based MNP | Dy-Based MNP | Ho-Based MNP | Tb-Based MNP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | + | ++ | ++ | |||
| T2 | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Dual-modal T1 and T2 | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tegafaw, T.; Liu, S.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Saidi, A.K.A.A.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Nam, S.-W.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based High-Performance Positive and Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061745
Tegafaw T, Liu S, Ahmad MY, Saidi AKAA, Zhao D, Liu Y, Nam S-W, Chang Y, Lee GH. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based High-Performance Positive and Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061745
Chicago/Turabian StyleTegafaw, Tirusew, Shuwen Liu, Mohammad Yaseen Ahmad, Abdullah Khamis Ali Al Saidi, Dejun Zhao, Ying Liu, Sung-Wook Nam, Yongmin Chang, and Gang Ho Lee. 2023. "Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based High-Performance Positive and Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061745
APA StyleTegafaw, T., Liu, S., Ahmad, M. Y., Saidi, A. K. A. A., Zhao, D., Liu, Y., Nam, S.-W., Chang, Y., & Lee, G. H. (2023). Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based High-Performance Positive and Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061745










